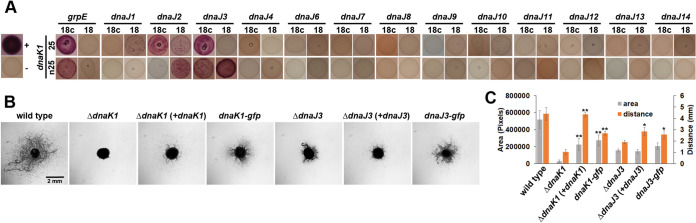
FIG 1.
Identification of the DnaK1/J3 chaperone system. (A) BACTH analysis between DnaK1 and GrpE or DnaJs encoded in the N. punctiforme genome fused to the C (25) and N (n25) terminus of the T25 fragment or C (18c) and N (18) terminus of the T18 fragment of B. pertussis adenylate cyclase. Depicted are the results from assays on MacConkey agar. The positive-control strain (+) harbors plasmids pKT25-zip and pUT18c-zip, while the negative-control strain (−) harbors the empty vectors pKT25 and pUT18c. (B) Plate motility assays of the wild-type, deletion strains, complemented deletion strains, and strains harboring gfp-tagged alleles (as indicated). Images were taken at 48 h post hormogonium induction. (C) Quantification of plate motility assays depicted in (B) based on the area covered by a spreading colony and the maximal distance traveled by individual filaments. Error bars = ±1 SD. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01 as determined by two-tailed Student’s t test between the dnaK1- or dnaJ3-deletion strains and the corresponding complemented or gfp-tagged allele strain, n = 3. All strains showed reduced motility compared to the wild-type as determined by the two-tailed Student’s t test, P < 0.05, except for maximal distance for ΔdnaK1 (+dnaK1).