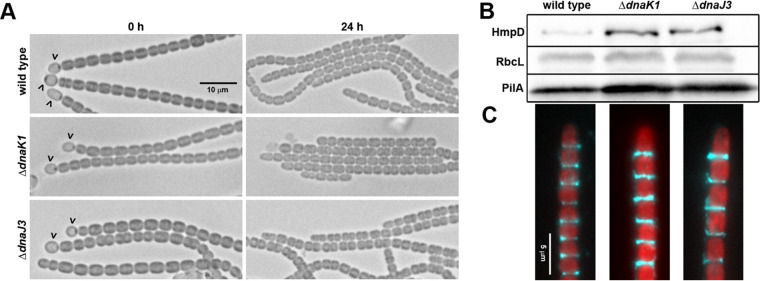
FIG 2.
Characterization of hormogonium development in the ΔdnaK1 and ΔdnaJ3 strains. (A) Light micrographs of the filament morphology for the wild-type and deletion strains at 0 h and 24 h post-hormogonium induction. Carets indicate the presence of heterocysts attached to filaments. Hormogonia can be distinguished from vegetative filaments by the absence of heterocysts, smaller cell size, and the presence of tapered cells at the filament termini. (B) Immunoblot analysis of cellular HmpD, PilA, and RbcL, and (C) immunofluorescence analysis of extracellular PilA in the wild-type and deletion strains 24 h after hormogonium induction. Immunoblot analysis was performed using protein extracted from an equivalent number of cells and represents total cellular and surface-associated protein, while immunofluorescence only represents surface-associated PilA. RbcL is the large subunit of RUBISCO and serves as a protein loading control. Depicted are merged images of fluorescence micrographs acquired using a 63× lens objective from cellular autofluorescence (red) and PilA immunofluorescence (cyan).