Figure 1.
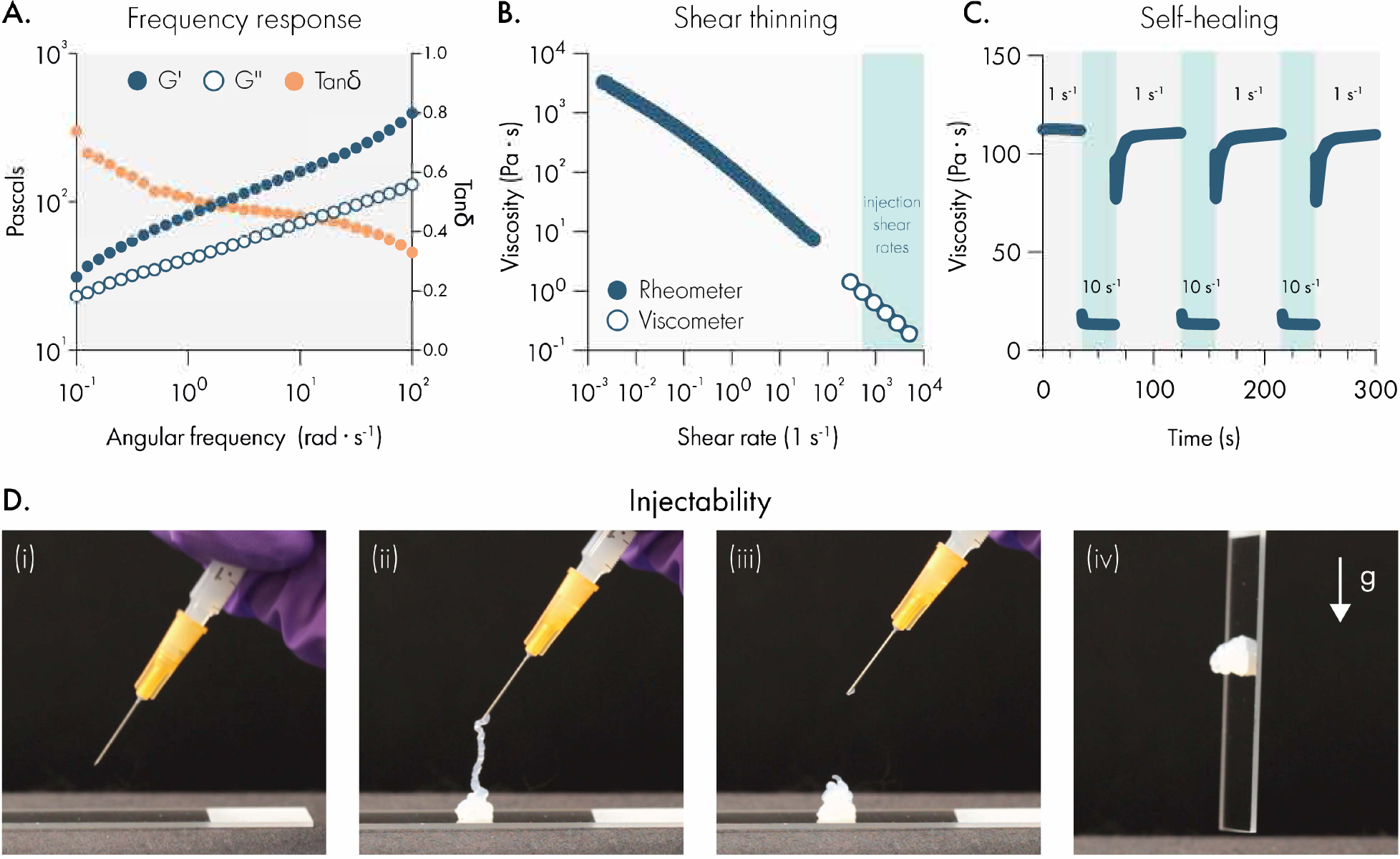
Liposomal hydrogels exhibit shear-thinning and self-healing mechanical properties that enable injection through needles. (A) Dynamic oscillatory shear rheology of liposomal hydrogels (2wt% HPMC-C12; 10wt% 50 nm extruded liposome) indicates the storage modulus (G’) is greater than the loss modulus (G”) over a broad range of frequencies, demonstrating robust solid-like properties. (B) Steady shear rheology measurements (filled circles) and viscometer measurements (empty circles) indicate that the viscosity of liposomal hydrogels steadily decreases by roughly 5-orders of magnitude as shear rates approach injection conditions. (C) Step-shear rheology measurements demonstrate that liposomal hydrogels can repeatedly regain their original viscosity after exposure to high shear conditions. (D) Representative photographs of liposomal hydrogels injected through a 26-gauge needle fitted onto a 1 mL syringe.
