Abstract
目的
探究阿托伐他汀(AVT)对人脑胶质瘤细胞生物学行为的影响及其对miR-146a/PI3K/Akt信号通路的作用。
方法
将人脑胶质瘤细胞U251分为4组:对照组(Conrtrol)、AVT组、AVT+转染miR-146a无关片段组(AVT+miR-146a NC)、AVT+转染miR-146a干扰组(AVT+miR-146a inhibitor)。Control组不加任何药物,AVT组加入8.0 μmol/L的AVT,AVT+miR-146a NC组转染miR-146a NC后加入8.0 μmol/L的AVT,AVT+miR-146a inhibitor组转染miR-146a inhibitor后加入8.0 μmol/L的AVT。RT-PCR检测miR-146a表达,MTT检测细胞增殖率,流式细胞术检测细胞凋亡情况,Transwell实验检测细胞侵袭和迁移情况,Western blot检测PI3K/Akt信号通路相关蛋白表达。
结果
药物干预48 h,与Control组相比,AVT组细胞miR-146a表达、细胞凋亡率均明显升高(P < 0.01),细胞增殖率、侵袭指数、迁移指数、p-PI3K和p-Akt蛋白表达均明显降低(P < 0.01)。与AVT组相比,AVT+miR-146a inhibitor组细胞miR-146a表达、细胞凋亡率均明显降低(P < 0.01),细胞增殖率、侵袭指数、迁移指数、p-PI3K和p-Akt蛋白表达均明显升高(P < 0.01),AVT+miR-146a NC组上述指标无显著性差异(P>0.05)。
结论
AVT能够抑制人脑胶质瘤细胞增殖、侵袭和迁移,促进细胞凋亡,其机制与上调miR-146a表达,抑制PI3K/Akt信号通路相关。
Keywords: 人脑胶质瘤, U251, 阿托伐他汀, miR-146a, PI3K/Akt, 生物学行为
Abstract
Objective
To explore the effect of atorvastatin (AVT) on biological behaviors and the miR-146a/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in human glioma cells.
Methods
Human glioma U251 cells were treated with 8.0 μmol/L AVT or transfected with a miR-146a inhibitor or a negative control fragment (miR-146a NC) prior to AVT treatment. RT-PCR was used to detect miR-146a expression in the cells, and the changes in cell proliferation rate, apoptosis, cell invasion and migration were detected using MTT assay, flow cytometry, and Transwell assay. Western blotting was performed to detect the changes in cellular expressions of proteins in the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.
Results
AVT treatment for 48 h resulted in significantly increased miR-146a expression and cell apoptosis (P < 0.01) and obviously lowered the cell proliferation rate, invasion index, migration index, and expressions of p-PI3K and p-Akt protein in U251 cells (P < 0.01). Compared with AVT treatment alone, transfection with miR-146a inhibitor prior to AVT treatment significantly reduced miR-146a expression and cell apoptosis (P < 0.01), increased the cell proliferation rate, promoted cell invasion and migration, and enhanced the expressions of p-PI3K and p-Akt proteins in the cells (P < 0.01); these effects were not observed following transfection with miR-146a NC group (P>0.05).
Conclusion
AVT can inhibit the proliferation, invasion and migration and promote apoptosis of human glioma cells possibly by up-regulating miR-146a expression and inhibiting the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.
Keywords: human glioma, U251 cells, atorvastatin, miR-146a, PI3K/Akt, biological behaviors
脑胶质瘤是一种极为常见的颅内恶性肿瘤,约占原发性颅内瘤46%[1]。虽然目前有多种治疗方式,但是存在手术切除不彻底以及血脑屏障的存在导致化疗药物难以到达肿瘤部位等情况,故导致患者预后不佳。阿托伐他汀(AVT)作为羟甲戊二酰辅酶还原酶抑制剂在临床上被广泛用于高胆固醇血症的治疗[2]。新近研究证实AVT对肿多种瘤细胞,如肺癌细胞、乳腺癌细胞以及胶质瘤细胞等具有显著的抑制作用[3-5]。其中AVT对胶质瘤细胞的显著抑制作用备受临床医生和科研工作者的密切关注。研究发现AVT能够诱导胶质瘤细胞的凋亡[6]。
AVT能够通过下调趋化因子受体4表达,从而抑制胶质瘤细胞侵袭[7]。但是目前有关AVT对胶质瘤细胞增殖和侵袭的具体作用机制尚不完全清楚。miR-146a是一类与胶质瘤细胞增殖密切相关的miRNA,可以通过调控Notch1基因的表达抑制胶质瘤细胞增殖[8]。另外,miR-146a能够通过介导磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B(PI3K/Akt)信号通路抑制肝星状细胞诱导的肝纤维化[9],而PI3K/Akt信号作为胶质瘤治疗的关键通路,抑制PI3K/Akt信号转导能够降低胶质瘤细胞增殖和侵袭[10]。那么有关AVT对胶质瘤的治疗作用是否涉及miR- 146a/PI3K/Akt信号传导尚不清楚。因此,本研究拟通过体外培养人脑胶质瘤细胞U251,观察AVT能否通过调控miR-146a/PI3K/Akt信号传导从而胶质瘤细胞生物学行为,以期为临床胶质瘤治疗提供新的理论基础。
1. 材料和方法
1.1. 材料
1.1.1. 细胞
人脑胶质瘤细胞U251,购自中科院上海分院细胞库。
1.1.2. 药品与主要试剂
阿托伐他汀(Sigma);RT-PCR检测试剂盒(广州锐博生物科技有限公司);二辛可宁酸(BCA)试剂盒(上海碧云天生物技术公司);牛血清白蛋白(BSA)(上海碧云天生物技术公司);胎牛血清(FBS)(Gibco);噻唑兰(3-(4, 5)-dimethylthiahiazo (-z-y1)-3, 5- di- phenytetrazoliumromide,MTT)检测试剂盒(上海碧云天生物技术公司);Annexin V-FITC/PI凋亡检测试剂盒(北京索莱宝科技有限公司);Transwell检测试剂盒(Corning);转染试剂盒(广州锐博生物科技有限公司);p-PI3K抗体(Abcam);PI3K抗体(Abcam);p-Akt抗体(Abcam);Akt抗体(Abcam);一抗、二抗稀释液(上海碧云天生物技术公司);山羊抗兔二抗(上海碧云天生物技术公司);山羊抗小鼠二抗(上海碧云天生物技术公司);显影液(碧云天生物技术公司);miR-146a引物设计与合成(上海生工生物工程股份有限公司)。
1.1.3. 主要仪器
TWK-FST32型组织匀浆仪(武汉泰普拓公司);Micro17R型高速冷冻离心机[赛默飞世尔科技(中国)有限公司];GPJ9-TS100-F型倒置荧光显微镜(Nikon);FC型全自动多功能酶标检测仪[赛默飞世尔科技(中国)有限公司];1658033型电泳仪(Bio-Rad);ChemiDoc XRS+成像系统(Bio-Rad)。
1.2. 方法
1.2.1. U251细胞培养
人脑胶质瘤细胞U251采用低糖DMEM培养基培养(含有10%的胎牛血清),并放置于37 ℃,5% CO2的培养箱内,细胞贴壁生长24~48 h,生长融合度达到90%左右,0.25%的胰酶消化处理,待细胞呈现卵圆形时终止消化,进行传代培养。期间每个24 h细胞换液处理1次。
1.2.2. U251细胞给药与分组
实验分为4组,即对照组(Control)、阿托伐他汀组(AVT)、阿托伐他汀+转染miR-146a无关片段组(AVT+miR-146a NC)和阿托伐他汀+转染miR-146a干扰组转染(AVT+miR-146a inhibitor)。其中VAT组细胞加入终浓度为8.0 μmol/L的VAT,AVT+miR-146a NC组和AVT+miR-146a inhibitor组转染miR-146a无关片段和miR-146a inhibitor 24 h后,加入8.0 μmol/L AVT处理48 h。Control组细胞常规培养,不加入药物处理。
1.2.3. RT-PCR检测miR-146a表达
依据RNA提取试剂盒说明书步骤提取U251细胞总RNA,并运用紫外分光光度计检测总RNA的浓度与纯度。以RNA为模板,参照逆转录试剂盒说明书步骤将其逆转录为单链cDNA。再以cDNA为模板,根据广州锐博公司设计合成的PCR引物进行扩增。扩增条件:92 ℃ 30 s;92 ℃ 5 s;60 ℃ 31 s,共进行31个循环。采用7300 System SDS Software分析数据,根据2-△△Ct值相对定量样本中目的基因表达水平。miR-146a引物序列如下:正义链:F:5'- GGGCCCAGTGTTCAGACTAC-3';反义链:5'-GTGCAGGGTCCGAGGT-3'。U6引物序列如下:正义链:5'-CCTCACTGTCCACCTTCCA-3';反义链:5'-GGGTGTAAAACGCAGCTCA-3'。
1.2.4. MTT检测细胞增殖率
将消化后的人脑胶质瘤细胞U251按照96孔板密度为:1×104/孔接种,按照细胞实验分组进行相关处理,每组设置6个复孔,重复实验6次,每孔加入MTT溶液10 μL(5 mg/mL)继续培养4 h,终止培养,弃去细胞上清,每孔加入150 μL的二甲基亚砜(DMSO)震荡10 min,使得充分溶解,利用酶标仪检测各孔的吸光度A570 nm,以吸光度值反应细胞的增殖活力。细胞增殖率(%)=各处理组细胞A570 nm/对照组A570 nm值×100%。
1.2.5. 式细胞术检测U251细胞凋亡率
胰蛋白酶消化处理后得到各组U251,加入磷酸盐缓冲溶液将细胞密度调控为1×105/mL;移液枪吸取200 μL的细胞悬液放于反应管内,之后加入Annexin V-FITC和PI各5 μL;充分混匀,避光环境下反应15 min;流式细胞仪检测各组U251凋亡情况。上述实验重复3次。
1.2.6. Transwell检测细胞侵袭和迁移率
侵袭实验:Transwell小室(24孔,孔径5.0 μm)的滤膜采用ECM gel覆盖,小室加入0.5 mL内含10 % FBS培养基,对上室中加入适当的细胞悬液,200 μL/孔,2×106/L,每组设置3个复孔。各组细胞常规培养48 h,4%的多聚甲醛固定,HE染色,400倍显微镜下随机选取5个视野观察穿过膜细胞平均数。U251细胞侵袭率=(各处理组侵袭细胞数/对照组侵袭细胞数)×100%。迁移实验:细胞常规处理,1000 r/min离心5 min,细胞重悬并计数;将小室放置于24孔板内,并于下室加入完全培养基(含有10% FBS),小室的上室中加入1×105细胞,保证下部小室膜与培养基无气泡,之后将24孔板防治培养箱内继续培养48 h,取出培养板后磷酸盐缓冲溶液润洗小室并擦拭上室残留细胞,多聚甲醛固定约15 min,最后使用0.1% 的结晶紫染色,洗涤、风干,于400倍显微镜下随机选取5个视野进行拍照计数。迁移指数=(各处理组迁移细胞数/对照组迁移细胞数)×100%。
1.2.7. Western blot检测PI3K/Akt信号通路蛋白相对表达量
收集各组细胞;4 ℃条件下裂解30 min,期间每隔5 min震荡1次;BCA法测定蛋白质浓度;上样(按照每孔上样量30 μg得出上样体积);凝胶电泳;湿转转膜;5% BSA室温封闭2 h,孵育对应抗体p-PI3K(1∶1000),PI3K(1∶1000)p-Akt(1∶1000),Akt(1∶1000)以及β-actin(1∶2000),4 ℃过夜,孵育对应的羊抗兔二抗体或者羊抗鼠二抗体(1∶5000)1~2 h;摇床摇晃上加TPBS洗涤3次,5 min/次,然后加入显影液,显影并拍照。p-PI3K和p-Akt蛋白表达水平以目的蛋白条带灰度值与β-actin灰度值相比反映。
1.2.8. 统计学分析
采用SPSS20.0软件进行分析,实验数据以均数±标准差表示,多组均数比较采用单因素方差分析,每组实验重复3次,P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1. 各组细胞miR-146a相对表达量比较
与Control组比较,AVT组细胞miR-146a相对表达量显著增加(P < 0.01);与AVT组相比,AVT+miR-146a inhibitor组细胞miR-146a相对表达量降低(P < 0.01),AVT+miR-146a NC组细胞miR-146a相对表达量无显著变化(P>0.05,图 1)。
1.
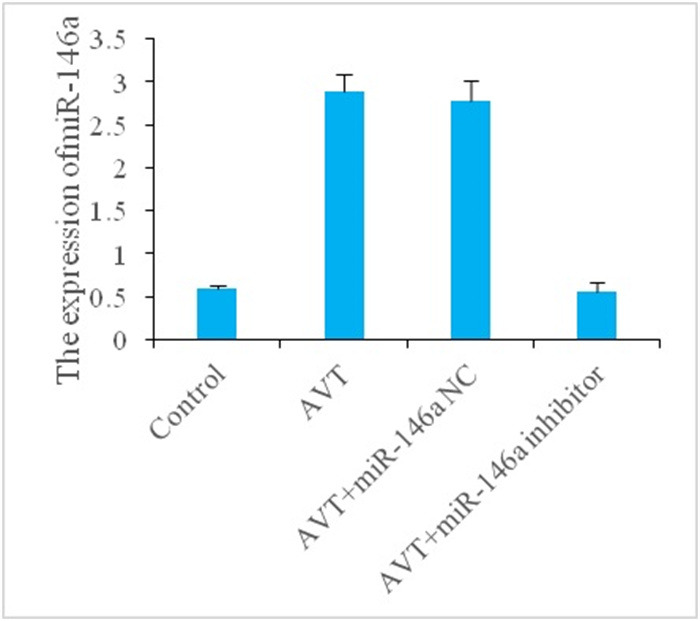
miR-146a相对表达量比较
Comparison of relative expression levels of miR-146a in different groups. **P < 0.01 vs control group; ##P < 0.01 vs AVT group.
2.2. 各组细胞增殖率比较
与Control组比较,AVT组细胞细胞增殖率显著降低(P < 0.05);与AVT组相比,AVT+miR-146a inhibitor组细胞增殖率显著升高(P < 0.01),AVT+miR-146a NC组细胞增殖无显著变化(P>0.05,图 2)。
2.
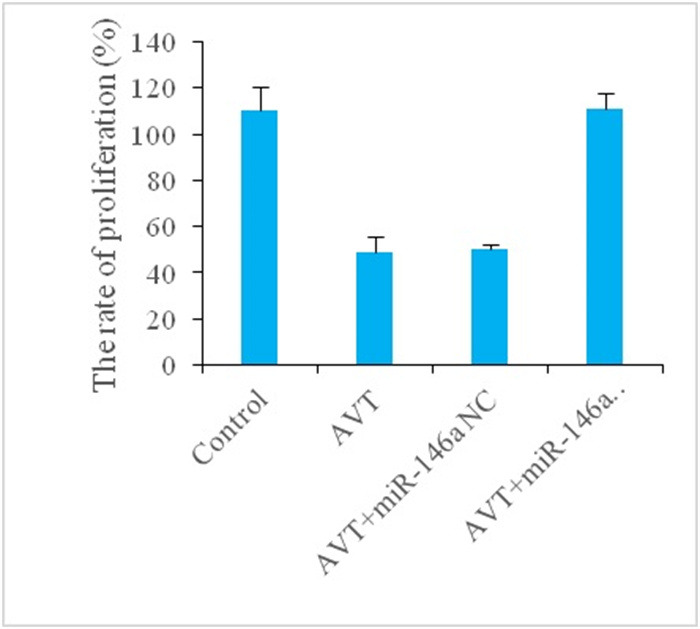
各组细胞增殖率比较
Comparison of cell proliferation rate in different groups. **P < 0.01 vs control group; ##P < 0.01 vs AVT group.
2.3. 各组细胞凋亡率比较
与Control组相比,AVT组细胞凋亡率明显升高(P < 0.01)。与AVT组相比,AVT+miR-146a inhibitor组细胞凋亡率明显降低(P < 0.01),AVT+miR-146a NC组细胞凋亡率无显著性变化(P>0.05,图 3)。
3.
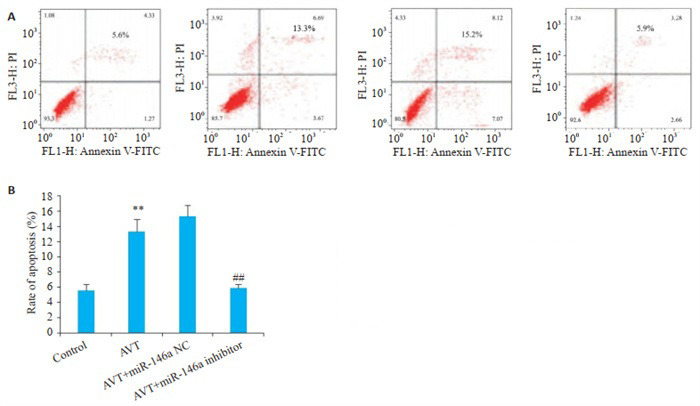
各组细胞凋亡率比较
Comparison of cell apoptosis rate in different groups. A: Flow cytometry for detecting cell apoptosis. B: Quantitative analysis of the results. **P < 0.01 vs control group; ##P < 0.01 vs AVT group.
2.4. 各组细胞侵袭率和迁移率比较
与Control组相比,AVT组细胞侵袭率和迁移率均明显降低(P < 0.01)。与AVT组相比,AVT+miR-146a inhibitor组细胞侵袭率和迁移率均明显升高(P < 0.01),AVT+miR-146a NC组细胞侵袭率和迁移率无显著性变化(P>0.05,图 4)。
4.
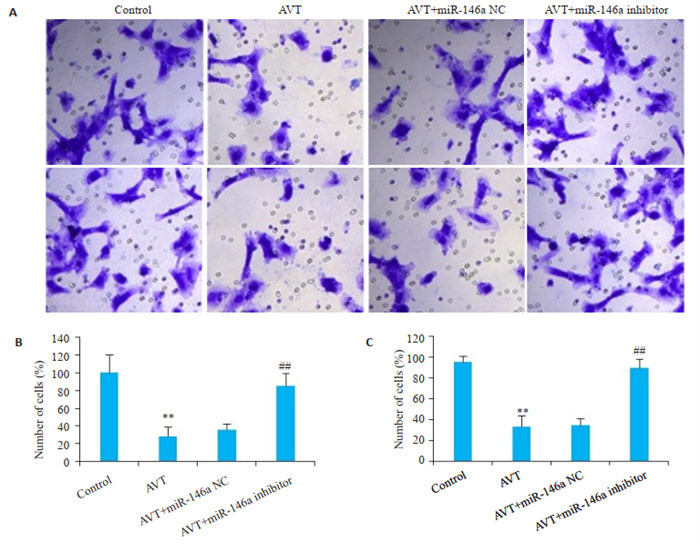
各组细胞迁移和侵袭能力比较
Comparison of cell migration and invasion abilities of the cells in different groups (Original magnification: ×400).A: Transwell assay for assessing cell migration and invasion. B: Quantitative analysis of the migration. C: Quantitative analysis of the invasion. **P < 0.01 vs control group; ##P < 0.01 vs AVT group.
2.5. 各组细胞PI3K/Akt信号通路蛋白相对表达量比较
与Control组相比,AVT组细胞p-PI3K和p-Akt蛋白表达均明显降低(P < 0.01)。与AVT组相比,AVT+ miR-146a inhibitor组细胞p-PI3K和p-Akt蛋白表达均明显升高(P < 0.01),AVT+miR-146a NC组细胞p-PI3K和p-Akt蛋白表达无显著性变化(P>0.05,图 5)。
5.
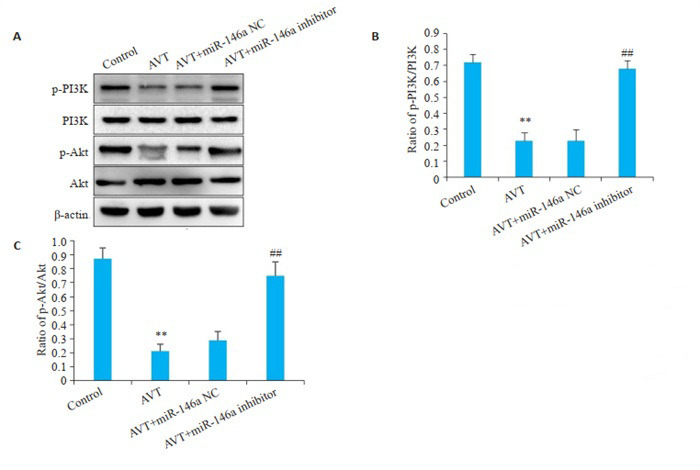
各组细胞PI3K/Akt信号通路相关蛋白表达
Expressions of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway-related proteins in different groups.A: Western blotting for detection of PI3K/Akt pathway proteins. B: Quantitative analysis of p-PI3K/PI3K. C: Quantitative analysis of pAkt/Akt. **P < 0.01 vs control group; ##P < 0.01 vs AVT group.
3. 讨论
AVT为脂溶性他汀类新药,可以透过血脑屏障,有利于胶质瘤临床治疗中的实际应用[11]。既往研究证实AVT能够通过阻断JNK、MMP2的表达抑制骨肉瘤细胞侵袭[12]。另外,AVT能够抑制胶质瘤细胞VEGF、Bcl-2和Caspase-3表达从而抑制胶质瘤球体血管生成,并最终抑制胶质瘤细胞增殖,诱导胶质瘤细胞凋亡[13]。以上研究给AVT抑制胶质瘤细胞恶性病变提供了新的启发。
胶质瘤细胞恶性病变涉及的生物学行为主要包括细胞凋亡、增殖、侵袭和转移等多环节复杂的生物学过程[14, 15]。miRNA是一类长度约22 nt的小分子非编码RNA,众多研究数据表明miRNA参与了包括肿瘤细胞增殖、凋亡、侵袭和迁移等生物学过程[16, 17]。因此,在肿瘤细胞研究中miRNA的生物学过程也是科研人员研究的热点之一。miR-146a是位于人的5号染色体中miR- 146中的一类[18]。研究表明与癌旁组织相比,胶质瘤癌组织中miR-146a表达显著降低,转染miR-146a模拟物能够抑制胶质瘤细胞生长[8]。另外,miR-146a能够靶向抑制SMAD4基因表达,参与调控胶质瘤细胞增殖和迁移[19]。上述研究表明miR-146a在胶质瘤细胞中发挥抑癌作用。另外,既往研究也显示AVT能够通过调控miR-146a抑制间充质干细胞迁移[20]。本研究首先通过RT-PCR检测AVT对人脑胶质瘤细胞miR-146a表达的影响。结果显示AVT能够促进miR-146a表达。胶质瘤细胞生物学行为检测显示AVT能够抑制细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭,促进细胞凋亡。为进一步明确AVT通过调控miR-146a表达,从而影响人脑胶质瘤细胞的生物学行为。实验通过转染miR-146a inhibitor,结果显示AVT+miR-146a inhibitor组细胞miR-146a表达明显降低,细胞增殖,迁移和侵袭指数降低,凋亡增加,表明AVT是通过促进miR-146a表达,发挥人脑胶质瘤细胞生物学行为调控作用。那么有关miR-146a下游的调控机制又是如何呢?以往研究证实PI3K/Akt信号转导在胶质瘤细胞恶性病变中发挥重要作用[21, 22]。研究发现激活PI3K/Akt信号传导能够促进胶质瘤细胞增殖、抑制细胞凋亡[23]。另外,PI3K/Akt信号通路的激活能够促进基质金属蛋白酶2表达增加,活性增强,从而介导细胞外基底膜胶原降解,并最终促进胶质瘤细胞向外周围浸润,促进细胞侵袭和转移[24],表明PI3K/Akt信号通路转导在胶质瘤细胞生物学行为变化中发挥关键性作用。但是目前有关miR-146a/PI3K/Akt信号在AVT抑制人脑胶质瘤细胞生物学行为中的作用及其调控关系尚不清楚。本研究通过Western blot检测显示AVT组细胞p-PI3K、p-Akt表达降低,转染miR-146a inhibitor后p-PI3K、p-Akt表达升高,细胞增殖,迁移和侵袭指数增加,凋亡降低。表明AVT能够通过促进miR-146a表达抑制PI3K/Akt信号,从而影响胶质瘤细胞生物学行为。以往研究证实miR-146a可以通过抑制PI3K/Akt信号通路促进心力衰竭大鼠心肌细胞凋亡[25]。miR- 146a能够负向调控PI3K/Akt信号促进甲状腺滤泡状癌细胞增殖、侵袭和迁移[26]。在骨关节炎细胞模型中PI3K基因的3'-UTR是miR-146a的靶点,而PI3K蛋白和mRNA表达以及下游Akt的激活在转染miR-146a模拟物后明显降低[27]。本研究结果与既往研究共同表明miR-146a能够负向调控PI3K/Akt信号从而影响细胞的生物学行为。
综上所述,本研究通过探究AVT对人脑胶质瘤细胞生物学行为的影响及其对miR-146a/PI3K/Akt信号通路的作用。结果显示AVT能够抑制人脑胶质瘤细胞增殖、侵袭和迁移,促进细胞凋亡,其机制与调控miR- 146a/PI3K/Akt信号通路相关。以上研究结果初步证实了AVT对胶质瘤的抑制作用及其可能的作用机制。但是本研究存在一定的局限性,即未在临床上研究AVT对胶质瘤患者的治疗效果及对miR-146a/PI3K/Akt的影响。在后续的研究中将通过探究AVT对胶质瘤患者的影响,以期为临床治疗提供更多的分子机制。
Biography
崔颖,副主任医师,E-maIl: cuiying197612@163.com
Funding Statement
安徽省自然科学基金(1908085QH334)
Contributor Information
崔 颖 (Ying CUI), Email: cuiying197612@163.com.
巢 青 (Qing CHAO), Email: ccbbahcty@163.com.
References
- 1.Gusyatiner O, Hegi ME. Glioma epigenetics: from subclassification to novel treatment options. Semin Cancer Biol. 2018;51(2):50–8. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2017.11.010. [Gusyatiner O, Hegi ME. Glioma epigenetics: from subclassification to novel treatment options[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2018, 51(2): 50-8.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.谭 万江, 刘 书红, 高 伟, et al. 阿托伐他汀钙片对冠心病患者小而密低密度脂蛋白胆固醇水平的影响. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLYZ202002002.htm. 中国临床药理学杂志. 2020;36(2):103-5, 117. [谭万江, 刘书红, 高伟, 等. 阿托伐他汀钙片对冠心病患者小而密低密度脂蛋白胆固醇水平的影响[J]. 中国临床药理学杂志, 2020, 36(2): 103-5, 117.] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Du XS, Li DF, Wang GJ, et al. Chemoprotective effect of atorvastatin against benzo(a)Pyrene-induced lung cancer via the inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammatory parameters. Ann Transl Med. 2021;9(4):355. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-7770. [Du XS, Li DF, Wang GJ, et al. Chemoprotective effect of atorvastatin against benzo(a)Pyrene-induced lung cancer via the inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammatory parameters[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2021, 9(4): 355.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Marti JLG, Beckwitt CH, Clark AM, et al. Atorvastatin facilitates chemotherapy effects in metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 2021;125(9):1285–98. doi: 10.1038/s41416-021-01529-0. [Marti JLG, Beckwitt CH, Clark AM, et al. Atorvastatin facilitates chemotherapy effects in metastatic triple-negative breast cancer[J]. Br J Cancer, 2021, 125(9): 1285-98.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Peng P, Wei W, Long C, et al. Atorvastatin augments temozolomide's efficacy in glioblastoma via prenylation-dependent inhibition of Ras signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;489(3):293–8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.05.147. [Peng P, Wei W, Long C, et al. Atorvastatin augments temozolomide's efficacy in glioblastoma via prenylation-dependent inhibition of Ras signaling[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2017, 489(3): 293-8.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Oliveira KA, Dal-Cim T, Lopes FG, et al. Atorvastatin promotes cytotoxicity and reduces migration and proliferation of human A172 glioma cells. Mol Neurobiol. 2018;55(2):1509–23. doi: 10.1007/s12035-017-0423-8. [Oliveira KA, Dal-Cim T, Lopes FG, et al. Atorvastatin promotes cytotoxicity and reduces migration and proliferation of human A172 glioma cells[J]. Mol Neurobiol, 2018, 55(2): 1509-23.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.贾 熙卓, 郑 天虎, 李 艳泽, et al. 阿托伐他汀抑制胶质瘤细胞U87侵袭性及相关机制研究. 国际遗传学杂志. 2014;37(3):103–8. [贾熙卓, 郑天虎, 李艳泽, 等. 阿托伐他汀抑制胶质瘤细胞U87侵袭性及相关机制研究[J]. 国际遗传学杂志, 2014, 37(3): 103-8.] [Google Scholar]
- 8.鲁 琼, 戴 冬伟, 韩 国胜, et al. microRNA-146a抑制胶质瘤细胞增殖的研究. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWCX201124008.htm. 现代生物医学进展. 2011;11(24):4821–3. [鲁琼, 戴冬伟, 韩国胜, 等. microRNA-146a抑制胶质瘤细胞增殖的研究[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2011, 11(24): 4821-3.] [Google Scholar]
- 9.杨 志欣, 付 淑姣. miR-146a介导PI3K/Akt信号通路抑制肝星状细胞诱导的肝纤维化. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJMY201904038.htm. 标记免疫分析与临床. 2019;26(4):699–703. [杨志欣, 付淑姣. miR-146a介导PI3K/Akt信号通路抑制肝星状细胞诱导的肝纤维化[J]. 标记免疫分析与临床, 2019, 26(4): 699-703.] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Chai C, Song LJ, Han SY, et al. microRNA-21 promotes glioma cell proliferation and inhibits senescence and apoptosis by targeting SPRY1 via the PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2018;24(5):369–80. doi: 10.1111/cns.12785. [Chai C, Song LJ, Han SY, et al. microRNA-21 promotes glioma cell proliferation and inhibits senescence and apoptosis by targeting SPRY1 via the PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway[J]. CNS Neurosci Ther, 2018, 24(5): 369-80.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 11.Yi YJ, Huang SY, Chen L, et al. Atorvastatin suppresses glioma invasion and migration by reducing microglial MT1-MMP expression. J Neuroimmunol. 2013;260(1/2):1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2013.04.020. [Yi YJ, Huang SY, Chen L, et al. Atorvastatin suppresses glioma invasion and migration by reducing microglial MT1-MMP expression[J]. J Neuroimmunol, 2013, 260(1/2): 1-8.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Fromigué O, Hamidouche Z, Marie PJ. Blockade of the RhoA-JNKc-Jun-MMP2 cascade by atorvastatin reduces osteosarcoma cell invasion. J Biol Chem. 2008;283(45):30549–56. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M801436200. [Fromigué O, Hamidouche Z, Marie PJ. Blockade of the RhoA-JNKc-Jun-MMP2 cascade by atorvastatin reduces osteosarcoma cell invasion[J]. J Biol Chem, 2008, 283(45): 30549-56.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Bayat N, Ebrahimi-Barough S, Norouzi-Javidan A, et al. Antiinflammatory effects of atorvastatin in human glioblastoma spheroids cultured in a three-dimensional model: possible relevance to glioblastoma treatment. Mol Neurobiol. 2018;55(3):2102–10. doi: 10.1007/s12035-017-0445-2. [Bayat N, Ebrahimi-Barough S, Norouzi-Javidan A, et al. Antiinflammatory effects of atorvastatin in human glioblastoma spheroids cultured in a three-dimensional model: possible relevance to glioblastoma treatment[J]. Mol Neurobiol, 2018, 55(3): 2102-10.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ruff M, Kizilbash S, Buckner J. Further understanding of glioma mechanisms of pathogenesis: implications for therapeutic development. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2020;20(5):355–63. doi: 10.1080/14737140.2020.1757440. [Ruff M, Kizilbash S, Buckner J. Further understanding of glioma mechanisms of pathogenesis: implications for therapeutic development[J]. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther, 2020, 20(5): 355-63.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ou A, Yung WKA, Majd N. Molecular mechanisms of treatment resistance in glioblastoma. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;22(1):351. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010351. [Ou A, Yung WKA, Majd N. Molecular mechanisms of treatment resistance in glioblastoma[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 22(1): 351.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Yu ZT, Liu Y, Li Y, et al. miRNA-338-3p inhibits glioma cell proliferation and progression by targeting MYT1L. Brain Res Bull. 2022;179:1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2021.11.016. [Yu ZT, Liu Y, Li Y, et al. miRNA-338-3p inhibits glioma cell proliferation and progression by targeting MYT1L[J]. Brain Res Bull, 2022, 179: 1-12.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Mishra S, Yadav T, Rani V. Exploring miRNA based approaches in cancer diagnostics and therapeutics. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2016;98:12–23. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2015.10.003. [Mishra S, Yadav T, Rani V. Exploring miRNA based approaches in cancer diagnostics and therapeutics[J]. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol, 2016, 98: 12-23.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.朱 嘉豪, 陈 婷, 习 欠云. miR-146a参与不同疾病的研究进展. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWGJ202109008.htm. 中国生物工程杂志. 2021;41(9):64–70. [朱嘉豪, 陈婷, 习欠云. miR-146a参与不同疾病的研究进展[J]. 中国生物工程杂志, 2021, 41(9): 64-70.] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Karthikeyan A, Gupta N, Tang C, et al. Microglial SMAD4 regulated by microRNA-146a promotes migration of microglia which support tumor progression in a glioma environment. Oncotarget. 2018;9(38):24950–69. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.25116. [Karthikeyan A, Gupta N, Tang C, et al. Microglial SMAD4 regulated by microRNA-146a promotes migration of microglia which support tumor progression in a glioma environment[J]. Oncotarget, 2018, 9 (38): 24950-69.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Li N, Guo XY, Zhou J, et al. Atorvastatin pretreatment ameliorates mesenchymal stem cell migration through miR-146a/CXCR4 signaling. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2021;18(5):863–73. doi: 10.1007/s13770-021-00362-z. [Li N, Guo XY, Zhou J, et al. Atorvastatin pretreatment ameliorates mesenchymal stem cell migration through miR-146a/CXCR4 signaling[J]. Tissue Eng Regen Med, 2021, 18(5): 863-73.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ji JW, Zhang YD, Lai YJ, et al. Mettl3 regulates the proliferation, migration and invasion of glioma cells by inhibiting PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(7):3818–28. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202004_20848. [Ji JW, Zhang YD, Lai YJ, et al. Mettl3 regulates the proliferation, migration and invasion of glioma cells by inhibiting PI3K/Akt signaling pathway[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2020, 24(7): 3818-28.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zhang ZQ, Wang X, Xue BH, et al. Chronic stress promotes glioma cell proliferation via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Oncol Rep. 2021;46(3):202. doi: 10.3892/or.2021.8153. [Zhang ZQ, Wang X, Xue BH, et al. Chronic stress promotes glioma cell proliferation via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway[J]. Oncol Rep, 2021, 46(3): 202.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wu DH, Wang CZ. miR-155 regulates the proliferation of glioma cells through PI3K/AKT signaling. Front Neurol. 2020;11:297. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00297. [Wu DH, Wang CZ. miR-155 regulates the proliferation of glioma cells through PI3K/AKT signaling[J]. Front Neurol, 2020, 11: 297.] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.孙 增峰, 王 乐, 谷 峰, et al. Notch1基质金属蛋白酶2基质金属蛋白酶9蛋白在胶质瘤中的表达及其临床意义. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXL201407020.htm. 中华肿瘤杂志. 2012;34(1):26–30. [孙增峰, 王乐, 谷峰, 等. Notch1基质金属蛋白酶2基质金属蛋白酶9蛋白在胶质瘤中的表达及其临床意义[J]. 中华肿瘤杂志, 2012, 34 (1): 26-30.] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.程 璐, 时 学昆, 张 超, et al. miR-146a调控PI3K/Akt信号通路促进心力衰竭大鼠心肌细胞凋亡. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWTX202003005.htm. 生物技术通讯. 2020;31(3):275–80. [程璐, 时学昆, 张超, 等. miR-146a调控PI3K/Akt信号通路促进心力衰竭大鼠心肌细胞凋亡[J]. 生物技术通讯, 2020, 31(3): 275-80.] [Google Scholar]
- 26.马蔚. miR-146a和miR-146b通过抑制ST8SIA4来促进甲状腺滤泡状癌的增殖性, 迁徙性, 侵袭性[D]. 大连: 大连医科大学, 2017.
- 27.Li HX, Xie SJ, Li HZ, et al. LncRNA MALAT1 mediates proliferation of LPS treated-articular chondrocytes by targeting the miR-146aPI3K/Akt/mTOR axis. Life Sci. 2020;254(4):116801. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116801. [Li HX, Xie SJ, Li HZ, et al. LncRNA MALAT1 mediates proliferation of LPS treated-articular chondrocytes by targeting the miR-146aPI3K/Akt/mTOR axis[J]. Life Sci, 2020, 254(4): 116801.] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


