Abstract
Introduction
Flood as the most common kind of the natural disasters has unpleased short, medium, and long-term consequences on the victims’ welfare, relationships, and physical and mental health. One of the most common mental health disorders in these victims is Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). The aim of this study is to investigate the prevalence of PTSD on the flood victims.
Methods
Data resources including PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, Science Direct, Embase, Google Scholar, conference and congress papers, key journals, the reference list of selected articles as well as systematic reviews were searched to identify studies that reported the prevalence of PTSD in flood victims. Random Effect Model was used to perform meta-analysis of the studies. Cochran test and I2 indicator were used to explore heterogeneity between the studies. Publication bias of the study was evaluated using Begg’test. Data were analyzed by STATA (version 14) software.
Results
After a comprehensive search, 515 papers were extracted. After eliminating duplicates and final screening, 23 studies were selected and entered the meta-analysis phase after qualitative evaluation. The results showed that the prevalence of PTSD in flood victims is 29.48% (95% CI: 18.64–40.31, I2 = 99.3%, p-value < 0.001).
Conclusion
The results of the present study showed that the prevalence of PTSD is relatively high in the flood victims. So, it is necessary to take preventive, supportive, therapeutic and effective actions for them.
Keywords: Post-traumatic stress disorder, PTSD, mental disorders, natural disasters, flood
Introduction
Flood is the most common kind of natural disaster and climate changes have increased its incidence (1). It also has obvious effects on the individuals’ life and in addition to economic damages, it has unpleased short, medium and long term consequences on the victims’ welfare, relationships and physical and mental health (1, 2). Disasters can have severe mental health consequences which are the result of encountering to the potentially traumatic events and tenacious stressors (3, 4). Floods make some changes in the people routine lives, so that their quality of life would be affected in different manners (5). Floods are associated with an increased prevalence of mental disorders such as Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety and depression in industrialized and non-industrialized countries (6). On the other hand, the studies have shown that PTSD can lead to other mental health problems such as depression, anxiety or substance abuse disorders (1). PTSD occurs as a delayed reaction to very threatening or catastrophic conditions in the short or long term (2). It disturbs the individual’s daily life function and is associated with decreased health function and increased physical and mental illness (7). The results of a study in Indonesia showed that 52% of flood victims had experienced PTSD and 98.3% of them experienced it again (8). A study in China had reported the prevalence of PTSD 9.2% among the floods victims (9). According to the results of a review study, the prevalence of PTSD was 28.44% among the earthquake victims (10). In a systematic review and meta-analysis study was conducted in 2015, the incidence of PTSD after the flood was 15.74% (11). The rate of the psychiatric illnesses in the victims have been varied based on some factors such as the vulnerable population, severity and type of the flood event as well as the social support of the country (12). Since the flood has various physical and mental consequences in the long and short term, no timely detection and diagnose of long-term psychological consequences can be followed by unpleasant circumstances that may disrupt the individual’s daily life. Considering that until 2015, the rate of PTSD after the flood has been reported using a systematic review and meta-analysis study and Several studies have been carried out on the prevalence of PTSD after the flood, but no comprehensive study has been done since 2015 on the overall prevalence of PTSD. Therefore, the present study was conducted to assess the prevalence of PTSD in flood survivors by a systematic review and meta-analysis. The results of the study can be used for planning and policy-making for the follow-up actions for the flood survivors.
Materials and Methods
In order to conduct the present review study the PRISMA (Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses) guideline was used (13). The review protocol was registered in the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO) under the code of CRD42021281715.
Search Strategy
The English information resources including PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, Science Direct, Google Scholar as well as Embase were searched by English keywords to retrieve the related studies. Also, other data resources, including conference and congress papers, key journals, the reference list of selected articles and systematic reviews were used. To formulate the search strategy in databases, keywords, tag field and operators were used. Searche English language were carried out from the beginning of 2015 to 31 June 2021. The search strategies for the types of databases were provided in Supplementary Appendix 1.
Inclusion Criteria
The studies that had reported the prevalent of PTSD among the flood survivors from the beginning of 2015 to 31.05.2021 were included in this review.
Exclusion Criteria
(1) Review, qualitative study and intervention studies, (2) Studies other than English language were the exclusion criteria of the study.
Selection of the Studies
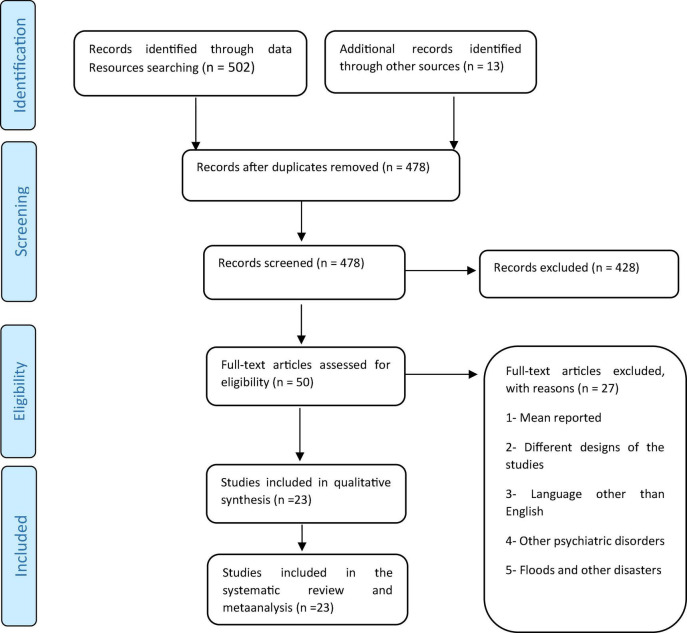
In order to manage the references, all the initial identified studies were entered into the Endnote software (version 7) and after deleting duplicates, titles and abstracts of 478 studies were screened. In the next step, two researchers (AS and MG) independently studied 50 possible related studies by details and finally 23 papers were selected. Any disagreement between them was resolved by a third person.
Qualitative Evaluation and Data Extraction
In order to evaluate the quality of the selected studies, two researchers (AS and MG) independently used Appraisal tool for Cross-Sectional Studies (AXIS) Tool (14). The tool has the score between 0 and 20. Based on the AXIS tool, higher scores indicate higher quality studies. Any disagreement between two evaluators was resolved by a third individual. Data extraction of all included studies was done by two researchers (AS and MG) independently by using a pre-prepared checklist. This checklist included these items: (a) the name of the first author, (b) the place, (c) the year and (d) the tool of the study, (e) sample size, the number of men and women, as well as the prevalence of PTSD. Any disagreement between two researchers was resolved by a third individual.
Statistical Analysis
Given that the prevalence of PTSD and the sample size were extracted in each study, a binomial distribution was used to calculate the variance of each study. The weighted average was used to combine the prevalence of different studies. Each study was weighted according to its inverse variance. Due to high heterogeneity, the simple random effects model was used for meta-analysis. The heterogeneity between the studies was calculated using the Cochran test and I2 indicator. The scores less than 25, 25–50, 50–75, and more than 75% indicates, no; moderate, high as well as very high heterogeneity, respectively (15). P < 0.05 was considered significant in the Cochrane test. Subgroup analysis was used to explore the source of heterogeneity. Publication bias of the study was assessed using Begg’ test. The significance level in the Begg’ test is 0.05 (16). Sensitivity analysis was performed to identify the effect of any single study on the overall prevalence. To investigate the relationship between the year of the study and the prevalence of PTSD, Meta-regression was used and the data were analyzed by STATA software (Version 14).
Results
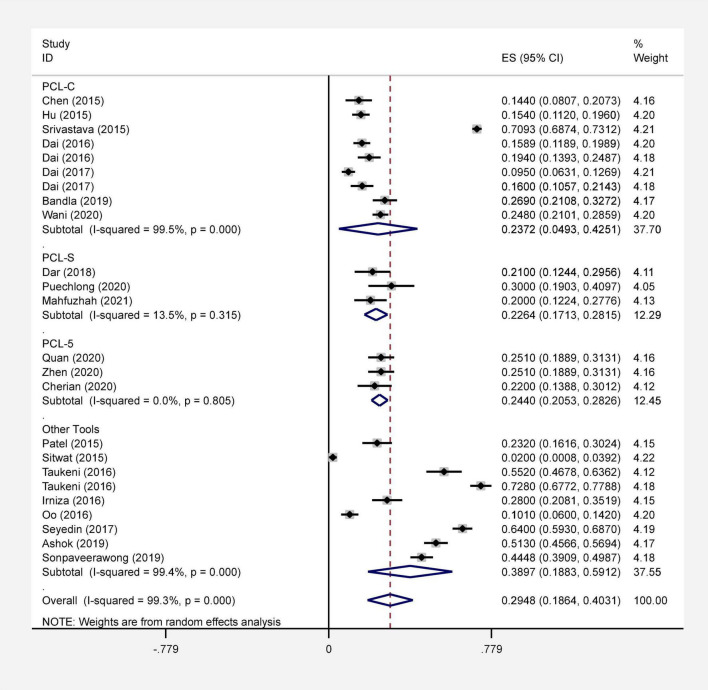
In the present review, 515 articles were retrieved by the initial search and after deleting the duplicates, 478 papers were screened. After the final screening, 23 articles were selected and assessed and they all entered the meta-analysis (Figure 1). All studies included were conducted between 2015 and 2021. Based on the AXIS tool, the quality score of the included studies varied from 12 to 19. The methodology of all selected studies was cross-sectional (Table 1). In this study, PTSD of the flood victims was reported 29.48% (95% CI: 18.64–40.31, I2 = 99.3%, p-value < 0.001) (Figure 2). Indicator I2 showed that the heterogeneity between the studies was very high.
FIGURE 1.
Flowchart of the study and selection of studies based on PRISMA steps.
TABLE 1.
The characteristics of the selected studies in meta-analysis.
| References | Tool** | Country | Sample size | Male | Female | Prevalence of PTSD |
| Bandla et al. (17) | PCL-C | India | 223 | 107 | 116 | 26.9% |
| Chen et al. (18) | PCL-C | China | 118 | 59 | 59 | 14.4% |
| Dai et al. (19) | PCL-C | China | 321 | 173 | 148 | 15.89% |
| Dai et al. (20) | PCL-C | China | 325 | 153 | 172 | 9.5% |
| Dai et al. (21) | PCL-C | China | 175 | 81 | 94 | 16% |
| Dai et al. (22) | PCL-C | China | 201 | 111 | 90 | 19.4% |
| Hu et al. (23) | PCL-C | China | 284 | 153 | 131 | 15.4% |
| Irniza et al. (24) | TSQ | Malaysia | 150 | 61 | 89 | 28% |
| Puechlong et al. (25) | PCL - S | France | 67 | 32 | 35 | 30% |
| Quan et al. (26) | PCL-5 | China | 187 | 94 | 84 (9*) | 25.1% |
| Sitwat et al. (27) | SCID-IV | Pakistan | 205 | – | 205 | 2% |
| Sonpaveerawong et al. (28) | GHQ- 12- Plus-R | Thailand | 326 | 177 | 149 | 44.48% |
| Taukeni et al.(29) | CTSQ | Southern Africa | 134 | 44 | 90 | 55.2% |
| Taukeni et al. (29) | CTSQ | Southern Africa | 295 | 114 | 181 | 72.8% |
| Zhen et al. (30) | PCL-5 | China | 187 | – | – | 25.1% |
| Oo et al. (31) | Researcher made | Malaysia | 208 | 98 | 110 | 10.1% |
| Mahfuzhah et al. (32) | PCL - S | Indonesia | 102 | 51 | 51 | 20% |
| Srivastava et al. (33) | PCL-C | India | 1651 | 739 | 912 | 70.93% |
| Seyedin et al. (34) | PTSS-10 | Iran | 400 | 238 | 162 | 64% |
| Ashok et al. (35) | IES-R | India | 302 | 120 | 182 | 51.3% |
| Wani (36) | PCL-C | India | 500 | 171 | 329 | 24.8% |
| Cherian et al. (37) | PCL-5 | India | 100 | 29 | 71 | 22% |
| Patel et al. (38) | IES-R | India | 138 | – | – | 23.2% |
| Dar et al. (39) | PCL - S | India | 87 | 39 | 48 | 21% |
*Unknown gender.
**PCL - S, post-traumatic stress disorder checklist – Specific; IES – R, impact of event scale – revised; PCL – 5, post-traumatic stress disorder checklist for DSM-5; PCL-C, post-traumatic stress disorder checklist - civilian version; PTSS-10, post-traumatic symptom scale-10; CTSQ, child trauma screening questionnaire; GHQ-12-Plus-R, general health questionnaire twelve plus R; TSQ, trauma screening questionnaire; SCID – IV, structured clinical interview for DSM – IV disorders.
FIGURE 2.
Forest plot of the prevalence of PTSD after the flood in general and separately with 95% confidence interval.
Subgroup Analysis
The research team performed a subgroup analysis using the type of tool used to assess the prevalence of PTSD. The prevalence of PTSD in flood victims based on PCL-C, PCL-S, PCL-5, and other tools were reported 23.27% (95% CI: 4.93–42.51, I2 = 99.5%, p-value < 0.001), 22.64% (95% CI: 17.13–28.15, I2 = 13.5%, p-value 0.315), 24.40% (95% CI: 20.53–28.26, I2 = 0.0%, p-value 0.805) and 38.97% (95% CI: 18.83–59, I2 = 99.4%, p-value < 0.001), respectively (Figure 2). Indicator I2 showed that the heterogeneity between the studies was very high in PCL – C (I2 = 99.5%) and no heterogeneity in PCL – 5 (I2 = 0.0%).
Meta-Regression, Publication Bias, and Sensitivity Analysis
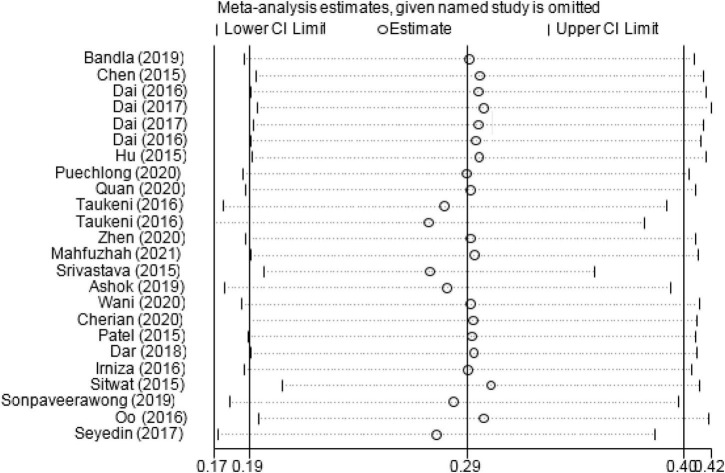
Based on the Begg test results, the publication bias of the subgroups analysis was not significant (PCL – C: P-value = 0.532, PCL – S: P-value = 0.117, PCL - 5: P-value = 0.297 and Other Tools: P-value = 0.677). The result of sensitivity analysis showed that the prevalence of PTSD did not change after the remove of any single study (Figure 3).
FIGURE 3.
Sensitivity analysis for the prevalence of PTSD.
Discussion
This review study assessed the prevalence of PTSD of the flood victims. In total, 23 studies were evaluated by meta-analysis. The results of the study showed that the prevalence of PTSD after the flood was 29.48% and the heterogeneity between the studies was 99.3%. Another meta-analysis study was conducted in 2015 and the results of the assessments on 14 studied papers showed that the incidence of PTSD after the flood was 15.74%. The degree of heterogeneity between the studies using the I2 Index was reported 98.3% (11). The results of another meta-analysis study showed that the prevalence of PTSD after the earthquakes and floods in the children and teenager in the first, second, third and fourth 6-month period was 19.2, 30, 24.4 as well as 20.4%, respectively (40). The results of another review study showed the prevalence of PTSD among Health Care Workers during the COVID-19 was 13.52% (41). By comparing the results of the present study with the previous studies, it can be concluded that the prevalence of PTSD after the flood is high like other natural disasters and all age groups are at risk of mental disorders after the flood, especially PTSD. Therefore, it is suggested to the support organizations to screen the flood survivors precisely in different periods. Parallel to the previous researches, the results of this study also showed very high heterogeneity among the studies, which can be resulted from the different sample sizes and various tools used in the studies. Given that each of the tools used in the studies has a different cut-off point, so it can increase the heterogeneity between the studies.
The results of this study showed that the most of the researches have been conducted in Asia and also based on the results of subgroup analysis, they were carried out in India and China with (34%) and (17%), respectively. Therefore, it can be concluded that the prevalence of PTSD in Asia is higher than in any other regions. The results of another study showed that the highest prevalence of PTSD in Asia is 57.3% and it was associated with the natural disasters (42). On the other hand, according to the epidemiological studies of the disasters, Asia has the highest rate of the natural disasters and the frequency and severity of the disasters is increasing (43). Based on the results of the studies, the experience of traumatic life significantly increases the probability of mental health disorders such as PTSD and these traumatic experiences have a greater impact on the mental health of the women than men (44). So, regarding to the results of the previous study and the present study, it can be concluded that the frequency of natural disasters in Asia and re-experience of the traumatic event by the individuals can increase the incidence of PTSD in these areas.
Gender is another factor that can affect the prevalence of PTSD in the victims of the floods and other disasters. According to the studies, PTSD was higher in female survivors after the earthquake than male (45). Therefore, the women are at more risk to suffer from PTSD after the disasters. This finding is in accordance with the previous studies (46–49). The results of other studies have also shown that the people who have lost their properties after the floods or were not supported by their families, like widowed or divorced women, have suffered from more stress and their scores of PTSD were more (50, 51). Other studies have shown that risk factors such as gender, socioeconomic status, education, and symptoms of previous mental illness are associated with increased vulnerability of survivors’ mental health in natural disasters (52). Therefore, it is suggested that communities and support organizations use various strategies such as increasing community resilience and awareness, as well as improving access to the health and treatment cares to raise post-disaster adaptation.
The results of the present study showed that the prevalence of PTSD has a relatively decreasing trend in the flood survivors over time. The results of another review study that looked at the prevalence of PTSD in earthquake survivors showed that the prevalence of PTSD decreased over time (53, 54). Therefore, it can be concluded that the prevalence of PTSD following natural disasters has been declining. Nowadays, the factors like increasing public awareness and resilience, screening, as well as easy access to public health facilities can justify the decreasing trend of the prevalence of mental disorders, especially, PTSD in natural disasters survivors.
Study Limitations
Although disasters occur around the world and are studied globally, there are intercultural limitations in the use of PTSD assessment tools that have been originally designed and approved in developed countries. It is necessary to be more careful about the inferences that can be drawn from studies using these tools. Another limitation of this study was that most studies were performed in Asia, so the generalization of the results of this study to the whole world may be limited, so it is recommended that other studies be performed to assess PTSD in other parts of the world.
Conclusion
The results of the present systematic review and meta-analysis study showed that the prevalence of PTSD in the flood victims is relatively high. Therefore, it can affect negatively on their habits, behaviors, interests and lifestyle and create more mental and physical disorders. So, it is necessary to take preventive, supportive, therapeutic and effective actions. On the other hand, the findings of this study can be used as a basis for planning and policy-making in the follow-up of flood survivors. As due to the various problems, floods occur frequently in the developing countries, the suffered populations of these countries need more attention and care. To speed up the curing process and using the appropriate and timely treatment along with other therapeutic actions, it is required to prevent or at least reduce the psychological consequences of the flood.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author Contributions
AS, MB, EM, and MG designed the review, developed the inclusion criteria, screened titles and abstracts, appraised the quality of included manuscript, drafted the manuscript, and reviewed the study protocol and inclusion criteria and provided substantial input to the manuscript. AS and MG read and screened articles for inclusion. All authors critically reviewed drafts and approved the final manuscript.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Funding
This study was resulted from the research plan with Ethical No: IR.MEDILAM.REC.1400.128 approved by the Ilam University of Medical Sciences.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2022.890671/full#supplementary-material
References
- 1.Fernandez A, Black J, Jones M, Wilson L, Salvador-Carulla L, Astell-Burt T, et al. Flooding and mental health: a systematic mapping review. PLoS One. (2015) 10:e0119929. 10.1371/journal.pone.0119929 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Fontalba-Navas A, Lucas-Borja M, Gil-Aguilar V, Arrebola J, Pena-Andreu J, Perez J. Incidence and risk factors for post-traumatic stress disorder in a population affected by a severe flood. Public Health. (2017) 144:96–102. 10.1016/j.puhe.2016.12.015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.James LE, Welton-Mitchell C, Noel JR, James AS. Integrating mental health and disaster preparedness in intervention: a randomized controlled trial with earthquake and flood-affected communities in Haiti. Psychol Med. (2020) 50:342–52. 10.1017/S0033291719000163 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Adibi A, Golitaleb M, Farrahi-Ashtiani I, Pirani D, Yousefi K, Jamshidbeigi Y, et al. The prevalence of generalized anxiety disorder among health care workers during the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Psychiatry. (2021) 12:658846. 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.658846 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Othman AZ, Dahlan A, Borhani SN, Rusdi H. Posttraumatic stress disorder and quality of life among flood disaster victims. Proc Soc Behav Sci. (2016) 234:125–34. 22661030 [Google Scholar]
- 6.Munro A, Kovats RS, Rubin GJ, Waite TD, Bone A, Armstrong B, et al. Effect of evacuation and displacement on the association between flooding and mental health outcomes: a cross-sectional analysis of UK survey data. Lancet Planet Health. (2017) 1:e134–41. 10.1016/S2542-5196(17)30047-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Aslam N, Kamal A. Frequency of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) among flood affected individuals. PAFMJ. (2014) 64:100–4. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Nasri RI, Seniwati T, Erfina E. Screening of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) among flood victims in Indonesia. Enferm Clin. (2020) 30:345–9. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Huang P, Tan H, Liu A, Feng S, Chen M. Prediction of posttraumatic stress disorder among adults in flood district. BMC Public Health. (2010) 10:207. 10.1186/1471-2458-10-207 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Cénat JM, McIntee S-E, Blais-Rochette C. Symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder, depression, anxiety and other mental health problems following the 2010 earthquake in Haiti: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Affect Disord. (2020) 273:55–85. 10.1016/j.jad.2020.04.046 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Chen L, Liu A. The incidence of posttraumatic stress disorder after floods: a meta-analysis. Disaster Med Public Health Prep. (2015) 9:329–33. 10.1017/dmp.2015.17 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Asim M, Mekkodathil A, Sathian B, Elayedath R, Kumar R, Simkhada P, et al. Post-traumatic stress disorder among the flood affected population in Indian subcontinent. Nepal J Epidemiol. (2019) 9:755. 10.3126/nje.v9i1.24003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Group P. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. (2009) 6:e1000097. 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Downes MJ, Brennan ML, Williams HC, Dean RS. Development of a critical appraisal tool to assess the quality of cross-sectional studies (AXIS). BMJ Open. (2016) 6:e011458. 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-011458 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Sahebi A, Abdi K, Moayedi S, Torres M, Golitaleb M. The prevalence of insomnia among health care workers amid the COVID-19 pandemic: an umbrella review of meta-analyses. J Psychosom Res. (2021) 149:110597. 10.1016/j.jpsychores.2021.110597 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sahebi A, Nejati-Zarnaqi B, Moayedi S, Yousefi K, Torres M, Golitaleb M. The prevalence of anxiety and depression among healthcare workers during the COVID-19 pandemic: an umbrella review of meta-analyses. Prog Neuro Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. (2021) 107:110247. 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2021.110247 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Bandla S, Nappinnai NR, Gopalasamy S. Psychiatric morbidity in December 2015 flood-affected population in Tamil Nadu. India. Int J Soc Psychiatry. (2019) 65:338–44. 10.1177/0020764019846166 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Chen L, Tan H, Cofie R, Hu S, Li Y, Zhou J, et al. Prevalence and determinants of chronic post-traumatic stress disorder after floods. Disaster Med Public Health Prep. (2015) 9:504–8. 10.1017/dmp.2015.64 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Dai W, Chen L, Tan H, Wang J, Lai Z, Kaminga AC, et al. Association between social support and recovery from post-traumatic stress disorder after flood: a 13-14 year follow-up study in Hunan, China chronic disease epidemiology. BMC Public Health. (2016) 16:194. 10.1186/s12889-016-2871-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Dai W, Kaminga AC, Tan H, Wang J, Lai Z, Wu X, et al. Long-term psychological outcomes of flood survivors of hard-hit areas of the 1998 Dongting Lake flood in China: prevalence and risk factors. PLoS One. (2017) 12:e0171557. 10.1371/journal.pone.0171557 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Dai W, Kaminga AC, Wu X, Wen SW, Tan H, Yan J, et al. Brain-derived neurotropic factor val66met polymorphism and posttraumatic stress disorder among survivors of the 1998 Dongting Lake flood in China. Biomed Res Int. (2017) 2017:4569698. 10.1155/2017/4569698 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Dai W, Wang J, Kaminga AC, Chen L, Tan H, Lai Z, et al. Predictors of recovery from post-traumatic stress disorder after the Dongting Lake flood in China: a 13-14 year follow-up study. BMC Psychiatry. (2016) 16:382. 10.1186/s12888-016-1097-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hu S, Tan H, Cofie R, Zhou J, Yang T, Tang X, et al. Recovery from post-traumatic stress disorder after a flood in China: a 13-year follow-up and its prediction by degree of collective action. BMC Public Health. (2015) 15:615. 10.1186/s12889-015-2009-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Irniza R, Emilia ZA, Sharifah Norkhadijah SI, Vivien H, Praveena SM, Karmegam K, et al. The association between KAP on disasters with depression, GAD and PTSD among flood victims. Indian J Environ Protect. (2016) 36:888–94. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Puechlong C, Weiss K, Le Vigouroux S, Charbonnier E. Role of personality traits and cognitive emotion regulation strategies in symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder among flood victims. Int J Disaster Risk Reduct. (2020) 50:101688. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Quan L, Zhen R, Yao B, Zhou X. Traumatic exposure and posttraumatic stress disorder among flood victims: testing a multiple mediating model. J Health Psychol. (2020) 25:283–97. 10.1177/1359105317707568 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Sitwat A, Asad S, Yousaf A. Psychopathology, psychiatric symptoms and their demographic correlates in female adolescents flood victims. J Coll Phys Surg Pak. (2015) 25:886–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Sonpaveerawong J, Limmun W, Chuwichian N. Prevalence of psychological distress and mental health problems among the survivors in the flash floods and landslide in Southern Thailand. Walailak J Sci Technol. (2019) 16:255–64. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Taukeni S, Chitiyo G, Chitiyo M, Asino I, Shipena G. Post-traumatic stress disorder amongst children aged 8-18 affected by the 2011 Northern-Namibia floods. Jamba. (2016) 8:169. 10.4102/jamba.v8i2.169 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Zhen R, Quan L, Zhou X. Co-occurring patterns of post-traumatic stress disorder and depression among flood victims: a latent profile analysis. J Health Psychol. (2020) 25:1543–55. 10.1177/1359105318763505 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Oo SS, Amin RBM, Aziz ABA, Aung MMT, Husain RB. Prevalence and perceived severity of post-traumatic stress disorder among flood victims in Kuala Terengganu, Malaysia. Malays J Public Health Med. (2016) 16:30–40. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Mahfuzhah AS, Widianti E, Emaliyawati E. Screening of post-traumatic stress disorder among adolescent victims of the Garut flash flood in 2016. NurseLine J. (2021) 6:8–17. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Srivastava M, Goel D, Semwal J, Gupta R, Dhyani M. Posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms in the population of Uttarkashi, Tehri, and Pauri Garhwal India in reference to Uttarakhand flood – June 2013. Int J Health Syst Disaster Manag. (2015) 3:37–43. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Seyedin H, HabibiSaravi R, Sayfouri N, Hoseini Djenab V, Ghasemi Hamedani F. Psychological sequels of flood on residents of southeast Caspian region. Nat Hazards. (2017) 88:965–75. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ashok V, Premarajan K, Rajkumar R, Naik B. Mental health status of flood-affected adults in rural Tamil Nadu: a cross-sectional study. CHRISMED J Health Res. (2019) 6:97–101. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Wani SM. Prevelance of PTSD in people affected by flood in Kashmir. Int J Adv Med Sci. (2020) 4:1–6. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Cherian V, Philip J, John A. Prevalence and factors associated with post-traumatic stress disorder among flood-affected adults in a panchayat in Ernakulam district in Kerala. Kerala J Psychiatry. (2020) 33:147–52. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Patel FM, Oswal RM, Mehta RY. Posttraumatic stress disorders in adult victims of 2006 flood in Surat, Gujarat. J Res Med Dent Sci. (2015) 3:303. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Dar KA, Iqbal N, Prakash A, Paul MA. PTSD and depression in adult survivors of flood fury in Kashmir: the payoffs of social support. Psychiatry Res. (2018) 261:449–55. 10.1016/j.psychres.2018.01.023 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Rezayat AA, Sahebdel S, Jafari S, Kabirian A, Rahnejat AM, Farahani RH, et al. Evaluating the prevalence of PTSD among children and adolescents after earthquakes and floods: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychiatr Q. (2020) 91:1265–90. 10.1007/s11126-020-09840-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Sahebi A, Yousefi A, Abdi K, Jamshidbeigi Y, Moayedi S, Torres M, et al. The prevalence of post-traumatic stress disorder among health care workers during the COVID-19 pandemic: an umbrella review and meta-analysis. Front psychiatry. (2021) 12:764738. 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.764738 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Udomratn P. Mental health and the psychosocial consequences of natural disasters in Asia. Int Rev Psychiatry. (2008) 20:441–4. 10.1080/09540260802397487 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Chan E, Man A, Lam H. Scientific evidence on natural disasters and health emergency and disaster risk management in Asian rural-based area. Br Med Bul. (2019) 129:91. 10.1093/bmb/ldz002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Axinn WG, Ghimire DJ, Williams NE, Scott KM. Gender, traumatic events, and mental health disorders in a rural Asian setting. J Health Soc Behav. (2013) 54:444–61. 10.1177/0022146513501518 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Dai W, Chen L, Lai Z, Li Y, Wang J, Liu A. The incidence of post-traumatic stress disorder among survivors after earthquakes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Psychiatry. (2016) 16:188. 10.1186/s12888-016-0891-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Acierno R, Ruggiero KJ, Galea S, Resnick HS, Koenen K, Roitzsch J, et al. Psychological sequelae resulting from the 2004 Florida hurricanes: implications for postdisaster intervention. Am J Public Health. (2007) 97(Supplement. 1):S103–8. 10.2105/AJPH.2006.087007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Christodoulou GN, Paparrigopoulos TJ, Soldatos CR. Acute stress reaction among victims of the 1999 Athens earthquake: help seekers’ profile. World Psychiatry. (2003) 2:50. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Doocy S, Daniels A, Packer C, Dick A, Kirsch TD. The human impact of earthquakes: a historical review of events 1980-2009 and systematic literature review. PLoS Curr. (2013) 16:5. 10.1371/currents.dis.67bd14fe457f1db0b5433a8ee20fb833 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Zhang Z, Wang W, Shi Z, Wang L, Zhang J. Mental health problems among the survivors in the hard-hit areas of the Yushu earthquake. PLoS One. (2012) 7:e46449. 10.1371/journal.pone.0046449 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Reacher M, McKenzie K, Lane C, Nichols T, Kedge I, Iversen A, et al. Health impacts of flooding in Lewes: a comparison of reported gastrointestinal and other illness and mental health in flooded and non-flooded households. Commun Dis Public Health. (2004) 7:39–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Telles S, Singh N, Joshi M. Risk of posttraumatic stress disorder and depression in survivors of the floods in Bihar, India. Indian J Med Sci. (2009) 63:330–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Manning C, Clayton S. Threats to mental health and wellbeing associated with climate change. In: Clayton S, Manning C. editors. Psychology and Climate Change. (San Diego, CA: Elsevier; ) (2018). p. 217–44. [Google Scholar]
- 53.Hosseinnejad M, Yazdi-Feyzabadi V, Hajebi A, Bahramnejad A, Baneshi R, Sarabi RE, et al. Prevalence of posttraumatic stress disorder following the earthquake in Iran and Pakistan: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Disaster Med Public Health Prep. (2021) 1:1–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Harorani M, Noruzi Zamenjani M, Golitaleb M, Davodabady F, Zahedi S, Jadidi A, et al. Effects of relaxation on self-esteem of patients with cancer: a randomized clinical trial. Support Care Cancer. (2020) 28:405–11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.