The packing of the title disubstituted ferrocene derivative is stabilized by weak C—H⋯X (X = I, Cl), C—H⋯π(Cp) and C—Cl⋯π(phenyl) interactions, building a three-dimensional network. The cation has planar chirality with S p(Fc) absolute configuration. The structure of the title compound is compared with related disubstituted (trimethylammonio)methyl ferrocenes.
Keywords: 1,2-disubstitued ferrocene; planar chirality; chiral ligands; asymetric catalysis; disordered dichloromethane; crystal structure
Abstract
As a follow-up to our research on the chemistry of disubstituted ferrocene derivatives, the synthesis and the structure of the title compound, [Fe(C5H5)(C15H19N)]I·CH2Cl2, is described. The cation molecule is built up from a ferrocene disubstituted by a trimethylammonium methyl group and a phenyl ring. The asymmetric unit contains the iodide to equilibrate the charge and a disordered dichloromethane solvate. The disordered model results from a roughly statistical exchange (0.6/0.4) between one Cl and one H. The packing of the structure is stabilized by weak C—H⋯X (X = I, Cl), C—H⋯π(Cp) and C—Cl⋯π(phenyl) interactions, building a three-dimensional network. The cation has planar chirality with Sp (Fc) absolute configuration. The structure of the title compound is compared with related disubstituted (trimethylammonio)methyl ferrocenes.
1. Chemical context
Asymmetric catalysis by transition metals has received considerable attention over the last few decades and numerous chiral ligands and complexes allowing high activity and enantioselectivity have been reported (Jacobsen et al., 1999 ▸; Börner, 2008 ▸). For this purpose, catalysts need a chiral ligand presenting at least a chiral center, a chiral axis or a planar chirality. Amongst the various chiral ligands that have been synthesized, ferrocenyl phosphines have proven to be particularly efficient for numerous asymmetric reactions (Buergler et al., 2012 ▸; Gómez Arrayás et al., 2006 ▸; Toma et al., 2014 ▸)
Over the last few years, our team has developed the synthesis of various chiral ferrocenyl ligands for asymmetric catalysis (Audin et al., 2010 ▸; Labande et al., 2007 ▸; Bayda et al., 2014 ▸; Daran et al., 2010 ▸; Wei et al., 2012 ▸, 2014 ▸; Loxq et al., 2014 ▸). We mainly focused on a series of chiral bidentate PX ferrocenyl ligands (X = OR, SR, NHC) bearing planar chirality, which have been successfully used in different homogeneous asymmetric catalytic reactions: allylic substitution, methoxycarbonylation, hydrogenation (Kozinets et al., 2012 ▸; Le Roux et al., 2007 ▸; Diab et al., 2008 ▸; Routaboul et al., 2005 ▸). All of these ligands present a planar chiral 1,2-disubstituted ferrocenyl group with coordination sites on both substituents. More recently, we wanted to extend the application of planar chiral 1,2-disubstituted ferrocenyl groups to the synthesis of ligands with only one substituent bearing a coordination site for fine tuning of existing ligands. To this aim, we needed an enantiomerically pure planar chiral building block bearing a good leaving group in order to introduce a planar chiral substituent on nucleophilic atoms. In this context, we report here the two-step synthesis of the title [(Sp
)-(2-phenylferrocenyl)methyl]trimethylammonium iodide salt.

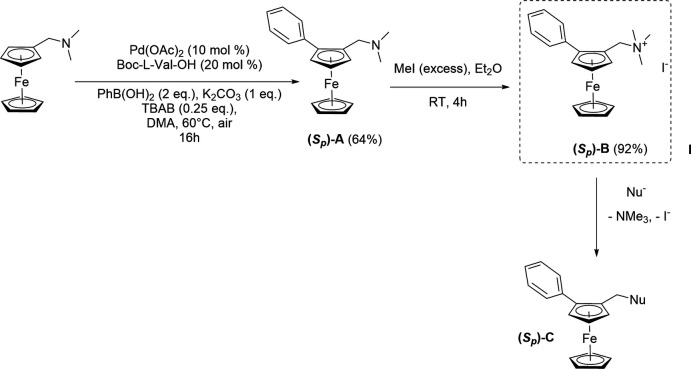
The latter is synthesized in two steps, the first consists in the enantioselective synthesis of (Sp )-A following the procedure developed by S.-L. You and co-workers (Gao et al., 2013 ▸), the second step is a quaternization of the tertiary amine to the ammonium salt by reaction with an excess of iodo methane. (Ferrocenylmethyl) ammoniums have been used successfully as electrophiles because of the stabilization of carbocations in an α position of ferrocene derivatives and because of the presence of a good leaving group: trimethylamine. Nucleophilic[EM2] substitution (Lin et al., 2020 ▸) on the methylene carbon atom in the α position of the ferrocene moiety in compound B, [(Sp)-(2-phenylferrocenyl)methyl]trimethylammonium iodide, should then be favoured and should provide an efficient access to a wide range of various enantiomerically pure ferrocene derivatives of type C including ligands, by reaction with various nucleophiles (amines, thiols, alcohols) (Fig. 1 ▸).
Figure 1.
Synthesis of the title (Sp )-1-dimethylaminomethyl-2-phenylferrocenium iodide salt
2. Structural commentary
The molecular structure is based on a ferrocene moiety in which one of the Cp rings is disubstituted in the 1,2 position by a tri-methylammonium-methyl and a phenyl substituent. The molecule has a positive charge, which is counterbalanced by an iodide (Fig. 2 ▸). Moreover, there is one disordered dichloromethane solvate molecule per asymmetric unit. The disordered model results from the exchange between one Cl and one H in the ratio 0.6/0.4 (Fig. 3 ▸). This disorder might be induced by the occurence of weak C—Cl⋯I intramolecular and C—H⋯Cl intermolecular interactions. There are weak intramolecular C—H⋯I interactions within the asymmetric unit.
Figure 2.
View of the asymmetric unit of the title compound with the atom-labelling scheme. Ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level and the H atoms are represented as small circles of arbitrary radii. C—H⋯X (X = I, Cl) interactions are represented as dashed lines.
Figure 3.
ORTEP view of the disordered CH2Cl2 solvent molecule. Ellipsoids are drawn at the 20% probability level. H atoms are represented as small circles of arbitrary radii.
As a result of the presence of the two substituents on the Cp ring, the cation molecule has planar chirality and its absolute structure is Sp , which is confirmed by the refinement of the Flack parameter (Parsons et al., 2013 ▸). The phenyl ring is twisted with respect to the Cp ring by 48.74 (17)° and the C1–C11–N1 unit is roughly perpendicular to the Cp ring to which it is attached, making a dihedral angle of 89.7 (2)°.
3. Supramolecular features
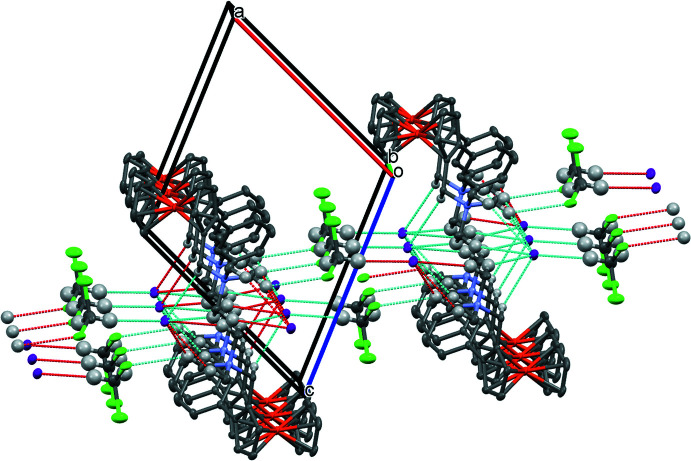
The crystal packing is governed by the occurrence of weak C—H⋯X (X = Cl, I), C—H⋯π and C—Cl⋯π interactions (Table 1 ▸). The iodine atom is engaged in many weak C—H⋯I interactions involving some of the H atoms of the methyl groups, one H atom of the methylene group and the non-disordered H atoms of the dichloromethane solvate. These interactions build up a ribbon developing parallel to the b axis (Fig. 4 ▸). Then the Cl2 atom of the chloroform solvate interacts with the C12—H12C methyl group, thus building a link between the strips, resulting in a layer parallel to the (
 01) plane (Fig. 4 ▸). Moreover, there are two weak C—H⋯π interactions involving atom H13B of the C13 methyl group with the centroid of the Cp ring (C6–C10; Ct2) and atom C23 of the phenyl group with the centroid of the substituted Cp ring (C1–C5; Ct1). Finally, there is also a C—Cl⋯π interaction involving the Cl1 atom of the solvate [C30—Cl1⋯Ct3 (C21–C26), 1.757 (8), 3.4096 (2) and 4.7694 (3) Å, 132.13 (1)°]. All these interactions build up a three-dimensional network.
01) plane (Fig. 4 ▸). Moreover, there are two weak C—H⋯π interactions involving atom H13B of the C13 methyl group with the centroid of the Cp ring (C6–C10; Ct2) and atom C23 of the phenyl group with the centroid of the substituted Cp ring (C1–C5; Ct1). Finally, there is also a C—Cl⋯π interaction involving the Cl1 atom of the solvate [C30—Cl1⋯Ct3 (C21–C26), 1.757 (8), 3.4096 (2) and 4.7694 (3) Å, 132.13 (1)°]. All these interactions build up a three-dimensional network.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C11—H11A⋯I1i | 0.99 | 3.17 | 3.988 (4) | 140 |
| C12—H12C⋯I1 | 0.98 | 3.21 | 4.117 (5) | 154 |
| C12—H12B⋯Cl2C | 0.98 | 3.51 | 3.787 (7) | 99 |
| C13—H13A⋯I1 | 0.98 | 3.27 | 4.158 (5) | 151 |
| C14—H14A⋯I1 | 0.98 | 3.14 | 4.057 (5) | 157 |
| C14—H14B⋯I1i | 0.98 | 3.25 | 4.077 (5) | 143 |
| C30A—H30A⋯I1ii | 1.00 | 2.89 | 3.867 (7) | 166 |
| C13—H13B⋯CT2iii | 0.98 | 2.98 | 3.901 (6) | 158 |
| C23—H23⋯CT1iv | 0.95 | 2.69 | 3.600 (7) | 160 |
Symmetry codes: (i)
 ; (ii)
; (ii)
 ; (iii)
; (iii)
 ; (iv)
; (iv)
 .
.
Figure 4.
Partial packing view showing the C—H⋯X (X = I, Cl) intermolecular interactions resulting in the formation of ribbons parallel to the b axis and C—H⋯Cl interactions linking the ribbons to form a layer parallel to (
 01) plane. The dichloromethane solvate builds the link between the layers.
01) plane. The dichloromethane solvate builds the link between the layers.
4. Database survey
A search in the Cambridge Structural Database (version 5.36; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) using a fragment containing a ferrocenyl disubsituted by a trimethylamoniummethyl and at least a C atom gave six hits that could be compared with the title compound. A comparison of C1—C11, C11—N1 distances and dihedral angles between the Cp ring and the C1–C11–N1 plane is shown in Table 2 ▸. In all these compounds, the bulky N(CH3)3 group is always above the Cp ring to which it is attached. The dihedral angles between the Cp and the C–C–N plane range from 69.8 to 89.7° for the title compound.
Table 2. Comparison of the geometry (Å, °) within the methylamine C–CH2–N fragment for the title compound with related structures.
| C1—C11 | C11—N1 | Cp1/C1>N1 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Title compound | 1.493 (5) | 1.531 (4) | 89.7 (2) |
| BECKUQ | 1.509 | 1.534 | 85.6 |
| LIFWUS | 1.465 | 1.544 | 69.8 |
| LIFWUS | 1.509 | 1.536 | 78.6 |
| LIFXAZ | 1.494 | 1.525 | 70.4 |
| PIJLEB | 1.494 | 1.519 | 86.9 |
| VIKZIA | 1.485 | 1.538 | 86.0 |
| XEQKIN | 1.497 | 1.531 | 84.2 |
5. Synthesis and crystallization
Synthesis of ( Sp )-1-dimethylaminomethyl-2-phenylferrocene [( Sp )-A]: To a solution of phenylboronic acid (110 mg, 1 mmol) in DMA (8 mL) were added Boc–L–Val–OH (43.5 mg, 0.2 mmol), Pd(OAc)2 (22.5 mg, 0.1 mmol), K2CO3 (138.21 mg, 1 mmol), TBAB (tetrabutyl ammonium bromide; 80 mg, 0.25 mmol) and N,N-dimethylferrocenylmethylamine (243 mg, 1 mmol) successively. The mixture was stirred at 333 K under air (open flask). When the reaction was complete (TLC monitoring), the mixture was quenched with saturated aqueous NaHCO3 and the organic phase was extracted three times with EtOAc. The combined organic layers were washed with H2O and brine successively, dried (Na2SO4) and filtered. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure and the residue purified by column chromatography (ethyl acetate/petroleum ether = 1/10, v/v, 2% Et3N) to afford the desired product A as a yellow oil (205 mg, 64% yield). The results are in agreement with published analytical data (Gao et al., 2013 ▸).
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm 7.79–7.71 (m, 2H, CH Ph), 7.41–7.31 (m, 2H, CH Ph), 7.30–7.21 (m, 1H, CH Ph), 4.53–4.47 (m, 1H, CH subst Cp), 4.33 (dd, J = 2.5, 1.5 Hz, 1H, CH subst Cp), 4.26 (t, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H, CH subst Cp), 4.08 (s, 5H, CH Cp), 3.67 (d, J = 12.8 Hz, 1H, CH2), 3.18 (d, J = 12.8 Hz, 1H, CH2), 2.21 (s, 6H, CH3). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm 138.91 (Cq, Ph), 129.36 (CH Ph), 127.93 (CH Ph), 126.06 (CH Ph), 88.17 (Cq subst Cp), 82.24 (Cq subst Cp), 71.56 (CH subst Cp), 70.06 (CH Cp), 69.94 (CH subst Cp), 67.10 (CH subst Cp), 57.93 (CH2), 45.08 (CH3).
Synthesis of [( Sp )-(2-phenylferrocenyl)methyl]trimethylammonium iodide salt [( Sp )-B]: An excess of MeI (1 mL, 1.62 mmol) was added to a solution of A (250 mg, 0.78 mmol) in Et2O (3 mL). The reaction mixture was stirred for 4 h at RT. An abundant yellow solid precipitated. The yellow solid was filtered, washed with Et2O and dried to yield B as a yellow solid (332 mg, 92% yield), which was crystallized in dichloromethane.
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm 7.58–7.50 (m, 2H, CH Ph), 7.46–7.37 (m, 2H, CH Ph), 7.37–7.26 (m, 1H, CH Ph), 5.33 (d, J = 13.4 Hz, 1H, CH2), 4.91 (dd, J = 2.5, 1.5 Hz, 1H, CH subst Cp), 4.83 (d, J = 13.4 Hz, 1H, CH2), 4.56 (dd, J = 2.5, 1.5 Hz,1H, CH subst Cp), 4.52 (t, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H, CH subst Cp), 4.34 (s, 5H, CH Cp), 3.02 (s, 9H, CH3). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm 136.54 (Cq, Ph), 129.86 (CH Ph), 129.05 (CH Ph), 127.72 (CH Ph), 90.61 (Cq subst Cp), 73.44 (CH subst Cp), 72.15 (Cq subst Cp), 70.96 (CH Cp), 70.44 (Cq subst Cp), 70.04 (Cq subst Cp), 65.21 (CH2), 52.76 (CH3).
6. Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 3 ▸. All H atoms attached to C atoms were fixed geometrically and treated as riding with C—H = 1.0 Å (methine), 0.95 Å (aromatic), 0.99 Å (methylene) and 0.98 Å (methyl) with U iso(H) = 1.2Ueq(CH aromatic, methylene) or U iso(H) = 1.5U eq(CH3).
Table 3. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | [Fe(C5H5)(C15H19N)]I·CH2Cl2 |
| M r | 546.08 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21 |
| Temperature (K) | 110 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 10.7919 (7), 10.2128 (5), 11.2941 (7) |
| β (°) | 113.031 (3) |
| V (Å3) | 1145.57 (12) |
| Z | 2 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 2.24 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.30 × 0.10 × 0.10 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Bruker APEXII CCD |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Krause et al., 2015 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.520, 0.746 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 58547, 6993, 6822 |
| R int | 0.052 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.715 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.033, 0.092, 1.06 |
| No. of reflections | 6993 |
| No. of parameters | 247 |
| No. of restraints | 1 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 1.50, −0.69 |
| Absolute structure | Flack x determined using 3144 quotients [(I +)−(I −)]/[(I +)+(I −)] (Parsons et al., 2013 ▸) |
| Absolute structure parameter | 0.018 (6) |
The occurrence of three large residual densities around the C atom of the solvate with distances around 1.76 Å initially suggested the presence of a chloroform solvate molecule. However, if one of the Cl atoms (Cl1) could be refined correctly with full occupancy, the two others display large and elongated ellipsoids. Refining their occupancy factors using the restraints available in SHELXL gave a ratio of 0.6/0.4. So the disordered model is based on an exchange between one H and one Cl (Fig. 3 ▸). The model has been refined using the PART instruction to model two CH2Cl2 models. The non-disordered atoms C30, H30 and Cl1 were split with occupancy factor 0.5 and introduced in the two models (C30A, C30B, H30A, H30B, Cl1A, Cl1B). Their coordinates and thermal parameters were constrained to be identical using the EXYZ and EADP commands available in SHELXL. This disordered model is not perfect, as suggested by a large residual electron density in the vicinity of the atom H30B.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022006053/dj2043sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022006053/dj2043Isup2.hkl
CCDC reference: 2177602
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS), the Institut Universitaire de Technologie (IUT) Paul Sabatier and the Chemistry Department of the IUT Castres for offering access to laboratories and analytical equipment.
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| [Fe(C5H5)(C15H19N)]I·CH2Cl2 | F(000) = 544 |
| Mr = 546.08 | Dx = 1.583 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 10.7919 (7) Å | Cell parameters from 9989 reflections |
| b = 10.2128 (5) Å | θ = 2.8–28.3° |
| c = 11.2941 (7) Å | µ = 2.24 mm−1 |
| β = 113.031 (3)° | T = 110 K |
| V = 1145.57 (12) Å3 | Stick, yellow |
| Z = 2 | 0.30 × 0.10 × 0.10 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 6993 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: micro-focus sealed tube | 6822 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.052 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 30.5°, θmin = 2.1° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Krause et al., 2015) | h = −15→15 |
| Tmin = 0.520, Tmax = 0.746 | k = −14→14 |
| 58547 measured reflections | l = −16→16 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.033 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.092 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0507P)2 + 0.9038P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.06 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 6993 reflections | Δρmax = 1.50 e Å−3 |
| 247 parameters | Δρmin = −0.68 e Å−3 |
| 1 restraint | Absolute structure: Flack x determined using 3144 quotients [(I+)-(I-)]/[(I+)+(I-)] (Parsons et al., 2013) |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Absolute structure parameter: 0.018 (6) |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| Fe1 | 0.94060 (5) | 0.53142 (6) | 0.79508 (5) | 0.02716 (11) | |
| I1 | 0.22433 (3) | 0.13532 (3) | 0.79999 (3) | 0.04532 (10) | |
| N1 | 0.5997 (3) | 0.3408 (3) | 0.8610 (3) | 0.0281 (6) | |
| C1 | 0.7697 (3) | 0.4388 (3) | 0.7817 (3) | 0.0243 (6) | |
| C2 | 0.7375 (3) | 0.5512 (4) | 0.6967 (3) | 0.0248 (6) | |
| C3 | 0.8016 (4) | 0.5304 (5) | 0.6083 (4) | 0.0323 (7) | |
| H3 | 0.797426 | 0.587679 | 0.540618 | 0.039* | |
| C4 | 0.8728 (4) | 0.4085 (5) | 0.6395 (4) | 0.0361 (8) | |
| H4 | 0.924513 | 0.371724 | 0.596435 | 0.043* | |
| C5 | 0.8532 (4) | 0.3521 (4) | 0.7450 (4) | 0.0316 (7) | |
| H5 | 0.888964 | 0.270870 | 0.784766 | 0.038* | |
| C6 | 1.0323 (5) | 0.6035 (7) | 0.9762 (5) | 0.0588 (18) | |
| H6 | 0.996901 | 0.602449 | 1.041048 | 0.071* | |
| C7 | 1.1125 (5) | 0.5035 (6) | 0.9540 (6) | 0.0546 (14) | |
| H7 | 1.139685 | 0.424007 | 1.000841 | 0.065* | |
| C8 | 1.1439 (4) | 0.5440 (6) | 0.8501 (6) | 0.0482 (11) | |
| H8 | 1.196503 | 0.496477 | 0.814202 | 0.058* | |
| C9 | 1.0835 (5) | 0.6679 (6) | 0.8081 (6) | 0.0517 (13) | |
| H9 | 1.088663 | 0.717959 | 0.739283 | 0.062* | |
| C10 | 1.0143 (5) | 0.7038 (6) | 0.8864 (7) | 0.0542 (14) | |
| H10 | 0.964387 | 0.782051 | 0.879465 | 0.065* | |
| C11 | 0.7314 (3) | 0.4163 (4) | 0.8937 (3) | 0.0262 (6) | |
| H11A | 0.723121 | 0.502191 | 0.930581 | 0.031* | |
| H11B | 0.804794 | 0.367396 | 0.960681 | 0.031* | |
| C12 | 0.4841 (4) | 0.4146 (5) | 0.7671 (6) | 0.0463 (11) | |
| H12A | 0.496041 | 0.423269 | 0.685738 | 0.069* | |
| H12B | 0.479920 | 0.501808 | 0.801502 | 0.069* | |
| H12C | 0.400292 | 0.367326 | 0.752068 | 0.069* | |
| C13 | 0.6057 (5) | 0.2094 (4) | 0.8064 (5) | 0.0389 (9) | |
| H13A | 0.518810 | 0.165131 | 0.783295 | 0.058* | |
| H13B | 0.676498 | 0.156995 | 0.870448 | 0.058* | |
| H13C | 0.625814 | 0.219443 | 0.729424 | 0.058* | |
| C14 | 0.5803 (6) | 0.3216 (6) | 0.9844 (5) | 0.0501 (13) | |
| H14A | 0.494379 | 0.277179 | 0.966431 | 0.075* | |
| H14B | 0.579953 | 0.406942 | 1.023851 | 0.075* | |
| H14C | 0.654042 | 0.268085 | 1.043360 | 0.075* | |
| C21 | 0.6496 (4) | 0.6618 (3) | 0.6930 (3) | 0.0279 (7) | |
| C22 | 0.5483 (5) | 0.6960 (5) | 0.5744 (4) | 0.0425 (10) | |
| H22 | 0.539718 | 0.649794 | 0.498588 | 0.051* | |
| C23 | 0.4595 (6) | 0.7987 (7) | 0.5682 (6) | 0.0594 (16) | |
| H23 | 0.390870 | 0.820909 | 0.487518 | 0.071* | |
| C24 | 0.4694 (5) | 0.8671 (5) | 0.6747 (6) | 0.0469 (11) | |
| H24 | 0.408025 | 0.935960 | 0.668760 | 0.056* | |
| C25 | 0.5712 (5) | 0.8348 (5) | 0.7930 (5) | 0.0372 (8) | |
| H25 | 0.579600 | 0.882142 | 0.868150 | 0.045* | |
| C26 | 0.6603 (4) | 0.7334 (4) | 0.8012 (4) | 0.0308 (7) | |
| H26 | 0.729624 | 0.712896 | 0.882019 | 0.037* | |
| C30A | 0.1255 (9) | 0.5103 (11) | 0.4280 (8) | 0.086 (3) | 0.5 |
| H30C | 0.160640 | 0.586709 | 0.485441 | 0.103* | 0.5 |
| H30A | 0.029108 | 0.526078 | 0.374882 | 0.103* | 0.5 |
| Cl1A | 0.2146 (3) | 0.4929 (2) | 0.3278 (2) | 0.0790 (6) | 0.5 |
| Cl2B | 0.1425 (3) | 0.3690 (3) | 0.5204 (3) | 0.0674 (8) | 0.6 |
| C30B | 0.1255 (9) | 0.5103 (11) | 0.4280 (8) | 0.086 (3) | 0.5 |
| H30D | 0.032076 | 0.537089 | 0.374507 | 0.103* | 0.5 |
| H30B | 0.121215 | 0.423883 | 0.465898 | 0.103* | 0.5 |
| Cl1B | 0.2146 (3) | 0.4929 (2) | 0.3278 (2) | 0.0790 (6) | 0.5 |
| Cl2C | 0.1919 (5) | 0.6201 (4) | 0.5491 (4) | 0.0680 (11) | 0.4 |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Fe1 | 0.0183 (2) | 0.0300 (2) | 0.0302 (2) | −0.00341 (18) | 0.00622 (17) | −0.0044 (2) |
| I1 | 0.03471 (13) | 0.05047 (17) | 0.04750 (16) | −0.00545 (12) | 0.01253 (11) | 0.00816 (14) |
| N1 | 0.0238 (13) | 0.0291 (14) | 0.0308 (15) | −0.0013 (11) | 0.0099 (11) | −0.0001 (11) |
| C1 | 0.0183 (13) | 0.0244 (15) | 0.0269 (14) | −0.0016 (11) | 0.0052 (11) | −0.0012 (12) |
| C2 | 0.0205 (13) | 0.0268 (15) | 0.0230 (13) | −0.0016 (12) | 0.0041 (10) | −0.0013 (11) |
| C3 | 0.0294 (16) | 0.0410 (19) | 0.0267 (15) | −0.0056 (16) | 0.0113 (13) | −0.0044 (15) |
| C4 | 0.0301 (17) | 0.041 (2) | 0.040 (2) | −0.0051 (15) | 0.0170 (16) | −0.0133 (17) |
| C5 | 0.0237 (15) | 0.0258 (16) | 0.043 (2) | −0.0018 (12) | 0.0102 (14) | −0.0055 (14) |
| C6 | 0.035 (2) | 0.095 (5) | 0.040 (2) | −0.026 (3) | 0.0078 (18) | −0.027 (3) |
| C7 | 0.030 (2) | 0.060 (3) | 0.051 (3) | −0.014 (2) | −0.0078 (19) | 0.011 (2) |
| C8 | 0.0196 (16) | 0.059 (3) | 0.062 (3) | −0.0088 (19) | 0.0115 (17) | −0.013 (3) |
| C9 | 0.036 (2) | 0.053 (3) | 0.058 (3) | −0.020 (2) | 0.010 (2) | 0.003 (2) |
| C10 | 0.030 (2) | 0.048 (3) | 0.072 (4) | −0.0106 (19) | 0.007 (2) | −0.024 (3) |
| C11 | 0.0221 (14) | 0.0273 (15) | 0.0253 (14) | −0.0034 (12) | 0.0050 (12) | −0.0001 (12) |
| C12 | 0.0215 (16) | 0.045 (2) | 0.065 (3) | 0.0037 (16) | 0.0092 (18) | 0.016 (2) |
| C13 | 0.036 (2) | 0.0298 (19) | 0.050 (2) | −0.0059 (15) | 0.0161 (18) | −0.0073 (17) |
| C14 | 0.054 (3) | 0.062 (3) | 0.042 (2) | −0.023 (2) | 0.027 (2) | −0.010 (2) |
| C21 | 0.0245 (14) | 0.0288 (18) | 0.0265 (14) | 0.0016 (12) | 0.0058 (12) | 0.0030 (12) |
| C22 | 0.041 (2) | 0.045 (2) | 0.0309 (19) | 0.0142 (19) | 0.0026 (17) | 0.0023 (17) |
| C23 | 0.050 (3) | 0.064 (3) | 0.046 (3) | 0.030 (3) | −0.001 (2) | 0.007 (2) |
| C24 | 0.044 (2) | 0.041 (2) | 0.057 (3) | 0.018 (2) | 0.021 (2) | 0.010 (2) |
| C25 | 0.041 (2) | 0.0325 (17) | 0.044 (2) | 0.0020 (16) | 0.0226 (18) | −0.0021 (15) |
| C26 | 0.0319 (17) | 0.0299 (17) | 0.0298 (16) | 0.0016 (14) | 0.0112 (14) | 0.0025 (13) |
| C30A | 0.071 (5) | 0.121 (8) | 0.060 (4) | 0.051 (5) | 0.021 (3) | 0.005 (4) |
| Cl1A | 0.1058 (16) | 0.0728 (11) | 0.0816 (12) | 0.0165 (10) | 0.0615 (12) | 0.0079 (9) |
| Cl2B | 0.0526 (12) | 0.107 (2) | 0.0579 (13) | 0.0290 (14) | 0.0379 (11) | 0.0377 (14) |
| C30B | 0.071 (5) | 0.121 (8) | 0.060 (4) | 0.051 (5) | 0.021 (3) | 0.005 (4) |
| Cl1B | 0.1058 (16) | 0.0728 (11) | 0.0816 (12) | 0.0165 (10) | 0.0615 (12) | 0.0079 (9) |
| Cl2C | 0.105 (3) | 0.0471 (19) | 0.0525 (17) | 0.005 (2) | 0.0320 (19) | −0.0071 (15) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Fe1—C1 | 2.025 (3) | C9—H9 | 0.9500 |
| Fe1—C6 | 2.030 (5) | C10—H10 | 0.9500 |
| Fe1—C7 | 2.034 (5) | C11—H11A | 0.9900 |
| Fe1—C8 | 2.037 (4) | C11—H11B | 0.9900 |
| Fe1—C5 | 2.037 (4) | C12—H12A | 0.9800 |
| Fe1—C10 | 2.038 (5) | C12—H12B | 0.9800 |
| Fe1—C9 | 2.041 (5) | C12—H12C | 0.9800 |
| Fe1—C2 | 2.043 (3) | C13—H13A | 0.9800 |
| Fe1—C4 | 2.048 (4) | C13—H13B | 0.9800 |
| Fe1—C3 | 2.055 (4) | C13—H13C | 0.9800 |
| N1—C12 | 1.488 (6) | C14—H14A | 0.9800 |
| N1—C13 | 1.489 (5) | C14—H14B | 0.9800 |
| N1—C14 | 1.500 (6) | C14—H14C | 0.9800 |
| N1—C11 | 1.529 (5) | C21—C26 | 1.390 (5) |
| C1—C5 | 1.435 (5) | C21—C22 | 1.402 (5) |
| C1—C2 | 1.449 (5) | C22—C23 | 1.404 (7) |
| C1—C11 | 1.495 (5) | C22—H22 | 0.9500 |
| C2—C3 | 1.435 (5) | C23—C24 | 1.359 (9) |
| C2—C21 | 1.465 (5) | C23—H23 | 0.9500 |
| C3—C4 | 1.433 (7) | C24—C25 | 1.398 (8) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C24—H24 | 0.9500 |
| C4—C5 | 1.412 (6) | C25—C26 | 1.391 (6) |
| C4—H4 | 0.9500 | C25—H25 | 0.9500 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | C26—H26 | 0.9500 |
| C6—C10 | 1.400 (10) | C30A—Cl2B | 1.748 (11) |
| C6—C7 | 1.422 (10) | C30A—Cl1A | 1.758 (8) |
| C6—H6 | 0.9500 | C30A—H30C | 0.9900 |
| C7—C8 | 1.406 (9) | C30A—H30A | 0.9900 |
| C7—H7 | 0.9500 | C30B—Cl2C | 1.695 (11) |
| C8—C9 | 1.418 (9) | C30B—Cl1B | 1.758 (8) |
| C8—H8 | 0.9500 | C30B—H30D | 0.9900 |
| C9—C10 | 1.411 (9) | C30B—H30B | 0.9900 |
| C1—Fe1—C6 | 108.39 (19) | C7—C6—Fe1 | 69.7 (3) |
| C1—Fe1—C7 | 119.30 (19) | C10—C6—H6 | 125.7 |
| C6—Fe1—C7 | 41.0 (3) | C7—C6—H6 | 125.7 |
| C1—Fe1—C8 | 153.2 (2) | Fe1—C6—H6 | 126.0 |
| C6—Fe1—C8 | 68.1 (2) | C8—C7—C6 | 107.3 (5) |
| C7—Fe1—C8 | 40.4 (2) | C8—C7—Fe1 | 69.9 (3) |
| C1—Fe1—C5 | 41.37 (15) | C6—C7—Fe1 | 69.3 (3) |
| C6—Fe1—C5 | 126.6 (2) | C8—C7—H7 | 126.4 |
| C7—Fe1—C5 | 106.4 (2) | C6—C7—H7 | 126.4 |
| C8—Fe1—C5 | 117.9 (2) | Fe1—C7—H7 | 126.0 |
| C1—Fe1—C10 | 127.2 (2) | C7—C8—C9 | 108.2 (5) |
| C6—Fe1—C10 | 40.3 (3) | C7—C8—Fe1 | 69.7 (3) |
| C7—Fe1—C10 | 68.5 (3) | C9—C8—Fe1 | 69.8 (3) |
| C8—Fe1—C10 | 68.3 (2) | C7—C8—H8 | 125.9 |
| C5—Fe1—C10 | 164.6 (2) | C9—C8—H8 | 125.9 |
| C1—Fe1—C9 | 164.8 (2) | Fe1—C8—H8 | 126.2 |
| C6—Fe1—C9 | 67.8 (3) | C10—C9—C8 | 108.0 (5) |
| C7—Fe1—C9 | 68.3 (2) | C10—C9—Fe1 | 69.7 (3) |
| C8—Fe1—C9 | 40.7 (2) | C8—C9—Fe1 | 69.5 (3) |
| C5—Fe1—C9 | 152.8 (2) | C10—C9—H9 | 126.0 |
| C10—Fe1—C9 | 40.5 (3) | C8—C9—H9 | 126.0 |
| C1—Fe1—C2 | 41.75 (14) | Fe1—C9—H9 | 126.4 |
| C6—Fe1—C2 | 120.6 (2) | C6—C10—C9 | 107.8 (5) |
| C7—Fe1—C2 | 155.2 (2) | C6—C10—Fe1 | 69.6 (3) |
| C8—Fe1—C2 | 163.3 (2) | C9—C10—Fe1 | 69.9 (3) |
| C5—Fe1—C2 | 69.89 (15) | C6—C10—H10 | 126.1 |
| C10—Fe1—C2 | 108.24 (19) | C9—C10—H10 | 126.1 |
| C9—Fe1—C2 | 126.2 (2) | Fe1—C10—H10 | 126.1 |
| C1—Fe1—C4 | 68.89 (16) | C1—C11—N1 | 114.3 (3) |
| C6—Fe1—C4 | 163.1 (3) | C1—C11—H11A | 108.7 |
| C7—Fe1—C4 | 124.6 (2) | N1—C11—H11A | 108.7 |
| C8—Fe1—C4 | 106.3 (2) | C1—C11—H11B | 108.7 |
| C5—Fe1—C4 | 40.44 (18) | N1—C11—H11B | 108.7 |
| C10—Fe1—C4 | 154.4 (3) | H11A—C11—H11B | 107.6 |
| C9—Fe1—C4 | 119.1 (2) | N1—C12—H12A | 109.5 |
| C2—Fe1—C4 | 69.31 (16) | N1—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| C1—Fe1—C3 | 69.09 (15) | H12A—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| C6—Fe1—C3 | 155.3 (2) | N1—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C7—Fe1—C3 | 162.3 (2) | H12A—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C8—Fe1—C3 | 125.5 (2) | H12B—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C5—Fe1—C3 | 68.75 (18) | N1—C13—H13A | 109.5 |
| C10—Fe1—C3 | 120.5 (2) | N1—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| C9—Fe1—C3 | 107.8 (2) | H13A—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| C2—Fe1—C3 | 40.99 (14) | N1—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C4—Fe1—C3 | 40.88 (19) | H13A—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C12—N1—C13 | 108.7 (4) | H13B—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C12—N1—C14 | 110.2 (4) | N1—C14—H14A | 109.5 |
| C13—N1—C14 | 108.1 (4) | N1—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C12—N1—C11 | 110.9 (3) | H14A—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C13—N1—C11 | 111.6 (3) | N1—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C14—N1—C11 | 107.2 (3) | H14A—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C5—C1—C2 | 108.2 (3) | H14B—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C5—C1—C11 | 124.2 (3) | C26—C21—C22 | 118.3 (4) |
| C2—C1—C11 | 127.5 (3) | C26—C21—C2 | 123.4 (3) |
| C5—C1—Fe1 | 69.8 (2) | C22—C21—C2 | 118.3 (4) |
| C2—C1—Fe1 | 69.78 (19) | C21—C22—C23 | 119.8 (4) |
| C11—C1—Fe1 | 123.7 (2) | C21—C22—H22 | 120.1 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 106.7 (3) | C23—C22—H22 | 120.1 |
| C3—C2—C21 | 125.2 (3) | C24—C23—C22 | 121.6 (5) |
| C1—C2—C21 | 127.9 (3) | C24—C23—H23 | 119.2 |
| C3—C2—Fe1 | 70.0 (2) | C22—C23—H23 | 119.2 |
| C1—C2—Fe1 | 68.47 (19) | C23—C24—C25 | 119.0 (4) |
| C21—C2—Fe1 | 129.6 (3) | C23—C24—H24 | 120.5 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 108.4 (4) | C25—C24—H24 | 120.5 |
| C4—C3—Fe1 | 69.3 (2) | C26—C25—C24 | 120.3 (4) |
| C2—C3—Fe1 | 69.0 (2) | C26—C25—H25 | 119.9 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 125.8 | C24—C25—H25 | 119.9 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 125.8 | C21—C26—C25 | 121.1 (4) |
| Fe1—C3—H3 | 127.5 | C21—C26—H26 | 119.5 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 108.6 (3) | C25—C26—H26 | 119.5 |
| C5—C4—Fe1 | 69.4 (2) | Cl2B—C30A—Cl1A | 110.2 (5) |
| C3—C4—Fe1 | 69.8 (2) | Cl2B—C30A—H30C | 109.6 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 125.7 | Cl1A—C30A—H30C | 109.6 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 125.7 | Cl2B—C30A—H30A | 109.6 |
| Fe1—C4—H4 | 126.7 | Cl1A—C30A—H30A | 109.6 |
| C4—C5—C1 | 108.1 (4) | H30C—C30A—H30A | 108.1 |
| C4—C5—Fe1 | 70.2 (2) | Cl2C—C30B—Cl1B | 114.9 (7) |
| C1—C5—Fe1 | 68.9 (2) | Cl2C—C30B—H30D | 113.2 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 126.0 | Cl1B—C30B—H30D | 109.6 |
| C1—C5—H5 | 126.0 | Cl2C—C30B—H30B | 108.5 |
| Fe1—C5—H5 | 126.5 | Cl1B—C30B—H30B | 108.5 |
| C10—C6—C7 | 108.7 (5) | H30D—C30B—H30B | 101.0 |
| C10—C6—Fe1 | 70.2 (3) | ||
| N1—C11—C1—C2 | 92.4 (4) | N1—C11—C1—C5 | −91.2 (4) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C11—H11A···I1i | 0.99 | 3.17 | 3.988 (4) | 140 |
| C12—H12C···I1 | 0.98 | 3.21 | 4.117 (5) | 154 |
| C12—H12B···Cl2C | 0.98 | 3.51 | 3.787 (7) | 99 |
| C13—H13A···I1 | 0.98 | 3.27 | 4.158 (5) | 151 |
| C14—H14A···I1 | 0.98 | 3.14 | 4.057 (5) | 157 |
| C14—H14B···I1i | 0.98 | 3.25 | 4.077 (5) | 143 |
| C30A—H30A···I1ii | 1.00 | 2.89 | 3.867 (7) | 166 |
| C13—H13B···CT2iii | 0.98 | 2.98 | 3.901 (6) | 158 |
| C23—H23···CT1iv | 0.95 | 2.69 | 3.600 (7) | 160 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, y+1/2, −z+2; (ii) −x, y+1/2, −z+1; (iii) −x+2, y−1/2, −z+2; (iv) −x+1, y+1/2, −z+1.
Funding Statement
Funding for this research was provided by: Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS), Midi-Pyrénnées region, Institut Universitaire de Technologie (IUT) Paul Sabatier and the Syndicat Mixte de Castres Mazamet (PhD grant ALDOCT000431.
References
- Audin, C., Daran, J.-C., Deydier, E., Manoury, E. & Poli, R. (2010). CR Chimie 13, 890-899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Bayda, S., Cassen, A., Daran, J.-C., Audin, C., Poli, R., Manoury, E. & Deydier, E. (2014). J. Organomet. Chem. 772–773, 258–264.
- Börner, A. (2008). Editor. Phosphorus Ligands in Asymmetric Catalysis, Vols. 1–3. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH.
- Bruker (2015). APEX2. and SAINT. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Buergler, J. F., Niedermann, K. & Togni, A. (2012). Chem. Eur. J. 18, 632–640. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Burnett, M. N. & Johnson, C. K. (1996). ORTEPIII. Report ORNL-6895. Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Tennessee, USA.
- Butler, I. R., Horton, P. N. & Hursthouse, M. B. (2002). University of Southampton, Crystal Structure Report Archive, 908.
- Daran, J.-C., Audin, C., Deydier, E., Manoury, E. & Poli, R. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, m1417–m1418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Deck, P. A., Lane, M. J., Montgomery, J. L., Slebodnick, C. & Fronczek, F. R. (2000). Organometallics, 19, 1013–1024.
- Diab, L., Gouygou, M., Manoury, E., Kalck, P. & Urrutigoïty, M. (2008). Tetrahedron Lett. 49, 5186–5189.
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Gao, D.-W., Shi, Y.-C., Gu, Q., Zhao, Z.-L. & You, S.-L. (2013). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 86–89. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Gómez Arrayás, R., Adrio, J. & Carretero, J. C. (2006). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 45, 7674–7715. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Hitchcock, P. B., Leigh, G. J. & Togrou, M. (2002). J. Organomet. Chem. 664, 245–257.
- Jacobsen, E. N., Pfalz, A. & Yamamoto, H. (1999). Editors. Comprehensive Asymmetric Catalysis, Vols. 1–3. Berlin: Springer.
- Kozinets, E. M., Koniev, O., Filippov, O. A., Daran, J.-C., Poli, R., Shubina, E. S., Belkova, N. V. & Manoury, E. (2012). Dalton Trans. 41, 11849–11859. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Krause, L., Herbst-Irmer, R., Sheldrick, G. M. & Stalke, D. (2015). J. Appl. Cryst. 48, 3–10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Labande, A., Daran, J.-C., Manoury, E. & Poli, R. (2007). Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. pp. 1205–1209.
- Le Roux, E., Malacea, R., Manoury, E., Poli, R., Gonsalvi, L. & Peruzzini, A. (2007). Adv. Synth. Catal. 349, 309–313.
- Lin, Y., Ong, Y. C., Keller, S., Karges, J., Bouchene, R., Manoury, E., Blacque, O., Müller, J., Anghel, N., Hemphill, A., Häberli, C., Taki, A. C., Gasser, R. B., Cariou, K., Keiser, J. & Gasser, G. (2020). Dalton Trans. 49, 6616–6626. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Loxq, P., Debono, N., Gülcemal, S., Daran, J.-C., Manoury, E., Poli, R., Çetinkaya, B. & Labande, A. (2014). New J. Chem. 38, 338–347.
- Macrae, C. F., Sovago, I., Cottrell, S. J., Galek, P. T. A., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Platings, M., Shields, G. P., Stevens, J. S., Towler, M. & Wood, P. A. (2020). J. Appl. Cryst. 53, 226–235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Malezieux, B., Gruselle, M., Troitskaya, L. L., Sokolov, V. I. & Vaissermann, J. (1994). Organometallics, 13, 2979–2986.
- Parsons, S., Flack, H. D. & Wagner, T. (2013). Acta Cryst. B69, 249–259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Routaboul, L., Vincendeau, S., Daran, J.-C. & Manoury, E. (2005). Tetrahedron Asymmetry, 16, 2685–2690.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Toma, Š., Csizmadiová, J., Mečiarová, M. & Šebesta, R. (2014). Dalton Trans. 43, 16557–16579. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Wei, M.-M., Audin, C., Manoury, E., Deydier, E. & Daran, J.-C. (2014). Acta Cryst. C70, 281–284. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Wei, M.-M., García-Melchor, M., Daran, J.-C., Audin, C., Lledós, A., Poli, R., Deydier, E. & Manoury, E. (2012). Organometallics, 31, 6669–6680.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022006053/dj2043sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022006053/dj2043Isup2.hkl
CCDC reference: 2177602
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report