The synthesis and crystal structure of rac-2-[7-methyl-4-(4-methylphenyl)-4-(phenylimino)-6,6-bis(propan-2-yl)-3-oxa-4λ6-thia-5-aza-6-silaoct-4-en-1-yl]-2,3-dihydro-1H-isoindole-1,3-dione are reported.
Keywords: sulfondiimidoate, sulfondiimidate, crystal structure, bioisosters
Abstract
The title compound {systematic name: rac-2-[7-methyl-4-(4-methylphenyl)-4-(phenylimino)-6,6-bis(propan-2-yl)-3-oxa-4λ6-thia-5-aza-6-silaoct-4-en-1-yl]-2,3-dihydro-1H-isoindole-1,3-dione}, C32H41N3O3SSi, was synthesized by desoxychlorination of 4-methyl-N-phenyl-N′-(triisopropylsilyl)benzenesulfonimidamide and subsequent reaction with 2-(2-hydroxyethyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione. The racemic compound was crystallized from isopropanol. The structural characterization by single-crystal X-ray diffraction revealed two double-bonded nitrogen atoms to the central sulfur atom and an overall crystal packing driven by its aromatic interactions.
1. Chemical context
Since 2013 (Lücking, 2013 ▸, 2019 ▸), there has been an increased research interest in bioisosters of sulfonamides and sulfones. In addition to vigorous interest in the development of new synthetic procedures towards sulfonimidamides (Nandi & Arvidsson, 2018 ▸; Chen & Gibson, 2015 ▸; Wen et al., 2016 ▸; Izzo et al., 2017 ▸; Greed et al., 2020 ▸; Liu et al., 2021 ▸), activities towards the synthesis of sulfondiimides have recently just begun (Zhang et al., 2019 ▸; Bohmann et al., 2019 ▸). With the synthesis of stable sulfondiimidamides, Zhang & Willis (2022 ▸) introduced a new functional group for medicinal chemistry.
The different aza-analogs of sulfonamides and sulfones have interesting properties for medicinal chemistry due to the (additional) nitrogen atom(s). Besides the potential centrochirality of sulfur, the nitrogen substituents offer new possibilities for functionalization optimizing steric demand, solubility and reactivity.
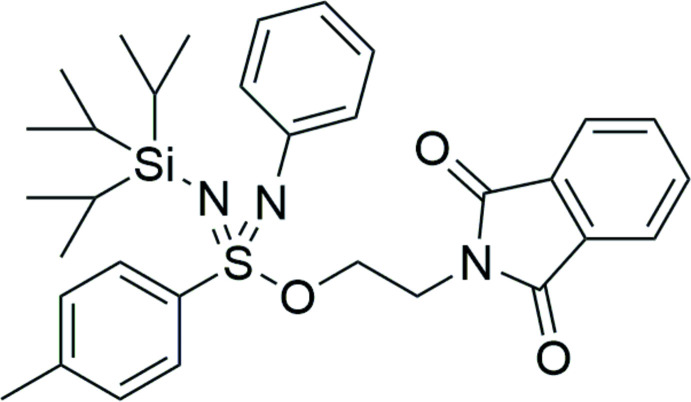
The herein reported sulfondiimidoate 1 is, based on extensive database searches, not yet described in the literature and therefore represents the first member of a new substance class. It can be described as an aza-oxo-inverse sulfonamide or an aza-analogue of a sulfonimidoate.
2. Structural commentary
The title compound 1 crystallizes in the triclinic crystal system and P
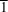 as the centrosymmetric space group, having one molecule in the asymmetric unit (Fig. 1 ▸). Geometric parameters may be regarded as normal. A selection is listed in Table 1 ▸.
as the centrosymmetric space group, having one molecule in the asymmetric unit (Fig. 1 ▸). Geometric parameters may be regarded as normal. A selection is listed in Table 1 ▸.
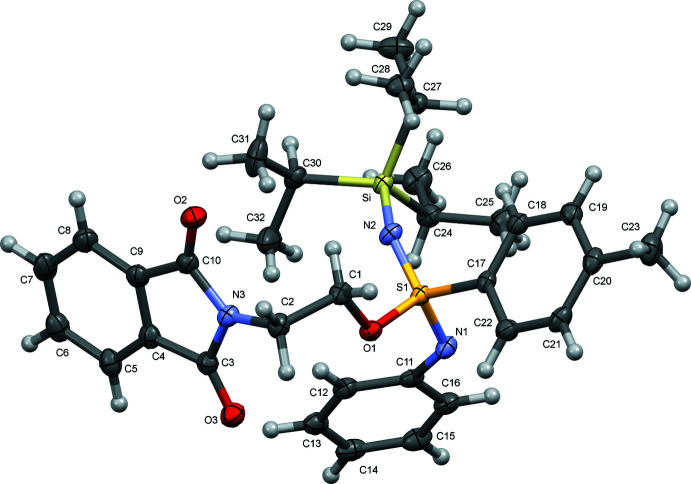
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of 2-(1,3-dioxoisoindolin-2-yl)ethyl-4-methyl-N-phenyl-N′-(triisopropylsilyl)benzenesulfondiimidoate (1) with the atomic numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Table 1. Selected geometric parameters (Å, °).
| S1—N1 | 1.5139 (16) | S1—C17 | 1.7718 (19) |
| S1—N2 | 1.4838 (16) | Si—N2 | 1.7240 (17) |
| S1—O1 | 1.6257 (14) | N1—C11 | 1.412 (2) |
| N1—S1—O1 | 105.93 (8) | N2—S1—N1 | 126.60 (9) |
| N1—S1—C17 | 101.98 (9) | S1—N2—Si | 142.24 (11) |
| N2—S1—O1 | 107.27 (8) | N2—Si—C27 | 105.99 (9) |
The tetrahedral molecular structure shows a sulfur as the central atom, surrounded by four substituents, including two sulfur–nitrogen double bonds. As a result of the steric repulsion of the aniline ring and the bulky triisopropylsilyl group, the angle N2—S1—N1 at 126.60 (9)° is larger than the typical tetrahedral angle (109.5°), whereas the angle between the aniline and toluene ring (N1—S1—C17) and also the 1,3-dioxoisoindolin moiety (N1—S1—O1) are smaller at 101.98 (9) and 105.93 (8)°, respectively. The remaining angle (N2—S1—O1) is 107.27 (8)°. The bond lengths between S1—N1 [1.5139 (16) Å] and S1—N2 [1.4838 (16) Å] are similar to those observed in crystal structures of sulfoximines [1.484 Å; CSD refcode: LISJAZ (Lemasson et al., 2007 ▸) or 1.518 Å; CSD refcode: NADNAH; (Mash et al., 1996 ▸)], and therefore confirming the presence of the double bonds (Reggelin & Zur, 2000 ▸). The ring systems are planar (r.m.s values of 0.003 and 0.007 Å for the phenyl rings and 0.022 Å for the phthalimide).
3. Supramolecular features
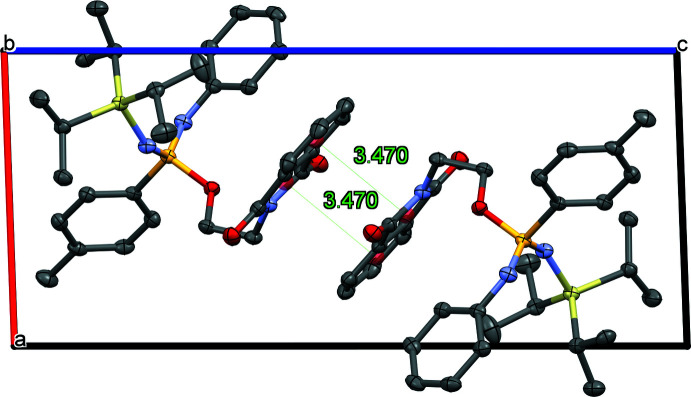
The title compound 1 contains secondary nitrogen groups and a dicarboximide, which are hydrogen-bond acceptors, but no strong or moderate intermolecular hydrogen bonds were detected in the crystal. Geometric details of some possible weak hydrogen bonds are listed in Table 2 ▸. This includes three borderline C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, which link the chains via the operators 1 + x, −1 + y, z and 2 − x, 1 − y, 1 − z. The contact C31—H31⋯N1, involving a tertiary methyl group, connects the molecules via the operator x, 1 + y, z. Fig. 2 ▸ shows the unit cell of the compound along the b-axis. It appears that the crystal structure contains anti-parallel π stacking interactions of the phthalimide between its electron-rich six-membered ring and electron-poor five-membered ring (Ahmed et al., 2019 ▸). The centroid-to-centroid distance of 3.470 (1) Å, which is in the range of π–π stacking interactions, confirms its presence. The crystal packing is mainly driven by its attractive intermolecular aromatic interactions, as can be shown by the Aromatics Analyser (feature available in Mercury as part of the CSD-Materials and CSD-Enterprise suites). The distance between centroids for which the assessment was labelled ‘strong’ equals to 4.11 Å (score: 9.3) and for the ‘moderate’ ones between 4.48 and 6.39 Å (score: 6.9–3.7) by the CCDC’s Aromatics Analyser using a score from 0 (no stabilizing contribution) to 10 (an ideal aromatic interaction geometry) (assessment: ‘weak’ 0–3, ‘moderate’ 3–7, ‘strong’ 7–10. Mercury 2021.3.0 (Build 333817) used (Macrae et al., 2020 ▸).
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C15—H15⋯O2i | 0.95 | 2.52 | 3.429 (3) | 160 |
| C22—H22⋯O2ii | 0.95 | 2.64 | 3.348 (3) | 132 |
| C14—H14⋯O3iii | 0.95 | 2.52 | 3.429 (3) | 161 |
| C31—H31B⋯N1iv | 0.98 | 2.60 | 3.361 (3) | 135 |
Symmetry codes: (i)
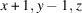 ; (ii)
; (ii)
 ; (iii)
; (iii)
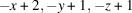 ; (iv)
; (iv)
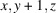 .
.
Figure 2.
Crystal packing in rac-2-(1,3-dioxoisoindolin-2-yl)ethyl-4-methyl-N-phenyl-N′-(triisopropylsilyl)benzenesulfondiimidoate (1) viewed along the b axis. Antiparallel stacking of the phthalimide occurs with a centroid–centroid distance of 3.470 (1) Å. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level and H atoms are omitted for clarity.
4. Database survey
The herein reported sulfondiimidoate 1 is, based on extensive database searches, not yet described in the literature. A Scifindern structure search with undefined bonds on all substituents of the sulfur and a substituent on the oxygen atom resulted in no structure matches as drawn (SciFinder; Chemical Abstracts Service: Columbus, OH; https://scifinder.cas.org; accessed: 06.05.2022). A broadly defined Cambridge Structural Database search with the five central atoms and any type of bonds (SMARTS pattern [#7]∼[#16](∼[#8])(∼[#6])∼[#7]) on CSD version 5.43 November 2021 plus update of March 2022 found 85 hits (Groom et al., 2016 ▸), all of which are sulfonimidamides.
Restricting this query to a single bond (instead of any bond) between the sulfur and the oxygen returns zero hits. The mean distance between sulfur and oxygen in the 85 hits dataset is 1.436 with a standard deviation of 0.014. The distance S1—O1 (see also Table 1 ▸) is hence clearly a single bond and similar functional groups have not been missed by setting the query in too narrow a way.
5. Synthesis and crystallization
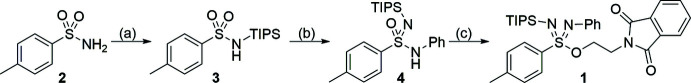
Molecular schemes with the atom numbering used in the NMR assignments can be found in Figures S1–S3 in the supporting information. Solvent residue signals were used as internal standard according to the literature [1H-NMR: δ (CHCl3) = 7.26 ppm; 13C-NMR: δ (CDCl3) = 77.16 ppm; (Gottlieb et al., 1997 ▸)]. The synthesis is shown in Fig. 3 ▸.
Figure 3.
Synthesis of the sulfondiimidoate 1. (a) TIPS-Cl, NEt3; (b) C2Cl6, PPh3, NEt3, aniline; (c) C2Cl6, PPh3, NEt3, N-hydroxyethylphthalimide.
N -(Tri -iso -propylsilyl)-4-methylbenzenesulfonamide (3)
7.51 mL (6.82 g, 35.0 mmol, 1.2 eq.) of TIPS-Cl and 12.1 mL (8.87 g, 87.6 mmol, 3.0 eq.) of NEt3 were added to a suspension of 5.00 g (29.2 mmol, 1.0 eq.) of p-toluenesulfonamide (2) in 100 mL of CH2Cl2. After stirring for 62 h, 100 mL of 1M HCl were added to the reaction mixture. The aqueous layer was extracted with CH2Cl2 three times, the combined organic layers were dried over MgSO4, the solvent was removed under reduced pressure and the crude product was dissolved in 100 mL of CH2Cl2. After addition of 300 mL of petroleum ether, the CH2Cl2 was removed under reduced pressure. The resulting precipitate was filtered off and washed with pentane. After drying, the protected sulfonamide 3 (9.12 g, 27.8 mmol, 95%) was obtained as a colorless solid. Rf 0.75 (20% EtOAc in pentane). M.p. = 427 K. IR (ATR)/cm−1 1462, 1344, 1286, 1154, 1094, 1004, 936. 1H-NMR (CDCl3, 500 MHz, 300 K): δ = 7.80 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 4-H2), 7.27 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 3-H2), 4.43 (bs, 6-H1), 2.42 (s, 1-H3), 1.29 (hep., J = 7.5 Hz, 7-H3), 1.15 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 8-H18) ppm. 13C-NMR (CDCl3, 125 MHz, 300 K): δ = 142.6 (2-C), 141.1 (5-C), 129.5 (3-C2), 126.2 (4-C2), 21.6 (1-C), 18.1 (8-C6), 12.1 (7-C3) ppm. Calculated for C16H29NO2SSi: C 58.67, H 8.92, N 4.28; found: C 58.68, H 9.30, N 4.53. ESI–MS: m/z = 328.18 [M + H]+, 677.33 [2M + Na]+.
4-Methyl- N -phenyl- N ′-(tri- iso -propylsilyl)benzenesulfonimidamide (4)
3.98 g (16.8 mmol, 1.1 eq) of C2Cl6 and 4.40 g (16.8 mmol, 1.1 eq) of PPh3 were heated to reflux of the solvent in 60 mL of CHCl3 for 6 h. After cooling to room temperature, 3.19 mL (2.32 g, 22.9 mmol, 1.5 eq) of NEt3 was added via syringe. After five minutes, the reaction mixture was cooled to 273 K. After another five minutes, 5.00 g (15.3 mmol, 1.0 eq) of 4-methyl-N-(triisopropylsilyl)benzenesulfonamide (3) were added. After ten more minutes, 5.58 mL (5.69 g, 61.1 mmol, 4.0 eq) of aniline were added via syringe and the mixture was stirred for one h, at which point the reaction was stopped by the addition of 100 mL of saturated NH4Cl solution. The aqueous phase was extracted three times with 50 mL of CH2Cl2. The combined organic layers were dried over MgSO4, the solvent was removed under reduced pressure and the crude product was purified by flash chromatography (5% EtOAc in pentane) affording the sulfonimidamide 4 (5.64 g, 14.0 mmol, 92%) as a colorless solid. Rf 0.63 (20% EtOAc in pentane). M.p. = 364 K. IR (ATR)/cm−1 3228, 1600, 1480, 1410, 1347, 1282, 1141, 1091, 895. 1H-NMR (CDCl3, 500 MHz, 300 K): δ = 7.68 (d, J = 8.3Hz, 4-H2), 7.19–7.13 (m, 3/8-H4), 7.03–6.97 (m, 9/10-H3), 6.30 (bs, 6-H), 2.34 (s, 1-H3), 1.18–1.03 (m, 11/12-H21) ppm. 13C-NMR (CDCl3, 125 MHz, 300 K): δ = 142.2 (7-C), 141.0 (2-C), 138.9 (5-C), 129.2 (9-C2), 129.0 (3-C2), 127.1 (4-C2), 124.2 (8-C2), 121.2 (10-C), 21.5 (1-C), 18.5 (12-C6), 13.3 (11-C3) ppm. Calculated for C22H34N2OSSi: C 65.62, H 6.96, N 8.51; found: C 65.65, H 6.97, N 8.55. ESI–MS: m/z = 403.22 [M + H]+.
rac -2-(1,3-Dioxo- iso -indolin-2-yl)ethyl-4-methyl- N -phenyl- N ′-(tri- iso -propylsilyl)benzenesulfondiimidoate (1)
282 mg (1.19 mmol, 1.2 eq) of C2Cl6 and 313 mg (1.19 mmol, 1.2 eq) of PPh3 were heated to reflux of the solvent in 5 mL of CHCl3 for 6 h. After cooling to room temperature, 0.83 mL (603 mg, 5.96 mmol, 6.0 eq) of NEt3 were added via syringe. After five minutes, the reaction mixture was cooled to 273 K. After five more minutes, 400 mg (0.99 mmol, 1.0 eq) of 4-methyl-N-phenyl-N′-(triisopropylsilyl)benzenesulfonimidamide (4) were added and the reaction mixture was stirred for 20 more minutes at 273 K, at which point 1.52 g (7.95 mmol, 8.0 eq) of 2-(2-hydroxyethyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione were added. The mixture was stirred for another 30 min and then quenched with 20 mL of saturated NH4Cl solution. After phase separation, the aqueous solution was extracted three times with 20 mL of CH2Cl2, the combined organic layers were dried over MgSO4, the solvent was removed under reduced pressure and the resulting crude product was purified by flash chromatography (8% EtOAc in pentane) affording the sulfondiimidoate 1 (447 mg, 0.78 mmol, 78%) as a colorless solid. Crystals suitable for X-ray structure analysis were obtained by recrystallization from iso-propanol. Rf 0.16 (10% EtOAc in pentane). M.p. = 380 K. IR (ATR)/cm−1 2941, 2862, 1712, 1594, 1488, 1391, 1294, 1056, 995. 1H-NMR (CDCl3, 500 MHz, 300 K): δ = 7.83–7.77 (m, 4/16-H4), 7.75–7.70 (m, 17-H2), 7.11–7.04 (m, 3/10-H4), 6.98–6.96 (m, 9-H2), 6.82 (t, J = 7.3 Hz, 11-H), 4.19–4.06 (m, 12-H2), 3.88 (t, J = 5.6 Hz, 13-H2), 2.30 (s, 1-H3), 0.94–0.88 (m, 6/7-H21) ppm. 13C-NMR (CDCl3, 125 MHz, 300 K): δ = 167.9 (14-C2), 144.6 (8-C), 142.4 (2-C), 139.3 (5-C), 134.0 (17-C2), 132.2 (1-C2), 129.3 (3-C2), 128.7 (10-C2), 127.5 (4-C2), 123.7 (9-C2), 123.4 (16-C2), 121.2 (11-C), 64.5 (12-C), 37.2 (13-C), 21.6 (1-C), 18.3 (7-C3), 18.3 (7′-C3), 13.3 (6-C3) ppm. Calculated for C32H41N3O3SSi: C 66.75, H 7.18, N 7.30; found: C 66.62, H 6.86, N 7.13. ESI–MS: m/z = 576.27 [M + H]+.
6. Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 3 ▸. Hydrogen atoms were refined isotropically using a riding model. The C—H bond distances were constrained to 0.95 Å for aromatic C—H moieties, and to 1.00, 0.99 and 0.98 Å for aliphatic C—H, CH2 and CH3 moieties, respectively. Methyl-H atoms were allowed to rotate but not to tip to best fit the experimental electron density. U iso(H) values were set to a multiple of U eq(C) with 1.5 for CH3, and 1.2 for C—H, CH2 groups, respectively.
Table 3. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C32H41N3O3SSi |
| M r | 575.83 |
| Crystal system, space group | Triclinic, P
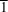
|
| Temperature (K) | 100 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 8.6752 (2), 8.8765 (2), 20.2299 (6) |
| α, β, γ (°) | 78.107 (2), 87.922 (2), 89.512 (2) |
| V (Å3) | 1523.37 (7) |
| Z | 2 |
| Radiation type | Cu Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 1.61 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.21 × 0.16 × 0.06 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | XtaLAB Synergy R, HyPix-Arc 150 |
| Absorption correction | Gaussian (CrysAlis PRO; Rigaku, 2021 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.555, 1.000 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 28106, 5410, 4426 |
| R int | 0.047 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.597 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.041, 0.108, 1.05 |
| No. of reflections | 5410 |
| No. of parameters | 368 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.56, −0.38 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022005904/zl5029sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022005904/zl5029Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022005904/zl5029Isup4.cdx
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022005904/zl5029Isup5.cdx
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022005904/zl5029Isup6.cdx
Molecular schemes with atom numbering used in the NMR assignments. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022005904/zl5029sup3.pdf
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022005904/zl5029Isup7.cml
CCDC reference: 2163661
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C32H41N3O3SSi | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 575.83 | F(000) = 616 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.255 Mg m−3 |
| a = 8.6752 (2) Å | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54184 Å |
| b = 8.8765 (2) Å | Cell parameters from 4930 reflections |
| c = 20.2299 (6) Å | θ = 4.5–72.1° |
| α = 78.107 (2)° | µ = 1.61 mm−1 |
| β = 87.922 (2)° | T = 100 K |
| γ = 89.512 (2)° | Needle, colourless |
| V = 1523.37 (7) Å3 | 0.21 × 0.16 × 0.06 mm |
Data collection
| XtaLAB Synergy R, HyPix-Arc 150 diffractometer | 5410 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Rotating-anode X-ray tube, PhotonJet R (Cu) X-ray Source | 4426 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Mirror monochromator | Rint = 0.047 |
| Detector resolution: 10.0000 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 67.1°, θmin = 4.5° |
| ω scans | h = −10→9 |
| Absorption correction: gaussian (CrysAlisPro; Rigaku, 2021) | k = −10→10 |
| Tmin = 0.555, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −24→24 |
| 28106 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: dual |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.041 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.108 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0575P)2 + 0.4269P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.05 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 5410 reflections | Δρmax = 0.56 e Å−3 |
| 368 parameters | Δρmin = −0.38 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.64242 (5) | 0.36921 (5) | 0.76180 (2) | 0.01884 (13) | |
| Si | 0.82253 (6) | 0.58177 (6) | 0.83046 (3) | 0.01969 (14) | |
| O1 | 0.53274 (15) | 0.43170 (15) | 0.69843 (7) | 0.0213 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.37133 (16) | 0.92827 (16) | 0.67134 (7) | 0.0286 (3) | |
| O3 | 0.61871 (16) | 0.63745 (16) | 0.53826 (7) | 0.0293 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.75807 (18) | 0.26207 (18) | 0.73756 (9) | 0.0224 (4) | |
| N3 | 0.47858 (18) | 0.75010 (18) | 0.61476 (8) | 0.0220 (4) | |
| N2 | 0.67766 (18) | 0.50250 (18) | 0.79249 (8) | 0.0215 (4) | |
| C17 | 0.5169 (2) | 0.2380 (2) | 0.81561 (10) | 0.0191 (4) | |
| C11 | 0.8812 (2) | 0.3081 (2) | 0.69029 (10) | 0.0215 (4) | |
| C4 | 0.6598 (2) | 0.9038 (2) | 0.54781 (10) | 0.0238 (4) | |
| C30 | 0.8671 (2) | 0.7773 (2) | 0.77709 (11) | 0.0249 (5) | |
| H30 | 0.941234 | 0.829050 | 0.801923 | 0.030* | |
| C16 | 1.0089 (2) | 0.2104 (2) | 0.69474 (11) | 0.0252 (5) | |
| H16 | 1.013655 | 0.123095 | 0.730762 | 0.030* | |
| C9 | 0.5850 (2) | 0.9926 (2) | 0.58821 (10) | 0.0247 (4) | |
| C20 | 0.3301 (2) | 0.0244 (2) | 0.90149 (11) | 0.0252 (5) | |
| C18 | 0.5129 (2) | 0.2342 (2) | 0.88389 (10) | 0.0227 (4) | |
| H18 | 0.573253 | 0.304358 | 0.901627 | 0.027* | |
| C3 | 0.5901 (2) | 0.7473 (2) | 0.56355 (10) | 0.0226 (4) | |
| C21 | 0.3360 (2) | 0.0304 (2) | 0.83209 (11) | 0.0268 (5) | |
| H21 | 0.275146 | −0.039010 | 0.814108 | 0.032* | |
| C10 | 0.4654 (2) | 0.8955 (2) | 0.63090 (10) | 0.0234 (4) | |
| C12 | 0.8784 (2) | 0.4379 (2) | 0.63815 (10) | 0.0239 (4) | |
| H12 | 0.792938 | 0.506435 | 0.634980 | 0.029* | |
| C22 | 0.4293 (2) | 0.1361 (2) | 0.78878 (11) | 0.0246 (4) | |
| H22 | 0.433214 | 0.138741 | 0.741556 | 0.030* | |
| C1 | 0.4033 (2) | 0.5309 (2) | 0.70767 (10) | 0.0231 (4) | |
| H1A | 0.429808 | 0.598387 | 0.738910 | 0.028* | |
| H1B | 0.312386 | 0.468228 | 0.727047 | 0.028* | |
| C19 | 0.4200 (2) | 0.1271 (2) | 0.92686 (11) | 0.0256 (5) | |
| H19 | 0.417784 | 0.123993 | 0.974110 | 0.031* | |
| C24 | 0.9990 (2) | 0.4556 (2) | 0.83641 (11) | 0.0243 (4) | |
| H24 | 1.024122 | 0.441481 | 0.789435 | 0.029* | |
| C2 | 0.3681 (2) | 0.6264 (2) | 0.63933 (11) | 0.0239 (4) | |
| H2A | 0.366244 | 0.558188 | 0.606327 | 0.029* | |
| H2B | 0.263929 | 0.671795 | 0.641762 | 0.029* | |
| C13 | 0.9999 (2) | 0.4674 (2) | 0.59088 (11) | 0.0278 (5) | |
| H13 | 0.997509 | 0.556827 | 0.555804 | 0.033* | |
| C27 | 0.7421 (2) | 0.5970 (2) | 0.91717 (11) | 0.0246 (4) | |
| H27 | 0.750357 | 0.492007 | 0.946548 | 0.030* | |
| C8 | 0.6216 (3) | 1.1462 (2) | 0.58321 (11) | 0.0317 (5) | |
| H8 | 0.570588 | 1.207038 | 0.610828 | 0.038* | |
| C28 | 0.5708 (2) | 0.6429 (3) | 0.91904 (12) | 0.0294 (5) | |
| H28A | 0.558879 | 0.749867 | 0.894987 | 0.044* | |
| H28B | 0.533930 | 0.632856 | 0.966109 | 0.044* | |
| H28C | 0.510518 | 0.575262 | 0.897214 | 0.044* | |
| C25 | 0.9721 (2) | 0.2933 (2) | 0.87942 (12) | 0.0296 (5) | |
| H25A | 0.947197 | 0.300481 | 0.926309 | 0.044* | |
| H25B | 1.065707 | 0.231402 | 0.877778 | 0.044* | |
| H25C | 0.886315 | 0.244644 | 0.861586 | 0.044* | |
| C5 | 0.7750 (2) | 0.9636 (2) | 0.50117 (11) | 0.0282 (5) | |
| H5 | 0.826384 | 0.902115 | 0.473913 | 0.034* | |
| C15 | 1.1291 (2) | 0.2406 (3) | 0.64663 (12) | 0.0301 (5) | |
| H15 | 1.215207 | 0.172932 | 0.649736 | 0.036* | |
| C14 | 1.1246 (2) | 0.3683 (3) | 0.59417 (12) | 0.0303 (5) | |
| H14 | 1.206057 | 0.387532 | 0.560883 | 0.036* | |
| C7 | 0.7370 (3) | 1.2071 (3) | 0.53569 (11) | 0.0344 (5) | |
| H7 | 0.764486 | 1.312400 | 0.530483 | 0.041* | |
| C23 | 0.2284 (3) | −0.0901 (3) | 0.94846 (12) | 0.0357 (6) | |
| H23A | 0.120046 | −0.067014 | 0.938481 | 0.054* | |
| H23B | 0.246165 | −0.083527 | 0.995349 | 0.054* | |
| H23C | 0.252958 | −0.194293 | 0.942108 | 0.054* | |
| C26 | 1.1435 (2) | 0.5273 (3) | 0.85938 (12) | 0.0333 (5) | |
| H26A | 1.161285 | 0.629633 | 0.830942 | 0.050* | |
| H26B | 1.233053 | 0.461466 | 0.855196 | 0.050* | |
| H26C | 1.128079 | 0.536457 | 0.906621 | 0.050* | |
| C29 | 0.8374 (3) | 0.7056 (3) | 0.94995 (12) | 0.0371 (6) | |
| H29A | 0.945592 | 0.672665 | 0.951077 | 0.056* | |
| H29B | 0.797407 | 0.702220 | 0.996161 | 0.056* | |
| H29C | 0.829942 | 0.810909 | 0.923502 | 0.056* | |
| C6 | 0.8126 (3) | 1.1179 (3) | 0.49584 (11) | 0.0323 (5) | |
| H6 | 0.891433 | 1.162922 | 0.464320 | 0.039* | |
| C31 | 0.7218 (3) | 0.8771 (3) | 0.76655 (14) | 0.0431 (6) | |
| H31A | 0.639953 | 0.820185 | 0.750234 | 0.065* | |
| H31B | 0.744630 | 0.971775 | 0.733154 | 0.065* | |
| H31C | 0.687716 | 0.903397 | 0.809501 | 0.065* | |
| C32 | 0.9431 (3) | 0.7677 (3) | 0.70892 (13) | 0.0485 (7) | |
| H32A | 1.035816 | 0.703364 | 0.716090 | 0.073* | |
| H32B | 0.971724 | 0.871329 | 0.684381 | 0.073* | |
| H32C | 0.870715 | 0.722351 | 0.682492 | 0.073* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0187 (2) | 0.0157 (2) | 0.0222 (3) | −0.00142 (18) | 0.00128 (19) | −0.00441 (18) |
| Si | 0.0192 (3) | 0.0161 (3) | 0.0241 (3) | −0.0013 (2) | 0.0001 (2) | −0.0050 (2) |
| O1 | 0.0210 (7) | 0.0205 (7) | 0.0231 (8) | 0.0017 (5) | −0.0009 (6) | −0.0061 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0307 (8) | 0.0274 (8) | 0.0293 (8) | 0.0035 (6) | 0.0014 (7) | −0.0099 (6) |
| O3 | 0.0310 (8) | 0.0248 (8) | 0.0324 (9) | 0.0012 (6) | 0.0034 (7) | −0.0072 (7) |
| N1 | 0.0217 (8) | 0.0165 (8) | 0.0285 (10) | −0.0009 (7) | 0.0028 (7) | −0.0043 (7) |
| N3 | 0.0216 (8) | 0.0197 (8) | 0.0248 (9) | −0.0007 (7) | −0.0004 (7) | −0.0048 (7) |
| N2 | 0.0200 (8) | 0.0174 (8) | 0.0284 (10) | −0.0009 (7) | −0.0009 (7) | −0.0079 (7) |
| C17 | 0.0173 (9) | 0.0145 (9) | 0.0250 (11) | 0.0001 (7) | 0.0016 (8) | −0.0028 (8) |
| C11 | 0.0200 (10) | 0.0218 (10) | 0.0258 (11) | −0.0034 (8) | 0.0006 (8) | −0.0125 (8) |
| C4 | 0.0222 (10) | 0.0243 (10) | 0.0241 (11) | −0.0004 (8) | −0.0059 (8) | −0.0020 (8) |
| C30 | 0.0274 (11) | 0.0192 (10) | 0.0296 (12) | −0.0060 (8) | −0.0017 (9) | −0.0079 (9) |
| C16 | 0.0242 (11) | 0.0237 (10) | 0.0300 (12) | 0.0011 (8) | −0.0012 (9) | −0.0111 (9) |
| C9 | 0.0265 (11) | 0.0247 (10) | 0.0229 (11) | −0.0026 (9) | −0.0067 (9) | −0.0040 (9) |
| C20 | 0.0204 (10) | 0.0188 (10) | 0.0344 (13) | −0.0001 (8) | 0.0052 (9) | −0.0015 (9) |
| C18 | 0.0232 (10) | 0.0189 (9) | 0.0264 (11) | −0.0016 (8) | 0.0008 (8) | −0.0056 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0213 (10) | 0.0231 (10) | 0.0230 (11) | 0.0008 (8) | −0.0030 (8) | −0.0035 (9) |
| C21 | 0.0223 (10) | 0.0193 (10) | 0.0395 (13) | −0.0033 (8) | −0.0017 (9) | −0.0078 (9) |
| C10 | 0.0249 (10) | 0.0228 (10) | 0.0235 (11) | 0.0011 (8) | −0.0066 (9) | −0.0061 (8) |
| C12 | 0.0226 (10) | 0.0226 (10) | 0.0285 (12) | −0.0012 (8) | 0.0002 (9) | −0.0097 (9) |
| C22 | 0.0260 (11) | 0.0230 (10) | 0.0259 (11) | −0.0016 (8) | 0.0009 (9) | −0.0076 (9) |
| C1 | 0.0188 (10) | 0.0239 (10) | 0.0264 (11) | 0.0010 (8) | 0.0025 (8) | −0.0054 (9) |
| C19 | 0.0281 (11) | 0.0229 (10) | 0.0248 (11) | 0.0018 (9) | 0.0037 (9) | −0.0032 (9) |
| C24 | 0.0218 (10) | 0.0239 (10) | 0.0283 (12) | 0.0000 (8) | −0.0008 (9) | −0.0076 (9) |
| C2 | 0.0194 (10) | 0.0230 (10) | 0.0287 (12) | −0.0034 (8) | 0.0010 (8) | −0.0042 (9) |
| C13 | 0.0311 (11) | 0.0255 (11) | 0.0284 (12) | −0.0091 (9) | 0.0047 (9) | −0.0100 (9) |
| C27 | 0.0231 (10) | 0.0251 (10) | 0.0265 (11) | 0.0004 (8) | −0.0001 (8) | −0.0074 (9) |
| C8 | 0.0402 (13) | 0.0267 (11) | 0.0292 (12) | −0.0027 (10) | −0.0073 (10) | −0.0068 (9) |
| C28 | 0.0256 (11) | 0.0321 (11) | 0.0329 (13) | −0.0004 (9) | 0.0039 (9) | −0.0131 (10) |
| C25 | 0.0263 (11) | 0.0248 (11) | 0.0376 (13) | 0.0044 (9) | −0.0068 (9) | −0.0055 (10) |
| C5 | 0.0242 (11) | 0.0304 (11) | 0.0274 (12) | −0.0012 (9) | −0.0035 (9) | 0.0008 (9) |
| C15 | 0.0211 (11) | 0.0327 (12) | 0.0409 (14) | 0.0001 (9) | 0.0015 (9) | −0.0183 (10) |
| C14 | 0.0241 (11) | 0.0350 (12) | 0.0365 (13) | −0.0104 (9) | 0.0085 (9) | −0.0193 (10) |
| C7 | 0.0419 (13) | 0.0284 (11) | 0.0319 (13) | −0.0137 (10) | −0.0111 (11) | −0.0014 (10) |
| C23 | 0.0301 (12) | 0.0289 (12) | 0.0441 (15) | −0.0060 (10) | 0.0086 (10) | 0.0008 (10) |
| C26 | 0.0219 (11) | 0.0357 (12) | 0.0435 (14) | 0.0002 (9) | −0.0011 (10) | −0.0111 (11) |
| C29 | 0.0293 (12) | 0.0521 (15) | 0.0368 (14) | −0.0035 (11) | 0.0009 (10) | −0.0254 (12) |
| C6 | 0.0297 (12) | 0.0353 (12) | 0.0290 (12) | −0.0102 (10) | −0.0053 (10) | 0.0011 (10) |
| C31 | 0.0372 (13) | 0.0207 (11) | 0.0650 (18) | −0.0019 (10) | −0.0084 (12) | 0.0075 (11) |
| C32 | 0.0789 (19) | 0.0266 (12) | 0.0378 (15) | −0.0098 (13) | 0.0190 (14) | −0.0045 (11) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S1—N1 | 1.5139 (16) | C19—H19 | 0.9500 |
| S1—N2 | 1.4838 (16) | C24—H24 | 1.0000 |
| S1—O1 | 1.6257 (14) | C24—C25 | 1.537 (3) |
| S1—C17 | 1.7718 (19) | C24—C26 | 1.539 (3) |
| Si—N2 | 1.7240 (17) | C2—H2A | 0.9900 |
| Si—C30 | 1.881 (2) | C2—H2B | 0.9900 |
| Si—C24 | 1.882 (2) | C13—H13 | 0.9500 |
| Si—C27 | 1.894 (2) | C13—C14 | 1.383 (3) |
| O1—C1 | 1.452 (2) | C27—H27 | 1.0000 |
| O2—C10 | 1.211 (2) | C27—C28 | 1.539 (3) |
| O3—C3 | 1.211 (2) | C27—C29 | 1.539 (3) |
| N1—C11 | 1.412 (2) | C8—H8 | 0.9500 |
| N3—C3 | 1.396 (2) | C8—C7 | 1.394 (3) |
| N3—C10 | 1.398 (2) | C28—H28A | 0.9800 |
| N3—C2 | 1.459 (2) | C28—H28B | 0.9800 |
| C17—C18 | 1.374 (3) | C28—H28C | 0.9800 |
| C17—C22 | 1.392 (3) | C25—H25A | 0.9800 |
| C11—C16 | 1.394 (3) | C25—H25B | 0.9800 |
| C11—C12 | 1.394 (3) | C25—H25C | 0.9800 |
| C4—C9 | 1.388 (3) | C5—H5 | 0.9500 |
| C4—C3 | 1.489 (3) | C5—C6 | 1.392 (3) |
| C4—C5 | 1.380 (3) | C15—H15 | 0.9500 |
| C30—H30 | 1.0000 | C15—C14 | 1.386 (3) |
| C30—C31 | 1.531 (3) | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| C30—C32 | 1.525 (3) | C7—H7 | 0.9500 |
| C16—H16 | 0.9500 | C7—C6 | 1.387 (3) |
| C16—C15 | 1.389 (3) | C23—H23A | 0.9800 |
| C9—C10 | 1.486 (3) | C23—H23B | 0.9800 |
| C9—C8 | 1.385 (3) | C23—H23C | 0.9800 |
| C20—C21 | 1.393 (3) | C26—H26A | 0.9800 |
| C20—C19 | 1.392 (3) | C26—H26B | 0.9800 |
| C20—C23 | 1.507 (3) | C26—H26C | 0.9800 |
| C18—H18 | 0.9500 | C29—H29A | 0.9800 |
| C18—C19 | 1.389 (3) | C29—H29B | 0.9800 |
| C21—H21 | 0.9500 | C29—H29C | 0.9800 |
| C21—C22 | 1.387 (3) | C6—H6 | 0.9500 |
| C12—H12 | 0.9500 | C31—H31A | 0.9800 |
| C12—C13 | 1.387 (3) | C31—H31B | 0.9800 |
| C22—H22 | 0.9500 | C31—H31C | 0.9800 |
| C1—H1A | 0.9900 | C32—H32A | 0.9800 |
| C1—H1B | 0.9900 | C32—H32B | 0.9800 |
| C1—C2 | 1.505 (3) | C32—H32C | 0.9800 |
| O1—S1—C17 | 101.13 (8) | N3—C2—C1 | 113.82 (17) |
| N1—S1—O1 | 105.93 (8) | N3—C2—H2A | 108.8 |
| N1—S1—C17 | 101.98 (9) | N3—C2—H2B | 108.8 |
| N2—S1—O1 | 107.27 (8) | C1—C2—H2A | 108.8 |
| N2—S1—N1 | 126.60 (9) | C1—C2—H2B | 108.8 |
| N2—S1—C17 | 111.06 (9) | H2A—C2—H2B | 107.7 |
| N2—Si—C30 | 107.57 (9) | C12—C13—H13 | 119.6 |
| N2—Si—C24 | 110.09 (9) | C14—C13—C12 | 120.8 (2) |
| S1—N2—Si | 142.24 (11) | C14—C13—H13 | 119.6 |
| N2—Si—C27 | 105.99 (9) | Si—C27—H27 | 106.6 |
| C30—Si—C24 | 110.30 (9) | C28—C27—Si | 114.45 (15) |
| C30—Si—C27 | 111.23 (9) | C28—C27—H27 | 106.6 |
| C24—Si—C27 | 111.50 (9) | C29—C27—Si | 112.48 (14) |
| C1—O1—S1 | 118.87 (12) | C29—C27—H27 | 106.6 |
| C11—N1—S1 | 125.44 (14) | C29—C27—C28 | 109.50 (17) |
| C3—N3—C10 | 112.05 (16) | C9—C8—H8 | 121.6 |
| C3—N3—C2 | 123.98 (16) | C9—C8—C7 | 116.8 (2) |
| C10—N3—C2 | 122.95 (16) | C7—C8—H8 | 121.6 |
| C18—C17—S1 | 119.20 (15) | C27—C28—H28A | 109.5 |
| C18—C17—C22 | 120.93 (18) | C27—C28—H28B | 109.5 |
| C22—C17—S1 | 119.81 (15) | C27—C28—H28C | 109.5 |
| C16—C11—N1 | 116.63 (18) | H28A—C28—H28B | 109.5 |
| C12—C11—N1 | 124.22 (17) | H28A—C28—H28C | 109.5 |
| C12—C11—C16 | 119.04 (19) | H28B—C28—H28C | 109.5 |
| C9—C4—C3 | 108.23 (18) | C24—C25—H25A | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—C9 | 121.8 (2) | C24—C25—H25B | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 129.93 (19) | C24—C25—H25C | 109.5 |
| Si—C30—H30 | 107.8 | H25A—C25—H25B | 109.5 |
| C31—C30—Si | 111.13 (14) | H25A—C25—H25C | 109.5 |
| C31—C30—H30 | 107.8 | H25B—C25—H25C | 109.5 |
| C32—C30—Si | 112.26 (14) | C4—C5—H5 | 121.5 |
| C32—C30—H30 | 107.8 | C4—C5—C6 | 117.0 (2) |
| C32—C30—C31 | 110.0 (2) | C6—C5—H5 | 121.5 |
| C11—C16—H16 | 119.9 | C16—C15—H15 | 119.7 |
| C15—C16—C11 | 120.2 (2) | C14—C15—C16 | 120.6 (2) |
| C15—C16—H16 | 119.9 | C14—C15—H15 | 119.7 |
| C4—C9—C10 | 108.12 (18) | C13—C14—C15 | 119.2 (2) |
| C8—C9—C4 | 121.5 (2) | C13—C14—H14 | 120.4 |
| C8—C9—C10 | 130.3 (2) | C15—C14—H14 | 120.4 |
| C21—C20—C23 | 121.1 (2) | C8—C7—H7 | 119.2 |
| C19—C20—C21 | 118.59 (18) | C6—C7—C8 | 121.6 (2) |
| C19—C20—C23 | 120.3 (2) | C6—C7—H7 | 119.2 |
| C17—C18—H18 | 120.2 | C20—C23—H23A | 109.5 |
| C17—C18—C19 | 119.65 (19) | C20—C23—H23B | 109.5 |
| C19—C18—H18 | 120.2 | C20—C23—H23C | 109.5 |
| O3—C3—N3 | 125.02 (18) | H23A—C23—H23B | 109.5 |
| O3—C3—C4 | 129.27 (19) | H23A—C23—H23C | 109.5 |
| N3—C3—C4 | 105.70 (16) | H23B—C23—H23C | 109.5 |
| C20—C21—H21 | 119.4 | C24—C26—H26A | 109.5 |
| C22—C21—C20 | 121.12 (19) | C24—C26—H26B | 109.5 |
| C22—C21—H21 | 119.4 | C24—C26—H26C | 109.5 |
| O2—C10—N3 | 124.20 (19) | H26A—C26—H26B | 109.5 |
| O2—C10—C9 | 129.97 (19) | H26A—C26—H26C | 109.5 |
| N3—C10—C9 | 105.82 (17) | H26B—C26—H26C | 109.5 |
| C11—C12—H12 | 119.9 | C27—C29—H29A | 109.5 |
| C13—C12—C11 | 120.15 (19) | C27—C29—H29B | 109.5 |
| C13—C12—H12 | 119.9 | C27—C29—H29C | 109.5 |
| C17—C22—H22 | 120.5 | H29A—C29—H29B | 109.5 |
| C21—C22—C17 | 118.94 (19) | H29A—C29—H29C | 109.5 |
| C21—C22—H22 | 120.5 | H29B—C29—H29C | 109.5 |
| O1—C1—H1A | 110.2 | C5—C6—H6 | 119.4 |
| O1—C1—H1B | 110.2 | C7—C6—C5 | 121.2 (2) |
| O1—C1—C2 | 107.48 (15) | C7—C6—H6 | 119.4 |
| H1A—C1—H1B | 108.5 | C30—C31—H31A | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—H1A | 110.2 | C30—C31—H31B | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—H1B | 110.2 | C30—C31—H31C | 109.5 |
| C20—C19—H19 | 119.6 | H31A—C31—H31B | 109.5 |
| C18—C19—C20 | 120.8 (2) | H31A—C31—H31C | 109.5 |
| C18—C19—H19 | 119.6 | H31B—C31—H31C | 109.5 |
| Si—C24—H24 | 106.0 | C30—C32—H32A | 109.5 |
| C25—C24—Si | 113.53 (14) | C30—C32—H32B | 109.5 |
| C25—C24—H24 | 106.0 | C30—C32—H32C | 109.5 |
| C25—C24—C26 | 110.03 (18) | H32A—C32—H32B | 109.5 |
| C26—C24—Si | 114.45 (14) | H32A—C32—H32C | 109.5 |
| C26—C24—H24 | 106.0 | H32B—C32—H32C | 109.5 |
| S1—O1—C1—C2 | 154.80 (13) | C9—C4—C3—N3 | −1.7 (2) |
| S1—N1—C11—C16 | 153.82 (16) | C9—C4—C5—C6 | −0.5 (3) |
| S1—N1—C11—C12 | −30.1 (3) | C9—C8—C7—C6 | −0.7 (3) |
| S1—C17—C18—C19 | −177.16 (14) | C20—C21—C22—C17 | −0.5 (3) |
| S1—C17—C22—C21 | 177.63 (15) | C18—C17—C22—C21 | 0.5 (3) |
| O1—S1—N1—C11 | 71.56 (18) | C3—N3—C10—O2 | 176.21 (19) |
| O1—S1—N2—Si | −143.37 (17) | C3—N3—C10—C9 | −2.9 (2) |
| O1—S1—C17—C18 | −138.15 (15) | C3—N3—C2—C1 | 105.9 (2) |
| O1—S1—C17—C22 | 44.69 (16) | C3—C4—C9—C10 | 0.0 (2) |
| O1—C1—C2—N3 | −74.8 (2) | C3—C4—C9—C8 | −177.80 (19) |
| N1—S1—O1—C1 | 176.34 (13) | C3—C4—C5—C6 | 177.5 (2) |
| N1—S1—N2—Si | −17.3 (2) | C21—C20—C19—C18 | 0.4 (3) |
| N1—S1—C17—C18 | 112.72 (16) | C10—N3—C3—O3 | −176.40 (19) |
| N1—S1—C17—C22 | −64.45 (17) | C10—N3—C3—C4 | 2.9 (2) |
| N1—C11—C16—C15 | 174.52 (18) | C10—N3—C2—C1 | −86.5 (2) |
| N1—C11—C12—C13 | −174.88 (18) | C10—C9—C8—C7 | −177.2 (2) |
| N2—S1—O1—C1 | −46.09 (15) | C12—C11—C16—C15 | −1.8 (3) |
| N2—S1—N1—C11 | −55.1 (2) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | −1.8 (3) |
| N2—S1—C17—C18 | −24.57 (18) | C22—C17—C18—C19 | 0.0 (3) |
| N2—S1—C17—C22 | 158.26 (15) | C19—C20—C21—C22 | 0.1 (3) |
| N2—Si—C30—C31 | 55.01 (18) | C24—Si—N2—S1 | −0.8 (2) |
| N2—Si—C30—C32 | −68.60 (19) | C24—Si—C30—C31 | 175.10 (16) |
| N2—Si—C24—C25 | −61.52 (17) | C24—Si—C30—C32 | 51.5 (2) |
| N2—Si—C24—C26 | 171.01 (15) | C24—Si—C27—C28 | −157.85 (14) |
| N2—Si—C27—C28 | −38.05 (17) | C24—Si—C27—C29 | 76.34 (17) |
| N2—Si—C27—C29 | −163.87 (15) | C2—N3—C3—O3 | −7.7 (3) |
| C17—S1—O1—C1 | 70.31 (14) | C2—N3—C3—C4 | 171.58 (17) |
| C17—S1—N1—C11 | 176.97 (17) | C2—N3—C10—O2 | 7.4 (3) |
| C17—S1—N2—Si | 106.97 (18) | C2—N3—C10—C9 | −171.74 (17) |
| C17—C18—C19—C20 | −0.5 (3) | C27—Si—N2—S1 | −121.54 (18) |
| C11—C16—C15—C14 | 0.6 (3) | C27—Si—C30—C31 | −60.64 (18) |
| C11—C12—C13—C14 | 0.7 (3) | C27—Si—C30—C32 | 175.74 (17) |
| C4—C9—C10—O2 | −177.3 (2) | C27—Si—C24—C25 | 55.82 (18) |
| C4—C9—C10—N3 | 1.7 (2) | C27—Si—C24—C26 | −71.65 (18) |
| C4—C9—C8—C7 | 0.0 (3) | C8—C9—C10—O2 | 0.2 (4) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −0.1 (3) | C8—C9—C10—N3 | 179.2 (2) |
| C30—Si—N2—S1 | 119.40 (18) | C8—C7—C6—C5 | 0.7 (3) |
| C30—Si—C24—C25 | 179.92 (15) | C5—C4—C9—C10 | 178.36 (18) |
| C30—Si—C24—C26 | 52.46 (18) | C5—C4—C9—C8 | 0.6 (3) |
| C30—Si—C27—C28 | 78.57 (17) | C5—C4—C3—O3 | −0.7 (4) |
| C30—Si—C27—C29 | −47.24 (18) | C5—C4—C3—N3 | −179.9 (2) |
| C16—C11—C12—C13 | 1.1 (3) | C23—C20—C21—C22 | 179.82 (19) |
| C16—C15—C14—C13 | 1.2 (3) | C23—C20—C19—C18 | −179.31 (18) |
| C9—C4—C3—O3 | 177.6 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C15—H15···O2i | 0.95 | 2.52 | 3.429 (3) | 160 |
| C22—H22···O2ii | 0.95 | 2.64 | 3.348 (3) | 132 |
| C14—H14···O3iii | 0.95 | 2.52 | 3.429 (3) | 161 |
| C31—H31B···N1iv | 0.98 | 2.60 | 3.361 (3) | 135 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x+1, y−1, z; (ii) x, y−1, z; (iii) −x+2, −y+1, −z+1; (iv) x, y+1, z.
Funding Statement
Funding for this research was provided by: Merck KGaA.
References
- Ahmed, M. N., Arif, M., Jabeen, F., Khan, H. A., Yasin, K. A., Tahir, M. N., Franconetti, A. & Frontera, A. (2019). New J. Chem. 43, 8122–8131.
- Bohmann, R. A., Schöbel, J.-H., Unoh, Y., Miura, M. & Bolm, C. (2019). Adv. Synth. Catal. 361, 2000–2003.
- Chen, Y. & Gibson, J. (2015). RSC Adv. 5, 4171–4174.
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst. 42, 339–341.
- Gottlieb, H. E., Kotlyar, V. & Nudelman, A. (1997). J. Org. Chem. 62, 7512–7515. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Greed, S., Briggs, E. L., Idiris, F. I. M., White, A. J. P., Lücking, U. & Bull, J. A. (2020). Chem. Eur. J. 26, 12533–12538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Izzo, F., Schäfer, M., Stockman, R. & Lücking, U. (2017). Chem. Eur. J. 23, 15189–15193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Lemasson, F., Gais, H.-J. & Raabe, G. (2007). Tetrahedron Lett. 48, 8752–8756.
- Liu, Y., Pan, Q., Hu, X., Guo, Y., Chen, Q.-Y. & Liu, C. (2021). Org. Lett. 23, 3975–3980. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Lücking, U. (2013). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 52, 9399–9408. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Lücking, U. (2019). Org. Chem. Front. 6, 1319–1324.
- Macrae, C. F., Sovago, I., Cottrell, S. J., Galek, P. T. A., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Platings, M., Shields, G. P., Stevens, J. S., Towler, M. & Wood, P. A. (2020). J. Appl. Cryst. 53, 226–235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Mash, E. A., Gregg, T. M. & Kaczynski, M. A. (1996). J. Org. Chem. 61, 2743–2752. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Nandi, G. C. & Arvidsson, P. I. (2018). Adv. Synth. Catal. 360, 2976–3001.
- Reggelin, M. & Zur, C. (2000). Synthesis, pp. 1–64.
- Rigaku (2021). CrysAlis PRO. Rigaku Oxford Diffraction, Yarnton, England.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Wen, J., Cheng, H., Dong, S. & Bolm, C. (2016). Chem. Eur. J. 22, 5547–5550. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.-X., Davies, T. Q. & Willis, M. C. (2019). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 141, 13022–13027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.-X. & Willis, M. C. (2022). Chem, 8, 1137–1146.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022005904/zl5029sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022005904/zl5029Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022005904/zl5029Isup4.cdx
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022005904/zl5029Isup5.cdx
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022005904/zl5029Isup6.cdx
Molecular schemes with atom numbering used in the NMR assignments. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022005904/zl5029sup3.pdf
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022005904/zl5029Isup7.cml
CCDC reference: 2163661
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report