The crystals of methyl 3,5-dimethylbenzoate are composed of strands of C—H⋯O=C bonded molecules, which are further arranged into layers. As a result of the presence of two bromomethyl substituents in 3,5-bis(bromomethyl)phenyl acetate, molecular dimers formed by crystallographically non-equivalent molecules are connected to structurally different two-dimensional aggregates in which the bromine atoms participate in Br⋯Br bonds of type I and type II. In the case of 5-hydroxybenzene-1,3-dicarbaldehyde,which possesses three donor/acceptor substituents, the molecular association in the crystal creates a close three-dimensional network comprising Caryl—H⋯Ohydroxy, Cformyl—H⋯Oformyl and O—H⋯Oformyl bonds.
Keywords: crystal structures; 1,3,5-trisubstituted benzene derivatives; hydrogen bonding; C–H⋯π and π–π interactions
Abstract
The crystal structures of the title compounds, methyl 3,5-dimethylbenzoate (C10H12O2; 1), 3,5-bis(bromomethyl)phenyl acetate (C10H10Br2O2; 2) and 5-hydroxybenzene-1,3-dicarbaldehyde (C8H6O3; 3) were determined by single-crystal X-ray analysis. The crystals of 1 are composed of strands of C—H⋯O=C bonded molecules, which are further arranged into layers. As a result of the presence of two bromomethyl substituents in compound 2, molecular dimers formed by crystallographically non-equivalent molecules are connected to structurally different two-dimensional aggregates in which the bromine atoms participate in Br⋯Br bonds of type I and type II. In the case of compound 3, which possesses three donor/acceptor substituents, the molecular association in the crystal creates a close three-dimensional network comprising Caryl—H⋯Ohydroxy, Cformyl—H⋯Oformyl and O—H⋯Oformyl bonds.
1. Chemical context
Studies on molecular recognition of carbohydrates by artificial receptors revealed that macrocyclic compounds bearing two flexible side-arms represent effective and selective receptors for complexation of glucopyranosides. The binding properties of these compounds depend on the nature of their building blocks, among others, the type of bridging units that connect two aromatic platforms (Lippe & Mazik, 2013 ▸, 2015 ▸; Amrhein et al., 2016 ▸, 2021 ▸; Amrhein & Mazik, 2021 ▸). The design of such receptor architectures was inspired by the results of our crystallographic studies on receptor–carbohydrate complexes (Mazik et al., 2005 ▸; for recent examples, see Köhler et al., 2020 ▸, 2021 ▸). For the syntheses of macrocycles consisting of benzene-based bridges, various 2- or 5-substituted benzene-1,3-dicarbaldehydes have proven to be useful starting materials. Benzene derivatives with methyl or bromomethyl groups in positions 1 and 3 are used to prepare the latter compounds. The crystal structures of three 1,3,5-substituted benzenes, serving as precursors for the syntheses of the macrocyclic compounds mentioned above, are described in this work.

2. Structural commentary
The title compounds 1 and 3 crystallize in the monoclinic system (space group P21/c, Z = 4), whereas compound 2 crystallizes in the triclinic space group P
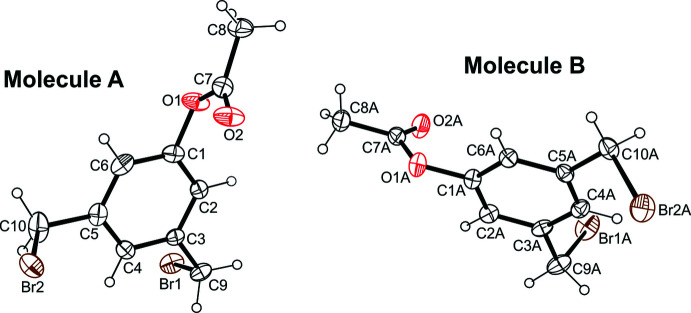
 with two independent but conformationally similar molecules (A and B) in the asymmetric unit of the cell. In compound 1 (Fig. 1 ▸), the plane through the methyloxycarbonyl unit is tilted at an angle of 8.70 (8) ° with respect to the benzene ring. In the independent molecules of 2 (Fig. 2 ▸), the planes passing through the ester units are inclined at angles of 62.9 (1) and 81.3 (1)°, respectively, to the plane of their arene ring. The two bromine atoms of each molecule are located on opposite sides of the benzene ring. In the crystal of the 5-hydroxybenzene-1,3-dicarbaldehyde (3) (Fig. 3 ▸), the molecule deviates slightly from planarity, with the formyl groups rotated out of the benzene ring at angles of 4.43 (16) and 4.04 (16)°.
with two independent but conformationally similar molecules (A and B) in the asymmetric unit of the cell. In compound 1 (Fig. 1 ▸), the plane through the methyloxycarbonyl unit is tilted at an angle of 8.70 (8) ° with respect to the benzene ring. In the independent molecules of 2 (Fig. 2 ▸), the planes passing through the ester units are inclined at angles of 62.9 (1) and 81.3 (1)°, respectively, to the plane of their arene ring. The two bromine atoms of each molecule are located on opposite sides of the benzene ring. In the crystal of the 5-hydroxybenzene-1,3-dicarbaldehyde (3) (Fig. 3 ▸), the molecule deviates slightly from planarity, with the formyl groups rotated out of the benzene ring at angles of 4.43 (16) and 4.04 (16)°.
Figure 1.
Perspective view of the molecular structure of 1. Anisotropic displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Figure 2.
Perspective view of the molecular structure of 2. Anisotropic displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Figure 3.
Perspective view of the molecular structure of 3. Anisotropic displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
3. Supramolecular features
In the crystal structure of 1, the molecules are arranged into layers extending parallel to the crystallographic [101] plane (see Fig. 4 ▸). Within a given layer, the molecules are linked in strands via C—H⋯O=C bonds [d(H⋯O) 2.57 Å; Table 1 ▸], with a methyl H atom acting as the donor. No directional interactions are present between the molecular strands of a layer. With the participation of a H atom of the methyl ester unit, the linkage between the molecules of adjacent layers occurs by C—H⋯π contacts (Nishio et al., 2009 ▸) with a H⋯Cg distance of 2.77 Å. Fig. 5 ▸ shows a packing excerpt of the crystal structure viewed in the direction of the layer normal.
Figure 4.
Packing diagram of 1 viewed down the crystallographic b-axis.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for 1 .
Cg1 represents the centroid of the C1–C6 ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C10—H10B⋯O1i | 0.98 | 2.57 | 3.5215 (19) | 163 |
| C8—H8B⋯Cg1ii | 0.98 | 2.76 | 3.445 (2) | 127 |
Symmetry codes: (i)
 ; (ii)
; (ii)
 .
.
Figure 5.
Excerpt of the packing structure of 1 viewed in the direction of the layer normal. Dashed lines represent hydrogen-bonding interactions.
The excerpt of the crystal structure of 2 shown in Fig. 6 ▸ reveals two different inversion-symmetric dimers as the smallest supramolecular entities, in which the molecules are linked in an identical manner by C—H⋯O=C and C—H⋯Br bonds (Table 2 ▸) (Desiraju & Steiner, 1999 ▸). These dimers, however, form differently structured domains within the crystal. The dimers formed by molecule A are connected via Br⋯Br bonds (Pedireddy et al., 1999 ▸) of type I [d(Br⋯Br) = 3.562 (1) Å; θ1 = 150.2°, θ2 = 158.5°] and of type II [d(Br⋯Br) = 3.859 (1) Å; θ1 = 135.0°, θ2 = 84.6°] as well as C—H⋯Br hydrogen bonds to form two-dimensional aggregates extending parallel to crystallographic [011] plane, in which the bromine atoms contribute to the formation of a cyclic four-membered synthon (Br4) and an eight-membered bonding motif (Fig. 7 ▸ a). The structure of the domains created by molecule B is fundamentally different from those formed by molecule A. In them, the dimers are linked in a strand-like fashion via type I Br⋯Br interactions [d(Br⋯Br) = 3.638 (1) Å; θ 1 = 152.3°, θ2 = 145.9°] (Fig. 7 ▸ b), which are part of an eight-membered ring motif. In the direction of the crystallographic a-axis, the connection of the dimers occurs through π–·π (face-to-face) interactions (Tiekink & Zukerman-Schpector, 2012 ▸) with a centroid–centroid distance of 3.653 (1) Å and an offset of 1.592 Å between the interacting arene rings.
Figure 6.
(a) Structures of the dimers formed by molecule A (left) and molecule B (right) in the crystal structure of 2. (b) Packing structure of 2 viewed down the a-axis. Hydrogen bonds and Br⋯Br interactions are shown as dashed lines.
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for 2 .
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C10A—H10D⋯O2A i | 0.97 | 2.28 | 3.236 (3) | 168 |
| C10A—H10C⋯Br1A i | 0.97 | 2.89 | 3.836 (3) | 164 |
| C8A—H8A3⋯O2 | 0.96 | 2.58 | 3.521 (4) | 168 |
| C10—H10B⋯Br2A i | 0.97 | 3.01 | 3.757 (3) | 135 |
| C10—H10A⋯O2ii | 0.97 | 2.58 | 3.449 (3) | 150 |
| C9—H9B⋯Br2iii | 0.97 | 2.95 | 3.854 (3) | 156 |
| C9—H9A⋯O2iii | 0.97 | 2.45 | 3.334 (3) | 151 |
Symmetry codes: (i)
 ; (ii)
; (ii)
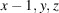 ; (iii)
; (iii)
 .
.
Figure 7.
Patterns of intermolecular interactions created by (a) molecule A and (b) molecule B in the crystal structure of 2.
Viewing the crystal structure of compound 3 in the direction of the a-axis reveals a stacking arrangement of molecules (Fig. 8 ▸). Along the stacking axis the centroid-centroid distance of 3.735 (1) Å between consecutive molecules indicates the presence of offset π–π interactions. As is obvious from Fig. 9 ▸, showing the mode of non-covalent bonding in the crystal, the H atom of the hydroxy group forms an intermolecular O—H⋯O bond [O1—H1⋯O3 = 1.91 (2) Å, 150 (2)°; Table 3 ▸], while its O atom forms a C—H⋯O bond [C2—H2⋯O1 = 2.43 Å, 159.6°; Table 3 ▸], thus creating a supramolecular synthon with the graph set
 (17) (Etter, 1990 ▸; Etter et al., 1990 ▸; Bernstein et al., 1995 ▸) in which four molecules take part. The OH group is also involved in formation of an inversion-symmetric ring motif of the structure
(17) (Etter, 1990 ▸; Etter et al., 1990 ▸; Bernstein et al., 1995 ▸) in which four molecules take part. The OH group is also involved in formation of an inversion-symmetric ring motif of the structure
 (8). Another supramolecular motif corresponding to the
(8). Another supramolecular motif corresponding to the
 (14) graph set is formed by the formyl groups of inversion-related molecules.
(14) graph set is formed by the formyl groups of inversion-related molecules.
Figure 8.
Packing diagram of 3 viewed down the a-axis. Dashed lines represent hydrogen bonds.
Figure 9.
Mode of intermolecular non-covalent interactions in the crystal structure of 3. The cyclic supramolecular synthons are marked by colour highlighting.
Table 3. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for 3 .
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C2—H2⋯O1i | 0.95 | 2.43 | 3.3354 (16) | 160 |
| C8—H8⋯O2ii | 0.95 | 2.58 | 3.1973 (18) | 123 |
| O1—H1⋯O3iii | 0.85 (2) | 1.91 (2) | 2.6795 (13) | 150 (2) |
Symmetry codes: (i)
 ; (ii)
; (ii)
 ; (iii)
; (iii)
 .
.
4. Database survey
A search in the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD, Version 5.43, update November 2021; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) for benzene derivates containing the corresponding substituents resulted in several hits, but with relatively strong structural differences from the searched structures. The compound with the closest relation to 1 is ethyl 2,3,5,6-tetramethylbenzoate (FICVET; Pinkus et al. 2005 ▸), the crystal structure of which features C—H⋯O and C—H⋯π interactions. In the case of bromomethyl-substituted benzenes, the crystal structures of 1,2,4,5-tetrakis(bromomethyl)-3,6-dimethoxybenzene, 1,2,4,5-tetrakis(bromomethyl)-3,6-bis(hexyloxy)benzene and 1,2,4,5-tetrakis(bromomethyl)-3,6-bis(2-ethylbutoxy)benzene (BASZIG, BASZOM, BASZUS; Velde et al. 2012 ▸) as well as 1,3,5-tris(bromomethyl)-2,4,6-trimethoxybenzene (IDOBAG; Koch et al. 2013 ▸) are worth mentioning. The crystal structure of IDOBAG, for example, is characterized by the presence of C—H⋯O and C—H⋯Br hydrogen bonds as well as C—Br⋯Br halogen bonds of type II, as observed also in the crystal structure of 2. In the crystal structure of 2-hydroxyisophthalaldehyde (NEJJOB; Zondervan et al. 1997 ▸), an analogue of 3, the molecules interact via O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming chains. In addition, the hydroxy group is involved in an intramolecular O—H⋯O hydrogen bond with the neighbouring carbonyl oxygen atom.
5. Synthesis and crystallization
Compounds 1–3 were prepared according to literature procedures (Kurz & Göbel, 1996 ▸; Battaini et al., 2003 ▸; Star et al., 2003 ▸).
Suitable crystals of compounds 2 and 3 for X-ray analysis were obtained by slow evaporation from a hexane solution, while crystals of 1 were grown from a subcooled melt.
6. Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 4 ▸. Hydrogen atom H1 in 3 was located in a difference-Fourier map and freely refined. Other H atoms were positioned geometrically and refined isotropically using a riding model with C—H = 0.93–0.98 Å and U iso(H) = 1.2–1.5U eq(C).
Table 4. Experimental details.
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crystal data | |||
| Chemical formula | C10H12O2 | C10H10Br2O2 | C8H6O3 |
| M r | 164.20 | 322.00 | 150.13 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/n | Triclinic, P

|
Monoclinic, P21/n |
| Temperature (K) | 153 | 130 | 153 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 8.4631 (6), 7.9793 (4), 13.4042 (9) | 7.7936 (2), 9.1655 (2), 17.2292 (4) | 3.7345 (1), 11.9549 (4), 15.0846 (5) |
| α, β, γ (°) | 90, 98.835 (6), 90 | 88.1637 (12), 80.9050 (12), 65.8659 (11) | 90, 94.212 (2), 90 |
| V (Å3) | 894.44 (10) | 1108.30 (5) | 671.64 (4) |
| Z | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα | Mo Kα | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.08 | 7.29 | 0.12 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.40 × 0.25 × 0.16 | 0.46 × 0.39 × 0.27 | 0.42 × 0.28 × 0.19 |
| Data collection | |||
| Diffractometer | Stoe IPDS 2T | Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD area detector | Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD area detector |
| Absorption correction | – | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2014 ▸) | – |
| T min, T max | – | 0.134, 0.244 | – |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 7437, 1762, 1449 | 29065, 5842, 5305 | 11533, 1819, 1519 |
| R int | 0.046 | 0.033 | 0.058 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.617 | 0.680 | 0.691 |
| Refinement | |||
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.041, 0.116, 1.05 | 0.028, 0.070, 1.04 | 0.047, 0.131, 1.06 |
| No. of reflections | 1762 | 5842 | 1819 |
| No. of parameters | 112 | 255 | 104 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained | H-atom parameters constrained | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.24, −0.19 | 1.21, −0.98 | 0.33, −0.28 |
Computer programs: X-AREA and X-RED (Stoe & Cie, 2002 ▸), APEX2 and SAINT (Bruker, 2014 ▸), SIR2014 (Burla et al., 2015 ▸), SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▸), SHELXL (Sheldrick, 2015 ▸), ShelXle (Hübschle et al., 2011 ▸), XP (Sheldrick, 2008 ▸), ORTEP-3 for Windows and WinGX (Farrugia, 2012 ▸) and publCIF (Westrip, 2010 ▸).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) 1, 2, 3, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022005643/ex2057sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) 1. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022005643/ex20571sup4.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022005643/ex20571sup5.cml
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) 2. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022005643/ex20572sup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022005643/ex20572sup6.cml
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) 3. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022005643/ex20573sup3.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022005643/ex20573sup7.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
Open access funding by the Publication Fund of the Technische Universität Bergakademie Freiberg is gratefully acknowledged.
supplementary crystallographic information
Methyl 3,5-dimethylbenzoate (1). Crystal data
| C10H12O2 | F(000) = 352 |
| Mr = 164.20 | Dx = 1.219 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 8.4631 (6) Å | Cell parameters from 7437 reflections |
| b = 7.9793 (4) Å | θ = 2.7–27.2° |
| c = 13.4042 (9) Å | µ = 0.08 mm−1 |
| β = 98.835 (6)° | T = 153 K |
| V = 894.44 (10) Å3 | Piece, colorless |
| Z = 4 | 0.40 × 0.25 × 0.16 mm |
Methyl 3,5-dimethylbenzoate (1). Data collection
| Stoe IPDS 2T diffractometer | 1449 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: sealed X-ray tube, 12 x 0.4 mm long-fine focus | Rint = 0.046 |
| Plane graphite monochromator | θmax = 26.0°, θmin = 2.7° |
| Detector resolution: 6.67 pixels mm-1 | h = −10→9 |
| rotation method scans | k = −9→9 |
| 7437 measured reflections | l = −16→16 |
| 1762 independent reflections |
Methyl 3,5-dimethylbenzoate (1). Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 0 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.041 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.116 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0548P)2 + 0.2723P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.05 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 1762 reflections | Δρmax = 0.24 e Å−3 |
| 112 parameters | Δρmin = −0.19 e Å−3 |
Methyl 3,5-dimethylbenzoate (1). Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
Methyl 3,5-dimethylbenzoate (1). Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.27708 (14) | 0.33954 (14) | 0.48553 (8) | 0.0433 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.20755 (12) | 0.58613 (12) | 0.54594 (7) | 0.0309 (3) | |
| C1 | 0.12649 (14) | 0.34326 (16) | 0.62305 (9) | 0.0244 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.10405 (16) | 0.16993 (17) | 0.62357 (10) | 0.0276 (3) | |
| H2 | 0.1406 | 0.1027 | 0.5733 | 0.033* | |
| C3 | 0.02860 (16) | 0.09507 (16) | 0.69720 (10) | 0.0283 (3) | |
| C4 | −0.02303 (16) | 0.19629 (17) | 0.77063 (10) | 0.0279 (3) | |
| H4 | −0.0747 | 0.1458 | 0.8211 | 0.033* | |
| C5 | −0.00096 (15) | 0.36934 (17) | 0.77210 (10) | 0.0257 (3) | |
| C6 | 0.07405 (15) | 0.44202 (17) | 0.69705 (10) | 0.0249 (3) | |
| H6 | 0.0894 | 0.5599 | 0.6965 | 0.030* | |
| C7 | 0.21123 (15) | 0.41859 (17) | 0.54403 (10) | 0.0271 (3) | |
| C8 | 0.29088 (18) | 0.6711 (2) | 0.47431 (11) | 0.0361 (4) | |
| H8A | 0.2808 | 0.7926 | 0.4822 | 0.054* | |
| H8B | 0.2442 | 0.6387 | 0.4056 | 0.054* | |
| H8C | 0.4042 | 0.6398 | 0.4866 | 0.054* | |
| C9 | 0.00480 (19) | −0.09303 (17) | 0.69749 (12) | 0.0383 (4) | |
| H9A | −0.0136 | −0.1291 | 0.7647 | 0.057* | |
| H9B | 0.1005 | −0.1487 | 0.6805 | 0.057* | |
| H9C | −0.0879 | −0.1231 | 0.6475 | 0.057* | |
| C10 | −0.05669 (18) | 0.47866 (18) | 0.85204 (11) | 0.0333 (3) | |
| H10A | 0.0340 | 0.5428 | 0.8870 | 0.050* | |
| H10B | −0.1010 | 0.4080 | 0.9008 | 0.050* | |
| H10C | −0.1392 | 0.5560 | 0.8201 | 0.050* |
Methyl 3,5-dimethylbenzoate (1). Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0488 (7) | 0.0417 (6) | 0.0461 (7) | 0.0006 (5) | 0.0280 (5) | −0.0072 (5) |
| O2 | 0.0345 (6) | 0.0299 (6) | 0.0308 (5) | −0.0021 (4) | 0.0126 (4) | 0.0040 (4) |
| C1 | 0.0207 (6) | 0.0273 (7) | 0.0253 (7) | 0.0015 (5) | 0.0035 (5) | −0.0001 (5) |
| C2 | 0.0262 (7) | 0.0260 (7) | 0.0300 (7) | 0.0039 (5) | 0.0025 (5) | −0.0042 (5) |
| C3 | 0.0269 (7) | 0.0232 (7) | 0.0329 (7) | 0.0006 (5) | −0.0012 (5) | 0.0017 (5) |
| C4 | 0.0283 (7) | 0.0284 (7) | 0.0265 (7) | −0.0026 (5) | 0.0023 (5) | 0.0046 (5) |
| C5 | 0.0249 (7) | 0.0274 (7) | 0.0247 (6) | 0.0005 (5) | 0.0034 (5) | −0.0001 (5) |
| C6 | 0.0245 (6) | 0.0221 (6) | 0.0280 (7) | 0.0004 (5) | 0.0040 (5) | 0.0004 (5) |
| C7 | 0.0223 (6) | 0.0316 (7) | 0.0276 (7) | 0.0001 (5) | 0.0045 (5) | −0.0024 (5) |
| C8 | 0.0320 (8) | 0.0441 (9) | 0.0337 (8) | −0.0061 (6) | 0.0098 (6) | 0.0092 (6) |
| C9 | 0.0418 (9) | 0.0237 (8) | 0.0480 (9) | −0.0012 (6) | 0.0024 (7) | 0.0011 (6) |
| C10 | 0.0388 (8) | 0.0339 (8) | 0.0300 (7) | −0.0009 (6) | 0.0140 (6) | −0.0028 (6) |
Methyl 3,5-dimethylbenzoate (1). Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C7 | 1.2073 (16) | C5—C6 | 1.3956 (18) |
| O2—C7 | 1.3375 (17) | C5—C10 | 1.5121 (18) |
| O2—C8 | 1.4448 (16) | C6—H6 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C6 | 1.3917 (18) | C8—H8A | 0.9800 |
| C1—C2 | 1.3961 (19) | C8—H8B | 0.9800 |
| C1—C7 | 1.4936 (17) | C8—H8C | 0.9800 |
| C2—C3 | 1.3900 (19) | C9—H9A | 0.9800 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9500 | C9—H9B | 0.9800 |
| C3—C4 | 1.3944 (19) | C9—H9C | 0.9800 |
| C3—C9 | 1.5144 (19) | C10—H10A | 0.9800 |
| C4—C5 | 1.3931 (19) | C10—H10B | 0.9800 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9500 | C10—H10C | 0.9800 |
| C7—O2—C8 | 116.20 (11) | O1—C7—C1 | 124.76 (13) |
| C6—C1—C2 | 119.92 (12) | O2—C7—C1 | 111.94 (11) |
| C6—C1—C7 | 121.19 (12) | O2—C8—H8A | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—C7 | 118.86 (12) | O2—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 120.46 (12) | H8A—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.8 | O2—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 119.8 | H8A—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 118.70 (12) | H8B—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—C9 | 120.23 (13) | C3—C9—H9A | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—C9 | 121.07 (13) | C3—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 121.89 (12) | H9A—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.1 | C3—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.1 | H9A—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 118.46 (12) | H9B—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—C10 | 121.74 (12) | C5—C10—H10A | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—C10 | 119.80 (12) | C5—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 120.57 (12) | H10A—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—H6 | 119.7 | C5—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.7 | H10A—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| O1—C7—O2 | 123.30 (12) | H10B—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 0.43 (19) | C7—C1—C6—C5 | −178.18 (12) |
| C7—C1—C2—C3 | 178.69 (11) | C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.48 (19) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.42 (19) | C10—C5—C6—C1 | 179.82 (12) |
| C1—C2—C3—C9 | −179.91 (13) | C8—O2—C7—O1 | −1.2 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.0 (2) | C8—O2—C7—C1 | 178.09 (11) |
| C9—C3—C4—C5 | 179.44 (13) | C6—C1—C7—O1 | 170.41 (14) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.5 (2) | C2—C1—C7—O1 | −7.8 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C10 | −179.82 (12) | C6—C1—C7—O2 | −8.91 (17) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.03 (19) | C2—C1—C7—O2 | 172.85 (12) |
Methyl 3,5-dimethylbenzoate (1). Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg1 represents the centroid of the C1–C6 ring.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C10—H10B···O1i | 0.98 | 2.57 | 3.5215 (19) | 163 |
| C8—H8B···Cg1ii | 0.98 | 2.76 | 3.445 (2) | 127 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x−1/2, −y+1/2, z+1/2; (ii) −x+1/2, y+3/2, −z+3/2.
3,5-Bis(bromomethyl)phenyl acetate (2). Crystal data
| C10H10Br2O2 | Z = 4 |
| Mr = 322.00 | F(000) = 624 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.930 Mg m−3 |
| a = 7.7936 (2) Å | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| b = 9.1655 (2) Å | Cell parameters from 9654 reflections |
| c = 17.2292 (4) Å | θ = 2.7–36.8° |
| α = 88.1637 (12)° | µ = 7.29 mm−1 |
| β = 80.9050 (12)° | T = 130 K |
| γ = 65.8659 (11)° | Irregular, colourless |
| V = 1108.30 (5) Å3 | 0.46 × 0.39 × 0.27 mm |
3,5-Bis(bromomethyl)phenyl acetate (2). Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD area detector diffractometer | 5305 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| φ and ω scans | Rint = 0.033 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2014) | θmax = 28.9°, θmin = 1.2° |
| Tmin = 0.134, Tmax = 0.244 | h = −10→10 |
| 29065 measured reflections | k = −12→12 |
| 5842 independent reflections | l = −23→22 |
3,5-Bis(bromomethyl)phenyl acetate (2). Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 0 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.028 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.070 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0273P)2 + 2.052P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.04 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 5842 reflections | Δρmax = 1.21 e Å−3 |
| 255 parameters | Δρmin = −0.98 e Å−3 |
3,5-Bis(bromomethyl)phenyl acetate (2). Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
3,5-Bis(bromomethyl)phenyl acetate (2). Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Br1 | −0.08475 (4) | 0.81672 (3) | 0.00562 (2) | 0.02904 (7) | |
| Br2 | 0.48472 (4) | 0.08778 (3) | 0.11939 (2) | 0.03302 (8) | |
| O1 | 0.5485 (3) | 0.6991 (2) | 0.19580 (10) | 0.0223 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.8281 (3) | 0.4838 (2) | 0.16971 (12) | 0.0300 (4) | |
| C1 | 0.4550 (3) | 0.6259 (3) | 0.15806 (14) | 0.0180 (4) | |
| C2 | 0.3764 (3) | 0.7009 (3) | 0.09361 (13) | 0.0177 (4) | |
| H2 | 0.3906 | 0.7927 | 0.0756 | 0.021* | |
| C3 | 0.2757 (3) | 0.6375 (3) | 0.05580 (13) | 0.0168 (4) | |
| C4 | 0.2561 (3) | 0.5002 (3) | 0.08395 (14) | 0.0183 (4) | |
| H4 | 0.1896 | 0.4570 | 0.0587 | 0.022* | |
| C5 | 0.3346 (3) | 0.4268 (3) | 0.14936 (14) | 0.0189 (4) | |
| C6 | 0.4351 (3) | 0.4903 (3) | 0.18721 (14) | 0.0190 (4) | |
| H6 | 0.4879 | 0.4425 | 0.2312 | 0.023* | |
| C7 | 0.7388 (4) | 0.6174 (3) | 0.19617 (14) | 0.0204 (4) | |
| C8 | 0.8159 (4) | 0.7190 (3) | 0.23218 (15) | 0.0262 (5) | |
| H8A | 0.9257 | 0.6518 | 0.2548 | 0.039* | |
| H8B | 0.7203 | 0.7887 | 0.2725 | 0.039* | |
| H8C | 0.8515 | 0.7817 | 0.1925 | 0.039* | |
| C9 | 0.1944 (3) | 0.7141 (3) | −0.01535 (14) | 0.0221 (5) | |
| H9A | 0.2349 | 0.6337 | −0.0575 | 0.026* | |
| H9B | 0.2432 | 0.7937 | −0.0326 | 0.026* | |
| C10 | 0.3063 (4) | 0.2828 (3) | 0.18047 (17) | 0.0258 (5) | |
| H10A | 0.1767 | 0.2972 | 0.1783 | 0.031* | |
| H10B | 0.3249 | 0.2712 | 0.2351 | 0.031* | |
| Br1A | 0.43346 (3) | 0.44424 (3) | 0.61006 (2) | 0.02337 (6) | |
| Br2A | 0.92345 (4) | −0.40729 (3) | 0.60976 (2) | 0.02744 (7) | |
| O1A | 0.9262 (3) | 0.0059 (2) | 0.34359 (11) | 0.0285 (4) | |
| O2A | 0.6523 (3) | 0.1522 (3) | 0.30204 (12) | 0.0443 (6) | |
| C1A | 0.8337 (3) | 0.0113 (3) | 0.42092 (14) | 0.0200 (4) | |
| C2A | 0.7921 (3) | 0.1409 (3) | 0.47025 (16) | 0.0219 (5) | |
| H2A | 0.8118 | 0.2296 | 0.4509 | 0.026* | |
| C3A | 0.7203 (3) | 0.1375 (3) | 0.54912 (15) | 0.0210 (5) | |
| C4A | 0.6907 (3) | 0.0042 (3) | 0.57655 (14) | 0.0192 (4) | |
| H4A | 0.6413 | 0.0022 | 0.6292 | 0.023* | |
| C5A | 0.7340 (3) | −0.1266 (3) | 0.52649 (13) | 0.0171 (4) | |
| C6A | 0.8055 (3) | −0.1220 (3) | 0.44763 (13) | 0.0178 (4) | |
| H6A | 0.8340 | −0.2079 | 0.4133 | 0.021* | |
| C7A | 0.8205 (4) | 0.0866 (3) | 0.28849 (14) | 0.0219 (5) | |
| C8A | 0.9420 (4) | 0.0791 (4) | 0.21112 (16) | 0.0317 (6) | |
| H8A1 | 0.9001 | 0.0369 | 0.1712 | 0.048* | |
| H8A2 | 1.0722 | 0.0109 | 0.2145 | 0.048* | |
| H8A3 | 0.9317 | 0.1846 | 0.1980 | 0.048* | |
| C9A | 0.6879 (4) | 0.2709 (3) | 0.60537 (19) | 0.0323 (6) | |
| H9A1 | 0.7829 | 0.3134 | 0.5893 | 0.039* | |
| H9A2 | 0.7036 | 0.2291 | 0.6574 | 0.039* | |
| C10A | 0.7074 (3) | −0.2710 (3) | 0.55685 (15) | 0.0225 (5) | |
| H10C | 0.6986 | −0.3315 | 0.5136 | 0.027* | |
| H10D | 0.5896 | −0.2386 | 0.5938 | 0.027* |
3,5-Bis(bromomethyl)phenyl acetate (2). Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Br1 | 0.02417 (13) | 0.02849 (13) | 0.03098 (14) | −0.00553 (10) | −0.01021 (10) | 0.00568 (10) |
| Br2 | 0.03039 (14) | 0.01534 (12) | 0.05357 (18) | −0.00887 (10) | −0.00889 (12) | 0.00249 (11) |
| O1 | 0.0273 (9) | 0.0173 (8) | 0.0254 (9) | −0.0095 (7) | −0.0116 (7) | 0.0010 (7) |
| O2 | 0.0238 (9) | 0.0277 (10) | 0.0385 (11) | −0.0103 (8) | −0.0035 (8) | −0.0084 (8) |
| C1 | 0.0183 (10) | 0.0160 (10) | 0.0198 (11) | −0.0063 (8) | −0.0051 (8) | −0.0011 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0205 (10) | 0.0141 (10) | 0.0182 (10) | −0.0069 (8) | −0.0028 (8) | 0.0009 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0170 (10) | 0.0163 (10) | 0.0139 (10) | −0.0042 (8) | −0.0005 (8) | −0.0014 (8) |
| C4 | 0.0159 (10) | 0.0169 (10) | 0.0218 (11) | −0.0068 (8) | −0.0020 (8) | −0.0019 (8) |
| C5 | 0.0152 (10) | 0.0162 (10) | 0.0228 (11) | −0.0055 (8) | 0.0010 (8) | 0.0012 (8) |
| C6 | 0.0194 (10) | 0.0174 (10) | 0.0186 (10) | −0.0056 (8) | −0.0049 (8) | 0.0037 (8) |
| C7 | 0.0248 (11) | 0.0231 (11) | 0.0166 (10) | −0.0126 (9) | −0.0045 (9) | 0.0028 (9) |
| C8 | 0.0337 (13) | 0.0302 (13) | 0.0228 (12) | −0.0199 (11) | −0.0081 (10) | 0.0016 (10) |
| C9 | 0.0238 (11) | 0.0252 (12) | 0.0163 (11) | −0.0088 (9) | −0.0040 (9) | 0.0007 (9) |
| C10 | 0.0232 (12) | 0.0225 (12) | 0.0330 (13) | −0.0118 (10) | −0.0019 (10) | 0.0063 (10) |
| Br1A | 0.02379 (12) | 0.01843 (11) | 0.01960 (11) | −0.00036 (9) | −0.00319 (9) | 0.00021 (8) |
| Br2A | 0.02581 (13) | 0.02373 (13) | 0.03068 (14) | −0.00786 (10) | −0.00669 (10) | 0.00987 (10) |
| O1A | 0.0182 (8) | 0.0409 (11) | 0.0200 (9) | −0.0068 (8) | −0.0022 (7) | 0.0120 (8) |
| O2A | 0.0272 (10) | 0.0641 (15) | 0.0212 (10) | 0.0028 (10) | −0.0076 (8) | 0.0062 (10) |
| C1A | 0.0124 (9) | 0.0250 (11) | 0.0187 (11) | −0.0037 (8) | −0.0039 (8) | 0.0067 (9) |
| C2A | 0.0141 (10) | 0.0168 (10) | 0.0339 (13) | −0.0041 (8) | −0.0091 (9) | 0.0083 (9) |
| C3A | 0.0131 (10) | 0.0183 (11) | 0.0285 (12) | −0.0013 (8) | −0.0081 (9) | −0.0012 (9) |
| C4A | 0.0136 (10) | 0.0228 (11) | 0.0175 (10) | −0.0032 (8) | −0.0035 (8) | −0.0003 (8) |
| C5A | 0.0116 (9) | 0.0193 (10) | 0.0195 (11) | −0.0048 (8) | −0.0047 (8) | 0.0027 (8) |
| C6A | 0.0144 (9) | 0.0192 (10) | 0.0180 (10) | −0.0041 (8) | −0.0051 (8) | 0.0000 (8) |
| C7A | 0.0280 (12) | 0.0197 (11) | 0.0194 (11) | −0.0101 (10) | −0.0076 (9) | 0.0039 (9) |
| C8A | 0.0399 (15) | 0.0364 (15) | 0.0227 (13) | −0.0211 (13) | −0.0022 (11) | 0.0086 (11) |
| C9A | 0.0200 (12) | 0.0241 (13) | 0.0471 (17) | −0.0002 (10) | −0.0115 (11) | −0.0131 (12) |
| C10A | 0.0176 (10) | 0.0240 (12) | 0.0267 (12) | −0.0091 (9) | −0.0050 (9) | 0.0045 (9) |
3,5-Bis(bromomethyl)phenyl acetate (2). Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Br1—C9 | 1.962 (2) | Br1A—C9A | 1.960 (3) |
| Br2—C10 | 1.965 (3) | Br2A—C10A | 1.979 (2) |
| O1—C7 | 1.362 (3) | O1A—C7A | 1.353 (3) |
| O1—C1 | 1.407 (3) | O1A—C1A | 1.403 (3) |
| O2—C7 | 1.196 (3) | O2A—C7A | 1.184 (3) |
| C1—C2 | 1.379 (3) | C1A—C2A | 1.379 (4) |
| C1—C6 | 1.383 (3) | C1A—C6A | 1.380 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.392 (3) | C2A—C3A | 1.390 (4) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C2A—H2A | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.392 (3) | C3A—C4A | 1.389 (3) |
| C3—C9 | 1.492 (3) | C3A—C9A | 1.498 (4) |
| C4—C5 | 1.389 (3) | C4A—C5A | 1.392 (3) |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C4A—H4A | 0.9300 |
| C5—C6 | 1.391 (3) | C5A—C6A | 1.391 (3) |
| C5—C10 | 1.495 (3) | C5A—C10A | 1.488 (3) |
| C6—H6 | 0.9300 | C6A—H6A | 0.9300 |
| C7—C8 | 1.492 (3) | C7A—C8A | 1.494 (4) |
| C8—H8A | 0.9600 | C8A—H8A1 | 0.9600 |
| C8—H8B | 0.9600 | C8A—H8A2 | 0.9600 |
| C8—H8C | 0.9600 | C8A—H8A3 | 0.9600 |
| C9—H9A | 0.9700 | C9A—H9A1 | 0.9700 |
| C9—H9B | 0.9700 | C9A—H9A2 | 0.9700 |
| C10—H10A | 0.9700 | C10A—H10C | 0.9700 |
| C10—H10B | 0.9700 | C10A—H10D | 0.9700 |
| C7—O1—C1 | 118.16 (18) | C7A—O1A—C1A | 118.43 (19) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 122.2 (2) | C2A—C1A—C6A | 121.8 (2) |
| C2—C1—O1 | 116.6 (2) | C2A—C1A—O1A | 119.6 (2) |
| C6—C1—O1 | 121.1 (2) | C6A—C1A—O1A | 118.3 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 119.2 (2) | C1A—C2A—C3A | 119.3 (2) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.4 | C1A—C2A—H2A | 120.3 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.4 | C3A—C2A—H2A | 120.3 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 119.3 (2) | C4A—C3A—C2A | 119.4 (2) |
| C4—C3—C9 | 120.7 (2) | C4A—C3A—C9A | 120.0 (2) |
| C2—C3—C9 | 120.0 (2) | C2A—C3A—C9A | 120.5 (2) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 120.8 (2) | C3A—C4A—C5A | 121.0 (2) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.6 | C3A—C4A—H4A | 119.5 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.6 | C5A—C4A—H4A | 119.5 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 119.9 (2) | C6A—C5A—C4A | 119.2 (2) |
| C4—C5—C10 | 120.1 (2) | C6A—C5A—C10A | 120.1 (2) |
| C6—C5—C10 | 120.0 (2) | C4A—C5A—C10A | 120.7 (2) |
| C1—C6—C5 | 118.6 (2) | C1A—C6A—C5A | 119.3 (2) |
| C1—C6—H6 | 120.7 | C1A—C6A—H6A | 120.3 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 120.7 | C5A—C6A—H6A | 120.3 |
| O2—C7—O1 | 123.3 (2) | O2A—C7A—O1A | 122.4 (2) |
| O2—C7—C8 | 126.2 (2) | O2A—C7A—C8A | 126.0 (2) |
| O1—C7—C8 | 110.5 (2) | O1A—C7A—C8A | 111.6 (2) |
| C7—C8—H8A | 109.5 | C7A—C8A—H8A1 | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—H8B | 109.5 | C7A—C8A—H8A2 | 109.5 |
| H8A—C8—H8B | 109.5 | H8A1—C8A—H8A2 | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—H8C | 109.5 | C7A—C8A—H8A3 | 109.5 |
| H8A—C8—H8C | 109.5 | H8A1—C8A—H8A3 | 109.5 |
| H8B—C8—H8C | 109.5 | H8A2—C8A—H8A3 | 109.5 |
| C3—C9—Br1 | 111.76 (16) | C3A—C9A—Br1A | 112.24 (17) |
| C3—C9—H9A | 109.3 | C3A—C9A—H9A1 | 109.2 |
| Br1—C9—H9A | 109.3 | Br1A—C9A—H9A1 | 109.2 |
| C3—C9—H9B | 109.3 | C3A—C9A—H9A2 | 109.2 |
| Br1—C9—H9B | 109.3 | Br1A—C9A—H9A2 | 109.2 |
| H9A—C9—H9B | 107.9 | H9A1—C9A—H9A2 | 107.9 |
| C5—C10—Br2 | 111.29 (17) | C5A—C10A—Br2A | 110.38 (16) |
| C5—C10—H10A | 109.4 | C5A—C10A—H10C | 109.6 |
| Br2—C10—H10A | 109.4 | Br2A—C10A—H10C | 109.6 |
| C5—C10—H10B | 109.4 | C5A—C10A—H10D | 109.6 |
| Br2—C10—H10B | 109.4 | Br2A—C10A—H10D | 109.6 |
| H10A—C10—H10B | 108.0 | H10C—C10A—H10D | 108.1 |
| C7—O1—C1—C2 | −116.6 (2) | C7A—O1A—C1A—C2A | −81.9 (3) |
| C7—O1—C1—C6 | 66.7 (3) | C7A—O1A—C1A—C6A | 104.9 (3) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.8 (4) | C6A—C1A—C2A—C3A | 0.2 (3) |
| O1—C1—C2—C3 | −177.5 (2) | O1A—C1A—C2A—C3A | −172.7 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.2 (3) | C1A—C2A—C3A—C4A | −0.4 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C9 | −178.3 (2) | C1A—C2A—C3A—C9A | 175.3 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.4 (3) | C2A—C3A—C4A—C5A | 0.8 (3) |
| C9—C3—C4—C5 | 178.8 (2) | C9A—C3A—C4A—C5A | −175.0 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.3 (3) | C3A—C4A—C5A—C6A | −0.9 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C10 | 177.8 (2) | C3A—C4A—C5A—C10A | 178.1 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.9 (4) | C2A—C1A—C6A—C5A | −0.3 (3) |
| O1—C1—C6—C5 | 177.4 (2) | O1A—C1A—C6A—C5A | 172.73 (19) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.3 (3) | C4A—C5A—C6A—C1A | 0.6 (3) |
| C10—C5—C6—C1 | −178.5 (2) | C10A—C5A—C6A—C1A | −178.4 (2) |
| C1—O1—C7—O2 | −4.0 (3) | C1A—O1A—C7A—O2A | −5.1 (4) |
| C1—O1—C7—C8 | 174.9 (2) | C1A—O1A—C7A—C8A | 175.6 (2) |
| C4—C3—C9—Br1 | 70.6 (2) | C4A—C3A—C9A—Br1A | −95.8 (3) |
| C2—C3—C9—Br1 | −111.0 (2) | C2A—C3A—C9A—Br1A | 88.5 (3) |
| C4—C5—C10—Br2 | 80.7 (2) | C6A—C5A—C10A—Br2A | 99.1 (2) |
| C6—C5—C10—Br2 | −101.1 (2) | C4A—C5A—C10A—Br2A | −79.9 (2) |
3,5-Bis(bromomethyl)phenyl acetate (2). Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C10A—H10D···O2Ai | 0.97 | 2.28 | 3.236 (3) | 168 |
| C10A—H10C···Br1Ai | 0.97 | 2.89 | 3.836 (3) | 164 |
| C8A—H8A3···O2 | 0.96 | 2.58 | 3.521 (4) | 168 |
| C10—H10B···Br2Ai | 0.97 | 3.01 | 3.757 (3) | 135 |
| C10—H10A···O2ii | 0.97 | 2.58 | 3.449 (3) | 150 |
| C9—H9B···Br2iii | 0.97 | 2.95 | 3.854 (3) | 156 |
| C9—H9A···O2iii | 0.97 | 2.45 | 3.334 (3) | 151 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y, −z+1; (ii) x−1, y, z; (iii) −x+1, −y+1, −z.
5-Hydroxybenzene-1,3-dicarbaldehyde (3). Crystal data
| C8H6O3 | F(000) = 312 |
| Mr = 150.13 | Dx = 1.485 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 3.7345 (1) Å | Cell parameters from 6158 reflections |
| b = 11.9549 (4) Å | θ = 2.7–30.5° |
| c = 15.0846 (5) Å | µ = 0.12 mm−1 |
| β = 94.212 (2)° | T = 153 K |
| V = 671.64 (4) Å3 | Rod, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.42 × 0.28 × 0.19 mm |
5-Hydroxybenzene-1,3-dicarbaldehyde (3). Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD area detector diffractometer | Rint = 0.058 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 29.4°, θmin = 2.7° |
| 11533 measured reflections | h = −5→4 |
| 1819 independent reflections | k = −16→16 |
| 1519 reflections with I > 2σ(I) | l = −20→20 |
5-Hydroxybenzene-1,3-dicarbaldehyde (3). Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 0 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.047 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.131 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0692P)2 + 0.2868P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.06 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 1819 reflections | Δρmax = 0.33 e Å−3 |
| 104 parameters | Δρmin = −0.28 e Å−3 |
5-Hydroxybenzene-1,3-dicarbaldehyde (3). Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
5-Hydroxybenzene-1,3-dicarbaldehyde (3). Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.6355 (3) | 0.48950 (8) | 0.38804 (7) | 0.0332 (3) | |
| O2 | 1.0631 (3) | 0.10838 (8) | 0.62211 (7) | 0.0336 (3) | |
| O3 | 0.2117 (3) | 0.11521 (8) | 0.23777 (6) | 0.0291 (3) | |
| C1 | 0.6468 (4) | 0.37799 (10) | 0.40378 (8) | 0.0214 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.8207 (3) | 0.34507 (10) | 0.48515 (8) | 0.0207 (3) | |
| H2 | 0.9189 | 0.4000 | 0.5254 | 0.025* | |
| C3 | 0.8496 (3) | 0.23282 (10) | 0.50697 (7) | 0.0197 (3) | |
| C4 | 0.7080 (4) | 0.15111 (10) | 0.44830 (8) | 0.0214 (3) | |
| H4 | 0.7294 | 0.0740 | 0.4631 | 0.026* | |
| C5 | 0.5354 (3) | 0.18440 (10) | 0.36798 (8) | 0.0206 (3) | |
| C6 | 0.5036 (3) | 0.29757 (10) | 0.34512 (8) | 0.0204 (3) | |
| H6 | 0.3850 | 0.3191 | 0.2899 | 0.024* | |
| C7 | 1.0363 (4) | 0.20285 (11) | 0.59351 (8) | 0.0235 (3) | |
| H7 | 1.1419 | 0.2615 | 0.6290 | 0.028* | |
| C8 | 0.3862 (4) | 0.09684 (11) | 0.30752 (9) | 0.0253 (3) | |
| H8 | 0.4289 | 0.0210 | 0.3240 | 0.030* | |
| H1 | 0.519 (7) | 0.5065 (19) | 0.3394 (16) | 0.056 (7)* |
5-Hydroxybenzene-1,3-dicarbaldehyde (3). Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0477 (7) | 0.0190 (5) | 0.0297 (5) | −0.0017 (4) | −0.0184 (5) | 0.0031 (4) |
| O2 | 0.0445 (7) | 0.0281 (5) | 0.0269 (5) | 0.0034 (4) | −0.0066 (4) | 0.0052 (4) |
| O3 | 0.0329 (6) | 0.0298 (5) | 0.0233 (5) | −0.0024 (4) | −0.0071 (4) | −0.0047 (4) |
| C1 | 0.0228 (7) | 0.0204 (6) | 0.0203 (5) | −0.0004 (4) | −0.0036 (4) | 0.0005 (4) |
| C2 | 0.0214 (7) | 0.0217 (6) | 0.0183 (5) | −0.0005 (4) | −0.0034 (4) | −0.0010 (4) |
| C3 | 0.0184 (6) | 0.0228 (6) | 0.0175 (5) | 0.0005 (4) | −0.0012 (4) | 0.0005 (4) |
| C4 | 0.0227 (7) | 0.0206 (5) | 0.0204 (5) | 0.0000 (4) | −0.0011 (4) | 0.0002 (4) |
| C5 | 0.0193 (6) | 0.0234 (6) | 0.0187 (5) | −0.0008 (4) | −0.0011 (4) | −0.0025 (4) |
| C6 | 0.0194 (6) | 0.0236 (6) | 0.0175 (5) | −0.0006 (4) | −0.0023 (4) | −0.0003 (4) |
| C7 | 0.0248 (7) | 0.0257 (6) | 0.0195 (5) | 0.0022 (5) | −0.0027 (4) | 0.0006 (4) |
| C8 | 0.0267 (7) | 0.0248 (6) | 0.0236 (6) | −0.0025 (5) | −0.0026 (5) | −0.0026 (5) |
5-Hydroxybenzene-1,3-dicarbaldehyde (3). Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C1 | 1.3541 (15) | C3—C7 | 1.4781 (16) |
| O1—H1 | 0.85 (2) | C4—C5 | 1.3882 (16) |
| O2—C7 | 1.2105 (16) | C4—H4 | 0.9500 |
| O3—C8 | 1.2163 (16) | C5—C6 | 1.3991 (17) |
| C1—C6 | 1.3870 (16) | C5—C8 | 1.4709 (17) |
| C1—C2 | 1.4022 (16) | C6—H6 | 0.9500 |
| C2—C3 | 1.3840 (17) | C7—H7 | 0.9500 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9500 | C8—H8 | 0.9500 |
| C3—C4 | 1.3958 (16) | ||
| C1—O1—H1 | 113.2 (16) | C4—C5—C6 | 121.19 (11) |
| O1—C1—C6 | 124.40 (11) | C4—C5—C8 | 117.88 (11) |
| O1—C1—C2 | 115.87 (11) | C6—C5—C8 | 120.92 (11) |
| C6—C1—C2 | 119.73 (11) | C1—C6—C5 | 119.43 (11) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 120.23 (11) | C1—C6—H6 | 120.3 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.9 | C5—C6—H6 | 120.3 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 119.9 | O2—C7—C3 | 124.21 (12) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.56 (11) | O2—C7—H7 | 117.9 |
| C2—C3—C7 | 117.95 (11) | C3—C7—H7 | 117.9 |
| C4—C3—C7 | 121.49 (11) | O3—C8—C5 | 124.23 (12) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 118.86 (11) | O3—C8—H8 | 117.9 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.6 | C5—C8—H8 | 117.9 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.6 | ||
| O1—C1—C2—C3 | −179.31 (12) | O1—C1—C6—C5 | 179.13 (13) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 0.0 (2) | C2—C1—C6—C5 | −0.1 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.3 (2) | C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.1 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3—C7 | 179.88 (12) | C8—C5—C6—C1 | 179.87 (12) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.5 (2) | C2—C3—C7—O2 | 176.10 (14) |
| C7—C3—C4—C5 | 179.96 (12) | C4—C3—C7—O2 | −4.3 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.3 (2) | C4—C5—C8—O3 | 175.61 (14) |
| C3—C4—C5—C8 | −179.58 (12) | C6—C5—C8—O3 | −4.3 (2) |
5-Hydroxybenzene-1,3-dicarbaldehyde (3). Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C2—H2···O1i | 0.95 | 2.43 | 3.3354 (16) | 160 |
| C8—H8···O2ii | 0.95 | 2.58 | 3.1973 (18) | 123 |
| O1—H1···O3iii | 0.85 (2) | 1.91 (2) | 2.6795 (13) | 150 (2) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+2, −y+1, −z+1; (ii) −x+1, −y, −z+1; (iii) −x+1/2, y+1/2, −z+1/2.
References
- Amrhein, F., Lippe, J. & Mazik, M. (2016). Org. Biomol. Chem. 14, 10648–10659. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Amrhein, F. & Mazik, M. (2021). Eur. J. Org. Chem. pp. 6282–6303.
- Amrhein, F., Schwarzer, A. & Mazik, M. (2021). Acta Cryst. E77, 233–236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Battaini, G., Monzani, E., Perotti, A., Para, C., Casella, L., Santagostini, L., Gullotti, M., Dillinger, R., Näther, C. & Tuczek, F. (2003). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125, 4185–4198. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
- Bruker, (2014). APEX2 and SAINT. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Burla, M. C., Caliandro, R., Carrozzini, B., Cascarano, G. L., Cuocci, C., Giacovazzo, C., Mallamo, M., Mazzone, A. & Polidori, G. (2015). J. Appl. Cryst. 48, 306–309.
- Desiraju, G. R. & Steiner, T. (1999). In The Weak Hydrogen Bond. Oxford University Press.
- Etter, M. C. (1990). Acc. Chem. Res. 23, 120–126.
- Etter, M. C., MacDonald, J. C. & Bernstein, J. (1990). Acta Cryst. B46, 256–262. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Hübschle, C. B., Sheldrick, G. M. & Dittrich, B. (2011). J. Appl. Cryst. 44, 1281–1284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Koch, N., Seichter, W. & Mazik, M. (2013). Acta Cryst. E69, o679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Köhler, L., Seichter, W. & Mazik, M. (2020). Eur. J. Org. Chem. pp. 7023–7034.
- Köhler, L., Hübler, C., Seichter, W. & Mazik, M. (2021). RSC Adv. 11, 22221–22229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Kurz, K. & Göbel, M. W. (1996). Helv. Chim. Acta, 79, 1967–1979.
- Lippe, J. & Mazik, M. (2013). J. Org. Chem. 78, 9013–9020. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Lippe, J. & Mazik, M. (2015). J. Org. Chem. 80, 1427–1439. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Mazik, M., Cavga, H. & Jones, P. G. (2005). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 9045–9052. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Nishio, M., Umezawa, Y., Honda, K., Tsuboyama, S. & Suezawa, H. (2009). CrystEngComm, 11, 1757–1788.
- Pedireddy, V. R., Reddy, D. S., Goud, B. S., Craig, D. C., Rae, A. D. & Desiraju, G. R. (1999). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. 2353–2360.
- Pinkus, A. G., Klausmeyer, K. K., Feazell, R. P. & Lin, E. C. H. Y. (2005). Acta Cryst. E61, o662–o663.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Star, A., Liu, Y., Grant, K., Ridvan, L., Stoddart, J. F., Steuerman, D. W., Diehl, M. R., Boukai, A. & Heath, J. R. (2003). Macromolecules, 36, 553–560.
- Stoe & Cie (2002). X-AREA and X-RED. Stoe & Cie GmbH, Darmstadt, Germany.
- Tiekink, E. R. T. & Zukerman-Schpector, J. (2012). In The Importance of Pi-Interactions in Crystal Engineering. Frontiers in Crystal Engineering. Chichester: Wiley.
- Velde, C. M. L. V., Zeller, M. & Azov, V. A. (2012). J. Mol. Struct. 1016, 109–117.
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
- Zondervan, C., van den Beuken, E. K., Kooijman, H., Spek, A. L. & Feringa, B. L. (1997). Tetrahedron Lett. 38, 3111–3114.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) 1, 2, 3, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022005643/ex2057sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) 1. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022005643/ex20571sup4.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022005643/ex20571sup5.cml
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) 2. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022005643/ex20572sup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022005643/ex20572sup6.cml
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) 3. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022005643/ex20573sup3.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022005643/ex20573sup7.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report