Correction to: Bone Research 10.1038/s41413-022-00210-3, published online 27 May 2022
Following publication of the original article [1], the authors regretted to find misinterpretation of data in Fig. 5e, f and Fig. S8b-d. These plots actually showed pseudotime gene expression analysis in the whole bone marrow cells in KO and WT mice, not in the specific clusters as indicated in the original paper. Therefore, Fig. 5e and Fig. 5f showed identical results and so was Fig. S8b–d. To correct this mistake, we deleted the duplicate figures and rearranged the panels in Fig. 5e, f and Fig. S8b–d. The correspondent text (Lines 10-13 of the right column in page 9) and legends (page 10) were also corrected. Since the genes analyzed in these plots were known markers specific for monocyte development, the pseudotime gene analysis among the entire bone marrow cells also strongly supported our conclusion that there were increased myelopoiesis and more rapid monocyte development in the TLR9-/- bone marrow. Although this correction does not affect the results and conclusion of the above paper, all the authors agree to correct this negligence, and feel sorry and sincerely apologize for all the inconvenience it caused.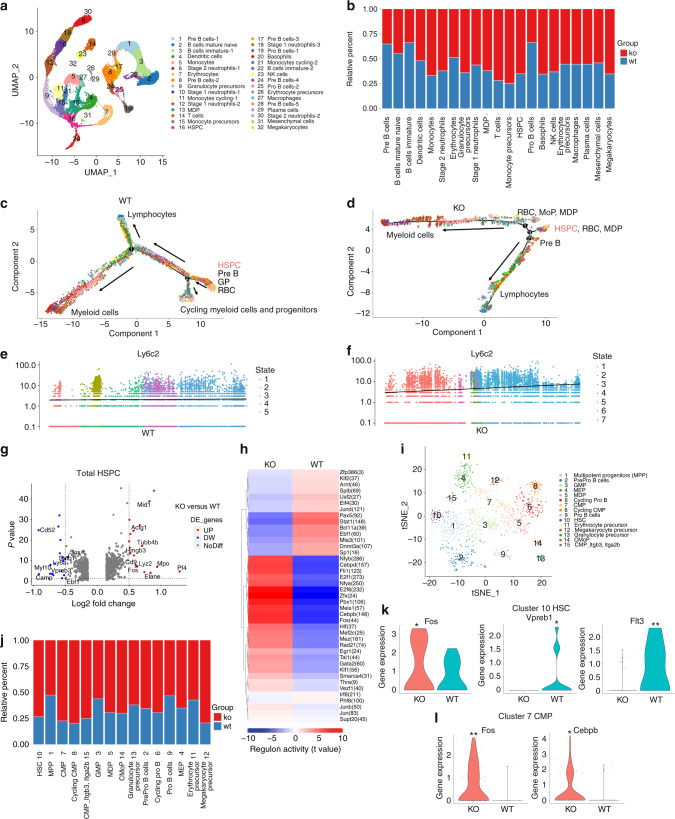
The original article [1] has been corrected.
Supplementary information
Footnotes
These authors contributed equally: Peng Ding, Qiyuan Tan, Zhanying Wei
Contributor Information
Changqing Zhang, Email: zhangcq@sjtu.edu.cn.
Chen Yao, Email: chen.yao@shsmu.edu.cn.
Supplementary information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1038/s41413-022-00221-0.
Reference
- 1.Ding, P. et al. Toll-like receptor 9 deficiency induces osteoclastic bone loss via gut microbiota-associated systemic chronic inflammation. Bone Res. 10, 42 (2022). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


