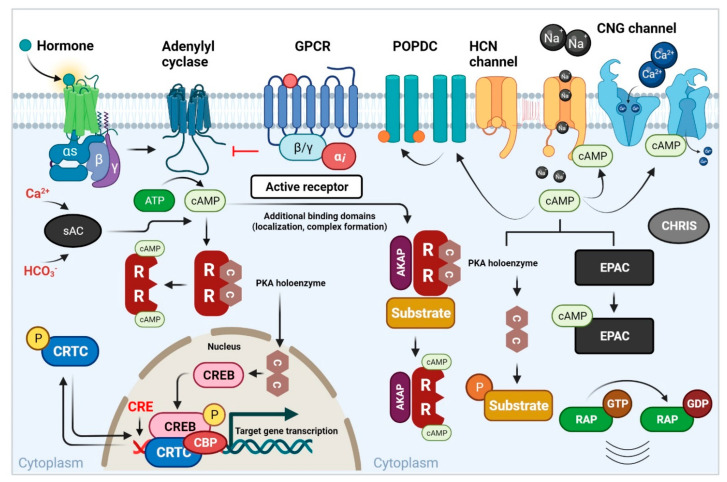
Figure 1.
An overview of mammalian second messenger cAMP signaling pathways [10]. Upstream stimulation of Gαs-coupled GPCRs, which then activate AC to create cAMP, is required for signaling through the PKA pathway. The activation of Gαi-coupled GPCRs inhibits the synthesis of AC and cAMP. Ca2+ and HCO3− activate soluble AC (sAC), which leads to cAMP synthesis. The generation of cAMP in the cell is regulated by multiple ACs as well as its breakdown by PDEs. The tetrameric PKA holoenzyme is made up of two R subunits and two C subunits. Regulatory subunits and substrates are coordinated by AKAPs. Additional binding domains on AKAPs aid in the building of protein complexes and allow them to be targeted to specific sites inside the cell. When cAMP binds to regulatory subunits, the holoenzyme dissociates, allowing catalytic subunits to phosphorylate substrates. CREB-mediated transcription is mediated by PKA. A hormone binds to Gαs-linked GPCRs on the cell surface, stimulating cAMP synthesis and PKA activation through adenylyl cyclase signaling. Adenylyl cyclase and cAMP generation are inhibited when Gαi-coupled GPCRs are activated. C subunits translocate to the nucleus to phosphorylate CREB on serine 133 when they are active. To enhance binding to CREs and transcription of target genes, phosphorylated CREB binds coactivators such as CBP. CREB-mediated transcription is regulated by other coactivators such as CRTCs. Phosphorylation of CRTCs by other kinases causes them to be sequestered in the cytoplasm, while dephosphorylation by phosphatase allows them to be translocated to the nucleus. Beyond PKA, cAMP binds to and activates effectors. cAMP modulates channel opening and cation currents through binding to CNG ion channels. HCN channels bind cAMP to help membrane hyperpolarization open the channel. In the Ras-associated protein (RAP) family of small GTPases, cAMP binds to EPAC to enable the exchange of GDP for GTP. POPDC proteins exist as dimers on the cell surface that bind cAMP. GPCR, G protein–coupled receptor; AC, adenylyl cyclase; PKA, protein kinase A; PDE, phosphodiesterase; AKAP, A-kinase anchoring protein; CREB, cAMP responsive element-binding protein; CRTC, cAMP-regulated transcriptional coactivator; CBP, CREB-binding protein; CRE, cAMP response element; CNG, cyclic nucleotide–gated; HCN, hyperpolarization-activated; POPDC, Popeye domain containing; EPAC, exchange protein directly activated by cAMP.