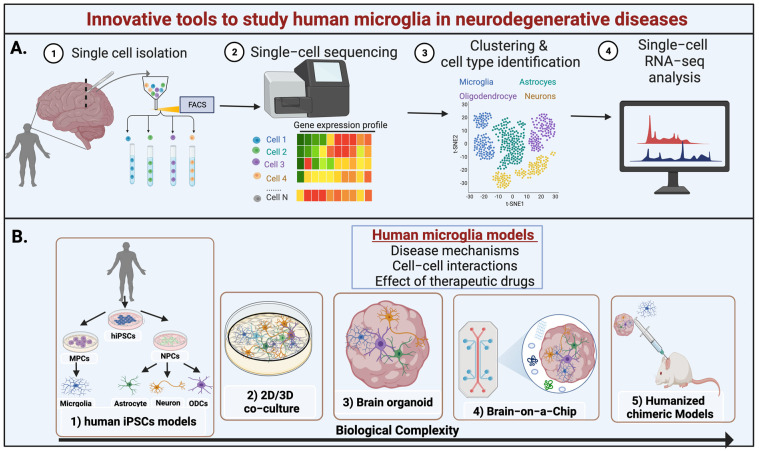
Figure 4.
Innovative tools to study human microglia in neurodegenerative diseases. (A) Single-cell sequencing can be performed by isolating single cells from live or postmortem brains. This tool assists in characterizing the gene expression profiles of various cell types, which helps to understand the heterogeneous phenotypes of microglia in human diseases. (B) The generation of microglia-like cells from human-induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) has advanced mechanistic studies. iPSC can be derived from patients with neurodegenerative diseases or can be genetically modified to study human microglia responses in a specific disease environment. iPSC-derived microglia can also be co-cultured in two/three-dimensional systems or incorporated into brain organoids to study complex interactions of microglia with neurons and other cells. Brain-on-a-Chip technology employs a continuous flow of microscopic fluid in organoid systems, which enables the addition of extracellular matrix components to mimic the complex properties of the brain or incorporates pathogenic stimuli to emulate disease-specific brain microenvironment. Humanized microglia models, created through xenotransplantation of human iPSC-derived microglia models, help to study human microglia in intact models, and this technology is beneficial for translational research, such as therapeutic drug testing. Figure created using BioRender.com (accessed on 14 April 2022).