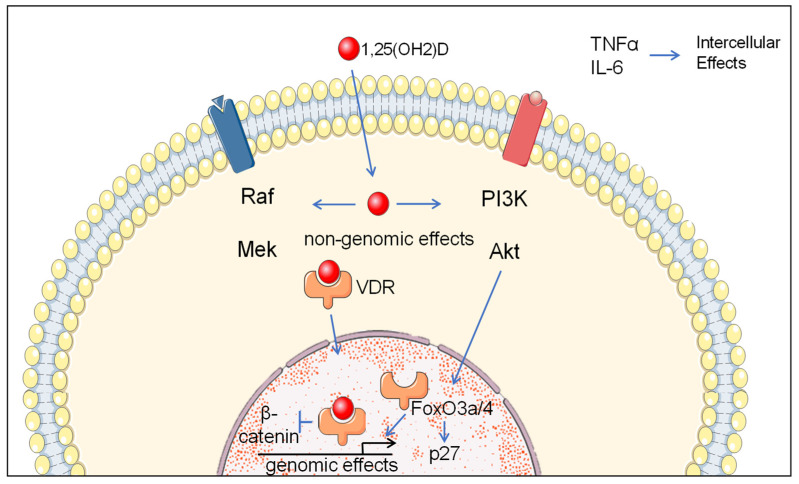
Figure 1.
Vitamin D-regulated pathways in cancer. Cancer-related intracellular non-genomic and genomic mechanisms of molecular pathway regulation by vitamin D and intracellular molecular factors regulated by vitamin D. Non-genomic activation of PI3K and MAP kinases occurs downstream of ligand-bound VDR. FoxO3a/4 signalling and the expression of p27 cyclin-dependent kinase accumulation can result from vitamin D/VDR activation of PI3K signalling. Genomic effects involve regulatory effects of nuclear ligand-bound VDR at responsive gene elements. Nuclear ligand-bound VDR also inhibits β-catenin signalling. Decreased TNFα and IL-6 signalling induced by vitamin-D can have intercellular effects by inhibition of pro-tumorigenic inflammation.