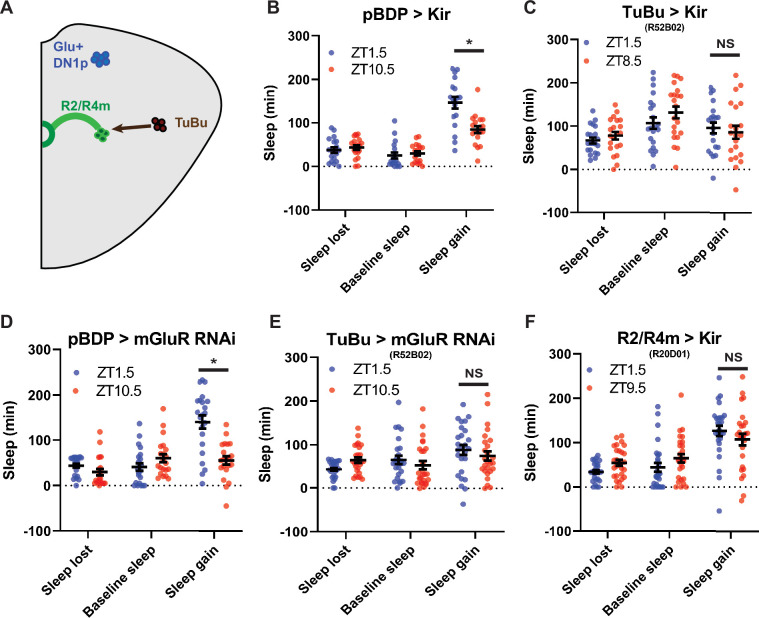
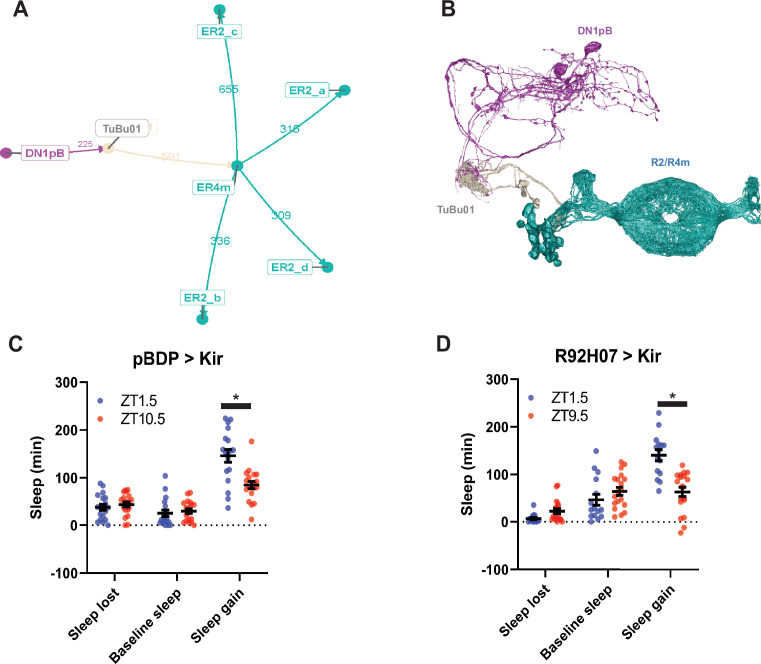
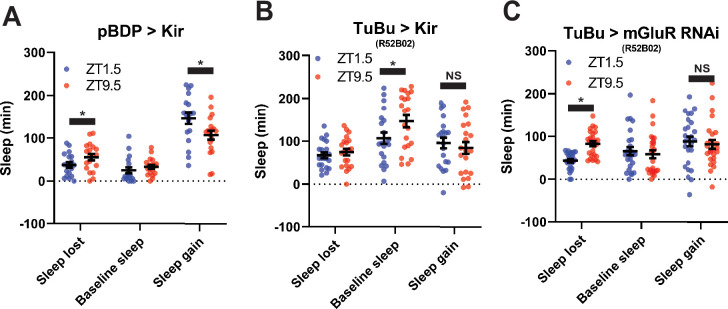
Figure 5. TuBu intermediates convey enhanced morning glutamatergic signal to R2/R4m ellipsoid body neurons (A) Cartoon illustrating proposed link between Glu+ DN1ps and R2/R4m with Tubu intermediates.
(B–F) Comparison of sleep lost, baseline sleep, and sleep gain following deprivation at morning and evening timepoints while modulating neurons linking DN1ps to the EB. Morning times are matched with evening time points with similar baselines. (B) Enhancerless-Gal4 control flies (pBDP >Kir) (N=21) exhibit greater rebound in the morning compared to a matched evening time point (p<0.01, paired t-test). (C) Flies with TuBu neurons silenced (R52B02>Kir) (N=21) do not exhibit a difference in rebound between matched morning/evening time points (p>0.38, paired t-test). (D) Enhancerless-Gal4 driver paired with UAS-GluR-RNAi (pBDP >GluR RNAi) control (N=32) exhibit greater rebound in the morning compared to matched evening time point (p<0.00001, paired t-test). (E) Flies with KD of GluR in TuBu neurons (R52B02>GluR RNAi) do not exhibit a significant difference between matched morning/evening time points (p>0.28, paired t-test). (F) Flies with R2/R4m neurons silenced (R20D01>Kir) (N=32) do not exhibit a significant difference in rebound between matched morning/evening time points (p>0.26, paired t-test). Data are means +/- SEM.