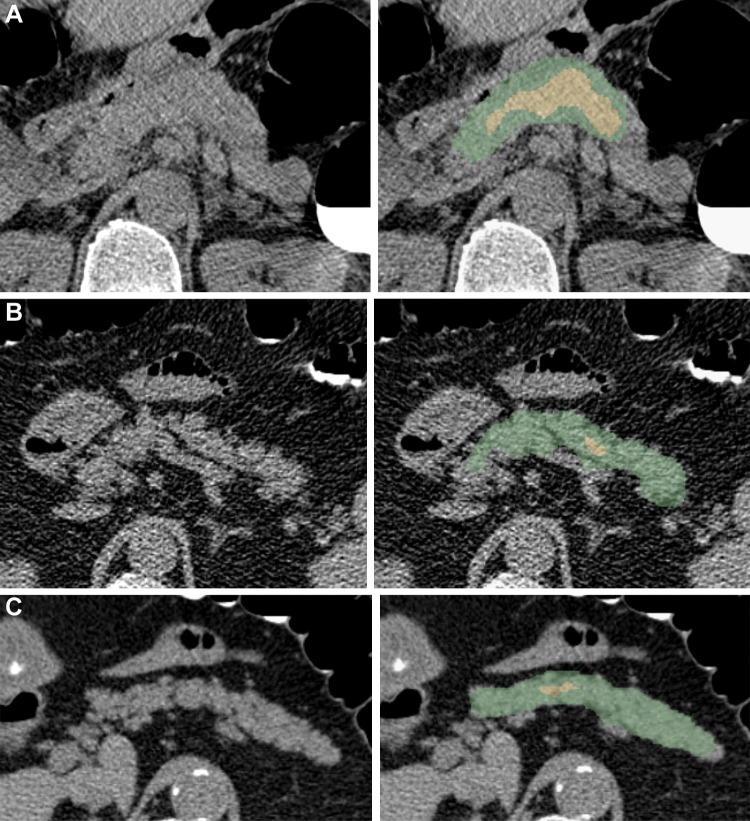
Figure 5:
Examples of pancreas segmentations on unenhanced axial abdominal CT images in healthy participants and patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Images on left are original CT images, and images on right show segmentations overlaid on the original CT images. (A) Images in a nondiabetic 61-year-old man with average pancreas CT attenuation of 35.50 HU ± 47.96 and pancreatic volume of 97.6 mL. (B) Images in a 59-year-old man with type 2 diabetes who was diagnosed 144 days before CT. Average pancreas CT attenuation was 20.66 HU ± 81.99 and pancreatic volume was 77.10 mL. (C) Images in a 67-year-old man with type 2 diabetes who was diagnosed 595 days after CT. Average pancreas CT attenuation was 18.46 HU ± 48.30 and pancreatic volume was 72.88 mL. The green area indicates full segmentation and the yellow area indicates segmentation after erosion.