Abstract
Objective
Compared to microscopes, exoscopes have advantages in field-depth, ergonomics, and educational value. Exoscopes are especially well-poised for adaptation into fluorescence-guided surgery (FGS) due to their excitation source, light path, and image processing capabilities. We evaluated the feasibility of near-infrared FGS using a 3-dimensional (3D), 4 K exoscope with near-infrared fluorescence imaging capability. We then compared it to the most sensitive, commercially-available near-infrared exoscope system (3D and 960 p). In-vitro and intraoperative comparisons were performed.
Methods
Serial dilutions of indocyanine-green (1–2000 μg/mL) were imaged with the 3D, 4 K Olympus Orbeye (system 1) and the 3D, 960 p VisionSense Iridium (system 2). Near-infrared sensitivity was calculated using signal-to-background ratios (SBRs). In addition, three patients with brain tumors were administered indocyanine-green and imaged with system 1, with two also imaged with system 2 for comparison.
Results
Systems 1 and 2 detected near-infrared fluorescence from indocyanine green concentrations of >250 μg/L and >31.3 μg/L, respectively. Intraoperatively, system 1 visualized strong near-infrared fluorescence from two, strongly gadolinium-enhancing meningiomas (SBR=2.4, 1.7). The high-resolution, bright images were sufficient for the surgeon to appreciate the underlying anatomy in the near-infrared mode. However, system 1 was not able to visualize fluorescence from a weakly-enhancing intraparenchymal metastasis. In contrast, system 2 successfully visualized both the meningioma and the metastasis but lacked high resolution stereopsis.
Conclusion
Three-dimensional exoscope systems provide an alternative visualization platform for both standard microsurgery and near-infrared fluorescent guided surgery. However, when tumor fluorescence is weak (i.e., low fluorophore uptake, deep tumors), highly sensitive near-infrared visualization systems may be required.
Keywords: Neuroimaging, 3D exoscope, Fluorescence, Indocyanine-green, Central nervous system neoplasms, Molecular imaging
INTRODUCTION
Since its introduction, the optical neurosurgical microscope has revolutionized microneurosurgery. Today, microscopes remain the gold-standard visualization tool, with high magnification, illumination, and stereopsis. However, microscopes have limitations. At high magnifications, the field depth is incredibly short (<3 mm), forcing neurosurgeons to repeatedly refocus the microscope (up to 40% of operative time) [14,31]. Furthermore, microscopes have limited maneuverability, often forcing surgeons into uncomfortable positions [3,17,24,25,27]. Lastly, microscopes limit full-resolution, 3-dimensional (3D) observation to solely the primary surgeon and one assistant, restricting teaching opportunities.
Exoscopes were developed in response to these limitations. Since exoscopes project onto digital screens rather than eyepieces and because exoscopes are smaller and lighter (<1 kg vs. >100 kg), surgeons can potentially operate more ergonomically [27,33,34]. Furthermore, exoscopes often offer greater field depth (3.5–10 cm), reducing refocusing [17,22,24,26]. Lastly, exoscopes project the surgical field for the entire operating room, ideal for teaching institutions. While earlier generations of exoscopes were criticized for lacking stereopsis, recent models provide the much-needed stereopsis while maintaining the aforementioned benefits [24].
More recently, exoscopes have garnered further interest for their applicability to fluorescence-guided surgery (FGS). In FGS, fluorophores that specifically accumulate in neoplastic tissue help surgeons better identify neoplastic tissue, with most novel fluorophores being developed in the near-infrared (NIR) spectrum [1,2,4,6,11,13,15,18,29,30,35]. When visualizing fluorophores, exoscopes offer several advantages over conventional microscopes.
Visualizing fluorescence begins with the excitation light source, which can be filtered white-light, laser diodes, and/or light-emitting diodes (LED) [36]. Most conventional neurosurgical microscopes use filtered Xenon white-light, letting through a pre-selected range of photons that overlap with the fluorophore excitation profile. However, the filter rejects a large portion of the photon output, decreasing the overall fluorescence yield [9]. Laser diodes are tunable to a very narrow spectrum and allow efficient excitation of fluorophores at their peak excitation wavelengths. Finally, LEDs are available in a wide array of spectrums and have highly efficient light output. Lasers and LEDs are superior excitation light sources and are more common in exoscopes than in microscopes.
The second step in visualizing fluorescence is proper filtering of the returning photons. Having proper filters maximize detection sensitivity by reducing background light from the reflection of the excitation light or from the autofluorescence of the surrounding tissue.
The next step, where microscopes and exoscopes differ significantly, is the light path. In microscopes, the light returning from the surgical area splits to reach the eyepieces as well as the camera sensor. For example, a conventional neurosurgical microscope sends approximately 40% to each eyepiece and the remaining 20% to the sensor (personal communication Zeiss engineer). This can be especially problematic for visible-spectrum fluorophores because the surgeon must rely on using less than 50% of the elicited fluorescence to make operative decisions, while the recording camera receives even less at 20% for postoperative image analysis. In contrast, exoscopes send 100% of the returning light to the sensor.
In the last step of light transmission, the emitted fluorescence can be detected by the naked eye or a digital sensor. Imaging with a digital sensor, as is done in exoscopes, can be useful for post-acquisition image-processing or objective quantification of fluorescence intensity, which cannot be done by the naked eye.
Given the benefits of exoscopes over microscopes, the potential values of exoscopes in fluorescence-guided neurosurgery must be evaluated. Indeed, a recent study of a 3D exoscope in FGS with 5-aminolevulinic-acid demonstrated clearer fluorescence images with the exoscope than with a standard microscope [21]. However, these new exoscopes have not been evaluated for their utility in NIR FGS with dyes such as indocyanine green (ICG). Thus, in this study, we assessed and compared the intraoperative utility and NIR sensitivity of two exoscopes during NIR FGS using Second-Window ICG (SWIG).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by Institutional Review Board of University of Pennsylvania (IRB protocol No. 818012; ClinicalTrials.gov identifier : NCT02280954).
Fluorophore
ICG (excitation, 650–900 nm; emission, 750–950 nm) is the only Food and Drug Administration-approved NIR fluorophore. We tested visualization of ICG in laboratory conditions as well as in the operating room in patients using our established protocol of intravenous administration of high dose ICG (<5 mg/kg) 24 hours prior to the induction of anesthesia and subsequent intraoperative visualization [35].
In-vitro NIR imaging
Twelve serial dilutions of ICG (Akorn Pharmaceuticals, Decatur, IL, USA) were prepared in 96-well plates (1.0-2000 µg/L in two-fold dilutions; sterile water as control) to measure the sensitivity and dynamic range of the two systems. The plates were imaged from approximately 25 cm away. All extraneous light sources were eliminated. The two systems were placed side-by-side to ensure equivalent room testing conditions.
NIR imaging – Orbeye (system 1)
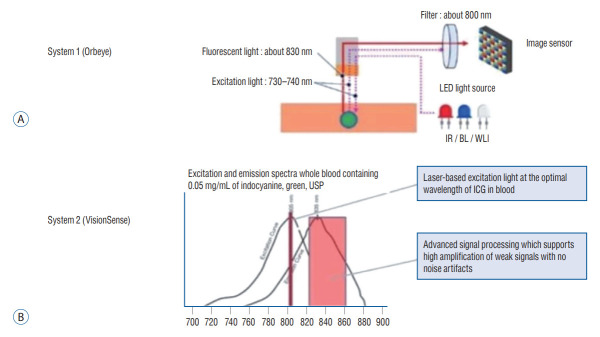
During the cases, the Orbeye 3D exoscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) was used instead of the traditional surgical microscope. It uses complementary right and left cameras for dual optics 3D imaging, which are projected to a 4096×2160 pixels screen for high-resolution stereopsis. The magnification ranges from 1.1-25.8×, the focal length is 220-550 mm, and the field of view ranges from 7.5-171 mm. System 1 provides white-light illumination through its broad-spectrum LED. In the NIR visualization mode, the additional infrared LED (730-740 nm) turns on, and a long-pass filter blocks photons <800 nm from reaching the image sensor (Fig. 1A). The NIR fluorescence is projected in 3D and black-and-white.
Fig. 1.
Excitation and emission profile for system 1 and system 2. A : System 1 is a high-resolution exoscope offering 3-dimensional (3D), 4 K visualization to those wearing circular polarization glasses. It uses light-emitting diodes (LEDs) for illumination. In its near-infrared (NIR) mode, the IR LED turns on, which emits photons of 730–740 nm to excite NIR fluorophores. All returning photons are then collected and filtered by a long-pass filter that blocks photons below 800 nm. A portion of photons <800 nm are let through in order to increase the overall field brightness and allow surgeons to operate in the NIR mode. These photons are then captured by a digital sensor. B : System 2 does not offer stereopsis in its NIR mode but provides enhanced NIR sensitivity. It uses a laser that is tuned to 805 nm to match the peak excitation wavelength of ICG, as seen above. The resulting fluorescence is then filtered through a band-pass filter that allows only photons 820–860 nm to pass. Then, there is an advanced signal processing algorithm which amplifies weaker NIR signal without significant increases in background noise, which enhances NIR signal to background contrast when fluorescence is relatively weaker. Adopted from Cho et al. [8] with permission from the publisher.
NIR imaging – VisionSense (system 2)
The VisionSense Iridium exoscope (Medtronic, Minneapolis, MN, USA) was also used for NIR fluorescence imaging. It has a resolution of 960×720 pixels, magnification of 1-2×, and field of view of 10-45 cm. It uses an 805 nm laser for excitation, an 820-860 nm bandpass emission filter, and a sensor with an advanced signal processing algorithm to amplify and detect NIR signal (Fig. 1B). Furthermore, system 2’s unique insect-eye technology utilizing dual light-paths allows not only stereopsis in white-light, but also simultaneous imaging of white-light and NIR fluorescence to provide a real-time overlay of the two spectra in a pseudo-colored map for preservation of the anatomy visualization.
Patient enrollment
Patients presenting for resection of intracranial tumors were administered ICG according to our SWIG protocol. Exclusion criteria were allergy to iodinated contrast agents and/or shellfish. Patients consented to ICG administration and intraoperative imaging.
Image analysis
Post-hoc calculation of the NIR signal-to-background ratio (SBR), a measure of relative NIR fluorescence intensity, was performed by importing the NIR images into ImageJ (NIH, Bethesda, MD, USA) and measuring the pixel intensity within each area of interest.
RESULTS
In-vitro data
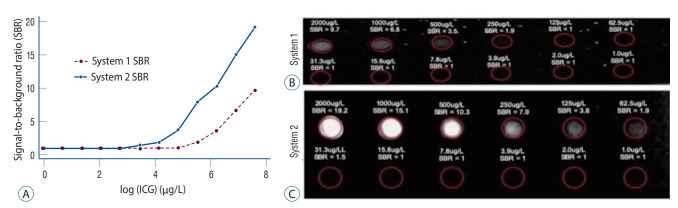
The two systems were compared using ICG serial dilutions (Fig. 2A). System 1 detected ICG >250 µg/L, with an SBR of 1.9. At 2 mg/L, the SBR was 9.7 (Fig. 2B). System 2 detected ICG >31.3 µg/L, with an SBR of 1.5. At 2 mg/L, the SBR was 19.2 (Fig. 2C and Table 1).
Fig. 2.
In-vitro analysis of near-infrared (NIR) sensitivity of the two exoscope systems. A : The two exoscope systems were compared directly by imaging serial dilutions of indocyanine green (ICG) from 1.0-2000 μg/L; the results are plotted on a log-scale for the X-axis. System 1 began discriminating the ICG from the control at 250 μg/L, while system 2 was able to detect down to 31.3 μg/L. B : Serial dilution images using system 1. System 1 achieved a signal-to-background ratio (SBR) of 9.7 at the highest concentration of 2000 μg/L. Although image analysis demonstrated the SBR to be 1.9 at 250 μg/L, NIR fluorescence was not visually distinguishable on the screen until the ICG concentration was 500 μg/L. C : Serial dilution images using system 2. System 2 achieved an SBR of 19.2 at the highest concentration of 2000 μg/L. Although image analysis demonstrated the SBR to be 1.5 at 31.3 μg/L, NIR fluorescence was not visually distinguishable on the screen until the ICG concentration was 62.5 μg/L.
Table 1.
Comparing the specifications of system 1 and system 2
| System 1 | System 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Country of origin | Japan | Israel |
| Stereopsis | Available (white-light and NIR) | Available (white-light) |
| Resolution | 4096×2160 pixels | 960×720 pixels |
| Magnification | 1.1–25.8× | 1.0–2.0× |
| Field of view | 7.5–171 mm | 100–450 mm |
| NIR excitation source | 730–740 nm LED | 805 nm laser |
| Emission filter | Long-pass filter allowing >800 nm | Band-pass filter allowing 820–860 nm |
| Advanced NIR signal processing | No | Yes |
| NIR overlay on white-light | Not Available | Available |
| In-vitro NIR sensitivity | Minimum 250 µg/L of ICG | Minimum 31.1 µg/L of ICG |
NIR : near-infrared, LED : light-emitting diodes, ICG : indocyanine green
Case 1 : system 1 in meningioma
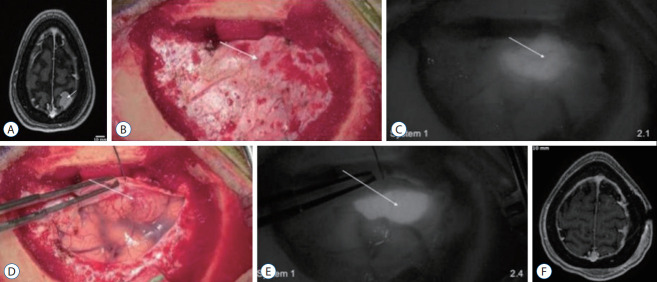
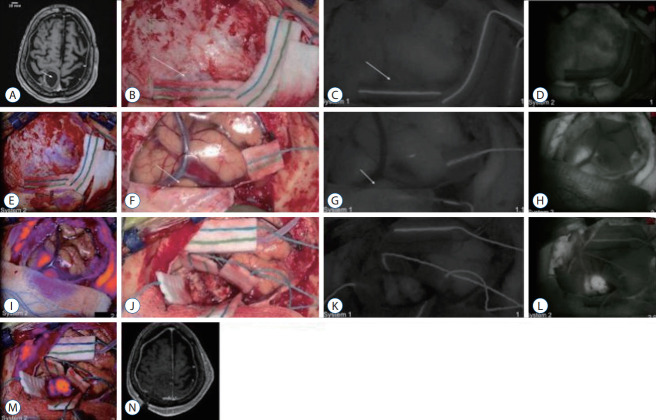
A 38-year-old female presented to the office with new headaches (Supplementary Video 1). An magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) demonstrated a left parietal parasagittal meningioma measuring 11×10×10 mm. Neurologic exam was normal and the patient received imaging follow-up. Over 4 years, the meningioma grew to 17×16×15 mm (Fig. 3A) and the patient elected to undergo surgical resection with SWIG. After craniotomy, the intact dura was visualized using system 1’s NIR mode. While the tumor was not visible under white-light, NIR fluorescence was clearly visible through the dura with an SBR of 2.1 (Fig. 3B and C). The dura was then opened under white-light and the tumor was revealed with an SBR of 2.4 (Fig. 3D and E). The surgery proceeded under white-light visualization with intermittent NIR imaging. After resection, no NIR fluorescence was detected in the surgical area and closure was performed using system 1. Postoperative MRI demonstrated gross-total-resection of the meningioma (Fig. 3F). The patient was discharged without neurologic deficits.
Fig. 3.
Demonstration of near-infrared (NIR) fluorescence visualization of a meningioma using system 1 (see Supplementary Video 1). A : Preoperative axial T1 magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with gadolinium showed a left parietal parasagittal meningioma measuring 17×16×15 mm. The tumor (arrow) enhanced strongly and homogenously with gadolinium. Over the intact dura, white-light imaging (B) did not visualize this superficial tumor (arrow). However, under NIR fluorescence visualization (C), the tumor (arrow) outline was clearly delineated. The tumor demonstrated signal to background ratio of 2.1. With the dura open and the tumor in direct line of sight, the white-light imaging (D) successfully visualized the highly vascular tumor (arrow). Under NIR fluorescence (E), the tumor (arrow) fluoresced even more brightly, with a signal-to-background ratio of 2.4. F : Postoperative axial T1 MRI with gadolinium showed gross total resection of the parietal meningioma without residual neoplasm.
Case 2 : system 1 and 2 in meningioma
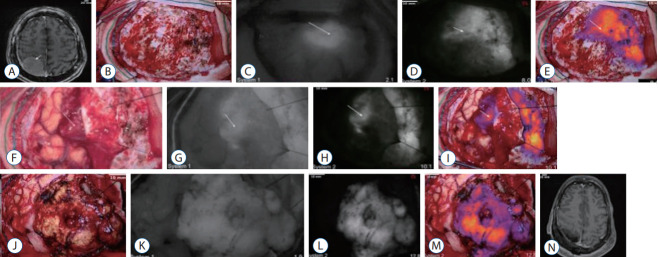
A 62-year-old female presented to the office with prosopagnosia and inability to recognize her left hand, although strength was normal bilaterally. An MRI revealed a large right parietal convexity meningioma measuring 46×30×22 mm (Fig. 4A) and the patient agreed to surgical resection. After craniotomy, the intact dura was visualized using both system 1 and 2. Under white-light alone, the tumor was not visible. However, with NIR imaging, the tumor was clearly visible through the dura for both system 1 (SBR, 1.6) and system 2 (SBR, 8.0) (Fig. 4B-E). Upon dura opening, the tumor fluoresced with an SBR 1.7 (system 1) and 10.1 (system 2) (Fig. 4F-I). After resection, the tumor specimen was imaged again, with system 1 (SBR, 1.9) and system 2 (SBR, 12.8) (Fig. 4J-M). Finally, NIR imaging of the resection cavity showed no residual fluorescence. Postoperative MRI demonstrated gross-total-resection of the meningioma (Fig. 4N). The patient was discharged to rehabilitation.
Fig. 4.
Demonstration of near-infrared (NIR) fluorescence visualization of a meningioma using system 1 and system 2. A : Preoperative axial T1 magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with gadolinium showed a right parietal convexity meningioma measuring 46×30×22 mm. The tumor (arrow) enhanced strongly and homogenously with gadolinium. B-E : Over the intact dura, white-light imaging (B) did not visualize this superficial tumor. NIR imaging with system 1 (C) delineated the tumor (arrow) boundaries, with a signal-to-background ratio (SBR) of 1.6. NIR imaging with system 2 in black and white (D) and pseudocolor overlay (E) delineated the tumor more clearly with an SBR of 8.0. F-I : With the dura open and the tumor in direct line of sight, the white-light imaging (F) successfully visualized the tumor (arrow). NIR imaging with system 1 (G) demonstrated high indocyanine green (ICG) accumulation in the tumor, with an NIR SBR of 1.7. System 2 imaging (H and I) demonstrated higher contrast, with an SBR of 10.1. J-M : After devascularization and resection under white-light visualization (J), the tumor specimen was examined under both exoscopes. System 1 (K) again confirmed high ICG accumulation in the tumor, with an SBR of 1.9. System 2 (L and M) also demonstrated very high contrast between the tumor tissue and normal brain, with an SBR of 12.8. N : Postoperative axial T1 MRI with gadolinium showed gross total resection of the convexity meningioma without residual neoplasm.
Case 3 : system 1 and 2 in parietal metastasis
Finally, the two imaging systems were used in a patient with a cystic parietal breast cancer metastasis (Fig. 5A). Neither system accurately localized the tumor through the dura (Fig. 5B-E). With system 1, there was no discernible signal; in contrast, system 2 delineated the tumor, but also showed significant background signal, obscuring the tumor boundaries. Upon exposure of the cortex (Fig. 5F-I) and then the tumor itself (Fig. 5J-M), system 2 detected fluorescence (SBR, 2.5 and 2.9, respectively), while system 1 demonstrated no significant fluorescence. The surgery was completed under system 1’s whitelight visualization with no further NIR imaging. Postoperative MRI demonstrated gross total resection of the metastasis (Fig. 5N) and the patient was discharged to rehabilitation.
Fig. 5.
Demonstration of near-infrared (NIR) fluorescence visualization in a weakly-enhancing metastasis using system 1 and system 2. A : Preoperative axial T1 magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with gadolinium showed a cystic, right parietal metastasis. The cystic portion did not enhance with gadolinium and the enhancing portion of the tumor (arrow) did not enhance as intensely as the previous meningiomas. B-E : Over the intact dura, neither white-light imaging (B), system 1 NIR imaging (C), nor system 2 NIR imaging (D and E) could reliably delineate the tumor borders. F-I : With the dura open and over the intact cortex, white-light imaging (F) could not visualize the tumor (arrow). NIR imaging with system 1 (G) also did not detect any NIR fluorescence above that of the surrounding parenchyma (signal-to-background ratio [SBR], 1.15). With system 2 (H and I), NIR fluorescence with an SBR of 2.5 was detected through the cortex in an area consistent with the tumor location. J-M : After exposing the tumor under white-light visualization (J), system 1 NIR visualization showed faint NIR fluorescence in the tumor (K); however, there was not enough signal to distinguish the tumor from the surrounding parenchyma (SBR, 1). With system 2 (L and M), more NIR signal was detected from the tumor, resulting in an SBR of 2.9. N : Postoperative axial T1 MRI with gadolinium showed gross total resection of the parietal metastasis without residual neoplasm.
DISCUSSION
Working with delicate structures requires clear visualization and high magnification; since the mid-20th century, optical neurosurgical microscopes have greatly bolstered the ability of neurosurgeons to perform delicate surgeries within the calvarium. However, with advances in digital imaging and that are improving magnification, image quality, and stereopsis, exoscopes are well-poised to replace microscopes. Specifically, the increasing use of FGS mandates that imaging systems stay updated with fluorescence imaging capabilities, especially in the NIR spectrum [16,18,23,28,32].
In this study, we compared two exoscope systems during FGS with the NIR fluorophore ICG both in-vitro and in-vivo. The in-vitro study consisted of imaging ICG serial dilutions in an isolated, dark environment to quantitatively evaluate both systems’ NIR sensitivity. Overall, system 2 demonstrated higher NIR sensitivity, detecting fluorescence from 31.3 µg/L of ICG versus system 1 requiring >250 µg/L. At each of the concentrations measured, system 2’s SBR was approximately two-fold higher.
We investigated whether this in-vitro finding would carry over to the intraoperative setting. For the in-vivo study, the Second-Window-ICG technique was used; SWIG relies on the enhanced permeability and retention of nanoparticle-size dyes to leak into the tumor and then to remain over time [12,20,35]. This is similar to how gadolinium accumulates in contrast-enhancing tissue [6]. In all three cases demonstrated here, ICG accumulated properly within the neoplastic tissue and delineated the tumor through the intact dura/cortex. Both meningiomas demonstrated strong NIR fluorescence with system 1 and one further demonstrated strong NIR fluorescence with system 2. In contrast, the metastasis demonstrated significantly weaker NIR fluorescence that was only distinguishable with system 2.
While neither system offers measures of absolute fluorescence, we hypothesize that the difference in the fluorescence intensities between the meningiomas and the metastasis is related to the difference in the degree of gadolinium-enhancement on preoperative MRI, since ICG accumulates in gadolinium-enhancing tissue. The two meningiomas enhanced avidly and homogenously on the preoperative MRI. The parietal metastasis, however, was mostly cystic and enhanced less avidly.
The importance of high NIR sensitivity is demonstrated by comparing cases #2 and #3. When the tumor demonstrated strong fluorescence (case #2), system 1 was able to reliably visualize the fluorescence, allowing for high-resolution NIR FGS. In contrast, when the tumor accumulated ICG less avidly (case #3), system 1 was not able to discriminate tumor fluorescence, and the highly-sensitive system 2 was necessary.
Having high NIR sensitivity has implications beyond simply better visualization of the gross tumor; it offers opportunities for more accurate assessment of the surgical margins and earlier detection of non-superficial tumors. While NIR imaging of the margins were not specifically assessed here, we have shown previously that NIR fluorescence can localize residual tumors as small as 0.3 mL at the margins [5]. To detect such minute areas of fluorescence, highly sensitive imaging devices are necessary, since the magnitude of fluorescence from small tumor volumes are significantly lower than from the gross tumors. Furthermore, we have previously demonstrated that one of the main benefits of NIR fluorescence imaging over visible-light fluorophores, such as 5-aminolevulinic acid, is the ability of the NIR photons penetrate deeper tissue (>10 mm for NIR vs. <1 mm for visible light) [7]. However, as fluorescence intensity decays as a function of the tissue-depth-squared, deep lesions require sensitive imaging modalities to be visualized. Thus, to take full advantage of the benefits of NIR FGS, having a sensitive NIR imaging device is crucial.
Many factors play a role in NIR sensitivity. The quality of the excitation source and emission filter, type of imaging sensor, and processing algorithm all play a role [10]. In the case of system 2, its laser is specifically tuned to maximally excite ICG, its filter effectively reduces background signal, and it is equipped with an algorithm that boosts its sensitivity to weaker fluorescence. These components likely contribute to its higher sensitivity compared to system 1, which uses a more broad-spectrum LED, has a filter that allows more of the excitation light through (intentionally to enhance overall visualization) and lacks an advanced algorithm. However, certain simple modifications to existing systems may moderately improve NIR sensitivity. Our group previously compared a state-of-the-art operating microscope to system 2 and documented the significantly lower sensitivity and dynamic range of the microscope [8]. In a subsequent publication, we demonstrated that we could measurably increase the sensitivity of the operating microscope simply by adding a laser excitation source [19]. Efficient excitation leads to optimal fluorescence imaging and is a relatively easy modification that neurosurgeons can make to existing microscopes or exoscopes. While system 2 has higher NIR sensitivity, its significantly lower resolution and lack of stereopsis in NIR-mode prevents surgeons from operating with it alone. Thus, bolstering the superb resolution and stereopsis of modern exoscopes with increased NIR fluorescence sensitivity will likely lead to an enhanced FGS experience.
This study has some limitations. First, since neither system offers NIR fluorescence quantification, we could not compare their sensitivity directly. We attempted to circumvent this with ICG serial dilutions, but this does not fully recapitulate the operative environment. Second, we did not perform a detailed analysis of the surgical margins with biopsies or correlate to postoperative MRI. We have performed such in-depth analyses with system 2 in prior publications. Our objective for this study was to document the feasibility of using system 1 for NIR FGS and to compare it to system 2 for improvements. Future studies to inspect the margins and biopsy specimens with system 1 will be done to better document these findings. Finally, we did not investigate both systems in-vitro at high enough ICG concentrations to reach the maximum imaging threshold. Unfortunately, limited laboratory access during the COVID-19 pandemic of 2020 has limited lab access.
CONCLUSION
In this study, we assessed the utility of a state-of-the-art, 4 K-resolution, 3D exoscope (system 1) in NIR fluorescence-guided neurosurgery using indocyanine-green. We then compared it to an existing, dedicated NIR imaging platform (system 2). In-vitro, we observed higher NIR sensitivity using system 2. This observation carried over to the intraoperative setting, in which system 2 demonstrated higher NIR fluorescence contrast and detected fluorescence from a tumor that was not detected with system 1. We hypothesize that this difference in sensitivity is due to differences in the excitation light source, emission filter efficiency, and imaging algorithm. Overall, for optimal NIR fluorescence-guided neurosurgery, we must combine high NIR sensitivity with high-resolution and stereopsis. With such technological advances, the potential of NIR FGS to improve patient outcomes may be fully realized.
Acknowledgments
Supported in part by the Institute for Translational Medicine and Therapeutics of the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania (JYKL). Research reported in this publication was also supported by the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the National Institutes of Health under Award Number UL1TR000003 (JYKL). The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the NIH.
Footnotes
Conflicts of interest
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Informed consent
This type of study does not require informed consent.
Author contributions
Conceptualization : SSC, JYKL; Data curation : SSC, CWT, EDR, YBS, JYKL; Formal analysis : SSC, JYKL; Funding acquisition : JYKL; Methodology : SSC, JYKL; Project administration : JYKL; Visualization : SSC, CWT, EDR, YBS, JYKL; Writing - original draft : SSC, CWT, EDR; Writing - review & editing : YBS, JYKL
Data sharing
None
Preprint
None
Supplementary materials
The online-only data supplement is available with this article at https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2021.0202.
This video demonstrates two cases of meningiomas resected using near-infrared fluorescence-guided surgery.
References
- 1.Acerbi F, Broggi M, Eoli M, Anghileri E, Cavallo C, Boffano C, et al. Is fluorescein-guided technique able to help in resection of high-grade gliomas? Neurosurg Focus. 2014;36:E5. doi: 10.3171/2013.11.FOCUS13487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Belykh E, Miller EJ, Patel AA, Yazdanabadi MI, Martirosyan NL, Yağmurlu K, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of a confocal laser endomicroscope for in vivo differentiation between normal injured and tumor tissue during fluorescein-guided glioma resection: laboratory investigation. World Neurosurg. 2018;115:e337–e348. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2018.04.048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Chakravarthy V, Sheikh S, Schmidt E, Steinmetz M. Imaging technologies in spine surgery. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2020;31:93–101. doi: 10.1016/j.nec.2019.08.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Cho SS, Jeon J, Buch L, Nag S, Nasrallah M, Low PS, et al. Intraoperative near-infrared imaging with receptor-specific versus passive delivery of fluorescent agents in pituitary adenomas. J Neurosurg. 2018;131:1974–1984. doi: 10.3171/2018.7.JNS181642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cho SS, Salinas R, De Ravin E, Teng CW, Li C, Abdullah KG, et al. Near-infrared imaging with second-window indocyanine green in newly diagnosed high-grade gliomas predicts gadolinium enhancement on postoperative magnetic resonance imaging. Mol Imaging Biol. 2020;22:1427–1437. doi: 10.1007/s11307-019-01455-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cho SS, Salinas R, Lee JYK. Indocyanine-green for fluorescence-guided surgery of brain tumors: evidence, techniques, and practical experience. Front Surg. 2019;6:11. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2019.00011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Cho SS, Teng CW, Ramayya A, Buch L, Hussain J, Harsch J, et al. Surface-registration frameless stereotactic navigation is less accurate during prone surgeries: intraoperative near-infrared visualization using second window indocyanine green offers an adjunct. Mol Imaging Biol. 2020;22:1572–1580. doi: 10.1007/s11307-020-01495-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Cho SS, Zeh R, Pierce JT, Salinas R, Singhal S, Lee JYK. Comparison of near-infrared imaging camera systems for intracranial tumor detection. Mol Imaging Biol. 2018;20:213–220. doi: 10.1007/s11307-017-1107-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Connally R, Jin D, Piper J. High intensity solid-state UV source for time-gated luminescence microscopy. Cytometry A. 2006;69:1020–1027. doi: 10.1002/cyto.a.20326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.DSouza AV, Lin H, Henderson ER, Samkoe KS, Pogue BW. Review of fluorescence guided surgery systems: identification of key performance capabilities beyond indocyanine green imaging. J Biomed Opt. 2016;21:80901. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.21.8.080901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Eljamel MS, Mahboob SO. The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of intraoperative imaging in high-grade glioma resection; a comparative review of intraoperative ALA, fluorescein, ultrasound and MRI. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2016;16:35–43. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2016.07.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Fang J, Nakamura H, Maeda H. The EPR effect: unique features of tumor blood vessels for drug delivery, factors involved, and limitations and augmentation of the effect. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2011;63:136–151. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2010.04.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hadjipanayis CG, Stummer W. 5-ALA and FDA approval for glioma surgery. J Neurooncol. 2019;141:479–486. doi: 10.1007/s11060-019-03098-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Herlan S, Marquardt JS, Hirt B, Tatagiba M, Ebner FH. 3D exoscope system in neurosurgery-comparison of a standard operating microscope with a new 3D exoscope in the cadaver lab. Oper Neurosurg (Hagerstown) 2019;17:518–524. doi: 10.1093/ons/opz081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kaibori M, Matsui K, Ishizaki M, Iida H, Okumura T, Sakaguchi T, et al. Intraoperative detection of superficial liver tumors by fluorescence imaging using indocyanine green and 5-aminolevulinic acid. Anticancer Res. 2016;36:1841–1849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Keating J, Newton A, Venegas O, Nims S, Zeh R, Predina J, et al. Near-infrared intraoperative molecular imaging can locate metastases to the lung. Ann Thorac Surg. 2017;103:390–398. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2016.08.079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kwan K, Schneider JR, Du V, Falting L, Boockvar JA, Oren J, et al. Lessons learned using a high-definition 3-dimensional exoscope for spinal surgery. Oper Neurosurg (Hagerstown) 2019;16:619–625. doi: 10.1093/ons/opy196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lee JYK, Cho SS, Stummer W, Tanyi JL, Vahrmeijer AL, Rosenthal E, et al. Review of clinical trials in intraoperative molecular imaging during cancer surgery. J Biomed Opt. 2019;24:1–8. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.24.12.120901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Li C, Buch L, Cho S, Lee JYK. Near-infrared intraoperative molecular imaging with conventional neurosurgical microscope can be improved with narrow band “boost” excitation. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2019;161:2311–2318. doi: 10.1007/s00701-019-04054-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Maeda H. The enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect in tumor vasculature: the key role of tumor-selective macromolecular drug targeting. Adv Enzyme Regul. 2001;41:189–207. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2571(00)00013-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Murai Y, Sato S, Yui K, Morimoto D, Ozeki T, Yamaguchi M, et al. Preliminary clinical microneurosurgical experience with the 4K3-dimensional microvideoscope (ORBEYE) system for microneurological surgery: observation study. Oper Neurosurg (Hagerstown) 2019;16:707–716. doi: 10.1093/ons/opy277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Nishiyama K. From exoscope into the next generation. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2017;60:289–293. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2017.0202.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Pagoto A, Garello F, Marini GM, Tripepi M, Arena F, Bardini P, et al. Novel gastrin-releasing peptide receptor targeted near-infrared fluorescence dye for image-guided surgery of prostate cancer. Mol Imaging Biol. 2020;22:85–93. doi: 10.1007/s11307-019-01354-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ricciardi L, Chaichana KL, Cardia A, Stifano V, Rossini Z, Olivi A, et al. The exoscope in neurosurgery: an innovative “point of view”. A systematic review of the technical, surgical and educational aspects. World Neurosurg. 2019;124:136–144. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2018.12.202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ricciardi L, Mattogno PP, Olivi A, Sturiale CL. Exoscope era: next technical and educational step in microneurosurgery. World Neurosurg. 2019;128:371–373. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2019.05.162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Rossini Z, Cardia A, Milani D, Lasio GB, Fornari M, D’Angelo V. VITOM 3D: preliminary experience in cranial surgery. World Neurosurg. 2017;107:663–668. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2017.08.083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Sack J, Steinberg JA, Rennert RC, Hatefi D, Pannell JS, Levy M, et al. Initial experience using a high-definition 3-dimensional exoscope system for microneurosurgery. Oper Neurosurg (Hagerstown) 2018;14:395–401. doi: 10.1093/ons/opx145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Samkoe KS, Sardar HS, Bates BD, Tselepidakis NN, Gunn JR, Hoffer-Hawlik KA, et al. Preclinical imaging of epidermal growth factor receptor with ABY-029 in soft-tissue sarcoma for fluorescence-guided surgery and tumor detection. J Surg Oncol. 2019;199:1077–1086. doi: 10.1002/jso.25468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Stummer W, Pichlmeier U, Meinel T, Wiestler OD, Zanella F, Reulen HJ, et al. Fluorescence-guided surgery with 5-aminolevulinic acid for resection of malignant glioma: a randomised controlled multicentre phase III trial. Lancet Oncol. 2006;7:392–401. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(06)70665-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Stummer W, Tonn JC, Goetz C, Ullrich W, Stepp H, Bink A, et al. 5-Aminolevulinic acid-derived tumor fluorescence: the diagnostic accuracy of visible fluorescence qualities as corroborated by spectrometry and histology and postoperative imaging. Neurosurgery. 2014;74:310–320. doi: 10.1227/NEU.0000000000000267. discussion 319-320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Yasargil MG. Microneurosurgery, Vol 1: Microsurgical Anatomy of the Basal Cisterns and Vessels of the Brain, Diagnostic Studies, General Operative Techniques and Pathological Considerations of the Intracranial Aneurysms. New York: Georg Thieme Verlag Stuttgart; 1984. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Yazaki P, Lwin T, Minnix M, Li L, Sherman A, Molnar J, et al. Improved antibody-guided surgery with a near-infrared dye on a pegylated linker for CEA-positive tumors. J Biomed Opt. 2019;24:1–9. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.24.6.066012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Yu D, Green C, Kasten SJ, Sackllah ME, Armstrong TJ. Effect of alternative video displays on postures, perceived effort, and performance during microsurgery skill tasks. Appl Erg. 2016;53:281–289. doi: 10.1016/j.apergo.2015.10.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Yu D, Sackllah M, Woolley C, Kasten S, Armstrong T. Quantitative posture analysis of 2D, 3D, and optical microscope visualization methods for microsurgery tasks. Work 41 Suppl. 2012;1:1944–1947. doi: 10.3233/WOR-2012-0412-1944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Zeh R, Sheikh S, Xia L, Pierce J, Newton A, Predina J, et al. The second window ICG technique demonstrates a broad plateau period for near infrared fluorescence tumor contrast in glioblastoma. PLoS One. 2017;24:e0182034. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0182034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Zhang DY, Singhal S, Lee JYK. Optical principles of fluorescence-guided brain tumor surgery: a practical primer for the neurosurgeon. Neurosurgery. 2019;85:312–324. doi: 10.1093/neuros/nyy315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
This video demonstrates two cases of meningiomas resected using near-infrared fluorescence-guided surgery.