Abstract
Introduction
Chemotherapy has significantly improved cancer survival rates at the cost of irreversible and frequent cardiovascular toxicity. As the main dose-dependent adverse effect, cardiotoxic effects not only limit the usage of chemotherapeutic agents, but also cause the high risk of severe poor prognoses for cancer survivors. Therefore, it is of great significance to seek more effective cardioprotective strategies. Some nutrients have been reported to diminish cardiac oxidative damage associated with chemotherapy. However, the currently available evidence is unclear, which requires a rigorous summary. As such, we conducted a systematic review of all available evidence and demonstrated whether nutrients derived from food could prevent cardiotoxicity caused by chemotherapy.
Methods
We searched Medline (via PubMed), Embase and the Cochrane Library from inception to Nov 9, 2021 to identify studies reporting dietary nutrients against cancer chemotherapy-related cardiotoxicity. We performed descriptive summaries on the included studies, and used forest plots to demonstrate the effects of various dietary nutrients.
Results
Fifty-seven eligible studies were identified, involving 53 animal studies carried on rats or mice and four human studies in cancer patients. Seven types of dietary nutrients were recognized including polyphenols (mainly extracted from grapes, grape seeds, and tea), allicin (mainly extracted form garlic), lycopene (mainly extracted from tomatoes), polyunsaturated fatty acids, amino acids (mainly referring to glutamine), coenzyme Q10, and trace elements (mainly referring to zinc and selenium). Dietary nutrients ameliorated left ventricular dysfunctions and myocardial oxidative stress at varying degrees, which were caused by chemotherapy. The overall risk of bias of included studies was at moderate to high risk.
Conclusion
The results indicated that dietary nutrients might be a potential strategy to protect cardiovascular system exposed to the chemotherapeutic agents, but more human studies are urged in this field.
Systematic Review Registration: https://inplasy.com/inplasy-2022-3-0015/.
Keywords: chemotherapy, cardiotoxicity, heart diseases, oral nutrition, diet therapy, systematic review
Introduction
Advances in chemotherapy and comprehensive supportive care have contributed to the steadily declined cancer mortality rates over the past decades (1–3). As a result, the survivors have been an increasingly large population (e.g., more than 16.9 million in the USA in 2019) with longer life expectancy (4, 5). However, the great success of chemotherapy has been accompanied by severe cardiovascular toxicity, which is caused by the direct damage to the myocardium through production of oxygen free radicals (5–7). Cardiac toxicity could manifest as subclinical cardiomyopathies at the early stage, such as asymptomatic changes along with left ventricular dysfunction and abnormal cardiac markers. Around 12% (123/1022) pediatric patients with acute myeloid leukemia were reported to suffer cardiotoxicity during and after the chemotherapy regimens over a five-year follow-up (8). In addition, cardiotoxicity would progress to congestive heart failure (CHF) and even cardiac death (5, 9) and these complications have been the leading cause of long-term morbidity and mortality (10–13). The incidence of CHF reported in patients treated with doxorubicin (DOX) was 2.2% (88/4018) (14) and the two-year mortality rate associated with anthracyclines-induced cardiovascular diseases (CVD) was up to 60% (15). Therefore, appropriate early prevention and management for cancer survivors should be implemented to prevent and avoid chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxic progression (16, 17).
Early detection and treatment of chemotherapy-induced cardiac damage have been gradually studied. The common used monitoring methods are echocardiography and cardiac biomarkers. Several drugs were previously investigated as cardioprotective agents for preventing cardiotoxicity (6, 7, 18, 19), but only dexrazoxane was approved by Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to protect the chemotherapy-exposed heart (7, 20). However, dexrazoxane has not been routinely applied in the clinic at present along with debate about its long-term safety. This is largely due to the concerns over its impact on anticancer treatments (21, 22). In addition, the cost and accessibility have also been quite essential impediments for cancer survivors who have already borne considerable treatment overheads in the long-term survivals (5). So, it is of great significance to explore alternative effective, safe, economical, and consistent cardiac protection strategies for long-term cancer survivors.
Dietary nutrients (defined as various nutrients derived from food) are increasingly playing an important role in medicine. Due to the restriction of conventional medicine treatments for cancer, complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) has been playing a broader and more active role in cancer patients (23). Currently, several studies indicated that some fruit and vegetables have been considered as natural antioxidants that could reduce oxidative stress and inhibit chemotherapy-related cardiotoxicity (24–26). Furthermore, dietary factors such as polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) and coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) have also been reported to be able to protect the chemotherapy-exposed heart on animal models (27, 28). Although there are some narrative reviews (27, 29–32), it seems that the evidence on whether dietary nutrients could alleviate cardiotoxicity induced by chemotherapy has not been systematically summarized.
As such, we hypothesized that dietary nutrients could serve as a novel cardioprotective strategy to prevent cancer chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity and conducted a systematic review of the current evidence.
Methods
This systematic review was conducted based on the guidelines of Systematic Review Protocol for Animal Intervention Studies (33) and the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) (34), and was registered at https://inplasy.com as INPLASY202230015.
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) subjects: cancer patients or healthy/tumor-bearing animal models, treated with chemotherapeutic agents, with no restrictions on cancer types, animal species and chemotherapeutic agents; (2) intervention: oral intake of dietary nutrients; If the source of the nutrient was reported in the article, we only included cases which the nutrient source was food rather than non-food like drugs. If it was not reported, then we included articles that the nutrient can be obtained from food; (3) comparison: placebo or no intervention (without dietary nutrients mentioned above); (4) outcomes: imaging or biological measures of cardiotoxicity, including echocardiography, serum cardiac markers, oxidative stress markers, and histopathological examinations. Echocardiography is the most common and noninvasive method which measures left ventricular systolic functions like left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and left ventricular fractional shortening (LVFS). It is also the most widely used screening method for monitoring cardiotoxicity both during and years after anticancer treatment (16). Cardiac markers, such as cardiac troponin (cTn), N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), creatine kinase (CK), creatine kinase-MB (CK-MB) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), can indicate abnormal left ventricular structure and increased cardiac stress (17). Measurements of antioxidant defense can reflect the cardiac oxidative stress status in cancer patients, including malondialdehyde (MDA), superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione (GSH). The details of detection indicators are represented in Supplementary Table 1. Conference abstracts, case reports, reviews, trial protocols, duplicate publications, in vitro experiments, and non-controlled studies were excluded.
Search Strategy and Study Selection
A comprehensive search was performed through three separate electronic databases, including Medline (via PubMed), Embase, and the Cochrane Library, from the inception to Nov 9, 2021. In addition, a manual search was also conducted by screening the reference lists from relevant reviews. The search strategies used are provided in Supplementary Table 2.
Two reviewers (X-YZ and K-LY) screened the titles and abstracts of records retrieved from the databases and independently screened the full text for eligible studies. Any disagreements between the two reviewers were resolved through discussion by achieving a consensus.
Data Extraction
Two reviewers (X-YZ and K-LY) independently used a data extraction sheet to extract data from the included studies. The following information was extracted: first author, year of publication, characteristics of subjects, study design, intervention characteristics, and outcome measures. The primary outcomes included LVEF and cTn, and the secondary outcomes were LVFS, CK, CK-MB, LDH, MDA, SOD, and GSH.
Risk of Bias Assessment
Two reviewers (X-YZ and YL) independently assessed the risk of bias for the included studies. For animal studies, we used the risk of bias tool of Systematic Review Center for Laboratory Animal Experimentation (SYRCLE). This tool is designed based on the Cochrane Risk of Bias (RoB) tool for animal experiments. It consists of 10 items, including selection bias, performance bias, detection bias, attrition bias, reporting bias, and other biases (35). Each item is rated as “Y” (low risk of bias), “N” (high risk of bias), and “U” (unclear risk of bias). For randomized controlled trials (RCT), we used the Cochrane risk of bias tool (36). It covers 6 domains of bias, namely sequence generation, allocation concealment, blinding of participants and personnel, blinding of outcome assessment, incomplete outcome data, selective outcome reporting, and other biases. The items are also assessed as “Y” (low risk of bias), “N” (high risk of bias), and “U” (unclear risk of bias). For non-randomized clinical trials and observational studies, we used the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) which contains 8 items in three dimensions of selection, comparability, and outcome (37). It scores from 0 to 9 and higher scores show the lower risk of bias. Any disagreements were resolved by consulting a third reviewer (QW).
Data Analysis
The primary and secondary outcomes of the review were treated as continuous variables represented by mean ± standard deviation. Number of cases and percentages were used to indicate the number of included studies. Effectiveness of dietary nutrients against cardiotoxicity was presented by the comparison between chemotherapy with dietary nutrients groups and chemotherapy groups. Statistical analyses of all outcomes were performed in forest plots using RevMan Software (Version 5.3). When there were more than two arms in the included studies, we presented all the results separately. Due to high heterogeneity from the variations in the baseline of included studies, we used a random-effects model and didn't provide a pooled result as well.
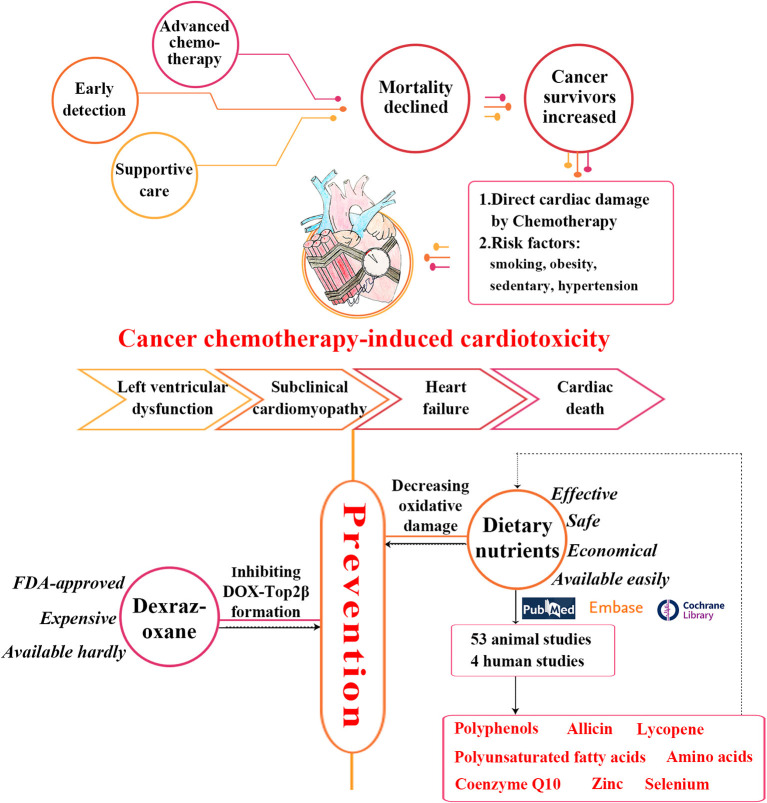
The work flowchart describing the process of the study is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
The work flowchart of the study process. Epidemiology, clinical symptoms and current cardioprotective strategies of cancer chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity are shown. Our search strategy and main results are also presented. DOX, doxorubicin; FDA, Food and Drug Administration; Top2β, topoisomerase 2β.
Results
Literature Search and Study Selection
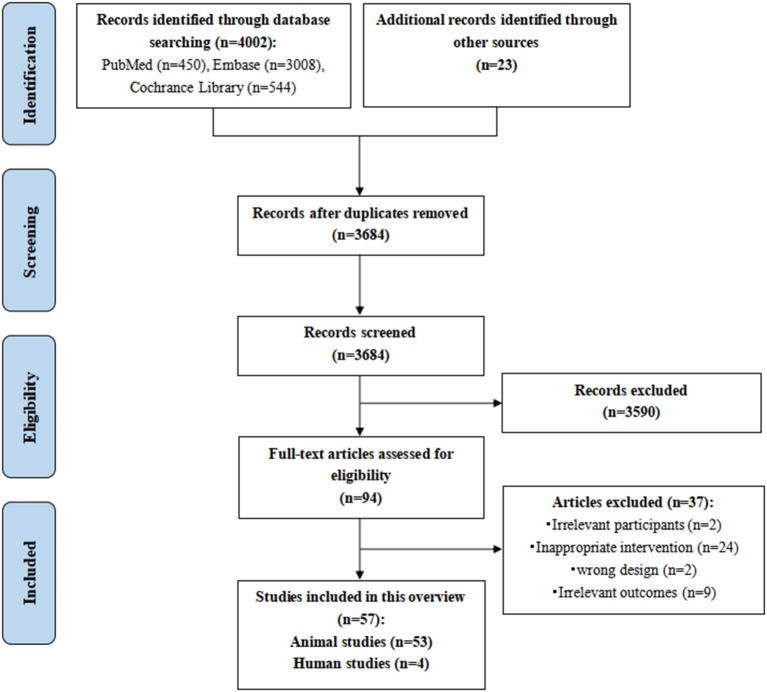
A total of 4025 potentially relevant records were initially identified. However, 341 of those were excluded due to duplication, 3,590 studies were excluded by reading titles and abstracts based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria, and 94 potential studies were eligible for full-text screening. We finally included 57 studies, including 53 animal studies and four human studies. The PRISMA flowchart of the literature search and study selection process is shown in Figure 2. The reasons for excluding reviews are listed in Supplementary Table 3.
Figure 2.
The PRISMA flowchart of the literature search and study selection.
Animal Studies
Study Characteristics
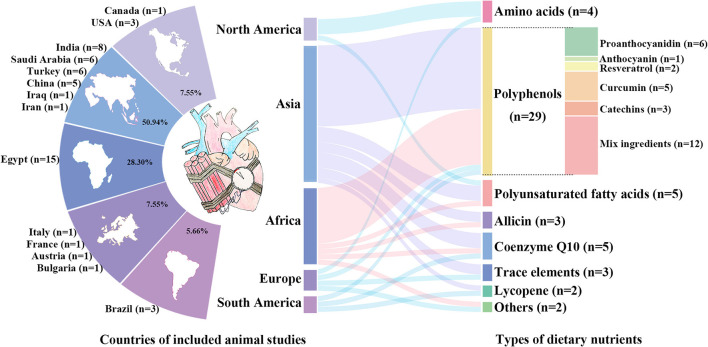
The 53 animal studies included were conducted in 14 countries, with most in Egypt (n = 15), India (n = 8), Saudi Arabia (n = 6), Turkey (n = 6), and China (n = 5). The publication years ranged from 1996 to 2021, with 42 before 2010. DOX (n = 48) comprised a significant majority of the included studies, and the other chemotherapeutic agents were cisplatin (n = 3), mitoxantrone (n = 1), and fluorouracil (n = 1). The covered dietary nutrients contained polyphenols (n = 29) (38–66), allicin (n = 3) (67–69), lycopene (n = 2) (70, 71), PUFA (n = 5) (72–76), amino acids (n = 4) (77–80), CoQ10 (n = 5) (81–85), trace elements (n = 3) (86–88), and others (n = 2) (89, 90). 79.24% of the included studies were investigated in Asia and Africa and most studies commonly used allicin from garlic (67–69) and polyphenols from local fruit such as grape (38–43), date palm (55, 56), cranberry (58), cardamom (59), pomegranate (60) and hawthorn (61) as the nutritional interventions. However, American and European studies tended to use amino acid like glycine and glutamine which were rich in animal food or special supplements (77–80). The characteristics of the included animal studies are summarized in Table 1 and Figure 3.
Table 1.
The characteristics of the included animal studies.
| Dietary nutrients | Studies | Country | Randomization | Animals | Intervention | Comparison | Outcomes | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | Tumor-bearing | Chemotherapeutic agents | Food intake | Main ingredients | Duration | Sample size | Grouping | Control groups | Treated groups | |||||
| Polyphenols | Adiyaman et al. (38) | Turkey | Not reported | Rats, sprague dawley | Healthy | DOX | Grape seed extract | Proanthocyanidin | 35 days | 28 | 4 | (1) CON (2) grape seed extract (3) DOX |
(4) DOX+grape seed extract | b, c, d |
| Ammar et al. (39) | Egypt | Not reported | Rats, sprague dawley | Healthy | DOX | Proanthocyanidin | Proanthocyanidin | 10 days | 24 | 4 | (1) CON (2) proanthocyanidin (3) DOX |
(4) DOX+proanthocyanidin | b, c, e | |
| Boghdady (40) | Egypt | Yes | Rats, wistar albino | Healthy | DOX | Grape seed extract | Proanthocyanidin | 15 days | 32 | 4 | (1) CON (2) DOX |
(3) DOX+grape seed extract (4) DOX+ginkgo biloba extract |
b, c, d | |
| Yalcin et al. (41) | Turkey | Yes | Mice, albino | Healthy | DOX | Grape seed extract | Proanthocyanidin | 21 days | 36 | 6 | (1) CON (2) DOX (3) grape seed extract 50 (4) grape seed extract 150 |
(5) DOX+grape seed extract 50 (6) DOX+grape seed extract 150 |
c, d | |
| Yousef et al. (42) | Egypt | Not reported | Rats, sprague dawley | Healthy | Cisplatin | Grape seed extract | Proanthocyanidin | 15 days | 32 | 4 | (1) CON (2) grape seed extract (3) cisplatin |
(4) cisplatin+grape seed extract | b, c, f | |
| Zhang et al. (43) | China | Yes | Mice, balb/c | Sarcoma | DOX | Proanthocyanidin | Proanthocyanidin | 10 days | 56 | 4 | (1) CON (2) DOX (3) proanthocyanidin |
(4) DOX+proanthocyanidin | b, c | |
| Petroni et al. (44) | Italy | Not reported | Mice, c57bl/6j | Healthy | DOX | Cyanidin 3-glucoside | Anthocyanin | 74 days | 24 | 2 | (1) DOX+yellow diet | (2) DOX+red diet | f | |
| Shoukry et al. (45) | Egypt | Yes | Rats, wister | Healthy | DOX | Resveratrol | Resveratrol | 42 days | 32 | 4 | (1) CON (2) DOX |
(3) DOX+resveratrol(pre) (4) DOX+resveratrol(post) |
a, b, d, f | |
| Arafa et al. (46) | Egypt | Not reported | Rats, wistar albino | Healthy | DOX | Resveratrol | Resveratrol | 28 days | 40 | 4 | (1) CON (2) resveratrol (3) DOX |
(4) DOX+resveratrol | b, c, d, f | |
| Ibrahim Fouad and Ahmed. (47) | Egypt | Yes | Rats, wistar albino | Healthy | DOX | Curcumin | Curcumin | / | 24 | 4 | (1) CON (2) DOX (3) curcumin |
(4) DOX+curcumin | b, c | |
| Bahadir et al. (48) | Turkey | Yes | Rats, wistar albino | Healthy | Cisplatin | Curcumin | Curcumin | 14 days | 49 | 7 | (1) CON (2) placebo (3) cisplatin (4) beta-carotene (6) curcumin |
(5) cisplatin+beta-carotene (7) cisplatin+curcumin |
b, c, d | |
| Benzer et al. (49) | Turkey | Yes | Rats, wistar albino | Healthy | DOX | Curcumin | Curcumin | 7 days | 35 | 5 | (1) CON (2) curcumin 200 (3) DOX |
(4) DOX+curcumin 100 (5) DOX+curcumin 200 |
b, c, d | |
| Swamy et al. (50) | India | Yes | Rats, albino | Healthy | DOX | Curcumin | Curcumin | 14 days | 24 | 4 | (1) CON (2) DOX (3) curcumin |
(4) DOX+curcumin | b, c, d, f | |
| Venkatesan (51) | India | Not reported | Rats, wistar | Healthy | DOX | Curcumin | Curcumin | 7 days | 24 | 4 | (1) CON (2) curcumin (3) DOX |
(4) DOX+curcumin | b, c, e | |
| Ibrahim et al. (52) | Saudi Arabia | Yes | Mice, balb/c | Healthy | Cisplatin | Green tea extract, vitamin E | Catechins, vitamin E | 30 days | 48 | 6 | (1) CON (2) green tea extract (3) vitamin E (4) cisplatin |
(5) cisplatin+green tea extract (6) cisplatin+vitamin E |
b, c, f | |
| Saeed et al. (53) | Egypt | Yes | Rats, wistar | Healthy | DOX | Epigallocatechin-3-gallate | Catechins | 12 days | 40 | 5 | (1) CON (2) DOX |
(3) DOX+epigallocatechin-3-gallate 10 (4) DOX+epigallocatechin-3-gallate 20 (5) DOX+epigallocatechin-3-gallate 40 |
b, c, d, e | |
| Amanullah et al. (54) | India | Not reported | Rats, wistar albino | Healthy | DOX | Black tea extract, resveratrol | Catechins, polyphenols | 30 days | 30 | 6 | (1) CON (2) DOX (3) black tea extract+ resveratrol |
(4) DOX+black tea extract (5) DOX+resveratrol (6) DOX+black tea extract +resveratrol |
b, c, f | |
| Mubarak et al. (55) | Egypt | Not reported | Rats, albino | Healthy | DOX | Date palm fruit extract | Anthocyanins, quercetin, procyanidins | 30 days | 40 | 4 | (1) CON (2) date (3) DOX |
(4) DOX+date | b, c | |
| Sabbah et al. (56) | Saudi Arabia | Yes | Rats, wistar albino | Healthy | DOX | Ajwa date aqueous extract | Polyphenols, flavonoids, Mn | 28 days | 60 | 6 | (1) CON (2) date 0.75 (3) date 1.5 (4) DOX |
(5) DOX+date 0.75 (6) DOX+date 1.5 |
b, c, d | |
| Ribeiro et al. (57) | Brazil | Not reported | Rats, wistar | Healthy | DOX | Pera orange juice, Moro orange juice | Hesperidin, anthocyanins | 28 days | 120 | 6 | (1) CON (2) Pera juice (3) Moro juice (4) DOX |
(5) DOX+Pera juice (6) DOX+Moro juice |
a, c, f | |
| Elberry et al. (58) | Saudi Arabia | Yes | Rats, wister | Healthy | DOX | Cranberry extract | Flavonols, flavonoids | 10 days | 30 | 4 | (1) CON (2) cranberry extract (4) DOX |
(4) DOX+cranberry extract | b, c, e | |
| Abu Gazia and El-Magd (59) | Egypt | Yes | Rats, albino | Healthy | DOX | Cardamom extract | Flavonoids | 21 days | 30 | 3 | (1) CON (2) DOX |
(3) DOX+cardamom extract | b, c, d | |
| Hassanpour Fard et al. (60) | India | Not reported | Rats, wistar albino | Healthy | DOX | Whole fruit extract of pomegranate | Gallic acid, quercetin | 18 days | 24 | 3 | (1) CON (2) DOX |
(3) DOX+pomegranate extract | b, c, d, e, f | |
| Shatoor and Said Ahmed, (61) | Saudi Arabia | Yes | Rats, wistar albino | Healthy | DOX | Hawthorn extrat | Flavonoids, polyphenols | 28 days | 36 | 6 | (1) CON (2) hawthorn (3) DOX |
(4) DOX+hawthorn(st) (5) DOX+hawthorn(post) (6) hawthorn+DOX(pre) |
b, c, d, f | |
| Subburaman et al. (62) | India | Not reported | Rats, albino | Healthy | DOX | Naringenin | Flavonoids | 70 days | 18 | 3 | (1) CON (2) DOX |
(3) DOX+naringenin | b, c, d, f | |
| Abdel-Wahab et al. (63) | Egypt | Not reported | Rats, swiss albino | Healthy | DOX | P-coumaric acid | p-coumaric acid (pca) | 5 days | 24 | 4 | (1) CON (2) P-coumaric acid (3) DOX |
(4) DOX+p-coumaric acid | b, c | |
| Alhumaydhi (64) | Saudi Arabia | Yes | Mice, balb/c | Healthy | DOX | Honey | Polyphenols, fructose, glucose | 10 days | 40 | 4 | (1) CON (2) honey (3) DOX |
(4) DOX+honey | b | |
| Abu-Elsaad et al. (65) | Egypt | Not reported | Rats, sprague dawley | Healthy | DOX | Tested food: yogurt, green tea extract, carrot | Lactobacillus acidophilus, polyphenols, carrot | 154 days | 60 | 5 | (1) CON (2) DOX (3) DOX+carvedilol |
(4) DOX+tested food (5) DOX+tested food+carvedilol |
b, c, d, e | |
| Lin et al. (66) | China | Yes | Rats, sprague dawley | Healthy | DOX | Yellow wine polyphenolic compounds | Polyphenolic compounds | 28 days | 50 | 5 | (1) CON (2) yellow wine (3) DOX |
(4) DOX+yellow wine | a, c, d, e, f | |
| Allicin | Abdel-Daim et al. (67) | Egypt | Yes | Mice, swiss albino | Healthy | DOX | Allicin | Allicin | 14 days | 40 | 5 | (1) CON (2) allicin 20 (3) DOX |
(4) DOX+allicin 10 (5) DOX+allicin 20 |
b, c |
| Demirkaya et al. (68) | Turkey | Yes | Rats,wistar albino | Healthy | DOX | Aged garlic extract, grape seed extract, hazelnut | Allicin, proanthocyanidin | 42 days | 135 | 9 | (1) CON (2) DOX 15 (3) DOX 7.5 |
(4) DOX 15+aged garlic extract (5) DOX 7.5+aged garlic extract (6) DOX 15+grape seed extract (7) DOX 7.5+grape seed extract (8) DOX 15+ hazelnut (9) DOX 7.5+hazelnut |
b, c, d | |
| Mukherjee et al. (69) | India | Not reported | Rats, wistar albino | Healthy | DOX | Garlic homogenate | Allicin | 30 days | 40 | 5 | (1) CON (2) DOX (3) DOX+PRO |
(4) DOX+garlic 250 (5) DOX+garlic 500 |
c, f | |
| Lycopene | Ferreira et al. (70) | Brazil | Not reported | Rats, wistar | Healthy | DOX | Tomato-oleoresin supplement | Lycopene | 49 days | 34 | 4 | (1) CON (2) lycopene (3) DOX |
(4) DOX+lycopene | d |
| Yilmaz et al. (71) | Turkey | Not reported | Rats, sprague dawley | Healthy | DOX | Lycopene | Lycopene | 10 days | 24 | 4 | (1) CON (2) DOX |
(3) DOX+lycopene(pre) (4) DOX+lycopene(post) |
c, d | |
| PUFA | Ahmed et al. (72) | India | Yes | Rats, wistar | Healthy | DOX | Chia seed oil | PUFA | 7 days | 24 | 4 | (1) CON (2) DOX |
(3) DOX+chia seed oil 2.5 (4) DOX+chia seed oil 5 |
b, c, d, e |
| Asselin et al. (73) | Canada | Yes | Mice, c57bl/6 | Healthy | DOX+TRZ | Flaxseed, α-linolenic acid, secoisolariciresinol diglucoside | α-Linolenic acid, secoisolariciresinol diglucoside | 42 days | 84 | 5 | (1) CON (2) DOX+TRZ |
(3) DOX+TRZ+flaxseed (4) DOX+TRZ+α-linolenic acid (5) DOX+TRZ+secoisolariciresinol diglucoside |
a, d, e | |
| Saleh et al. (74) | Egypt | Not reported | Rats, wistar albino | Healthy | DOX | N-3 PUFA | n-3 PUFA | 28 days | 35-40 | 5 | (1) CON (2) DOX |
(3) DOX+n-3 PUFA 25 (4) DOX+n-3 PUFA 50 (5) DOX+n-3 PUFA100 |
b, c, d, e, f | |
| Saleem et al. (75) | India | Not reported | Rats, wistar albino | Healthy | DOX | Sesame oil | Linoleic acid, α-linolenic acid, sesamin | 30 days | 30 | 5 | (1) CON (2) DOX (5) DOX+probucol |
(3) DOX+sesame oil 1 (4) DOX+sesame oil 2 |
b, c, d | |
| Teng et al. (76) | China | Yes | Rats, sprague dawley | Healthy | DOX | N-3 PUFA | Timnodonic acid, docosahexaenoic acid | 112 days | 32 | 3 | (1) CON (2) DOX |
(3) DOX+n-3 PUFA | a, d | |
| Amino acids |
Maneikyte et al. (77) | Austria | Yes | Rats, wag/rij | Colorectal cancer liver metastasis | FOLFOX | Glycine | Glycine | 21 days | 44 | 6 | (1) casein+sham (2) glycine+sham (3) casein+CON (5) casein+FOLFOX |
(4) glycine+CON (6) glycine+FOLFOX |
a, b, d |
| Todorova et al. (78) | USA | Yes | Rats, fisher344 | Mammary carcinoma | DOX | Glutamine | Glutamine | / | 50 | 3 | (1) CON (2) DOX+water |
(3) DOX+glutamine | a, b | |
| Todorova et al. (79) | USA | Yes | Rats, fisher344 | Mammary carcinoma | DOX | Glutamine | Glutamine | 7 days | 20 | 2 | (1) DOX+CON | (2) DOX+glutamine | a, c | |
| Cao et al. (80) | USA | Yes | Rats, fisher 344 | Healthy | DOX | Glutamine | Glutamine | 28 days | 42 | 6 | (1) H2O+saline (2) H2O+DOX |
(3) glutamine+saline (4) glutamine+DOX |
c | |
| CoQ10 | Rahmanifard et al. (81) | Iran | Yes | Rats, sprague dawley | Healthy | DOX | CoQ10 | CoQ10 | 21 days | 42 | 6 | (1) CON (2) lisinopril (3) CoQ10 (4) DOX |
(5) DOX+lisinopril (6) DOX+CoQ10 |
c, d, e, f |
| Shabaan et al. (82) | Egypt | Yes | Rats, wistar | Healthy | DOX | CoQ10 | CoQ10 | 7 days | 28 | 4 | (1) CON (2) CoQ10 (3) DOX |
(4) DOX+CoQ10 | c, d | |
| Botelho et al. (83) | Brazil | Yes | Rats, wistar albino | Healthy | DOX | CoQ10 | CoQ10 | 14 days | 20 | 4 | (1) CON (2) CoQ10 (3) DOX |
(4) DOX+CoQ10 | b, c, d, e | |
| Chen et al. (84) | China | Yes | Rats, sprague dawley | Healthy | DOX | CoQ10 | CoQ10 | 21 days | 24 | 4 | (1) CON (2) DOX (4) CoQ10 |
(3) DOX+CoQ10 | d, f | |
| Mustafa et al. (85) | Saudi Arabia | Not reported | Rats, wistar albino | Healthy | DOX | CoQ10 | CoQ10 | 15 days | 72 | 6 | (1) CON (2) DOX (3) CoQ10 |
(4) DOX+CoQ10 | b, c, e, f | |
| Trace elements | Maryoosh et al. (86) | Iraq | Yes | Rats, wistar albino | Healthy | mitoxantrone | Zinc sulfate | Zinc | 20 days | 48 | 6 | (1) CON (2) Zinc 15 (3) Zinc 30 (4) mitoxantrone |
(5) mitoxantrone+Zinc 15 (6) mitoxantrone+Zinc 30 |
b, c |
| Wu et al. (87) | China | Yes | Rats, sprague dawley | Healthy | DOX | ZnCM | Zinc, curcumin | 28 days | 42 | 6 | (1) CON (2) DOX |
(3) DOX+curcumin 100 (4) DOX+ZnCM 25 (5) DOX+ZnCM 50 (6) DOX+ZnCM 100 |
a, b, e | |
| Coudray et al. (88) | France | Not reported | Rats, wistar | Healthy | DOX | Selenium | Selenium | 49 days | 60 | 5 | (1) CON (2) saline (3) DOX (4) selenium |
(5) DOX+selenium | c, f | |
| Others | Radeva-Ilieva et al. (89) | Bulgaria | Yes | Rats, wistar | Healthy | DOX | Methylxanthine from bancha | Methylxanthine | 17 days | 36 | 6 | (1) CON (2) DOX (3) methylxanthine 5 (4) methylxanthine 1 |
(5) DOX+methylxanthine 5 (6) DOX+methylxanthine 1 |
b |
| Wahab et al. (90) | Egypt | Yes | Mice, swiss albino | Ehrlich ascites carcinoma | DOX | Vitamin E | Vitamin E | 30 days | 140 | 4 | (1) DOX | (2) DOX+vitamin E | c | |
CON, control; CoQ10, coenzyme Q10; DOX, doxorubicin; FOLFOX, 5-fluorouracil+leucovorin+oxaliplatin; PUFA, polyunsaturated fatty acids; TRZ, trastuzumab; ZnCM, zinc+curcumin.
a, echocardiography; b, serum cardiac markers; c, oxidative stress markers; d, histopathological examinations; e, electrocardiogram; f, survival, body weight, heart weight.
Figure 3.
The characteristics of the included animal studies. Distribution of countries of included animal studies are shown in the left. The percentages represent the proportion of included studies in each continent, and the numbers are the number of studies in each country. Among them, African and Asian countries account for the largest share with most studies in Egypt (n = 15), India (n = 8), Saudi Arabia (n = 6), Turkey (n = 6), and China (n = 5). Types of dietary nutrients are listed in the right, containing polyphenols, allicin, lycopene, polyunsaturated fatty acids, amino acids, coenzyme Q10, and trace elements.
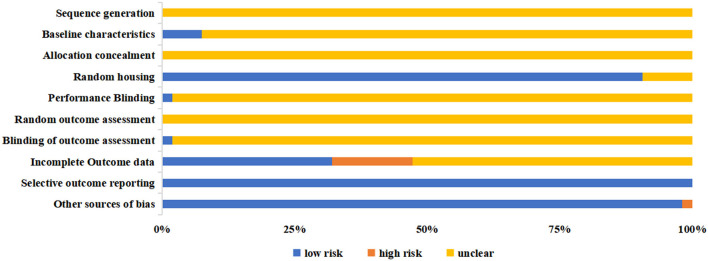
Risk of Bias Assessment
The overall risk of bias of included animal studies was at moderate to high risk and most of the items of SYRCLE depicted unclear risk (Figure 4 and Supplementary Table 4). All animal studies failed to report the sequence generation methods (item 1), allocation concealment (item 3), and random outcome assessment (item 6). Other items also revealed poor outcomes. Four studies (73, 77–79) reported baseline characteristics (item 2), one (84) mentioned the methods of performance blinding (item 5), and another (77) documented the blinded outcome assessment (item 7). In comparison, all the animal studies were free from selective outcome reporting (item 9), and 52 studies did not involve any other sources of bias (item 10).
Figure 4.
The risk of bias assessment of the included animal studies.
Effectiveness of Dietary Nutrients
The protective effects of dietary nutrients above on myocardium against cardiac toxicity can be observed by the comparison between chemotherapy with nutrients groups and chemotherapy groups in Supplementary Figures 1–7.
Polyphenols
In animal studies of our review, polyphenols were defined as a broad class of compounds with multiple phenolic hydroxyls (PhOH) and were reported in 29 studies (38–66). These covered proanthocyanidin (n = 6, all derived from grape seed extract) (38–43), anthocyanin (n = 1, derived from purple corn) (44), resveratrol (n = 2) (45, 46), curcumin (n = 5) (47–51), catechins (n = 3, derived from green tea and black tea) (52–54), and mixed phenolic compounds extracted from local products [n = 12, derived from date (55, 56), orange (57), cranberry (58), cardamom (59), pomegranate (60), hawthorn (61), naringenin (62), p-coumaric acid (63), honey (64), yogurt (65) and yellow wine (66)]. Three studies demonstrated that supplementation of polyphenols could improve DOX-induced cardiac dysfunctions evaluated by echocardiography (45, 57, 66). LVEF significantly reduced in DOX groups, but was similar in DOX+Nutrients groups and control groups. Cardiac morphological and systolic changes led by DOX were attenuated by polyphenolic nutrients through scavenging free radicals and blocking lipid peroxidation. Biochemical analyses were estimated by serum cardiac markers and antioxidant parameters in 28 studies (38–43, 45–66). LDH, MDA and SOD were reported most. The concentrations of myocardial enzymes in animals received chemotherapy and nutrients were significantly lower compared with those treated with chemotherapeutic agents alone. Oral administration of polyphenols improved the cardiac oxidative changes led by chemotherapy and enhanced the antioxidant enzymatic activities. Histopathological analyses of cardiac tissue captured under the microscope were reported in 16 studies (38, 40, 41, 45, 46, 48–50, 53, 56, 59–62, 65, 66). The incidences of myocardial atrophy, cytoplasmic vacuoles, nuclear pyknosis, and cytoplasmic eosinophilia were significantly higher in heart exposed to DOX, while the polyphenolic substance protected or even restored cardiac disrupted histological structure induced by DOX (Supplementary Figure 1).
Allicin and Lycopene
Three studies showed that allicin (all derived from garlic extract) effectively decreased the expression of myocardial tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and mitigated cardiac oxidative damage (67–69) (Supplementary Figure 2). Abdel-Daim et al. (67) referred that allicin could be a promising cytoprotective agent against DOX-related cardiotoxicity. Two studies revealed that lycopene (all derived from tomatoes) reduced the levels of cardiac oxidative markers and made the histopathological changes maintain nearly normal after the injection of DOX (70, 71) (Supplementary Figure 3).
Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids
PUFA were reported in five studies, derived from black chia seed (72), flaxseed (73), fish oil (74, 76), and sesame oil (75). All these studies proved that PUFA attenuated the myocardial necrosis and overall myocardium enlargement and alleviated histopathological alteration in rats/mice treated with DOX (Supplementary Figure 4). PUFA were considered as a potential chemoprotectant nutraceutical in combination with chemotherapy to limit the cardiotoxic side effects (72).
Amino Acids, Coenzyme Q10, and Trace Elements
Four studies reported that amino acids [derived from glycine (77) and glutamine (78–80)] could diminish chemotherapy-induced cardiac oxidative damage (Supplementary Figure 5). As a vital role in maintaining the cellular redox state, dietary glutamine remained normal cardiac GSH levels in animal models treated with chemotherapeutic drugs and prevented cardiac lipid peroxidation (78–80). Coenzyme Q10 (n = 5) (81–85) was proven to be prophylactic in prevention of cardiovascular toxicity through participating with redox function directly in the mitochondrial respiratory chain (Supplementary Figure 6), and trace elements [n = 3, derived from zinc (Zn) (86, 87) and selenium (Se) (88)] were also exhibited to protect myocardium by preventing mitochondrial dysfunctions and acting in concert with SOD and catalase (Supplementary Figure 7).
The details of outcomes are summarized in Supplementary Table 5.
Human Studies
Study Characteristics
Four human studies were conducted in Egypt [in 2021 (91) and 2020 (92)], Italy [in 1994 (93)] and the USA [in 1978 (94)]. Three studies (91–93) recruited pediatric patients diagnosed with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) aged 1 to 16 years and one (94) recruited adults with bronchogenic carcinoma. Two studies (91, 92) were RCTs using DOX as the chemotherapy agent, and the other two studies (93, 94) were non-randomized controlled trials using anthracyclines. The covered dietary nutrients contained PUFA [n = 2, derived from omega 3 fatty acids (91) and black seed oil (92)] and CoQ10 (n = 2) (93, 94). The characteristics of the included human studies are summarized in Table 2.
Table 2.
The characteristics of the included human studies.
| Dietary nutrients | Studies | Country | Study design | Participants | Intervention | Comparison | Outcomes | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cancer type | Gender | Age | Chemotherapeutic agents | Food intake | Main ingredients | Duration | Sample size | Grouping | Control groups | Treated groups | |||||
| PUFA | El Amrousy et al. (91) | Egypt | RCT | Acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Male, 36 Female, 24 |
8.7 ± 1.9 years old | DOX | Omega 3 fatty acids | Omega 3 fatty acids | 180 days | 60 | 2 | (1) DOX | (2) DOX+omega 3 fatty acids | a, b, c |
| Hagag et al. (92) | Egypt | RCT | Acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Male, 25 Female, 15 |
2-16 years old |
DOX | Black seed oil | PUFA (linoleic acid, oleic acid, palmitic acid) | 7 days | 40 | 2 | (1) DOX+placebo | (2) DOX+black seed oil | a | |
| CoQ10 | Iarussi et al. (93) | Italy | Non-randomized controlled trial | Acute lymphoblastic leukemia, non-hodgkin lymphoma | / | 1-15 years old |
Anthracyclines | CoQ10 | CoQ10 | / | 20 | 2 | (1) anthracyclines | (2) anthracyclines+CoQ10 | a |
| Cortes et al. (94) | USA | Non-randomized controlled trial | Bronchogenic carcinoma, other carcinoma | Male, 11 Female, 7 |
56.87 years old | DOX | CoQ10 | CoQ10 | 150 days | 18 | 2 | (1) DOX | (2) DOX+CoQ10 | a, d | |
CON, control; CoQ10, coenzyme Q10; DOX, doxorubicin; PUFA, polyunsaturated fatty acids; RCT, randomized controlled trial.
a: echocardiography; b: serum cardiac markers; c: oxidative stress markers; d: electrocardiograph.
Risk of Bias Assessment
The overall risk of bias of included human studies was at moderate to high risk. All items of Cochrane risk of bias tool were rated as low risk in one RCT (91), and three items (blinding of participants and personnel, blinding of outcome assessment, and selective outcome reporting) were rated as unclear risk in another RCT (92). The NOS's scores of the non-randomized trials were 5(93) and 6 (94) respectively, due to the lack of blind evaluation, follow-up and loss to follow up, and the inadequate reports of confounders adjustment. The details of the assessment are presented in Supplementary Tables 6, 7.
Effectiveness of Dietary Nutrients
Four studies all showed the cardioprotective effects of the dietary nutrient used in the trials. El Amrousy et al. (91) randomly divided the children with newly diagnosed ALL into two groups of 30 each. Children in intervention group received 1,000 mg omega 3 fatty acids capsule per day after the administration of DOX for 6 months, and children in control group received the DOX alone. The left ventricular systolic function was preserved in children who took omega 3 for 6 months, while the children in control group experienced significant impairments of cardiac function. Similarly, significantly lower MDA level and higher GSH and SOD levels of children in intervention group revealed that omega 3 fatty acids could decrease the early cardiac damage induced by DOX. Hagag et al. (92) recruited 40 ALL pediatric patients under DOX therapy, including 20 patients treated with black seed oil campus for 1 week and 20 patients treated with equivalent dose of placebo for the same amount of time. A larger reduction in parameters of systolic function arose in children with placebo compared to those with black seed oil. Iarussi et al. (93) carried a controlled trial on 20 children with ALL treated with anthracyclines, consisting of 10 patients with CoQ10 oral therapy and 10 without. Septum wall motion abnormalities were only detected in patients without CoQ10, which demonstrated prophylactic effects of CoQ10 on myocardial function from chemotherapeutic cardiotoxicity. Cortes et al. (94) enrolled 93 consecutive patients with advanced carcinoma to detect DOX-induced cardiotoxicity and the protective effects of CoQ10. Only 10 patients treated with DOX alone for more than 5 months and 8 patients treated with DOX and CoQ10 for more than 5 months were evaluated by systolic time intervals (STI). The mean of serial STIs in ten patients with DOX alone gradually increased during the course of DOX therapy and two patients had CHF. However, STIs were improved in eight patients with DOX and CoQ10 and only one patient had CHF. The effectiveness of dietary nutrients and the details of outcomes are summarized in Supplementary Figure 8 and Supplementary Table 8.
Discussion
Our systematic review included 57 studies published in 14 countries from 1978 to 2021 consisting of 53 animal studies and four human studies, and summarized the cardioprotective effects of dietary nutrients derived from food on target subjects treated with chemotherapy. The descriptive synthetic evidence demonstrated that seven types of dietary nutrients (polyphenols, allicin, lycopene, PUFA, amino acids, CoQ10, and trace elements) might alleviate cardiovascular toxicity induced by chemotherapeutic agents.
As post-mitotic cells, cardiomyocytes are more sensitive to free radical damage due to their high oxidative metabolism and low antioxidant defense level (24). As a result, clinical and subclinical cardiac injuries related with chemotherapy have been a notorious issue. The incidence rates of CHF caused by anthracyclines and cyclophosphamides range 0.14–48% and 7–28%, respectively (6, 95). The childhood cancer survivors are 15 and 10 times more likely to suffer CHF and coronary artery disease, respectively than their siblings (96, 97). As early as in 1967, Tan et al. (98) first described the anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity and reported that the development of tachycardia, arrhythmia and CHF in daunomycin patients could be associated with daunomycin. Simultaneously, it was found that cardiovascular toxicity was dose-dependent with a 5% incidence of cardiomyopathy at a cumulative dose of 400 mg/m2 of anthracyclines, 26% at a cumulative dose of 550 mg/m2 and up to 48% at 700 mg/m2 (99). That is the reason why the recommended cumulative dose is limited to 450–500 mg/m2 (100). Currently, cardiotoxic effects led by anthracyclines, especially DOX, have been most thoroughly studied (7, 19). And this is consistent with our review, in which 90.6% of the included animal studies generated cardiac dysfunctions by the injection of DOX in rats/mice. The most widely proposed mechanism is the anthracyclines' inhibition of topoisomerase 2β, which leads to promote cell apoptosis and generate oxidative damage in cardiomyocytes (13). At present, cardiotoxicity is a broader term without a formal definition (7, 101). The American Society of Echocardiography defines it as a ≥10% drop of LVEF from baseline or the absolute value <53% (101). 2016 European Society of Cardiology Position Paper considers the lower limit of normal LVEF as 50% (102). A clinical trial conducted on pediatric patients with acute myeloid leukemia also defined cardiotoxicity as LVEF <50% on the basis of the National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (version 3) definitions (8). However, significantly abnormal cardiac parameters were considered as cardiotoxicity in most of the studies included in our review. Similarly, improved measurements or even back to normal was recognized as the signs of positive cardioprotective effects of nutritional intervention.
The relevant guideline recommended that oncologists considered prevention against chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity through long-term management during the early stage of anticancer treatment with support from cardiologists (6). Compared with dexrazoxane, dietary nutrition is more accessible at ordinary times and easier to comply with in long-term survivals. In other words, it can meet the two main advantages of daily and long-term usage. Consequently, it is an additional prevention measure that cancer survivors cannot miss. While the nutritional support has been depicted to improve the adverse effects of chemotherapy (103–105), the current evidence against cardiotoxicity was limited due to the lack of enough clinical studies (29, 30). In addition, the guidelines did not report in detail the aspect of nutrition against cardiomyopathy associated with cancer chemotherapy (6, 20, 96). Several published reviews introduced the application of nutritional intervention in the prevention of cardiac toxicity and covered CoQ10, grape seed extract and ω-3 PUFA (27, 28, 106). But none of them systematically summarized the effectiveness of overall dietary nutrients in this respect. Koss-Mikołajczyk et al. (29) showed that natural products (including fruit, vegetables, herbs, mushrooms, and phytochemicals) could counteract cardiac injury caused by DOX. Despite the comprehensive list of products included in this study, these were all edible plant extracts and foodborne phytochemicals. Nutrients derived from animal food as cardioprotective agents have not been explored. Therefore, our review summarized the current available evidence and filled in the corresponding gaps.
Seven types of dietary nutrients were represented in our review. Among them, polyphenols were in more than half of the included studies possibly due to more than 8,000 species in nature (including flavonoids and non-flavonoids) (107, 108). Polyphenols can eliminate oxygen free radicals by owning multiple PhOH (107) and the oxidation resistance has also made itself as a toxicity-related preventive strategy in some reviews (24, 26, 109). Thus, the extract of fresh fruit (rich in flavonols and flavonoids), grape seeds (rich in proanthocyanidin), and green tea (rich in catechins) were commonly used to ameliorate the chemotherapy-related cardiac damage in the included studies. Besides vegetable food, animal food was also made clear to protect the heart exposed to chemotherapy. PUFA are dietary factors with multiple beneficial effects and could likely protect cardiovascular tissues by adjusting cellular processes and molecular pathways (27, 110). The amino acids can preserve myocardial high-energy phosphate levels and prevent lactate accumulation. Our study refers to glutamine and glycine, which involve GSH synthesis (a vital intracellular antioxidant) (111). CoQ10 is a free-radical scavenger primarily present in metabolically active organs, such as the heart, liver, and kidney (82). Zn has a critical role in maintaining health, primarily through antioxidative stress and anti-inflammation, by catalyzing more than 300 enzymes and binding with over 2,500 proteins. Se prevents oxidative stress and maintains antioxidant enzymes such as the four glutathione peroxidases (GPx) (112, 113).
There were several limitations in our systematic review. First, 93.0% of the included records (53/57) were animal studies along with a relatively moderate to high risk of bias, so the interpretation of results should be more cautious. Second, our findings may still remain a certain distance approaching the clinical application due to the majority of the included studies being animal research. Third, due to the lack of standardization in definition of cardiotoxicity and the high heterogeneity from the variations of included studies, it was a pity that we couldn't provide pooled results in our review.
Conclusion
Early prevention and management of cancer chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity have been increasingly focused due to the attention to event-free survival during and after cancer therapy. The existing studies have indicated that cardiotoxicity not only puts the patients under high risk of suffering cardiac deterioration but also develops as a social issue concerning the increase of Health System spending (114). The evidence of dietary nutrients against cardiovascular toxicity was still lacking. Our systematic review demonstrated that dietary nutrients (comprising polyphenols, allicin, lycopene, PUFA, amino acids, CoQ10, Zn, and Se) may be a potential strategy to protect cardiovascular system exposed to the chemotherapeutic agents, but more human studies are needed in future. On this basis, the development of cardioprotective strategies for special population, like children, the pregnant, and the elderly, is now essential for the reason that their vulnerable physical conditions demand much more cardiac protection.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Author Contributions
K-WJ, QW, and X-NL contributed to the conception and design of the study. X-YZ and K-LY carried out the search strategy independently and wrote the draft manuscript. YL and YZ contributed to the analysis of the included studies. All authors are responsible for the final content of the manuscript and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by Disciplinary Booster Program of Xijing Hospital, China (Project Nos. XJZT21CM27, XJZT19X11, and XJZT18Z22).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Acknowledgments
We appreciate the guidance of Dang Wei, Department of Global Public Health, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, Sweden (dang.wei@ki.se).
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcvm.2022.921609/full#supplementary-material
References
- 1.Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. (2021) 71:7–33. 10.3322/caac.21654 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Richards MA. The National Awareness and Early Diagnosis Initiative in England: assembling the evidence. Br J Cancer. (2009) 101:S1–4. 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605382 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Urruticoechea A, Alemany R, Balart J, Villanueva A, Vinals F, Capella G. Recent advances in cancer therapy: an overview. Curr Pharm Des. (2010) 16:3–10. 10.2174/138161210789941847 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Miller KD, Nogueira L, Mariotto AB, Rowland JH, Yabroff KR, Alfano CM, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. (2019) 69:363–85. 10.3322/caac.21565 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Conway A, McCarthy AL, Lawrence P, Clark RA. The prevention, detection and management of cancer treatment-induced cardiotoxicity: a meta-review. BMC Cancer. (2015) 15:366. 10.1186/s12885-015-1407-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Curigliano G, Lenihan D, Fradley M, Ganatra S, Barac A, Blaes A, et al. Management of cardiac disease in cancer patients throughout oncological treatment: ESMO consensus recommendations. Ann Oncol. (2020) 31:171–90. 10.1016/j.annonc.2019.10.023 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bansal N, Adams MJ, Ganatra S, Colan SD, Aggarwal S, Steiner R, et al. Strategies to prevent anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity in cancer survivors. Cardio-Oncol. (2019) 5:18. 10.1186/s40959-019-0054-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Getz KD, Sung L, Ky B, Gerbing RB, Leger KJ, Leahy AB, et al. Occurrence of treatment-related cardiotoxicity and its impact on outcomes among children treated in the AAML0531 clinical trial: a report from the children's oncology group. J Clin Oncol. (2019) 37:12–21. 10.1200/JCO.18.00313 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Middleman E, Luce J, Frei E. Clinical trials with adriamycin. Cancer. (1971) 28:844–50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Tukenova M, Guibout C, Oberlin O, Doyon F, Mousannif A, Haddy N, et al. Role of cancer treatment in long-term overall and cardiovascular mortality after childhood cancer. J Clin Oncol. (2010) 28:1308–15. 10.1200/JCO.2008.20.2267 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Reulen RC, Winter DL, Frobisher C, Lancashire ER, Stiller CA, Jenney ME, et al. British childhood cancer survivor study steering group. Long-term cause-specific mortality among survivors of childhood cancer. JAMA. (2010) 304:172. 10.1001/jama.2010.923 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Mavrogeni SI, Sfendouraki E, Markousis-Mavrogenis G, Rigopoulos A, Noutsias M, Kolovou G, et al. Cardio-oncology, the myth of Sisyphus, and cardiovascular disease in breast cancer survivors. Heart Fail Rev. (2019) 24:977–87. 10.1007/s10741-019-09805-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Varghese SS, Eekhoudt CR, Jassal DS. Mechanisms of anthracycline-mediated cardiotoxicity and preventative strategies in women with breast cancer. Mol Cell Biochem. (2021) 476:3099–109. 10.1007/s11010-021-04152-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Von Hoff DD, Layard M, Basa P, Davis HJ, Von Hoff A, Rozencweig R, et al. Risk factors for doxorubicin-lnduced congestive heart failure. Ann Intern Med. (1979) 91:710–7. 10.7326/0003-4819-91-5-710 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lancellotti P, Anker SD, Donal E, Edvardsen T, Popescu BA, Farmakis D, et al. EACVI/HFA cardiac oncology toxicity registry in breast cancer patients: rationale, study design, and methodology (EACVI/HFA COT registry)–EURObservational research program of the European society of cardiology. Eur Heart J - Cardiovasc Imaging. (2015) 16:466–70. 10.1093/ehjci/jev024 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Chow EJ, Leger KJ, Bhatt NS, Mulrooney DA, Ross CJ, Aggarwal S, et al. Paediatric cardio-oncology: epidemiology, screening, prevention, and treatment. Cardiovasc Res. (2019) 115:922–34. 10.1093/cvr/cvz031 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ryan TD, Nagarajan R, Godown J. Pediatric cardio-oncology: development of cancer treatment-related cardiotoxicity and the therapeutic approach to affected patients. Curr Treat Options Oncol. (2019) 20:56. 10.1007/s11864-019-0658-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Paris S, Tarantini L, Navazio A, Faggiano P. Cardio-oncology: the new frontier of clinical and preventive cardiology. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis. (2020) 90:1348. 10.4081/monaldi.2020.1348 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.McGowan JV, Chung R, Maulik A, Piotrowska I, Walker JM, Yellon DM. Anthracycline chemotherapy and cardiotoxicity. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. (2017) 31:63–75. 10.1007/s10557-016-6711-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Armenian SH, Lacchetti C, Barac A, Carver J, Constine LS, Denduluri N, et al. Prevention and monitoring of cardiac dysfunction in survivors of adult cancers: american society of clinical oncology clinical practice guideline. J Clin Oncol. (2017) 35:893–911. 10.1200/JCO.2016.70.5400 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Aboumsallem JP, Moslehi J, de Boer RA. Reverse cardio-oncology: cancer development in patients with cardiovascular disease. J Am Heart Assoc. (2020) 9:754. 10.1161/JAHA.119.013754 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Alexandre J, Cautela J, Ederhy S, Damaj GL, Salem J, Barlesi F, et al. Cardiovascular toxicity related to cancer treatment: a pragmatic approach to the american and european cardio-oncology guidelines. J Am Heart Assoc. (2020) 9:18403. 10.1161/JAHA.120.018403 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Astin JA. Why patients use alternative medicine: results of a national study. JAMA. (1998) 279:1548–53. 10.1001/jama.279.19.1548 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Granados-Principal S, Quiles JL, Ramirez-Tortosa CL, Sanchez-Rovira P, Ramirez-Tortosa MC. New advances in molecular mechanisms and the prevention of adriamycin toxicity by antioxidant nutrients. Food Chem Toxicol. (2010) 48:1425–38. 10.1016/j.fct.2010.04.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Conklin KA. Dietary antioxidants during cancer chemotherapy: impact on chemotherapeutic effectiveness and development of side effects. Nutr Cancer. (2000) 37:1–18. 10.1207/S15327914NC3701_1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Prasad KN. Multiple dietary antioxidants enhance the efficacy of standard and experimental cancer therapies and decrease their toxicity. Integr Cancer Ther. (2004) 3:310–22. 10.1177/1534735404270936 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Serini S, Ottes Vasconcelos R, Nascimento Gomes R, Calviello G. Protective effects of ω-3 PUFA in anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity: a critical review. Int J Mol Sci. (2017) 18:2689. 10.3390/ijms18122689 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Roffe L, Schmidt K, Ernst E. Efficacy of coenzyme Q10 for improved tolerability of cancer treatments: a systematic review. J Clin Oncol. (2004) 22:4418–24. 10.1200/JCO.2004.02.034 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Koss-Mikołajczyk I, Todorovic V, Sobajic S, Mahajna J, Gerić M, Tur JA, et al. Natural products counteracting cardiotoxicity during cancer chemotherapy: the special case of doxorubicin, a comprehensive review. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:10037. 10.3390/ijms221810037 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Othman SNN, Lum PT, Gan SH, Mani S, Sekar M. Protective effect of natural products against chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity: a review. Pharmacogn J. (2020) 12:1180–9. 10.5530/pj.2020.12.166 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Czepas J, Gwozdziński K. The flavonoid quercetin: Possible solution for anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity and multidrug resistance. Biomed Pharmacother. (2014) 68:1149–59. 10.1016/j.biopha.2014.10.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Tan ML, Hamid SBS. Beetroot as a potential functional food for cancer chemoprevention, a narrative review. J Cancer Prev. (2021) 26:1–17. 10.15430/JCP.2021.26.1.1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.de Vries RBM, Hooijmans CR, Langendam MW, van Luijk J, Leenaars M, Ritskes-Hoitinga M, et al. Protocol format for the preparation, registration and publication of systematic reviews of animal intervention studies: protocol format for animal systematic reviews. Evid-Based Preclin Med. (2015) 1:1–9. 10.1002/ebm2.7 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. (2021) 372:n71. 10.1136/bmj.n71 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hooijmans CR, Rovers MM, de Vries RB, Leenaars M, Ritskes-Hoitinga M, Langendam MW. SYRCLE's risk of bias tool for animal studies. BMC Med Res Methodol. (2014) 14:43. 10.1186/1471-2288-14-43 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, Jüni P, Moher D, Oxman AD, et al. The cochrane collaboration's tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. (2011) 343:d5928. 10.1136/bmj.d5928 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Stang A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol. (2010) 25:603–5. 10.1007/s10654-010-9491-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Adiyaman MS, Adiyaman ÖA, Dagli AF, Karahan MZ, Kaya I, Dagli MN. Effects of grapeseed extract on doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats. Herz. (2021) 46:103–8. 10.1007/s00059-019-04888-w [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Ammar E-SM, Said SA, El-Damarawy SL, Suddek GM. Cardioprotective effect of grape-seed proanthocyanidins on doxorubicin-induced cardiac toxicity in rats. Pharm Biol. (2013) 51:339–44. 10.3109/13880209.2012.729065 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Boghdady NAE. Antioxidant and antiapoptotic effects of proanthocyanidin and ginkgo biloba extract against doxorubicin-induced cardiac injury in rats: modulation of doxorubicin cardiotoxicity. Cell Biochem Funct. (2013) 31:344–51. 10.1002/cbf.2907 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Yalçin E, Oruç E, Çavuşoglu K, Yapar K. Protective role of grape seed extract against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity and genotoxicity in albino mice. J Med Food. (2010) 13:917–25. 10.1089/jmf.2009.0162 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Yousef MI, Saad AA, El-Shennawy LK. Protective effect of grape seed proanthocyanidin extract against oxidative stress induced by cisplatin in rats. Food Chem Toxicol. (2009) 47:1176–83. 10.1016/j.fct.2009.02.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Zhang XY, Li WG, Wu YJ, Gao MT. Amelioration of doxorubicin-induced myocardial oxidative stress and immunosuppression by grape seed proanthocyanidins in tumour-bearing mice. J Pharm Pharmacol. (2005) 57:1043–52. 10.1211/0022357056523 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Petroni K, Trinei M, Fornari M, Calvenzani V, Marinelli A, Micheli LA, et al. Dietary cyanidin 3-glucoside from purple corn ameliorates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in mice. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. (2017) 27:462–9. 10.1016/j.numecd.2017.02.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Shoukry HS, Ammar HI, Rashed LA, Zikri MB, Shamaa AA. Abou elfadl SG, et al. Prophylactic supplementation of resveratrol is more effective than its therapeutic use against doxorubicin induced cardiotoxicity. PLOS ONE. (2017) 12:e0181535. 10.1371/journal.pone.0181535 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Arafa MH, Mohammad NS, Atteia HH, Abd-Elaziz HR. Protective effect of resveratrol against doxorubicin-induced cardiac toxicity and fibrosis in male experimental rats. J Physiol Biochem. (2014) 70:701–11. 10.1007/s13105-014-0339-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Ibrahim Fouad G, Ahmed KA. Curcumin ameliorates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity and hepatotoxicity via suppressing oxidative stress and modulating iNOS, NF-κB, and TNF-α in rats. Cardiovasc Toxicol. (2022) 22:152–66. 10.1007/s12012-021-09710-w [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Bahadir A, Ceyhan A, Öz Gergin Ö, Yalçin B, Ülger M, Özyazgan TM, et al. Protective effects of curcumin and beta-carotene on cisplatin-induced cardiotoxicity: an experimental rat model. Anatol J Cardiol. (2018) 19:213–21. 10.14744/AnatolJCardiol.2018.53059 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Benzer F, Kandemir FM, Ozkaraca M, Kucukler S, Caglayan C. Curcumin ameliorates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by abrogation of inflammation, apoptosis, oxidative DNA damage, and protein oxidation in rats. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. (2018) 32:e22030. 10.1002/jbt.22030 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Swamy A, Gulliaya S, Thippeswamy A, Koti B, Manjula D. Cardioprotective effect of curcumin against doxorubicin-induced myocardial toxicity in albino rats. Indian J Pharmacol. (2012) 44:73–7. 10.4103/0253-7613.91871 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Venkatesan N. Curcumin attenuation of acute adriamycin myocardial toxicity in rats: special Report. Br J Pharmacol. (1998) 124:425–7. 10.1038/sj.bjp.0701877 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Ibrahim MA, Bakhaat GA, Tammam HG, Mohamed RM, El-Naggar SA. Cardioprotective effect of green tea extract and vitamin E on Cisplatin-induced cardiotoxicity in mice: toxicological, histological and immunohistochemical studies. Biomed Pharmacother. (2019) 113:108731. 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108731 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Saeed NM, El-Naga RN, El-Bakly WM, Abdel-Rahman HM, Salah ElDin RA, El-Demerdash E. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate pretreatment attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats: a mechanistic study. Biochem Pharmacol. (2015) 95:145–55. 10.1016/j.bcp.2015.02.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Amanullah A, Ekbbal R, Haque SE. Evaluation of combinational therapy of resveratrol and black tea extract on doxorubicin-induced myocardial infarction in wistar rats. J Pharm Res. (2015) 9:581–7. Available online at: www.jprsolutions.info [Google Scholar]
- 55.Mubarak S, Hamid SA, Farrag AR, Samir N, Hussein JS. Cardioprotective effect of date palm against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Asian J Pharm Clin Res. (2018) 11:141. 10.22159/ajpcr.2018.v11i7.24453 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Sabbah MF, Alshubali FA, Baothman OAS, Zamzami M, Shash L, Hassan IA, et al. Cardioprotective effect of Ajwa date aqueous extract on doxorubicin-induced toxicity in rats. Biomed Pharmacol J. (2018) 11:1521–36. 10.13005/bpj/1519 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Ribeiro APD, Pereira AG, Todo MC, Fujimori ASS, dos Santos PP, Dantas D, et al. Pera orange (Citrus sinensis) and Moro orange (Citrus sinensis. (L.) Osbeck) juices attenuate left ventricular dysfunction and oxidative stress and improve myocardial energy metabolism in acute doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats. Nutrition. (2021) 91:111350. 10.1016/j.nut.2021.111350 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Elberry AA, Abdel-Naim AB, Abdel-Sattar EA, Nagy AA, Mosli HA, Mohamadin AM, et al. Cranberry (Vaccinium macrocarpon) protects against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats. Food Chem Toxicol. (2010) 48:1178–84. 10.1016/j.fct.2010.02.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Abu Gazia M, El-Magd MA. Ameliorative effect of cardamom aqueous extract on doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats. Cells Tissues Organs. (2018) 206:62–72. 10.1159/000496109 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Hassanpour Fard M, Ghule AE, Bodhankar SL, Dikshit M. Cardioprotective effect of whole fruit extract of pomegranate on doxorubicin-induced toxicity in rat. Pharm Biol. (2011) 49:377–82. 10.3109/13880209.2010.517758 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Shatoor AS, Said Ahmed MAA. Cardioprotective effect of Crataegus aronia syn. Azarolus (L) Aqueous extract against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity and heart failure in Wistar Rats. J Basic Appl Sci Res. (2014) 4:102–14. Available online at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/26 [Google Scholar]
- 62.Subburaman S, Ganesan K, Ramachandran M. Protective role of Naringenin against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in a rat model: histopathology and mRNA expression profile studies. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. (2014) 33:363–76. 10.1615/JEnvironPatholToxicolOncol.2014010625 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Abdel-Wahab MH, El-Mahdy MA, Abd-Ellah MF, Helal GK, Khalifa F, Hamada FMA. Influence of p-coumaric acid on doxorubicin-induced oxidative stress in rat's heart. Pharmacol Res. (2003) 48:461–5. 10.1016/S1043-6618(03)00214-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Alhumaydhi FA. Biochemical studies on the protective effect of honey against doxorubicin-induced toxicity in BALB/C mice. Int J Health Sci. (2020) 14:31–37. Available online at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7644457/ [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Abu-Elsaad NM, Abd Elhameed AG, El-Karef A, Ibrahim TM. Yogurt containing the probacteria Lactobacillus acidophilus combined with natural antioxidants mitigates doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy in rats. J Med Food. (2015) 18:950–9. 10.1089/jmf.2014.0104 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Lin H, Zhang J, Ni T, Lin N, Meng L, Gao F, et al. Yellow wine polyphenolic compounds prevents doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity through activation of the Nrf2 signalling pathway. J Cell Mol Med. (2019) 23:6034–47. 10.1111/jcmm.14466 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Abdel-Daim MM. kilany OE, Khalifa HA, Ahmed AAM. Allicin ameliorates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats via suppression of oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. (2017) 80:745–53. 10.1007/s00280-017-3413-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Demirkaya E, Avci A, Kesik V, Karslioglu Y, Oztas E, Kismet E, et al. Cardioprotective roles of aged garlic extract, grape seed proanthocyanidin, and hazelnut on doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. (2009) 87:633–40. 10.1139/Y09-051 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Mukherjee S, Banerjee S, Maulik M, Dinda A, Talwar KK, Maulik S. Protection against acute adriamycin-induced cardiotoxicity by garlic: role of endogenous antioxidants and inhibition of TNF-α expression. BMC Pharmacol. (2003) 3:16. 10.1186/1471-2210-3-16 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Ferreira ALA, Salvadori DMF, Nascimento MCMO, Rocha NS, Correa CR, Pereira EJ, et al. Tomato-oleoresin supplement prevents doxorubicin-induced cardiac myocyte oxidative DNA damage in rats. Mutat Res. (2007) 631:26–35. 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2007.04.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Yilmaz S, Atessahin A, Sahna E, Karahan I, Ozer S. Protective effect of lycopene on adriamycin-induced cardiotoxicity and nephrotoxicity. Toxicology. (2006) 218:164–71. 10.1016/j.tox.2005.10.015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Ahmed AZ, Mumbrekar KD, Satyam SM, Shetty P, D'Souza MR, Singh VK. Chia seed oil ameliorates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in female Wistar rats: an electrocardiographic, biochemical and histopathological approach. Cardiovasc Toxicol. (2021) 21:533–42. 10.1007/s12012-021-09644-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Asselin CY, Lam A, Cheung DYC, Eekhoudt CR, Zhu A, Mittal I, et al. The cardioprotective role of flaxseed in the prevention of doxorubicin- and trastuzumab-mediated cardiotoxicity in C57BL/6 mice. J Nutr. (2020) 150:2353–63. 10.1093/jn/nxaa144 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Saleh D, Abdelbaset M, Hassan A, Sharaf O, Mahmoud S, Hegazy R. Omega-3 fatty acids ameliorate doxorubicin-induced cardiorenal toxicity: in-vivo regulation of oxidative stress, apoptosis and renal Nox4, and in-vitro preservation of the cytotoxic efficacy. PLoS One. (2020) 15:e0242175. 10.1371/journal.pone.0242175 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Saleem MTS, Chetty MC, Kavimani S. Antioxidants and tumor necrosis factor alpha-inhibiting activity of sesame oil against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. (2014) 8:4–11. 10.1177/1753944713516532 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Teng L, Shao L, Zhao Y, Yu X, Zhang D, Zhang H. The beneficial effect of n−3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on doxorubicin-induced chronic heart failure in rats. J Int Med Res. (2010) 38:940–8. 10.1177/147323001003800320 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Maneikyte J, Bausys A, Leber B, Feldbacher N, Hoefler G, Kolb-Lenz D, et al. Dietary Glycine prevents folfox chemotherapy-induced heart injury: a colorectal cancer liver metastasis treatment model in rats. Nutrients. (2020) 12:2634. 10.3390/nu12092634 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Todorova VK, Kaufmann Y, Hennings LJ, Klimberg VS. Glutamine regulation of doxorubicin accumulation in hearts versus tumors in experimental rats. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. (2010) 66:315–23. 10.1007/s00280-009-1165-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Todorova VK, Kaufmann Y, Hennings L, Klimberg VS. Oral glutamine protects against acute doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity of tumor-bearing rats. J Nutr. (2010) 140:44–8. 10.3945/jn.109.113415 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Cao Y, Kennedy R, Klimberg VS. Glutamine protects against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. J Surg Res. (1999) 85:178–82. 10.1006/jsre.1999.5677 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Rahmanifard M, Vessal M, Noorafshan A, Karbalay-Doust S, Naseh M. The Protective effects of coenzyme Q10 and Lisinopril against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats: a stereological and electrocardiogram study. Cardiovasc Toxicol. (2021) 21:936–46. 10.1007/s12012-021-09685-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Shabaan DA, Mostafa N, El-Desoky MM, Arafat EA. Coenzyme Q10 protects against doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy via antioxidant and anti-apoptotic pathway. Tissue Barriers. (2021) 3:2019504. 10.1080/21688370.2021.2019504 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Botelho AFM, Lempek MR, Branco SEMT, Nogueira MM, de Almeida ME, Costa AG, et al. Coenzyme Q10 cardioprotective effects against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in Wistar rat. Cardiovasc Toxicol. (2020) 20:222–34. 10.1007/s12012-019-09547-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Chen PY, Hou CW, Shibu MA, Day CH, Pai P, Liu ZR, et al. Protective effect of Co-enzyme Q10 On doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy of rat hearts. Environ Toxicol. (2017) 32:679–89. 10.1002/tox.22270 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Mustafa HN, Hegazy GA, Awdan SAE, AbdelBaset M. Protective role of CoQ10 or L-carnitine on the integrity of the myocardium in doxorubicin induced toxicity. Tissue Cell. (2017) 49:410–26. 10.1016/j.tice.2017.03.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Maryoosh TM. N. Al-Shawi N, S Salih E. Effects of two different doses of zinc sulfate on serum troponin I 3 enzyme level and cardiac malondialdehyde contents in mitoxantrone-induced cardiotoxicity in rats Iraqi. J Pharm Sci. (2020) 29:115–22. 10.31351/vol29iss1pp115-122 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Wu R, Mei X, Wang J, Sun W, Xue T, Lin C, et al. Zn (II) -Curcumin supplementation alleviates gut dysbiosis and zinc dyshomeostasis during doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats. Food Funct. (2019) 10:5587–604. 10.1039/C9FO01034C [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Coudray C, Boucher F, Hida H, Tirard V, de Leiris J, Favier A. Selenium supplementation decreases the pro-oxidant and cardiotoxicity effects of adriamycin in the rat. Redox Rep. (1996) 2:323–32. 10.1080/13510002.1996.11747068 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Radeva-Ilieva MP, Georgiev KD, Hvarchanova NR, Stoeva SS, Slavov IJ, Dzhenkov DL, et al. Protective effect of methylxanthine fractions isolated from Bancha tea leaves against doxorubicin-induced cardio- and nephrotoxicities in rats. BioMed Res Int. (2020) 2020:1–9. 10.1155/2020/4018412 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Wahab MHA, Akoul E-SEMS, Abdel-Aziz AA. Modulatory effects of melatonin and vitamin E on doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in Ehrlich ascites carcinoma-bearing mice. Tumori. (2000) 86:157–62. Available online at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10855855/ [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.El Amrousy D, El-Afify D, Khedr R, Ibrahim AM. Omega 3 fatty acids can reduce early doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr Blood Cancer. (2021) 6:e29496. 10.1002/pbc.29496 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Hagag AA, Badraia IM, El-Shehaby WA, Mabrouk MM. Protective role of black seed oil in doxorubicin-induced cardiac toxicity in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Oncol Pharm Pract. (2020) 26:1397–406. 10.1177/1078155219897294 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Iarussi D, Auricchio U, Agretto A, Murano A, Giuliano M, Casale F, et al. Protective effect of coenzyme Q10 on anthracyclines cardiotoxicity: control study in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Mol Aspects Med. (1994) 15:s207–12. 10.1016/0098-2997(94)90030-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Cortes EP, Gupta M, Chou C, Amin VC, Folkers K. Adriamycin cardiotoxicity: early detection by systolic time interval and possible prevention by coenzyme Q10. Cancer Treat Rep. (1978) 62:887–91. Available online at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/667863/ [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Senkus E, Jassem J. Cardiovascular effects of systemic cancer treatment. Cancer Treat Rev. (2011) 37:300–11. 10.1016/j.ctrv.2010.11.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Lipshultz SE, Adams MJ, Colan SD, Constine LS, Herman EH, Hsu DT, et al. Long-term cardiovascular toxicity in children, adolescents, and young adults who receive cancer therapy: pathophysiology, course, monitoring, management, prevention, and research directions: a scientific statement from the American heart association. Circulation. (2013) 128:1927–95. 10.1161/CIR.0b013e3182a88099 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Oeffinger KC, Mertens AC, Sklar CA, Kawashima T, Hudson MM, Meadows AT, et al. Chronic health conditions in adult survivors of childhood cancer. N Engl J Med. (2006) 355:1572–82. 10.1056/NEJMsa060185 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Tan C, Tasaka H, Yu K-P, Murphy ML, Karnofsky DA. Daunomycin, an antitumor antibiotic, in the treatment of neoplastic disease. Clinical evaluation with special reference to childhood leukemia. Cancer. (1967) 20:333–53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Li DL, Hill JA. Cardiomyocyte autophagy and cancer chemotherapy. J Mol Cell Cardiol. (2014) 71:54–61. 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2013.11.007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Cavarretta E, Mastroiacovo G, Lupieri A, Frati G, Peruzzi M. The Positive Effects of Exercise in Chemotherapy-Related Cardiomyopathy. In: Xiao J. editor. Exercise for Cardiovascular Disease Prevention and Treatment. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. Singapore: Springer Singapore; (2017). p. 103–129 10.1007/978-981-10-4304-8_8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Cardinale D, Colombo A, Bacchiani G, Tedeschi I, Meroni CA, Veglia F, et al. Early detection of anthracycline cardiotoxicity and improvement with heart failure therapy. Circulation. (2015) 131:1981–8. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.013777 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Zamorano JL, Lancellotti P, Rodriguez Muñoz D, Aboyans V, Asteggiano R, Galderisi M, et al. 2016 ESC Position Paper on cancer treatments and cardiovascular toxicity developed under the auspices of the ESC committee for practice guidelines: the task force for cancer treatments and cardiovascular toxicity of the European society of cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. (2016) 37:2768–801. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw211 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.de van der Schueren MAE, Laviano A, Blanchard H, Jourdan M, Arends J, Baracos VE. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the evidence for oral nutritional intervention on nutritional and clinical outcomes during chemo(radio)therapy: current evidence and guidance for design of future trials. Ann Oncol. (2018) 29:1141–53. 10.1093/annonc/mdy114 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Kim SH, Lee SM, Jeung HC, Lee IJ, Park JS, Song M, et al. The effect of nutrition intervention with oral nutritional supplements on pancreatic and bile duct cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy. Nutrients. (2019) 11:1145. 10.3390/nu11051145 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Qin N, Jiang G, Zhang X, Sun D, Liu M. The effect of nutrition intervention with oral nutritional supplements on ovarian cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy. Front Nutr. (2021) 8:685967. 10.3389/fnut.2021.685967 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Olaku OO, Ojukwu MO, Zia FZ, White JD. The role of grape seed extract in the treatment of chemo/radiotherapy induced toxicity: a systematic review of preclinical studies. Nutr Cancer. (2015) 67:730–40. 10.1080/01635581.2015.1029639 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Luca SV, Macovei I, Bujor A, Miron A, Skalicka-Wozniak K, Aprotosoaie AC, et al. Bioactivity of dietary polyphenols: the role of metabolites. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2020) 60:626–59. 10.1080/10408398.2018.1546669 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Bravo L. Polyphenols: Chemistry, dietary sources, metabolism, and nutritional significance. Nutr Rev. (1998) 56:317–33. 10.1111/j.1753-4887.1998.tb01670.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Fraga CG, Croft KD, Kennedy DO, Tomás-Barberán FA. The effects of polyphenols and other bioactives on human health. Food Funct. (2019) 10:514–28. 10.1039/C8FO01997E [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Sanders TAB. Protective effects of dietary PUFA against chronic disease: evidence from epidemiological studies and intervention trials. Proc Nutr Soc. (2014) 73:73–9. 10.1017/S0029665113003789 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Gaurav K, Goel R, Shukla M, Pandey M. Glutamine: A novel approach to chemotherapy-induced toxicity. Indian J Med Paediatr Oncol. (2012) 33:13–20. 10.4103/0971-5851.96962 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Choi S, Liu X, Pan Z. Zinc deficiency and cellular oxidative stress: prognostic implications in cardiovascular diseases. Acta Pharmacol Sin. (2018) 39:1120–32. 10.1038/aps.2018.25 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Mohammadifard N, Humphries KH, Gotay C, Mena-Sánchez G, Salas-Salvadó J, Esmaillzadeh A, et al. Trace minerals intake: risks and benefits for cardiovascular health. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2019) 59:1334–46. 10.1080/10408398.2017.1406332 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Bassareo PP, Monte I, Romano C, Deidda M, Piras A, Cugusi L, et al. Mercuro G. Cardiotoxicity from anthracycline and cardioprotection in paediatric cancer patients: J Cardiovasc Med. (2016) 17:e55–63. 10.2459/JCM.0000000000000375 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.