Abstract
Background
Histone deacetylation is one of the most important epigenetic modifications and plays diverse roles in plant development. However, the detailed functions and mechanisms of histone deacetylation in fiber development of cotton are still unclear. HDAC inhibitors (HDACi) have been commonly used to study the molecular mechanism underlying histone deacetylation or to facilitate disease therapy in humans through hindering the histone deacetylase catalytic activity. Trichostatin A (TSA)—the most widely used HDACi has been extensively employed to determine the role of histone deacetylation on different developmental stages of plants.
Results
Through in vitro culture of ovules, we observed that exogenous application of TSA was able to inhibit the fiber initiation development. Subsequently, we performed a transcriptomic analysis to reveal the underlying mechanisms. The data showed that TSA treatment resulted in 4209 differentially expressed genes, which were mostly enriched in plant hormone signal transduction, phenylpropanoid biosynthesis, photosynthesis, and carbon metabolism pathways. The phytohormone signal transduction pathways harbor the most differentially expressed genes. Deeper studies showed that some genes promoting auxin, Gibberellic Acid (GA) signaling were down-regulated, while some genes facilitating Abscisic Acid (ABA) and inhibiting Jasmonic Acid (JA) signaling were up-regulated after the TSA treatments. Further analysis of plant hormone contents proved that TSA significantly promoted the accumulation of ABA, JA and GA3.
Conclusions
Collectively, histone deacetylation can regulate some key genes involved in different phytohormone pathways, and consequently promoting the auxin, GA, and JA signaling, whereas repressing the ABA synthesis and signaling to improve the fiber cell initiation. Moreover, the genes associated with energy metabolism, phenylpropanoid, and glutathione metabolism were also regulated by histone deacetylation. The above results provided novel clues to illuminate the underlying mechanisms of epigenetic modifications as well as related different phytohormones in fiber cell differentiation, which is also very valuable for the molecular breeding of higher quality cotton.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s13578-022-00840-4.
Keywords: Fiber initiation, Histone deacetylation, HDAC inhibitor, TSA, Phytohormones
Background
Histone acetylation functions as one type of the most important chromatin modifications in eukaryotes, which generally is mediated by the opposite functions of histone acetyltransferases (HATs) and histone deacetylases (HDACs) to sustain the balance of lysine acetylation for regulation of gene expression in context [1]. Many HDAC genes have been identified and characterized from animals, fungi and plants to involve diverse developmental stages or stress tolerances [2–9]. Up to now, HDACs were classified into three subfamilies in eukaryotes. The first is most closely related to yeast RPD3, and the second is related to yeast HDA1 [10]. Moreover, the third subfamily of HDACs (HD2) is unrelated to yeast RPD3 and is unique in plants [11–14]. HDACs generally function as a part of multiprotein complexes consisting of transcriptional repressors, scaffold proteins, and a variety of cofactors [8].
In mammals and humans, HDACs play vital roles in cell migration, growth, and survival, and are closely correlated with various diseases such as tumors, cancers, a group of diseases related to metabolic abnormalities, and so on [7, 15, 16]. HDAC inhibitors (HDACi) can repress histone deacetylation mediated by HDAC through several different approaches and have been studied widely to be applied in diverse disease therapies. According to the different structures and characteristics of the HDAC subfamilies, a variety of HDACi were identified and designed to cure human diseases [17–20]. Some HDACs function with zinc in their catalytic site, hence the main target of HDAC inhibitors is to suppress the inherent activity of HDACs by occupying the catalytic core of the Zn2+ binding site [15, 21, 22]. Trichostatin A (TSA) and vorinostat [suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA)] have been identified to inhibit HDACs catalytic activity, among which TSA was the first discovered natural hydroxamate and HDACi used in treating patients with malignancy together successfully with vorinostat (e.g., cutaneous T-cell lymphoma) [7, 23, 24]. Furthermore, some aminosuberoyl hydroxamic acids have shown the ability to repress HDACs and cell proliferation at nanomolar concentrations [21], facilitating the application of HDACi in disease therapy. Basically, HDACi promotes the accumulation of acetylated histones and non-histone proteins that are involved in the regulation of gene expression, enzymatic activity, cell proliferation, and so on. Even so, the molecular mechanisms underlying the HDACi-mediated cell growth retardation and cell death associated with antitumor are complex and not completely elucidated [17, 25–27]. The development of small molecule HDACi for various disease conditions including cancer, is an emerging target in recent times [16].
In insects, life-history traits such as longevity and fecundity are severely affected by the suppression of HAT/HDAC activity, achieved by the application of chemical inhibitors. Bea aphid (Acyrthosiphon pisum)-a model insect is often used to study complex life-history traits. Specific chemical inhibitors of HATs/HDACs showed a remarkably severe impact on life-history traits including reducing survival, delaying development, and limiting the number of offspring. The selective inhibition of HATs and HDACs also had opposing effects on aphid body weight [5].
Furthermore, many studies have proved that HDACs play critical and versatile roles in plant development including seed germination, vegetative and reproduction tissues development, trichome development, root hair cell differentiation, as well as abiotic stress tolerance [2, 3, 5, 6, 28]. In Arabidopsis, it also showed that TSA and diallyl disulfide (DADS) inhibited the seedling development in MS medium [28]. In rice, using TSA resulted in impaired callus formation of mature embryos and increased global histone H3 acetylation levels, decreased auxin response, and cell proliferation in callus formation [29]. Cotton fiber, the principal natural resource for the textile industry, is also an excellent model to study cell differentiation and development. Thirty HDAC genes were identified from the tetraploid variety Gossypium hirsutum, and of them, GhHDA5 has shown the negative regulation of fiber cell differentiation, indicating some clues for the mechanisms of HDACs and the crucial roles of histone deacetylation in fiber development [6]. However, the underlying mechanism associated with histone deacetylation for fiber development is unclear.
The application of HDACi in plants also provided some interesting results. For example, plant cell cultures are good for the output of recombinant proteins, with lower costs than mammalian cells except the only flaw being the lower yields obtained. After adding HDACi into the culture, higher levels of transgene expression and protein accumulation were observed, showing HDACi as an enhancer of recombinant protein production in plant cell suspensions. This offers the potential to improve the yields of the recombinant protein in plant cell cultures with epigenetic strategies [30], providing evidence of the correlation between histone acetylation and increased transcription levels and the production of recombinant proteins. Moreover, TSA showed negative roles in fiber development through in vitro culture of ovules [6], supporting the key role of histone deacetylation in fiber development.
Here, the HDACi-TSA was used for in vitro culture of ovules before and after fiber cells initiation (i.e. ovules at 0 DPA and −2 DPA). The results revealed that TSA inhibits not only fiber elongation, but also fiber cell initiation and differentiation. The subsequent transcriptomic analysis identified some phytohormone and secondary metabolism-related genes, which may play important roles in fiber development through histone deacetylation-mediated pathways and other complicated interactions.
Results
In vitro TSA treatment of ovule inhibits fiber initiation and earlier elongation
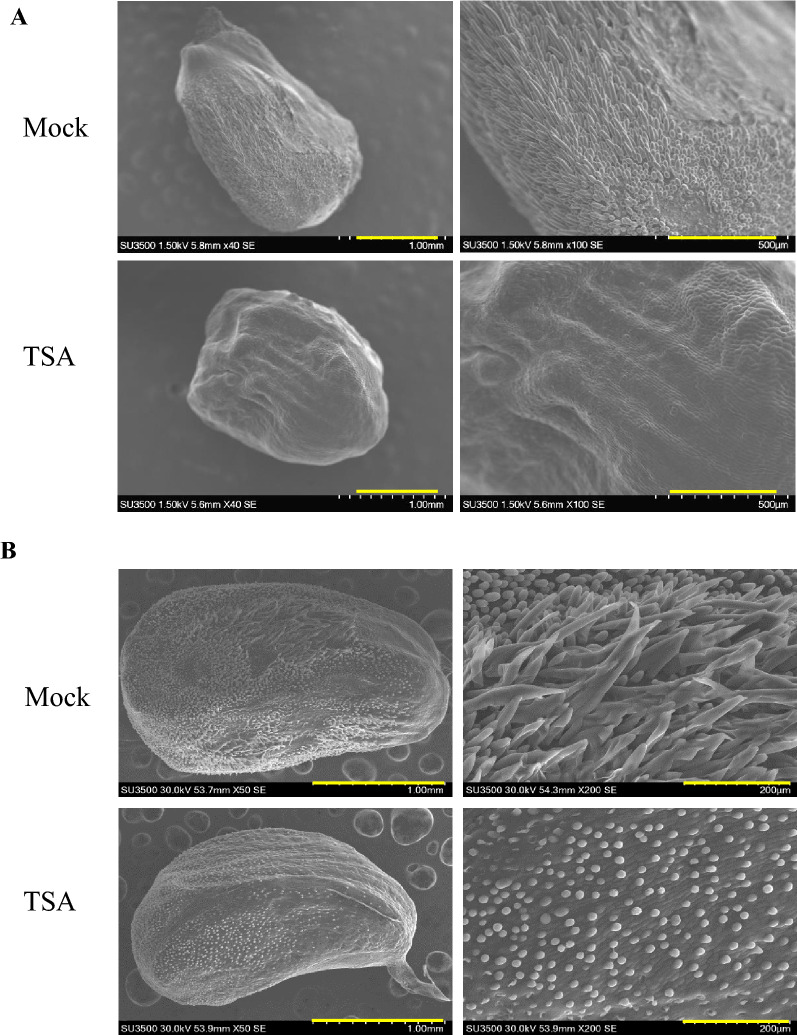
The previous study has shown the important roles of TSA in fiber elongation [6], but the effect of TSA in fiber cell initiation and the underlying mechanisms are still unclear. We used the ovules before and after anthesis (−2 DPA and 0 DPA, respectively) to test the roles of TSA for fiber cell initiation and earlier elongation. The results showed that TSA significantly inhibits the fiber cell initiation as well as the earlier fiber elongation compared with mock in vitro culture (Fig. 1), indicating the important roles of histone deacetylation in fiber cell initiation. The long-term in vitro culture of 0 DPA ovules further confirmed the inhibition of TSA on the fiber elongation (Additional file 5: Fig. S1). Subsequently, the ovules of −2 DPA treated with TSA (10 μM) for 6 days in vitro culture were used for RNA extraction and RNA-Seq with Illumina sequencing platform.
Fig. 1.
Application of TSA repress fiber cell initiation and elongation in vitro. A Ovules of −2 DPA (days post anthesis) were treated with 10 μM TSA for 6 days in vitro, and then the ovules surface were observed and captured by Scanning Electron Microscope. B 0 DPA ovules were treated with 10 μM TSA for 2 days in vitro, and the ovules surface were observed and captured by SEM. Bar = 1 mm (intact ovules) and Bar = 200 μm (magnification). The pictures on the right are the magnification of the regions of the pictures on the left
RNA-Seq of ovules after TSA treatment and data analysis
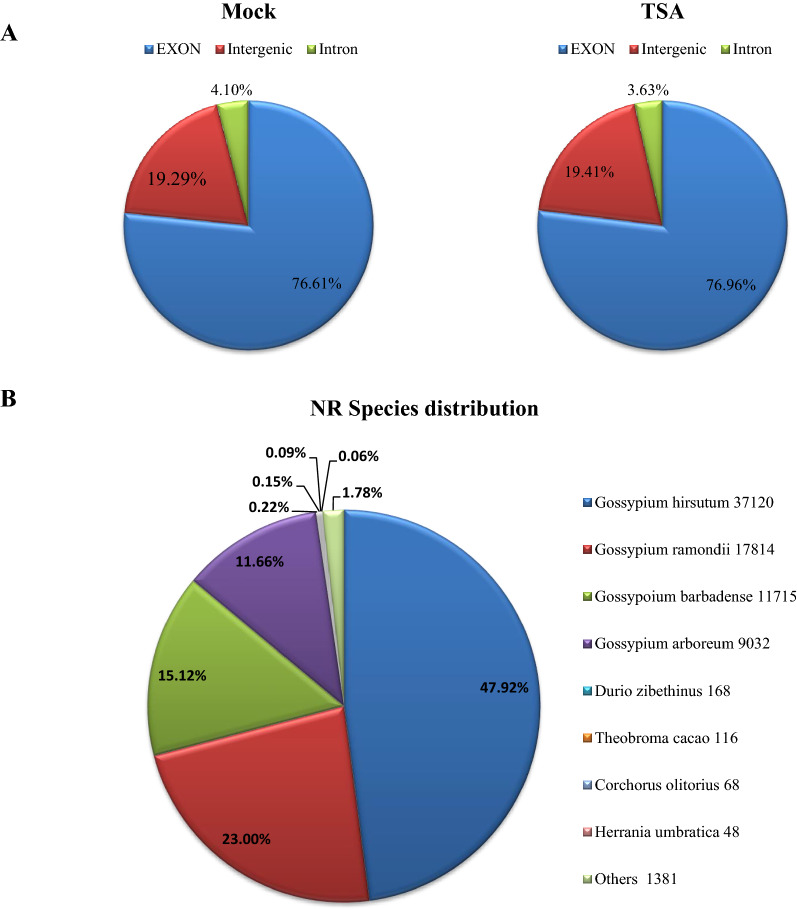
In total, more than 9.01G of clean data was obtained for each sample. The clean sequence reads were used to assemble the transcriptome for each sample by mapping the reads to the cotton reference genome (http://mascotton.njau.edu.cn/info/1054/1118.htm). More than 90.0% of the reads could be mapped to the cotton reference genome, and more than 75%, approximately 20%, and 4% of the mapped reads were mapped to exon, intergenic, and intron regions, respectively (Fig. 2A). The mapped reads from all samples were then remapped to the reference genome and 77,691 unigenes were defined by assembling clean reads with Trinity. All unigenes obtained by transcriptome sequencing were annotated into the NR, KEGG, GO, COG, eggNOG, Swiss-Prot, Pfam, and KOG databases. As a result, 77,555 (NR: 99.82%), 28,174 (KEGG: 36.26%), 57,846 (GO: 74.46%), 26,087 (COG: 33.58%), 70,960 (eggNOG: 91.34%), 55,767 (Swiss-Prot: 71.77%), 59,214 (Pfam: 76.22%) and 41,302 (KOG: 53.16%) unigenes were functionally annotated, respectively. In the NR database, the results showed that G. hirsutum had the highest matching degree with the unigene sequence (47.92%), followed by G. ramondii (23%), G. barbadense (15.12%), and G. arboretum (11.66%). The matched genes are less than 2% in other close species (i.e. Durio zibethinus, Theobroma cacao, Corchorus olitorius, Herrania umbratica), and 1.78% of the unigenes did not match the protein sequences of other species (Fig. 2B), indicating the accuracy of RNA-Seq and some specificity of the cotton genes.
Fig. 2.
Reads distribution in the genome and natural species distribution of identified genes. A All the reads obtained were mapped to the cotton genome. Reads distribution in exon, intergenic, and intron regions were represented for ovules treatment with mock and TSA. B A total of 77,555 unigenes were annotated to the Nr protein database. For the species distribution, about 31,720 (47.92%), 17,814 (23%), 11,715 (15.12%), and 9030 (11.66%) unigenes were matched with Gossypium hirsutum, G. ramondii, G. barbadense and G. arboretum. The matched genes are less than 2% in other close species (i.e. Durio zibethinus, Theobroma cacao, Corchorus olitorius, Herrania umbratica)
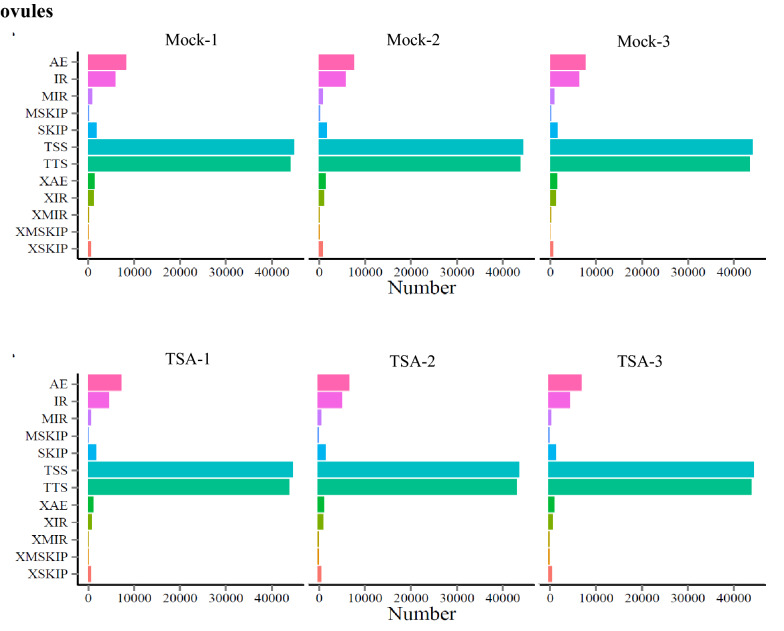
Alternative splicing (AS), generating distinct mRNA species and non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) from one primary transcript, functions as an additional regulatory mechanism for gene expression and function after transcription. This endows AS with the importance of bringing protein and function diversity from a definite gene [31]. The conserved AS events were identified and there were 12 types of AS events found across all the samples. Two types of ASs at the 5' first exon (TSS, transcription start site) and 3' last exon (TTS, transcription terminal site) are the most, followed by alternative exon ends (AE) at the 5' end, 3' end, or both and intron retention (IR) (Fig. 3), which indicates the various and complicated regulatory mechanisms of gene post-transcription.
Fig. 3.
Alternative splicing analysis of transcripts identified in Mock and TSA treated ovules. In the six libraries including mock and TSA treated, alternative splicing of the transcripts was analyzed. In total, 12 kinds of AS events were defined as follows, and the results showed that TSS and TSS are the dominant AS events identified. (1) TSS: Alternative 5’first exon (transcription start site); (2) TTS: Alternative 3’ last exon (transcription terminal site); (3) SKIP: Skipped exon (SKIP_ON, SKIP_OFF pair); (4) XSKIP: Approximate SKIP (XSKIP_ON, XSKIP_OFF pair); (5) MSKIP: Multi-exon SKIP (MSKIP_ON, MSKIP_OFF pair); (6) XMSKIP: Approximate MSKIP (XMSKIP_ON, XMSKIP_OFF pair); (7) IR: Intron retention (IR_ON, IR_OFF pair); (8) XIR: Approximate IR (XIR_ON, XIR_OFF pair); (9) MIR: Multi-IR (MIR_ON, MIR_OFF pair); (10) XMIR: Approximate MIR (XMIR_ON, XMIR_OFF pair); (11) AE: Alternative exon ends (5′, 3′, or both); (12) XAE: Approximate AE. X: exact boundary match for SKIP, approximate (simple exon overlap) for XSKIP; An exon skipping event as a pair between an exon containing (‘on’) splice form and an exon-skipping (‘off’) splice
Analysis of differentially expressed genes in ovules after TSA treatment
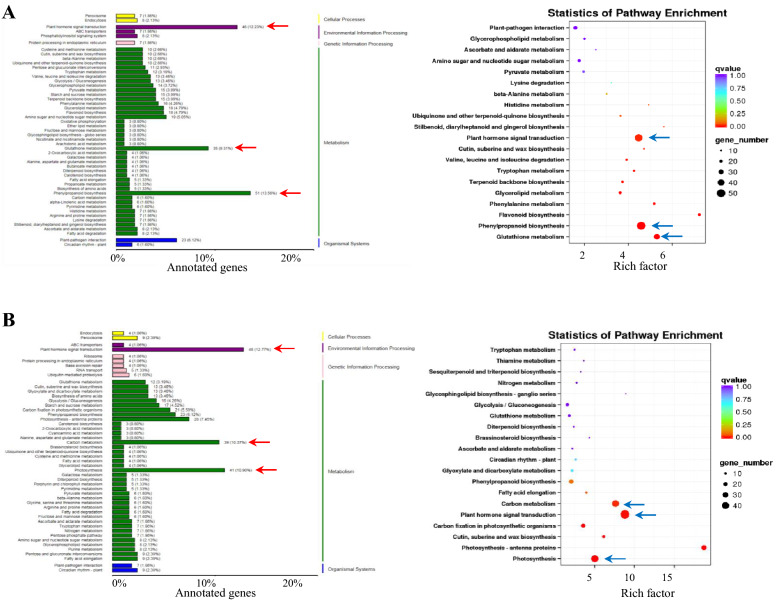
To explore the underlying mechanisms of TSA inhibiting fiber initiation, DEG were identified between mock and TSA-treated ovules. The MA plots showed that most genes did not change in transcription level (black plots); the numbers of up-regulated and down-regulated genes were similar with significant alteration of transcription (red and green plots) (Additional file 5: Fig. S2). In total, 4209 genes were identified with 2025 genes up-regulated and 2184 down-regulated in response to TSA. Among which, 4196 genes were annotated including 3980 known genes and 216 new genes (annotated), as well as 13 unknown genes (without annotation and locus) (Table 1 and Additional file 1: Table S1). To illuminate the potent causal pathways and key genes, KEGG enrichment pathway analysis was performed. The up-regulated genes were classified into 95 pathways among five categories: cell process, environmental information processing, genetic information processing, metabolism, and organismal systems. Of these five categories, the top 50 pathways were presented (Fig. 4A). Metabolism accounted for the largest proportion amongst the five categories. Furthermore, the plant hormone signal transduction (46 genes) and phenylpropanoid biosynthesis pathways (51 genes) showed the most genes observed. The statistical analysis of enrichment pathways showed the lowest q-value (red arrow) and their reliable enrichment significance (Fig. 4A). The down-regulated genes were classified into 97 pathways among five categories, and the top 50 pathways were represented. The plant hormone signal transduction (48 genes), photosynthesis (41 genes), and carbon metabolism pathways (39 genes) showed the most genes observed. The statistical analysis of the three enrichment pathways showed their lowest q-value (red arrow) and their reliable enrichment significance (Fig. 4B). The above results suggest that many genes related to plant hormone signal transduction may play important roles in the initial ovule and fiber development mediated by histone deacetylation. Moreover, up-regulated DEGs were also largely enriched in phenylpropanoid biosynthesis (Fig. 4A); while carbon metabolism and photosynthesis-related genes were enriched in the down-regulated genes (Fig. 4B), providing evidence that histone deacetylation functions upstream of diverse metabolism pathways in order to regulate fiber initiation.
Table 1.
The summary of differentially expressed genes in the ovules after TSA treatment
| Mock_vs_TSA | Gene numbers | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Total identified gene number | 77,691 | ||
| Total DEG Number | 4209 |
2025 (up-regulated) |
2184 (down-regulated) |
| Annotated genes | 4196 |
216 new genes (without loci) |
3980 known genes (with defined loci) |
| Unknown new gene | 13 | ||
Fig. 4.
KEGG analysis of up-and down-regulated genes after TSA treatment. KEGG analysis was performed and the differentially expressed genes were classified into five categories: cell process, environmental information processing, genetic information processing, metabolism, and organismal systems. The top 50 pathways were presented here. A Among the up-regulated genes, metabolism accounted for the largest proportion of all the categories. Furthermore, the plant hormone signal transduction (46 genes), glutathione metabolism (35 genes), and phenylpropanoid biosynthesis pathways (51 genes) showed the most genes (red arrows). The statistical analysis of enrichment pathways showing the lowest q-value of plant hormone signal transduction, carbon metabolism, and phenylpropanoid biosynthesis pathways also indicated the reliable enrichment significance (blue arrows). B In the down-regulated genes, plant hormone signal transduction (48 genes), photosynthesis (41 genes), and carbon metabolism pathways (39 genes) showed the most genes (red arrows). The statistical analysis of the three enrichment pathways showed their lowest q-value and the reliable significance of enrichment pathways (blue arrows). Statistics of pathway enrichment of DEGs were analyzed using Rich Factor and q-value. Circle size indicates the gene numbers of the different pathways, which is the ratio of differentially expressed gene numbers to all gene numbers in this pathway term. A larger size means a greater number of genes. Q-value is the corrected p-value ranging from 0 to 1, and a lower q-value means greater intensiveness
Phytohormones signal transduction play important roles in fiber initiation downstream of histone deacetylation
In total, 94 up-and down-regulated DEGs associated with hormone signal transduction were used to draw the heat map with the FPKM values in all the samples (Fig. 5 and Additional file 2: Table S2). The resulting heat map divided the DEGs into four classifications a, b, c, and d. In class a, the genes were significantly up-regulated in response to TSA treatment, while genes were significantly down-regulated in response to TSA treatment in class d. In classes b and c, the difference in transcription level is significantly less weak in ovules of Mock compared with TSA treatments. The FPKM values of each gene in class b were less than 6, while those in class c were greater than 8 (Additional file 3: Table S3).
Fig. 5.
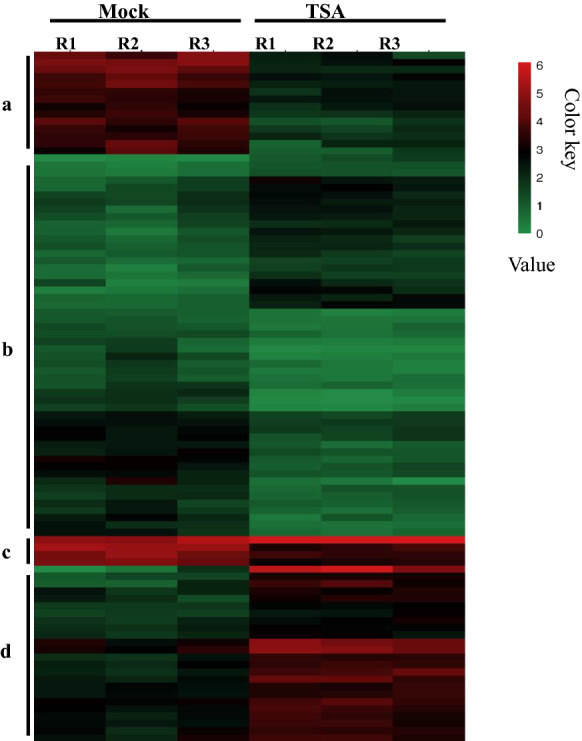
Heatmap of the 94 DEGs associated with hormonal pathways after TSA treatment. The heatmap of FPKM (fragments per kilobase of transcript per million reads mapped) of 94 DEGs associated with hormone signal transduction in three biological replicates of Mock and TSA treatment ovules. The DEGs were then divided into four groups (a–d) according to the expression profiles in ovules of mock and TSA treatments. a The genes significantly up-regulated in response to TSA treatment; b the genes that showed a weak difference with less FPKM values; c the genes that showed a weak difference with more FPKM values; d the genes significantly down-regulated in response to TSA treatment. Log10-transformed (FPKM + 1) expression values were used to create the heat map. The red and green colors represent the higher and lower relative abundance of each transcript in each sample, respectively
To understand the detailed hormonal pathways, we analyzed the up-and down-regulated genes. It is shown that most of the down-regulated genes are related with the auxin pathway. This includes small auxin up-regulated RNA (SAUR), INDOLE-3-ACETIC ACID INDUCIBLE (IAA), AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR (ARF), auxin receptor, and genes associated with IAA synthesis and homeostasis which accounts for about 65.4% of the down-regulated genes, indicating the positive role of auxin in fiber initiation (Table 2). Interestingly, among the up-regulated members, auxin-related genes (e.g., small auxin up-regulated RNA and auxin influx carrier), The JASMONATE-ZIM DOMAIN (JAZ)-like factors associated with JASMONIC ACID (JA), ABA associated genes (e.g., ABA receptors, signaling factors) account for 32.6%, 30.4%, and 15.2%, respectively. Furthermore, three GA receptors also showed clear up-regulated expression (Table 3). Auxin plays important positive roles in fiber initiation downstream of histone deacetylation, whereas some small auxin up-regulated RNA encoding genes and auxin influx carriers also play negative roles in fiber initiation. ABA pathways and JA inhibitory factor JAZ2 play negative roles in fiber initiation downstream of histone deacetylation similar to previous studies [32–34], which suggest that histone deacetylation plays a vital role in fiber initiation and earlier elongation through regulating various phytohormone signaling pathways.
Table 2.
Summary and identification of the down-regulated genes associated with phytohormone pathways in response to TSA treatment
| Gene ID | Gene name | Annotation | Regulated type | Fold change (Log2) | Associated pathway |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gh_A10G1020 | GhIAA3_A10 | INDOLE-3-ACETIC ACID INDUCIBLE 3 | Down | − 2.0372 | Auxin |
| Gh_D02G0405 | GhIAA4_D02 | INDOLE-3-ACETIC ACID INDUCIBLE 4 | Down | − 2.2086 | Auxin |
| Gh_A09G1945 | GhIAA4_A09 | Down | − 2.7903 | Auxin | |
| Gh_A02G0340 | GhIAA4_A02 | Down | − 1.5551 | Auxin | |
|
Gossypium_hirsutum _newGene_23351 |
GhIAA4_N | Down | − 1.0348 | Auxin | |
| Gh_D01G0947 | GhIAA4_D01 | Down | − 2.7321 | Auxin | |
| Gh_A02G0341 | GhIAA14_A02 | INDOLE-3-ACETIC ACID INDUCIBLE 14 | Down | − 1.1472 | Auxin |
| Gh_A11G1164 | GhIAA16_A11 | INDOLE-3-ACETIC ACID INDUCIBLE 16 | Down | − 2.6413 | Auxin |
| Gh_D05G0472 | GhIAA18_D05 | INDOLE-3-ACETIC ACID INDUCIBLE 18 | Down | − 3.8157 | Auxin |
| Gh_A05G0356 | GhIAA18_A05 | Down | − 1.5554 | Auxin | |
| Gh_A06G1644 | GhIAA19_A06 | INDOLE-3-ACETIC ACID INDUCIBLE 19 | Down | − 3.9605 | Auxin |
| Gh_D10G1512 | GhIAA19_D10 | Down | − 6.1937 | Auxin | |
| Gh_A05G1607 | GhIAA24_A05 | INDOLE-3-ACETIC ACID INDUCIBLE 24 | Down | − 1.319 | Auxin |
| Gh_D05G1792 | GhIAA24_D05 | Down | − 1.1334 | Auxin | |
| Gh_D11G1228 | GhIAA29_D11 | INDOLE-3-ACETIC ACID INDUCIBLE 29 | Down | − 1.8453 | Auxin |
| Gh_D11G0514 | GhGH3.1_D11 | ENCODING A PROTEIN SIMILAR TO IAA-AMIDO SYNTHASES GH3.1 | Down | − 2.4801 | Auxin |
| Gh_A11G1077 | GhGH3.3_A11 | ENCODING AN PROTEIN SIMILAR TO IAA-AMIDO SYNTHASES GH3.3 | Down | − 1.6851 | Auxin |
| Gh_D13G0668 | GhGH3-10_D13 | ENCODING AN PROTEIN SIMILAR TO IAA-AMIDO SYNTHASES GH3-10 | Down | − 2.692 | Auxin |
| Gh_A11G0443 | GhGH3-10_A11 | Down | − 2.0607 | Auxin | |
| Gh_A13G0480 | GhGH3-10_A13 | Down | − 1.2652 | Auxin | |
| Gh_D02G2216 | GhSAUR1_D02 | SMALL AUXIN UP-REGULATED RNA11 | Down | − 2.3625 | Auxin |
| Gh_D12G0291 | GhSAUR12_D12 | SMALL AUXIN UPREGULATED RNA12 | Down | − 2.747 | Auxin |
| Gh_A13G0578 | GhSAUR48_A13 | SMALL AUXIN UPREGULATED RNA48 | Down | − 1.0704 | Auxin |
| Gh_D12G0289 | GhSAUR52_D12 | SAUR52, SMALL AUXIN UPREGULATED RNA52 | Down | − 1.0695 | Auxin |
| Gh_D10G0616 | GhPAP1_D10 | PURPLE ACID PHOSPHATASE 1 | Down | − 1.998 | Auxin |
| Gh_A02G1156 | GhPAP2_A02 | PURPLE ACID PHOSPHATASE 2 | Down | − 1.7051 | Auxin |
| Gh_A05G1076 | GhPAP2_A05 | Down | − 1.289 | ||
| Gh_A03G1804 | GhLAX2_A03 | LIKE AUXIN RESISTANT 2 | Down | − 2.3804 | Auxin |
| Gh_D01G1617 | GhLAX2_D01 | Down | − 3.069 | Auxin | |
| Gh_A01G1374 | GhLAX2_A01 | Down | − 2.3246 | Auxin | |
| Gh_D09G1378 | GhTIR1_D09 | AUXIN RECEPTOR, TRANSPORT INHIBITOR RESPONSE 1 | Down | − 3.9574 | Auxin |
| Gh_D09G2152 | GhTIR1_D09 | Down | − 2.3805 | Auxin | |
| Gh_A12G1016 | GhARF11_A12 | AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR 11 | Down | − 1.6769 | Auxin |
| Gh_A07G1254 | GhARF18_A07 | AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR 18 | Down | − 1.345 | Auxin |
| Gh_Sca005214G02 | GhARR2_S | RESPONSE REGULATOR 2 | Down | − 1.8818 | Cytokinin |
| Gh_D05G2656 | GhARR7_D05 | RESPONSE REGULATOR 7 | Down | − 1.2673 | Cytokinin |
| Gh_A11G2364 | GhAHP5_A11 | HISTIDINE-CONTAINING PHOSPHOTRANSFER FACTOR 5 | Down | − 1.0153 | Cytokinin |
| Gh_A11G1389 | GhAHK2_A11 | HISTIDINE KINASE 2 | Down | − 1.151 | Cytokinin |
| Gh_D01G1042 | GhCYCD3;2_D01 | CYCLIN D3;2 | Down | − 2.2107 | Cytokinin |
| Gh_D05G0138 | GhTGA7_D05 | TGACG SEQUENCE-SPECIFIC BINDING PROTEIN 7 | Down | − 1.4757 | SA |
| Gh_A02G0775 | GhTGA7_A02 | Down | − 2.0558 | SA | |
| Gh_D12G1679 | GhTGA8_D12 | TGACG SEQUENCE-SPECIFIC BINDING PROTEIN 8 | Down | − 3.7153 | SA |
| Gh_A09G0903 | GhTGA9_A09 | TGACG SEQUENCE-SPECIFIC BINDING PROTEIN 9 | Down | 1.3068 | SA |
| Gh_A07G1202 | GhPIF3_A07 | PHYTOCHROME INTERACTING FACTOR 3 | Down | − 1.1952 | GA |
| Gh_D13G1847 | GhGID1C_D13 | GA INSENSITIVE DWARF1C | Down | − 1.7948 | GA |
| Gh_A05G0308 | GhHAB1_A05 | HYPERSENSITIVE TO ABA1, NEGATIVE IN ABA SIGNALING | Down | − 1.0137 | ABA |
| Gh_D01G1881 | GhBAK1_D01 | BRI1-ASSOCIATED RECEPTOR KINASE | Down | − 1.1379 | BR |
| Gh_D05G2975 | GhJAI3_D05 | JASMONATE-INSENSITIVE 3 | Down | − 1.8414 | JA |
Table 3.
Summary and identification of the up-regulated genes associated with phytohormone pathways in response to TSA treatment
| Gene ID | Gene name | ANNOTATION | Regulated type | Fold change (Log2) | Associated pathway |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gh_A01G1955 | GhAUX1_A01 | AUXIN RESISTANT 1 | Up | 1.26685 | Auxin |
| Gh_A05G3362 | GhGH3.17_A05 | ENCODING A PROTEIN SIMILAR TO IAA-AMIDO SYNTHASES GH3.17 | Up | 1.51936 | Auxin |
| Gossypium_hirsutum_newGene_7580 | GhGH3.6_N | ENCODING A PROTEIN SIMILAR TO IAA-AMIDO SYNTHASES GH3.17 | Up | 1.49656 | Auxin |
| Gh_D08G1987 | GhGH3.7_D08 | ENCODING A PROTEIN SIMILAR TO IAA-AMIDO SYNTHASES GH3.17 | Up | 1.48741 | Auxin |
| Gh_A06G0351 | GhLAX3_A06 | LIKE AUX1 3 | Up | 1.23712 | Auxin |
| Gh_A03G1990 | GhSAUR34_A03 | SMALL AUXIN UP-REGULATED RNA34 | Up | 1.10734 | Auxin |
| Gh_D03G1541 | GhSAUR34_D03 | Up | 1.33354 | Auxin | |
| Gh_D08G1114 | GhSAUR31_D08 | SMALL AUXIN UP-REGULATED RNA31 | Up | 1.02448 | Auxin |
| Gh_A12G2237 | GhSAUR31_A12 | Up | 2.45374 | Auxin | |
| Gh_D13G2504 | GhSAUR49_D13 | SMALL AUXIN UP-REGULATED RNA49 | Up | 1.49511 | Auxin |
| Gh_A03G1766 | GhSAUR50_A03 | SMALL AUXIN UP-REGULATED RNA50 | Up | 2.5748 | Auxin |
| Gh_D12G2759 | GhSAUR55_D12 | SMALL AUXIN UP-REGULATED RNA55 | Up | 1.99109 | Auxin |
| Gh_D08G2457 | GhSAUR72_D08 | SMALL AUXIN UP-REGULATED RNA55 | Up | 1.0073 | Auxin |
| Gh_D08G1506 | GhSAUR59_D08 | SMALL AUXIN UP-REGULATED RNA55 | Up | 1.68807 | Auxin |
| Gh_D02G2199 | GhSAUR8_D02 | SMALL AUXIN UP-REGULATED RNA55 | Up | 2.19574 | Auxin |
| Gh_A08G2199 | GhJAZ1_A08 | JASMONATE-ZIM-DOMAIN PROTEIN 1 | Up | 1.82836 | JA |
| Gh_D08G2564 | GhJAZ1_D08 | Up | 1.7424 | JA | |
| Gh_A05G0260 | GhJAZ1_A05 | Up | 1.79396 | JA | |
| Gh_D05G0352 | GhJAZ1_D05 | Up | 1.93514 | JA | |
| Gh_D06G0810 | GhJAZ1_D06 | Up | 1.09472 | JA | |
| Gh_D02G1776 | GhJAZ10_D02 | JASMONATE-ZIM-DOMAIN PROTEIN 10 | Up | 2.0817 | JA |
| Gh_D01G0196 | GhJAZ10_D01 | Up | 1.39144 | JA | |
| Gh_A03G1341 | GhJAZ10_A03 | Up | 2.58634 | JA | |
| Gh_A01G0153 | GhJAZ10_A01 | Up | 5.02041 | JA | |
| Gh_A05G1155 | GhJAZ6_A05 | JASMONATE-ZIM-DOMAIN PROTEIN 6 | Up | 1.10218 | JA |
| Gh_D10G0531 | GhJAZ6_D10 | Up | 1.29964 | JA | |
| Gh_A12G2172 | GhMYC4_A12 | A BHLH TRANSCRIPTIONAL REGULATOR INTERACTING WITH JAZ | Up | 2.22509 | JA |
| Gh_D02G0731 | GhCOI1_D02 | CORONATINE INSENSITIVE 1 | Up | 1.71994 | JA |
| Gh_D01G1903 | GhTGA10_D01 | TGACG SEQUENCE-SPECIFIC BINDING PROTEIN 10 | Up | 1.86541 | SA |
| Gh_A12G0274 | GhPR1_A12 | PATHOGENESIS-RELATED GENE 1 | Up | 5.6104 | SA |
| Gh_A10G0769 | GhBZIP_A10 | BASIC LEUCINE-ZIPPER | Up | 1.53952 | SA |
| Gh_A12G2380 | GhAHG1_A12 | ABA-HYPERSENSITIVE GERMINATION 1 | Up | 1.23584 | ABA |
| Gh_D10G2388 | GhPYL5_D10 | PYRABACTIN RESISTANCE 1-LIKE 5 | Up | 1.73882 | ABA |
| Gh_A10G2142 | GhPYR5_A10 | Up | 1.10077 | ABA | |
| Gh_D11G0290 | GhPYR1_D11 | PYRABACTIN RESISTANCE 1-LIKE 1 | Up | 1.26703 | ABA |
| Gh_A06G1418 | GhPYR6_A06 | PYRABACTIN RESISTANCE 1-LIKE 6 | Up | 2.40182 | ABA |
| Gh_A05G1922 | GhSRK2C_A05 | SNF1-RELATED PROTEIN KINASE 2C | Up | 1.12806 | ABA |
| Gh_D11G3472 | GhSRK2E_D11 | SNF1-RELATED PROTEIN KINASE 2E | Up | 1.53833 | ABA |
| Gh_A08G1649 | GhGID1_A08 | GA INSENSITIVE DWARF1 | Up | 1.44491 | GA |
| Gh_D11G1242 | GhGID1B_D11 | GA INSENSITIVE DWARF1B | Up | 1.19774 | GA |
| Gh_D08G1981 | GhGID1B_D08 | Up | 1.55219 | GA | |
| Gh_D13G0548 | GhBAK1_D13 | BRI1-ASSOCIATED RECEPTOR KINASE | Up | 2.87103 | BR |
| Gh_A01G0972 | GhBKI_A01 | BRI1 KINASE INHIBITOR 1 | Up | 1.94267 | BR |
| Gh_A10G0769 | GhBZIP_A10 | BASIC LEUCINE-ZIPPER | Up | 1.53952 | SA |
| Gh_D02G0430 | GhERF1_D02 | ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR 1 | Up | 2.85319 | Ethylene |
| Gh_Sca115107G01 | GhERF1B | ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR 1B | Up | 3.76382 | Ethylene |
| Gh_A01G0218 | GhARR2_A01 | RESPONSE REGULATOR 2 | Up | 1.2164 | cytokinin |
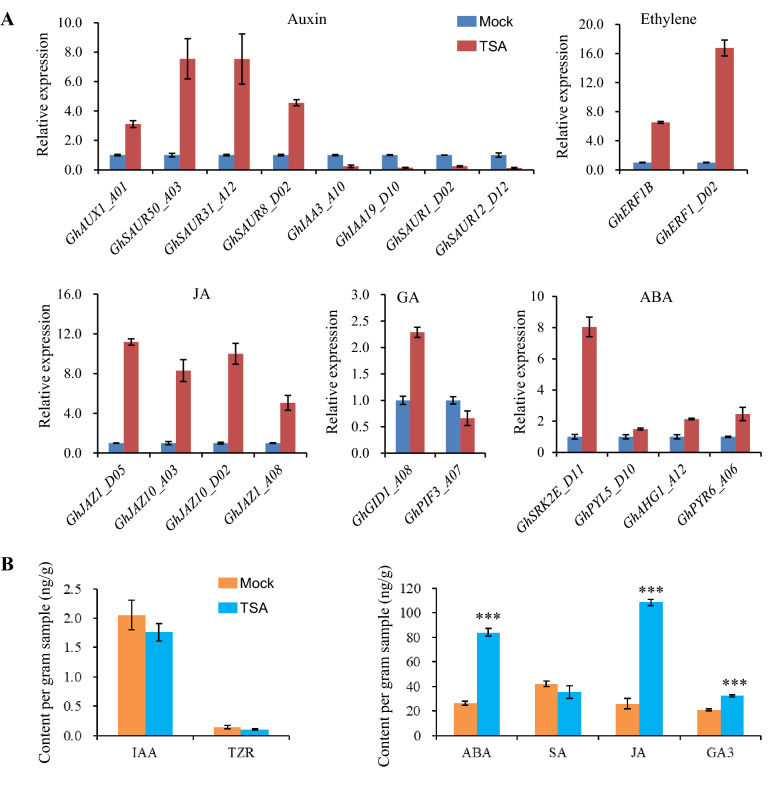
Moreover, some key genes' transcription expression in phytohormone pathways were validated in TSA-treated ovules with quantitative PCR (Fig. 6A). The results showed that some genes such as GhIAA3_A10, GhIAA19_D10, GhSAUR1_D02, and GhSAUR12_D12 were significantly down-regulated, while some genes, including GhAUX1_A01, GhSAUR50_A03, GhSAUR31_A12, and GhSAUR8_D02 were clearly up-regulated in the auxin signaling pathway. Two ethylene response factors GhERF1B and GhERF1_D02, as well as four negative regulators in the JA pathway- JAZ protein-coding genes GhJAZ1_A08/D05 and GhJAZ10_A03/D02 showed obvious up-regulation. Two factors in the gibberellin (GA) pathways GhGID1_A08 and GhPIF3_A07 showed up-and down-regulation respectively in TSA-treated ovules. Four abscisic acids (ABA) signaling genes GhSRK2E_D11, GhPYL5_D10, GhPYL6_A06, and GhAHG1_A12 showed significant up-regulation in response to TSA treatment. Simultaneously, we further detected different hormone contents in TSA-treated ovule. Compared to mock, TSA significantly promoted the accumulation of ABA, JA and GA3, while inhibiting the synthesis of IAA and not influencing SA and TZA contents significantly (Fig. 6B). All the results point to the regulation of different plant hormones by histone deacetylation in fiber initiation and elongation.
Fig. 6.
Verification of some key genes transcription associated with TSA and determination of phytohormones content in response to TSA during fiber initiation. A The expression profiles of key genes associated with phytohormone pathways were determined in the mock and TSA-treated ovules by RT-qPCR. All the expression levels were normalized to UBQ7, the gene was then expressed as a ratio relative to mock, which was set to a value of 1. Primers are listed in the Additional file 4: Table S4. B Different plant hormone levels were determined in TSA-treated ovules of − 1 DPA culture for 5 days. Error bars indicated SD (standard deviation) of three biological replicates
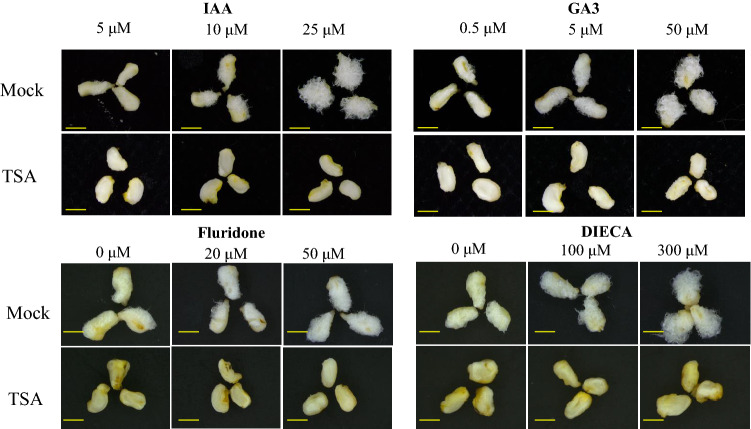
To verify the important role of phytohormones in regulating fiber initiation and elongation, the ovules of −2 DPA were incubated in modified BT- mediums without GA3 or IAA, supplemented with 20 μM ABA or Methyl Jasmonate (MeJA) of different concentrations (0.05, 0.5, and 5 μM) for 7 or 14 days in vitro. The results show that both fiber initiation and development are severely inhibited when GA3 or IAA is deficient, especially for GA3. Similarly, no fiber initiated after 7 days of culture, and little fiber was present after 14 days in response to 20 μM ABA (Additional file 5: Fig. S3A). However, in the medium containing MeJA, the fibers were longer than that in the mock medium. Among the different concentrations, 0.05 μM MeJA promoted fiber elongation most effectively (Additional file 5: Fig. S3B). These results demonstrate the positive regulation of GA, auxin and MeJA, and the inhibitory effect of ABA on fiber initiation and development. To further verify the effect of TSA on these hormones during fiber development, we supplemented different concentration gradients of IAA (5, 10, 25 μM), GA3 (0.5, 5, 50 μM), Fluridone (an inhibitor of ABA biosynthesis, 0, 20, 50 μM), and sodium diethyldithiocarbamate (DIECA, an inhibitor of jasmonic acid synthesis, 0, 100, 300 μM) into the BT medium containing 10 μM TSA. After 5 days, we observed that IAA, GA3, Fluridone, and DIECA promoted fiber elongation dependent on the concentrations in BT medium without TSA, while not restoring any inhibitory phenotype of TSA on fiber development when 10 μM TSA was supplied (Fig. 7). These results suggest that TSA inhibits fiber initiation by regulating different phytohormone pathways such as IAA, GA3, ABA and MeJA.
Fig. 7.
TSA inhibits the promotion on fiber initiation of IAA and GA3 and the inhibitors of ABA and MeJA. Ovules of −1 DPA (days post anthesis) were cultured in BT medium supplemented with 10 μM DMSO (mock) or TSA for 5 days in vitro, and these media contained different concentration gradients of IAA (5,10,25 μM), GA3 (0.5, 5, 50 μM), Fluridone (0, 20, 50 μM) and DIECA (0, 100, 300 μM), Bar = 1 mm
Discussion
Cotton fiber is one of the most important products worldwide and the model for cell differentiation and elongation study [35]. Lots of research has been carried out to clarify the underlying mechanism of fiber development, and many important genes have been found to be involved in the different pathways to regulate fiber cell initiation, elongation, secondary cell wall deposition, and maturation [6, 32, 36]. Among the pathways involved in fiber development, histone (de)acetylation is one of the important epigenetic modifications found to be playing a crucial role. One such role is observed by the HDA5 gene, which was identified as a key histone deacetylase in fiber initiation [6, 37]. In total, eighteen HATs and thirty HDACs have been identified from G. hirsutum [6, 38]. However, the detailed roles of different HATs or HDACs and the associated regulatory networks remain unclear.
HDACi-TSA represses the fiber initiation and earlier elongation significantly
Due to the important roles of histone acetylation in eukaryotes development, HDACi, which can repress histone deacetylation, has been applied in eukaryote development studies and disease therapies [5, 21, 27–29]. The application of TSA in the In vitro culture of ovules has also showed its repressive role in fiber differentiation [6]. Here, we used TSA in the in vitro culture of ovules before and after anthesis, and the results showed that TSA inhibits the fiber cell initiation, as well as the primary elongation (Fig. 1). These findings indicate that histone acetylation plays a significant role in fiber development and moved us to explore the underlying mechanisms, thereby an RNA-Seq was made using the ovules treated with TSA and Mock.
DEGs analysis in the ovule after TSA treatment through RNA-Seq
From the libraries, a total of 77,691 genes were identified, which is very close to the total genes in the entire genome and indicates a greater library quality. Analysis of the mapped sequence reads showed that about 23% of reads were of the mapped intergenic and intron regions, which implied that some novel genes were identified from the libraries of ovules. The alternative splicing analysis of transcripts displayed that TSS and TTS types are the most AS types in cotton, which is what has been observed in previous studies [39–41]. In Arabidopsis and rice, ‘intron retention’ was the prevalent type [40, 42, 43]. By contrast, ‘exon skipping’ is the most dominant pattern in humans and yeast [39, 41], which proposed that AS varies during eukaryote evolution.
The DEGs in response to TSA treatment were identified to illuminate the underlying mechanism of fiber initiation involved by histone deacetylation. In total, 4209 DEGs including 229 new genes consisting of 216 annotated genes and 13 genes without annotation and locus information were found, which implies that the public genome data is still not perfect and more advanced technology of assembly is necessary. A KEGG analysis was then operated and the results showed that plant hormone signal transduction, phenylpropanoid biosynthesis, and glutathione metabolism are the most enriched groups in up-regulated genes. In contrast, plant hormone signal transduction, carbon metabolism, and photosynthesis are the most enriched groups in down-regulated genes (Fig. 4). Phenylpropanoid pathway is associated with flavonoid biosynthesis, which competes with the fatty acid pathway for malonyl-CoA [44, 45], and the fatty acid metabolism mediates fiber development [46, 47]. Moreover, a previous study demonstrated that flavonoid naringenin is negatively associated with fiber development and that the flavonoid metabolism mediated by flavanone 3-hydroxylase is important in fiber development [48], which is in agreement with our findings and provides clues for the underlying mechanism associated with flavonoid biosynthesis regulated by histone deacetylation. Glutathione (GSH), an α-amino acid and a tripeptide, functions as a molecule that protects cells against oxidation through providing the cell with its reducing milieu which maintains various cellular components including enzymes in a reduced state. Furthermore, glutathione also functions as a storage and transport form of cysteine moieties [49, 50]. Cysteine is an important intermediate of sulfur metabolism in plants and functions as the reduction state of sulfite, which is reduced by the enzyme APS reductase and the cysteine synthase complex, as a result of the interaction of the enzymes serine acetyltransferase and O‐acetylserine‐(thiol)‐lyase, in order to control flux through the pathway [51–53]. Therefore, the up-regulated phenylpropanoid biosynthesis and glutathione metabolism indicate that the fatty acid pathway and sulfur metabolism are involved in the fiber initiation regulation which is at least partially dependent on histone acetylation, which supports the previous studies as well as provides novel clues for fiber cell development studies [46, 47].
Carbon metabolism and photosynthesis are closely related and control the energy production, transport, and application in the life cycle of plants [54–56]. The repressed carbon metabolism and photosynthesis after TSA treatment led to attenuated energy metabolism in the ovules, which is consistent with the retarded fiber development. More interestingly, the phytohormone signal transduction was enriched in both up-and down-regulated pathways, indicating that different hormones may be involved in the fiber development downstream of histone deacetylation, which is also in line with the previous studies [36, 57, 58].
Histone deacetylation functions upstream of the phytohormones to regulate fiber development
Many studies have shown that phytohormones such as auxin, GA, ethylene, cytokinin (CK), brassinosteroids (BR), and ABA play important roles in fiber development [35, 36, 57, 59]. Our RNA-Seq results supported the roles of phytohormones and provided some potential regulatory mechanisms associated with histone acetylation modification. The intensive analysis of the hormone pathway revealed that 49 auxin pathway-related genes showed differential expression. This included 34 up-regulated and 15 down-regulated genes after TSA treatment, illustrating the dominant role of auxin in the fiber development of cotton which supports the pivotal role of auxin in fiber cell initiation [60]. In Arabidopsis, HDA6, HDA9, and HDA19 have shown the regulatory roles in transcription expression of AUX1 and some ARFs through histone deacetylation modification which regulate the auxin pathway, seed germination, and valve cell elongation [61, 62]. Some IAAs are also regulated by histone deacetylation to respond to aberrant ambient light and temperature of the plant [63, 64]. Here, GhAUX1_A01 and some GhSAURs (e.g., GhSAUR50_A03, GhSAUR31_A12, and GhSAUR8_D02) exhibited up-regulation indicating the potential auxin import and accumulation of non-fiber cells. Inversely, the down-regulation of GhIAAs and GhSAURs and resulting decreased IAA content, hints at the conceivable repression of auxin signal in fiber cells, which inhibits the fiber initiation downstream of histone deacetylation. Interestingly, auxin has been shown to be the key role in the fiber cell initiation through the proper spatiotemporal accumulation and distribution, in which the auxin efflux carrier PIN3 plays an important positive role [65]. Moreover, CK inhibits the non-fiber-localized protein GhPIN3a and damages the normal auxin concentration gradient, negatively impacting fiber cell initiation [58, 60]. All this suggests that different auxin pathway genes involved in auxin synthesis, transport, and signaling play distinct roles in fiber development, and auxin partially promotes fiber cell initiation through histone acetylation regulation.
As an important hormone in plant development and abiotic stress tolerance, ABA also exhibits a negative role in fiber cell development [32, 34, 35, 57], although the underlying mechanism is ambiguous. Here, all the identified ABA pathway genes encoding receptors and signaling factors except HAB1 (a negative regulator in ABA signaling), as well as ABA content were all significantly up-regulated leading to its negative function in fiber initiation and offering the potential epigenetic mechanism upstream of the ABA pathway. JAZ2 is a key negative regulator in cotton fiber initiation [32] and some of its homologues (e.g., GhJAZ1_A08/D05 and GhJAZ10_A03/D02) showed higher expression after TSA treatment, which was consistent with the increased JA accumulation and supported the negative role of JAZ in fiber initiation and providing clues between histone deacetylation and JA pathway in fiber initiation. In contrast, the GA receptor gene GhGID1_A08 displayed a significant up-regulation, matching the increased GA content in response to TSA. These results implied that TSA might suppress GA signaling through some genes such as GhPIF3_A07 in fiber initiation, and also raised some clues about the relationship between phytohormones and epigenetic modifications in fiber development. In order to further confirm the effect of histone deacetylation on fiber development, we used another histone deacetylation inhibitor-diallyl disulfide (DADS) [28], which inhibited fiber initiation and even considerably affected ovule development similar to TSA (Additional file 5: Fig. S4). However, the relationship between phytohormones and different secondary metabolism/carbon metabolisms still needs much more work.
Conclusions
In short, we highlighted that histone deacetylation inhibitor-trichostatin A (TSA) represses the fiber cell initiation and elongation of cotton in in vitro cultures, indicating the crucial roles of histone deacetylation in cell differentiation and development. RNA-Seq revealed that there are 2025 up-regulated genes associated with plant hormone signal transduction and phenylpropanoid biosynthesis, and 2184 down-regulated genes associated with plant hormone signal transduction, photosynthesis, and carbon metabolism, in response to TSA treatment. Further studies showed that TSA repressed auxin, GA, and JA signaling, while promoting ABA signaling in order to inhibit fiber cell initiation and earlier elongation. Phytohormones play versatile roles in plant development, including the development of fiber. Our work demonstrated that histone deacetylation contributes a great deal to the signaling of different phytohormones in fiber initiation, which is very helpful for us to understand the detailed molecular mechanisms of phytohormone pathway regulation and fiber development.
Materials and methods
In vitro culture and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis of cotton ovules
Cotton cultivar ZM24 (also known as CCRI24), obtained from the Institute of Cotton Research, the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences were grown under field conditions in Zhengzhou China for the following study [66]. Flowers were harvested at − 2 and 0 days post-anthesis (DPA), and ovaries were surface sterilized by using 75% ethanol. Ovules were carefully dissected from the ovaries under sterile conditions and immediately floated on liquid BT media supplemented with optimized concentrations of phytohormones including IAA (Sigma-Aldrich, I2886), GA3 (Sigma, G7645), ABA (Sigma, A1049), MeJA (Sigma-Aldrich, 392707) as well as Fluridone (A inhibitor for ABA synthesis, Supelco, 45511) and DIECA (A inhibitor for MeJA synthesis, Sigma-Aldrich, 228680). In addition, various concentrations of TSA and DADS (Sigma-Aldrich, SMB00378) were included in culture plates [67]. The ovules were then incubated at 32 °C in the dark without agitation, and TSA (Millipore, 647925) were dissolved in 95% DMSO to make a 1 mM stock solution. Fiber development for all cultural ovules was analyzed after the indicated time of incubation by SEM (Hitachi SU3500). Moreover, the cultured ovules with different times were frozen in liquid nitrogen or at − 80 °C for the following experiments.
Library preparation, RNA-Seq, and data analysis
Total RNA was extracted from the −2 DPA ovules after 6 days of in vitro culture with TSA and the mock. RNA quantification, qualification, and RNA concentration was measured using NanoDrop 2000 (Thermo). RNA integrity was assessed with the RNA Nano 6000 Assay Kit of the Agilent Bioanalyzer 2100 system (Agilent Technologies, CA, USA).
A total amount of 1 μg RNA per sample was used as input material for the library construction. Sequencing libraries were generated using NEBNext UltraTM RNA Library Prep Kit for Illumina (NEB, USA) following manufacturer’s recommendations by Beijing Biomarker Technologies Co., Ltd (Beijing, China). Six libraries including three biological repeats for each sample were used for the RNA-Seq. Clean data in Illumina sequencing was obtained by removing the containing adapter, containing ploy-N and low quality reads from raw data. Only reads with a perfect match or one mismatch were further analyzed and annotated based on the reference genome. Hisat2 tools was used to map with reference TM-1 (AD1) genome NAU-NBI (Nanjing Agricultural University-Novogene Bioinformatics Technology) assembly v1.1 and annotated v1.1 (https://www.cottongen.org) [68]. The raw data can be accessible from the following BioProject ID: PRJNA733691 in the NCBI SAR database.
Alternative splicing was analyzed with the non-redundant transcript sequences, which were directly used to run all-vs-all BLAST with high identity settings. BLAST alignments that met all criteria were considered products of the candidate AS events: (1) both sequence lengths exceeded 1000 bp and the alignment contained 2 high-scoring segment pairs (HSPs); (2) the alternative splicing gap exceeded 100 bp and was located ≥ 100 bp from the 3′/5′ end; and (3) a 5-bp overlap was allowed for all alternative transcripts.
Gene function was annotated against the databases NR (NCBI non-redundant protein sequences), Nt (NCBI non-redundant nucleotide sequences), Pfam (Protein family) [69], KOG/COG (Clusters of Orthologous Groups of proteins), Swiss-Prot (A manually annotated and reviewed protein sequence database), KO (KEGG Ortholog database) and GO (Gene Ontology) [70].
GATK2 or Samtools software was used to perform SNP calling. Raw vcf files were filtered with GATK standard filter method and other parameters (cluster WindowSize: 10; MQ0 > = 4 and (MQ0/(1.0*DP)) > 0.1; QUAL < 10; QUAL < 30.0 or QD < 5.0 or HRun > 5), and only SNPs with distance > 5 were retained. Quantification of gene expression levels was estimated by fragments per kilobase of transcript per million fragments mapped. The formula is shown as follow:
Differential expression analysis and KEGG pathway enrichment analysis
Differential expression analysis of two samples (Mock and TSA treatments) was performed using the DEseq [71]. Genes with at least twofold change and an adjusted P-value < 0.01 established by DEseq were assigned as differentially expressed. KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) database and KOBAS software were used to test the statistical enrichment of differential expression genes [72, 73].
RNA extraction and qRT–PCR
Total RNA from cotton ovules was extracted using the Qiagen RNeasy kit and RNAqueous small-scale phenol-free total RNA isolation kit (Ambion) according to the manufacturer’s instructions and reverse transcribed using the SuperScript RT-PCR system (Invitrogen). The qRT-PCR for each gene was performed in three biological replicates using the KAPA SYBR FAST qPCR Kits (KAPA) and the expression value was quantified and normalized to the value of UBIQUITIN 7 [32]. Mean values and standard errors for each gene were calculated from three biological replicates. Primers are listed in Additional file 4: Table S4.
Assays of the different phytohormones in ovules after TSA treatments
Ovules of −1 DPA (days post anthesis) were cultured in BT medium supplemented with 10 μM DMSO (mock) or TSA in vitro. Samples of 200–500 mg were collected after 5 days of culture and ground into fine powder in liquid nitrogen. Contents of the Plant hormones IAA, TZR, ABA, SA, JA and GA3 were determined by high performance liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry (HPLC–MS/MS) (KC SEQHEALTH, Wuhan). The ground sample was mixed with acetonitrile solution (v/v), each containing 20 ng deuterium-labeled internal standard. Extracted at 4 ℃ overnight, then centrifugation at 12,000g for 5 min and the supernatant was taken. The precipitate was added to acetonitrile solution again, and combined to obtain the supernatant. A C18 Sep-Pak column was added and violently shaken for 30 s, and then the supernatant was taken. Purified extract was dried with nitrogen gas and redissolved with 100% methanol. The supernatant was transferred into the HPLC vials and subjected to liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC–MS) analysis on a SCIEX-6500QTRAP LC/MS/MS system, equipped with an ESI Turbo Ion-Spray interface.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Table S1. The gene ID list of 4,209 DEGs identified between mock and TSA-treated ovules.
Additional file 2: Table S2. The gene ID list of 94 up-and down-regulated DEGs associated with hormone signal transduction after TSA treatment.
Additional file 3: Table S3. The FPKM values of each gene in classifications a, b, c, and d.
Additional file 4: Table S4. The Q-PCR primers used in this study.
Additional file 5: Fig. S1. Application of TSA repress fiber elongation after long-term in vitro culture. Fig. S2. MA plot analysis of DEGs in the ovules. Fig. S3. Phenotypic observation on initiation and elongation of cultured fibrocytes in vitro under different hormones. Fig. S4. Phenotype of cultured fibrocytes in vitro treated with diallyl disulfide.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the participants in this study. We also would like to thank Elizabeth Tokarz at Yale University for her assistance with English language and grammatical editing.
Abbreviations
- ABA
Abscisic Acid
- AE
Alternative exon ends
- ARF
Auxin response factor
- AS
Alternative splicing
- BR
Brassinosteroids
- CK
Cytokinin
- DEGs
Differentially expressed genes
- DPA
Days post-anthesis
- GA
Gibberellic Acid
- GO
Gene Ontology
- GSH
Glutathione
- HATs
Histone acetyltransferases
- HDACs
Histone deacetylases
- HDACi
HDAC inhib HDAC inhibitors
- IAA
Indole-3-acetic acid inducible
- IR
Intron retention
- JA
Jasmonic Acid
- JAZ
Jasmonate-zim domain
- KEGG
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
- KO
KEGG Ortholog database
- KOG/COG
Clusters of Orthologous Groups of proteins
- MeJA
Methyl Jasmonate
- NcRNAs
Non-coding RNAs
- NR
NCBI non-redundant protein sequences
- Nt
NCBI non-redundant nucleotide sequences
- Pfam
Protein family
- SA
Salicylic acid
- SAHA
Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid
- SEM
Scanning electron microscopy
- Swiss-Prot
A manually annotated and reviewed protein sequence database
- TSA
Trichostatin A
- TSS
Transcription start site
Author contributions
ZWang and YX: Conceptualization, funding acquisition, methodology, data curation, writing—original draft and review and editing. ZWei, YL: Methodology, data curation, writing—review and editing. FA and YW: Writing—review and editing. ZY: Investigation. JL and FL: Resources. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32072022), the Creative Research Groups of China (31621005), Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund (1610162020010202), and Hainan Yazhou Bay Seed Laboratory (B21HJ0215).
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
I declare on behalf of my co-authors that no conflict of interest exists in the submission of this manuscript which is approved by all authors.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Zhenzhen Wei and Yonghui Li contributed equally to this work
Contributor Information
Yadi Xing, Email: xingyadi@zzu.edu.cn.
Fuguang Li, Email: aylifug@caas.cn.
References
- 1.Gan L, Wei Z, Yang Z, Li F, Wang Z. Updated mechanisms of GCN5-the monkey king of the plant kingdom in plant development and resistance to abiotic stresses. Cells. 2021 doi: 10.3390/cells10050979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Geng YK, Zhang PX, Liu Q, Wei ZW, Riaz A, Chachar S, et al. Rice homolog of Sin3-associated polypeptide 30, OsSFL1, mediates histone deacetylation to regulate flowering time during short days. Plant Biotechnol J. 2020;18(2):325–327. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hu Y, Lu Y, Zhao Y, Zhou DX. Histone acetylation dynamics integrates metabolic activity to regulate plant response to stress. Front Plant Sci. 2019;10:1236. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.01236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Huang F, Yuan WY, Tian S, Zheng QJ, He YH. SIN3 LIKE genes mediate long-day induction of flowering but inhibit the floral transition in short days through histone deacetylation in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2019;100(1):101–113. doi: 10.1111/tpj.14430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kirfel P, Skaljac M, Grotmann J, Kessel T, Seip M, Michaelis K, et al. Inhibition of histone acetylation and deacetylation enzymes affects longevity, development, and fecundity in the pea aphid (Acyrthosiphon pisum) Arch Insect Biochem. 2020 doi: 10.1002/arch.21614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kumar V, Singh B, Singh SK, Rai KM, Singh SP, Sable A, et al. Role of GhHDA5 in H3K9 deacetylation and fiber initiation in Gossypium hirsutum. Plant J. 2018;95(6):1069–1083. doi: 10.1111/tpj.14011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Marks P, Rifkind RA, Richon VM, Breslow R, Miller T, Kelly WK. Histone deacetylases and cancer: causes and therapies. Nat Rev Cancer. 2001;1(3):194–202. doi: 10.1038/35106079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ng HH. Bird A Histone deacetylases: silencers for hire. Trends Biochem Sci. 2000;25(3):121–126. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)01551-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Wang Z, Cao H, Chen F, Liu Y. The roles of histone acetylation in seed performance and plant development. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2014;84:125–133. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2014.09.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Johnson CA, Turner BM. Histone deacetylases: complex transducers of nuclear signals. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 1999;10(2):179–188. doi: 10.1006/scdb.1999.0299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kolle D, Brosch G, Lechner T, Pipal A, Helliger W, Taplick J, et al. Different types of maize histone deacetylases are distinguished by a highly complex substrate and site specificity. Biochemistry. 1999;38(21):6769–6773. doi: 10.1021/Bi982702v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lechner T, Lusser A, Pipal A, Brosch G, Loidl A, Goralik-Schramel M, et al. RPD3-type histone deacetylases in maize embryos. Biochemistry. 2000;39(7):1683–1692. doi: 10.1021/bi9918184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lusser A, Brosch G, Loidl A, Haas H, Loidl P. Identification of maize histone deacetylase HD2 as an acidic nucleolar phosphoprotein. Science. 1997;277(5322):88–91. doi: 10.1126/science.277.5322.88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wu KQ, Tian LN, Malik K, Brown D, Miki B. Functional analysis of HD2 histone deacetylase homologues in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2000;22(1):19–27. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2000.00711.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.An XL, Wei ZK, Ran BT, Tian H, Gu HY, Liu Y, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A suppresses cell proliferation and induces apoptosis by regulating the PI3K/AKT signalling pathway in gastric cancer cells. Anti-Cancer Agent Me. 2020;20(17):2114–2124. doi: 10.2174/1871520620666200627204857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sarkar R, Banerjee S, Amin SA, Adhikari N, Jha T. Histone deacetylase 3 (HDAC3) inhibitors as anticancer agents: a review. Eur J Med Chem. 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Bolden JE, Peart MJ, Johnstone RW. Anticancer activities of histone deacetylase inhibitors. Nat Rev Drug Discovery. 2006;5(9):769–784. doi: 10.1038/nrd2133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Dokmanovic M, Marks PA. Prospects: histone deacetylase inhibitors. J Cell Biochem. 2005;96(2):293–304. doi: 10.1002/jcb.20532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Miller TA, Witter DJ, Belvedere S. Histone deacetylase inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2003;46(24):5097–5116. doi: 10.1021/jm0303094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Rasheed WK, Johnstone RW, Prince HM. Histone deacetylase inhibitors in cancer therapy. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2007;16(5):659–678. doi: 10.1517/13543784.16.5.659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Belvedere S, Witter DJ, Yan J, Secrist JP, Richon V, Miller TA. Aminosuberoyl hydroxamic acids (ASHAs): a potent new class of HDAC inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2007;17(14):3969–3971. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2007.04.089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Yoon S, Eom GH. HDAC and HDAC inhibitor: from cancer to cardiovascular diseases. Chonnam Med J. 2016;52(1):1–11. doi: 10.4068/cmj.2016.52.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Duvic M, Talpur R, Ni X, Zhang C, Hazarika P, Kelly C, et al. Phase 2 trial of oral vorinostat (suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid, SAHA) for refractory cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) Blood. 2007;109(1):31–39. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-06-025999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Richon VM, Emiliani S, Verdin E, Webb Y, Breslow R, Rifkind RA, et al. A class of hybrid polar inducers of transformed cell differentiation inhibits histone deacetylases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95(6):3003–3007. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.6.3003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Dokmanovic M, Clarke C, Marks PA. Histone deacetylase inhibitors: overview and perspectives. Mol Cancer Res. 2007;5(10):981–989. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-07-0324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kaushik D, Vashistha V, Isharwal S, Sediqe SA, Lin MF. Histone deacetylase inhibitors in castration-resistant prostate cancer: molecular mechanism of action and recent clinical trials. Ther Adv Urol. 2015;7(6):388–395. doi: 10.1177/1756287215597637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Marks PA, Breslow R. Dimethyl sulfoxide to vorinostat: development of this histone deacetylase inhibitor as an anticancer drug. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25(1):84–90. doi: 10.1038/nbt1272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wang Z, Cao H, Sun Y, Li X, Chen F, Carles A, et al. Arabidopsis paired amphipathic helix proteins SNL1 and SNL2 redundantly regulate primary seed dormancy via abscisic acid-ethylene antagonism mediated by histone deacetylation. Plant Cell. 2013;25(1):149–166. doi: 10.1105/tpc.112.108191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Zhang HD, Guo F, Qi PP, Huang YZ, Xie YY, Xu L, et al. OsHDA710-mediated histone deacetylation regulates callus formation of rice mature embryo. Plant Cell Physiol. 2020;61(9):1646–1660. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcaa086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Santos RB, Pires AS, Abranches R. Addition of a histone deacetylase inhibitor increases recombinant protein expression in plant cell cultures. Free Radical Bio Med. 2018;120:S135–S135. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.04.444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Zhu LY, Zhu YR, Dai DJ, Wang X, Jin HC. Epigenetic regulation of alternative splicing. Am J Cancer Res. 2018;8(12):2346–2358. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Hu H, He X, Tu L, Zhu L, Zhu S, Ge Z, et al. GhJAZ2 negatively regulates cotton fiber initiation by interacting with the R2R3-MYB transcription factor GhMYB25-like. Plant J. 2016;88(6):921–935. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Li Y, Tu L, Ye Z, Wang M, Gao W, Zhang X. A cotton fiber-preferential promoter, PGbEXPA2, is regulated by GA and ABA in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep. 2015;34(9):1539–1549. doi: 10.1007/s00299-015-1805-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Wang YH, Liu JJ, Chen BL, Zhou ZG. Physiological mechanisms of growth regulators 6-BA and ABA in mitigating low temperature stress of cotton fiber development. J Appl Ecol. 2011;22(5):1233–1239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kim HJ, Triplett BA. Cotton fiber growth in planta and in vitro. Models for plant cell elongation and cell wall biogenesis. Plant Physiol. 2001;127(4):1361–1366. doi: 10.1104/pp.010724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Wang Z, Yang Z, Li F. Updates on molecular mechanisms in the development of branched trichome in Arabidopsis and nonbranched in cotton. Plant Biotechnol J. 2019;17(9):1706–1722. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Singh PK, Gao W, Liao P, Li Y, Xu FC, Ma XN, et al. Comparative acetylome analysis of wild-type and fuzzless-lintless mutant ovules of upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum Cv. Xu142) unveils differential protein acetylation may regulate fiber development. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2020;150:56–70. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.02.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Imran M, Shafiq S, Farooq MA, Naeem MK, Widemann E, Bakhsh A, et al. Comparative genome-wide analysis and expression profiling of histone acetyltransferase (HAT) gene family in response to hormonal applications, metal and abiotic stresses in cotton. Int J Mol Sci. 2019 doi: 10.3390/ijms20215311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Sultan M, Schulz MH, Richard H, Magen A, Klingenhoff A, Scherf M, et al. A global view of gene activity and alternative splicing by deep sequencing of the human transcriptome. Science. 2008;321(5891):956–960. doi: 10.1126/science.1160342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Wang BB, Brendel V. Genomewide comparative analysis of alternative splicing in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103(18):7175–7180. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0602039103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Wang ET, Sandberg R, Luo S, Khrebtukova I, Zhang L, Mayr C, et al. Alternative isoform regulation in human tissue transcriptomes. Nature. 2008;456(7221):470–476. doi: 10.1038/nature07509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Ner-Gaon H, Halachmi R, Savaldi-Goldstein S, Rubin E, Ophir R, Fluhr R. Intron retention is a major phenomenon in alternative splicing in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2004;39(6):877–885. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02172.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Yang W, Yoon J, Choi H, Fan Y, Chen R, An G. Transcriptome analysis of nitrogen-starvation-responsive genes in rice. BMC Plant Biol. 2015;15:31. doi: 10.1186/s12870-015-0425-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Deschamps C, Simon JE. Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis in leaves and glandular trichomes of basil (Ocimum basilicum L.) Methods Mol Biol. 2010;643:263–273. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-723-5_18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Vogt T. Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis. Mol Plant. 2010;3(1):2–20. doi: 10.1093/mp/ssp106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Qin YM, Hu CY, Pang Y, Kastaniotis AJ, Hiltunen JK, Zhu YX. Saturated very-long-chain fatty acids promote cotton fiber and Arabidopsis cell elongation by activating ethylene biosynthesis. Plant Cell. 2007;19(11):3692–3704. doi: 10.1105/tpc.107.054437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Wang XC, Li Q, Jin X, Xiao GH, Liu GJ, Liu NJ, et al. Quantitative proteomics and transcriptomics reveal key metabolic processes associated with cotton fiber initiation. J Proteomics. 2015;114:16–27. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2014.10.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Tan JF, Tu LL, Deng FL, Hu HY, Nie YC, Zhang XL. A Genetic and metabolic analysis revealed that cotton fiber cell development was retarded by flavonoid naringenin. Plant Physiol. 2013;162(1):86–95. doi: 10.1104/pp.112.212142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Meister A. Glutathione metabolism. Methods Enzymol. 1995;251:3–7. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(95)51106-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Schoenberg MH, Buchler M, Pietrzyk C, Uhl W, Birk D, Eisele S, et al. Lipid peroxidation and glutathione metabolism in chronic pancreatitis. Pancreas. 1995;10(1):36–43. doi: 10.1097/00006676-199501000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Crawhall JC, Purkiss P, Stanbury JB. Metabolism of sulfur-containing amino acids in a patient excreting -mercaptolactate-cysteine disulfide. Biochem Med. 1973;7(1):103–111. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(73)90105-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Stipanuk MH. Sulfur amino acid metabolism: pathways for production and removal of homocysteine and cysteine. Annu Rev Nutr. 2004;24:539–577. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nutr.24.012003.132418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Thomas SA, Catty P, Hazemann JL, Michaud-Soret I, Gaillard JF. The role of cysteine and sulfide in the interplay between microbial Hg(ii) uptake and sulfur metabolism. Metallomics. 2019;11(7):1219–1229. doi: 10.1039/c9mt00077a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Friedl MA, Schmoll M, Kubicek CP, Druzhinina IS. Photostimulation of Hypocrea atroviridis growth occurs due to a cross-talk of carbon metabolism, blue light receptors and response to oxidative stress. Microbiology. 2008;154(Pt 4):1229–1241. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2007/014175-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Singh AK, Elvitigala T, Bhattacharyya-Pakrasi M, Aurora R, Ghosh B, Pakrasi HB. Integration of carbon and nitrogen metabolism with energy production is crucial to light acclimation in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis. Plant Physiol. 2008;148(1):467–478. doi: 10.1104/pp.108.123489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Vargas WA, Pontis HG, Salerno GL. New insights on sucrose metabolism: evidence for an active A/N-Inv in chloroplasts uncovers a novel component of the intracellular carbon trafficking. Planta. 2008;227(4):795–807. doi: 10.1007/s00425-007-0657-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Kim HJ, Hinchliffe DJ, Triplett BA, Chen ZJ, Stelly DM, Yeater KM, et al. Phytohormonal networks promote differentiation of fiber initials on pre-anthesis cotton ovules grown in vitro and in planta. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(4):e0125046. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Zeng J, Zhang M, Hou L, Bai W, Yan X, Hou N, et al. Cytokinin inhibits cotton fiber initiation via disrupting PIN3a-mediated IAA asymmetric accumulation in ovule epidermis. J Exp Bot. 2019;70:13. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erz162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Sun Y, Veerabomma S, Abdel-Mageed HA, Fokar M, Asami T, Yoshida S, et al. Brassinosteroid regulates fiber development on cultured cotton ovules. Plant Cell Physiol. 2005;46(8):1384–1391. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pci150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Zhang M, Zheng X, Song S, Zeng Q, Hou L, Li D, et al. Spatiotemporal manipulation of auxin biosynthesis in cotton ovule epidermal cells enhances fiber yield and quality. Nat Biotechnol. 2011;29(5):453–458. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Wang Z, Chen FY, Li XY, Cao H, Ding M, Zhang C, et al. Arabidopsis seed germination speed is controlled by SNL histone deacetylase-binding factor-mediated regulation of AUX1. Nat Commun. 2016;7:13412. doi: 10.1038/ncomms13412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Yuan LB, Chen X, Chen HH, Wu KQ, Huang SZ. Histone deacetylases HDA6 and HDA9 coordinately regulate valve cell elongation through affecting auxin signaling in Arabidopsis. Biochem Bioph Res Co. 2019;508(3):695–700. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.11.082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Benhamed M, Bertrand C, Servet C, Zhou DX. Arabidopsis GCN5, HD1, and TAF1/HAF2 interact to regulate histone acetylation required for light-responsive gene expression. Plant Cell. 2006;18(11):2893–2903. doi: 10.1105/tpc.106.043489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Shen Y, Lei T, Cui X, Liu X, Zhou S, Zheng Y, et al. Arabidopsis histone deacetylase HDA15 directly represses plant response to elevated ambient temperature. Plant J. 2019;100(5):991–1006. doi: 10.1111/tpj.14492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Zhang M, Zeng JY, Long H, Xiao YH, Yan XY, Pei Y. Auxin regulates cotton fiber initiation via GhPIN-mediated auxin transport. Plant Cell Physiol. 2017;58(2):385–397. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcw203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Yang Z, Zhang C, Yang X, Liu K, Wu Z, Zhang X, et al. PAG1, a cotton brassinosteroid catabolism gene, modulates fiber elongation. New Phytol. 2014;203(2):437–448. doi: 10.1111/nph.12824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Beasley CA, Ting IP. Effects of plant growth substances on in vitro fiber development from unfertilized cotton ovuleS. Am J Bot. 1974;61(2):188–194. doi: 10.1002/j.1537-2197.1974.tb06045.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Yu J, Jung S, Cheng CH, Ficklin SP, Lee T, Zheng P, et al. CottonGen: a genomics, genetics and breeding database for cotton research. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42(Database issue):D1229–1236. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.El-Gebali S, Mistry J, Bateman A, Eddy SR, Luciani A, Potter SC, et al. The Pfam protein families database in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(D1):D427–D432. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Young MD, Wakefield MJ, Smyth GK, Oshlack A. Gene ontology analysis for RNA-seq: accounting for selection bias. Genome Biol. 2010;11(2):R14. doi: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-2-r14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Anders S, Huber W. Differential expression analysis for sequence count data. Genome Biol. 2010;11(10):R106. doi: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-10-r106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Mao XZ, Cai T, Olyarchuk JG, Wei LP. Automated genome annotation and pathway identification using the KEGG Orthology (KO) as a controlled vocabulary. Bioinformatics. 2005;21(19):3787–3793. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Kanehisa M, Araki M, Goto S, Hattori M, Hirakawa M, Itoh M, et al. KEGG for linking genomes to life and the environment. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36(Database issue):D480–484. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1: Table S1. The gene ID list of 4,209 DEGs identified between mock and TSA-treated ovules.
Additional file 2: Table S2. The gene ID list of 94 up-and down-regulated DEGs associated with hormone signal transduction after TSA treatment.
Additional file 3: Table S3. The FPKM values of each gene in classifications a, b, c, and d.
Additional file 4: Table S4. The Q-PCR primers used in this study.
Additional file 5: Fig. S1. Application of TSA repress fiber elongation after long-term in vitro culture. Fig. S2. MA plot analysis of DEGs in the ovules. Fig. S3. Phenotypic observation on initiation and elongation of cultured fibrocytes in vitro under different hormones. Fig. S4. Phenotype of cultured fibrocytes in vitro treated with diallyl disulfide.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.