Abstract
Background
The rare form and mildest variant of Langerhans cell histiocytosis is eosinophilic granuloma (EG). In the clinical presentation, EG can be monostotic, polyostotic, or can encompass many organs. The parietal bone is the most common location of the skull bones that are affected by EG. So far, there have been no reported cases of EG with skull odor as an unexplained presentation.
Case presentation
An 8-year-old girl presented with a 4 months history of a right parietal bone swelling of the skull with an offensive odor. There was no discharge and no history of vomiting or trauma. An MRI scan of the brain showed swelling with a bone lesion of the right parietal bone. Infection was the source of the swelling and the bad odor. Treatment was done by surgical excision of the lesion.
Conclusion
EG has a variety of presentations and should be suspected when tenderness and local swelling are present. Radiography was found to be helpful in the diagnosis and surgical treatment was done to manage the case.
Keywords: Eosinophilic granuloma, Langerhans cell histiocytosis, Parietal bone, Bony lytic lesion, Offensive odor, Case report
Highlights
-
•
Most common site to be affected by EG in the Skull is the parietal bone.
-
•
EG may be infected and present with an offensive odor.
-
•
EG cells Stains positive for S-100 and CD1a.
-
•
Most of the Cases are reported among children and most of them present with Headache.
1. Introduction
Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH) is an idiopathic disorders group characterized by disordered histiocytes proliferation. LCH is rare, but it is more common in children than in adults [1]. Unifocal LCH is the modern name for eosinophilic granuloma. Eosinophilic granuloma is an uncommon subtype of LCH and it is the mildest form of it [2]. The progression of the disease is slow and is characterized by the expansion of Langerhans cells, which usually affect the bones of the skull as a destructive lesion [1]. We report here an extremely rare case of eosinophilic granuloma affecting the parietal bone of the skull in an 8-year-old girl presenting with an offensive head odor.
This case has been reported in line with SCARE criteria which is mentioned in Methods section.
2. Case presentation
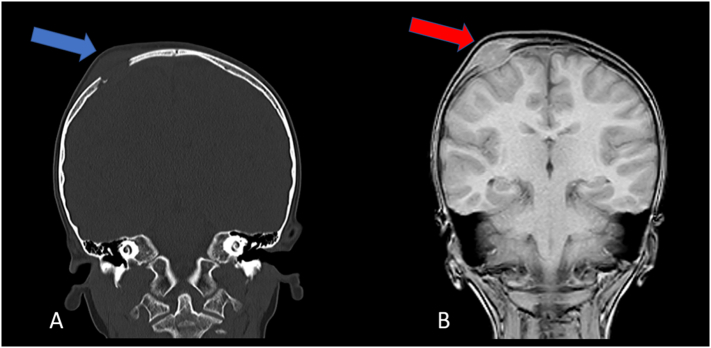
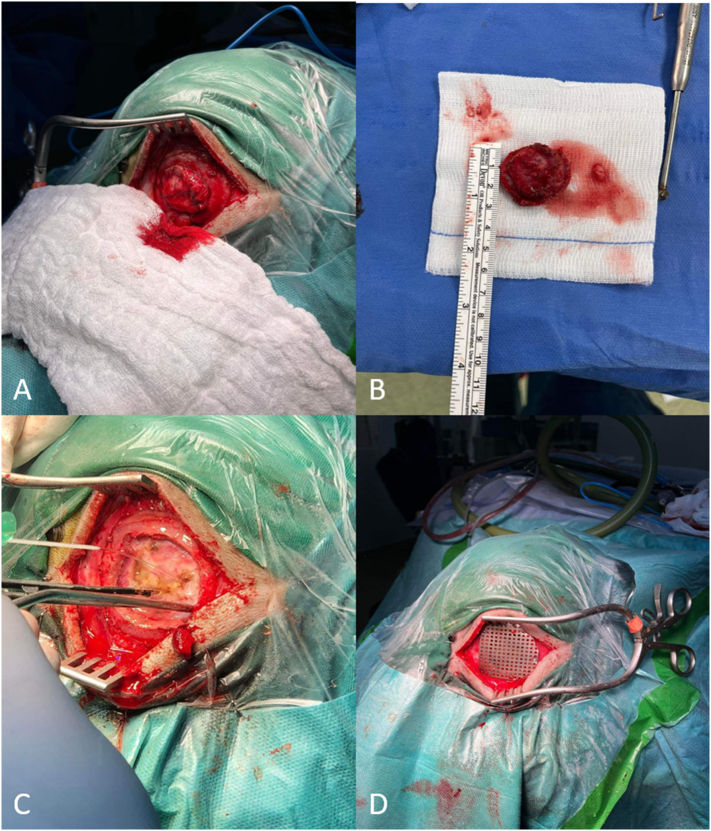
An 8-year-old girl presented with a 4 months history of right parietal bone swelling with an offensive odor. There was no discharge and no history of vomiting or trauma. She has taken no medications lately and had no allergic reactions. In the clinic, she had a mild headache with no fever, no symptoms of increased intracranial pressure, and no neurological abnormalities. A head computed tomography (CT) scan showed a parietal bone lesion. After that, an MRI scan of the brain showed a 2.5 × 1.5 cm bone lesion extended as swelling and suggested the diagnosis of EG (Fig. 1). Histopathology was performed and revealed proliferation of monotonous population of discohesive cells composed of oval nuclei with open chromatin and coffee bean grooves with abundant pale cytoplasm. Immunohistochemistry for these cells was positive for CD1a and S100 (Fig. 2). Initial treatment with augmentin was performed to relieve the infection and the odor. After that, a CT scan showed that the swelling is disappeared, but there was a lytic bone lesion (Fig. 3). On examination, there was a feeling of soft tissue. Thereupon, a surgical procedure was done by excision of the lesion with a 3 mm safety margin, and a titanium mesh was inserted (Fig. 4). During the surgery, the patient was given cefazolin. Laboratory values before and after the surgery were within the normal range. The patient was discharged home with augmentin and analgesia. In the clinic, the follow-up of the patient was performed with no post-operative complications.
Fig. 1.
(A) CT scan shows a lytic bony lesion (Blue Arrow). (B) MRI scan shows a 2.5 × 1.5 cm bone lesion extended as swelling (Red Arrow). (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)
Fig. 2.
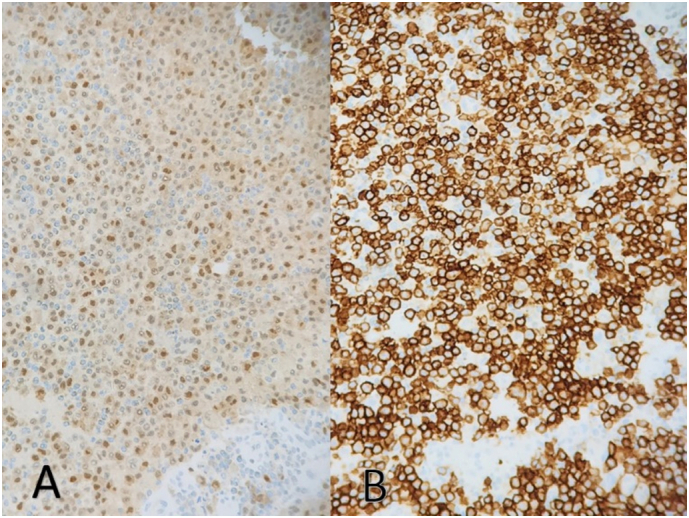
(A) Shows that the lesion stained positive for S100. (B) Shows that the lesion stained positive for CD1a.
Fig. 3.
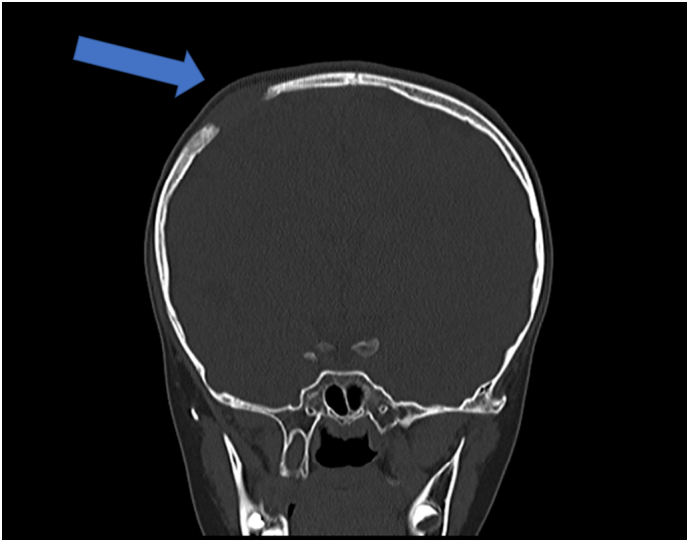
CT scan shows a lytic lesion after treating the infection (Blue Arrow). (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)
Fig. 4.
(A and B) Show the 2.5 × 1.5 cm bone lesion. (C) The excision of the lesion with a 3 mm safety margin. (D) The insertion of titanium mesh.
3. Discussion
Eosinophilic granuloma (EG) is one type of Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH) that involves any bone. The most frequent sites of EG vary with age. The skull (40 %), rib, femur, humerus, and vertebra are the most common sites in children [3]. EG is a rare tumor-like lesion that represents less than 1 % of all bone lesions [4]. Tenderness and local swelling are usually the presenting symptoms [5]. Differential diagnoses of EG include dermoid cysts and sebaceous cysts, osteoblastomas, hemangiomas, and osteogenic sarcomas [6].
The presence of eosinophilic granuloma may be indicated by its location, symptoms, or radiologic appearance. The evaluation of EG includes radiographic tests, laboratory tests, and histopathology to confirm a diagnosis [7]. In our case, the initial concept that came to our minds was an infected sebaceous cyst. But on physical examination, the case was not correlated with sebaceous cyst. Laboratory tests have been done and the results were within the normal range. Thus, this finding ruled out osteomyelitis and other malignancies. We proceeded to the CT scan and eosinophilic granuloma was suspected. Computed tomographic scan and magnetic resonance imaging may detect punched-out lesions as well as soft tissue involvement adjacent to the bony structure [7]. Accordingly, CT and MRI were done. Moreover, tumor cells have to stain positively for CD1a and S100 on immunohistochemistry to be identified as Langerhans cells [8]. As a result, a biopsy was taken and the case was diagnosed.
The pathophysiology of eosinophilic granuloma is unclear. However, the proliferation of Langerhans cells may be induced by viral infection, immune dysfunction, or bacterial infection. As a result, interleukin-1 and interleukin-10 may be elevated [9]. Therefore, antibiotics could be used to relieve the bacterial infection and the swelling that results from it [7].
Treatment and prognosis for eosinophilic granuloma of the skull depend on age and number of bones involved at the time of diagnosis [10]. In terms of treatment, it is divided into two groups, non-operative and operative. The non-operative methods include observation; solitary lesions usually resolve spontaneously, irradiation and chemotherapy [7]. As for the operative treatment, surgical excision and grafting are performed. In our case, operative treatment was done and grafting was performed by inserting a titanium mesh.
After reviewing the literature, there was only one case with EG that presented with an offensive odor. In that case, the mandible was the affected site [11]. The well-defined lytic lesion of eosinophilic granuloma in the skull is most commonly seen in the parietal and frontal bones [12]. EG frequently occurs in children as seen in Table 1. Most of the cases in the table were presented with headache which varied in severity. Some cases presented with other symptoms such as nausea and vomiting. On the other hand, the minority of the cases were found to have neurological symptoms such as seizures. 4 cases were reported with extradural hematoma, and one of them had a history of trauma [13]. Noteworthy, there is a remarkable presentation that has been reported in our case which is the offensive odor in the parietal bone.
Table 1.
Summary of unusual findings in reported cases of eosinophilic granuloma affecting the parietal bone as reported in the literature.
| Year | Gender | Age/years | Presentation |
Radiographic findings | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mass | Duration | Trauma | Symptoms | ||||
| 1970 [14] | Female | 38 | Tender | 3 months | No | Seizure activity on EEG | Large irregular osteolytic defect |
| 1973 [15] | Male | 5 | Smooth, non-tender | – | No | None | Circular localized area of destruction with clear cut margins |
| 1990 [16] | Male | 2 | Soft and tender with smooth surfaces | 1 month | No | None | Soft tissue masses with destruction in the frontal and right parietal areas |
| 1990 [16] | Male | 2 | Soft, painless | 1 month | No | None | Punched-out and well-defined lytic lesion |
| 2006 [6] | Female | 26 | Tender and firm | 2 weeks | No | Progressive headache and nausea | Hyperintense osteolytic lesion |
| 2007 [17] | Male | 32 | Edematous | – | Yes/3 years | Headache | Hypointense lesion with perilesional edema |
| 2007 [18] | Male | 37 | Soft tissue | 2 months | No | Headache and epileptic attacks | Osteolytic lesion with a large epidural and subcutaneous mass |
| 2009 [19] | Female | 36 | Tender | 2 months | No | Headache | Single punched out area of bone destruction with sharp margins |
| 2010 [20] | Male | 10 | Tender | 1 months | No | None | Lytic bone lesion extended as swelling with extradural hematoma |
| 2011 [21] | Male | 4 | Large and gradually decreasing in size | 1 month | Yes/1 month | Unremitting headache and projectile vomiting | Lytic lesion, scalp swelling and hematoma |
| 2013 [22] | Female | 14 | Tender and soft | 1 month | No | Headache, malaise and nausea | Osteolytic change with extracranial swelling |
| 2013 [23] | Male | 44 | Immobile palpable masses | – | No | Multiple cranial swellings accompanied by pain | Radiolucent areas in the right frontoparietal, parietal and temporal bones |
| 2016 [24] | Male | 7 | Non-tender | 2 months | No | Progressive headache, decreased level of consciousness and vomiting | Heterogeneous osteolytic mass with extradural hematoma |
| 2018 [25] | Female | 8 | No mass was felt | 6 weeks | No | Focal pain at the scalp | Large osteolytic defect with non-sclerotic margins and beveled edges. |
| 2019 [26] | Female | 10 | Tender | 3 weeks | Yes/2 weeks | None | Single osteolytic lesion without sclerosis |
| 2020 [13] | Male | 3 | Non-tender | 2 days | No | Recurrent and progressive vomiting and drowsiness | Iso-dense subcutaneous scalp lesion, underlying osteolytic bony defect and mixed density extradural lesion with extradural hematoma |
| 2021 [27] | Female | 18 | Tender | 3 weeks | No | Headache | Lytic lesion with disruption of the external tabula and an epicranial soft tissue extension of the lesion |
| 2021 [28] | Male | 10 | Non-tender and gradually increasing in size | – | Yes | Pain in the local area of the swelling | 3 cm sized defect in the right temporoparietal calvarial with scalloped margin |
| 2022 | Female | 8 | Non-Tender | 4 months | No | Offensive odor with mild headache | Lytic bone lesion extended as swelling |
4. Conclusion
We present here a case report of an extremely rare eosinophilic granuloma in the parietal bone of a pediatric patient. Noteworthy, EG should be suspected when tenderness and local swelling are present. Our case was presented with an offensive odor with no clear reason. After reviewing the literature, we did not detect any cases to have a similar finding. In our case, radiography was found to be helpful in the diagnosis. Furthermore, surgical treatment was done to manage the case.
Methods
This case has been reported in line with SCARE Criteria [29].
Source of funding
The study did not receive any funding.
Ethical approval
This study is exempt from ethical approval at our hospital.
Consent
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for reporting this case. The consent is available for review on request.
Authors' contributions
Data collection: Osama N. Dukmak, Mohammad Emar.
Writing the manuscript: Osama N. Dukmak, Sulaiman M. S. Abualia, Yara J. I. Meqbil.
Study concept or design: Osama N. Dukmak, Sulaiman M. S. Abualia, Yara J. I. Meqbil.
Review & editing the manuscript: Osama N. Dukmak, Yara J. I. Meqbil, Sulaiman M. S. Abualia, Mohammad Emar.
Registration of research studies
N/A.
Guarantor
Dr. Saeed Idkedek.
Provenance and peer review
Not commissioned, externally peer-reviewed.
Declaration of competing interest
There is no conflict of interest to declare.
References
- 1.Chen H.C., Shen W.C., Chou D.Y., Chiang I.P. Langerhans cell histiocytosis of the skull complicated with an epidural hematoma. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2002;23(3):493–495. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Okamoto K., Ito J., Furusawa T., Sakai K., Tokiguchi S. Imaging of calvarial eosinophil granuloma. Neuroradiology. 1999;41(10):723–728. doi: 10.1007/s002340050831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Slater J.M., Swarm O.J. Eosinophilic granuloma of bone. Med. Pediatr. Oncol. 1980;8(2):151–164. doi: 10.1002/mpo.2950080208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.David R., Oria R.A., Kumar R., Singleton E.B., Lindell M.M., Shirkhoda A., et al. Radiologic features of eosinophilic granuloma of bone. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1989;153(5):1021–1026. doi: 10.2214/ajr.153.5.1021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Weitzman S., Egeler R.M. Langerhans cell histiocytosis: update for the pediatrician. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2008;20(1):23–29. doi: 10.1097/MOP.0b013e3282f45ba4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bruno M.C., Del Basso De Caro M.L., Panagiotopoulos K., Elefante A., Tortora F., De Notaris M.G., et al. Aggressive eosinophilic granuloma of the parietal bone. An immunohystochemical study of Ki-67 expression. J. Neurosurg. Sci. 2006;50(4):111–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Suman K., ODJ Jha. Eosinophilic Granuloma StatPearls Publishing2022, January 17. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559038/ Available from:
- 8.Saliba I., Sidani K., El Fata F., Arcand P., Quintal M.C., Abela A. Langerhans' cell histiocytosis of the temporal bone in children. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2008;72(6):775–786. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2008.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chadha M., Agarwal A., Agarwal N., Singh M.K. Solitary eosinophilic granuloma of the radius. An unusual differential diagnosis. Acta Orthop. Belg. 2007;73(3):413–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Park S.H., Park J., Hwang J.H., Hwang S.K., Hamm I.S., Park Y.M. Eosinophilic granuloma of the skull: a retrospective analysis. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 2007;43(2):97–101. doi: 10.1159/000098380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Agarwal A., Agrawal G.P., Alam S., Husain B. A case of unifocal eosinophilic granuloma of the mandible in an adult female: a case report. Case Rep. Dent. 2012;2012 doi: 10.1155/2012/521726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Golla S.K., Kavanagh E.C. MRI, CT, scintigraphic and histological features of a vanishing scapular eosinophilic granuloma. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2009;178(1):107–110. doi: 10.1007/s11845-008-0133-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Al-Mousa A., Altarawneh M., Alqatawneh O., Bashir Z., Al-Dwairy S., Shtaya A. Eosinophilic granuloma of the skull presenting as non-traumatic extradural haematoma in children. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2020;13:1229–1234. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S288512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Benua R.S. Abnormal brain scan in eosinophilic granuloma of the skull. J. Nucl. Med. 1970;11(2):89–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Krishna R.V., Reddy D.R., Tilak T.B., Rao P.V., Reddy M.L. Eosinophilic granuloma in the parietal bone. Report of a case. Indian J. Pediatr. 1973;40(305):229–230. doi: 10.1007/BF02817847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kuwabara S., Takahashi M. Eosinophilic granuloma of the skull in identical twins–case report. Neurol. Med. Chir. (Tokyo) 1990;30(13):1043–1046. doi: 10.2176/nmc.30.1043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Caroli E., Ferrante L. Intradural eosinophilic granuloma with intraparenchymal invasion: a new growth pattern. Zentralbl. Neurochir. 2007;68(2):79–82. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-980172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Tatli M., Guzel A., Guzel E. Solitary eosinophilic granuloma of the parietal bone in an adult patient. Neurosciences (Riyadh) 2007;12(2):160–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kaul R., Gupta N., Gupta S., Gupta M. Eosinophilic granuloma of skull bone. J Cytol. 2009;26(4):156–157. doi: 10.4103/0970-9371.62188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Bhat A.R., Jain A.K., Kirmani A.R., Nizami F. Pathological intracranial extradural hematoma in a 10-year-old child. J. Pediatr. Neurosci. 2010;5(2):164–166. doi: 10.4103/1817-1745.76121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Pawar R.V., Hagiwara M., Milla S., Wisoff J., George A.E. Eosinophilic granuloma presenting as post-traumatic scalp hematoma with epidural hemorrhage. A case report. Neuroradiol J. 2011;24(5):767–771. doi: 10.1177/197140091102400516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Oguro K., Sakai H., Arai M., Igarashi T. Eosinophilic granuloma of bone: two case reports. Brain and Development. 2013;35(4):372–375. doi: 10.1016/j.braindev.2012.06.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hasturk A.E., Basmaci M. Multifocal extradural and intradural eosinophilic granuloma. J Craniofac Surg. 2013;24(3):e214–e216. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0b013e3182801b87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Bakhaidar M.G., Alghamdi F.A., Baeesa S.S. Spontaneous extradural hemorrhage due to langerhans cell histiocytosis of the skull in a child: a rare presentation. J. Pediatr. Neurosci. 2016;11(1):52–55. doi: 10.4103/1817-1745.181248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Vanhoenacker F.M., Verlooy J., De Praeter M. Spontaneous resolution of unifocal langerhans cell histiocytosis of the skull: potential role of ultrasound in detection and imaging follow-up. J. Ultrason. 2018;18(74):265–270. doi: 10.15557/JoU.2018.0038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Matsushita K., Shimono T., Miki Y. Langerhans cell histiocytosis with multiple fluid-fluid levels in the parietal bone. Magn. Reson. Med. Sci. 2020;19(1):5–6. doi: 10.2463/mrms.ci.2018-0152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Pires T., Duarte Santos C., Gonzalez Santos M., Luz L., Ferrao A., Banza M.J. Eosinophilic granuloma: a rare and often benign condition presenting as a lump on the head, which was easily treated. Eur. J. Case Rep. Intern. Med. 2021;8(7) doi: 10.12890/2021_002727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Mishra A., Gyawali S., Kharel S., Mishra A., Kuikel S., Pathak N., et al. Incidental finding of langerhans cell histiocytosis of temporoparietal bone - a case report. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2021;85 doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2021.106179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Agha R.A., Franchi T., Sohrabi C., Mathew G., Kerwan A., Thoma A., Beamish A.J., Noureldin A., Rao A., Vasudevan B., Challacombe B., Perakath B., Kirshtein B., Ekser B., Pramesh C.S., Laskin D.M., Machado-Aranda D., Miguel D., Pagano D., Millham F.H., Roy G., Kadioglu H., Nixon I.J., Mukhejree I., McCaul J.A., Chi-Yong Ngu J., Albrecht J., Rivas J.G., Raveendran K., Derbyshire L., Ather M.H., Thorat M.A., Valmasoni M., Bashashati M., Chalkoo M., Teo N.Z., Raison N., Muensterer O.J., Bradley P.J., Goel P., Pai P.S., Afifi R.Y., Rosin R.D., Coppola R., Klappenbach R., Wynn R., De Wilde R.L., Surani S., Giordano S., Massarut S., Raja S.G., Basu S., Enam S.A., Manning T.G., Cross T., Karanth V.K., Kasivisvanathan V., Mei Z., The S.C.A.R.E. Guideline: updating consensus surgical CAse REport (SCARE) guidelines. Int. J. Surg. 2020;84(2020):226–230. doi: 10.1016/J.IJSU.2020.10.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]