Abstract
Objective
The narrow therapeutic window of lithium medications necessitates frequent serum monitoring, which can be expensive and inconvenient for the patient. Compared to blood, saliva collection is easier, non‐invasive, requires less processing, and can be done without the need for trained personnel. This study investigated the utility of longitudinal salivary lithium level monitoring.
Methods
We measured salivary lithium levels using ICP‐OES in n = 169 passive drool samples, collected both as single observations and longitudinally for up to 18 months, from a multi‐center cohort of n = 75 patients with bipolar disorder or other psychiatric conditions.
Results
Saliva and serum lithium levels were highly correlated. Adjustment for daily lithium dose, diabetes, and smoking improved this relationship (r = 0.77). Using the adjusted intersubject equation and a patient's salivary lithium value, we observed a strong correlation between the predicted vs. observed serum lithium levels (r = 0.70). Most patients had highly stable saliva/serum ratios across multiple visits, with longitudinal variability significantly greater with age. Use of the intrasubject saliva/serum ratio from a single prior observation had similar predictive power to the use of the adjusted intersubject equation. However, the use of the mean intrasubject ratio from three prior observations could robustly predict serum lithium levels (predicted vs. observed r = 0.90).
Conclusions
These findings strongly suggest that saliva could be used for lithium monitoring, and open the door for the development and implementation of a point‐of‐care salivary lithium device for use at home or the clinic. We propose that the use of saliva will dramatically improve treatment opportunities for patients with mood disorders.
Keywords: biofluid, bipolar disorder, blood, lithium, peripheral, saliva, therapeutic drug monitoring
1. INTRODUCTION
Lithium was identified as a treatment for bipolar disorder in 1949 and remains a first line of treatment for both mania and depression 1 , 2 with particular benefit in reducing suicidality. While highly effective, the use of lithium is limited by its narrow therapeutic range (0.4–1.2 mmol/L), and common occurrence of adverse effects, such as gastrointestinal discomfort, tremors, drowsiness, disorientation, and renal and thyroid dysfunction. These side effects are commonly dose related but can occur even at therapeutic doses. 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 At higher serum concentrations, the potential for side effects and risk of toxicity increases further. 8 , 9 The presence of side effects may contribute to poor outcomes and medication non‐adherence. 10 For these reasons, lithium requires frequent monitoring of blood serum levels. International guidelines recommend that patients on lithium medication undergo lithium level monitoring at least every 3–6 months, and even more frequently after dosage change, in case of relapse, or upon symptoms of intoxication. 11 , 12
Serum lithium monitoring requires attendance at a clinical laboratory and the collection of a blood sample, which can be uncomfortable, expensive, and inconvenient for patients. In particular, during acute episodes of bipolar illness and hospitalization, clinicians may request frequent blood sampling in order to titrate lithium levels. 8 On the other hand, and as outlined above, patients on stable lithium prophylaxis may only be prompted to provide a blood sample every 3–6 months. The results may vary across time due to a variety of factors including lifestyle and/or diet‐promoted changes in body composition and lithium clearance, and alterations in lithium levels may go undetected for months. 13 Furthermore, the optimal plasma lithium level within the therapeutic range may vary depending on the presentation of symptoms. For example, and in accordance with the Lithiumeter clinical guide, patients experiencing mania should be titrated to 0.6–1.0 mmol/L plasma lithium, whereas those experiencing depression can be titrated to 0.4–0.8 mmol/L if necessary, until resolution of symptoms at which point lithium levels should be adjusted to maintenance levels (often 0.6–0.8 mmol/L however patient dependent). 8 Lithium is stored in the adrenal glands, bone, lymph nodes, and pituitary gland and is eliminated predominantly via the kidneys. 3 As such, factors affecting renal function, such as age, dehydration, caffeine and heavy or chronic alcohol intake, sodium balance and hemodynamics, serum creatinine levels, and body mass index (BMI) also have the potential to impact on serum lithium levels. 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 Hence, providing an effective and more convenient means for testing would allow for more frequent lithium monitoring, optimal dosing, and improved patient outcomes with lithium medications.
Previous studies dating back 30 years have suggested the use of saliva as an alternative to blood monitoring in humans. 17 , 18 , 19 Several of these studies demonstrated significant correlations between serum lithium and salivary lithium in adult patients being treated with lithium carbonate, 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 although, other studies found only weaker associations. 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 These past studies suffered from inconsistencies in saliva collection and storage procedures, variations in saliva processing methods, differences in the lithium detection method and overall provided little information regarding patient demographic and clinical features. 17 Nonetheless, saliva sampling provides enormous potential clinical utility as a non‐invasive, cost‐effective approach for lithium level monitoring that can be carried out in any setting. Indeed, the potential for patients to collect saliva samples at home would reduce the need for trained laboratory personnel, and allow patients to collect a sample at a time that is not only convenient for them but can also be better coordinated with their daily dose, timing of other medication, food intake and/or emergence of acute illness. In addition, saliva collection is safer than blood draws, as it does not require the use of a needle, which can increase the transmission of blood‐borne pathogens.
In this study, we explored the relationships between lithium levels in saliva and serum in a multicenter cohort of patients taking lithium medications and confirmed a strong correlation between saliva and blood serum lithium levels. We further identified a number of clinical and lifestyle factors that affect the lithium levels in these two biological fluids, and demonstrate the potential for saliva to represent an alternative non‐invasive biofluid for lithium monitoring.
2. MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1. Human subjects
This study was approved by Institutional Review Boards at the University of California Irvine (UCI), University of California San Diego (UCSD), and VA San Diego Healthcare System (VASDHS), in accordance with the requirements of the Code of Federal Regulations on the Protection of Human Subjects. Patients were recruited from the UCI Medical Center (UCIMC), and VASDHS. Subjects (n = 75) were recruited through the physical and online posting of a flyer, and through recommendation from their psychiatrist. Individuals were eligible to participate if they were currently taking lithium medication, and were receiving either inpatient or outpatient psychiatric treatment. All individuals provided informed, written consent prior to sample collection. Subjects were given the opportunity to participate in this study up to eight times, providing up to eight longitudinal, time‐matched saliva/blood samples, spaced at least 1 month apart. After recruitment, two subjects were excluded due to non‐compliance with medications and a third due to a history of stage 3 kidney disease.
2.2. Medical data collection
Demographic, medical, and blood chemistry results were collected on the day of sample collection, through the electronic medical record system. Data collected included age, sex, smoking status, medical diagnoses including psychiatric and type 2 diabetes, lithium formulation and dose, and any concurrent psychiatric medications. Where available, blood chemistry data included the serum levels of sodium, potassium, creatinine, thyroid‐stimulating hormone, and white blood cell count. These demographic, lifestyle, clinical, and laboratory variables were chosen based on previous literature supporting their proposed association with serum lithium levels. 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 , 28 , 29
2.3. Sample collection
Saliva samples were collected using the gold standard passive drool method. 30 Briefly, participants were asked to lean forward in a seated position, with both feet planted firmly on the ground. Participants were instructed to allow saliva to pool at the bottom of their mouth and, when ready, to direct or ‘drool’ this saliva into a 5 ml collection tube. All donors were asked to refrain from smoking, eating, drinking, or oral hygiene procedures for at least 1 h prior to sample collection. Roughly 1–2 ml of unstimulated whole saliva was obtained. Samples were stored at −20℃ within an hour of collection, and remained at −20℃ for up to several weeks, and were then stored at −80℃. Following saliva collection, subjects were either accompanied, or directed to, the medical center pathology clinic, where serum lithium levels were measured using standard hospital procedures.
2.4. Lithium analysis
At the time of saliva sample analysis, occurring after at least 24 h storage at −80℃, saliva samples were thawed and centrifuged (10,000 g; 5 min; 4℃) to remove insoluble material and cellular debris. The resulting supernatant was collected and used for all assays. Salivary lithium levels were measured via Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectroscopy (ICP‐OES) (Avio200; Perkin Elmer) using the radial viewing window. Prior to analysis, the ICP‐OES was aligned with 0.1% manganese. For ICP‐OES analysis, samples were diluted 1:20 in 2% HNO3; output was normalized to the internal standard, 0.1% yttrium, and compared to a lithium standard curve. All yttrium recovery values fell between 89% and 106%. The second lithium standard curve point (1000 ppm lithium), as well as a HNO3 blank, were re‐run after every 10 samples, to ensure consistent analysis parameters and the absence of sample carry‐over, respectively. In addition, prior to the analysis of study samples, we first tested whether the levels of a spiked‐in, known amount of lithium varied according to saliva collection method (passive drool vs. swab), saliva processing method (centrifuged vs. uncentrifuged), storage conditions (−20℃, 4℃, room temperature), or the number of freeze‐thaw cycles. We found that lithium levels did not vary according to processing method, storage temperature up to 24 h, nor the number of freeze‐thaws up to three (Figure S1). However, we did observe that lithium recovery was slightly lower in swab collection devices compared to passive drool (p = 0.05) (Figure S1). As passive drool is considered the gold standard method approved for all salivary analytes, 30 this method of saliva collection was used for this study.
2.5. Total protein and cotinine assays
Salivary total protein was measured via Pierce™ BCA Protein Assay (Thermo Fisher Scientific) at a 1:10 dilution in dH2O. Salivary cotinine was assayed in duplicate using a commercially available ELISA kit (Salimetrics LLC) following the manufacturer's protocol. The assay has a test volume of 20 µl, range of standards from 0.8 to 200 ng/ml, and lower limit of detection of 0.15 ng/ml.
2.6. Determination and validation of lithium prediction models
For the development of a prediction model, data instances were randomly assigned to either a determination cohort, which contained 75% of all data points (n = 127), or a preliminary validation cohort, which contained the remaining 25% of data points (n = 42). Randomization was conducted using the Microsoft Excel random number generator, and splitting the resulting randomly ordered data sets into two consecutive groups. The determination cohort was used to determine the prediction model, the validation cohort was used to validate the prediction model.
2.7. Statistical analysis
Analyses were conducted with GraphPad Prism version 8.4.2 for Windows (GraphPad Software). Analyses that corrected for covariates were conducted using IBM® SPSS® Statistics version 25 for Windows (IBM Corp.). Outliers were identified using the ROUT outlier test (Q = 5%), resulting in the exclusion of two outlier salivary lithium measurements. The measurements of salivary lithium, serum lithium levels, and saliva/serum ratios were not normally distributed (Skewness = 0.99, 0.31, and 0.94, for saliva, serum, and ratio, respectively). Consequently, all data were analyzed using nonparametric analyses, with the exception of prediction model determination and validation. As outcome variable normality is not a required assumption for linear regression modeling, modeling was analyzed without data transformation and using Pearson correlations. Non‐parametric Spearman correlations which corrected for covariates were conducted by ranking continuous data, followed by multivariate linear regression. For the correlation comparison of lithium levels and blood chemistry data, as well as the comparison of lithium levels and other instance‐specific variables such as daily lithium dose, data points were included from all available visits. Comparisons between lithium levels and static continuous data, such as age and BMI, were conducted using all subjects' first time point data only.
3. RESULTS
3.1. Patient characteristics and study variables
In this study, we collected 171 saliva samples from n = 75 patients across two recruitment sites, UCIMC and VASDHS. After recruitment, two subjects were excluded due to non‐compliance with medications and a third due to a history of stage 3 kidney disease. Demographic characteristics for the cohorts recruited from UCIMC and VASDHS are outlined in Table 1. The age range for patients was 14–76 years, with 74.6% of patients being male. All patients recruited from VASDHS had a diagnosis of bipolar disorder, whereas 74% of patients from UCIMC had a diagnosis of bipolar disorder and 15% had a diagnosis of either schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder, major depressive disorder, or generalized anxiety disorder. Cohorts differed significantly in sex distribution, age, and BMI but not salivary or serum lithium levels (Table 1). Salivary lithium levels were two to three‐fold higher compared to those measured in serum, and these ratios were slightly different between sites (2.38 vs. 2.75, for UCIMC and VASDHS, respectively; Table 1).
TABLE 1.
Demographic and disease data for subjects included in this study (median, range)
| All subjects (n = 75) | Subjects by site | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UCIMC (n = 38) | VASDHS (n = 37) | p | ||
| Sex (M/F) | 56/19 | 22/16 | 34/3 | 0.002 |
| Diagnosis (BD/Scz/MD) | 65/5/5 | 28/5/5 | 37/0/0 | 0.001 |
| Age (years) a | 35.2, 14.5–76.0 | 28.6, 14.5–58.0 | 52.0, 26.0–76.0 | <0.0001 |
| BMI a | 29.1, 20.1–48.0 | 27.8, 20.1–39.0 | 31.0, 22.0–48.0 | 0.02 |
| Daily lithium dose (mg) | 900, 300–2400 | 900, 300–2400 | 900, 300–1800 | 0.95 |
| Saliva lithium levels (mmol/L) | 1.36, 0.23–3.54 | 1.34, 0.29–3.03 | 1.42, 0.23–3.54 | 0.32 |
| Serum lithium levels (mmol/L) | 0.58, 0.10–1.20 | 0.56, 0.10–1.14 | 0.61, 0.13–1.20 | 0.92 |
| Saliva/Serum lithium ratio | 2.44, 1.09–5.50 | 2.38, 1.09–5.50 | 2.75, 1.12–5.23 | 0.005 |
Sex and diagnosis differences were analyzed with a Fisher's exact test, with diagnoses grouped into ‘bipolar disorder’ or ‘other’; differences in continuous measures between sites were analyzed with the Mann‐Whitney U test; BD, bipolar disorder; Scz, schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder; MD, mood disorder (major depressive disorder or anxiety).
Variables compared using data from the first appointment only, all other measures above used data from multiple appointments.
Both salivary and serum lithium levels were positively correlated with daily lithium dose and serum lithium levels were significantly affected by dosing schedule (once or twice a day) (Table 2). A diagnosis of type 2 diabetes, and smoking, the latter confirmed through measurement of salivary cotinine levels, were associated with variations in the saliva/serum lithium ratios (Table 2). No significant effects of age, sex, BMI, lithium formulation (immediate release vs. sustained release) total salivary protein levels (a measure of dehydration), or time from last lithium dose to sample collection were found to be associated with lithium levels in saliva, serum, nor the saliva/serum ratios (Table 2).
TABLE 2.
Factors affecting serum and saliva lithium measures
| Variable | Continuous measures (Spearman rho, p) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Salivary lithium | Serum lithium | Ratio | |
| Age a | 0.12, 0.32 | 0.10, 0.40 | 0.09, 0.47 |
| BMI a | 0.01, 0.92 | −0.02, 0.85 | −0.06, 0.62 |
| Daily lithium dose | 0.26, 0.001 | 0.40, <0.0001 | −0.16, 0.06 |
| Salivary total protein | −0.04, 0.70 | N/A | −0.12, 0.28 |
| Time from last dose to sample collection b | 0.07, 0.52 | 0.02, 0.87 | −0.06, 0.62 |
| Non‐continuous measures (U, p) | |||
| Sex | 1916.0, 0.18 | 1898.0, 0.49 | 1768.0, 0.33 |
| Smoking status | 3007.0, 0.52 | 2760.0, 0.50 | 2203.0, 0.03 |
| Diabetes status | 1175.0, 0.36 | 1138.0, 0.40 | 832.5, 0.04 |
| Lithium formulation c | 3041.0, 0.76 | 2404.0, 0.08 | 2353.0, 0.14 |
| Lithium once vs twice per day | 2427.0, 0.42 | 1945.0, 0.02 | 1987.0, 0.08 |
Continuous measures were analyzed by Spearman correlation analysis. Categorical measures were analyzed using Kruskal‐Wallis non‐parametric tests. Values in bold are statistically significant (p < 0.05).
Variables compared using data from the first appointment only, all other measures above used data from multiple appointments.
Data was predominantly available and analyzed only for patients recruited from UCIMC.
Immediate versus sustained release formulation.
3.2. Correlation between saliva and serum lithium levels
Linear regression analysis across all samples revealed a significant correlation between saliva and serum lithium levels (unadjusted Spearman rho r = 0.74, p < 0.0001) (Figure 1A). Subsequently, multivariate regression including stepwise consideration of the significant variables from Table 2, as well as those that differed between recruitment sites (age, sex, and BMI) revealed significant effects of daily lithium dose (p < 0.0001), a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes (p = 0.01), and smoking (p = 0.03) on the association between salivary lithium and serum lithium. Incorporation of these covariates into the equation modestly improved the saliva‐to‐serum correlation (Spearman rho p = 0.77, p < 0.0001; Figure 1B). Significantly, this multivariate linear regression had a slope of b = 1.0, suggesting a 1:1 adjusted relationship between salivary and serum lithium levels (Figure 1B).
FIGURE 1.
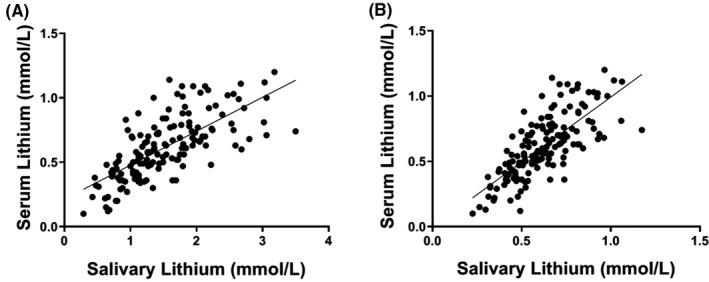
Correlations between salivary and serum lithium levels, unadjusted (A), and adjusted for relevant covariables, (B). Unadjusted correlation was determined by Spearman correlation analysis (r = 0.74; p < 0.0001). Adjusted correlation (Spearman rho = 0.77, p < 0.0001) was determined by multivariate linear regression analysis including adjustment for daily lithium dose, type 2 diabetes, and smoking
3.3. Associations between blood chemistry and lithium levels
Blood chemistry data, including serum sodium, potassium, and creatinine levels, were available for a subset of the samples (n = 80–85) enabling investigation into whether these factors affect lithium levels in serum or saliva or the saliva/serum ratio. Serum and salivary lithium levels were found to be significantly associated with serum potassium levels (Table 3); this correlation remained statistically significant after adjusting for recruitment site, daily lithium dose, dosing schedule, diabetes status, and smoking status (Table 3). In contrast, the saliva/serum lithium ratio was not correlated with any measure of blood chemistry (Table 3).
TABLE 3.
Relationships between biofluid lithium levels and blood chemistry
| Serum analyte (n) | Unadjusted (r, p) | Adjusted for covariates a (r, p) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saliva lithium | Serum lithium | Ratio | Saliva lithium | Serum lithium | Ratio | |
| Na+ (85) | 0.04, 0.71 | −0.07, 0.51 | 0.05, 0.65 | 0.03, 0.80 | −0.06, 0.60 | 0.01, 0.91 |
| K+ (82) | 0.26, 0.02 | 0.30, 0.007 | −0.08, 0.47 | 0.25, 0.03 | 0.32, 0.004 | −0.16, 0.17 |
| Cre (85) | 0.03, 0.76 | 0.00, 0.98 | 0.07, 0.57 | 0.10, 0.37 | 0.16, 0.16 | −0.09, 0.44 |
| TSH (80) | 0.14, 0.23 | 0.09, 0.45 | 0.07, 0.57 | 0.17, 0.15 | 0.07, 0.56 | 0.11, 0.35 |
| WBC (32) | 0.13, 0.48 | 0.12, 0.53 | 0.09, 0.63 | 0.06, 0.78 | −0.05, 0.82 | 0.21, 0.31 |
Abbreviations: Na+, sodium; K+, potassium; Cre, creatinine; TSH, thyroid‐stimulating hormone; WBC, white blood cell count.
Values in bold are statistically significant (p < 0.05).
Covariates: daily lithium dose, dosing schedule, recruitment site, diabetes, smoking.
3.4. Predicting serum lithium levels from salivary levels across patients
We next explored how well salivary lithium levels could predict serum lithium levels across all saliva samples, which were split into a “Determination” cohort (n = 127) and a preliminary “Validation” cohort (n = 42), as described in the “Methods” section. Multivariate linear regression carried out on the Determination cohort, including stepwise correction for daily lithium dose, type 2 diabetes, smoking, and recruitment site as covariables, revealed similar results to that observed with the entire cohort, with the exception of smoking status, which was no longer significant. The adjusted saliva‐to‐serum correlation coefficient value of the Determination cohort was identical to that observed with the whole cohort (Prediction model Pearson r = 0.77; Figure 2A).
FIGURE 2.
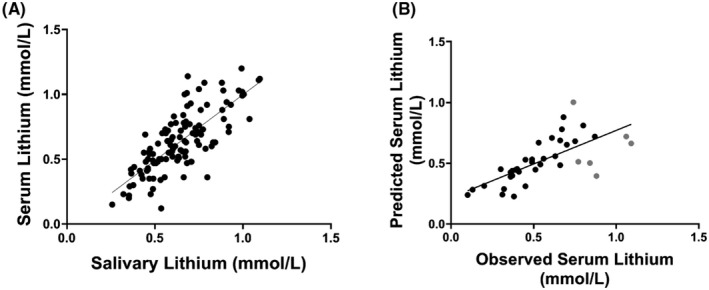
Relationship between salivary and serum lithium levels in the Determination cohort (A) and the relationship between predicted and observed serum lithium levels in the Validation cohort (B). The correlation between the salivary and serum lithium values in panel A were adjusted for daily lithium dose, diabetes status, and recruitment site (Pearson r = 0.77, p < 0.0001). The correlation between the observed and predicted serum lithium levels using the validation cohort equation from 2A was significant at a Pearson r = 0.70, p < 0.0001. Predicted serum lithium levels that differed from observed levels by more than 0.2 mmol/L are highlighted in grey in panel B
Next, we tested the prediction model on the validation cohort (n = 38) using the following linear equation, solving for Y (serum lithium levels): Y = 0.166 + 0.255*(Saliva lithium) −0.056* (1 if VASDHS, 0 if UCIMC) +0.145* (1 if diabetic, 0 if not). Daily lithium dose was not included in the prediction model, as it had a multivariate regression slope coefficient (b) of 0.0, and would therefore have had no effect on the outcome.
The salivary lithium levels predicted serum lithium levels with a Pearson correlation rho value of 0.70 (p < 0.0001). Of the 38 samples included in this model, 6 (16%) of the predicted serum levels differed from observed levels by more than 0.2 mmol/L (shown in grey in Figure 2B). Given that the recruitment site variable would not be one that would be available in a formula for general use, we also investigated the same correlation with the recruitment site variable removed (Figure S3). After removing the recruitment site variable from the equation (thus giving Y = 0.166 + 0.255*(Saliva lithium) +0.145* (1 if diabetic, 0 if not)), salivary lithium levels predicted serum lithium levels with a Pearson correlation rho of 0.69 (p < 0.0001) (Figure S3A). Prediction models with and without recruitment site adjustment were correlated with a Pearson rho of 0.99 (p < 0.0001) (Figure S3B). Therefore, the exclusion of the recruitment site variable is unlikely to affect the prediction model.
3.5. Predicting serum lithium levels from saliva levels within patients
Over half of the patients in our study (n = 40) provided samples on multiple visits, which allowed for the prediction of serum lithium levels using the patient's own previous salivary lithium data. We used the saliva/serum ratio from each observation in combination with their salivary lithium level from the patient's subsequent appointment to predict the serum level for that second appointment. The saliva/serum ratios for each appointment for these patients is shown in Table S1. Using this approach, we found the predicted vs. observed serum lithium levels to be significantly correlated (Pearson r = 0.71; p < 0.0001; Figure 3A), even when patients had a dose change from one appointment to the next. Patients attending four or more appointments allowed us to compare additional within‐subject data to determine if the prediction of serum lithium level would be improved by calculating the value based on the average of the saliva/serum ratios from the first three visits. The use of subjects' average within‐subject saliva/serum lithium ratio from three prior observations, dramatically improved the ability to predict serum levels from saliva on a fourth observation of the same subject. (Pearson r = 0.90, p < 0.0001), albeit with a small sample size (n = 16) (Figure 3B). Using this method, 75% of samples showed <0.1 mmol/L difference in the predicted versus observed serum lithium level and only two samples out of 16 showed a difference >0.2 mmol/L.
FIGURE 3.
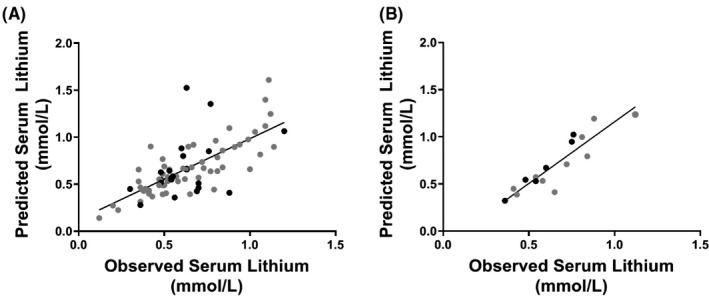
Comparisons of predicted vs. actual lithium levels, based on a single prior within‐subject saliva/serum lithium ratio (A) and an average of three prior within‐subject saliva/serum ratios (B). In panel A, the predicted versus observed serum lithium levels were significantly correlated (Pearson r = 0.71; p < 0.0001), however, this correlation improved dramatically when an average of three ratios were used to predict the 4th appointment (r = 0.90; p < 0.0001). Overall, patients 55 years of age and above showed the most variability in saliva/serum lithium ratio levels (black data points in A, B). Patients were included in Figure 3A if they attended two or more appointments, and Figure 3B if they attended four or more appointments
Overall, the within‐subject prediction of serum lithium levels based on salivary lithium levels from a single preceding appointment alone was not better than that calculated across different patients. This is likely due to the high variation in saliva/serum ratios observed from one appointment to the next for some patients (Figure 4; Table S1), although it is clear that many patients show stable saliva/serum ratios across several months, and even up to 18 months (Figure 4; Table S1). As lithium pharmacokinetics may be affected by age‐related physiological changes, and because of the very large age range of our patients (14–76 years), we assessed the effect of age on the variability in saliva/serum ratios across any two appointments. Indeed, there was a significant correlation between age and the variation of the saliva/serum ratio across observations (Spearman r = 0.40; p = 0.0001; Figure S2), an effect which was no longer significant after including only patients <55 years of age. Furthermore, when comparing within‐subject linear regressions from patients <55 years compared to ≥55 years (Figure 3A, grey vs. black data points), the regression of patients <55 years passed a test for homoscedasticity, whereas the regression of patients ≥55 years did not (p = 0.03). This increase in residual variation was overcome by using the average saliva/serum lithium ratio from the preceding three visits (both ps > 0.05; Figure 3B grey vs. black data points). When comparing the between‐subject prediction of serum lithium levels based on salivary lithium levels using the equation Y = 0.166 + 0.255*(Saliva lithium) +0.145* (1 if diabetic, 0 if not) (Figure 2; Figure S3), and separating patients <55 years and ≥55 years, the regression of patients <55 years did not pass a test for homoscedasticity (p = 0.002) but was significantly correlated (Pearson r = 0.73, p < 0.0001), whereas the regression of patients ≥55 years passed a test for homoscedasticity but was not significantly correlated (Pearson r = 0.45, p = 0.16) (Figure S4).
FIGURE 4.
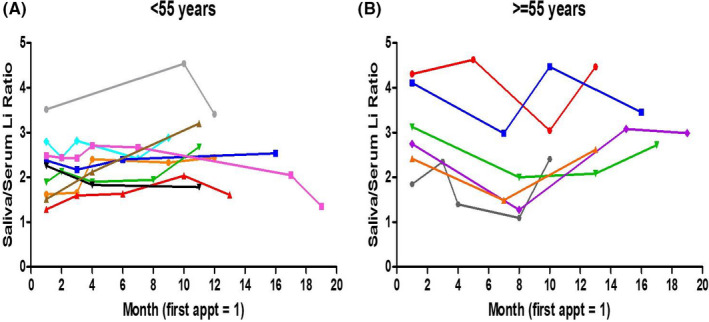
Saliva/serum ratios for individual patients across multiple visits in patients younger than 55 years (A) and equal or greater than 55 years (B). Patients' first study appointment is represented by month 1, followed by every subsequent appointment, spaced by months since the first appointment. For clarity, only data from patients attending visits spanning 10 months or greater from their initial appointment are shown. Each color represents an individual patient. Saliva/serum ratios for all patients attending at least two appointments are shown in Table S1
4. DISCUSSION
In this study, we found that salivary lithium levels are highly correlated with serum lithium levels across 169 matched saliva‐serum samples from 75 subjects recruited from two different sites, strongly supporting the suitability for use of saliva for monitoring of lithium levels in patients taking lithium medications. The use of saliva for drug monitoring has been reported previously. In fact, a large body of work dating back >30 years has suggested that salivary lithium might be useful for patient monitoring of lithium levels, with several previous studies demonstrating good correlation between saliva and serum lithium values (i.e. between 0.50 to 0.88). 17 , 20 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 However, in past studies, the sample sizes were small, saliva collection techniques varied, older methods for lithium quantification were used, and medical and lifestyle variables were not included. 17 Furthermore, few past studies have investigated the longitudinal within‐patient association between salivary and serum lithium levels 23 as we have in the current study. With improved methodology, inclusion of important covariates, and a larger sample derived from a multi‐center cohort, we have conducted the largest and most integrative study to date supporting the utility of saliva as a relevant biofluid for therapeutic lithium monitoring.
In this study, we have shown that incorporation of daily lithium dose, dose regimen, smoking status, and diabetes can improve the predictive power of saliva for serum lithium levels. Our covariate‐adjusted inter‐subject model had similar predictive power to the use of intra‐subject ratios from a patient's single preceding appointment but was less powerful than the use of an average intra‐subject ratio from a patient's preceding three appointments. In clinical practice, both measures have their own advantages. For example, the covariate‐adjusted between‐subject model could be used in the instance that a patient does not have three preceding, saliva/serum lithium ratio measurements.
Previous studies have shown that body weight, serum creatinine, serum potassium, and age are correlated with lithium levels in serum. 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 In this study, we did not observe an association with BMI, nor creatinine, on serum lithium levels, which is consistent with some other studies. 38 , 40 We did find significant associations between serum potassium levels and both saliva and serum lithium levels, but not with saliva/serum lithium ratios. Nonetheless, consideration of serum potassium could be important given that potassium intake has been proposed to play a role in chronic kidney disease, 41 which is associated with diabetes, a condition we found to significantly affect the saliva‐serum lithium correlation. Further, we found that the variability in saliva/serum lithium ratios across time was positively correlated with age. As glomerular filtration rate decreases with age, 16 older individuals may become more sensitive to lithium treatment. Indeed, blood lithium concentration appears to be higher in the elderly, after adjusting for dose, compared to younger patients, which could be due to an age‐related reduction in renal function and increase in disease comorbidity, and more use of common medications that may interfere with lithium elimination such as hydrochlorothiazide, NSAIDS, and ACE inhibitors and angiotensin receptor antagonists. 15 In addition, elderly subjects are more likely to have multiple comorbidities which could have yet‐undetermined effects on lithium distribution in the body. These previous studies may explain why patient saliva/serum lithium ratios were more variable across time in older patients, and why our proposed between‐subject prediction model was less effective when assessed on elderly patients alone. Together, this data suggest that both between‐subject and within‐subject lithium prediction models may be more appropriate when limited to younger populations. However, and importantly, our data also suggests that for patients age 55 and above, the use of their average saliva/serum lithium ratio from three preceding appointments, rather than one preceding appointment or the between‐subject regression, may circumvent this variation.
Advantages to using saliva rather than blood are many, including the fact that it doesn't require trained personnel to collect and can be carried out in any setting; these features could directly translate into more frequent and improved lithium monitoring for both outpatients and inpatients. For outpatients, saliva sampling could allow for at‐home collection, which would allow patients to schedule lithium measurements around last dosing, food, and other activities, without the need to arrange and attend a pathology clinic. In addition, lithium measurements could be taken from saliva samples collected during phases of acute bipolar illness, when an individual may be unable to attend a pathology clinic, but when knowledge of plasma lithium levels would help clinicians determine the optimal therapeutic dose. 8 Such results could be tabled in a Lithium therapy chart alongside symptoms, medication tolerability, general health, and significant life events, as outlined by the Lithiumeter guide, to provide a comprehensive overview of illness and treatment. 8 Overall, at‐home sampling would more accurately predict an individual's lithium level around these other, possibly confounding activities. This is important because the prescription of lithium medications is based on the level in the blood 12 h after an individual's last dose, which is difficult to capture precisely in a clinical appointment. While we found no association between time lapsed from the last dose to blood collection, and either salivary lithium, serum lithium, or saliva/serum lithium ratios, previous research by Serdarevic et al. which compared salivary lithium and serum lithium correlations at 2‐ and 12‐h post‐last dose, suggested that the saliva‐serum correlation may be improved by collecting samples closer to the last dose. 34 Notably, observations of within‐patient data suggest that the same patient had lower lithium levels at appointments attended later in the day (data not shown). This within‐patient qualitative trend between lithium levels and time from last dose may also explain the variation observed in some patients in Figure 4. Due to the known difference in lithium pharmacokinetics in saliva vs. serum, 27 , 34 the timing of the last dose is of critical importance. For inpatients, saliva measures could also be used to better optimize the timing of lithium levels used for clinical maintenance and monitoring, as saliva sampling would not be restricted to a phlebotomist's schedule. Further, and as we observed in our study, inpatients are much more likely to agree to a saliva collection versus a blood draw, although this feature is not limited to inpatients, as many outpatients, especially those in a manic state, are also averse to blood draws. Further research, which investigates the within‐subject diurnal pharmacokinetics of salivary lithium levels in the presence of potentially confounding factors, such as food intake, caffeine, and sleep pattern, will allow for the refinement of an at‐home saliva collection model and protocol.
Importantly, we found that lithium measurements were stable at 4℃ or room temperature for at least 24 h. This feature would further facilitate a home‐health care‐based program that could involve saliva sample collection at home, followed by samples sent to a centralized lab for lithium measurements. The results could then be monitored and discussed remotely via a telemedicine encounter. Such a process could avoid the costly office, and maybe even hospital, visits.
Our study is not without limitations. One limitation was that it included a limited number of samples from patients within the higher range of serum lithium levels (≥1.0 mmol/L), and it is within this range that the between‐subject prediction of serum lithium levels fell by greater than 0.2 mmol/L outside of the observed levels (see Figure 2B), and variability increased (see Figure S4). Given the upper limit of toxicity for serum lithium is 1.5 mmol/L, predicting serum levels from saliva levels in patients taking high doses of lithium could be problematic when using the intersubject model with regards to potential toxic side effects. However, when serum levels were predicted using the average intrasubject ratio from three appointments, the predicted serum level was less than 0.1 mmol/L from the observed level for 75% of the patients, with two patients having predicted levels >0.2 mmol/L. This suggests accurate estimations of serum lithium using the average ratios, although future studies to better characterize saliva lithium levels at the upper boundaries of the therapeutic range and into the toxic range will be needed to more fully characterize the value of saliva testing of lithium before implementation into routine clinical practice. Additionally, the value of salivary measures would need to be calibrated to an individual, as there are currently no FDA standards for a stand‐alone saliva measure.
Another limitation of our study was that some participants were non‐compliant with their dose, or missed their scheduled dose. Because we wanted to maximize the power of our study, these patients were not excluded; however, give the significant effect of lithium daily dose on the saliva‐serum relationship, we expect that improved results would be obtained using only those patients on stable medication and those who are compliant with their medications. Of note is that our prediction models included samples from some patients who changed their dose across subsequent visits, suggesting that a dose change or dose titration would not greatly affect the ability of saliva to predict the serum level. Nonetheless, the notion that the inter‐subject model would be best applied to patients who are clinically stable, as well as medically compliant and might only require testing every 3–6 months, was also suggested in a previous study by Rosman and colleagues. 23 Additionally, given that biweekly lithium testing is commonly indicated shortly after starting the drug and/or after changing dose, additional examination of saliva testing should focus on subjects undergoing these changes to better characterize the sensitivity and saliva/serum ratio when lithium levels are dynamic.
Considering the overall literature, despite variations in methods of salivary lithium collection and quantification, the majority of previous studies have reported saliva/serum lithium correlations similar to that observed in our study. 20 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 This consistency in results across studies, as well as the stability in saliva/serum lithium ratios in most patients across time observed in our study, opens the door for the development and implementation of a point‐of‐care (POC) salivary lithium device. A saliva‐based POC assay for lithium would have enormous value in the new era of personalized medicine, as it would lead to optimized treatment protocols for at‐home collection as well as patient compliance in the clinic. In 2005, the FDA approved the use of a finger‐prick in‐office test for serum lithium levels. 42 Use of this POC serum test can already reduce the frequency and need for laboratory‐conduced venepuncture, however, the kit is expensive, and has issues related to the separation of blood components. Conversely, saliva requires less processing than blood, and it is, therefore, estimated that it would not be as expensive to operate. While such devices would require standard collection procedures, our studies suggest that sampling at room temperature did not affect lithium quantitation and that levels did not vary whether the samples were centrifuged or not (Figure S1). It is important to note, however, that not all potential contributors to saliva/serum lithium level variation have been investigated. It is, therefore, possible that the use of a novel at‐home device may be improved further through the incorporation of, or affected by the presence of, other as of yet un‐identified variables. These could include factors, such as sugar intake, water intake, caffeine, and sleep patterns.
In summary, our findings show robust correlations between saliva lithium levels and those measured in serum, and that saliva lithium values can accurately predict serum lithium levels, especially when prior intrasubject data is considered. Implementation of salivary lithium monitoring, including a home‐based collection design, would lead to a personalized monitoring approach for patients taking lithium medications and would improve treatment opportunities for patients with mood disorders, although additional studies on the efficacy of salivary lithium measurements in a more controlled patient cohort would be needed. Additionally, a POC saliva assay would provide the basis for future technical innovations that could allow for lithium monitoring via POC devices that could transmit data directly to the patient's medical provider through cloud‐based data storage or a smartphone. The implementation of such devices in saliva samples is already underway. 43
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
DAG is founder and Chief Scientific and Strategy Advisor at Salimetrics LLC and Salivabio LLC. These relationships are managed by the policies of the committees on conflict of interest at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and the University of California at Irvine. No other authors declare competing interests. The founding sponsor had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Supporting information
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study was funded by the Elisabeth Severance Prentiss Foundation. The authors wish to thank Andrew Huang for excellent technical assistance.
Parkin GM, McCarthy MJ, Thein SH, et al. Saliva testing as a means to monitor therapeutic lithium levels in patients with psychiatric disorders: Identification of clinical and environmental covariates, and their incorporation into a prediction model. Bipolar Disord. 2021;23:679–688. 10.1111/bdi.13128
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
Anonymized summary data will be shared by reasonable formal request from qualified researchers, subject to a data sharing agreement, and in compliance with the requirements of the funding bodies and institutions.
REFERENCES
- 1. Shorter E. The history of lithium therapy. Bipolar Disord. 2009;11:4‐9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Cade JF. Lithium salts in the treatment of psychotic excitement. Med J Aust. 1949;2:349–352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Pérez‐Granados AM, Vaquero MP. Silicon, aluminium, arsenic and lithium: essentiality and human health implications. J Nutr Health. 2002;6(2):154‐162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Ozpoyraz N, Tamam L, Kulan E. Thyroid abnormalities in lithium‐treated patients. Adv Ther. 2002;19(4):176‐184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Finley PR, Warner MD, Peabody CA. Clinical relevance of drug interactions with lithium. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1995;29(3):172‐191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Cayköylü A, Capoğlu I, Ünüvar N, Erdem F, Cetinkaya R. Thyroid abnormalities in lithium‐treated patients with bipolar affective disorder. J Int Med Res. 2002;30(1):80‐84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Tredget J, Kirov A, Kirov G. Effects of chronic lithium treatment on renal function. J Affect Disord. 2010;126(3):436‐440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Malhi GS, Gershon S, Outhred S. Lithiumeter: Version 2.0. Bipolar Disord. 2016;18(8):631‐641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Schou M, Baastrup P, Grof P, Weis P, Angst J. Pharmacological and clinical problems of lithium prophylaxis. Br J Psychiatry. 1970;116(535):615‐619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Murru A, Pacchiarotti I, Amann B, Nivoli A, Vieta E, Colom F. Treatment adherence in bipolar I and schizoaffective disorder, bipolar type. J Affect Disord. 2013;151(3):1003‐1008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Ng F, Mammen OK, Wilting I, et al. The International Society for Bipolar Disorders (ISBD) consensus guidelines for the safety monitoring of bipolar disorder treatments. Bipolar Disord. 2009;11(6):559‐595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Kirkham E, Bazire S, Anderson T, Wood J, Grassby P, Desborough JA. Impact of active monitoring on lithium management in Norfolk. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2013;3(5):260‐265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Thomsen K, Schou M. Avoidance of lithium intoxication: advice based on knowledge about the renal lithium clearance under various circumstances. Pharmacopsychiatry. 1999;32(03):83‐86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Finley PR. Drug interactions with lithium: an update. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2016;55(8):925‐941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Sproule BA, Hardy BG, Shulman KI. Differential pharmacokinetics of lithium in elderly patients. Drugs Aging. 2000;16(3):165‐177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Weinstein JR, Anderson S. The aging kidney: physiological changes. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2010;17(4):302‐307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Gałuszko‐Węgielnik M, Jakuszkowiak‐Wojten K, Wiglusz MS, et al. Lithium therapeutic dose monitoring in human saliva. Psychiatr Danub. 2017;29(3):361‐364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Spring KR, Spirtes MA. Salivary excretion of lithium: I. Human parotid and submaxillary secretions. J Dent Res. 1969;48(4):546‐549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Shopsin B, Gershon S, Pinckney L. The secretion of lithium in human mixed saliva: effects of ingested lithium on electrolyte distribution in saliva and serum. Int Pharmacopsychiatry. 1969;2:148‐169. [Google Scholar]
- 20. Shetty SJ, Desai PB, Patil NM, Nayak RB. Relationship between serum lithium, salivary lithium, and urinary lithium in patients on lithium therapy. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2012;147(1–3):59‐62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Ben‐Aryeh H, Laor R, Szargel R, et al. Saliva for monitoring of patients with primary affective disorders. Isr J Med Sci. 1984;20(3):197‐201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Khare CB, Sankaranarayanan A, Goel A, Khandelwal SK, Srinivasa MR. Saliva lithium levels for monitoring lithium prophylaxis of manic depressive psychosis. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol. 1983;21(9):451‐453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Rosman AW, Sczupak CA, Pakes GE. Correlation between saliva and serum lithium levels in manic‐depressive patients. Am J Hosp Pharm. 1980;37(4):514‐518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Bowden CL, Houston JP, Shulman RS, Clothier JM. Clinical utility of salivary lithium concentration. Int Pharmacopsychiatry. 1982;17(2):104‐113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. McKeage MJ, Maling TJ. Saliva lithium: a poor predictor of plasma and erythrocyte levels. N Z Med J. 1989;102(878):559‐560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Nataraj GS, Bhat VK. Reliability of saliva lithium level‐a prospective study. Indian J Psychiatry. 1981;23(2):115‐119. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Obach R, Borja J, Prunonosa J, et al. Lack of correlation between lithium pharmacokinetic parameters obtained from plasma and saliva. Ther Drug Monit. 1988;10(3):265‐268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Guttuso T, Russak E, De Blanco MT, Ramanathan M. Could high lithium levels in tobacco contribute to reduced risk of Parkinson's disease in smokers? J Neurol Sci. 2019;397:179‐180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Stein RS, Hanson G, Koethe S, Hansen R. Lithium‐induced granulocytosis. Ann Intern Med. 1978;88(6):809‐810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Granger DA, Taylor MK. Salivary bioscience: foundations of interdisciplinary saliva research and applications. Springer Nature; 2020. [Google Scholar]
- 31. Sankaranarayanan A, Goel A, Pant V. Variation in the relationship between serum and saliva lithium levels. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol. 1985;23(7):365‐366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Verghese A, Indrani N, Kuruvilla K, Hill PG. Usefulness of saliva lithium estimation. Br J Psychiatry. 1977;130(2):148‐150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Othmer E, Powell B, Piziak V, Preskorn S. Prospective use of saliva lithium determinations to monitor lithium therapy. J Clin Psychiatry. 1979;40(12):525‐526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Serdarević N, Kozjek F, Malešič I. Saliva and serum lithium monitoring in hospitalized patients and possibility to replace serum to saliva. Bosnian J Basic Med Sci. 2008;6(4):32‐35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Ben‐Aryeh H, Naon H, Szargel R, Gutman D, Hefetz A. Salivary lithium concentration—a tool for monitoring psychiatric patients. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1980;50(2):127‐129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Sims A, White A, Garvey K. Problems associated with the analysis and interpretation of saliva lithium. Br J Psychiatry. 1978;132(2):152‐154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Yukawa E, Nomiyama N, Higuchi S, Aoyama T. Lithium population pharmacokinetics from routine clinical data: role of patient characteristics for estimating dosing regimens. Ther Drug Monit. 1993;15(2):75‐82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Xu YY, Xia QH, Liang J, et al. Factors related to lithium blood concentrations in Chinese Han patients with bipolar disorder. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2019;15:1929‐1937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Yoshida K, Uchida H, Suzuki T, et al. Prediction model of serum lithium concentrations. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2018;51(3):82‐88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Mathew B, Rao JM, Sundari U. Lithium‐induced changes in the body mass index. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1989;80(6):538‐540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Picard K, Barreto Silva MI, Mager D, Richard C. Dietary potassium intake and risk of chronic kidney disease progression in predialysis patients with chronic kidney disease: a systematic review. Adv Nutr. 2020;11(4):1002‐1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Jefferson JW. Finger‐stick lithium test. Curr Psychiatry. 2005;4(10):111‐117. [Google Scholar]
- 43. Goldoni R, Farronato M, Connelly ST, Tartaglia GM, Yeo WH. Recent advances in graphene‐based nanobiosensors for salivary biomarker detection. Biosens Bioelectron. 2021;171:112723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Material
Data Availability Statement
Anonymized summary data will be shared by reasonable formal request from qualified researchers, subject to a data sharing agreement, and in compliance with the requirements of the funding bodies and institutions.


