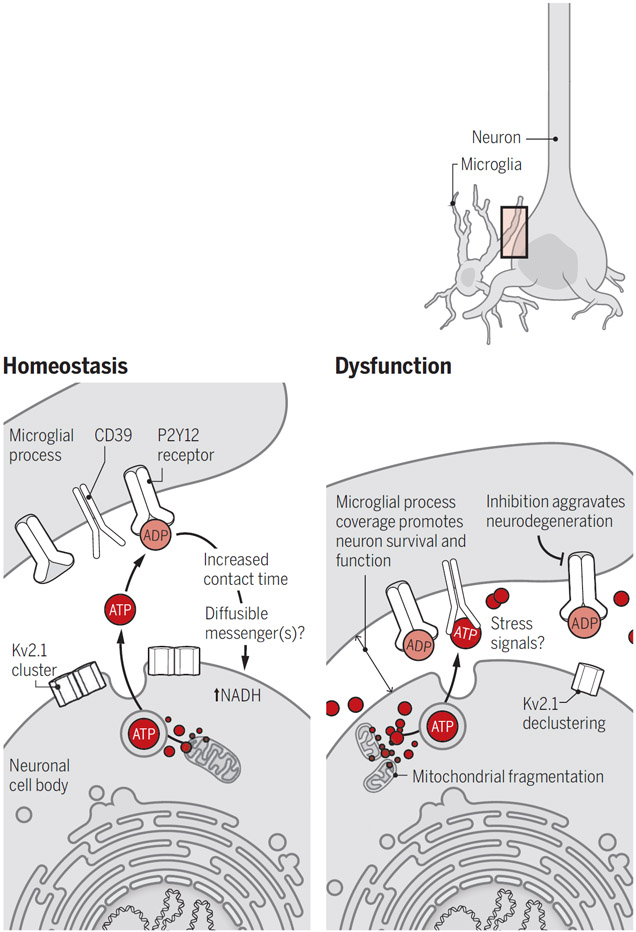
Microglia protect neurons.
During homeostasis, low amounts of ATP released from active neurons are converted to ADP and detected by microglial processes through P2Y12 receptors, leading to increased contact time with cell bodies and NADH in neurons. After neuronal injury, high concentrations of extracellular ATP increase coverage by microglial processes that protect viable neurons from cell death, although the precise mechanisms remain unknown.
ADP, adenosine diphosphate; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; Kv2.1, voltage-gated potassium channel 2.1; NADH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; P2Y12 receptor, P2Y purinoceptor 12.