Abstract
Introduction
Inflammation is a fundamental response of the immune system during tissue damage or pathogen infection to protect and maintain tissue homeostasis. However, inflammation may lead to life-threatening conditions. The most common treatment of inflammation is non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Nowadays, the development of safer new NSAIDs is critical as most of the existing NSAIDs have serious adverse effects, such as gastrointestinal (GI) toxicity and cardiotoxicity. In the present study, four compounds as Schiff base derivatives of 7-hydroxy-4-formyl coumarin and 7-methoxy-4-formyl coumarin were designed and synthesized aiming to develop a lead compound that exhibits anti-inflammatory activity and circumvents the side effects of NSAIDs, especially GI toxicity.
Materials and Methods
Lipinski’s rule of five was applied for each designed molecule to evaluate the drug-likeness properties. Molecular docking studies were performed using the ligands and the cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) protein to select the best-scored molecule using AutoDock 4.2.6. The molecules were then synthesized and characterized. An in vitro anti-inflammatory assay of the compounds against the COX-2 receptor was realized through a protein denaturation assay.
Results and Discussion
All four synthesized ligands passed Lipinski’s rule of five and exhibited higher binding free energy compared to the positive standard control (ibuprofen), and the Ki values of compounds 5, 7, and 8 were in the nanomolar range. However, only compounds 6 and 7 obtained a higher percentage of inhibition of protein denaturation relative to ibuprofen.
Conclusion
The present study suggested that compound 7 may be a lead molecule because this ligand not only exhibited the best computational and experimental results but also exhibited the strongest correlation between the concentration and percentage of protein denaturation (R = 0.986 and R2 = 0.972) with the lowest P-value (0.014).
Keywords: coumarin, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, ibuprofen, lead compound, cyclooxygenase, binding free energy, Schiff base derivatives
Introduction
Coumarins are naturally available polyphenolic compounds1 found in the leaves, roots, and seeds of plants from Rutacease and Apiacease families. In addition, coumarins can be isolated from microbial sources, such as aflatoxin and novobiocin. Coumarins are crystalline, colorless compounds2 consisting of benzene rings, alpha-pyrone, and a carbonyl group connected with the C2 of the pyrone ring, which are the secondary metabolites of pyran derivatives through condensation of alpha-pyrone with benzene in plants.3 Coumarins have diverse biological activities according to the benzopyran substitutions, such as anti-inflammatory, antiviral, antibacterial, growth regulation, antioxidant, anticoagulant, and antitumor activities. Some derivatives of coumarin are currently available as drugs, such as warfarin (anticoagulant) and novobiocin (antibacterial).4–10 The anti-inflammatory effects of coumarin are attributed to the inhibition of prostaglandin biosynthesis, lipoxygenase, and cyclooxygenase enzymes as well as neutrophil-dependent superoxide anion generation.11,12 Synthetic coumarins have a vital role in the drug discovery and development process.13–15 One coumarin derivative iminocoumarin, has anticancer, anti-inflammatory, and analgesic activities.16–18 Several selective, non-toxic organic compounds, including thiosemicarbazide,19 acetophenone,20 aminothiadiazole,21–23 hydrazone derivatives,24 and p-aminobenzoic acid have anti-inflammatory and analgesic activity.25,26 The expected analgesic and anti-inflammatory activity of both coumarin and the mentioned organic compounds prompted us to design and synthesize combined molecules, which are coumarin Schiff base derivatives of the organic molecules. The synthesis of iminocoumarin derivatives (Schiff base derivatives of coumarin) can be achieved via condensation of 7-hydroxy-4-formyl coumarin and 7-methoxy-4-formyl coumarin with the appropriate amount of organic compounds under reflux in ethyl alcohol and heating to 75–80 °C.27,28
The inflammatory response is defined as a protective mechanism of animal tissue including mankind against irritants, harmful stimuli, toxins, pathogens, and any damaging factors.29 Inflammation is presumably a favorable response of living tissues, specifically acute inflammation, as the host attempts to heal damaged tissues and remove injurious stimuli; nevertheless, persisting inflammation may be detrimental to health and cause tissue damage, such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which remains in host tissues for a long period, or autoimmune diseases when the immune system recognizes normal tissues as a foreign antigen and attacks them.30–32 At present, the most used drugs for the treatment of inflammation and pain, as over-the-counter (OTC) and prescribed medicines, are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).33 NSAIDs are suggested for menstrual pain, postoperative pain, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, chronic pain, and they are also used as antipyretics.34,35 NSAIDs are divided according to their chemical structures or their selectivity of enzyme isoform inhibition. However, all NSAIDs have relatively the same functions. NSAIDs can be classified chemically as follows: phenylpyrazolones; aryl ketones; aryl and heteroaryl acetic acids; anilides; anthranilates; propionic acid; salicylates; selective cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors; and oxicams.36 The second classification of NSAIDs is according to the selectivity of cyclooxygenase (COX) enzyme inhibition. The classical NSAIDs, such as aspirin, diclofenac, and ibuprofen, inhibit both COX enzyme isoforms, while the newer developed drugs possess more selectivity to the COX-2 isoform.33,37 The mechanism of NSAIDs occurs through inhibition of COX-1 and COX-2 to prevent the production of prostaglandins (PGs) from arachidonic acid.38
Despite the applicability and reputation of NSAIDs, they cause serious adverse effects, such as cardiovascular toxicities, gastrointestinal (GI) toxicities, hepatic injury, renal damage, and hypertension, resulting in a drawback and limitation of their use.39–41 According to the previous studies, the inhibition of the COX-2 enzyme leads to favorable anti-inflammatory activity, while COX-1 inhibition causes unfavorable side effects, such as kidney and gastric damage.42 However, traditional NSAIDs inhibit both COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes, and they cannot distinguish between the two isoforms, which causes gastric upset, irritation, and ulcers.43 Therefore, after revealing the disadvantages of conventional NSAIDs due to COX-1 inhibition, further development of NSAIDs has trended towards selective COX-2 inhibitors. Nevertheless, many selective COX-2 inhibitor drugs have been withdrawn from the market in the last few decades44 as many studies have indicated a strong correlation of elevated blood pressure, thrombosis, and cardiac attack with NSAID consumption, especially COX-2 inhibitors due to inhibition of prostacyclin.45–47 Moreover, selective COX-2 inhibitors do not entirely prevent enteropathy48 as a significant number of studies have confirmed that the PGs related to COX-2 have a vital role in GI protection and repair of mucosal damage.49–51 Lastly, some evidence suggests that the COX-1 isoform is a major inflammation contributor. These outcomes challenge the previous hypotheses of distinct housekeeping of the COX-1 isoform versus the inflammatory function of the COX-2 isoform emphasizing the significant involvement of COX-1 through prostanoid synthesis.52–55
Because NSAIDs are connected with life-threatening toxicities, including GI toxicity,50 different approaches have been applied to address such issues while maintaining the reputation of this class, such as prodrug formulations to mask the carboxylic acid functional group, as the presumed leading cause of GI toxicity, of NSAIDs.56 Furthermore, the topical drug delivery system, as an emulsion formula, is another approach to address NSAID toxicities.57 Other solutions to prevent enteropathy and cardiotoxicity are combining NSAIDs with anticholinergics, amino acids, carbohydrates, and antioxidants.50 In conclusion, nonselective COX inhibitors may be safer than the selective COX-2 inhibitors for the cardiovascular system, but they have significantly higher toxicity on the GI tract.58
Hence, in the current context, the quintessential scope of many researchers is to develop a safer NSAID therapeutic without compromising the clinical benefits.59 The goal of the present study was to design and synthesize effective and potent Schiff base derivatives of 7-hydroxy-4-methylcoumarin and 7-methoxy-4-methylcoumarin to overcome the main side effects of NSAIDs, such as GI toxicity, and preserve their clinical benefits. In the present study, ibuprofen was used as the positive control. Ibuprofen was the second developed NSAID after acetylsalicylic acid in 1969 in the UK, and it was changed from a prescription-only medicine (POM) to OTC in the USA and UK after studying the tolerability and safety profiles in the 1980s.60,61 Furthermore, ibuprofen is considered a prototypical NSAID and the gold standard for comparison of new analgesics due to its safety and efficacy, and it is neither a strong COX-1 nor strong COX-2 inhibitor. However, ibuprofen still has NSAID side effects, such as GI issues.62
Materials and Methods
Computational Study
Drug-Likeness Prediction of the Ligands
Drug-likeness properties of the small molecules can be predicted through Lipinski’s rule of five, which estimates the difficulties related to absorption and membrane permeation (oral bioavailability). Therefore, any small molecule that follows the rule may be considered an orally bioavailable compound. Currently, in the most modern drug discovery projects of small molecules, the lead compound should pass this rule before proceeding to a drug candidate.63 Chemicalize was used for the determination of the drug-likeness properties (https://chemicalize.com, developed by ChemAxon).64
Protein and Ligand Preparations
COX-2 protein was downloaded from the Protein Data Bank website (https://www.rcsb.org; access code 4PH9).65 The starting coordinate was the protein-bound with ibuprofen,66 and the ligands and water molecules were deleted. Kollman charges were then added (total charges = 16.76), and polar hydrogen was added. The file was saved as a pdbqt file using AutoDock 4.2.6.66,67 Regarding the preparation of the ligands, the 2D structures of the ligands were generated, and the 3D models were then produced through molecular dynamic (MD) simulations and energy minimizations using the ff94 forcefield. The molecules were saved as a mol2 file. Marvin was used for drawing the ligand structures (Marvin version 20.8.5, ChemAxon; https://chemaxon.com/products/marvin).68
Molecular Docking of Ligands with COX-2 Protein
All the designed ligands were docked with COX-2 protein to evaluate the binding free energy. Before docking, the Schiff base derivative molecules and the reference compounds were opened in the ADT tools of AutoDock. Rotatable bonds were determined, and the files were saved as pdbqt files. The macromolecule was then opened from the grid, and the ligand was selected. The grid box was generated by adjusting the grid points to 42×60 X 40, and the grid point spacing was 0.419 Å. Furthermore, the coordinates of the central grid points on the maps were set at 9.850, 18.844, and 24.537 to cover all the receptor pocket space. Moreover, a rigid macromolecule was generated. After preparing all data, glg and map files were generated. Finally, docking was run, and the dlg files were generated. During the docking process, AutoDock combines the Lamarckian genetic algorithm and empirical free energy force fields to calculate the best-bound conformations and energy of the protein-ligand interactions.69–73 Both glg and dlg files were generated using canonical Ubuntu 18.04.6 LTS (Bionic Beaver; https://releases.ubuntu.com/bionic) as an open-source operating system by applying the Linux kernel and based on Debian.74
After docking, the best-scored interactions between the ligands and the COX-2 protein were visualized, and the conformations were analyzed using UCSF Chimera 1.6 package from the Resource for Biocomputing, Visualization, and Informatics at the University of California San Francisco.75 In addition, all the receptor-ligand interactions were calculated, and schematic diagrams were generated using LigPlot Plus (version V.2.2.5, 2022).76
Experimental Section
Chemistry
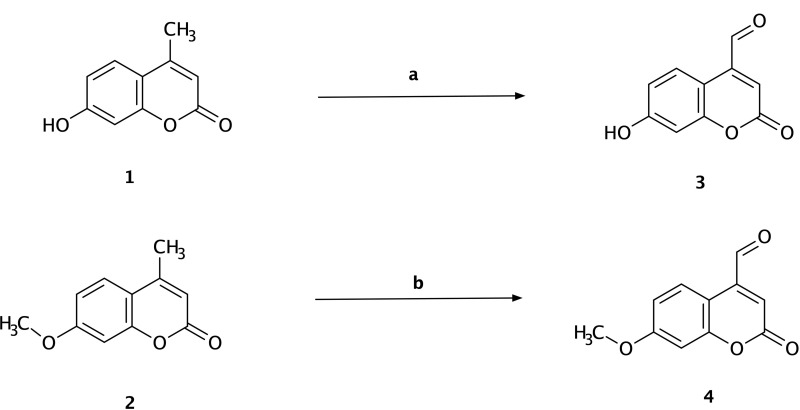
The synthesis of 7-hydroxy-4-formyl coumarin (3) and 7-methoxy-4-formyl coumarin (4) was started by dissolving 7-hydroxy-4-methyl coumarin (1) or 7-methoxy-4-methyl coumarin (2) (5 mmol, 1 g) in 50 mL of hot xylene. The solution was cooled, and selenium dioxide (9 mmol, 1 g) was then added. The solution was refluxed for a period of 12 h at 135–140 °C. The solution was then filtered to remove the insoluble selenium and evaporated using a rotary evaporator to remove the solvent. Finally, the yellow-colored product was recrystallized from ethanol (Scheme 1).
Scheme 1.
Synthesis of 7-hydroxy-4-formyl coumarin (3) and 7-methoxy-4-formyl coumarin (4). Reagents and conditions: (a) 7-hydroxy-4-methyl coumarin (1), hot xylene, selenium dioxide, reflux for 12 h, 135–140 °C, filtration, yield = 22%; (b) 7-methoxy-4-methyl coumarin (2), hot xylene, selenium dioxide, reflux for 12 h, 135–140 °C, filtration, yield = 31%.
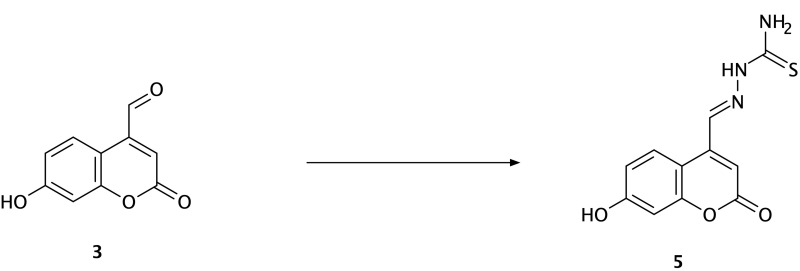
The synthesis of the Schiff base of thiosemicarbazide (5) was started by adding 5 mmol of thiosemicarbazide to the solution of 3 (5 mmol) and absolute ethanol (30 mL). The mixture was continuously stirred and then refluxed for 7 h at 75–80 °C. The yellow-colored precipitate was filtered, dried, and recrystallized from ethanol (Scheme 2).
Scheme 2.
Synthesis of compound (5) (thiosemicarbazide Schiff base derivative). Reagents and conditions: 7-hydroxy-4-formyl coumarin (3), thiosemicarbazide, ethanol, reflux for 7 h, 75–80 °C, filtration and recrystallization, yield = 67%.
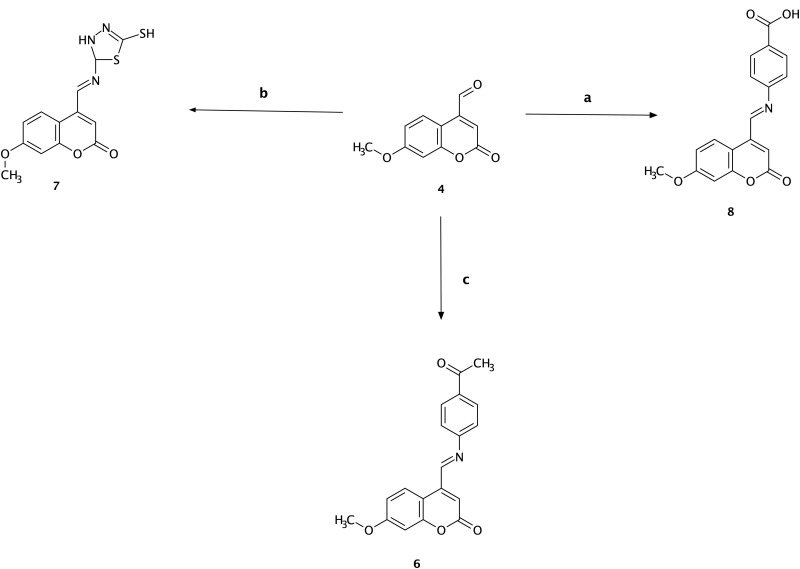
The synthesis of the Schiff base of p-amino acetophenone (6) was started by adding 5 mmol 4-amino acetophenone to the solution of 4 (5 mmol) and 30 mL of absolute ethanol with continuous stirring. The mixture was refluxed for 7 h at 75–80 °C. Finally, the precipitate was filtered, dried, and recrystallized from ethanol. The color of the compound was orange (Scheme 3).
Scheme 3.
Synthesis of compounds (6), (7), and (8). Reagents and conditions: (a) 7-methoxy-4-formyl coumarin (4), 4-aminobenzoic acid, ethanol, reflux for 7 h, 75–80 °C, filtration and recrystallization, yield = 87%; (b) 7-methoxy-4-formyl coumarin (4), 5-amino-1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-thiol, ethanol, reflux for 7 h, 75–80 °C, filtration and recrystallization, yield = 56%; (c) 7-methoxy-4-formyl coumarin (4), 4-aminoacetophenone, ethanol, reflux for 7 h, 75–80 °C, filtration and recrystallization, yield = 71%.
The synthesis of the Schiff base of 5-amino-1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-thiol (7) was started by adding 5 mmol 2-amino-5-mercapto-1,3,4-thiadiazole to 5 mmol of solution 4 and absolute ethanol (30 mL). The mixture was stirred and refluxed for 7 h at 75–80 °C. Finally, the yellow-colored precipitate was filtered, dried, and recrystallized from ethanol (Scheme 3).
The synthesis of the Schiff base of p-aminobenzoic acid (8) was started by adding 5 mmol 4-amino benzoic acid into the solution of 4 (5 mmol) and absolute ethanol (30 mL) with continuous stirring. The mixture was refluxed for 7 h at 75–80 °C. The precipitate (orange color) was then filtered, dried, and recrystallized from ethanol (Scheme 3).24,77
Compound Characterization Data
The FT-IR, 1H NMR, and Mass spectra of the compounds 5, 6, 7, and 8 are presented in the Supplementary Material (Figures S1–S12).
5
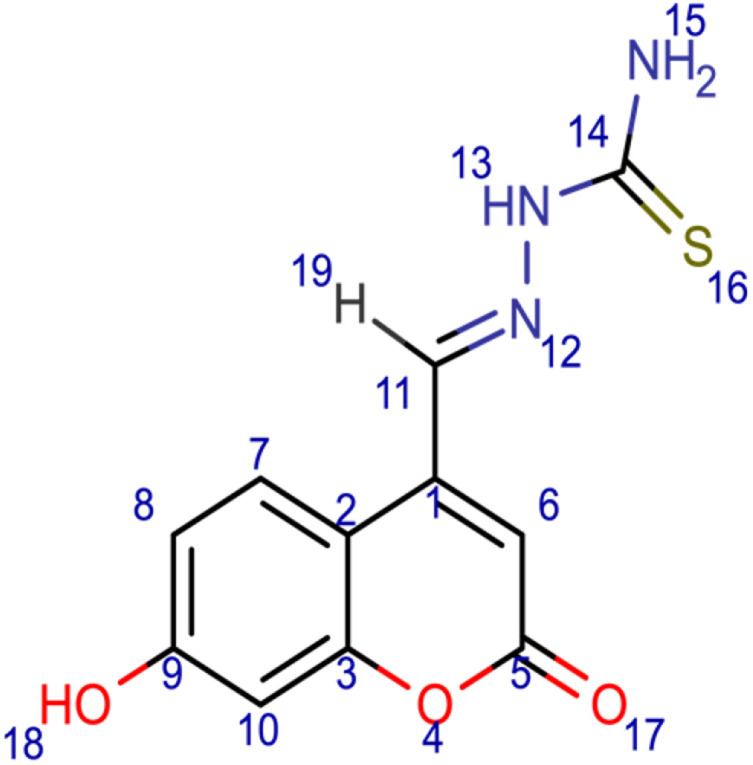
[(E)-[(7-hydroxy-2-oxo-2H-chromen-4-yl)methylidene]amino]thiourea (5); chemical formula C11H9N3O3S; calculated molar mass 263.27 g/mol; yellow powder; M.P. 204–206 °C; Rf 0.617; IR (KBr) ν,cm−1: 3375 (OH) str., 3264 (NH) str., 1726 (C=O) str. of lactone, 1640 (C=N) str., and 1601, 1620 (Ar-C=C) str.; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ = 6.55 (d, J = 7 Hz, 1H, 6-CH), 6.27 (s, 1H, 13-NH), 6.95 (d, 1H, 10-CH), 7.61 (d, 1H, 8-CH), 7.63 (s, 2H, 15-NH2), 7.83 (d, 1H, 7-CH), 8.07 (d, 1H, 19-H), 9.28 (s, 1H, 18-OH). MS (ESI, m/z): 132.6 ([M+2H]+).
6
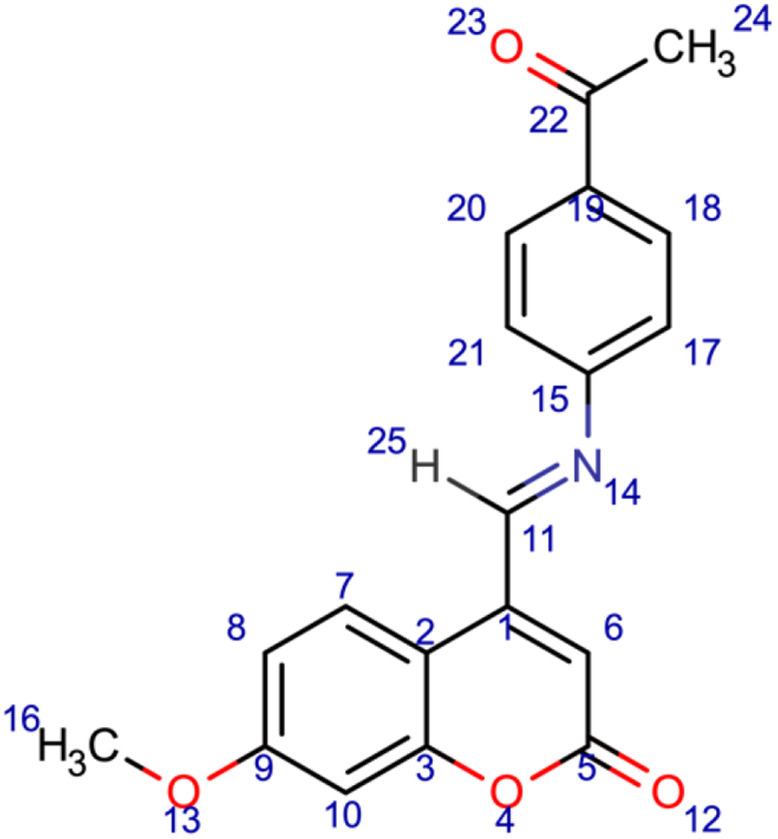
4-[(E)-[(4-acetylphenyl)imino]methyl]-7-methoxy-2H-chromen-2-one (6); chemical formula C19H15NO4; calculated molar mass 321.332 g/mol; orange powder; M.P. 190–192 °C; Rf 0.512; IR (KBr) ν,cm−1: 1742 (C=O) str. of lactone, 1678 (C=O) str. of ketone, 1630 (C=N) str., and 1589, 1563 (Ar-C=C) str.; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ = 2.93 (s, J = 7 Hz, 3H, 24-CH3), 3.54 (s, 3H, 16-CH3), 6.72 (d, 1H,10-CH), 7.41 (d, 1H, 8-CH), 7.91 (s, 1H, 7-CH), 8.56 (s,1H, 25-H). MS (ESI, m/z): 321.4 (M+).
7
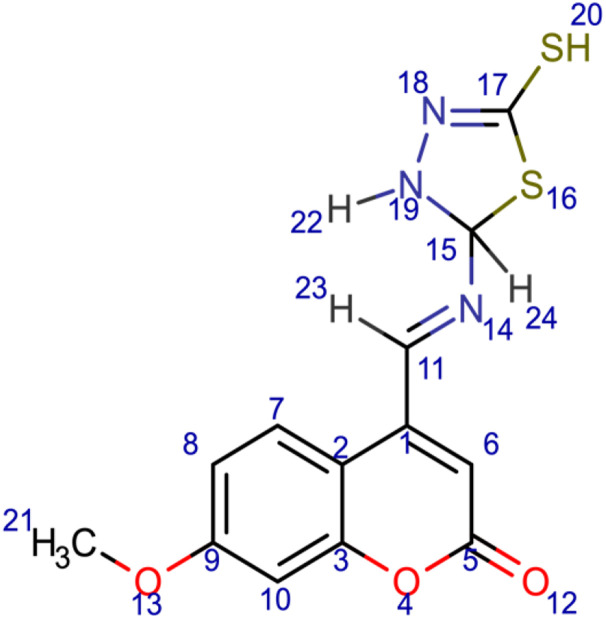
7-methoxy-4-[(E)-[(5-sulfanyl-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)imino]methyl]-2H-chromen-2-one (7); chemical formula C13H11N3O3S2; calculated molar mass 321.37 g/mol; yellow powder; M.P. 248–250 °C; Rf 0.554; IR (KBr) ν,cm−1: 1723 (C=O) str. of lactone, 1604 (C=N) str., and 1555, 1521 (Ar-C=C) str.; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ = 3.32 (d, J = 7 Hz, 3H, 21-CH3), 6.29 (s, 1H, 6-H), 6.59 (d, 1H, 10-H), 6.7 (s, 1H, 24-H), 6.95 (q, 1H, 8-H), 7.75 (d, 1H, 7-H), 7.94 (d, 1H, 22-H), 9.29 (s, 1H, 20-H), 10.43 (s, 1H, 23-H). MS (ESI, m/z): 321.1 (M+).
8
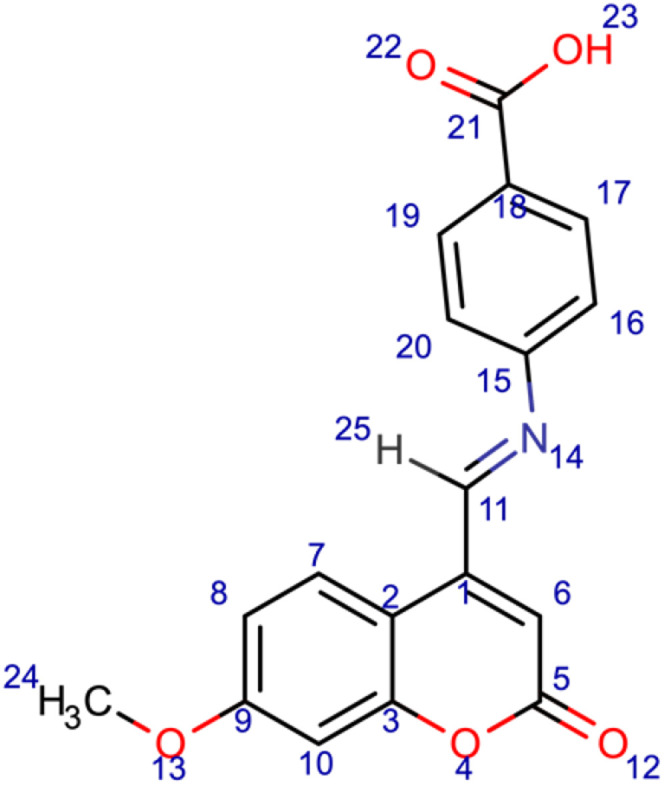
4-[(E)-[(7-methoxy-2-oxo-2H-chromen-4-yl)methylidene]amino]benzoic acid (8); chemical formula C18H13NO5; calculated molar mass 323.304 g/mol; orange powder; M.P. 207–209 °C; Rf 0.668; IR (KBr) ν,cm−1:3421 (OH) str., 1722 (C=O) str. of lactone, 1633 (C=N) str., and 1616, 1577 (Ar-C=C) str.; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ = 3.32 (s, J = 7 Hz, 3H, 24-CH3), 6.28 (s, 1H, 6-H), 6.97 (d, 2H, 16-H and 20-H), 7.6 (q, 1H, 8-H), 7.84 (d, 1H, 7-H), 8.03 (d, 2H, 17-H and 19-H), 9.29 (s, 1H, 25-H), 13.03 (s, 1H, 23-OH). MS (ESI, m/z): 323.3 (M+).
In vitro Anti-Inflammatory Activity Using Inhibition of Albumin Denaturation
The albumin denaturation assay was performed based on a previously reported procedure78 with minor adjustments. The reaction mixture of each sample was 5 mL, which consisted of 0.4 mL of synthesized Schiff base derivative, 0.4 mL of 1% bovine albumin, and 4.2 mL of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, pH 6.4) to adjust the pH of the mixture. Various concentrations of each synthesized Schiff base compound were tested (50–200 μg/mL). The sample mixtures were incubated in a water bath at 37 °C for 25 minutes. The mixtures were then heated at 65 °C for 15 minutes. The samples were then cooled, and the turbidity was measured by an Ultraviolet/Visible spectrophotometer at 660 nm. In this experiment, ibuprofen was used as a positive control, and PBS was used as a negative control. All the tests were performed in triplicate. The following formula was utilized to calculate the percentage inhibition of albumin denaturation:78–80
Percentage inhibition = (Abscontrol – Abssample) X 100/Abscontrol
Statistical Analysis
The values of the protein denaturation of each ligand were calculated as a mean ± standard deviation (n = 3).78 A correlation analysis (nonlinear regression) between the various concentrations of the ligands and the inhibition of protein denaturation was performed using GraphPad Prism Version 9.3.1 (GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA, USA; www.graphpad.com).
Results and Discussion
Although NSAIDs are widely used worldwide either as an OTC medicine or as POM, they have several off-target issues. The substantial side effect of non-selective COX inhibitors is GI complications (essentially due to the carboxylic acid functional group), and the most common side effect of selective COX-2 inhibitors is cardiotoxicity.81 The present study designed new molecules as Schiff base derivatives of coumarins to develop a potent orally bioavailable lead compound with fewer undesirable effects. Six compounds were designed and synthesized; however, compounds 3 and 4 were only intermediate molecules (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of the synthesized coumarin Schiff base derivatives. Compound 3, 7-hydroxy-4-formyl coumain; compound 4, 7-methoxy-4-formyl coumarin; compound 5, thiosemicarbazide derivative of 7-hydroxy-4-formyl coumarin; compound 6, p-aminoacetophenone derivative of 7-methoxy-4-formyl coumarin; compound 7, 5-amino-1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-thiol derivative of 7-methoxy-4-formyl coumarin; compound 8, p-aminobenzoic acid derivative of 7-methoxy-4-formyl coumarin.
For each ligand docking against the COX-2 protein, 10 genetic algorithms were run. The predicted binding free energy of the docked files was determined as comparative values and represented by the total score; the highest score represented the best interactions between the ligand and the receptor.63 As illustrated in Table 1, the post docking results showed that all the designed molecules observed higher binding free energy compared to the reference molecule (−7.68 kcal/mol), except the two intermediate molecules (3 and 4). Moreover, three ligands (5, 7, and 8) had Ki values in the nanomolar range (800 nM, 266.52 nM, and 102.15 nM, respectively). In addition, all the designed and reference molecules passed the criteria of Lipinski’s rule of five (Table 1).
Table 1.
Calculated Binding Free Energy, Ki, Run Number of the Highest Δgbinding, LogP, H-Bond Donor, H-Bond Acceptor, and Molar Mass of the Designed Molecules and Ibuprofen
| Name | Calculated ΔGbinding | Ki | Run no. | LogP | H-bond Donor | H-bond Acceptor | Molar Mass g/mol |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ibuprofen | −7.68 kcal/mol | 2.34 μM | 4 | 3.84 | 1 | 2 | 206.28 |
| Compound 3 | −6.47 kcal/mol | 18.17 μM | 1 | 1.229 | 1 | 3 | 190.15 |
| Compound 4 | −6.53 kcal/mol | 16.47 μM | 9 | 1.375 | 0 | 3 | 204.18 |
| Compound 5 | −8.32 kcal/mol | 800 nM | 2 | 1.208 | 3 | 3 | 263.00 |
| Compound 6 | −8.1 kcal/mol | 1.16 μM | 10 | 3.094 | 0 | 4 | 321.33 |
| Compound 7 | −8.97 kcal/mol | 266.52 nM | 4 | 3.791 | 2 | 5 | 321.37 |
| Compound 8 | −9.54 kcal/mol | 102.15 nM | 8 | 3.194 | 1 | 5 | 323.30 |
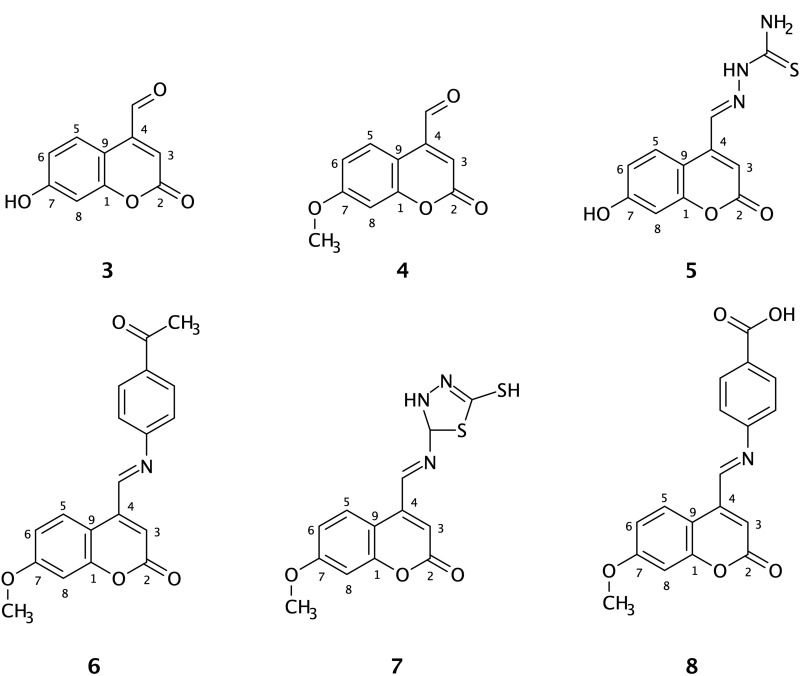
In the present study, ibuprofen was established as a positive control, and the binding interactions between ibuprofen and the COX-2 active site were realized. As illustrated by the 3D structure of the ibuprofen-COX-2 complex, the carboxylic acid functional group of ibuprofen was moved toward the side chains of Arg121 and Tyr356 of the receptor to form H-bonds. Furthermore, the hydrophobic group of the ligand (isobutyl phenyl group) was surrounded by lipophilic residue parts (Figure 2A). The 2D plot (Figure 2B) showed H-bonds and hydrophobic interactions. The notable H-bonds were between the carboxylic acid of ibuprofen with the guanidinium side chain of Arg121 (2.97 and 3.01 Å) and the phenolic hydroxyl group of Tyr356 (2.42 Å). Moreover, the isobutylphenyl group of ibuprofen was in the hydrophobic pocket of the protein surrounded by Val117, Val350, Val524, Gly527, Ser531, and Ala528.
Figure 2.
Binding interactions between ibuprofen and the COX-2 binding site. (A) Conformation of ibuprofen in the receptor-binding pocket. (B) The intermolecular binding interactions between ibuprofen and COX-2 presented by Ligplot plus program. The hydrophobic interactions between the ligand and COX-2, red lines; H-bonds, green lines; and protein residues involved in hydrophobic contacts, red spikes.
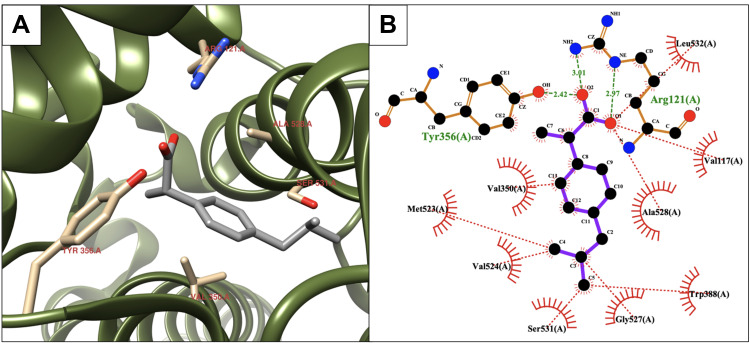
As shown in Table 1, compound 5 presented a higher calculated ΔGbinding than the reference molecule (8.32 kcal/mol) and a lower Ki (800 nM). Compound 5 produced various binding interactions with the active site of COX-2. However, compound 5 was more hydrophilic (LogP = 1.208) than ibuprofen due to the thiosemicarbazide group, which may have a negative impact on the permeability and bioavailability of the compound.82 As shown in Figure 3, two H-bonds were created due to conformations of the residues Gln193 and Leu353 (Figure 3A) as follows: the first was created with the side-chain of Gln193 (2.72 Å), and the second was created with the carbonyl backbone of Leu353 (2.8 Å). Furthermore, compound 5 was surrounded by several protein residues, such as Val350, Ile518, Phe519, Val524, Gly527, Ala528, and Leu532, to form hydrophobic interactions (Figure 3B).
Figure 3.
Binding interactions between compound 5 and the COX-2 binding site. (A) Conformation of the ligand in the receptor active site. (B) Intermolecular binding interaction displayed by Ligplot plus program. Hydrophobic bonds between compound 5 and COX-2, red dashed lines; H-bonds, green dashed lines; and protein residues involved in hydrophobic interactions, red arcs.
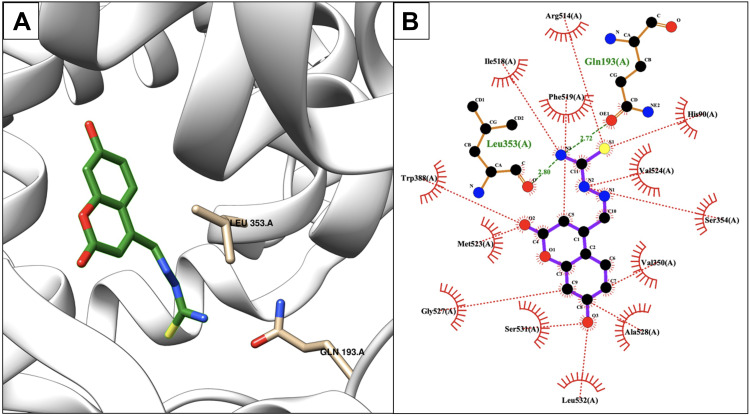
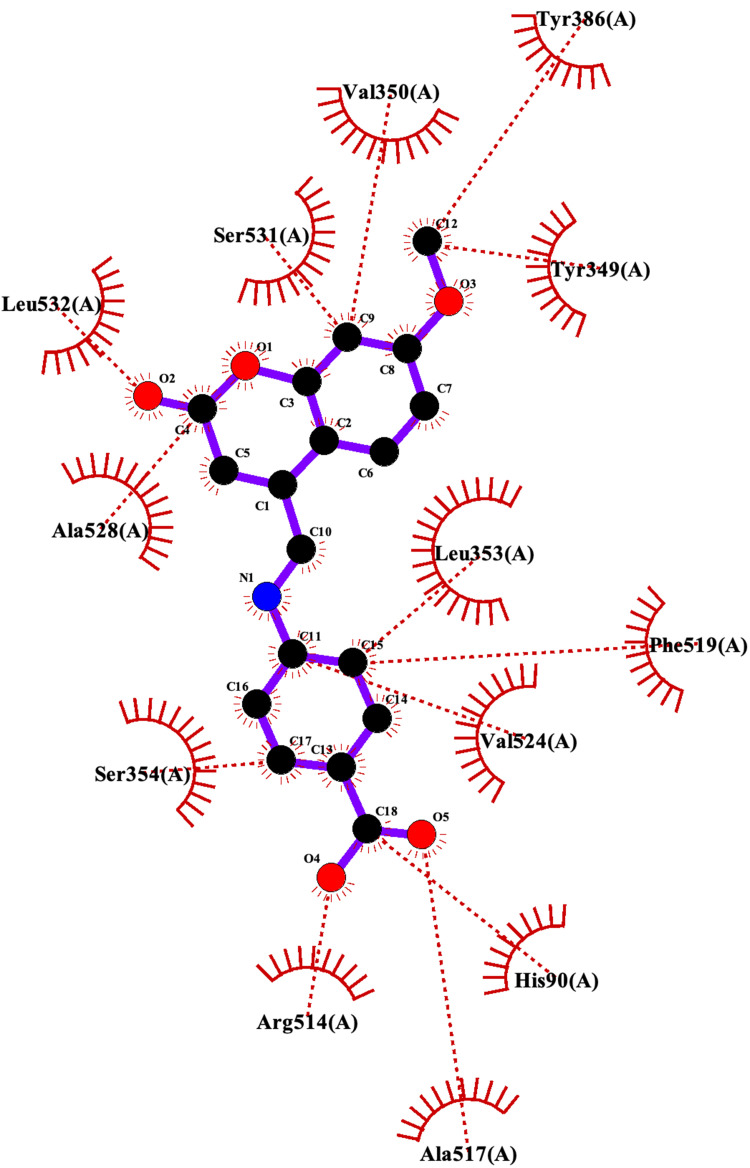
The post docking results indicated that compound 7 showed the second-highest calculated binding free energy after compound 8 with a Ki value in the nanomolar range (266.52 nM) (Table 1). After realizing the 2D plot and 3D conformation of the best-docked score, the following three H-bonds were created between compound 7 and the protein active site residues: the first H-bond was created between the main-chain carbonyl oxygen atom of Ser531 and 7-hydroxyl group of compound 7 (2.66 Å); the second and third H-bonds were created between the 2-thiol of 1,3,4-thiadiazole of compound 7 and both guanidinium groups of Arg514 (3.19 Å) and the backbone carbonyl of Phe519 (2.92 Å) (Figure 4A). The hydrophobic contacts of the ligand occurred with the following residues of the protein: Tyr 349, Val350, Leu353, Tyr356, Tyr386, Ala517, Val524, and Ala528 (Figure 4B). The lipophilicity of compound 7 was favorable, which was approximately the same as ibuprofen (LogP = 3.791).
Figure 4.
Binding interactions between compound 7 and COX-2 isoform. (A) Conformation of compound 7 in the receptor active pocket. (B) Demonstration of the binding interactions between compound 7 and COX-2. H-bonds, green dashed lines; receptor residues involved in hydrophobic contacts, red arcs; and ligand-protein hydrophobic interactions, red dotted lines.
According to the docked results, the last compound (8) possessed the highest predicted binding free energy (−9.54 kcal/mol) and the lowest Ki value (102.15 nM) (Table 1). Nevertheless, the 2D plot showed that all the H-bonds of compound 8 with the proteins were abrogated and that only hydrophobic interactions were available (Figure 5).
Figure 5.
Binding interactions between compound 8 and the COX-2 protein active site.
Inhibition of Albumin Denaturation
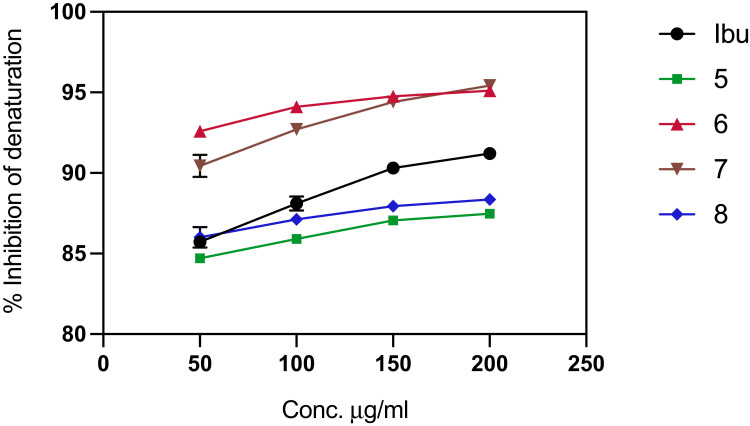
One of the documented in vitro-based assays to determine the anti-inflammatory activity of a molecule is through a protein denaturation assay as inflammation is one of the major causes of protein denaturation.83 NSAIDs, such as salicylic acid, phenylbutazone, and flufenamic acid, have a dose-dependent ability to inhibit protein denaturation thermally.79 In the present study, the competence of the Schiff base derivatives and the reference compound to inhibit albumin denaturation was investigated. The compounds successfully inhibited heat-induced protein denaturation when the percentage of inhibition was directly proportional to the concentration of each compound. The maximum inhibition was 95.42% at 200 μg/mL for compound 7 (Figure 6), but it was after compound 8 in the post docking results.
Figure 6.
Protein denaturation assay of the synthesized ligands (Schiff base derivatives) and ibuprofen based on the compound concentration. Values represent means of triplicate readings. Ibu, Ibuprofen; 5, compound 5; 6, compound 6; 7, compound 7; 8, compound 8.
Concerning the protein denaturation assay, each assay was performed in triplicate; therefore, each value represents the mean of all three replicates ± standard deviations (SD). Ibuprofen and the synthesized ligands decreased albumin denaturation, and the inhibition was dependent on the concentration. As shown in Figure 6, various concentrations of the compounds (50–200 μg/mL) were applied. The reference compound inhibition range was 85.73%-92.21%, whereas the inhibition ranges of compounds 6 and 7 were 92.59–95.1% and 90.44%-95.42%, respectively, which suggested that the anti-inflammatory activity of both compounds 6 and 7 was higher than ibuprofen due to their higher percentage of inhibition. In contrast, compounds 5 and 8 exhibited a lower inhibition rate relative to the reference compound (5 = 84.7–87.4% and 8 = 86–88.35%). However, according to the docked results, the predicted binding affinity of these two molecules was higher than ibuprofen, particularly compound 8, which showed the highest calculated binding free energy (−9.54 kcal/mol). Furthermore, the carboxylic acid functional group of compound 8 may cause gastric upset, indicating that it may not be a promising lead molecule.
Both Pearson’s correlation (R) and the coefficient of determination (R2) were calculated to assess the associations between increasing the ligand concentrations and inhibition percentage of the protein bindings.84 As illustrated in Table 2, all the designed molecules and the reference compound were highly correlative as increasing the concentration of the ligands was directly proportional to the percentage of albumin denaturation. Moreover, for all the assays, the statistical significance was p ≤ 0.05 and two-tailed. The strongest correlation between the rate of inhibition and the concentration was determined for compound 7 (R = 0.986, R2 = 0.972, and P = 0.014). Moreover, a comparable correlation was also observed for compounds 5 and 8. However, the significance of the correlation was diminished for compound 6 (P = 0.049).
Table 2.
Pearson’s Correlation, Coefficient of Determination, and the Level of Significance for the Schiff Base Derivative Ligands and Ibuprofen
| Ligand Name | R | R2 | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ibuprofen | 0.983 | 0.966 | 0.017 |
| Compound 5 | 0.981 | 0.962 | 0.019 |
| Compound 6 | 0.951 | 0.905 | 0.049 |
| Compound 7 | 0.986 | 0.972 | 0.014 |
| Compound 8 | 0.980 | 0.962 | 0.019 |
Conclusion
Overall, four Schiff base derivatives of coumarin were designed and synthesized to identify an effective lead molecule as an alternative to NSAIDs. The anti-inflammatory effect of these molecules was assessed using an in vitro protein denaturation assay. The present findings suggested that compound 7 has the potential to become a lead compound due as it had the highest predicted binding free energy compared to the other ligands and ibuprofen, the strongest correlation between concentration and percentage of protein denaturation (R = 0.986 and R2 = 0.972) with the lowest P-value (0.014), and a significantly higher rate of inhibition of protein denaturation relative to ibuprofen. Furthermore, compound 6 also exhibited excellent anti-inflammatory correlations and higher calculated binding free energies compared to the reference compound. In addition to the higher predicted binding free energy of compounds 5 and 8, they had a lower inhibition rate compared to the reference molecule. Moreover, compound 8 possesses a carboxylic acid functional group, which may lead to gastritis Therefore, compounds 5 and 8 may not be promising lead compounds. However, further studies, such as cytotoxicity tests and optimization of compound 7 are warranted.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the support from the College of Pharmacy, University of Sulaimani, Sulaymaniyah, Iraq.
Disclosure
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- 1.Hussein DM, Al juboory SB, Mahmood AA. Antibacterial evaluation with computational study of new Schiff bases derived from 7-hydroxy-4-methyl coumarin. Orient J Chem. 2017;33(2):768–782. doi: 10.13005/ojc/330224 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kupeli Akkol E, Genc Y, Karpuz B, Sobarzo-Sanchez E, Capasso R. Coumarins and coumarin-related compounds in pharmacotherapy of cancer. Cancers. 2020;12(7):1959. doi: 10.3390/cancers12071959 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Aoife L. Studies on coumarins and coumarin-related compounds to determine their therapeutic role in the treatment of cancer. Curr Pharm Des. 2004;10(30):3797–3811. doi: 10.2174/1381612043382693 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Zhu -J-J, Jiang J-G. Pharmacological and nutritional effects of natural coumarins and their structure–activity relationships. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2018;62(14):1701073. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201701073 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kirsch G, Abdelwahab AB, Chaimbault P. Natural and synthetic coumarins with effects on inflammation. Molecules. 2016;21(10):1322. doi: 10.3390/molecules21101322 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hassan MZ, Osman H, Ali MA, Ahsan MJ. Therapeutic potential of coumarins as antiviral agents. Eur J Med Chem. 2016;123:236–255. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.07.056 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Thakur A, Singla R, Jaitak V. Coumarins as anticancer agents: a review on synthetic strategies, mechanism of action and SAR studies. Eur J Med Chem. 2015;101:476–495. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.07.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Garro A, Pungitore C. Coumarins as potential inhibitors of DNA polymerases and reverse transcriptases. searching new antiretroviral and antitumoral drugs. Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2015;12(2):66–79. doi: 10.2174/1570163812666150716111719 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Zhang L, Xu Z. Coumarin-containing hybrids and their anticancer activities. Eur J Med Chem. 2019;181:111587. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.111587 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Menezes JC, Diederich M. Translational role of natural coumarins and their derivatives as anticancer agents. Future Med Chem. 2019;11(9):1057–1082. doi: 10.4155/fmc-2018-0375 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Konstantina CF, Dimitra JH-L, Konstantinos EL, Demetrios NN. Natural and synthetic coumarin derivatives with anti-inflammatory/antioxidant activities. Curr Pharma Des. 2004;10(30):3813–3833. doi: 10.2174/1381612043382710 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bansal Y, Sethi P, Bansal G. Coumarin: a potential nucleus for anti-inflammatory molecules. Medl Chem Res. 2012;22(7):3049–3060. doi: 10.1007/s00044-012-0321-6 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Gao L, Wang F, Chen Y, Li F, Han B, Liu D. The antithrombotic activity of natural and synthetic coumarins. Fitoterapia. 2021;154:104947. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2021.104947 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Carneiro A, Matos MJ, Uriarte E, Santana L. Trending topics on coumarin and its derivatives in 2020. Molecules. 2021;26(2):501. doi: 10.3390/molecules26020501 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Mishra S, Pandey A, Coumarin MS. An emerging antiviral agent. Heliyon. 2020;6(1):e03217. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03217 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Gouda MA, Hussein BH, El-Demerdash A, et al. A review: synthesis and medicinal importance of coumarins and their analogues (Part II). Curr Bioact Compd. 2020;16(7):993–1008. doi: 10.2174/1573407215666191111120604 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Makowska A, Wolff L, Saczewski F, Bednarski PJ, Kornicka A. Synthesis and cytotoxic evaluation of benzoxazole/benzothiazole-2-imino-coumarin hybrids and their coumarin analogues as potential anticancer agents. Pharmazie. 2019;74(11):648–657. doi: 10.1691/ph.2019.9664 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Utreja D, Jain N, Sharma S. Advances in synthesis and potentially bioactive of coumarin derivatives. Curr Org Chem. 2018;22(26):2509–2536. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Dziduch K, Kolodziej P, Paneth A, Bogucka-Kocka A, Wujec M. Synthesis and anthelmintic activity of new thiosemicarbazide derivatives-a preliminary study. Molecules. 2020;25(12):2770. doi: 10.3390/molecules25122770 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Soucy NV. Acetophenone. Wexler P, editor. 3rd: Academic Press; 2014:43–45. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Shkair A MH, Shakya A K, Raghavendra N M, Naik R R. Molecular modeling, synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of 1, 3, 4-thiadiazoles as anti-inflammatory and analgesic agents. Med Chem. 2016;12(1):90–100. doi: 10.2174/1573406411666150608102236 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Altintop MD, Can OD, Demir Ozkay U, Kaplancikli ZA. Synthesis and evaluation of new 1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives as antinociceptive agents. Molecules. 2016;21(8):1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hu Y, Li C-Y, Wang X-M, Yang Y-H, Zhu H-L. 1,3,4-thiadiazole: synthesis, reactions, and applications in medicinal, agricultural, and materials chemistry. Chem Rev. 2014;114(10):5572–5610. doi: 10.1021/cr400131u [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Angelova VT, Vassilev NG, Nikolova-Mladenova B, et al. Antiproliferative and antioxidative effects of novel hydrazone derivatives bearing coumarin and chromene moiety. Med Chem Res. 2016;25(9):2082–2092. doi: 10.1007/s00044-016-1661-4 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Nisa ZU, Akhtar T. para-aminobenzoic acid-A substrate of immense significance. Mini Rev Org Chem. 2020;17(6):686–700. doi: 10.2174/1570193X16666190828201234 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Eswayah A, Khaliel S, Saad S, et al. Synthesis and analgesic activity evaluation of some new benzimidazole derivatives. AASCIT. 2017;4(5):30–35. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Antonijevic MR, Simijonovic DM, Avdovic EH, et al. Green one-pot synthesis of coumarin-hydroxybenzohydrazide hybrids and their antioxidant potency. Antioxidants. 2021;10(7). doi: 10.3390/antiox10071106 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kotali A, Nasiopoulou DA, Tsoleridis CA, Harris PA, Kontogiorgis CA, Hadjipavlou-Litina DJ. Antioxidant Activity of 3-[N-(Acylhydrazono)ethyl]-4-hydroxy-coumarins. Molecules. 2016;21(2):138. doi: 10.3390/molecules21020138 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Guo H, Callaway JB, Ting JP-Y. Inflammasomes: mechanism of action, role in disease, and therapeutics. Nat Med. 2015;21(7):677–687. doi: 10.1038/nm.3893 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Michels da Silva D, Langer H, Graf T. Inflammatory and molecular pathways in heart failure-ischemia, HFpEF and transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(9):2322. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092322 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Zhang X, Wu X, Hu Q, et al. Mitochondrial DNA in liver inflammation and oxidative stress. Life Sci. 2019;236:116464. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.05.020 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Fritsch J, Abreu MT. The microbiota and the immune response: what is the chicken and what is the egg? Gastrointestinal Endosc Clin N Am. 2019;29(3):381–393. doi: 10.1016/j.giec.2019.02.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Bindu S, Mazumder S, Bandyopadhyay U. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and organ damage: a current perspective. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020;180:114147. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114147 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Gupta AK, Pandey J, Synthesis AA. Evaluation of some new 2-(5-(4-Benzamidobenzylidene)-2,4dioxothiazolidin-3-Yl) acetic acid analogs as aldose reductase inhibitors. Asian J Pharm Clin Res. 2016;10(1):62. doi: 10.22159/ajpcr.2017.v10i1.12073 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Budoff PW. Use of mefenamic acid in the treatment of primary dysmenorrhea. JAMA. 1979;241(25):2713–2716. doi: 10.1001/jama.1979.03290510021018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Kowalski ML, Makowska JS. Seven steps to the diagnosis of NSAIDs hypersensitivity: how to apply a new classification in real practice? Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2015;7(4):312–320. doi: 10.4168/aair.2015.7.4.312 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Tacconelli S, Bruno A, Grande R, Ballerini P, Patrignani P. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and cardiovascular safety – translating pharmacological data into clinical readouts. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2017;16(7):791–807. doi: 10.1080/14740338.2017.1338272 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Li J, Yin Y, Wang L, et al. Synthesis, characterization, and anti-inflammatory activities of methyl salicylate derivatives bearing piperazine moiety. Molecules. 2016;21(11):1544. doi: 10.3390/molecules21111544 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Dreischulte T, Morales DR, Bell S, Guthrie B. Combined use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs with diuretics and/or renin–angiotensin system inhibitors in the community increases the risk of acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2015;88(2):396–403. doi: 10.1038/ki.2015.101 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Arfè A, Scotti L, Varas-Lorenzo C, et al. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and risk of heart failure in four European countries: nested case-control study. BMJ. 2016;354:i4857. doi: 10.1136/bmj.i4857 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.James DS. The multisystem adverse effects of NSAID therapy. J Osteopath Med. 1999;99(11):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.García-Rayado G, Navarro M, Lanas A. NSAID induced gastrointestinal damage and designing GI-sparing NSAIDs. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2018;11(10):1031–1043. doi: 10.1080/17512433.2018.1516143 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ilango K, Valentina P, Kumar G, Dixit D, Nilewar S, Kathiravan M. Design, synthesis and QSAR studies on a series of 2, 5-Disubstituted- 1,3,4-oxadiazole derivatives of diclofenac and naproxen for analgesic and anti-inflammatory activity. Med Chem. 2015;11(8):753–763. doi: 10.2174/1573406411666150519112037 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Arora M, Choudhary S, Singh PK, Sapra B, Silakari O. Structural investigation on the selective COX-2 inhibitors mediated cardiotoxicity: a review. Life Sci. 2020;251:117631. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117631 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Schjerning A-M, McGettigan P, Gislason G. Cardiovascular effects and safety of (non-aspirin) NSAIDs. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2020;17(9):574–584. doi: 10.1038/s41569-020-0366-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Lichtenstein DR, Wolfe MM. COX-2–selective NSAIDs: new and improved? JAMA. 2000;284(10):1297–1299. doi: 10.1001/jama.284.10.1297 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Sharma V, Bhatia P, Alam O, et al. Recent advancement in the discovery and development of COX-2 inhibitors: insight into biological activities and SAR studies (2008–2019). Bioorg Chem. 2019;89:103007. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2019.103007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Wallace JL. NSAID gastropathy and enteropathy: distinct pathogenesis likely necessitates distinct prevention strategies. Br J Pharmacol. 2012;165(1):67–74. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01509.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Bakhriansyah M, Souverein PC, de Boer A, Klungel OH. Gastrointestinal toxicity among patients taking selective COX‐2 inhibitors or conventional NSAIDs, alone or combined with proton pump inhibitors: a case–control study. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2017;26(10):1141–1148. doi: 10.1002/pds.4183 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Suthar SK, Sharma M. Recent developments in chimeric NSAIDs as safer anti‐inflammatory agents. Med Res Rev. 2015;35(2):341–407. doi: 10.1002/med.21331 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Lin X-H, Young S-H, Luo J-C, et al. Risk factors for upper gastrointestinal bleeding in patients taking selective COX-2 inhibitors: a Nationwide population-based cohort study. Pain Med. 2018;19(2):225–231. doi: 10.1093/pm/pnx097 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Baothman BK, Smith J, Kay LJ, Suvarna SK, Peachell PT. Prostaglandin D2 generation from human lung mast cells is catalysed exclusively by cyclooxygenase-1. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018;819:225–232. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.12.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Daham K, Song WL, Lawson J, et al. Effects of celecoxib on major prostaglandins in asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 2011;41(1):36–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2010.03617.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Wallace JL, Bak A, McKnight W, Asfaha S, Sharkey KA, MacNaughton WK. Cyclooxygenase 1 contributes to inflammatory responses in rats and mice: implications for gastrointestinal toxicity. Gastroenterology. 1998;115(1):101–109. doi: 10.1016/S0016-5085(98)70370-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Chen M, Boilard E, Nigrovic PA, et al. Predominance of cyclooxygenase 1 over cyclooxygenase 2 in the generation of proinflammatory prostaglandins in autoantibody‐driven K/BxN serum–transfer arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2008;58(5):1354–1365. doi: 10.1002/art.23453 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Peesa JP, Yalavarthi PR, Rasheed A, Mandava VBR. A perspective review on role of novel NSAID prodrugs in the management of acute inflammation. J Acute Dis. 2016;5(5):364–381. doi: 10.1016/j.joad.2016.08.002 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Benbow T, Campbell J. Microemulsions as transdermal drug delivery systems for nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): a literature review. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2019;45(12):1849–1855. doi: 10.1080/03639045.2019.1680996 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Domper Arnal M-J, Hijos-Mallada G, Lanas A. Gastrointestinal and cardiovascular adverse events associated with NSAIDs. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2022;21(3):373–384. doi: 10.1080/14740338.2021.1965988 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Husain A, Khan M, Hasan S, Alam M. 2-Arylidene-4-(4-phenoxy-phenyl) but-3-en-4-olides: synthesis, reactions and biological activity. Eur J Med Chem. 2005;40(12):1394–1404. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2005.03.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Adams S. An interview with Stewart Adams. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2012;33(1):1–2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.BBC N. Ibuprofen: dr Stewart Adams who helped discover drug dies at 95. BBC; 2019. Available from: https://www.bbc.com/news/uk-england-nottinghamshire-47073913. Accessed January 31, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- 62.Varrassi G, Pergolizzi JV, Dowling P, Paladini A. Ibuprofen safety at the golden anniversary: are all NSAIDs the same? A narrative review. Adv Ther. 2020;37(1):61–82. doi: 10.1007/s12325-019-01144-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Salih T, Salih HA. In silico design and molecular docking studies of carbapenem analogues targeting acinetobacter baumannii PBP1A receptor. AJPS. 2020;20(3):35–50. doi: 10.32947/ajps.v20i3.759 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Swain M. chemicalize.org. J Chem Inf Model. 2012;52(2):613–615. doi: 10.1021/ci300046g [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Berman H, Henrick K, Nakamura H. Announcing the worldwide Protein Data Bank. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2003;10(12):980. doi: 10.1038/nsb1203-980 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Orlando BJ, Lucido MJ, Malkowski MG. The structure of ibuprofen bound to cyclooxygenase-2. J Struct Biol. 2015;189(1):62–66. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2014.11.005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Pacheco AB, Hpc L. Introduction to AutoDock and AutoDock Tools. Baton Rouge: Louisiana State University; 2012. [Google Scholar]
- 68.ChemAxon. Marvinsketch, Version 20.16. ChemAxon Ltd. Budapest, Hungary; 2020. [Google Scholar]
- 69.Gouthami K, Veeraraghavan V, Nagaraja P. In-silico characterization of phytochemicals identified from Vitex negundo (L) extract as potential therapy for Wnt-signaling proteins. Egypt J Med Hum Genet. 2022;23(1). doi: 10.1186/s43042-022-00219-7 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Hobani Y, Jerah A, Bidwai A. A comparative molecular docking study of curcumin and methotrexate to dihydrofolate reductase. Bioinformation. 2017;13(3):63. doi: 10.6026/97320630013063 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Morris GM, Huey R, Olson AJ. Using AUTODOCK for ligand-receptor docking. Curr Protoc Bioinform. 2008;24(1):8–14. doi: 10.1002/0471250953.bi0814s24 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Morris GM, Huey R, Lindstrom W, et al. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J Comput Chem. 2009;30(16):2785–2791. doi: 10.1002/jcc.21256 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Huey R, Morris GM, Forli S. Using AutoDock 4 and AutoDock vina with AutoDockTools: a tutorial. Scripps Res Inst Mol Graph Lab. 2012;10550:92037. [Google Scholar]
- 74.Sobell MG. A Practical Guide to Ubuntu Linux. Pearson Education; 2015. [Google Scholar]
- 75.Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, et al. UCSF chimera - A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem. 2004;25(13):1605–1612. doi: 10.1002/jcc.20084 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Laskowski RA, Swindells MB LigPlot+: multiple ligand–protein interaction diagrams for drug discovery. ACS Publications; 2011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Sinha D, Tiwari AK, Singh S, et al. Synthesis, characterization and biological activity of Schiff base analogues of indole-3-carboxaldehyde. Eur J Med Chem. 2008;43(1):160–165. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2007.03.022 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Gunathilake K, Ranaweera K, Rupasinghe HPV. In vitro anti-inflammatory properties of selected green leafy vegetables. Biomedicines. 2018;6(4):107. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines6040107 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Sakat S, Juvekar AR, Gambhire MN. In vitro antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity of methanol extract of Oxalis corniculata Linn. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2010;2(1):146–155. [Google Scholar]
- 80.Mizushima Y, Kobayashi M. Interaction of anti-inflammatory drugs with serum proteins, especially with some biologically active proteins. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2011;20(3):169–173. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1968.tb09718.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Sehajpal S, Prasad DN, Singh RK. Prodrugs of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): a long march towards synthesis of safer NSAIDs. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2018;18(14):1199–1219. doi: 10.2174/1389557518666180330112416 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Chmiel T, Mieszkowska A, Kempińska-Kupczyk D, Kot-Wasik A, Namieśnik J, Mazerska Z. The impact of lipophilicity on environmental processes, drug delivery and bioavailability of food components. Microchemical J. 2019;146:393–406. doi: 10.1016/j.microc.2019.01.030 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Osman NI, Sidik NJ, Awal A, Adam NA, Rezali NI. In vitro xanthine oxidase and albumin denaturation inhibition assay of Barringtonia racemosa L. and total phenolic content analysis for potential anti-inflammatory use in gouty arthritis. J Intercult Ethnopharmacol. 2016;5(4):343–349. doi: 10.5455/jice.20160731025522 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Moore DS, Notz W, Fligner MA The basic practice of statistics. W.H. Freeman and Company; 2013. Available from: https://books.google.iq/books?id=aw61ygAACAAJ. Accessed July 1, 2022. [Google Scholar]