ABSTRACT
Studies have shown that variants in bedaquiline-resistance genes can occur in isolates from bedaquiline-naive patients. We assessed the prevalence of variants in all bedaquiline-candidate-resistance genes in bedaquiline-naive patients, investigated the association between these variants and lineage, and the effect on phenotype. We used whole-genome sequencing to identify variants in bedaquiline-resistance genes in isolates from 509 bedaquiline treatment naive South African tuberculosis patients. A phylogenetic tree was constructed to investigate the association with the isolate lineage background. Bedaquiline MIC was determined using the UKMYC6 microtiter assay. Variants were identified in 502 of 509 isolates (98.6%), with the highest (85%) prevalence of variants in the Rv0676c (mmpL5) gene. We identified 36 unique variants, including 19 variants not reported previously. Only four isolates had a bedaquiline MIC equal to or above the epidemiological cut-off value of 0.25 μg/mL. Phylogenetic analysis showed that 14 of the 15 variants observed more than once occurred monophyletically in one Mycobacterium tuberculosis (sub)lineage. The bedaquiline MIC differed between isolates belonging to lineage 2 and 4 (Fisher’s exact test, P = 0.0004). The prevalence of variants in bedaquiline-resistance genes in isolates from bedaquiline-naive patients is high, but very few (<2%) isolates were phenotypically resistant. We found an association between variants in bedaquiline resistance genes and Mycobacterium tuberculosis (sub)lineage, resulting in a lineage-dependent difference in bedaquiline phenotype. Future studies should investigate the impact of the presence of variants on bedaquiline-resistance acquisition and treatment outcome.
KEYWORDS: antibiotic resistance, antimicrobial resistance, bedaquiline, drug-resistant tuberculosis, epidemiology, phenotypic drug susceptibility testing, phylogeny, tuberculosis, whole-genome sequencing
INTRODUCTION
Bedaquiline (BDQ) was the first drug approved for drug-resistant tuberculosis (DR-TB) treatment in 40 years. In 2018, the World Health Organization (WHO) included BDQ as one of three core drugs for treating rifampicin-resistant TB (RR-TB). Unfortunately, cases of BDQ treatment failure were reported soon after its introduction (1–4).
The WHO recently listed five tier 1 (atpE, Rv0678, Rv0676c, Rv0677c, and pepQ) and one tier 2 (Rv1979c) genes as BDQ candidate resistance genes (5). Clinical BDQ resistance has been mainly attributed to variants in genes involved in the MmpL5/MmpS5 Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) efflux pathway (6). Most reported variants occur in the Rv0678 gene, encoding a transcriptional repressor protein MmpR5. The Rv0676c and Rv0677c genes, encoding the MmpL5/MmpS5 transport proteins, respectively, have been implicated in BDQ resistance (7). Although rarely observed in clinical isolates, variants in the atpE gene, encoding the BDQ drug target ATP synthase, have been reported repeatedly in in vitro isolates (1, 8). While variants in the Rv2535c (pepQ) gene, encoding a cytoplasmatic peptidase, reduce efficacy of BDQ and clofazimine (CFZ) in mice, it remains unclear if loss of function pepQ variants lead to a reduced BDQ susceptibility in clinical setting (8–10). Lastly, evidence for the role of Rv1979c in BDQ resistance remains limited (5, 8).
It has been reported that variants in BDQ resistance-associated genes can occur at low prevalence (6% to 12%) in clinical Mtb isolates from BDQ-naive patients, with varying rate of phenotypic BDQ resistance (2.3% to 66.7%) (11–15). This is worrisome with regard to treatment outcomes, even if they do not confer phenotypic resistance at the current WHO endorsed critical concentration as they could serve as a steppingstone to higher MIC BDQ resistance (16).
In this study, we analyzed whole-genome sequencing (WGS) data of 509 isolates from South African BDQ-naive patients and performed BDQ MIC analyses on a subset to investigate the prevalence of variants in all tier 1 and tier 2 BDQ candidate resistance genes, assess their association with Mtb (sub)lineages, and evaluate the effect of these variants on BDQ MIC.
RESULTS
Prevalence of genomic variants.
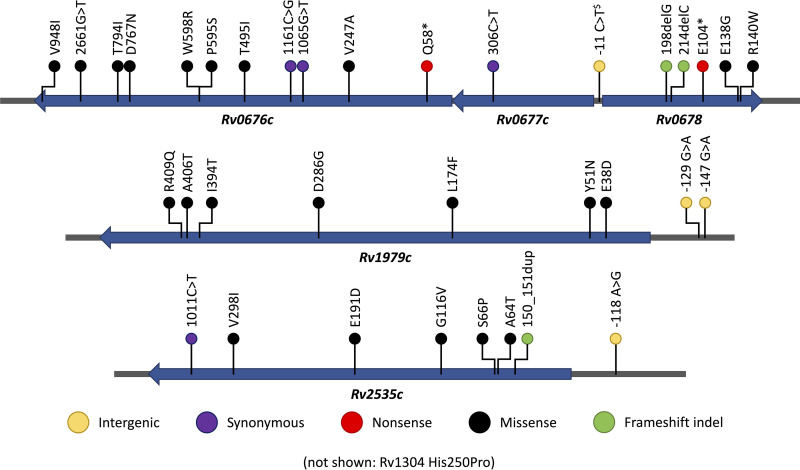
Almost all (98.6%, 502/509) isolates had a variant in a BDQ candidate resistance gene. Most (305 or 59.9%) isolates had a single, 188 (36.9%) had two, and nine samples (1.8%) had three variants in the genes analyzed. A total of 36 unique variants were identified in 32 combinations: one in the upstream (atpB) region of atpE, one in Rv0677c (mmpS5), six in Rv0678 (mmpR), eight in Rv2535c (pepQ), nine in Rv1979c, and 11 in Rv0676c (mmpL5) (Table 1 and Fig. 1).
TABLE 1.
All observed variants in the data set
| Observed variants in clinical isolates | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene | DNA level | Protein level | Frequency | Oldest sampling yr | WHO classification (5) | BDQa MIC range (μg/mL) |
| Rv1304 (atpB) | 749A>C | His250Pro | 1 | 2012 | Uncertain | 0.015 |
| Rv0678 (mmpR) | 310G>T | Glu104* | 1 | 2011 | NA | 0.06 |
| 198delG | Ile67fs | 1 | 2011 | NA | 0.015 | |
| –11C>A | NA | 102 | 2003 | NA | ≤0.008 to 0.06 | |
| 214delC | Arg72fs | 1 | 2010 | NA | 0.03 | |
| 413A>G | Glu138Gly | 1 | 2013 | NA | 0.03 | |
| 418C>T | Arg140Trp | 1 | 2013 | NA | ≤0.008 | |
| Rv2535c (pepQ) | 150_151dupCG | Asp51fs | 2 | 2012 | NA | 0.03 to 0.06 |
| 573G>C | Glu191Asp | 2 | 2010 | NA | ≤0.008 | |
| 347G>T | Gly116Val | 1 | 2013 | NA | NA | |
| −118A>G | NA | 1 | 2012 | NA | NA | |
| 190G>A | Ala64Thr | 1 | 2013 | NA | 0.03 | |
| 196T>C | Ser66Pro | 1 | 2005 | NA | 0.015 | |
| 892G>A | Val298Ile | 1 | 2011 | NA | ≤0.008 | |
| 1011C>T | Arg337Arg | 1 | 2015 | NA | ≤0.008 | |
| Rv1979c | −129G>A | NA | 4 | 2012 | Not assoc w Rc | 0.015 to 0.06 |
| 114G>C | Glu38Asp | 14 | 2006 | Uncertain | ≤0.008 to 0.12 | |
| 857A>G | Asp286Gly | 21 | 1998 | Uncertain | ≤0.008 to 0.12 | |
| 151T>A | Tyr51Asn | 24 | 2007 | Uncertain | ≤0.008 to 0.5 | |
| 1226G>A | Arg409Gln | 53 | 2010 | Uncertain | ≤0.008 to 0.25 | |
| 1216G>A | Ala406Thr | 1 | 2010 | NA | 0.03 | |
| −147G>A | NA | 1 | 2012 | NA | NA | |
| 520C>T | Leu174Phe | 1 | 2013 | Uncertain | ≤0.008 | |
| 1181T>C | Ile394Thr | 1 | 2012 | Uncertain | ≤0.008 | |
| Rv0676c (mmpL5) | 172>T | Gln58* | 2 | 2000 | NA | ≤0.008 |
| 1792T>A | Trp598Arg | 3 | 2012 | Uncertain | ≤0.008 to 0.03 | |
| 740T>C | Val247Ala | 3 | 2012 | Uncertain | NA | |
| 2842G>Ab | Val948Ileb | 5 | NA | Not assoc w Rc | 0.015 to 0.06 | |
| 1065G>T | Pro355Pro | 24 | 2007 | NA | ≤0.008 to 0.12 | |
| 2299G>A | Asp767Asn | 183 | 2003 | Not assoc w R | ≤0.008 to 0.5 | |
| 2381T>C | Ile794Thr | 245 | 2000 | Not assoc w Rc | ≤0.008 to 0.5 | |
| 1161C>G | Val387Val | 1 | 2012 | NA | ≤0.008 | |
| 1783C>T | Pro595Ser | 1 | 2013 | NA | 0.015 | |
| 1484C>T | Thr495Ile | 1 | 2015 | NA | ≤0.008 | |
| 2661G>T | Val887Val | 1 | 2012 | NA | 0.015 | |
| Rv0677c (mmpS5) | 306C>T | Asn102Asn | 1 | 2012 | NA | ≤0.008 |
BDQ, bedaquiline.
Variants were observed independently in the phylogenetic tree.
Classification based on variant identified through calling compared to H37Rv and likely observed due to acquired variant in the reference genome.
FIG 1.
Variants identified in bedaquiline candidate resistance genes Rv0676c, Rv0677c, Rv0678, Rv1979c, and Rv2535c, and flanking promoter regions. The single variant in Rv1304 (upstream of atpE) is not shown. Nucleotide positions are used for frameshift indels and intergenic variants, codon positions are used for synonymous, nonsense and missense variants. $-11 position is upstream relative to the Rv0678 gene.
The highest prevalence of genomic variants was observed in the Rv0676c (mmpL5) gene, with two of the 11 variants observed occurring at p.Ile794Thr (48.1%, 245/509) and p.Asp767Asn (36.0%, 183/509) (Table 1). Only one variant (c.306C>T) was observed in the Rv0677c (mmpS5) gene at low prevalence (0.2%, 1/509). Six variants were observed in the Rv0678 gene, of which the promoter variant n.-11C>A occurred frequently (20.0%, 102/509). The other five Rv0678 variants were observed once. All eight variants observed in the Rv2535c (pepQ) gene were rare (prevalence <0.5%). The nine variants observed in the Rv1979c gene occurred at low prevalence (<5%), with p.Arg409Gln being the most prevalent (10.4%, 53/509). One variant in the atpB gene, p.His250Pro, 53 nucleotides upstream of the atpE coding region, was observed in a single isolate. In the sensitivity analysis excluding the 58 isolates from unconfirmed BDQ naive patients, the same variants were observed, with the exception of the Rv0676c p.Thr495Ile variant (Table S2).
Prevalence of variants by Mtb lineage.
Most isolates belonged to lineage 2 (46.4%, 236/509) or 4 (48.1%, 245/509); few isolates to lineage 1 (4.1%, 21/509) or 3 (1.4%, 7/509). The prevalence of variants in the BDQ resistance genes differed by lineage (Table 2). While none of the seven lineage 3 isolates contained any variant in the BDQ candidate resistance genes, lineages 1, 2, and 4 isolates contained at least one variant (Table 2). For lineage 1 isolates, variants occurred frequently in the Rv1979c (100%, 21/21), and Rv0676c (14.3%, 3/21). For lineage 2, variants occurred at high prevalence in the Rv0676c (78.0%, 184/236), Rv0678 (44.1%, 104/236), and Rv1979c (33.5%, 79/236) genes. For lineage 4, variants were common in the Rv0676c (100%, 245/245) and Rv1979c (7.8%, 19/245) genes. Similar differences between lineages could be observed when excluding the 58 isolates from unconfirmed BDQ naive patients (Table S3).
TABLE 2.
Proportion of samples with mutated bedaquiline (BDQ) resistance gene, overall and stratified by lineage
| Proportion of samples with mutated BDQ resistance gene |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Rv1304 | Rv0678 | Rv2535c | Rv1979c | Rv0676c | Rv0677c |
| 1 | 0% (0/21) |
4.8% (1/21) |
0% (0/21) |
100% (21/21) |
14.3% (3/21) |
0% (0/21) |
| 2 | 0% (0/236) |
44.1% (104/236) |
0.8% (2/236) |
33.5% (79/236) |
78.0% (184/236) |
0% (0/236) |
| 3 | 0% (0/7) |
0% (0/7) |
0% (0/7) |
0% (0/7) |
0% (0/7) |
0% (0/7) |
| 4 | 0.4% (1/245) |
0.4% (1/245) |
3.3% (8/245) |
7.8% (19/245) |
100% (245/245) |
0.4% (1/245) |
| All | 0.2% (1/509) |
20.8% (106/509) |
2.0% (10/509) |
23.4% (119/509) |
84.9% (432/509) |
0.2% (1/509) |
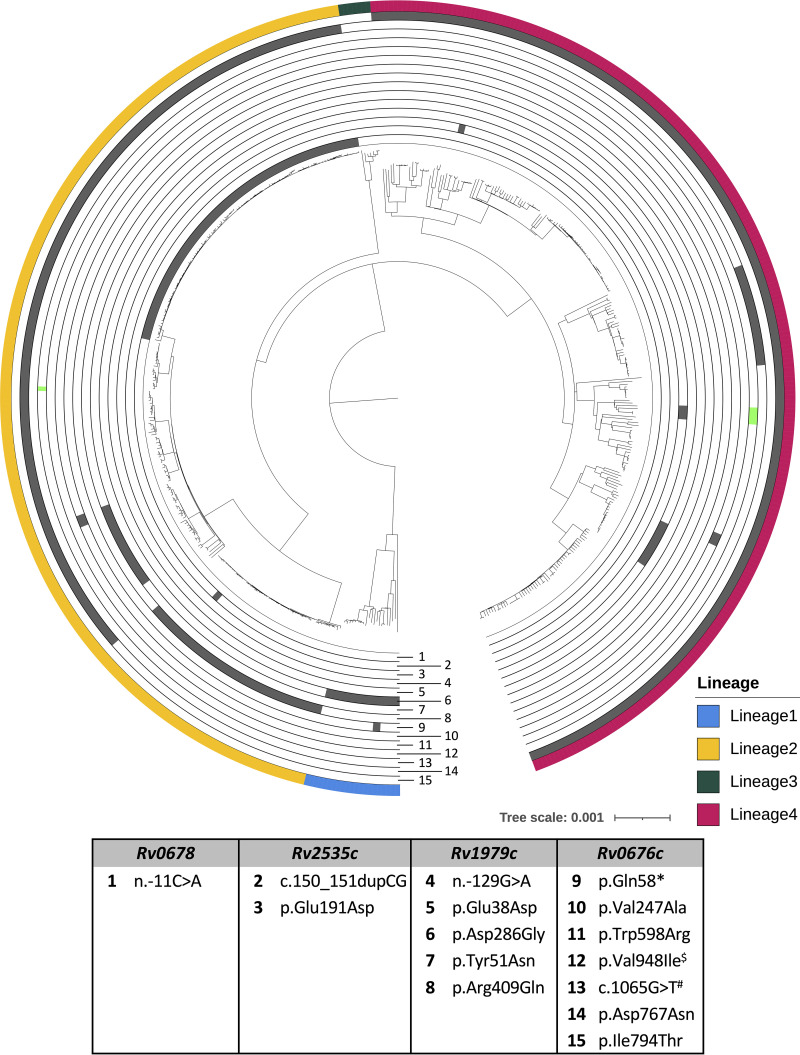
Of 36 unique variants identified, 15 were observed more than once. Of these, 14 were classified as monophyletic and one as homoplastic (Fig. 2; Data Set S1, S2, S3, and S4). The Rv0676c p.Ile794Thr variant was present in all lineage 4 (n = 245) isolates but absent in all other lineages. The Rv0676c p.Asp767Asn variant was observed in all sublineage 2.2.1 isolates (n = 183), but absent in all other (sub)lineages. Likewise, the Rv0678 n.-11C>A variant was exclusively observed in sublineage 2.2.1 isolates (n = 102), but absent in all other (sub)lineages. The Rv1979c p.Asp286Gly variant was present in all lineage 1 isolates (n = 21) and absent from all other lineages. The Rv1979c p.Arg409Gln variant was observed in all sublineage 2.2.2 (n = 50) and sublineage 2.2 (n = 3) isolates, but absent in all other (sub)lineages. The Rv1979c p.Tyr51Asn variant was observed in all 2.2.1.1 sublineage isolates (n = 24), but absent in all other (sub)lineages. The other monophyletic variants (Rv2535c p.Glu191Asp, Rv2535c c.150_151dupCG, Rv1979c n.-129G>A, Rv1979c p.Glu38Asp, Rv0676c p.Gln58*, Rv0676c p.Trp598Arg, Rv0676c p.Val247Ala, and Rv0676c c.1065G>T) were reported in subclades of a sublineage. The oldest sampling year of all monophyletic variants was prior to the introduction of BDQ, except for Rv0676c p.Thr495Ile, which was observed in an isolate collected in 2015. Only the Rv0676c p.Val948Ile variant was homoplastic as it was observed in both sublineage 4.9 and sublineage 2.2.1 isolates (Fig. 2; Table 1; Data Set S1, S2, S3, and S4).
FIG 2.
Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree of the 509 Mycobacterium tuberculosis samples collected from South African patients. Each concentric circle represents a unique variant (corresponding number in legend table) that was observed more than once (variants observed only once are listed in Table 1). Variants occurring exclusively in one clade are shown in gray. Homoplastic variants (occurring in independent samples) are shown in vibrant green (number 12). $Variants were observed independently in the phylogenetic tree; # Synonymous SNPs.
BDQ MIC by variant and lineage.
Phenotypic data could be obtained for 32 of the 36 observed variants (isolates containing Rv0676c p.Val247Ala, Rv1979c n.-147G>A, Rv2535c p. Gly116Val, or Rv2535c n.-118A>G lost viability). The BDQ MIC was below the epidemiological cut-off value (ECOFF) in 287 (98.6%) of 291 isolates tested (Fig. S1) with a wide distribution for almost all variants (Fig. 3; Fig. S2). The BDQ MIC was above the ECOFF for one isolate solely containing the Rv0676c p.Ile794Thr variant and one isolate containing the Rv1979c p.Tyr51Asn and Rv0676c p.Asp767Asn variants. The latter also contained one low frequency variant (Rv2535c c.306C>G) with allele frequency of 12% (Table 3). The BDQ MIC was equal to the ECOFF for one isolate solely containing the Rv0676c p.Ile794Thr variant and one isolate containing the Rv1979c p.Arg409Gln variant. The latter also contained six low frequency Rv0678 variants with varying frequencies (Table 3). All four samples with BDQ MIC above or equal to the ECOFF, originated from confirmed BDQ naive patients.
FIG 3.
Observed bedaquiline (BDQ) MIC values for each combination of variants in the data set for which phenotypic data were available. MIC reading was done after 2 weeks of incubation.
TABLE 3.
Low frequency variants identified in samples with high (≥0.25 μg/mL) bedaquiline MIC
| LoFreq variants in samples with high BDQ MIC | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample ID | BDQa MIC (μg/mL) | Sublineage | Gene | DNA level | Protein level | Allele frequency (%)b |
| R4330 | 0.5 | 2.2.1.1 | Rv0676c | c.2299G>A | p.Asp767Asn | 100 |
| Rv1979c | c.151T>A | p.Tyr51Asn | 100 | |||
| Rv2535c | c.306C>G | p.Val102Val | 12 | |||
| R7726 | 0.5 | 4.7 | Rv0676c | c.2381T>C | p.Ile794Thrc | NA c |
| R8361 | 0.25 | 2.2.2 | Rv0678 | c.38delA | NA | 3 |
| Rv0678 | c.198dupG | NA | 33 | |||
| Rv0678 | c.198delG | NA | 4 | |||
| Rv0678 | c.226C>A | p.Gln76Lys | 10 | |||
| Rv0678 | c.275dupA | NA | 6 | |||
| Rv0678 | c.466dupC | NA | 10 | |||
| Rv1979c | c.1226G>A | p.Arg409Gln | 100 | |||
| R2835 | 0.25 | 4.1.2.1 | Rv0676c | c.2381T>C | p.Ile794Thrc | NA c |
BDQ, bedaquiline.
Allele frequencies <50% are highlighted in gray.
Variants were identified by comparing with the ancestral genome; no allele frequencies can therefore be reported.
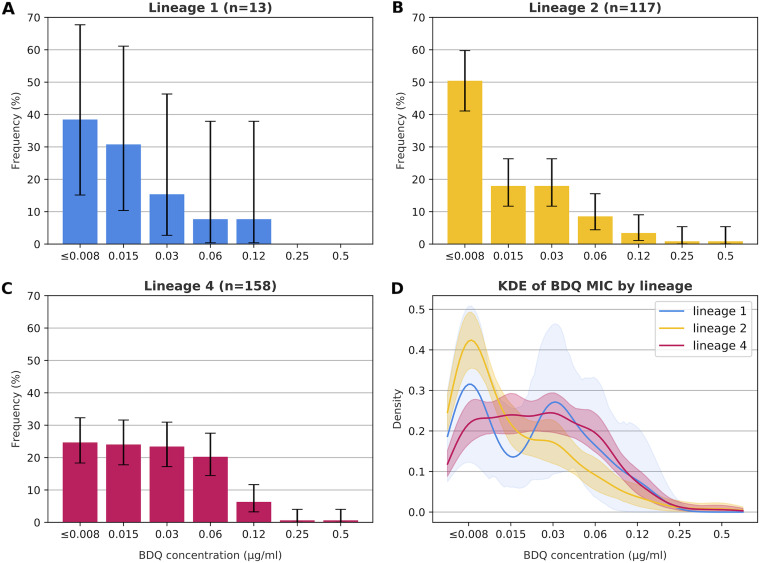
The MIC distribution of lineage 2 isolates differed from that of lineage 4 isolates as lineage 4 isolates had a median MIC of 0.03 μg/mL and a uniform distribution from ≤0.008 to 0.06 μg/mL, whereas the MIC distribution of lineage 2 isolates was skewed with a lower median (0.015 μg/mL) and a mode of ≤0.008 μg/mL (Fisher’s exact test P = 0.0004) (Fig. 4). No differences were observed between lineage 1 and lineage 2 (P = 0.65) or 4 (P = 0.68), likely due to the low number of lineage 1 isolates with phenotypic data (n = 13). Comparisons with lineage 3 were not performed due to scarce data (n = 3) (Fig. S5, panel C).
FIG 4.
Bedaquiline (BDQ) MIC stratified by lineage. (A) BDQ MIC using the CRyPTIC (UKMYC6) plates for lineage 1 isolates. (B) BDQ MIC using the CRyPTIC (UKMYC6) plates for lineage 2 isolates. (C) BDQ MIC using the CRyPTIC (UKMYC6) plates for lineage 4 isolates. (D) Kernel density estimation (KDE) of BDQ MIC of lineage 1, 2, and 4 isolates. KDE and corresponding confidence intervals were calculated using the prop.test function in the R stats package (version 4.0.0). MIC reading was done after 2 weeks of incubation.
In the sensitivity analysis excluding unconfirmed BDQ naive patients, similar phenotypic effects were observed (Fig. S3, S4, and S5) and the MIC difference between lineages 2 and 4 remained significant (P = 0.003).
DISCUSSION
We detected 36 unique variants in the six BDQ candidate resistance genes in isolates of 509 South African RR-TB patients, of which 89% were confirmed BDQ naive. While virtually all (98.6%, 502/509) isolates contained at least one variant, few (1.4%, 4/291 tested) had a MIC at or above the ECOFF. Interestingly, a variant-lineage dependency observed, which resulted in MIC distribution differences between lineage 2 and 4.
The prevalence of observed variants was higher than those reported by other studies of BDQ naive patients (11–14). In a clinical MDR-TB trial, 23 of 347 (6.6%) BDQ-naive participants harbored variants in Rv0678 (13). In a study from China, five of 90 (5.6%) isolates from BDQ naive patients harbored variants (four in Rv0678, one in Rv1979c) (14). In a larger study, 106 of 4795 (2.2%) isolates from patients likely not exposed to BDQ contained a variant (11). The lower prevalence of BDQ variants in these three studies may be explained by their exclusion of the Rv0676c (mmpL5) gene, which had the highest (84.9%) prevalence of variants in our study. Only one small Iranian study (n = 24 isolates) included all six genes in their analysis. Contrary to our findings, only three of the 24 (12.4%) isolates contained variants (two in Rv0676c and one in Rv1979c) even though the lineage distribution was similar to our study (10).
Of the 36 variants, 23 (63.9%) are not included in the WHO catalogue and 19 (52.8%) have not been reported previously (8). Of the 13 variants in the WHO catalogue, nine could not be classified and four were classified as “not associated with resistance.” Interestingly, three of these four variants (Rv0676c p.Thr794Ile, Rv1979c c.-129A>G, and Rv0676c p.Ile948Val) are likely acquired variants in the H37Rv reference genome and should be listed preferably as their ancestral equivalent (Rv0676c p.Ile794Thr, Rv1979c c.-129G>A, and Rv0676c p.Val948Ile) (Table 1).
The prevalence of phenotypic BDQ resistance (MIC > ECOFF) was only 0.69% (two of 291), much lower than what was observed in prior studies of BDQ-naive patients. In the MDR-TB clinical trial, 34.8% (eight of 23) of isolates with a variant in Rv0678 had a BDQ MIC above the critical concentration (13). In a study from China, 80.0% (four of five) of isolates with a Rv0678 variant had an increased BDQ MIC (14). In a study from Iran, 66.7% (two of three) samples with a variant in Rv0676c and Rv1979c had a BDQ MIC above the ECOFF (12). In a study with isolates originating from surveillance activities across six different high TB countries, 7.8% (four of 51 tested) of isolates with a Rv0678 variant had a BDQ MIC above the critical concentration (11). In the largest study to date conducted in South Africa, 3.6% (72 of 2004) of baseline isolates from patients with no previous exposure to BDQ (1987 patients) or unknown exposure status (17 patients) were phenotypically resistant to BDQ (15).
The variants observed in the four isolates with a MIC at or above the ECOFF in our study have been reported before. In contrast to our observation, the Rv0676c p.Asp767Asn was graded as not associated with BDQ resistance in the WHO Variant Catalog (5) and the Rv1979c p.Tyr51Asn variant was only reported in susceptible isolates (n = 152). The Rv1979c p.Arg409Gln variant has been reported in 146 susceptible and five resistant isolates (5). The Rv0676c p.Ile794Thr (or p.The794Ile variant in H37Rv) is graded as not associated with BDQ resistance (5). Of the low frequency variants observed in two of these four isolates, the pepQ c.306C>G variant and Rv0678 c.38delA and p.Gln76Lys variants have not been reported before. The Rv0678 c.198dupG variant has been reported in one susceptible and two resistant clinical isolates (13); the c.198delG variant in three susceptible clinical isolates from exposed patients and two resistant in vitro samples (1, 17); the c.275dupA variant in two resistant BDQ naive clinical isolates (11, 13) and three susceptible BDQ exposed clinical isolates (18); and the c.466dupC variant in two susceptible clinical isolates (1, 18). These results highlight the importance of, including low frequency variants analysis in studies investigating BDQ genotype-phenotype associations (19).
In contrast to most studies (11, 13), we found an association between variants in BDQ-resistance genes and lineages. The only prior report of lineage dependency is for the n.-11C>A Rv0678 promoter variant which was found exclusively in lineage 2 isolates (13), similar to our findings. Furthermore, our results suggest that genetic differences between (sub)lineages may result in phenotype differences between lineages. While the clinical relevance of this finding remains to be investigated, this is interesting given three recent observations: (i) diverging evolutionary trajectories between Mtb lineages, particularly lineages 2 and 4, in response to antibiotic pressure (20); (ii) different levels of resistance for variants in the rpoB, katG, and inhA genes depending on Mtb lineage (21); and (iii) patients with an increased MIC for rifampicin or isoniazid below the breakpoint are at increased risk of developing antibiotic resistance and relapse (22).
Several limitations should be considered. First, exposure to BDQ could not be excluded in 58 (11.4%) patients. BDQ exposure was unlikely as all 58 patients were diagnosed before the BDQ roll-out and homoplastic variants were rare. Furthermore, our sensitivity analysis showed similar findings when excluding these 58 isolates. Second, we could not assess the BDQ MIC for four of the 36 unique variants as some samples failed to grow. Third, reflecting the epidemiology of Mtb in South Africa (23), isolates of lineage 5, 6 or 7 were absent and isolates of lineages 1 and 3 were rare. Lastly, CFZ exposure, which can result in BDQ cross-resistance through mutations in the Rv0678 gene, was not considered because data on CFZ exposure status was not available (24).
In conclusion, while 98.6% of BDQ naive patients harbored Mtb with one or more variants in one of the six candidate genes for BDQ resistance, the proportion of isolates with a BDQ MIC at or above the ECOFF was low (1.4%). The identification of variants in these genes might not warrant exclusion of BDQ from the treatment regimen until further data have accumulated. Future studies should investigate which variants increase the risk of acquisition of phenotypic BDQ resistance and impact treatment outcomes. The observation that the prevalence of variants is (sub)lineage dependent may result in differential impact of these variants by geographic region.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Clinical Mtb isolates.
WGS data from 509 isolates collected from 509 RR-TB patients before BDQ treatment initiation were obtained from two sources. Data from 263 confirmed BDQ-naive patients enrolled in a prospective cohort study (“EXIT-RIF”) from 2012 and 2013 in three South African provinces were included in this analysis. Data from 246 patients diagnosed between 2001 and 2018 in South Africa with an isolate in the Mtb biobank at Stellenbosch University were added. Of these, 133 were classified as BDQ-naive as they were diagnosed before the introduction of BDQ in South Africa in January 2013 (25), and 55 were assumed BDQ-naive as they were diagnosed with RR-TB during the BDQ clinical access program but were not eligible for BDQ given their resistance profile. BDQ exposure could not be excluded for the remaining 58 patients who were eligible for the Bedaquiline Clinical Access Program.
Whole-genome sequencing.
Isolates were cultured on 7H10 media and DNA was extracted using the phenol chloroform method (26). Genomic libraries were prepared using either TruSeq DNA Sample Preparation Kits V2 (Illumina Inc., San Diego, CA, USA) or NEBNext Ultra II DNA library prep kit for Illumina (New England BioLabs). Samples were sequenced on an Illumina HiSeq 2000/4000 or NextSeq 550.
DNA sequence analysis.
Sequencing data were analyzed using the XBS pipeline (27). All FASTQ sequence data were mapped to the H37Rv reference genome using the Burrows-Wheeler alignment tool BWA-MEM (28). After marking duplicate reads with Genome Analysis Tool Kit (GATK [29]) MarkDuplicates, single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP), insertions, and deletions were called using GATK Haplotypecaller. Samples with a coverage depth of ≥10x and breadth of ≥90% were identified for inclusion in joint variant calling. QuanTB was used to filter out samples with ≥20% nontuberculous Mycobacteria (30). Genomic variant call format (GVCF) files were merged and genotypes were jointly called using GATK GenotypeGVCFs (31). Next, GATK VQSR was used to identify true variants (32) using a target sensitivity of 99.9%. Variants in the merged GVCF file were annotated and isolate lineage and sublineage were determined using TB-Profiler (33).
The Rv0676c, Rv0677c, Rv0678, Rv1305 (atpE), Rv1979c, and Rv2535c (pepQ) genes were investigated (Table S1). All variants were compared to their matching position in the Mtb ancestral genome to confirm whether they are true variants or due to acquired variants in H37Rv (sublineage 4.9) (34). The latter were translated to their ancestral equivalent (Rv1979c c.-129G>A, Rv0676c p.Val948Ile, and Rv0676c p.Ile794Thr). Variants were described using HGVS notation (35); nonsynonymous substitutions were described on protein level.
IQtree (version 1.6.12) was used to infer the best substitution model (36) (K3Pu+F+ASC+R5) and construct a maximum likelihood tree (37, 38). The phylogenetic tree was visualized using iTOL v6, rooted at midpoint, and annotated with variants occurring more than once in the data set and isolate lineage (39). For each variant, the oldest sampling year was identified based on the sampling dates of all isolates displaying that variant. A variant was classified as monophyletic when observed in a single clade which could be explained by common ancestry or as homoplastic when observed in two or more independent samples that could not be explained parsimoniously by common ancestry.
Bedaquiline MIC.
Bedaquiline MIC determined using the microtiter plate assay (UKMYC6) (40) was available for 291 isolates: 260 of the 509 (51.1%) isolates purposefully selected to represent all combinations of lineages and variants in the six BDQ candidate resistance genes and 31 isolates with incomplete variant calling. Plates containing standard inoculum aliquots of selected isolates and BDQ at concentrations 0.008, 0.015, 0.03, 0.06, 0.12, 0.25, 0.5, and 1 μg/mL were incubated at 35°C to 37°C and read after 14 and 21 days of incubation if growth was observed in both positive-control wells. For isolates with a BDQ MIC equal to or higher than the ECOFF of 0.25 μg/mL (41), LoFreq (version 2.1.5) was used to investigate low-frequency variants (42).
Statistical analysis.
For each Mtb lineage, BDQ MIC proportions and corresponding 95% confidence intervals were determined using the proportion test (R stats package, R version 4.0.0). Pairwise comparisons of the distribution of MICs between lineages were made using Fisher’s exact test with Monte Carlo simulated P-values. Differences between lineages were considered significant when P-value < 0.05. To investigate whether the inclusion of 58 isolates from unconfirmed BDQ-naive patients biased our results, we performed a sensitivity analysis in which these isolates were excluded.
Ethics.
All isolates and sequences originating from the SAMRC-CTR biobank were collected, stored, and analyzed under the ethical clearance obtained from Stellenbosch University Health Research Ethics Committee (N09/11/269). The EXIT-RIF study was approved by the institutional review board of the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, NC, USA (11-2273) and the Human Ethics Research Committee of the University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa (M111139).
Data availability.
Sequencing reads have been deposited at the European Nucleotide Archive (project accession number: PRJEB50385). Accession numbers and manuscript links of previously published data are listed supplemental materials.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Research Foundation (NRF) or the South African Medical Research Council (SAMRC). Library preparations and sequencing for 80% of isolates were done at the sequencing facility of Macrogen in Seoul, Korea. The remainder were sequenced through existing collaborations with the Translational Genomics Research Institute (David Engelthaler), Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (James Posey), University of California San Diego (Timothy C. Rodwell), FIND (Timothy C. Rodwell), and the Institute of Infectious Disease and Molecular Medicine (Helen Cox).
All authors interpreted the results. All authors critically reviewed the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of this manuscript.
E.R., L.V., A.D., S.G., E.D.V., E.S., B.C., F.B.-R., A.P., and T.H.H. report no conflict.
K.L. reports funding by Janssen, Pharmaceutical Companies of Johnson & Johnson. T.C.R. reports funding by FIND (Geneva, Switzerland) and NIH/NIAD (grant number R21AI135756) and is coinventor on a patent associated with the processing of sequencing files (European Patent Application No. 14840432.0 & USSN 14/912,918) and a provisional patent for a TB diagnostic assay (USSN Provisional Patent No. 63/048.989). R.M.W. reports baseline funding of the South African Medical Research Council. A.V.R. reports funding by Research Foundation Flanders (grant number G0F8316N).
This work was supported by the Research Foundation Flanders (FWO), under FWO Odysseus (grant number G0F8316N) and FWO Strategic Basic Research (grant number 1S39119N), the NRF, the SAMRC, and the Stellenbosch University Faculty of Medicine Health Sciences. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and interpretation, or the decision to submit the work for publication.
Footnotes
Supplemental material is available online only.
REFERENCES
- 1.Zimenkov DV, Nosova EY, Kulagina EV, Antonova OV, Arslanbaeva LR, Isakova AI, Krylova LY, Peretokina IV, Makarova MV, Safonova SG, Borisov SE, Gryadunov DA. 2017. Examination of bedaquiline- and linezolid-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates from the Moscow region. J Antimicrob Chemother 72:1901–1906. 10.1093/jac/dkx094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Somoskovi A, Bruderer V, Homke R, Bloemberg GV, Bottger EC. 2015. A mutation associated with clofazimine and bedaquiline cross-resistance in MDR-TB following bedaquiline treatment. Eur Respir J 45:554–557. 10.1183/09031936.00142914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bloemberg GV, Keller PM, Stucki D, Stuckia D, Trauner A, Borrell S, Latshang T, Coscolla M, Rothe T, Hömke R, Ritter C, Feldmann J, Schulthess B, Gagneux S, Böttger EC. 2015. Acquired resistance to bedaquiline and delamanid in therapy for tuberculosis. N Engl J Med 373:1986–1988. 10.1056/NEJMc1505196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Andries K, Villellas C, Coeck N, Thys K, Gevers T, Vranckx L, Lounis N, de Jong BC, Koul A. 2014. Acquired resistance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis to bedaquiline. PLoS One 9:e102135. 10.1371/journal.pone.0102135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.World Health Organization. 2021. Catalogue of mutations in Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex and their association with drug resistance. WHO. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Briffotaux J, Huang W, Wang X, Gicquel B. 2017. MmpS5/MmpL5 as an efflux pump in Mycobacterium species. Tuberculosis (Edinb) 107:13–19. 10.1016/j.tube.2017.08.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Vargas R, Jr, Freschi L, Spitaleri A, Tahseen S, Barilar I, Niemann S, Miotto P, Cirillo DM, Koser CU, Farhat MR. 2021. Role of epistasis in amikacin, kanamycin, bedaquiline, and clofazimine resistance in mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 65:e0116421. 10.1128/AAC.01164-21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ismail N, Rivière E, Limberis J, Huo S, Metcalfe JZ, Warren RM, Van Rie A. 2021. Genetic variants and their association with phenotypic resistance to bedaquiline in Mycobacterium tuberculosis: a systematic review and individual isolate data analysis. Lancet Microbe 2:e604–e616. 10.1016/S2666-5247(21)00175-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kadura S, King N, Nakhoul M, Zhu H, Theron G, Koser CU, Farhat M. 2020. Systematic review of mutations associated with resistance to the new and repurposed Mycobacterium tuberculosis drugs bedaquiline, clofazimine, linezolid, delamanid and pretomanid. J Antimicrob Chemother 75:2031–2043. 10.1093/jac/dkaa136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Almeida D, Ioerger T, Tyagi S, Li SY, Mdluli K, Andries K, Grosset J, Sacchettini J, Nuermberger E. 2016. Mutations in pepQ confer low-level resistance to bedaquiline and clofazimine in mycobacterium tuberculosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 60:4590–4599. 10.1128/AAC.00753-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Battaglia S, Spitaleri A, Cabibbe AM, Meehan CJ, Utpatel C, Ismail N, Tahseen S, Skrahina A, Alikhanova N, Mostofa Kamal SM, Barbova A, Niemann S, Groenheit R, Dean AS, Zignol M, Rigouts L, Cirillo DM. 2020. Characterization of genomic variants associated with resistance to bedaquiline and delamanid in naive mycobacterium tuberculosis clinical strains. J Clin Microbiol 58. 10.1128/JCM.01304-20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ghajavand H, Kargarpour Kamakoli M, Khanipour S, Pourazar Dizaji S, Masoumi M, Rahimi Jamnani F, Fateh A, Siadat SD, Vaziri F. 2019. High prevalence of bedaquiline resistance in treatment-naive tuberculosis patients and verapamil effectiveness. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 63. 10.1128/AAC.02530-18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Villellas C, Coeck N, Meehan CJ, Lounis N, de Jong B, Rigouts L, Andries K. 2017. Unexpected high prevalence of resistance-associated Rv0678 variants in MDR-TB patients without documented prior use of clofazimine or bedaquiline. J Antimicrob Chemother 72:684–690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Xu J, Wang B, Hu M, Huo F, Guo S, Jing W, Nuermberger E, Lu Y. 2017. Primary clofazimine and bedaquiline resistance among isolates from patients with multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 61. 10.1128/AAC.00239-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ismail NA, Omar SV, Moultrie H, Bhyat Z, Conradie F, Enwerem M, Ferreira H, Hughes J, Joseph L, Kock Y, Letsaolo V, Maartens G, Meintjes G, Ngcamu D, Okozi N, Padanilam X, Reuter A, Romero R, Schaaf S, Te Riele J, Variava E, van der Meulen M, Ismail F, Ndjeka N. 2022. Assessment of epidemiological and genetic characteristics and clinical outcomes of resistance to bedaquiline in patients treated for rifampicin-resistant tuberculosis: a cross-sectional and longitudinal study. Lancet Infect Dis 22:496–506. 10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00470-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Beckert P, Sanchez-Padilla E, Merker M, Dreyer V, Kohl TA, Utpatel C, Koser CU, Barilar I, Ismail N, Omar SV, Klopper M, Warren RM, Hoffmann H, Maphalala G, Ardizzoni E, de Jong BC, Kerschberger B, Schramm B, Andres S, Kranzer K, Maurer FP, Bonnet M, Niemann S. 2020. MDR M. tuberculosis outbreak clone in Eswatini missed by Xpert has elevated bedaquiline resistance dated to the pre-treatment era. Genome Med 12:104. 10.1186/s13073-020-00793-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ismail N, Ismail NA, Omar SV, Peters RPH. 2019. In vitro study of stepwise acquisition of rv0678 and atpE mutations conferring bedaquiline resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 63. 10.1128/AAC.00292-19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Peretokina IV, Krylova LY, Antonova OV, Kholina MS, Kulagina EV, Nosova EY, Safonova SG, Borisov SE, Zimenkov DV. 2020. Reduced susceptibility and resistance to bedaquiline in clinical M. tuberculosis isolates. J Infect 80:527–535. 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.de Vos M, Ley SD, Wiggins KB, Derendinger B, Dippenaar A, Grobbelaar M, Reuter A, Dolby T, Burns S, Schito M, Engelthaler DM, Metcalfe J, Theron G, van Rie A, Posey J, Warren R, Cox H. 2019. Bedaquiline microheteroresistance after cessation of tuberculosis treatment. N Engl J Med 380:2178–2180. 10.1056/NEJMc1815121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Oppong YEA, Phelan J, Perdigao J, Machado D, Miranda A, Portugal I, Viveiros M, Clark TG, Hibberd ML. 2019. Genome-wide analysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis polymorphisms reveals lineage-specific associations with drug resistance. BMC Genomics 20:252. 10.1186/s12864-019-5615-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Fenner L, Egger M, Bodmer T, Altpeter E, Zwahlen M, Jaton K, Pfyffer GE, Borrell S, Dubuis O, Bruderer T, Siegrist HH, Furrer H, Calmy A, Fehr J, Stalder JM, Ninet B, Bottger EC, Gagneux S, Swiss H, the Swiss Molecular Epidemiology of Tuberculosis Study G . 2012. Effect of mutation and genetic background on drug resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 56:3047–3053. 10.1128/AAC.06460-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Colangeli R, Jedrey H, Kim S, Connell R, Ma S, Chippada Venkata UD, Chakravorty S, Gupta A, Sizemore EE, Diem L, Sherman DR, Okwera A, Dietze R, Boom WH, Johnson JL, Mac Kenzie WR, Alland D, Teams DTTCS . 2018. Bacterial factors that predict relapse after tuberculosis therapy. N Engl J Med 379:823–833. 10.1056/NEJMoa1715849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Said H, Ratabane J, Erasmus L, Gardee Y, Omar S, Dreyer A, Ismail F, Bhyat Z, Lebaka T, van der Meulen M, Gwala T, Adelekan A, Diallo K, Ismail N. 2021. Distribution and clonality of drug-resistant tuberculosis in South Africa. BMC Microbiol 21:157. 10.1186/s12866-021-02232-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hartkoorn RC, Uplekar S, Cole ST. 2014. Cross-resistance between clofazimine and bedaquiline through upregulation of MmpL5 in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 58:2979–2981. 10.1128/AAC.00037-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Schnippel K, Ndjeka N, Maartens G, Meintjes G, Master I, Ismail N, Hughes J, Ferreira H, Padanilam X, Romero R, Te Riele J, Conradie F. 2018. Effect of bedaquiline on mortality in South African patients with drug-resistant tuberculosis: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet Respir Med 6:699–706. 10.1016/S2213-2600(18)30235-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Warren R, de Kock M, Engelke E, Myburgh R, Gey van Pittius N, Victor T, van Helden P. 2006. Safe Mycobacterium tuberculosis DNA extraction method that does not compromise integrity. J Clin Microbiol 44:254–256. 10.1128/JCM.44.1.254-256.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Heupink TH, Verboven L, Warren RM, Van Rie A. 2021. Comprehensive and accurate genetic variant identification from contaminated and low coverage Mycobacterium tuberculosis whole genome sequencing data. bioRxiv. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 28.Li H. 2013. Aligning sequence reads, clone sequences and assembly contigs with BWA-MEM. arXiv.
- 29.Van der Auwera GA, O’Connor BD. 2020. Genomics in the cloud: using Docker, GATK, and WDL in Terra (1st edition). O’Reilly Media. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Anyansi C, Keo A, Walker BJ, Straub TJ, Manson AL, Earl AM, Abeel T. 2020. QuantTB - a method to classify mixed Mycobacterium tuberculosis infections within whole genome sequencing data. BMC Genomics 21:80. 10.1186/s12864-020-6486-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Poplin R, Ruano-Rubio V, DePristo MA, Fennell TJ, Carneiro MO, Van der Auwera GA, Kling DE, Gauthier LD, Levy-Moonshine A, Roazen D, Shakir K, Thibault J, Chandran S, Whelan C, Lek M, Gabriel S, Daly MJ, Neale B, MacArthur DG, Banks E. 2018. Scaling accurate genetic variant discovery to tens of thousands of samples. bioRxiv. 10.1101/201178. [DOI]
- 32.DePristo MA, Banks E, Poplin R, Garimella KV, Maguire JR, Hartl C, Philippakis AA, del Angel G, Rivas MA, Hanna M, McKenna A, Fennell TJ, Kernytsky AM, Sivachenko AY, Cibulskis K, Gabriel SB, Altshuler D, Daly MJ. 2011. A framework for variation discovery and genotyping using next-generation DNA sequencing data. Nat Genet 43:491–498. 10.1038/ng.806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Phelan JE, O'Sullivan DM, Machado D, Ramos J, Oppong YEA, Campino S, O'Grady J, McNerney R, Hibberd ML, Viveiros M, Huggett JF, Clark TG. 2019. Integrating informatics tools and portable sequencing technology for rapid detection of resistance to anti-tuberculous drugs. Genome Med 11:41. 10.1186/s13073-019-0650-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Comas I, Chakravartti J, Small PM, Galagan J, Niemann S, Kremer K, Ernst JD, Gagneux S. 2010. Human T cell epitopes of Mycobacterium tuberculosis are evolutionarily hyperconserved. Nat Genet 42:498–503. 10.1038/ng.590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.den Dunnen JT, Dalgleish R, Maglott DR, Hart RK, Greenblatt MS, McGowan-Jordan J, Roux AF, Smith T, Antonarakis SE, Taschner PE. 2016. HGVS recommendations for the description of sequence variants: 2016 update. Hum Mutat 37:564–569. 10.1002/humu.22981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Kalyaanamoorthy S, Minh BQ, Wong TKF, von Haeseler A, Jermiin LS. 2017. ModelFinder: fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat Methods 14:587–589. 10.1038/nmeth.4285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ngabonziza JCS, Loiseau C, Marceau M, Jouet A, Menardo F, Tzfadia O, Antoine R, Niyigena EB, Mulders W, Fissette K, Diels M, Gaudin C, Duthoy S, Ssengooba W, Andre E, Kaswa MK, Habimana YM, Brites D, Affolabi D, Mazarati JB, de Jong BC, Rigouts L, Gagneux S, Meehan CJ, Supply P. 2020. A sister lineage of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex discovered in the African Great Lakes region. Nat Commun 11:2917. 10.1038/s41467-020-16626-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Minh BQ, Schmidt HA, Chernomor O, Schrempf D, Woodhams MD, von Haeseler A, Lanfear R. 2020. IQ-TREE 2: new models and efficient methods for phylogenetic inference in the genomic era. Mol Biol Evol 37:1530–1534. 10.1093/molbev/msaa015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Letunic I, Bork P. 2021. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v5: an online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res 49:W293–W296. 10.1093/nar/gkab301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Rancoita PMV, Cugnata F, Gibertoni Cruz AL, Borroni E, Hoosdally SJ, Walker TM, Grazian C, Davies TJ, Peto TEA, Crook DW, Fowler PW, Cirillo DM, Consortium CRCtCCtC . 2018. Validating a 14-drug microtiter plate containing bedaquiline and delamanid for large-scale research susceptibility testing of mycobacterium tuberculosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 62. 10.1128/AAC.00344-18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Fowler PW, CRyPTIC Consortium . 2021. Epidemiological cutoff values for a 96-well broth microdilution plate for high-throughput research antibiotic susceptibility testing of M. tuberculosis. medRXiv. 10.1101/2021.02.24.21252386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Wilm A, Aw PP, Bertrand D, Yeo GH, Ong SH, Wong CH, Khor CC, Petric R, Hibberd ML, Nagarajan N. 2012. LoFreq: a sequence-quality aware, ultra-sensitive variant caller for uncovering cell-population heterogeneity from high-throughput sequencing datasets. Nucleic Acids Res 40:11189–11201. 10.1093/nar/gks918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Whole-genome sequencing isolate accession numbers and Data Sets S1 to S4. Download aac.00322-22-s0001.xlsx, XLSX file, 0.06 MB (60.8KB, xlsx)
Fig. S1 to S5 and Tables S1 to S3. Download aac.00322-22-s0002.pdf, PDF file, 1.6 MB (1.6MB, pdf)
Data Availability Statement
Sequencing reads have been deposited at the European Nucleotide Archive (project accession number: PRJEB50385). Accession numbers and manuscript links of previously published data are listed supplemental materials.