Figure 1.
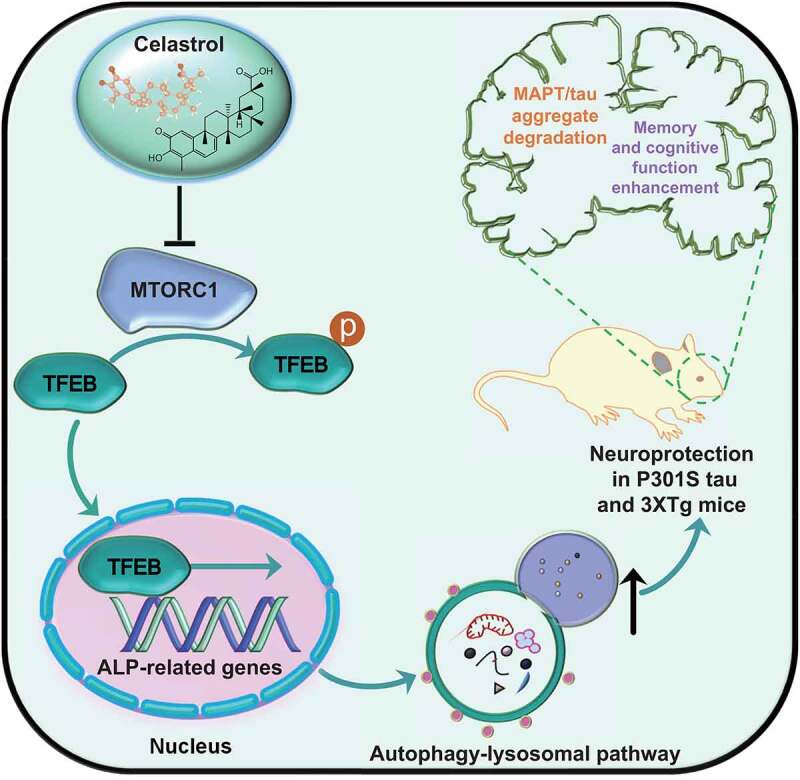
A schematic model of the neuroprotective effects of celastrol in experimental AD. Celastrol promotes the nuclear translocation of TFEB via MTORC1 inactivation. In the nucleus, dephosphorylated TFEB transcriptionally upregulates multiple autophagy-related genes to activate the autophagy-lysosomal pathway. Subsequently, celastrol promotes the degradation of phosphorylated MAPT/tau aggregates to improve memory and cognitive dysfunctions in AD animal models.
