Abstract
Humans are a unique reservoir of heterogeneous and vivacious group of microbes, which together forms the human-microbiome superorganism. Human gut serves as a home to over 100–1000 microbial species, which primarily modulate the host internal environment and thereby, play a major role in host health. This spectacular symbiotic relationship has attracted extensive research in this field. More specifically, these organisms play key roles in defense function, eupepsia along with catabolism and anabolism, and impact brain-gut responses. The emergence of microbiota with resistance and tolerance to existing conventional drugs and antibiotics has decreased the drug efficacies. Furthermore, the modern biotechnology mediated nano-encapsulated multiplex supplements appear to be high cost and inconvenient. Henceforth, a simple, low-cost, receptive and intrinsic approach to achieve health benefits is vital in the present era. Supplementation with probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics has shown promising results against various enteric pathogens due to their unique ability to compete with pathogenic microbiota for adhesion sites, to alienate pathogens or to stimulate, modulate and regulate the host’s immune response by initiating the activation of specific genes in and outside the host intestinal tract. Probiotics have also been shown to regulate fat storage and stimulate intestinal angiogenesis. Hence, this study aims to underline the possible beneficial impact of probiotics for human health and medical sectors and for better lifestyle.
Keywords: Microbiota, Human-gut, Pathogenic, Probiotics, Symbiotic relationship
1. Introduction
Probiotic is a phrase of the modern era, denotation “for life” and is in use to name bacterial association with beneficial effects on human and animal health [1]. In early nineties, Metchnikoff [2] expressed probiotics in a scientific context as modification of floral/microbial diversity in human bodies and replaces the harmful microbes with useful ones. However, the breakthrough was achieved through the works of Henry Tissier, who observed that the microbial concentration of a particular type of bacteria in stool samples of infected diarrhea childrens were significantly lower in comparision to healthy children [3]. His suggestions for oral administration of live organisms (bifidobacteria) to patients with diarrhea (infantile diarrhea) and help restore a healthy gut flora was a first of it kind. The modern definition of probiotic was put forward by Havenaar and Huisint Veld [4] as a viable mono or mixed culture of bacteria which, when applied to animal or man, affects the host beneficially by improving the properties of the indigenous flora.
Following initial hiccups, research in probiotic has progressed considerably in the past two decades and significant advances have been made in the selection and characterization of specific probiotic cultures along with substantial health benefits upon consumption. An ecological consideration of the gut flora is necessary to understand their relevance in human health, as well as the probiotic food concept. Each individual has a unique signature of more than 100–1000 microbial species in gastrointestinal tract (GIT) [5]. Bacterial cells comprise half of the wet weight of colonic material and their numbers exceed by 10-fold the number of tissue cells forming the human body. Normally, the stomach contains 103 different bacterial species, and the total microbial population of the colon comprises of about 1011–1012 cfu/g [6]. Bacterial colonization of the gut begins at birth when newborns are first exposed to a non-sterile environment. Henceforth, it evolves and transforms over a lifetime, depending on a complex and dynamic interplay between the diet, genome, and lifestyle of the host, as well as antibiotic use. Notable age-specific compositional shifts reported in gut microbiota composition include a decrease in the Bacteroidetes/Firmicutes ratio and a marked decrease in bifidobacteria in people aged > 60 years, around the time that the immune system starts to decline [7]. Generally, however, the composition of the core intestinal microflora is considered to be essentially stable throughout adulthood.
The beneficial usage of intestinal microflora, also referred to as “colonization resistance” or the “barrier effect” is an important mechanism used by the indigenous (autochthonous) gut bacteria to maintain their presence and confer niche protection against freshly ingested microorganisms, including pathogens [8,9]. Therefore, it could be assumed that manipulation of the gut microflora to increase the relative numbers of “beneficial bacteria”, which have certain impacts on immune function, digestion, metabolism, and brain-gut communication [10]. Any alterations in their diversity may result in several disorders and diseases, for which conventional medicines provide very limited efficacy mainly due to the emergence of antibiotic-resistant and tolerant pathogenic microbes [11]. Attempts to overcome such critical issue by increasing the drug delivery system to the target sites using nano-encapsulated multiplex supplements have been reported to as a possible solution [12], although, such approaches appear to be cost-effective, and inconvenient for common use. Hence, a simple, low-cost, receptive and intrinsic means to improve host health has become a critical issue in the present era. In this context, probiotics tends to serve as supplement to the host microflora and provide protection against various enteric pathogens. Probiotics are also known to demonstrate promising results like improved gut barrier function; adding to their unique ability to compete with pathogenic microbiota for adhesion to the gut and improve their colonization [13].
Probiotics also stimulate, modulate and regulate the host’s immune response by initiating the activation of specific genes of localized host cells. They even modulate the gastrointestinal hormone release and regulate brain behavior through bidirectional neuronal signaling, as part of the gut–brain axis [14]. Probiotics plays a significant role in inducing intestinal angiogenesis by vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) signaling that, in turn, regulates acute and chronic inflammation in intestinal mucosal tissue caused by the progression of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) [15,16]. Probiotics have physiological functions that contribute to the health of the host environment regulating microbes and are also helpful in combating overweight and obesity [17]. Although probiotics have considerable potential in nutritional and clinical applications, considerable researches are required for the implementation of probiotics into human health, nutrition and regulation of different abnormalities. The review is an attempt to emphasize the possible benefaction of probiotics for improving human health, nutrition optimization and regulation of common metabolic disorders or abnormalities.
2. Probiotics, prebiotics, postbiotics and synbiotics
There have been several definitions that had been prostulated for probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics, however they can be best explain as microbe or a group of microbes that inhabits within the gut and nourishes the host body internally [18,19]. They are commonly consumed as preparations with active live cultures and contain bacteria, such as lactobacilli, lactococci or bifidobacteria that has been isolated from natural environments [20].
As known that, the diverse characteristics of probiotics have been recognized as key health promoters, researches in recent years has mainly focused on investigating the culture conditions and viability of probiotic strains during processing and storage; sensitivity to low pH values, gastric fluid, bile, pancreatic and intestinal fluids and intestinal or respiratory mucus; adherence to isolated cells or cell cultures and interactions with other (pathogenic) microorganisms. A selective list of different bacterial species that are actively used as probiotics is listed in Table 1.
Table 1.
Current microorganisms used as probiotics.
| Sl. No. | Probiotic bacterial genera | Species involved | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lactobacillus | L. plantarum, L. paracasei, L. acidophilus, L. casei, L. rhamnosus, L. crispatus, L. gasseri, L. reuteri, L. bulgaricus | [97] |
| 2 | Propionibacterium | P. jensenii, P. freudenreichii | |
| 3 | Peptostreptococcus | P. productus | |
| 4 | Bacillus | B. coagulans, B. subtilis, B. laterosporus | [98] |
| 5 | Lactococcus | L. lactis, L. reuteri, L. rhamnosus, L. casei, L. acidophilus, L. curvatus, L. plantarum | [99] |
| 6 | Enterococcus | E. faecium | [100] |
| 7 | Pediococcus | P. acidilactici, P. pentosaceus | [101] |
| 8 | Streptococcus | S. sanguis, S. oralis, S. mitis, S. thermophilus, S. salivarius | [102] |
| 9 | Bifidobacterium | B. longum, B. catenulatum, B. breve, B. animalis, B. bifidum | [103] |
| 10 | Bacteroides | B. uniformis | [17] |
| 11 | Akkermansia | A. muciniphila | |
| B | Saccharomyces | S. boulardii | [16] |
2.1. Postbiotics
Recent data suggests that bacterial products, in the absence of viable organisms, may have similar effects on signaling pathways and barrier function. These bacterial products are broadly characterized as postbiotics and can be defined as non-viable bacterial products or metabolic byproducts from probiotic microorganisms that have biologic activity in the host [21]. General, postbiotics include bacterial metabolic byproducts, such as bacteriocins, organic acids, ethanol, diacetyl, acetaldehydes and hydrogen peroxide, but it is also found that certain heat-killed probiotics can also retain important bacterial structures that may exert biological activity in the host [22]. Research shows that these metabolic products have a broad inhibitory property toward pathogenic microbes and, therefore, can be used as an alternative to antibiotics [23]. Postbiotics are non-toxic, non-pathogenic and resistance to hydrolysis by mammalian enzymes, as these are non-viable bacterial products or metabolic byproducts from probiotics. In some instances, postbiotics can also enhance barrier function against species like Saccharomyces boulardii, and improve angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo in epithelial cells by activation of α2β1 integrin collagen receptors [24]. Similar properties have also been identified in several other probiotic species of Bifidobacterium breve, Bifidobacterium lactis, Bifidobacterium infantis, Bacteroides fragilis, Lactobacillus, Escherichia coli and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii [25] (Table 2).
Table 2.
Postbiotics and prebiotics and their natural sources.
| Bioactive compounds | Natural sources | References |
|---|---|---|
| Postbiotics | ||
| Bacteriocins | Lactobacillus plantarum I-UL4 | [23] |
| Heat-killed LGG | Lactobacillus rhamnosus | [22] |
| Soluble mediator | Lactobacillus paracasei | [104] |
| Butyrate | Faecalibacterium prausnitzii | [24] |
| Polyphosphate | Lactobacillus brevis | [105] |
| Exopolysaccharides | Lactobacillus pentosus | [101] |
| Short-chain fatty acids | Lactobacillus gasser | [106] |
| Prebiotics | ||
| Fructo-oligosaccharides | Onion, Leek, Asparagus, Chicory, Jerusalem artichoke, Garlic, Wheat, Oat | [107] |
| Inulin | Agave, Banana/Plantain, Burdock Camas, Chicory, Coneflower, Costus, Dandelion, Elecampane, Garlic, Globe artichoke, Jerusalem artichoke, Jicama, Leopard’s bane, Mugwort root, Onion, Wild yam, Yacón | [6] |
| Isomalto-oligosaccharides | Miso, Soy, Sauce, Sake, Honey | [108] |
| Lactulose | Skim milk | [109] |
| Lactosucrose | Milk sugar | [110] |
| Galacto-oligosaccharides | Lentil, Human milk, Chickpea/hummus, Green pea, Lima bean, Kidney bean | [111] |
| Soybean oligosaccharides | Soybean | [112] |
| Xylo-oligosaccharides | Bamboo shoot, Fruits, Vegetables, Milk, Honey | [113] |
| Fructo-oligosaccharides | Onion, Chicory, Garlic, Asparagus, Banana, Artichoke | [114] |
| Arabinoxylan | Bran of grasses | [44] |
| Arabinoxylan oligosaccharides | Cereals | |
| Resistant starch-1,2,3,4 | Beans/legumes, Starchy fruits and vegetables (e.g. bananas), Whole grains | [115] |
2.2. Prebiotics
Further exploration of probiotics have led to the development of prebiotics, which are certain nutrients that modify the gut microbial flora although not easily digested by humans but have a selective role in stimulation of growth or activity of beneficial bacterial species in the gut [26,27]. Some of the common known prebiotics includes bifidogenic properties of insulin, oligofructose, and fructo-oligosaccharides (FOS) synthetically produced from sucrose, as well as galactose-containing and xylose-containing oligosaccharides [28,29]. The fermentation of carbohydrates represents a major source of energy for epithelial cells in the colon and prebiotics can readily fulfill these requirements as a result of their fermentation by gut microbiota, such as bifidobacteria. Besides bifidobacteria, there are several other gut microorganisms that play a significant role in fermenting these non-digestible oligosaccharides. Some of the examples of the prebiotics, along with their natural sources and the associated fermentative microbiota are presented in Table 2.
Prebiotics can be obtained naturally from sources like vegetables, fruits, and grains consumed in our daily life. Prebiotics not only serve as an energy source but also have several health benefits such as reducing the prevalence and duration of diarrhea, providing relief from inflammation and other symptoms associated with intestinal bowel disorders, and exerting protective effects to prevent colon cancer [30]. Prebiotics are also implicated in enhancing the bioavailability and uptake of minerals, lowering of some risk factors for cardiovascular disease, and promoting satiety and weight loss [31]. Despite their vast nutritional and medicinal benefits, research regarding screening new versatile prebiotics is scarce. Therefore, more research should be focused on identifying new health supplements, where screening novel prebiotics must be a primary concern.
2.3. Synbiotics
Development in microbial research has led to formation of synbiotics which is a fusion of probiotics and prebiotics products and helps in enhancing the survival and the implantation of live microbial dietary supplements in the gut [18,32]. The synergistic benefits are more efficiently promoted when both the probiotic and prebiotic work together in the living system. There is mounting scientific evidence that the symbiotic relationship between prebiotics and probiotics contributes significantly to health. Commercial interest in functional foods containing synbiotics has consistently increased due to the awareness of the benefits for gut health, disease prevention and therapy. Research in this area is currently focused on developing new health-promoting foods, as well as on selecting new cultures demonstrating an enhanced ability to colonize the human gut, along with their ability to digest new forms of prebiotics. Some of the common synbiotic compositions currently under study are shown in Table 3.
Table 3.
Common synbiotics and their microbial sources.
| Synbiotics | References | |
|---|---|---|
|
| ||
| Prebiotics | Probiotics | |
| Fructo-oligosaccharides | Bifidobacteria, Bacteroides fragilis, Peptostreptococcaceae, Klebsiellae | [116] |
| Inulin | Bifidobacterium animalis, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus paracasei | [97] |
| Isomalto-oligosaccharides | Bifidobacteria, Bacteroides fragilis group | [108] |
| Lactulose | Bifidobacteria lactis, Lactobacillus bulgaricus, L. acidophilus, L. rhamnosus | [109] |
| Lactosucrose | Zymomonas mobilis | [117] |
| Xylo-oligosaccharides | Bifidobacterium adolescentis, L. plantarum | [113] |
| Galacto-oligosaccharides | Bifidobacterium longum, B. catenulatum | [118] |
| Fructo-oligosaccharides | Bifidobacterium bifidum, B. lactis | [119] |
| Arabinoxylan and Arabinoxylan oligosaccharides | Bifidobacterium sp. | [44] |
| Resistant starch-1,2,3,4 | Bacteroides, Eubacterium rectal | [120] |
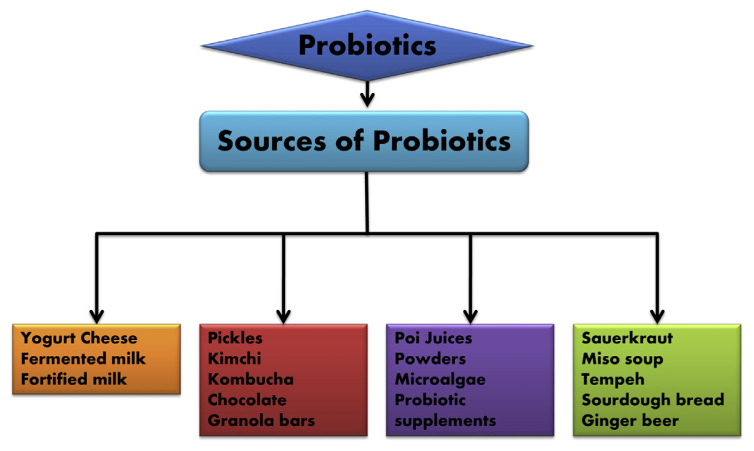
Conventional trials and investigation has shown that the various beneficiary effects of probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics are much more effective than their unitary use known till date. Therefore, studies aimed at developing new concoctions of probiotics and prebiotics are vital to exploit further possibilities of enhancing nutritional and clinical health benefits (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
Different sources of probiotics.
3. Clinical significance of probiotics and its potential applications
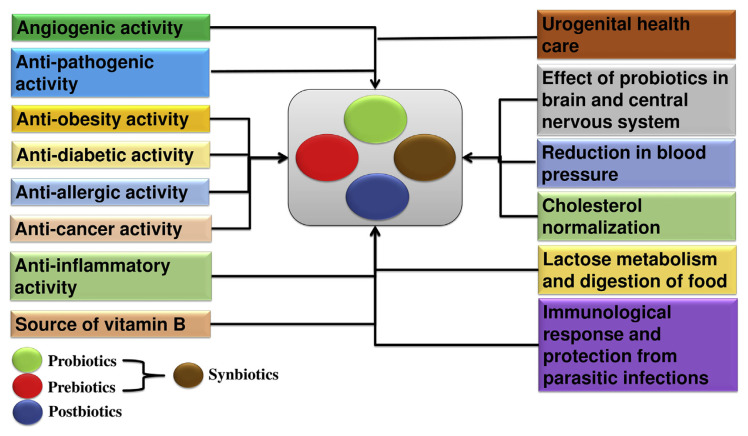
The use of probiotics for clinical health benefits is a fascinating area of research that the present era has yet to explore. Some of the elite properties of probiotics, such as anti-pathogenicity, anti-diabetic, anti-obesity, anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, anti-allergic, and angiogenic activities and their effect on the brain and central nervous system (CNS) are briefly discussed below and also depicted in Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.
Applications of probiotics and their mode of action.
3.1. Anti-pathogenic activity of probiotics
Anti-pathogenic activity is regarded as one of the most beneficial effects of probiotics because unlike classic antibiotics, disturbance or alteration in the composition of the complex population of the gut microbiota is inhibited. There has been considerable research on the anti-pathogenic activity of probiotics or a probiotic mixture. Tejero-Sarinena et al. [33] investigated the influence of probiotics on the survival of Salmonella enterica, Serovar typhimurium and Clostridium difficile in an in vitro model and postulated that probiotics inhibit pathogens by the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), such as acetic, propionic, butyric and lactic acids. SCFAs help to maintain an appropriate pH in the colonic lumen, which is imperative in the expression of numerous bacterial enzymes and in metabolism of foreign compounds and carcinogens in the gut [34]. Islam [22] also suggested that a wide variety of anti-pathogenic compounds, like bacteriocins, ethanol, organic acids, diacetyl, acetaldehydes, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and peptides are produced by many probiotics. Among these compounds, peptides and bacteriocins, in particular are mostly involved in increasing the membrane permeability of the target cells, which leads to the depolarization of the membrane potential and, ultimately, cell death [35]. Similarly, the production of H2O2 by these bacterial groups causes the oxidation of sulfhydryl groups, resulting in the denaturation of several enzymes results in the peroxidation of membrane lipids, thus, increasing membrane permeability of the pathogenic microorganism and consequently, cell death [36]. Some of these compounds may act by lowering pH by organic acids like lactic and acetic acids [34]. In addition to producing anti-pathogenic bioactive compounds that directly affect pathogens, probiotics also stimulate host anti-pathogenic defense pathways, such as stimulating or activating the pathway involved in the production of defensins that are cationic anti-microbial peptides produced in several cell types including Paneth cells in the crypts of the small intestine and intestinal epithelial cells [37]. Another mechanism by which probiotics exert anti-pathogenic activity is by competing for pathogen binding and receptor sites, as well as for available nutrients and growth.
3.2. Urogenital health care
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDCP), more than one billion women around the world suffer from non-sexually transmitted urogenital infections, such as bacterial vaginosis (BV), urinary tract infection (UTI) and several other yeast infections [38]. The species typically associated with BV include Gardnerella vaginalis, Ureaplasma urealyticum, and Mycoplasma hominis [39]. Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are also a significant cause of morbidity worldwide. The two most commonly documented bacterial STDs in some developed countries are gonorrhea and Chlamydia, which are caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis, respectively [40]. The major issue facing the current decade is that despite having sophisticated medicines to treat various medical conditions, these pathogenic microbes, among others, are concurrently becoming resistance to the present medicines. Therefore, instead of developing new medicines, our present focus should be on developing new live supplements, like non-pathogenic microbes that act against the pathogens.
It is well-known that there is an association between abnormal vaginal microbial flora and an increased incidence of urinary tract infection (UTI). There are about 50 different species inhabiting the vagina, like Lactobacillus species, Lactobacillus brevis, Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus vaginalis, Lactobacillus delbrueckii, Lactobacillus salivarius, Lactobacillus reuteri, and Lactobacillus rhamnosus that are regarded as the main regulators of the vaginal micro-environment. Imbalance in the microbial composition greatly influences the health of the vaginal microenvironment, potentially leading to compromised state of bacterial vaginosis (BV) and UTI. These compromised states can be reassured by balancing the number of Lactobacillus sp. via the supplementation of probiotics [38].
3.3. Anti-diabetic activities of probiotics
According to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) of Southeast Asia, 425 million people have diabetes worldwide including 78 million people in the Southeast Asian region [41]. Moreover, this number is expected to rise to 629 million by 2045 if nothing is done [41]. The management of this disorder includes multiple medications although there is no definitive cure for diabetes. Nonetheless, bimolecular and pharmacological researchers have made progress in understanding the importance of synbiotics in curing the disorder [42]. Based on large-scale 16 S rRNA gene sequencing, quantitative real-time PCR and fluorescent in situ hybridization, the connection between the composition of the intestinal microbiota and metabolic diseases, like obesity and diabetes, has been postulated by Larsen et al. [43]. Consequently, enhancing the beneficial microbiota by the use of probiotics is expected to play a significant role in neutralization of the disorder [43].
Gram-negative bacteroidetes and the Gram-positive firmicutes are two specific bacterial phyla that dominant the gut microenvironment. Recent research has proven that obesity is associated with increased bacteroidetes over time, concurrent with a reduction in firmicutes [44,17]. More specifically, patients with type-2 diabetes have significantly reduced numbers of firmicutes species, such that the bacteroidetes/firmicutes ratio has increased, which positively correlates with plasma glucose concentration [45]. A similar pattern has been implicated in the development of auto-immune diseases, such as type-1 diabetes [46–48]. Alterations in the microbiome also increase invasion of opportunistic pathogens, which are resistant to oxidative stress and simultaneously capable of reducing sulfates and inhibiting the growth of butyrate-producing bacteria [49].
Management of type-2 diabetes by modulating gut hormones, such as gastric inhibitory polypeptide and glucagon-like peptide-1, via probiotic and prebiotic interventions is another convincing strategy. In this context, hormones play an implicated role in glucose homeostasis, which results in neutralizing the disorder caused by peripheral insulin resistance or failure of β-cells to produce insulin [50]. Currently, research is focused on generating new prebiotics, such as arabinoxylan and arabinoxylan oligosaccharides, which show promising results in counteracting related metabolic disorders, because both carbohydrates have been linked to adiposity reduction.
3.4. Anti-obesity activity of probiotics
Abnormal or excessive fat (obesity) accumulation that directly impairs health is linked to an increase in energy availability, sedentariness and a greater control of ambient temperature, leading to an imbalance in energy intake and expenditure [17]. It has been evident that transplantation of the intestinal microflora from obese mice into germ-free mice could replicate the obese phenotype and may lead to more efficient at extracting energy from food and stimulating lipogenesis.
Probiotics possess physiological functions that contribute to the health of host environment regulating microbes. In most instances, weight loss is facilitated by thermogenic and lipolytic responses through stimulating the sympathetic nervous system [51]. Probiotic strains, Lactobacillus gasseri BNR17 have shown properties of inhibiting the increase in adipocyte tissue that are the main source of leptin and adiponectin and thereby, limiting leptin secretion [52]. Other probiotic microbes such as L. casei, Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium longum have also been reported to have hypo-cholesterolemic effects [51].
3.5. Anti-inflammatory activity of probiotics
Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC) are among the most chronic inflammatory diseases of the GIT and are collectively called IBD [42]. CD can affect any part of the GIT like the mucosa, submucosa, and serosa, and the inflammation can even spread to the whole GIT. In contrast, UC characteristically involves the large bowel; specifically the mucosa and submucosa of the colon [53]. Research has shown that an imbalance in the gut microbiota plays an important pathophysiological role in the positive regulation of IBD. It is also understood that the disorder could possibly be altered by supplementation with probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics [54–56]. IBD is being associated with impaired production of SCFAs, particularly, acetate, butyrate, and propionate. Moreover, these SCFAs have been known to play a key role in maintaining colonic homeostasis. They also possess anti-inflammatory effects and improve the propulsive colonic function [57]. Therefore, it is reasonable to consider that supplementation with indigestible carbohydrates and fiber (prebiotic) alone, or in combination with probiotics to increase the production of SCFAs could be useful therapeutic approaches. Presently, progress in the field is mostly concerned with developing genetically engineered probiotic bacterial strains that are able to produce and discharge immunomodulators, such as interleukin-10, trefoil factors (compact proteins co-expressed with mucins in the GIT), or lipoteichoic acid (a major constituent of the cell wall of Gram-positive bacteria) that can impact the host immune system, resulting in the restoration of the level of protective commensal bacterial species [58]. Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, Enterobacter and E. coli are the most widely used probiotics in foods. Apart from these organisms, new or genetically modified should be developed to counteract IBD [59].
3.6. Anti-cancer activity of probiotics
As per WHO cancer fact sheet [60], cancer has been a dreadful disease affecting peoples all over the globe and approximately 14 million new cases and 8.2 million cancer-related deaths added till 2012. More than 70% of the global cancer deaths are from Asian, African, and American continents [61]. In the present decade, intense research on cancer involving genomics, proteomics, and molecular pathology, has enhanced the knowledge about cancer and public awareness. Concurrently, many new drugs using nanotechnology and biotechnology (nanocapsule) with fascinating properties of luminescent have been discovered but still tolerance to their burden and side effect has been a major limitation to it. Natural sources that confer anti-carcinogenic effects, such as probiotics have been receiving prime focus in recent years [62]. These have attracted intense interest from clinical nutritionists, scientists, and industrialists to work in a collaborative manner to bring down the disease and develop an effective drug with minimal or no side-effects [63,64]. In vitro studies have demonstrated that probiotic strains, Lactobacillus fermentum NCIMB-5221 and -8829, have highly potent in suppressing colorectal cancer cells and promoting normal epithelial colon cell growth through the production of SCFAs (ferulic acid). This ability was also compared with other probiotics namely L. acidophilus ATCC 314 and L. rhamnosus ATCC 51303 both of which were previously characterized with–tumorigenic activity [65]. Again two different probiotic strains L. acidophilus LA102 and L. casei LC232 have also been found to show pronounced cytotoxic activities, with in vitro anti-proliferative activity against two colorectal cancer cell lines (Caco-2 and HRT-18) [66]. Though probiotics could play a significant role in neutralizing cancer, research is limited only to in vitro tests. Hence, the anti-cancer potential of probiotics must be proven in vivo models and proceed towards animal and clinical trials.
3.7. Anti-allergic activity of probiotics
The increasing prevalence of allergic diseases caused by immune disorders is a serious economic and social burden worldwide. Comprehending the fundamental molecular mechanism that contributes to the etiology of allergic diseases, as well as new treatment approaches is vital for the follow-up and prevention of these diseases [67]. In recent times, the beneficial role of probiotics in protection and management of allergic diseases had advanced the understanding of their cause and prevention. In vitro studies of certain probiotics, such as Lactobacillus plantarum L67, have shown the potential to prevent allergy-associated disorders with the production of interleukin-12 and interferon-γ in their host [68]. In another study, L. plantarum 06CC2 significantly alleviated allergic symptoms and reduced the levels of total immunoglobulin E, ovalbumin-specific immunoglobulin E, and histamine in the sera of ovalbumin-sensitized mice. In spleen cells of the mice, L. plantarum 06CC2 is known to significantly enhance the secretions of interferon-γ and interleukin-4, which are responsible for alleviating allergic symptoms [69]. Further work may be helpful in evaluating the anti-allergic activity of probiotics and their mode of action.
3.8. Angiogenic activity of probiotics
Angiogenesis has been an important phenomenon and is necessary for wound healing process through delineated cellular responses to regenerate damaged tissues [70]. The angiogenic program consists of a deliberately orchestrated series of cellular events by which new vessels arise from pre-existing ones by promoting recruitment of inflammatory cells and producing cytokines, matrix-degrading enzymes, and chemokines. Deregulated angiogenesis has a prominent impact on major human diseases, such as cancer, diabetic retinopathy, and IBD including CD and UC [16,71]. Non-pathogenic probiotic yeast, S. boulardii, has been reported to protect against intestinal injury and inflammation. The molecular mechanisms by which probiotics mediate these beneficial effects however remain unclear. The potential mechanisms of probiotics in angiogenesis process may include alteration of inflammatory cytokine profiles, down-regulation of pro-inflammatory cascades or induction of regulatory mechanisms in a strain-specific manner, epithelial barrier function enhancement, visceral hypersensitivity reduction, spinal afferent traffic, and stress response.
3.9. Effect of probiotics on brain and CNS
The colonization of microbiota in the GIT is well-associated with both GIT and gastrointestinal diseases. Moreover, in recent years, many studies have been devoted towards elucidating the influence of gut microbiota on the CNS. The “microbiota-gut-brain axis” is an interactive, bi-directional communication established by the exchange of regulatory signals between the GIT and CNS [72]. The effect of probiotics on the CNS has been mainly studied in clinical trials, where it has been evident that gut microbiota influence human brain development function [73]. In children with autism spectrum disorder, a daily dose of L. plantarum WCFS1 (4.5 × 1010 CFU/day) led to an improvement in their school records and attitude towards food [74]. Messaoudi et al. [75] discussed reduced psychological distress in a randomized trial involving healthy volunteers treated with oral administration of Lactobacillus helveticus R0052 and B. longum R0175. In another clinical trial, Rao et al. [76] showed a decrease in anxiety symptoms by administration of L. casei strain Shirota to patients suffering from chronic fatigue syndrome. However, despite an increase in the Lactobacillus and Bifidobacteria levels, the bowel functions were not studied. Hence, it is feasible that the reduced anxiety was due to improved bowel function. Szajewska [77] reported that autism spectrum and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorders in children could be prevented by L. rhamnosus administration to the mother at 4 weeks from expected delivery. It has been observed that many gut bacteria synthesize to neuroactive compounds similar to those produced in the host brain. Human intestinally derived strains of L. brevis DPC6108 and Bifidobacterium dentium were reported to produce large amounts of γ-aminobutyric acid, a brain neurotransmitter that helps humans to suppress anxiety and depression [46]. Doses of a multispecies probiotic containing L. brevis W, B. lactis W, L. acidophilus W37, Bifidobacterium bifidum W2, L. salivarius W2, L. casei W5, and Lactococcus lactis (W19 and W58) to healthy humans showed a significant overall reduction in the cognitive reactivity to sad mood [78]. However, probiotic trials involving patients suffering from anxiety and clinical depression are lacking and therefore require more time and work to validate this effect. Oral intake of L. acidophilus has been shown to assist people to regulate their mood towards rewards and addictive behavior [79].
4. Commercial significance of probiotics
Although probiotics are still in pipeline and requires further studies and development to overcome barriers related to their successful administration and minimal side effects several forms of probiotics are available commercially and are in use in large amount. Some of the common commercial microbial strains currently sold as probiotics and their sources are given in Table 4. The species in the following are listed as per manufacturer standards and amenities, which may not reflect the most current taxonomy.
Table 4.
Probiotics and their commercial sources.
| Strain | Commercial products | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM Bifidobacterium lactis HN019 (DR10) | Sold as ingredient | Danisco (Madison, WI) |
| Lactobacillus rhamnosus HN001 (DR20) | ||
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae boulardii | Florastor | Biocodex (Creswell, OR) |
| Bifidobacterium infantis 35,264 | Align | Procter and Gamble (Mason, OH) |
| Lactobacillus fermentum VRI003 (PCC) | Sold as ingredient | Probiomics (Eveleigh, Australia) |
| Lactobacillus rhamnosus R0011 | Sold as ingredient | Institut Rosell (Montreal, Canada) |
| Lactobacillus acidophilus R0052 | ||
| Lactobacillus acidophilus LA5 | Sold as ingredient | Chr. Hansen (Milwaukee, WI) |
| Lactobacillus paracasei CRL 431 | ||
| Bifidobacterium lactis Bb-12 | Sold as ingredient | Chr. Hansen (Milwaukee, WI) |
| Lactobacillus casei strain Shirota | Yakult | Yakult (Tokyo, Japan) |
| Bifidobacterium breve strain Yakult | ||
| Lactobacillus casei DN-114 001 (“L. casei Immunitas”) | DanActive fermented milk | Danone (Paris, France) |
| Bifidobacterium animalis DN173 010 (“Bifidis regularis”) | Activia yogurt | Dannon (Tarrytown, NY) |
| Lactobacillus reuteri RC-14 | Femdophilus | Chr. Hansens (Milwaukee, WI) |
| Lactobacillus rhamnosus GR-1 | Urex Biotech (London, Ontario, Canada) Jarrow Formulas (Los Angeles, CA) |
|
| Lactobacillus johnsonii Lj-1 (same as NCC533 and formerly Lactobacillus acidophilus La-1) | LC1 | Nestlé (Lausanne, Switzerland) |
| Lactobacillus plantarum 299 V | Sold as ingredient; Good Belly juice product | Probi AB (Lund, Sweden); NextFoods (Boulder, Colorado) |
| Lactobacillus rhamnosus 271 | Sold as ingredient | Probi AB (Lund, Sweden) |
| Lactobacillus reuteri ATCC 55,730 (“L. reuteri Protectis”) | BioGaia Probiotic chewable tablets or drops | Biogaia (Stockholm, Sweden) |
| Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (“LGG”) | Culturelle; Dannon Danimals | Valio Dairy (Helsinki, Finland) The Dannon Company (Tarrytown, NY) |
| Lactobacillus rhamnosus LB21 | Sold as ingredient | Essum AB (Umeå, Sweden) |
| Lactococcus lactis L1A | ||
| Lactobacillus salivarius UCC118 | – | University College Cork (Cork, Ireland) |
| Bifidobacterium longum BB536 | Sold as ingredient | Morinaga Milk Industry Co. Ltd. (Zama-City, Japan) |
| Lactobacillus acidophilus LB | Sold as ingredient | Lacteol Laboratory (Houdan, France) |
| Lactobacillus paracasei F19 | Sold as ingredient | Medipharm (Des Moines, Iowa) |
| Lactobacillus paracasei 33 | Sold as ingredient | GenMont Biotech (Taiwan) |
| Lactobacillus rhamnosus GM-020 | ||
| Lactobacillus paracasei GMNL-33 | ||
| Lactobacillus plantarum OM | Sold as ingredient | Bio-Energy Systems, Inc. (Kalispell, MT) |
| Bacillus coagulans BC30 | Sustenex, Digestive Advantage and sold as ingredient | Ganeden Biotech Inc. (Cleveland, Ohio) |
| Streptococcus oralis KJ3 | ProBiora3 | Oragenics Inc. (Alachua, FL) |
| Streptococcus uberis KJ2 | EvoraPlus | |
| Streptococcus rattus JH145 | ||
| Lactobacilli rhamnosus PBO1 | EcoVag | Bifodan (Denmark), www.ecovag.com |
| Lactobacilli gasseri EB01 |
5. Recent advancements and utility prebiotics
Like probiotics, prebiotics is also being widely explored for their utility in the various field of applied science, more specifically as nutrients and supplements. But still than the novel research on the usability of prebiotics are scanty. Some of these cutting age research where the understandings of prebiotics have reached a milestone is as follows. Basically, “prebiotics are a collection of nutritionally enriched compounds grouped together with the efficiency to enhance and support the growth and sustenance of specific beneficial gut microflora” [80]. In general, it can be said that prebiotics is those compounds that are non-digestible and able to specifically modulate the sustenance of health-promoting gut bacteria.
Presently the knowledge on the complexity as well as the usability of these non-digestible compounds has increased to a greater extent because of the development of various ‘omic’ tools such as proteomics, genomics, metabolomics, transcriptomics etc. [81]. Thus the research based on the various mode of synthesis has become the current focus of the present era. The food industries of the present decade require simple, sustainable, cost-effective and high efficient methods for large-scale production and application. Naturally, prebiotic oligosaccharides could be obtained from food; otherwise, theses could also be synthesized chemically or enzymatically from disaccharides or other substrates as well as by hydrolysis of polysaccharides. Most of the prebiotics of natural origin have already been evaluated for their beneficiary role; therefore the current search is for other novel prebiotic oligosaccharides by various enzyme-based technologies. Enzymes (β-galactosidase, fructosyltransferase etc.) from various sources such as microbes and plants are being utilized for their synthesis [82,83]. Moreover, enzymes are engineered to better regulate regioselectivity and the enhancement in the yield of reaction which further enhances the glycodiversification and the quality of the products attained [84,85]. Again, the emergence of genetically engineered microorganisms further resulted in boosting the production of oligosaccharides (2′fucosyllactose) by fermentation process for large-scale industrial production [86].
Due to the tangible association of prebiotics oligosaccharides with the gut microbiome as well as maintenance and restoration of microbial homeostasis which is again keenly associated with positive health outcome of the host, researches regarding prebiotics are given much emphasis in the current era. Prebiotic compounds are food-grade substances from which beneficial short-chain fatty acid could be produced as a result of degradation by microbes such as bifidobacteria and lactobacilli within the host further appeal for their utilization as nutrient supplements [87]. Their biomedical benefaction not only covers gastrointestinal system but also systems located away. Recent studies several rat models have demonstrated calcium absorption, retention bone density and strength is enhanced due to the intake of galactooligosaccharides (GOS) specifically [88]. Gut microbes influence the expression of gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor in the brain, prebiotics such as FOS and GOS is likely to exploit this connection to tune the brain-derived neurotrophic factors, d-serine, and other synaptic proteins such as synaptophysin and N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor subunit [89,90]. It has also been found that prebiotics such as oligofructose, β-fructan, oligofructose/inulin mix have immunomodulatory benefits in the case of pathogenic attack, atopic dermatitis, allergic prevention, chronic inflammation and up-regulated responses against vaccinations [88,91]. Benefactions of this non-digestible compound have also emerged for a variety of skin related-conditions. Improve water retention and prevention of erythema was observed in a hairless mice skin on GOS supplementation [92]. Studies also prove that skin’s barrier properties are improved by the increased dermal expression of cell adhesion and matrix formation markers CD44, and type 1 collagen on GOS treatment [88,93]. Again, GOS alone or with B. breve is found to impede water and keratin depletion effectuated by phenolic compounds [94]. Likewise, currently, prebiotics are widely being explored for their usefulness in the treatment of various types of disorder and diseases [95,96].
6. Conclusion
Probiotics possess important functional attributes that could fulfill most of our basic nutritional and clinical supplementation requirements. These microbes have shown positive responses to clinical treatment against several diseases and disorders, such as diarrhea associated with rotavirus, IBS and food allergies. Moreover, the contribution of probiotics in preventing and treatment of diabetes, obesity, cancer and diseases related to pathogenic microbes is an exciting and rapidly advancing research arena. Dietary probiotic supplementation generally involves dairy products but probiotics can also be incorporated into non-dairy fermented food products, presenting an alternative and more advantageous source in the process of evaluating new probiotic strains. Moreover, present clinical and nutritional evaluations have been successful in exposing some remarkable functions of particular probiotic strains. Specifically, regulation of energy in various catabolic and anabolic processes, acid and bile tolerance, ability to adhere to gut epithelial cells, to combat against pathogens, along with certain other properties, like their safety-enhancing property, serviceability as food and beneficial supplements for human health. Therefore, current focus is on evaluating new strains of probiotics and their applicability in biomedical/clinical research, paving a new direction for exploration and exploitation of probiotics aimed at improving human health.
Acknowledgement
Authors are grateful to the authorities of respective departments for support in doing this research. This work was supported by Korea Institute of Planning and Evaluation for Technology in Food, Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (IPET) through the Agricultural Research Center Project and Agricultural Bio-Technology Development Program funded by Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (MAFRA) (710003-07-7-SB120, 116075-3).
Funding Statement
Funded by Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (MAFRA) (710003-07-7-SB120, 116075-3).
Footnotes
Author’s contribution
RGK, JKP and SG collected literature, designed and wrote the manuscript. GD, HSS and JKP edited and revised the manuscript. All the author checked and approved the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
Author declares no conflict of interest.
REFERENCES
- 1. Bagchi T. Traditional food & modern lifestyle: impact of probiotics. Indian J Med Res. 2014;140(3):333–5. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Metchnikoff E, Mitchell PC, editors. Essais optimistes. London: Heinemann; 1907. [Google Scholar]
- 3. Tissier H. Tritement des infections intestinales par la methode de translormation de la flore bacterienne de lintestin. C R Soc Biol. 1906;60:359–61. [in French] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Havenaar R, Huis in’t Veld JHJ. Probiotics: a general view. In: Wood BJB, editor. The lactic acid bacteria in health and disease. London: Elsevier Applied Science; 1992. pp. 151–70. [Google Scholar]
- 5. Aziz Q, Dore J, Emmanuel A, Guarners F, Quigley EMM. Gut microbiota and gastrointestinal health: current concepts and future directions. Neuro Gastroenterol Motil. 2013;25:4–15. doi: 10.1111/nmo.12046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Slavin J. Fiber and prebiotics: mechanisms and health benefits. Nutrients. 2013;5:1417–35. doi: 10.3390/nu5041417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Lloyd-Price J, Abu-Ali G, Huttenhower C. The healthy human microbiome. Genome Med. 2016;8:1–11. doi: 10.1186/s13073-016-0307-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Lewis BB, Buffie CG, Carter R, Leiner I, Toussaint NC, Miller L, et al. Loss of microbiota-mediated colonization resistance to clostridium difficile infection is greater following oral vancomycin as compared with metronidazole. J Infect Dis. 2015;212:1656–65. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiv256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Perez-Cobas AE, Moya A, Gosalbes MJ, Latorre A. Colonization resistance of the gut microbiota against clostridium difficile. Antibiotics. 2015;4:337–57. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics4030337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Scott KP, Antoine J-M, Midtvedt T, van Hemert S. Manipulating the gut microbiota to maintain health and treat disease. Microb Ecol Health Dis. 2015:26. doi: 10.3402/mehd.v26.25877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Pamer EG. Resurrecting the intestinal microbiota to combat antibiotic-resistant pathogens. Science. 2016;352:535–8. doi: 10.1126/science.aad9382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Qadir MI. Phage therapy: a modern tool to control bacterial infections. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2015;28:265–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Rao SC, Athalye-Jape GK, Deshpande GC, Simmer KN, Patole SK. Probiotic supplementation and late-onset sepsis in preterm infants: a meta-analysis. Pediatrics. 2016;137:1–16. doi: 10.1542/peds.2015-3684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Kristensen NB, Bryrup T, Allin KH, Nielsen T, Hansen TH, Pedersen O. Alterations in fecal microbiota composition by probiotic supplementation in healthy adults: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Genome Med. 2016;8:1–11. doi: 10.1186/s13073-016-0300-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Bakirtzi K, Law IKM, Xue X, Iliopoulos D, Shah YM, Pothoulakis C. Neurotensin promotes the development of colitis and intestinal angiogenesis via Hif-1α–miR-210 signaling. J Immunol. 2016;196:4311–21. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1501443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Chen X, Yang G, Song J-H, Xu H, Li D, Goldsmith J, et al. Probiotic yeast inhibits VEGFR signaling and angiogenesis in intestinal inflammation. PLoS One. 2013;8:1–7. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Kobyliak N, Conte C, Cammarota G, Haley AP, Styriak I, Gaspar L, et al. Probiotics in prevention and treatment of obesity: a critical view. Nutr Metab. 2016;13:1–13. doi: 10.1186/s12986-016-0067-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Gibson GR, Roberfroid MB. Dietary modulation of the human colonic microbiota: introducing the concept of prebiotics. J Nutr. 1995;125:1401–12. doi: 10.1093/jn/125.6.1401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Hamasalim HJ. Synbiotic as feed additives relating to animal health and performance. Adv Microbiol. 2016;6:288–302. [Google Scholar]
- 20. Bongaerts GPA, Severijnen RSVM. A reassessment of the PROPATRIA study and its implications for probiotic therapy. Nature Biotechnol. 2016;34:55–63. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Patel RM, Denning PW. Therapeutic use of prebiotics, probiotics, and postbiotics to prevent necrotizing enterocolitis: what is the current evidence? Clin Perinatol. 2013;40:11–25. doi: 10.1016/j.clp.2012.12.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Islam SU. Clinical uses of probiotics. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016;95:1–5. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000002658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Ooi MF, Mazlan N, Foo HL, Loh TC, Mohamad R, Rahim RA, et al. Effects of carbon and nitrogen sources on bacteriocin-inhibitory activity of postbiotic metabolites produced by Lactobacillus plantarum I-UL4. Malays J Microbiol. 2015;11:176–84. [Google Scholar]
- 24. Giorgetti GM, Brandimarte G, Fabiocchi F, Ricci S, Flamini P, Sandri G, et al. Interactions between innate immunity, microbiota, and probiotics. J Immunol Res. 2015;501361:7. doi: 10.1155/2015/501361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Cicenia A, Scirocco A, Carabotti M, Pallotta L, Marignani M, Severi C. Postbiotic activities of lactobacilli-derived factors. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2014;48:S18–22. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000000231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Rastall RA, Gibson GR. Recent developments in prebiotics to selectively impact beneficial microbes and promote intestinal health. Curr Opinion Biotechnol. 2015;32:42–6. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2014.11.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Thomas LV. Probiotics-the journey continues. Int J Dairy Tech. 2016;69:1–12. [Google Scholar]
- 28. Hutkins RW, Krumbeck JA, Bindels LB, Cani PD, Fahey G, Goh YJ, et al. Prebiotics: why definitions matter. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2016;37:1–13. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2015.09.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Tanaka R, Takayama H, Morotomi M, Kuroshima T, Ueyama S, Matsumoto K, et al. Effects of administration of TOS and Bifidobacterium breve 4006 on the human fecal flora. Bifidobact Microflora. 1983;2:17–24. [Google Scholar]
- 30. Pena AS. Intestinal flora, probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics and novel foods. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2007;99:653–8. doi: 10.4321/s1130-01082007001100006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Pokusaeva K, Fitzgerald GF, Sinderen D. Carbohydrate metabolism in bifidobacteria. Genes Nutr. 2011;6:285–306. doi: 10.1007/s12263-010-0206-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Tufarelli V, Laudadio V. An overview on the functional food concept: prospectives and applied researches in probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics. J Exp Biol Agric Sci. 2016;4:274–8. [Google Scholar]
- 33. Tejero-Sarinena S, Barlow J, Costabile A, Gibson GR, Rowland I. Antipathogenic activity of probiotics against Salmonella Typhimurium and Clostridium difficile in anaerobic batch culture systems: is it due to synergies in probiotic mixtures or the specificity of single strains? Anaerobe. 2013;24:60–5. doi: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2013.09.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Kareem KY, Ling FH, Chwen LT, Foong OM, Asmara SA. Inhibitory activity of postbiotic produced by strains of Lactobacillus plantarum using reconstituted media supplemented with inulin. Gut Pathog. 2014;6:1–7. doi: 10.1186/1757-4749-6-23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Simova ED, Beshkova DB, Dimitrov P. Characterization and antimicrobial spectrum of bacteriocins produced by lactic acid bacteria isolated from traditional Bulgarian dairy products. J Appl Microbiol. 2009;106:692–701. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2008.04052.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Ammor S, Tauveron G, Dufour E, Chevallier I. Antibacterial activity of lactic acid bacteria against spoilage and pathogenic bacteria isolated from the same meat small-scale facility. Screening and characterization of the antibacterial compounds. Food Control. 2006;17:454–61. [Google Scholar]
- 37. Figueroa-Gonzalez I, Cruz-Guerrero A, Quijano G. The benefits of probiotics on human health. J Microb Biochem Technol. 2011;S1:003. [Google Scholar]
- 38. Waigankar SS, Patel V. Role of probiotics in urogenital healthcare. J Midlife Health. 2011;2:5–10. doi: 10.4103/0976-7800.83253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Hanson L, Vusse LV, Jerme M, Abad CL, Safdar N. Probiotics for treatment and prevention of urogenital infections in women: a systematic review. J Midwifery Womens Health. 2016;61:339–55. doi: 10.1111/jmwh.12472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Chan PA, Robinette A, Montgomery M, Almonte A, Cu-Uvin S, Lonks JR, et al. Extra genital infections caused by Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae: a review of the literature. Infect Dis Obstet Gynecol. 2016;5758387:17. doi: 10.1155/2016/5758387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.International Diabetes Federation. Diabetes atlas. Chausséede la Hulpe 166, 1170. Watermael-Boitsfort, Belgium: IDF Diabetes Atlas; 2017. [Accessed 15 November 2017]. http://www.diabetesatlas.org/resources/2017-atlas.html . [Google Scholar]
- 42. Iqbal MZ, Qadir MI, Hussain T, Janbaz KH, Khan YH, Ahmad B. Probiotics and their beneficial effects against various diseases. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2014;27:405–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Larsen N, Vogensen FK, van-den-Berg FW, Nielsen DS, Andreasen AS, Pedersen BK, et al. Gut microbiota in human adults with type 2 diabetes differs from non-diabetic adults. PLoS One. 2010;5:1–10. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Barz ML, Anhe FF, Varin TV, Desjardins Y, Levy E, Roy D, et al. Probiotics as complementary treatment for metabolic disorders. Diabetes Metab J. 2015;39:291–303. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2015.39.4.291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Barrett HL, Callaway LK, Nitert MD. Probiotics: a potential role in the prevention of gestational diabetes? Acta Diabetol. 2012;49:1–13. doi: 10.1007/s00592-012-0444-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Barrett E, Ross RP, O’Toole PW, Fitzgerald GF, Stanton C. γ-Aminobutyric acid production by culturable bacteria from the human intestine. J Appl Microbiol. 2012a;113:411–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2012.05344.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Hu C, Wong FS, Wen L. Type 1 diabetes and gut microbiota: friend or foe? Pharmacol Res. 2015;98:9–15. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2015.02.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Ljungberg M, Korpela R, Ilonen J, Ludvigsson J, Vaarala O. Probiotics for the prevention of beta cell autoimmunity in children at genetic risk of type-1 diabetes-the PRODIA study. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006;1079:360–4. doi: 10.1196/annals.1375.055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Hartstra AV, Bouter KEC, Backhed F, Nieuwdorp M. Insights into the role of the microbiome in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2015;38:159–65. doi: 10.2337/dc14-0769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Grover S, Rashmi HM, Srivastava AK, Batish VK. Probiotics for human health-new innovations and emerging trends. Gut Pathog. 2012;4:1–14. doi: 10.1186/1757-4749-4-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Karimi G, Sabran MR, Jamaluddin R, Parvaneh K, Mohtarrudin N, Ahmad Z, et al. The anti-obesity effects of Lactobacillus casei strain Shirota versus Orlistat on high fat diet-induced obese rats. Food Nutr Res. 2015;59:1–8. doi: 10.3402/fnr.v59.29273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Kang J-H, Yun S-I, Park M-H, Park J-H, Jeong S-Y, Park H-O. Anti-obesity effect of Lactobacillus gasseri BNR17 in high-sucrose diet-induced obese mice. PLoS One. 2013;8:1–8. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Palumbo VD, Marcello R, Gammazza AM, Carini F, Damiani P, Damiano G, et al. The long-term effects of probiotics in the therapy of ulcerative colitis: a clinical study. Biomed Pap. 2016;160:372–7. doi: 10.5507/bp.2016.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Cammarota G, Ianiro G, Cianci R, Bibbo S, Gasbarrini A, Curro D. The involvement of gut microbiota in inflammatory bowel disease pathogenesis: potential for therapy. Pharmacol Ther. 2015;149:191–212. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2014.12.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Cammarota G, Pecere S, Ianiro G, Masucci L, Curro D. Principles of DNA-based gut microbiota assessment and therapeutic efficacy of fecal microbiota transplantation in gastrointestinal diseases. Dig Dis. 2016;34:279–85. doi: 10.1159/000443362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Spiller R. Irritable bowel syndrome: new insights into symptom mechanisms and advances in treatment. F1000Research. 2016;5:1–11. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.7992.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Curro D, Ianiro G, Pecere S, Bibbo S, Cammarota G. Probiotics, fiber and herbal medicinal products for functional and inflammatory bowel disorders. Br J Pharmacol. 2016;173:61–8. doi: 10.1111/bph.13632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Shahverdi E. Probiotics and gastrointestinal diseases. Int J Dig Dis. 2016;2:1–2. [Google Scholar]
- 59. Gowri RS, Meenambigai P, Prabhavathi P, Rajeswari PR, Yesudoss LA. Probiotics and its effects on human health-a review. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci. 2016;5:384–92. [Google Scholar]
- 60.World Health Organization. Cancer fact sheet 2017. Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2017. [Google Scholar]
- 61. Vidya S, Thiruneelakandan G. Probiotic potentials of lactobacillus and its anti-cancer activity. Int J Curr Res. 2015;7:20680–4. [Google Scholar]
- 62. Gayathri D, Rashmi BS. Anti-cancer properties of probiotics: a natural strategy for cancer prevention. EC Nutrition. 2016;5:1191–202. [Google Scholar]
- 63.Vafaeie F. Critical review on probiotics and its effect on cancer. Vol. 2. Cancer Press; 2016. pp. 30–4. [Google Scholar]
- 64. So SS, Wan ML, El-Nezami H. Probiotics-mediated suppression of cancer. Curr Opinion Oncol. 2017;29:62–72. doi: 10.1097/CCO.0000000000000342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Kahouli I, Malhotra M, Alaoui-Jamali MA, Prakash S. In-vitro characterization of the anti-cancer activity of the probiotic bacterium Lactobacillus fermentum NCIMB 5221 and potential against colorectal cancer cells. J Cancer Sci Ther. 2015;7:224–35. [Google Scholar]
- 66. Awaisheh SS, Obeidat MM, Al-Tamimi HJ, Assaf AM, EL-Qudah JM, Al-khazaleh JM, et al. In vitro cytotoxic activity of probiotic bacterial cell extracts against Caco-2 and HRT-18 colorectal cancer cells. Milk Sci Int. 2016;69:27–31. [Google Scholar]
- 67. Akelma AZ, Topcu ZIK. Probiotics and allergic disease. World J Immunol. 2016;6I:75–82. [Google Scholar]
- 68. Song S, Lee SJ, Park D-J, Oh S, Lim K-T. The anti-allergic activity of Lactobacillus plantarum L67 and its application to yogurt. J Dairy Res. 2016;99:9372–82. doi: 10.3168/jds.2016-11809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69. Takeda S, Hidaka M, Yoshida H, Takeshita M, Kikuchi Y, Tsend-Ayush C, et al. Antiallergic activity of probiotics from Mongolian dairy products on type I allergy in mice and mode of antiallergic action. J Funct Foods. 2014;9:60–9. [Google Scholar]
- 70. Flkman J. Angiogenesis. Annu Rev Med. 2006;57:1–18. doi: 10.1146/annurev.med.57.121304.131306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71. Folkman J. Angiogenesis: an organizing principle for drug discovery? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2007;6:273–86. doi: 10.1038/nrd2115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72. Mayer EA, Tillisch K, Gupta A. Gut/brain axis and the microbiota. J Clin Invest. 2015;125:926–38. doi: 10.1172/JCI76304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73. Tillisch K. The effects of gut microbiota on CNS function in humans. Gut Microbes. 2014;5:404–10. doi: 10.4161/gmic.29232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74. Umbrello G, Esposito S. Microbiota and neurologic diseases: potential effects of probiotics. J Transl Med. 2016;14:1–11. doi: 10.1186/s12967-016-1058-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75. Messaoudi M, Lalonde R, Violle N, Javelot H, Desor D, Nejdi A, et al. Assessment of psychotropic-like properties of a probiotic formulation (Lactobacillus helveticus R0052 and Bifidobacterium longum R0175) in rats and human subjects. Br J Nutr. 2011;105:755–64. doi: 10.1017/S0007114510004319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76. Rao AV, Bested AC, Beaulne TM, Katzman MA, Iorio C, Berardi JM, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study of a probiotic in emotional symptoms of chronic fatigue syndrome. Gut Pathog. 2009;1:1–6. doi: 10.1186/1757-4749-1-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77. Szajewska H. What are the indications for using probiotics in children? Arch Dis Child. 2016;101:398–403. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2015-308656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78. Daliri EBM, Oh DH, Lee BH. Psychobiotics; a promise for neurodevelopmental therapy. J Probiotics Health. 2016;4:1–4. [Google Scholar]
- 79. Nogueiras R, Romero-Pico A, Vazquez MJ, Novelle MG, Lopez M. The opioid system and food intake: homeostatic and hedonic mechanisms. Obes Facts. 2012;5:196–207. doi: 10.1159/000338163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80. Kelly G. Inulin-type prebiotics – a review: Part 1. Altern Med Rev. 2008;13(4):315–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81. Moreno FJ, Corzo N, Montilla A, Villamiel M, Olano A. Current state and latest advances in the concept, production and functionality of prebiotic oligosaccharides. Curr Opin Food Sci. 2017;13:50–5. [Google Scholar]
- 82.Villamiel M, Montilla A, Olano A, Corzo N. Production and bioactivity of oligosaccharides derived from lactose. In: Moreno FJ, Sanz ML, editors. Food oligosaccharides: production, analysis and bioactivity. Wiley Blackwell; 2014. pp. 137–67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83. Trollope KM, van Wyk N, Kotjomela MA, Volschenk H. Sequence and structure-based prediction of fructosyltransferase activity for functional sub classification of fungal GH32 enzymes. FEBS J. 2015;282:4782–96. doi: 10.1111/febs.13536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84. Devlamynck T, Te Poele EM, Meng X, van Leeuwen SS, Dijkhuizen L. Glucansucrase Gtf180-DN of Lactobacillus reuteri 180: enzyme and reaction engineering for improved glycosylation of non-carbohydrate molecules. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016;100:7529–39. doi: 10.1007/s00253-016-7476-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85. Schmid J, Heider D, Wendel NJ, Sperl N, Sieber V. Bacterial glycosyltransferases: challenges and opportunities of a highly diverse enzyme class toward tailoring natural products. Front Microbiol. 2016;7:182. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.FDA. GRAS notice (GRN) No. 571. 20–Fucosyllactose. 2015. http://www.fda.gov/Food/IngredientsPackagingLabeling/GRAS/NoticeInventory/default.htm .
- 87. Collins S, Reid G. Distant site effects of ingested prebiotics. Nutrients. 2016;8:523. doi: 10.3390/nu8090523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88. Zhou Y, Kruger C, Ravi GS, Kumar DPS, Vijayasarathi SK, Lavingia M, et al. Safety evaluation of galactooligosaccharides: sub chronic oral toxicity study in Sprague-Dawley rats. Toxicol Res Appl. 2017;1:1–12. [Google Scholar]
- 89. Savignac HM, Corona G, Mills H, Chen L, Spencer JP, Tzortzis G, et al. Prebiotic feeding elevates central brain derived neurotrophic factor, N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor subunits and d-serine. Neurochem Int. 2013;63:756–64. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2013.10.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90. Williams S, Chen L, Savignac HM, Tzortzis G, Anthony DC, Burnet PW. Neonatal prebiotic (BGOS) supplementation increases the levels of synaptophysin, GluN2A-subunits and BDNF proteins in the adult rat hippocampus. Synapse. 2016;70:121–4. doi: 10.1002/syn.21880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91. Pretorius R, Prescott SL, Palmer DJ. Taking a prebiotic approach to early immunomodulation for allergy prevention. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2018;14(1):43–51. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2018.1411191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92. Hong KB, Jeong M, Han KS, Kim JH, Park Y, Suh HJ. Photoprotective effects of galacto-oligosaccharide and/or Bifidobacterium longum supplementation against skin damage induced by ultraviolet irradiation in hairless mice. Int J Food Sci Nutr. 2015;66:923–30. doi: 10.3109/09637486.2015.1088823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93. Gibson GR, Hutkins R, Sanders ML, Prescott SL, Reimer RA, Salminen SJ, et al. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;14:491–502. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2017.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94. Kano M, Masuoka N, Kaga C, Sugimoto S, Iizuka R, Manabe K, et al. Consecutive intake of fermented milk containing Bifidobacterium breve strain Yakult and galacto-oligosaccharides benefits skin condition in healthy adult women. Biosci Microbiota Food Health. 2013;32:33–9. doi: 10.12938/bmfh.32.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95. Roberfroid M, Gibson GR, Hoyles L, McCartney AL, Rastall R, Rowland I, et al. Prebiotic effects: metabolic and health benefits. Br J Nutr. 2010;104(2):S1–63. doi: 10.1017/S0007114510003363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96. Yoo JY, Kim SS. Probiotics and prebiotics: present status and future perspectives on metabolic disorders. Nutrients. 2016;8(3):173. doi: 10.3390/nu8030173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97. Dixit Y, Wagle A, Vakil B. Patents in the field of probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics: a review. J Food Microbiol Saf Hygiene. 2016;1:1–13. [Google Scholar]
- 98. Nguyen H-T, Truong D-H, Kouhounde S, Ly S, Razafindralambo H, Delvigne F. Biochemical engineering approaches for increasing viability and functionality of probiotic bacteria. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17:1–18. doi: 10.3390/ijms17060867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99. Eid R, Jakee JE, Rashidy A, Asfour H, Omara S, Kandil MM, et al. Potential antimicrobial activities of probiotic Lactobacillus strains isolated from raw milk. J Probiotics Health. 2016;4:1–8. [Google Scholar]
- 100. Onyenweaku F, Obeagu EI, Ifediora AC, Nwandikor UU. Health benefits of probiotics. Int J Innov Appl Res. 2016;4:21–30. [Google Scholar]
- 101. Sornplang P, Piyadeatsoontorn S. Probiotic isolates from unconventional sources: a review. J Anim Sci Tech. 2016;58:1–11. doi: 10.1186/s40781-016-0108-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102. Arora T, Singh S, Sharma RK. Probiotics: interaction with gut microbiome and antiobesity potential. Nutrition. 2013;29:591–6. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2012.07.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103. Westermann C, Gleinser M, Corr SC, Riedel CU. A critical evaluation of Bifidobacterial adhesion to the host tissue. Front Microbiol. 2016;7:1–8. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104. Tsilingiri K, Rescigno M. Postbiotics: what else? Benef Microbes. 2012;4:101–7. doi: 10.3920/BM2012.0046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105. Zagato E, Mileti E, Massimiliano L, Fasano F, Budelli A, Penna G, et al. Lactobacillus paracasei CBA L74 metabolic products and fermented milk for infant formula have anti-inflammatory activity on dendritic cells in vitro and protective effects against colitis and an enteric pathogen in vivo. PLoS One. 2014;9:1–14. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106. Tiptiri-Kourpeti A, Spyridopoulou K, Santarmaki V, Aindelis G, Tompoulidou E, Lamprianidou EE, et al. Lactobacillus casei exerts anti-proliferative effects accompanied by apoptotic cell death and up-regulation of TRAIL in colon carcinoma cells. PLoS One. 2016;11:1–20. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107. Sabater-Molina M, Larque E, Torrella F, Zamora S. Dietary fructo-oligosaccharides and potential benefits on health. J Physiol Biochem. 2009;65:315–28. doi: 10.1007/BF03180584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108. Patel S, Goyal A. The current trends and future perspectives of prebiotics research: a review. 3 Biotech. 2012;2:115–25. [Google Scholar]
- 109. Oliveira RPDS, Florence ACR, Perego P, De Oliveira MN, Converti A. Use of lactulose as prebiotic and its influence on the growth, acidification profile and viable counts of different probiotics in fermented skim milk. Int J Food Microbiol. 2011;145:22–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2010.11.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110. Zhou X, Ruan Z, Huang X, Zhou Y, Liu S, Yin Y. The prebiotic lactosucrose modulates gut metabolites and microbiota in intestinal inflammatory rats. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2014;23:157–63. [Google Scholar]
- 111. Torres DPM, Goncalves MPF, Teixeira JA, Rodrigues LR. Galacto-oligosaccharides: production, properties, applications, and significance as prebiotics. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2010;9:438–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1541-4337.2010.00119.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112. Rycroft CE, Jones MR, Gibson GR, Rastall RA. A comparative in vitro evaluation of the fermentation properties of prebiotic oligosaccharides. J Appl Microbiol. 2001;91:878–87. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2672.2001.01446.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113. Aachary AA, Prapulla SG. Xylooligosaccharides (XOS) as an emerging prebiotic: microbial synthesis, utilization, structural characterization, bioactive properties, and applications. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2011;10:1–16. [Google Scholar]
- 114. Moro G, Arslanoglu S, Stahl B, Jelinek J, Wahn U, Boehm G. A mixture of prebiotic oligosaccharides reduces the incidence of atopic dermatitis during the first six months of age. Arch Dis Child. 2006;91:814–9. doi: 10.1136/adc.2006.098251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115. Fuentes-Zaragoza E, Sanchez-Zapata E, Sendra E, Sayas E, Navarro C, Fernandez-Lopez J, et al. Resistant starch as prebiotic: a review. Starch Starke. 2011;63:406–15. [Google Scholar]
- 116. Hoseinifar SH, Ahmadi A, Raeisi M, Hoseini SH, Khalili M, Behnampour N. Comparative study on immunomodulatory and growth enhancing effects of three prebiotics (galactooligosaccharide, fructooligosaccharide and inulin) in common carp (Cyprinus carpio) Fish Shellfish Immunol 2016. 58 1 10 27574826 [Google Scholar]
- 117. Han W-C, Byun S-H, Kim M-H, Sohn EH, Lim JD, Um BH, et al. Production of lactosucrose from sucrose and lactose by a levansucrase from Zymomonas mobilis. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2009;19:1153–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118. Macfarlane GT, Steed H, Macfarlane S. Bacterial metabolism and health-related effects of galacto-oligosaccharides and other prebiotics. J Appl Microbiol. 2008;104:305–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2007.03520.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119. Bartosch S, Woodmansey EJ, Paterson JC, McMurdo ME, Macfarlane GT. Microbiological effects of consuming a synbiotic containing Bifidobacterium bifidum, Bifidobacterium lactis, and oligofructose in elderly persons, determined by real-time polymerase chain reaction and counting of viable bacteria. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;40:28–37. doi: 10.1086/426027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120. Bird AR, Brown IL, Topping DL. Starches, resistant starches, the gut microflora and human health. Curr Issues Intest Microbiol. 2000;1:25–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]