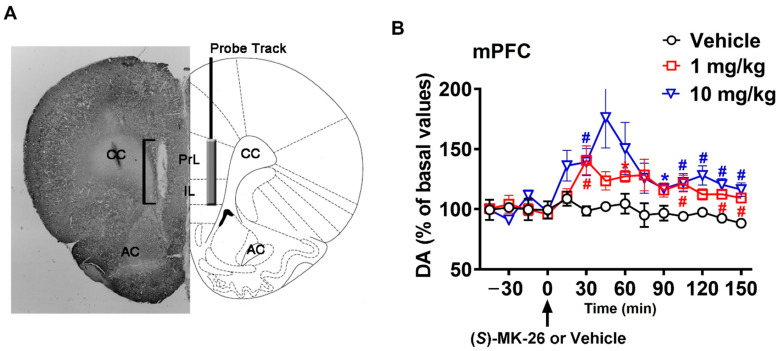
Figure 4.
Treatment with (S)-MK-26 enhanced brain extracellular concentration of dopamine in vivo. (A) Schematic representation of a coronal section of the rat brain (adapted from Paxinos and Watson, 2014 [45]) showing the track of the microdialysis probe in the PrL and IL portions of the mPFC. The square bracket in the microphotograph indicates the portion of the histological section showing the active part of the dialyzing membrane of the microdialysis probe. (B) Extracellular dopamine concentrations in the mPFC dialysates obtained from rats treated with (S)-MK-26 (1 and 10 mg/kg) or vehicle. Rats stereotaxically implanted with a microdialysis probe aimed at the mPFC were placed individually into the experimental cage and perfused with the dialysis buffer. During the experiment, four dialysate aliquots were collected every 15 min and then vehicle or (S)-MK-26 (1 or 10 mg/kg) was i.p. administered (indicated by the arrow in the figure) and 10 additional dialysate aliquots were also collected for dopamine determination. Data are charted as percentages (with 100% as the average of the last four dopamine basal values before treatment) with values expressed as means ± SEM of the measurements obtained by 3–5 rats per group. *: p < 0.05 compared to basal values (before treatment); #: p < 0.05 with respect to vehicle-treated rats (two-way RM-ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple-comparison test). Abbreviations: PrL, prelimbic area; IL, infralimbic area; AC, anterior commissura; CC, corpus callosum.