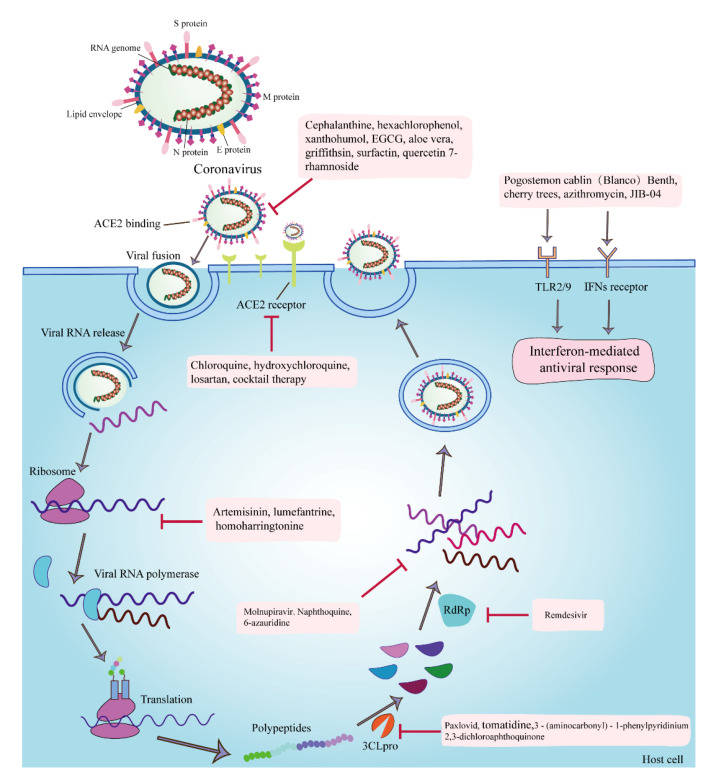
Figure 1.
The targets of anti-coronavirus drugs and the infection processes of coronavirus. The anti-coronavirus mechanisms or targets of cepharanthine are the inhibition of viral invasion through binding to the S protein; hexachlorophenol and xanthohumol are the antagonization of the Mpro; EGCG is the inhibition of the attachment, entry, replication, and assembly of viruses; aloe vera is the direct inactivation of PEDV; Griffithsin and surfactin are the inhibition of the viral attachment; quercetin 7-rhamnoside is the inhibition of the initial stage of viral infection; chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine, losartan, and cocktail therapy for coronavirus are the inhibition of the invasion of viruses by inhibiting the binding of SARS-CoV2 to the ACE2 receptor; artemisinin, lumefantrine, and homoharringtonine are the inhibition of the synthesis of early protein; Paxlovid, tomatidine, 3-(aminocarbonyl)-1-phenylpyridinium, and 2,3-dichloroaphthoquinone are the inhibition of the 3CLpro; remdesivir is the inhibition of the RdRp and nucleoside components; molnupiravir, naphthoquine, and 6-azauridine are the inhibition of the synthesis of viral RNA; Pogostemon cablin (Blanco) Benth and JIB-04 are the stimulation of antioxidant- and H3-mediated antiviral immune responses; and azithromycin exerts antiviral effects by inducing type I interferon immune responses.