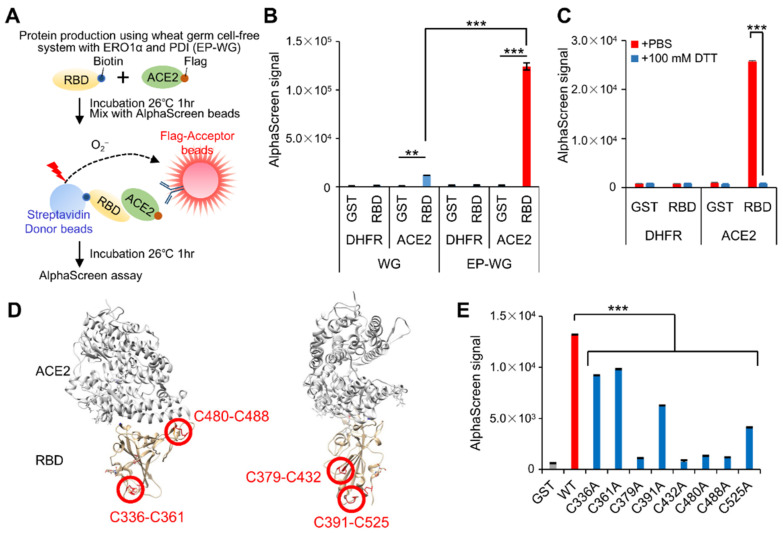
Figure 3.
Development of AlphaScreen assay to evaluate the RBD–ACE2 interaction. (A) Schematic representation of AlphaScreen assay to measure the binding between biotinylated RBD and flag-tagged ACE2 produced by wheat germ cell-free protein synthesis system with ERO1α and PDI (EP-WG). (B) Comparison of AlphaScreen signal of each protein synthesized by two different methods. Biotinylated GST and flag-tagged DHFR were used as negative controls. AlphaScreen signal was normalized by relative protein amounts. (C) Disulfide-bond-containing RBD protein was incubated with or without 100 mM of DTT for 30 min at 37 °C prior to AlphaScreen assay. (D) Localization of disulfide bonds in the RBD protein in the tertiary structure of the RBD bound to ACE2. Disulfide bonds in the SARS-CoV-2 RBD are shown as sticks and indicated by red circles. The protein structure was obtained from PDB ID 6m0j. (E) Mutation analysis of cysteine residues of RBD for ACE2 interaction. AlphaScreen assay was carried out using RBD possessing alanine substitution in each cysteine residue. AlphaScreen signal was normalized by relative protein amounts. WT, Wild Type. All graph data are presented as mean ± SD, Welch‘s t test (two-tailed), ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.