Fig. 2.
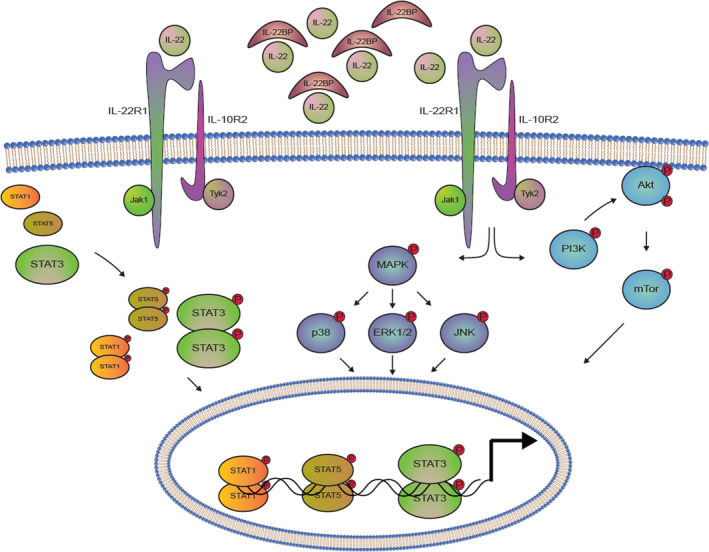
IL‐22R and its intracellular signalling. The heterodimeric IL‐22R consists of the IL‐22R1 and the IL‐10R2. When IL‐22 is not sequestered by the soluble protein, IL‐22BP, it is able to bind the IL‐22 receptor. Upon this binding, intracellular signalling is initiated, which starts with the activation of the receptor‐associated JAKs and TYKs. Activation of these kinases mediates the phosphorylation of various STAT molecules, with STAT3 phosphorylation being the most pronounced. This phosphorylation allows STAT3 to form homodimers, which can translocate to the nucleus and regulate the transcription of STAT3‐responsive genes. Furthermore, STAT1 and STAT5 molecules are also activated. IL‐22R signalling is also seen to activate the MAPK pathways involving ERK1/2, JNK and p38, as well as the PI3K‐Akt‐mTOR pathway. Akt, protein kinase B; ERK, extracellular signal‐regulated kinase; IL‐10R, IL‐10 receptor; IL‐22BP, IL‐22‐binding protein; IL‐22R, IL‐22 receptor; JAK, Janus kinases; JNK, c‐Jun N‐terminal kinase; MAPK, mitogen‐activated protein kinase; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; p38, p38 mitogen‐activated protein kinase; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3‐kinase; STAT, signal transducer of activated T cells; TYK, tyrosine kinases.
