Abstract
Background
Adenoma detection rate (ADR) and polyp detection rate (PDR) are both indicators for colonoscopy quality. Improving ADR or PDR is critical for reducing the incidence and mortality of colorectal cancer (CRC). Although several studies have focused on identifying the factors that may influence ADR or PDR, the evidence remains limited and inconclusive. We conducted a retrospective study to evaluate the effect of anesthesia assistance (AA) on ADR or PDR in patients undergoing colonoscopy screening and identify risk factors affecting ADR or PDR.
Methods
We reviewed electronic medical records of patients who underwent colonoscopy screening between May 2019 and August 2020. Patients were divided into two groups according to whether they received AA: patients in Group A underwent colonoscopy screening with AA, whereas patients in Group O underwent colonoscopy screening without AA. Propensity score matching (PSM) was utilized to account for differences in baseline characteristics. After, ADR and PDR were compared between the two groups. Binary logistic regression was employed to identify risk factors that affected ADR or PDR.
Results
Of 9432 patients who underwent colonoscopy examination during the study period, 7170 were included in the final analyses (Group A = 5756 and Group O = 1414). After PSM, 736 patients remained in each group for analyses. There was no significant difference between groups A and O (P > 0.05) in ADR or PDR. Binary logistic regression indicated that the endoscopic device version (Olympus HQ290), equipment image-based technique and number of images were independent risk factors that affected ADR, and the age (50–59 years and 60–69 years), gender (male), high-risk status, endoscopist seniority (senior endoscopist), equipment image-based technique and number of images were all independent risk factors that affected PDR.
Conclusions
We discovered that AA does not affect ADR or PDR. Despite improved patient satisfaction, using AA is unnecessary for improving colonoscopy quality. Endoscopists should consider all these factors as much as possible when performing colonoscopy screening.
Keywords: anesthesia assistance, colorectal cancer, adenoma detection rate, polyp detection rate, retrospective, propensity score matching
Introduction
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most malignant cancers worldwide. CRC incidence has been ranked fifth in China, and the new cases and deaths account for 20% of total global cases (1). Most CRCs can be cured early, and the 5-year survival rate can be as high as 90% (2). As a result, improving the early diagnostic yield of CRC is critical for patient survival.
Colonoscopy screening has been regarded as the preferred choice for detecting colorectal lesions (3, 4). It has been demonstrated that CRC incidence could be reduced by 76–90% following clearing colonoscopy (5). High-quality colonoscopy screening is critical to resolving the issue. Adenoma detection rate (ADR) has been extensively recommended as a key colonoscopy quality indicator (6–8). Removal of adenomas and precancerous lesions could reduce CRC incidence and mortality (9–11). Polyp detection rate (PDR) is another indicator of colonoscopy quality. Numerous studies indicate that PDR can serve as a good surrogate for ADR, with an average ADR to PDR ratio of 0.64 to 0.68 (12–15). As a result, investigations on how to improve ADR or PDR are worthwhile.
Certain factors influence the technical performance of colonoscopy screening in clinical practice, of which anesthesia assistance (AA) may be one of the major factors. Although several studies focused on the effect of sedation on ADR or PDR, the findings remained limited and inclusive. Accordingly, we employed a retrospective approach to observe whether AA could increase ADR or PDR in patients undergoing colonoscopy screening. This study aimed to assess the influence of AA on ADR or PDR using propensity score matching (PSM) analyses. Using binary logistic regression analyses, the secondary objective was to identify risk factors affecting ADR or PDR.
Methods
Study Population
All electronic records of patients were obtained from the Digestive Endoscopy Center of Liaocheng People's Hospital. Patients were included in the study if they underwent a colonoscopy screening between May 2019 and August 2020. Exclusion criteria included the following: inpatients, emergency patients, patients with bleeding, Boston bowel preparation scale (BBPS) score = 0; patients undergoing endoscopic treatment, patients aged <40 years, patients with intestinal obstruction, and patients undergoing intestinal resection surgery. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Liaocheng People's Hospital (Ethics number: 2021098).
Variables and Outcome Measurements
We obtained the following information from the electronic record system (Medcare Digital Digestive Endoscopy Workstation, Medcare Digital Engineering Co., Ltd, Qingdao, China): age, gender, endoscopist seniority, endoscopic device version, image-enhanced endoscopy, number of endoscopic images, whether the patient is a high-risk population of CRC, biopsy pathological results, recipient of AA or not, BBPS score, and cecum intubation rate (CIR).
Before colonoscopy screening, all patients underwent 12 h of fasting and polyethylene glycol for bowel preparation. BBPS score was used to determine the quality of bowel preparation (16). Each of the three segments of colon (right, including the cecum and ascending colon; transverse, including hepatic and splenic flexures; and left, including the descending colon, sigmoid, and rectum) is given a score from 0 to 3 defined as follows: 0 = unprepared colon segment with mucosa not observed due to inability to pass solid stool; 1 = portion of mucosa of the colon segment observed, but other areas of colon segment, not well-observed due to staining, residual stool, and/or opaque liquid; 2 = minor amount of residual staining, small fragments of stool and/or opaque liquid, but mucosa of colon segment well observed; 3 = entire mucosa of colon segment well-observed with no residual staining, small fragments of stool, or opaque liquid (16).
Anesthesiologists performed AA using propofol or midazolam-fentanyl according to standard AA guidelines set by the institute. The anesthesiologist adjusted the amount of anesthetic medication administered according to the clinical situation and was not collected in this study. All included patients were divided into two groups (A or O) according to whether they received AA. Patients in Group O did not receive any drug-related to anesthesia.
All colonoscopy screenings were performed by 25 endoscopists with a minimum of 500 colonoscopy examinations who had ≥ 1-year experience before initiating this study. Six endoscopists were classified into a junior group, 11 into an intermediate group, and eight into a senior group based on their intensive training time. All endoscopists in the senior group were experts who underwent intensive training for ≥ 5 years.
All colonoscopy screenings were performed using Sonoscape or Olympus with five versions of 550 (EG-550; Sonoscape, Shenzhen, China), 260 (Q260, H260; Olympus, Tokyo, Japan), and 290 (H290, HQ290; Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) series. HQ290 series was classed as high-definition. The procedure details were recorded on an endoscopy database (Medcare Digital Digestive Endoscopy Workstation, Medcare Digital Engineering Co., Ltd, Qingdao, China).
In our study, the term “high-risk population” referred to those with a high risk of CRC. People with a high risk of CRC included those with blood in the stool, melena, anemia, weight loss, CRC warning symptoms, and those aged 50–74 without CRC warning symptoms. Any one of the following is considered a high-risk group: 1) fecal occult blood positive; 2) first-degree relatives have a history of colorectal cancer; 3) past history of intestinal adenoma; 4) history of cancer; 5) changes in bowel habits; 6) those who met any two of the following: chronic diarrhea, chronic constipation, mucus blood in the stool, history of chronic appendicitis or appendectomy, history of chronic cholecystitis or cholecystectomy, long-term mental depression, and alarm signal.
All biopsy pathological results were reviewed, and diagnoses were made by two experienced pathologists. Difficult cases were confirmed after discussions between pathologists in the digestive subspecialty group. We interpreted the findings using the following definitions.
ADR is defined as the percentage of colonoscopies with at least one adenoma, whereas PDR is defined as the percentage of colonoscopies with at least one polyp.
The primary endpoint of the study was to observe the difference in ADR between groups A and O as well as PDR. The secondary endpoint was to identify the factors influencing ADR or PDR.
Statistical Analyses
The sample size was based on the available data from patients who underwent colonoscopy screening at the Digestive Endoscopy Center of Liaocheng People's Hospital from May 2019 to August 2020. The sample size was not statistically calculated because the parameters necessary to estimate the sample size cannot be determined in advance without references, and as an exploratory study, the number of cases collected is sufficient. As appropriate, the study results are presented as numbers (percentages) for categorical variables and means ± standard deviations (SD) for continuous variables. The normality of data was assessed using the normal quantile-quantile plot. To compare continuous and categorical variables between groups, independent samples t-tests and chi-square tests were employed, respectively.
PSM was utilized to reduce the potential confounding effect of each variable and assess differences in baseline characteristics between the two groups. The logistic regression analyses defined the propensity score as the probability of receiving AA. The variables used for matching included age, gender, endoscopist seniority, endoscopic device version, and high-risk status that appear to influence the probability of receiving AA. We matched patients at a ratio of 1:1 using the nearest neighbor method with a caliper of 0.0002 of the logit of the propensity score. In the propensity-matched cohort, paired chi-square and paired rank-sum tests were employed to compare the paired groups.
Binary logistic regression models were performed to identify the risk factors that affected ADR or PDR. All variables were adjusted in the binary logistic regression analyses using the enter method to assess the association between AA and ADR or PDR. To satisfy the linear relationship between age and dependent variable (Logit P), the patients were categorized into the following age groups: 40–49 years, 50–59 years, 60–69 years, 70–79 years, and ≥ 80 years.
The data were analyzed using SPSS software (version 26.0; SPSS Inc., Armonk, NY, United States) and reviewed by a statistician.
Results
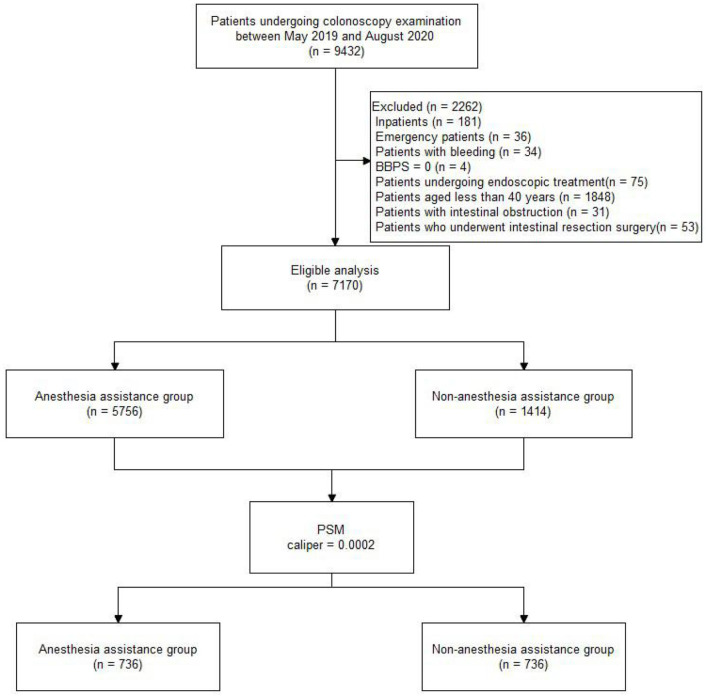
Of 9432 patients who underwent colonoscopy screening between May 2019 and August 2020, 7170 were included in the final analyses. The patients who underwent colonoscopy screening with and without AA were allocated to groups A (5756, 80%) and O (1414, 20%), respectively. Figure 1 displays the distribution of patients, and Table 1 shows the characteristics of the total study cohort.
Figure 1.
Flow diagram of the study population. BBPS, Boston bowel preparation scale; PSM, Propensity score matching.
Table 1.
Patient characteristics of the total study cohort.
| Characteristic | Group A (n = 5756) | Group O (n = 1414) | P-values | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Proportion (%) | n | Proportion (%) | ||
| Age, years | <0.001 | ||||
| 40–49 years | 1576 | 27.4% | 466 | 33.0% | |
| 50–59 years | 2222 | 38.6% | 544 | 38.5% | |
| 60–69 years | 1398 | 24.3% | 311 | 22.0% | |
| 70–79 years | 515 | 8.9% | 89 | 6.3% | |
| ≥ 80 years | 45 | 0.8% | 4 | 0.3% | |
| Gender | <0.001 | ||||
| Male | 2731 | 52.6% | 805 | 56.9% | |
| Female | 3025 | 47.4% | 609 | 43.1% | |
| High risk population of CRC | 823 | 14.3% | 206 | 14.6% | 0.800 |
| Endoscopist seniority | <0.001 | ||||
| Junior endoscopist | 496 | 8.6% | 560 | 39.6% | |
| Intermediate endoscopist | 3725 | 64.7% | 653 | 46.2% | |
| Senior endoscopist | 1535 | 26.7% | 201 | 14.2% | |
| Endoscopic device version | <0.001 | ||||
| Sonoscape EC-550 | 225 | 3.9% | 901 | 63.7% | |
| Olympus Q260 | 2557 | 44.4% | 240 | 17.0% | |
| Olympus H260 | 1935 | 33.6% | 179 | 12.7% | |
| Olympus H290 | 297 | 5.2% | 15 | 1.1% | |
| Olympus HQ290 | 742 | 12.9% | 79 | 5.6% | |
| Image-enhanced endoscopy | <0.001 | ||||
| WLE | 4039 | 70.2% | 1165 | 82.4% | |
| Equipment image-based techniques | 1685 | 29.3% | 246 | 17.4% | |
| Dyed-based technique | 32 | 0.6% | 3 | 0.2% | |
| Number of endoscopic images | 77.10 ± 29.674 | 79.15 ± 32.663 | <0.001 | ||
| BBPS score | 7.02 ± 1.326 | 6.78 ± 1.190 | <0.001 | ||
| CIR | 5673 | 98.6% | 1380 | 97.6% | 0.014 |
| Adenoma | 661 | 11.5% | 129 | 9.1% | 0.010 |
| Polyp | 2473 | 43.0% | 552 | 39.0% | 0.007 |
| SSA/P | 154 | 2.7% | 28 | 2.0% | 0.157 |
| LST | 15 | 0.3% | 3 | 0.2% | 1.000 |
| Advanced cancer | 149 | 2.6% | 36 | 2.5% | 1.000 |
| IBD | 83 | 1.4% | 33 | 2.3% | 0.025 |
Data are presented as the median (range) or number (percentage).
CRC, Colorectal cancer; WLE, white light endoscopy; BBPS, Boston bowel preparation scale; CIR, Cecum intubation rate.
SSA/P, Sessile serrated adenomas/polyps;LST, Laterally spreading tumor; IBD, Inflammatory bowel disease.
Following PSM with a caliper of 0.0002, 736 patients remained in each group, which was well-matched except for the endoscopic device version (P < 0.05). Table 2 indicates no significant difference in ADR or PDR (P > 0.05) between groups A and O in the propensity-matched cohort. Meanwhile, no significant difference was observed in detection rates of sessile serrated adenomas/polyps (SSA/P), laterally spreading tumor (LST), and advanced cancer (P > 0.05, Table 2). There was a significant difference in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) (P < 0.05, Table 2).
Table 2.
Patient characteristics of the propensity-matched cohort.
| Characteristic | Group A (n = 736) | Group O (n = 736) | P-values | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Proportion (%) | n | Proportion (%) | ||
| Age, years | 0.948 | ||||
| 40–49 years | 245 | 33.3% | 239 | 32.5% | |
| 50–59 years | 262 | 35.6% | 274 | 37.2% | |
| 60–69 years | 181 | 24.6% | 174 | 23.6% | |
| 70–79 years | 45 | 6.1% | 47 | 6.4% | |
| ≥ 80 years | 3 | 0.4% | 2 | 0.3% | |
| Gender | 0.251 | ||||
| Male | 375 | 51.0% | 353 | 48.0% | |
| Female | 361 | 49.0% | 383 | 52.0% | |
| High risk population of CRC | 103 | 14.0% | 101 | 13.7% | 0.880 |
| Endoscopist seniority | 0.183 | ||||
| Junior endoscopist | 171 | 23.2% | 186 | 25.3% | |
| Intermediate endoscopist | 411 | 55.8% | 423 | 57.5% | |
| Senior endoscopist | 154 | 20.9% | 127 | 17.3% | |
| Endoscopic device version | <0.001 | ||||
| Sonoscape EC-550 | 224 | 30.4% | 224 | 30.4% | |
| Olympus Q260 | 240 | 32.6% | 240 | 32.6% | |
| Olympus H260 | 179 | 24.3% | 178 | 24.2% | |
| Olympus H290 | 43 | 5.8% | 15 | 2.0% | |
| Olympus HQ290 | 50 | 6.8% | 79 | 10.7% | |
| Image-enhanced endoscopy | <0.001 | ||||
| WLE | 473 | 64.3% | 599 | 81.4% | |
| Equipment image-based techniques | 258 | 35.1% | 135 | 18.3% | |
| Dyed-based technique | 5 | 0.7% | 2 | 0.3% | |
| Number of endoscopic images | 76.52 ± 31.716 | 71.93 ± 28.379 | 0.003 | ||
| BBPS score | 6.94 ± 1.286 | 6.87 ± 1.182 | 0.264 | ||
| CIR | 722 | 98.1% | 724 | 98.4% | 0.692 |
| Adenoma | 80 | 10.9% | 69 | 9.4% | 0.342 |
| Polyp | 301 | 40.9% | 266 | 36.1% | 0.061 |
| SSA/P | 14 | 1.9% | 13 | 1.8% | 0.846 |
| LST | 1 | 0.1% | 3 | 0.4% | 0.317 |
| Advanced cancer | 19 | 2.6% | 20 | 2.7% | 0.871 |
| IBD | 9 | 1.2% | 20 | 2.7% | 0.039 |
Data are presented as the median (range) or number (percentage).
PSM, Propensity score matching; CRC, Colorectal cancer; WLE, white light endoscopy; BBPS, Boston bowel preparation scale; CIR, Cecum intubation rate; SSA/P, Sessile serrated adenomas/polyps; LST, Laterally spreading tumor; IBD, Inflammatory bowel disease.
In the propensity-matched cohort, univariate analyses were employed to screen for variables that may affect ADR or PDR, and the results revealed that age, gender, high-risk status, equipment image-based technique, the number of images, endoscopic device version, and endoscopist seniority were all significant variables (P < 0.05). Subsequently, a binary logistic regression model was constructed to evaluate the association between AA and ADR or PDR. After controlling for confounding variables, the results indicated that AA does not affect ADR (P = 0.906) or PDR (P = 0.770).
For ADR, the results revealed that the endoscopic device version (Olympus HQ290), equipment image-based technique, and number of images were independent risk factors (Table 3). ADR was 2.166 times higher in patients who underwent colonoscopy with Olympus HQ290 than Sonoscape EG-550 (95% CI: 1.058–4.433, P = 0.034). Compared with colonoscopy with white light endoscopy (WLE), ADR was 2.326 times higher in patients who underwent colonoscopy with equipment image-based technique (95% CI: 1.565–3.459, P < 0.001). For every additional endoscopic image, ADR increased by 1.009-fold (95% CI: 1.003-1.015, P = 0.002). In addition, it has been demonstrated that ADR was unaffected by AA, age, gender, high-risk status, endoscopist seniority, endoscopic device version (Olympus Q260, H260, H290), dyed-based technique, and BBPS score (Table 3).
Table 3.
Logistic regression analysis for ADR in the propensity-matched cohort.
| Detection rate, % | Unadjusted | Adjusted | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | P–value | OR | 95% CI | P–values | ||
| Colonoscopy without AA | 9.4% | Reference | Reference | ||||
| Colonoscopy with AA | 10.9% | 1.179 | 0.839–1.656 | 0.342 | 0.978 | 0.680–1.408 | 0.906 |
| Age | |||||||
| 40–49 years | 8.7% | Reference | Reference | ||||
| 50–59 years | 9.7% | 1.131 | 0.738–1.732 | 0.573 | 1.157 | 0.744–1.799 | 0.518 |
| 60–69 years | 13.0% | 1.567 | 1.006–2.439 | 0.047 | 1.354 | 0.849–2.159 | 0.204 |
| 70–79 years | 9.8% | 1.141 | 0.535–2.433 | 0.733 | 1.005 | 0.454–2.224 | 0.990 |
| ≥ 80 years | 0 | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| Gender | |||||||
| Female | 7.3% | Reference | Reference | ||||
| Male | 12.9% | 1.887 | 1.327–2.684 | <0.001 | 1.451 | 1.000–2.106 | 0.050 |
| High risk population | |||||||
| None | 8.9% | Reference | Reference | ||||
| High risk population of CRC | 17.6% | 2.190 | 1.456–3.295 | <0.001 | 1.548 | 0.985–2.431 | 0.058 |
| Endoscopist seniority | |||||||
| Junior endoscopist | 9.8% | Reference | Reference | ||||
| Intermediate endoscopist | 9.0% | 0.909 | 0.596–1.386 | 0.658 | 0.631 | 0.373–1.068 | 0.086 |
| Senior endoscopist | 13.9% | 1.483 | 0.912–2.410 | 0.112 | 1.190 | 0.654–2.168 | 0.569 |
| Endoscopic device version | |||||||
| Sonoscape EG−550 | 7.8% | Reference | Reference | ||||
| Olympus Q260 | 10.0% | 1.311 | 0.831–2.069 | 0.244 | 1.491 | 0.838–2.651 | 0.174 |
| Olympus H260 | 11.8% | 1.573 | 0.981–2.522 | 0.060 | 1.733 | 0.965–3.113 | 0.066 |
| Olympus H290 | 10.3% | 1.362 | 0.547–3.392 | 0.508 | 1.257 | 0.453–3.484 | 0.661 |
| Olympus HQ290 | 14.0% | 1.914 | 1.044–3.507 | 0.036 | 2.166 | 1.058–4.433 | 0.034 |
| Image–enhanced endoscopy | |||||||
| WLE | 6.8% | Reference | Reference | ||||
| Equipment image–based technique | 18.8% | 3.175 | 2.244–4.492 | <0.001 | 2.326 | 1.565–3.459 | <0.001 |
| Dyed–based technique | 28.6% | 5.474 | 1.044–28.702 | 0.044 | 4.715 | 0.843–26.375 | 0.077 |
| Number of images | / | 1.011 | 1.006–1.016 | <0.001 | 1.009 | 1.003–1.015 | 0.002 |
| BBPS score | / | 1.014 | 0.884–1.163 | 0.841 | 0.926 | 0.801–1.071 | 0.303 |
Data are presented as the number (percentage).
ADR, Adenoma detection rate; AA, Anesthesia assistance; OR, odd ratio; CI, confidence interval; CRC, Colorectal cancer; WLE, white light endoscopy; BBPS, Boston bowel preparation scale.
For PDR, the results revealed that age (50–59 years and 60–69 years), gender (male), high-risk status, endoscopist seniority (senior endoscopist), equipment image-based technique, and number of images were all independent risk factors (Table 4). Compared with patients of 40–49 years, PDR was 1.510 times higher in those of 50–59 years (95% CI: 1.134–2.011, P = 0.005) and 1.879 times higher in those of 60–69 years (95% CI: 1.370–2.576, P < 0.001). Compared with female patients, PDR was 1.622 times higher in male patients (95% CI: 1.278–2.058, P < 0.001). Compared with patients without a high risk of CRC, PDR was 1.857 times higher in those with a high risk of CRC (95% CI: 1.310-2.632, P = 0.001). Compared with colonoscopy performed by a junior endoscopist, PDR was 1.547 times higher in patients who underwent colonoscopy performed by a senior endoscopist (95% CI: 1.039–2.304, P = 0.032). Compared with colonoscopy with WLE, PDR was 3.210 times higher in patients who underwent colonoscopy with equipment image-based technique (95% CI: 2.421–4.255, P < 0.001). For every additional endoscopic image, PDR increased by 1.017-fold (95% CI: 1.012–1.021, P = 0.001). In addition, PDR was unaffected by AA, age (70-79 years and ≥ 80 years), endoscopist seniority (intermediate endoscopist), endoscopic device version, dyed-based technique, and BBPS score (Table 4).
Table 4.
Logistic regression analysis for PDR in the propensity–matched cohort.
| Detection rate, % | Unadjusted | Adjusted | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | P–value | OR | 95% CI | P–values | ||
| Colonoscopy without AA | 36.1% | Reference | Reference | ||||
| Colonoscopy with AA | 40.9% | 1.223 | 0.991–1.509 | 0.061 | 0.965 | 0.759–1.227 | 0.770 |
| Age | |||||||
| 40–49 years | 30.6% | Reference | Reference | ||||
| 50–59 years | 38.6% | 1.428 | 1.101–1.853 | 0.007 | 1.510 | 1.134–2.011 | 0.005 |
| 60–69 years | 48.2% | 2.110 | 1.588–2.803 | <0.001 | 1.879 | 1.370–2.576 | <0.001 |
| 70–79 years | 43.5% | 1.746 | 1.108–2.753 | 0.016 | 1.463 | 0.876–2.442 | 0.146 |
| ≥ 80 years | 20.0% | 0.568 | 0.063–5.121 | 0.614 | 0.411 | 0.043–3.906 | 0.439 |
| Sex | |||||||
| Female | 29.9% | Reference | Reference | ||||
| Male | 46.9% | 2.067 | 1.668–2.561 | <0.001 | 1.622 | 1.278–2.058 | <0.001 |
| High risk population | |||||||
| None | 35.3% | Reference | Reference | ||||
| High risk population of CRC | 58.3% | 2.562 | 1.896–3.463 | <0.001 | 1.857 | 1.310–2.632 | 0.001 |
| Endoscopist seniority | |||||||
| Junior endoscopist | 38.7% | Reference | Reference | ||||
| Intermediate endoscopist | 36.2% | 0.901 | 0.698–1.163 | 0.423 | 0.835 | 0.604–1.153 | 0.272 |
| Senior endoscopist | 45.2% | 1.309 | 0.953–1.797 | 0.096 | 1.547 | 1.039–2.304 | 0.032 |
| Endoscopic device version | |||||||
| Sonoscape EG−550 | 38.2% | Reference | Reference | ||||
| Olympus Q260 | 37.9% | 0.989 | 0.759–1.290 | 0.937 | 0.983 | 0.700–1.380 | 0.920 |
| Olympus H260 | 38.7% | 1.021 | 0.767–1.359 | 0.888 | 1.047 | 0.730–1.502 | 0.803 |
| Olympus H290 | 41.4% | 1.143 | 0.656–1.994 | 0.637 | 0.775 | 0.403–1.493 | 0.446 |
| Olympus HQ290 | 40.3% | 1.094 | 0.733–1.632 | 0.660 | 1.156 | 0.714–1.871 | 0.555 |
| Image–enhanced endoscopy | |||||||
| WLE | 29.2% | Reference | Reference | ||||
| Equipment image–based technique | 63.4% | 4.193 | 4.193–5.351 | <0.001 | 3.210 | 2.421–4.255 | <0.001 |
| Dyed–based technique | 71.4% | 6.062 | 6.062–31.412 | 0.032 | 5.424 | 0.900–32.675 | 0.065 |
| Number of images | / | 1.019 | 1.015–1.023 | <0.001 | 1.017 | 1.012–1.021 | 0.001 |
| BBPS score | / | 0.961 | 0.883–1.046 | 0.357 | 0.874 | 0.793–0.963 | 0.077 |
Data are presented as the number (percentage).
PDR: Polyp detection rate; AA, Anesthesia assistance; OR, odd ratio; CI, confidence interval; CRC, Colorectal cancer; WLE, white light endoscopy; BBPS, Boston bowel preparation scale.
Discussion
In this study, no significant difference exists in ADR or PDR between groups A and O. Binary logistic regression analyses revealed that the endoscopic device version (Olympus HQ290), equipment image-based technique, and number of images were independent risk factors that affected ADR, and the age (50–59 years and 60–69 years), gender (male), high-risk status, endoscopist seniority (senior endoscopist), equipment image-based technique, and number of images were all independent risk factors that affected PDR.
Colonoscopy screening is extremely important because it is linked to a substantially reduced incidence of CRC (17, 18). Numerous studies have proved the remarkable efficacy of colonoscopy in preventing cancer (19–25). The protective effect of CRC is achieved by comprehensively detecting and subsequently resecting precancerous lesions via colonoscopy. Although colonoscopy screening has been demonstrated to reduce CRC-related mortality (26), interval cancer (IC), which occurred between consecutive inspections, still hampered the benefit of colonoscopy screening. It has been shown that IC represents up to 9% of all patients diagnosed with CRC (27–30). A study discovered that ADR was inversely associated with IC risks (31). Each 1.0% increase in ADR was linked to a 3.0% decrease in CRC risk (31). In addition, PDR, with a much simpler calculation than ADR, is another valuable quality indicator of colonoscopy. According to Sastre Lozano VM, IC prevalence was inversely and strongly associated with PDR of endoscopists (32). Therefore, ADR and PDR have been widely advocated as important quality indicators for colonoscopy screening.
Due to their fear of imaginary pain, numerous patients selected colonoscopy screening with AA. Once the patients are sedated, it is easy to fill more air and allow the endoscopist to thoroughly inspect the mucosa. However, sedation will bring more adverse problems, such as falling tongue, aspiration, and even hypoxia. Although many studies focus on the impact of sedation on ADR or PDR, the results remain controversial. A retrospective study of 48,838 procedures revealed that sedation is linked to increased CIR, but ADR and PDR remain unchanged (33). Christina Bannert has revealed that sedation does not increase ADR or PDR (34). Another randomized controlled trial demonstrated no difference in PDR when colonoscopy was performed under deep or moderate sedation (35). Compared with colonoscopist-administrated sedation, using AA did not affect ADR of trainees (36). These findings are consistent with our finding that AA does not affect ADR or PDR during colonoscopy screening. However, some studies reached the opposite conclusion. Fatima Khan revealed that colonoscopy with sedation, as opposed to no sedation, was significantly linked to higher ADR (37). Qiongmei Zhang indicated that sedation was an independent factor associated with higher ADR (38). A study revealed that midazolam/fentanyl sedation administered by colonoscopists might increase PDR during colonoscopy (39). These findings are contrary to our results. On the one hand, because these studies were all retrospective, the results may be biased. In our study, we adopt PSM to reduce the influence of confounding factors, hence minimizing bias. On the other hand, previous studies did not consider the impact of endoscopic device version, image-enhanced endoscopy, or a high-risk status, but we have considered all these factors in our study. The reason that AA could not affect ADR or PDR during colonoscopy screening is possible due to the following: 1) compared with esogastroduodenoscopy, the pain associated with colonoscopy screening is tolerant for patients; 2) sedation makes the patient's body position changes impossible, which may affect the detection rate of lesions; and 3) small doses of opioids used in AA could not decrease the bowel movement which may affect the detection rate of lesions during a colonoscopy screening.
There are still many other factors affecting ADR. Binary logistic regression analyses revealed that the endoscopic device version (Olympus HQ290) is an independent risk factor affecting ADR, which was 2.166 times higher than Sonoscape EG-550, consistent with previous research results. Ashley Bond observed that colonoscopy screening with Olympus HQ290 could improve ADR within the moderate-risk population (40). Narrow-band imaging (NBI) is one of the equipment image-based techniques. Our study demonstrated that equipment image-based technique is an independent risk factor affecting ADR. Compared with colonoscopy with WLE, ADR was 2.326 times higher in patients who underwent colonoscopy with equipment image-based technique. A meta-analysis revealed that NBI has a higher ADR than WLE when bowel preparation is optimal (41). Irina Ioana Vi?ovan found that ADR in NBI group was significantly higher than non-NBI group (35.3% vs. 20%) (42), consistent with our study. On the contrary, Tatsunori Minamide revealed that second-generation NBI could not surpass WLI in terms of ADR but improved the detection of easily overlooked flat and depressed lesions (43). The reason may be that patients enrolled in this study are over 20 years old, which is different from our study, which included patients over 40 years. The incidence of lesions is higher in patients over 40 years. A study indicated that longer withdrawal times were linked to higher ADR (44). In our study, we could not obtain data regarding colonoscopy examination time. The endoscopic images were taken by an endoscopist during the withdrawal procedure so that the number of images could reflect the withdrawal time to some extent. As a result, we used the number of endoscopic images as a proxy for examination time in our study and found a 1.009-fold increase in ADR with every additional image. However, the overall ADR in our study is 11.5%, lower than that recommended by the current guidelines (45, 46). The reason may be that the withdrawal times of some endoscopists were too short to find adenoma. In addition, Margaret J. Zhou found that increasing age was independently associated with ADR, and female sex was inversely correlated with ADR (47, 48). However, it is inconsistent with our study that ADR was unaffected by age and gender. The reason may be attributed to different sample sizes and inclusion criteria. Although ADR has been established as a quality target in average-risk individuals, high-risk status was unrelated to ADR (49). It is consistent with our study that ADR was unaffected by high-risk status. We also found that ADR was unaffected by endoscopist seniority. It is consistent with the result of a prior study that ADR was not significantly associated with any endoscopist characteristic (50). Our study also found that ADR was unaffected by dyed-based technique, consistent with prior studies that ADR was not improved by the dyed-based technique (51, 52). ADR has been associated with bowel preparation but is not proportional to BBPS. ADR is the highest in good bowel preparation rather than excellent preparation (53, 54). It is consistent with our study that ADR was unaffected by BBPS. The reason may be that residual stool may help the endoscopist pay attention to the mucosa and thus identify lesions.
For PDR, binary logistic regression analyses revealed that age (50–59 years and 60–69 years) is an independent risk factor. Compared with patients of 40–49 years, PDR was 1.510 times higher in those of 50–59 years and 1.879 times higher in those of 60–69 years. A cross-sectional study found that PDR is significantly higher in most patients after the age of 50, without providing detailed statistics on PDR for each age group (55). This study also found that the percentage of male patients with polyps was significantly higher than that of female patients (55), consistent with our study that PDR was 1.622 times higher in male patients. Our study stated that PDR was 1.857 times higher in patients with a high-risk of CRC than those without a high-risk of CRC. The reason may be that the lifestyle risk factor for polyps and CRC partially overlaps (56). Da Kyoung Jung demonstrated that PDR increased when colonoscopy was performed by experienced endoscopists (57). It is consistent with our study that PDR was 1.547 times higher in patients who underwent colonoscopy performed by a senior endoscopist. Our study revealed that PDR was 3.210 times higher in patients who underwent colonoscopy with equipment image-based technique, consistent with a prior study that increased PDR for NBI colonoscopy (42). As in the previous discussion of ADR, we use the number of endoscopic images instead of the withdrawal time. For every additional endoscopic image, PDR increased by 1.017-fold. It is consistent with the prior study, in which longer withdrawal times were associated with higher PDR (44). In addition, our study demonstrated that PDR was unaffected by the endoscopic device version. It is inconsistent with a prior study that using high-definition equipment was the most important factor associated with a higher PDR (58). The inconsistency may be attributed to different inclusion criteria and study populations in our study. In addition, PDR has been demonstrated to be unaffected by BBPS score, consistent with a prior study in which PDR is the highest in good bowel preparation rather than excellent preparation (53). As in the previous discussion of ADR, the reason may be that residual stool may help the endoscopist pay attention to the mucosa and thus identify lesions.
Several limitations should be considered when interpreting the results of this study. First, this work was a retrospective study. Although we employed PSM to control for confounding variables, many real cases were missed. This will result in increasing internal validity while reducing external validity. Second, we used the number of endoscopic images as an alternative since colonoscopy examination time was unavailable and found a 1.009-fold increase in ADR and 1.017-fold increase in PDR, respectively, with every additional image. However, this could be the result rather than the cause of increased detection. There were more adenomas or polyps, and many images were taken to document the findings. This may affect our findings. Third, AA included sedation with propofol or midazolam-fentanyl, which were not classified separately. We will conduct further research to address this issue in the future.
Conclusions
In summary, we demonstrate that ADR or PDR, important indicators for colonoscopy screening quality, are unaffected by AA. The results also revealed that endoscopic device version (Olympus HQ290), equipment image-based technique, and number of images were independent risk factors that affected ADR. All independent risk factors that affected PDR included the following: age (50–59 years and 60–69 years), gender (male), high-risk status, endoscopist seniority (senior endoscopist), equipment image-based technique, and number of images. Despite improved patient satisfaction, using AA is unnecessary for improving colonoscopy quality. Endoscopists should consider all these factors as much as possible when performing colonoscopy screening.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics Statement
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by Ethics Committee of Liaocheng People's Hospital. Written informed consent for participation was not required for this study in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements.
Author Contributions
ML and CX collected data and wrote the manuscript. XZ assisted in collecting literature and participated in discussions. ML reviewed the statistical analyses. ZZ and JC designed the study. ZZ examined and verified the study. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Glossary
Abbreviations
- ADR
Adenoma detection rate
- PDR
Polyp detection rate
- CRC
Colorectal cancer
- AA
Anesthesia assistance
- PSM
Propensity score matching
- BBPS
Boston bowel preparation scale
- CIR
Cecum intubation rate
- SSA/P
Sessile serrated adenomas/polyps
- LST
Laterally spreading tumor
- IBD
Inflammatory bowel disease
- IC
Interval cancer
- WLE
White light endoscopy
- NBI
Narrow-band imaging.
References
- 1.Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. (2016) 66:115–32. 10.3322/caac.21338 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Courtney RJ, Paul CL, Carey ML, Sanson-Fisher RW, Macrae FA, D'Este C., et al. A population-based cross-sectional study of colorectal cancer screening practices of first-degree relatives of colorectal cancer patients. BMC Cancer. (2013) 13:13. 10.1186/1471-2407-13-13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Pan J, Xin L, Ma YF, Hu LH. Li ZS. Colonoscopy reduces colorectal cancer incidence and mortality in patients with non-malignant findings: a meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. (2016) 111:355–65. 10.1038/ajg.2015.418 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Brenner H, Altenhofen L, Stock C., Hoffmeister M. Prevention, early detection, and overdiagnosis of colorectal cancer within 10 years of screening colonoscopy in German. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2015) 13:717–23. 10.1016/j.cgh.2014.08.036 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Winawer SJ, Zauber AG, Ho MN, Brien MJ, Gottlieb LS, et al. Prevention of colorectal cancer by colonoscopic polypectomy The National Polyp Study Workgroup. N Engl J Med. (1993) 329:1977–81. 10.1056/NEJM199312303292701 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Rex DK. Maximizing detection of adenomas and cancers during colonoscopy. Am J Gastroenterol. (2006) 101:2866–77. 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00905.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ruiz-Rebollo ML, Alcaide-Suárez N, Burgueño-Gómez B, Antolin-Melero B, MªF M, Alonso-Martín C., et al. Adenoma detection rate and cecal intubation rate: Quality indicators for colonoscopy. Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2019) 42:253–5. 10.1016/j.gastre.2018.05.022 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Garborg K, de Lange T. Bretthauer M. Quality indicators in colonoscopy. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol. (2017) 15:416–28. 10.1007/s11938-017-0140-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Atkin WS, Edwards R, Kralj-Hans I, Wooldrage K, Hart AR, Northover JM, et al. Once-only flexible sigmoidoscopy screening in prevention of colorectal cancer: a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet. (2010) 375:1624–33. 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60551-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Schoen RE, Pinsky PF, Weissfeld JL, Yokochi LA, Church T, Laiyemo AO, et al. Colorectal-cancer incidence and mortality with screening flexible sigmoidoscopy. N Engl J Med. (2012) 366:2345–57. 10.1056/NEJMoa1114635 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Holme Ø, Løberg M, Kalager M, Bretthauer M, Hernán MA, Aas E., et al. Effect of flexible sigmoidoscopy screening on colorectal cancer incidence and mortality: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. (2014) 312:606–15. 10.1001/jama.2014.8266 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Patel NC, Islam RS, Wu Q, Gurudu SR, Ramirez FC, Crowell MD, et al. Measurement of polypectomy rate by using administrative claims data with validation against the adenoma detection rate. Gastrointest Endosc. (2013) 77:390–4. 10.1016/j.gie.2012.09.032 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Francis DL, Rodriguez-Correa DT, Buchner A, Harewood GC. Wallace M. Application of a conversion factor to estimate the adenoma detection rate from the polyp detection rate. Gastrointest Endosc. (2011) 73:493–7. 10.1016/j.gie.2011.01.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Williams JE, Holub JL. Faigel DO. Polypectomy rate is a valid quality measure for colonoscopy: results from a national endoscopy database. Gastrointest Endosc. (2012) 75:576–82. 10.1016/j.gie.2011.12.012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Schramm C, Scheller I, Franklin J, Demir M, Kuetting F, Nierhoff D, et al. Predicting ADR from PDR and individual adenoma-to-polyp-detection-rate ratio for screening and surveillance colonoscopies: A new approach to quality assessment. United European Gastroenterol J. (2017) 5:742–9. 10.1177/2050640616675220 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Calderwood AH. Jacobson BC. Comprehensive validation of the boston bowel preparation scale. Gastrointest Endosc. (2010) 72:686–92. 10.1016/j.gie.2010.06.068 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Atkin W, Wooldrage K, Brenner A, Martin J, Shah U, Perera S, et al. Adenoma surveillance and colorectal cancer incidence: a retrospective, multicentre, cohort study. Lancet Oncol. (2017) 18:823–34. 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30187-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ladabaum U, Dominitz JA, Kahi C. Schoen RE. Strategies for colorectal cancer screening. Gastroenterology. (2020) 158:418–32. 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.06.043 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Mandel JS, Church TR, Bond JH, Ederer F, Geisser MS, Mongin SJ, et al. The effect of fecal occult-blood screening on the incidence of colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. (2000) 343:1603–7. 10.1056/NEJM200011303432203 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Zauber AG, Winawer SJ., O', Brien MJ, Lansdorp-Vogelaar I, van Ballegooijen M, et al. Colonoscopic polypectomy and long-term prevention of colorectal-cancer deaths. N Engl J Med. (2012) 366:687–96. 10.1056/NEJMoa1100370 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kahi CJ, Imperiale TF, Juliar BE, Rex DK. Effect of screening colonoscopy on colorectal cancer incidence and mortality, Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2009) 7:770–5. 10.1016/j.cgh.2008.12.030 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Brenner H, Chang-Claude J, Seiler CM, Rickert A. Hoffmeister M. Protection from colorectal cancer after colonoscopy: a population-based, case-control study. Ann Intern Med. (2011) 154:22–30. 10.7326/0003-4819-154-1-201101040-00004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Doubeni CA, Weinmann S, Adams K, Kamineni A, Buist DS, Ash AS, et al. Screening colonoscopy and risk for incident late-stage colorectal cancer diagnosis in average-risk adults: a nested case-control study. Ann Intern Med. (2013) 158:312–20. 10.7326/0003-4819-158-5-201303050-00003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Brenner H, Chang-Claude J, Jansen L, Knebel P, Stock C. Hoffmeister M. Reduced risk of colorectal cancer up to 10 years after screening, surveillance, or diagnostic colonoscopy. Gastroenterology. (2014) 146:709–17. 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.09.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kaminski MF, Regula J, Kraszewska E, Polkowski M, Wojciechowska U, Didkowska J., et al. Quality indicators for colonoscopy and the risk of interval cancer. N Engl J Med. (2010) 362:1795–803. 10.1056/NEJMoa0907667 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Dekker E. Rex DK. Advances in CRC prevention: screening and surveillance. Gastroenterology. (2018) 154:1970–84. 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.01.069 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Baxter NN. Understanding postcolonoscopy colorectal cancers: the next frontier. Gastroenterology. (2016) 151:793–5. 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.09.039 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Patel SG. Ahnen DJ. Prevention of interval colorectal cancers: what every clinician needs to know. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2014) 12:7–15. 10.1016/j.cgh.2013.04.027 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Samadder NJ, Curtin K, Tuohy TM, Pappas L, Boucher K, Provenzale D, et al. Characteristics of missed or interval colorectal cancer and patient survival: a population-based study. Gastroenterology. (2014) 146:950–60. 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.01.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Strum WB. Colorectal adenomas. N Engl J Med. (2016) 374:1065–75. 10.1056/NEJMra1513581 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Corley DA, Jensen CD, Marks AR, Zhao WK, Lee JK, Doubeni CA, et al. Adenoma detection rate and risk of colorectal cancer and death. N Engl J Med. (2014) 370:1298–306. 10.1056/NEJMoa1309086 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Sastre Lozano VM, Morán Sánchez S, García Solano J, Conesa Zamora P. Ruiz Merino G. Relationship between the polyp detection rate and the post-colonoscopy colorectal cancer rate. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. (2019) 111:598–602. 10.17235/reed.2019.5889/2018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Zhao S, Deng XL, Wang L, Ye JW, Liu ZY, Huang B., et al. The impact of sedation on quality metrics of colonoscopy: a single-center experience of 48,838 procedures. Int J Colorectal Dis. (2020) 35:1155–61. 10.1007/s00384-020-03586-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Bannert C, Reinhart K, Dunkler D, Trauner M, Renner F, Knoflach P., et al. Sedation in screening colonoscopy: impact on quality indicators and complications. Am J Gastroenterol. (2012) 107:1837–48. 10.1038/ajg.2012.347 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Paspatis GA, Tribonias G, Manolaraki MM, Konstantinidis K, Chainaki I, Theodoropoulou A., et al. Deep sedation compared with moderate sedation in polyp detection during colonoscopy: a randomized controlled trial. Colorectal Dis. (2011) 13:e137–44. 10.1111/j.1463-1318.2011.02555.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Krigel A, Patel A, Kaplan J, Kong XF, Garcia-Carrasquillo R, Lebwohl B, et al. Anesthesia assistance in screening colonoscopy and adenoma detection rate among trainees. Dig Dis Sci. (2020) 65:961–8. 10.1007/s10620-019-05820-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Khan F, Hur C, Lebwohl B. Krigel A. Unsedated colonoscopy: impact on quality indicators. Dig Dis Sci. (2020) 65:3116–22. 10.1007/s10620-020-06491-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Zhang Q, Dong Z, Jiang Y, Zhan T, Wang J. Xu S. The impact of sedation on adenoma detection rate and cecal intubation rate in colonoscopy. Gastroenterol Res Pract. (2020) 2020:3089094. 10.1155/2020/3089094 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Chen CW, Chiu CT, Su MY, Lin CJ, Hsu CM, Lim SN, et al. Factors associated with polyp detection during colonoscopy: a retrospective observational study. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. (2019) 35:572–7. 10.1002/kjm2.12090 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Bond A., O, Toole P, Fisher G, Subramanian S, Haslam N, et al. New-Generation high-definition colonoscopes increase adenoma detection when screening a moderate-risk population for colorectal cancer. Clin Colorectal Cancer. (2017) 16:44–50. 10.1016/j.clcc.2016.07.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Atkinson N, Ket S, Bassett P, Aponte D, De Aguiar S, Gupta N., et al. Narrow-Band imaging for detection of neoplasia at colonoscopy: a meta-analysis of data from individual patients in randomized controlled trials. Gastroenterology. (2019) 157:462–71. 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.04.014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Vi?ovan II, Tan?ău M, Pascu O, Ciobanu L. Tan?ău A. The role of narrow band imaging in colorectal polyp detection. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. (2017) 17:152–8. 10.17305/bjbms.2017.1686 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Minamide T, Sashiyama H, Muramatsu Y, Yada T, Matsumura T, Takeda S, et al. Second-generation narrow-band imaging to detect colorectal adenomas: A prospective study including community hospitals, J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2021). 36:3084–91. 10.1111/jgh.15621 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Wong WJ, Arafat Y, Wang S, Hawes S. Hung K. Colonoscopy withdrawal time and polyp/adenoma detection rate: a single-site retrospective study in regional Queensland. ANZ J Surg. (2020) 90:314–6. 10.1111/ans.15652 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Rex DK, Schoenfeld PS, Cohen J, Pike IM, Adler DG, Fennerty MB, et al. Quality indicators for colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. (2015) 81:31–53. 10.1016/j.gie.2014.07.058 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Kaminski MF, Thomas-Gibson S, Bugajski M, Bretthauer M, Rees CJ, Dekker E., et al. Performance measures for lower gastrointestinal endoscopy: a European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) quality improvement initiative. Endoscopy. (2017) 49:378–97. 10.1055/s-0043-103411 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Chen H, Li N, Ren J, Feng X, Lyu Z, Wei L, et al. Participation and yield of a population-based colorectal cancer screening programme in China. Gut. (2019) 68:1450–7. 10.1136/gutjnl-2018-317124 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Zhou MJ, Lebwohl B. Krigel A. Patient and physician factors associated with adenoma and sessile serrated lesion detection rates. Dig Dis Sci. (2020) 65:3123–31. 10.1007/s10620-020-06419-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Sanaka MR, Rai T, Navaneethan U, Gohel TD, Podugu A, Thota PN, et al. Adenoma detection rate in high-risk patients differs from that in average-risk patients. Gastrointest Endosc. (2016) 83:172–8. 10.1016/j.gie.2015.04.019 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Sarvepalli S, Garber A, Rothberg MB, Mankaney G, McMichael J, Morris-Stiff G., et al. Association of adenoma and proximal sessile serrated polyp detection rates with endoscopist characteristics. JAMA Surg. (2019) 154:627–35. 10.1001/jamasurg.2019.0564 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Brooker JC, Saunders BP, Shah SG, Thapar CJ, Thomas HJ, Atkin WS, et al. Total colonic dye-spray increases the detection of diminutive adenomas during routine colonoscopy: a randomized controlled trial. Gastrointest Endosc. (2002) 56:333–8. 10.1016/S0016-5107(02)70034-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Kahi CJ, Anderson JC, Waxman I, Kessler WR, Imperiale TF Li X, et al. High-definition chromocolonoscopy vs. high-definition white light colonoscopy for average-risk colorectal cancer screening. Am J Gastroenterol. (2010) 105:1301–7. 10.1038/ajg.2010.51 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Calderwood AH, Thompson KD, Schroy PC 3rd, Lieberman DA, Jacobson BC. Good is better than excellent: bowel preparation quality and adenoma detection rates, Gastrointest Endosc. (2015) 81:691–9.e1. 10.1016/j.gie.2014.10.032 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Adike A, Buras MR, Gurudu SR, Leighton JA, Faigel DO, Ruff KC., et al. Is the level of cleanliness using segmental Boston bowel preparation scale associated with a higher adenoma detection rate. Ann Gastroenterol. (2018) 31:217–23. 10.20524/aog.2018.0231 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Asadzadeh Aghdaei H, Nazemalhosseini Mojarad E, Ashtari S, Pourhoseingholi MA, Chaleshi V, Anaraki F, et al. Polyp detection rate and pathological features in patients undergoing a comprehensive colonoscopy screening. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. (2017) 8:3–10. 10.4291/wjgp.v8.i1.3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Fu Z, Shrubsole MJ, Smalley WE, Wu H, Chen Z, Shyr Y, et al. Lifestyle factors and their combined impact on the risk of colorectal polyps. Am J Epidemiol. (2012) 176:766–76. 10.1093/aje/kws157 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Jung DK, Kim TO, Kang MS, Kim MS, Kim MS. Moon YS. The colonoscopist's expertise affects the characteristics of detected polyps. Clin Endosc. (2016) 49:61–8. 10.5946/ce.2016.49.1.61 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Spada C, Koulaouzidis A, Hassan C, Amaro P, Agrawal A, Brink L, et al. Factors associated with polyp detection rate in european colonoscopy practice: findings of the european colonoscopy quality investigation (ECQI) Group, Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2022) 19:3388. 10.3390/ijerph19063388 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.