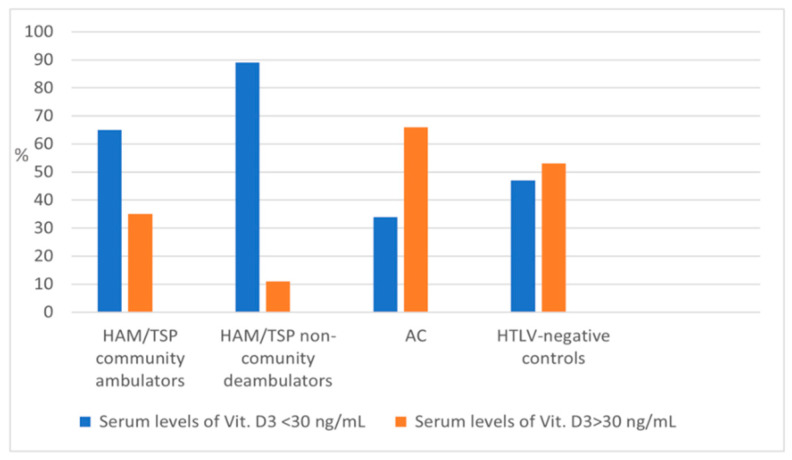
Error in Figure
In the original publication [1], there was a mistake in the Figure 1 labels of the vertical axis, which were not properly formatted: The values in the vertical axis were shown as RAL1900, due to an error in the figure’s uploading process. The correct values are 0, 20, 40, 60, 80 and 100.
Figure 1.
Proportion (%) of subjects with normal/abnormal vitamin D levels according to HTLV status and ambulation capacity.
The corrected Figure 1 appears below. The authors apologize for any inconvenience caused and state that the scientific conclusions are unaffected. The original publication has also been updated.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Reference
- 1.Netto E.C., Silva A.C., Pedroso C., Brites C. Hypovitaminosis D Is Associated with Higher Levels of Inflammatory Cytokines and with HAM/TSP in HTLV-Infected Patients. Viruses. 2021;13:2223. doi: 10.3390/v13112223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]