Abstract
Background
CCAAT/Enhancer Binding Protein D (CEBPD), a pleiotropic glucocorticoid-responsive transcription factor, modulates inflammatory responses. Of relevance to asthma, expression of CEBPD in airway smooth muscle (ASM) increases with glucocorticoid exposure. We sought to characterize CEBPD-mediated transcriptomic responses to glucocorticoid exposure in ASM by measuring changes observed after knockdown of CEBPD and its impact on asthma-related ASM function.
Methods
Primary ASM cells derived from four donors were transfected with CEBPD or non-targeting (NT) siRNA and exposed to vehicle control, budesonide (100 nM, 18 h), TNFα (10 ng/ml, 18 h), or both budesonide and TNFα. Subsequently, RNA-Seq was used to measure gene expression levels, and pairwise differential expression results were obtained for exposures versus vehicle and knockdown versus control conditions. Weighted gene co-expression analysis was performed to identify groups of genes with similar expression patterns across the various experimental conditions (i.e., CEBPD knockdown status, exposures).
Results
CEBPD knockdown altered expression of 3037 genes under at least one exposure (q-value < 0.05). Co-expression analysis identified sets of 197, 152 and 290 genes that were correlated with CEBPD knockdown status, TNFα exposure status, and both, respectively. JAK-STAT signaling pathway genes, including IL6R and SOCS3, were among those influenced by both TNFα and CEBPD knockdown. Immunoblot assays revealed that budesonide-induced IL-6R protein expression and augmented IL-6-induced STAT3 phosphorylation levels were attenuated by CEBPD knockdown in ASM.
Conclusions
CEBPD modulates glucocorticoid responses in ASM, in part via modulation of IL-6 receptor signaling.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s12931-022-02119-1.
Keywords: Airway smooth muscle, Asthma, CEBPD, Inflammatory response, Glucocorticoid response, RNA-Seq, TNFα
Background
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory respiratory disease characterized by variable airflow limitation and airway hyperresponsiveness to specific environmental stimuli that affects over 22 million Americans and incurs an annual cost of $81.9 billion in the U.S. [1]. Treatment of asthma according to established guidelines includes use of inhaled glucocorticoids to control symptoms in patients with persistent asthma, and “bursts” or long-term use of oral formulations to treat exacerbations or severe forms of asthma, respectively [2]. Chronic use of glucocorticoids elicits considerable adverse effects and may alter tissue sensitivity [3]. Studies to better understand glucocorticoid responses have thus been undertaken to identify mechanisms of resistance and improve personalized treatment strategies [3].
Airway smooth muscle (ASM) is a prominent asthma-related cell type that is directly involved in airway remodeling and airway narrowing [4, 5]. In addition to reducing inflammation, glucocorticoids reduce asthma symptoms by modulating other ASM-dependent processes, including impaired bronchodilation [6], airway hyperresponsiveness [7], and increased ASM contractility [8]. In cells, glucocorticoids exert some of their effects via direct modulation of gene transcription through glucocorticoid receptor (GR) binding to DNA at glucocorticoid response elements (GREs) [3]. Some targets of glucocorticoids include TNFα-inducible pro-inflammatory genes whose expression is modulated by nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) and interferons [9, 10].
CCAAT/Enhancer Binding Proteins (C/EBPs) are a family of six transcription factors that regulate immune responses, as well as cell growth, arrest and differentiation [11]. One of these proteins, CCAAT/enhancer binding protein δ (CEBPD), has been linked to various conditions with altered inflammatory responses [12], including cancers [13], lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury [14–16], pulmonary Aspergillus fumigatus conidia infection [17], atherosclerosis [18], and Alzheimer’s disease [19]. According to gene expression microarray and RNA-Seq studies, CEBPD expression increases with glucocorticoid exposure in ASM [20, 21]. Additionally, exposure to the glucocorticoid dexamethasone increases GR occupancy near CEBPD in A549 cells, suggesting that CEBPD is a primary glucocorticoid-responsive GR target [22]. Activation of CEBPD by inflammatory factors, including interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNFα), has also been observed in a variety of tissues, indicating that the modulation of inflammation by CEBPD involves complex tissue-specific signaling pathways that may have opposing outcomes depending on cellular context [12, 13, 23]. Inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6, induce the binding of C/EBPs to promoters of acute phase genes to control their transcription [23], and this binding can be inhibited by steroids [24, 25] via the activation of GR and direct interaction between GR and C/EBPs [26].
Previously, we identified hundreds of ASM glucocorticoid-responsive genes, most of which were consistently differentially expressed in cells derived from asthma donors versus donors without asthma [20]. The greatest difference in fold change based on asthma status that we observed among these genes was for CEBPD, suggesting that it may contribute to differences in glucocorticoid responses in people with asthma via complex interactions with signaling pathways involving pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNFα), which are also differentially expressed in asthma. Here, we sought to characterize the effects of CEBPD knockdown on the ASM transcriptomic response to glucocorticoid and TNFα exposures, as well as its impact on related ASM function.
Methods
Detailed methods are provided in the Additional file 1.
ASM RNA-Seq library construction, sequencing and data analysis
Total RNA was extracted from ASM cells derived from four non-asthma donors that were transfected with CEBPD or NT siRNA, and exposed to vehicle control, the glucocorticoid budesonide (BUD) (100 nM), TNFα (10 ng/ml), or BUD + TNFα for 18 h. Stranded RNA-Seq libraries were prepared and sequenced on an Illumina HiSeq 2500 instrument. RNA-Seq data are available in the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) under accession GSE146017.
The RAVED pipeline was used to analyze RNA-Seq data [27]. Differential expression analysis was performed for ten pairwise comparisons: CEBPD siRNA versus NT siRNA under the four exposure conditions (control, BUD, TNFα, BUD + TNFα); TNFα versus control in cells transfected with NT siRNA and CEBPD siRNA; and BUD versus control and BUD + TNFα versus TNFα in cells transfected with NT siRNA or CEBPD siRNA. Genes with Benjamini–Hochberg adjusted p-values (i.e., q-values) < 0.05 were considered significant. Results of individual gene’s expression across samples were visualized as boxplots, where the line in the center represents the median value, the box spans the inter-quartile range, and the whiskers show the minimum and maximum (without outliers) of the normalized read counts.
Weighted gene co-expression network analysis
Weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) was performed using the WGCNA R package [28] to identify groups of genes with similar expression patterns. Correlations between the resultant groups of genes and 11 phenotype variables (based on transfection, exposure, and donor status) were obtained.
Ontological category enrichment analysis
Overall gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) was performed using the fgsea R package [29]. For select WGCNA co-expression groups, enrichment analysis was performed using modified Fisher’s exact tests [30]. Ontological categories with q-values < 0.05 were considered significant.
ChIP-Seq data analysis
CEBPD-binding sites were identified using the brocade pipeline [31] applied to ChIP-Seq data from GEO entry GSE32465, which measured CEBPD binding in HepG2 and K562 cell lines [32].
Immunoblots
ASM cells derived from 6 non-asthma donors were transfected with CEBPD or NT siRNA and exposed to DMSO (control), IL-6 (10 ng/ml, 30 min), BUD (100 nM, 24 h), or BUD + IL-6. Immunoblot signals were developed for CEBPD, IL-6Rα, α Tubulin, STAT3, and phosphorylated STAT3 (pSTAT3) from protein samples and changes in band intensities were assessed with paired Student’s t-tests. The ratios of signals were visualized as barplots of height equivalent to the mean across donors and error bars representing standard errors (SEs) across replicates.
ASM traction microscopy
Primary human ASM cells from non-asthma donors were transfected with CEBPD or NT siRNA. Fourier transfer traction microscopy (FTTM) [33] was used to measure traction forces in cells at baseline or exposed to either the contractile agonist histamine (1 μM) or the β2-agonist isoproterenol (1 μM) for 5 min. Traction forces were normalized to the baseline traction and visualized as barplots of height equivalent to the mean across five donors and error bars representing SEs across replicates.
Results
RNA-Seq data met quality control (QC) considerations
Thirty-two ASM samples corresponding to four non-smoking donors without chronic disease, four exposure conditions and either CEBPD or NT siRNA transfection status were prepared. Expression of CEBPD in knockdown cells compared to their donor-paired NT siRNA-transfected cells was decreased an average of 67% according to RT-qPCR measurements for all but one sample that showed no change in CEBPD expression levels and thus, was excluded from RNA-Seq library preparation, resulting in 31 samples selected for RNA-Seq (Additional file 1: Fig. E1). These RT-qPCR measurements also showed that CXCL8 expression increased more than tenfold with TNFα exposure, demonstrating an expected pro-inflammatory response, and the increased CXCL8 expression was blunted by BUD, demonstrating an expected decrease in inflammatory response with glucocorticoid exposure. The RNA-Seq data for the 31 samples sequenced was deemed of high quality (Additional file 1: Fig. E2A, B, Table E1), and all samples were included in differential expression analyses. Normalized CEBPD read counts decreased by 70% in the knockdown cells compared to NT siRNA transfected cells (Additional file 1: Fig. E2C). In NT siRNA cells, genes differentially expressed in response to BUD exposure included well-known glucocorticoid-responsive genes (e.g., FKBP5, TSC22D3, GLUL, PER1, CRISPLD2) [20, 21]. Genes differentially expressed in response to TNFα exposure included well-known pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL6, CXCL8) [9, 10].
Overall ASM transcriptomic changes in response to CEBPD knockdown
Comparison of CEBPD siRNA versus NT siRNA samples found 1,617, 1,459, 1,330 and 1,985 differentially expressed genes within control, TNFα, BUD and BUD + TNFα exposure conditions, respectively (Table 1). A total of 3037 genes were differentially expressed under at least one of these exposure conditions, and 588 of the genes were in common across the four exposure groups. The five top-ranked genes influenced by CEBPD knockdown according to lowest q-value for each of the four exposure conditions, representing 13 unique genes, included TNFRSF10D, a TNF receptor gene with an inhibitory role in apoptosis [34], whose expression was increased by CEBPD knockdown, and TXNIP, an NF-κB inhibitor gene [35] whose expression was decreased by CEBPD knockdown (Table 2). GSEA found that 23 ontological categories were significantly enriched in at least one exposure group with CEBPD knockdown (Additional file 1: Table E2, Fig. E3). Seven of these categories were shared across all exposures: peptide chain elongation, ribosome, 3' UTR mediated translational regulation, influenza viral RNA transcription and replication, nonsense mediated decay enhanced by the exon junction, SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane, and influenza life cycle.
Table 1.
Number of significantly differentially expressed genes in various comparisons
| Genes whose expression differed with CEBPD knockdown | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CEBPD siRNA versus NT siRNA across various exposures | |||||
| Control | TNFα | BUD | BUD + TNFα | Overlap | Total |
| 1617 | 1459 | 1330 | 1985 | 588 | 3037 |
| Genes whose expression differed with TNFα and/or budesonide exposure | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NT siRNA | CEBPD siRNA | Overlap | Total | |
| TNFα versus control | 2315 | 1953 | 1515 | 2753 |
| BUD versus control | 470 | 421 | 276 | 615 |
| BUD + TNFα versus TNFα | 535 | 474 | 264 | 745 |
BUD budesonide
Genes with q-value < 0.05 are considered significant
Table 2.
Top differentially expressed genes in CEBPD siRNA versus NT siRNA cells under exposures of control, BUD, TNFα, or BUD + TNFα
| Gene symbol (gene name) | Ensembl ID | Control | BUD | TNFα | BUD + TNFα | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log2 FC |
Q-value | Mean normalized counts | Log2 FC |
Q-value | Mean normalized counts | Log2 FC |
Q-value | Mean normalized counts | Log2 FC |
Q-value | Mean normalized counts | ||||||
| NT | CEBPD | NT | CEBPD | NT | CEBPD | NT | CEBPD | ||||||||||
| CEBPD (CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP), delta) | ENSG00000221869 | − 1.73 | 6.40E−54 | 1086 | 328 | − 1.84 | 2.20E−30 | 1578 | 465 | − 1.47 | 4.70E−14 | 897 | 322 | − 1.48 | 2.70E−38 | 1139 | 411 |
| TNFRSF10D (tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 10d) | ENSG00000173530 | 1.47 | 3.40E−43 | 1153 | 3071 | 1.11 | 1.20E−21 | 1126 | 2053 | 1.15 | 8.10E−03 | 1074 | 2621 | 1.11 | 9.10E−23 | 918 | 2045 |
| CDKN1A (cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A (p21, Cip1)) | ENSG00000124762 | 1.07 | 6.80E−39 | 6008 | 12,477 | 1.30 | 6.20E−42 | 5028 | 10,959 | 1.19 | 4.20E−29 | 4853 | 10,939 | 1.21 | 8.30E−20 | 4720 | 10,733 |
| PDIA4 (protein disulfide isomerase family A member 4) | ENSG00000155660 | − 1.69 | 2.00E−37 | 3825 | 1197 | − 1.38 | 4.00E−33 | 3203 | 1204 | − 1.61 | 1.30E−44 | 5132 | 1686 | − 1.66 | 2.90E−29 | 4427 | 1412 |
| RPS15 (ribosomal protein S15) | ENSG00000115268 | − 1.25 | 7.30E−31 | 2974 | 1268 | − 1.15 | 2.00E−27 | 3090 | 1470 | − 1.19 | 1.50E−53 | 2745 | 1201 | − 1.37 | 3.00E−45 | 2945 | 1142 |
| DPP4 (dipeptidyl-peptidase 4) | ENSG00000197635 | − 1.19 | 3.20E−26 | 1877 | 831 | − 1.08 | 5.00E−15 | 1882 | 1124 | − 1.18 | 2.10E−26 | 3342 | 1477 | − 1.17 | 9.20E−35 | 3793 | 1693 |
| TXNIP (thioredoxin interacting protein) | ENSG00000265972 | − 1.37 | 4.10E−25 | 3320 | 1317 | − 1.13 | 3.00E−18 | 3708 | 1876 | − 1.36 | 1.40E−37 | 2387 | 952 | − 1.46 | 2.70E−21 | 2544 | 1018 |
| ELN (elastin) | ENSG00000049540 | 1.21 | 3.80E−23 | 7693 | 16,628 | 1.00 | 5.20E−04 | 14,062 | 26,557 | 1.46 | 6.70E−29 | 5276 | 12,817 | 1.42 | 6.90E−33 | 6815 | 15,927 |
| VGLL3 (vestigial like family member 3) | ENSG00000206538 | − 1.09 | 1.10E−22 | 2351 | 1096 | − 0.88 | 8.60E−09 | 3369 | 1924 | − 1.00 | 9.80E−33 | 2038 | 1020 | − 0.70 | 3.20E−08 | 2966 | 1832 |
| CPM (carboxypeptidase M) | ENSG00000135678 | − 1.28 | 1.30E−18 | 896 | 385 | − 1.40 | 2.50E−18 | 728 | 237 | − 1.39 | 5.60E−24 | 1053 | 407 | − 1.26 | 3.60E−33 | 1043 | 440 |
| IGFBP5 (insulin like growth factor binding protein 5) | ENSG00000115461 | − 0.58 | 3.50E−06 | 251,976 | 174,891 | − 0.36 | 5.80E−01 | 179,541 | 140,387 | − 1.02 | 3.50E−29 | 253,204 | 127,426 | − 1.06 | 3.10E−27 | 165,764 | 78,967 |
| ADH1B (alcohol dehydrogenase 1B (class I), beta polypeptide) | ENSG00000196616 | − 2.06 | 2.70E−04 | 6291 | 1905 | − 2.18 | 7.50E−76 | 11,133 | 2493 | − 2.29 | 1.10E−04 | 2143 | 693 | − 1.97 | 3.20E−05 | 5099 | 1540 |
| PRELP (proline/arginine-rich end leucine-rich repeat protein) | ENSG00000188783 | − 1.66 | 7.80E−02 | 500 | 142 | − 2.35 | 7.60E−39 | 657 | 149 | − 1.53 | 4.20E−02 | 367 | 116 | − 1.06 | 3.80E−01 | 366 | 223 |
Top five genes with smallest q-values were selected from each comparison yielding 13 genes in total
Influence of CEBPD knockdown on ASM transcriptomic response to TNFα exposure
When comparing TNFα versus control exposure, there were 2315 and 1953 differentially expressed genes in NT siRNA and CEBPD siRNA cells, respectively, 1515 of which were in common (Table 1). The log2 fold changes corresponding to the differentially expressed genes were broadly similar in NT siRNA and CEBPD siRNA cells (Additional file 1: Fig. E4A). The five top-ranked genes according to lowest q-value whose expression was altered by TNFα in each of the two transfection status conditions, representing seven unique genes, are shown in Table 3. Although these seven genes, which included the cytokines IL32 and IL6, were significantly differentially expressed regardless of CEBPD knockdown status, genes such as IER3 and ICAM1 had reduced levels of expression with CEBPD knockdown and were significantly differentially expressed when comparing CEBPD knockdown versus NT siRNA status within TNFα-exposed cells (q-value = 7.73 × 10–5 for IER3 and 5.47 × 10–4 for ICAM1). GSEA found that the ontological categories overrepresented by genes in response to TNFα exposure were the same regardless of knockdown status (Additional file 1: Table E3, Fig. E5). In contrast, the ontological categories obtained for the CEBPD siRNA versus NT siRNA comparison among TNFα-exposed cells found that the categories smooth muscle contraction and nitric oxide stimulates guanylate cyclase were affected by CEBPD knockdown (Additional file 1: Table E2, Fig. E3). Individual genes that drove these differences in ontological category overrepresentation included ITGA1 and MYL9 for smooth muscle contraction (CEBPD siRNA versus NT siRNA q-value = 2.24 × 10–17 and 3.95 × 10–8, respectively) and GUCY1B3 and MRVI1 for nitric oxide stimulates guanylate cyclase (CEBPD siRNA versus NT siRNA q-value = 6.92 × 10–3 and 1.08 × 10–14, respectively) (Additional file 1: Fig. E6).
Table 3.
Top differentially expressed genes in TNFα versus control in NT siRNA or CEBPD siRNA cells
| Gene symbol (gene name) | Ensembl ID | NT siRNA | CEBPD siRNA | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| log2FC | Q-value | Mean normalized counts | log2FC | Q-value | Mean normalized counts | ||||
| no TNFα | TNFα | no TNF | TNFα | ||||||
| IL32 (interleukin 32) | ENSG00000008517 | 3.04 | 6.50E−118 | 284 | 2213 | 3.27 | 5.20E−189 | 237 | 2306 |
| IL6 (interleukin 6) | ENSG00000136244 | 3.57 | 3.10E−80 | 892 | 11,217 | 3.56 | 8.50E−97 | 878 | 10,187 |
| TNFAIP3 (TNF alpha induced protein 3) | ENSG00000118503 | 3.40 | 5.30E−79 | 901 | 9453 | 3.36 | 5.50E−27 | 916 | 9196 |
| COL7A1 (collagen, type VII, alpha 1) | ENSG00000114270 | 1.40 | 1.90E−75 | 3896 | 10,229 | 1.60 | 7.70E−58 | 3237 | 9913 |
| NFKB2 (nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 2 (p49/p100)) | ENSG00000077150 | 2.13 | 2.70E−70 | 666 | 2909 | 2.26 | 1.90E−86 | 515 | 2463 |
| IER3 (immediate early response 3) | ENSG00000137331 | 1.95 | 1.70E−50 | 1141 | 4313 | 1.89 | 3.50E−83 | 797 | 2903 |
| ICAM1 (intercellular adhesion molecule 1) | ENSG00000090339 | 3.20 | 2.20E−24 | 490 | 4243 | 3.45 | 1.00E−68 | 268 | 2715 |
Top five genes with smallest q-values were selected from each comparison yielding seven genes in total
Influence of CEBPD knockdown on ASM transcriptomic response to budesonide exposure
When comparing BUD versus control exposure, there were 470 and 421 differentially expressed genes among NT siRNA and CEBPD siRNA samples, respectively, 276 of which were in common (Table 1). When comparing BUD + TNFα versus TNFα exposure, there were 535 and 474 differentially expressed genes in NT siRNA and CEBPD siRNA, respectively, 264 of which overlapped. Table 4 lists the five top-ranked genes according to q-value for BUD versus control or BUD + TNFα versus TNFα in either transfection condition, yielding 15 unique genes, which include the well-known glucocorticoid-responsive genes GLUL and DUSP1 [20, 21]. Some top-ranked genes, such as IL1B and PTGS2, had expression levels that were highly induced by TNFα exposure (TNFα versus control q-values < 10–10) and therefore, had greater observed differences in expression with glucocorticoid exposure in the BUD + TNFα co-stimulation than the BUD condition. Overall, however, the log2 fold changes of the differentially expressed genes in BUD versus control and BUD + TNFα versus TNFα were broadly similar by transfection status (Additional file 1: Fig. E4B, C).
Table 4.
Top differentially expressed genes in BUD versus control and BUD + TNFα versus TNFα in NT siRNA or CEBPD siRNA cells
| Gene symbol (gene name) | Ensembl ID | BUD versus control in NT siRNA | BUD versus control in CEBPD siRNA | BUD + TNF versus TNFα in NT siRNA | BUD + TNF versus TNFα in CEBPD siRNA |
||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log2 FC |
Q-value | Mean normalized counts | Log2 FC |
Q-value | Mean normalized counts | Log2 FC |
Q-value | Mean normalized counts | Log2 FC |
Q-value | Mean normalized counts | ||||||
| No BUD | BUD | No BUD | BUD | No BUD | BUD | No BUD | BUD | ||||||||||
| PER3 (period circadian clock 3) | ENSG00000049246 | − 2.58 | 8.10E−81 | 602 | 101 | − 2.26 | 1.00E−37 | 456 | 107 | − 2.80 | 7.60E−34 | 287 | 43 | − 2.67 | 1.00E−21 | 217 | 37 |
| ANGPTL2 (angiopoietin like 2) | ENSG00000136859 | − 1.05 | 3.90E−33 | 3939 | 1889 | − 1.20 | 2.70E−40 | 3603 | 1608 | − 1.06 | 2.20E−32 | 1624 | 782 | − 1.13 | 6.80E−24 | 1580 | 712 |
| GLUL (glutamate-ammonia ligase) | ENSG00000135821 | 0.87 | 9.90E−33 | 3762 | 6921 | 0.58 | 2.00E−16 | 2859 | 4276 | 0.46 | 5.30E−08 | 3276 | 4504 | 0.21 | 5.90E−02 | 2671 | 3091 |
| DUSP1 (dual specificity phosphatase 1) | ENSG00000120129 | 0.95 | 8.40E−27 | 1279 | 2440 | 0.61 | 4.00E−15 | 2010 | 2801 | 0.60 | 4.30E−02 | 2464 | 3809 | 0.56 | 5.10E−09 | 3249 | 4834 |
| MAOA (monoamine oxidase A) | ENSG00000189221 | 1.58 | 8.40E−27 | 213 | 600 | 1.82 | 2.20E−02 | 165 | 334 | 1.57 | 4.20E−06 | 275 | 724 | 1.61 | 1.60E−17 | 182 | 561 |
| ADH1B (alcohol dehydrogenase 1B (class I), beta polypeptide) | ENSG00000196616 | 0.82 | 3.70E−14 | 6291 | 11,133 | 1.23 | 3.90E−50 | 1905 | 2493 | 1.40 | 6.50E−04 | 2143 | 5099 | 1.71 | 6.00E−03 | 693 | 1540 |
| MMP10 (matrix metallopeptidase 10) | ENSG00000166670 | − 1.12 | 1.90E−13 | 615 | 313 | − 0.71 | 9.70E−03 | 620 | 140 | − 1.17 | 6.00E−22 | 1457 | 665 | − 1.10 | 3.90E−33 | 1911 | 901 |
| NRG1 (neuregulin 1) | ENSG00000157168 | − 0.94 | 1.30E−12 | 1095 | 538 | − 0.85 | 1.40E−10 | 1476 | 416 | − 1.18 | 1.00E−28 | 2334 | 1111 | − 1.03 | 7.70E−46 | 3254 | 1626 |
| NR1D2 (nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group D member 2) | ENSG00000174738 | − 0.75 | 3.80E−11 | 1871 | 1116 | − 0.50 | 3.90E−08 | 1888 | 1250 | − 1.06 | 1.70E−26 | 1572 | 743 | − 0.74 | 4.90E−14 | 1493 | 888 |
| GABBR2 (gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) B receptor, 2) | ENSG00000136928 | 0.86 | 4.00E−11 | 427 | 739 | 1.16 | 3.50E−02 | 529 | 868 | 1.20 | 4.30E−21 | 393 | 854 | 1.50 | 6.30E−30 | 482 | 1294 |
| PTX3 (pentraxin 3) | ENSG00000163661 | 0.69 | 1.50E−10 | 1778 | 2645 | 0.81 | 2.10E−02 | 1729 | 3765 | 1.24 | 7.10E−36 | 3294 | 8292 | 0.83 | 1.90E−25 | 3512 | 6464 |
| KLF9 (Kruppel-like factor 9) | ENSG00000119138 | 0.75 | 2.50E−10 | 1692 | 2736 | 0.91 | 5.40E−29 | 1694 | 2361 | 0.55 | 1.40E−08 | 1472 | 2142 | 0.94 | 2.30E−13 | 1680 | 3156 |
| MMP1 (matrix metallopeptidase 1) | ENSG00000196611 | − 0.93 | 1.90E−06 | 19,142 | 10,575 | − 0.88 | 1.80E−36 | 22,018 | 11,185 | − 0.84 | 8.40E−14 | 78,174 | 47,428 | − 1.00 | 6.50E−25 | 70,242 | 37,456 |
| IL1B (interleukin 1 beta) | ENSG00000125538 | − 1.05 | 2.50E−02 | 68 | 35 | − 1.80 | 8.00E−06 | 97 | 35 | − 1.54 | 1.60E−05 | 911 | 349 | − 1.62 | 5.20E−34 | 1217 | 454 |
| PTGS2 (prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 (prostaglandin G/H synthase and cyclooxygenase)) | ENSG00000073756 | − 0.83 | 1.20E−01 | 946 | 565 | − 0.85 | 1.30E−12 | 928 | 549 | − 1.78 | 2.00E−15 | 5682 | 1671 | − 1.30 | 2.00E−48 | 6348 | 2738 |
Top five genes with smallest q-values were selected from each comparison yielding 15 genes in total
We found that 23 ontological categories were significantly enriched in at least one of the four comparisons involving BUD (i.e., BUD versus control in: (1) NT siRNA, and (2) CEBPD siRNA samples; and BUD + TNFα versus TNFα in: (3) NT siRNA, and (4) CEBPD siRNA samples; Additional file 1: Table E4 and Fig. E7). Six of these categories were shared across the four comparisons, including smooth muscle contraction, suggesting that contraction-related gene expression changes were influenced by BUD regardless of transfection or TNFα co-stimulation status. In contrast, some categories were enriched only under conditions that also involved CEBPD knockdown and/or TNFα exposure. For example, the cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction category was not enriched in the BUD versus control within NT siRNA condition, but it was enriched in the BUD versus control within CEBPD knockdown and/or TNFα exposure conditions due to the differential expression of genes such as IL6, IL1A, and IL1B observed under the latter conditions. An example of a category that was enriched only with co-stimulation of TNFα was extracellular matrix organization, which was driven by the collagen-related genes COL12A1, COL7A1, COL5A3 and COL13A1 that were differentially expressed with TNFα + BUD exposure but not BUD alone.
Identification of gene co-expression groups and their association with CEBPD knockdown and TNFα exposure status
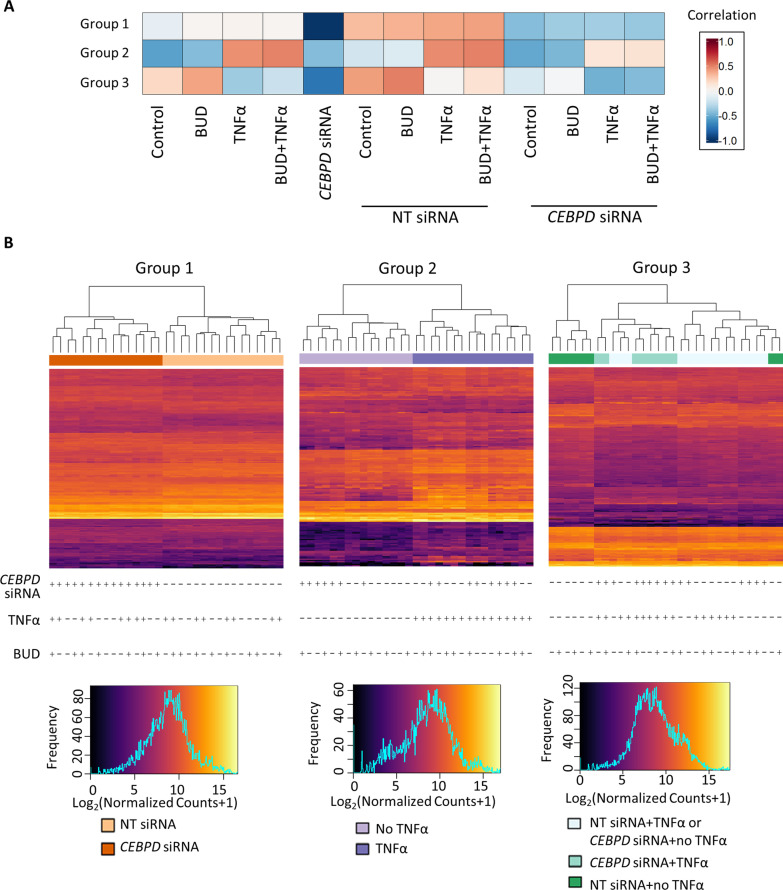
We selected the 1,365 genes that were differentially expressed with CEBPD knockdown in any exposure condition for WGCNA analysis. Soft-thresholding power (β) of 18 was chosen to generate an unsigned weighted co-expression network (Additional file 1: Fig. E8). Of eight groups of co-expressed genes identified, three that were significantly correlated with CEBPD knockdown or exposure status, but not donor status, were considered further (Additional file 1: Fig. E9). Correlation coefficients showed that Group 1 (composed of 197 genes) was correlated with CEBPD knockdown status only, Group 2 (composed of 152 genes) was correlated with TNFα exposure status, and Group 3 (composed of 290 genes) was correlated with both CEBPD knockdown and TNFα exposure status (Fig. 1A). To a lesser extent, Groups 2 and 3 were correlated with BUD exposure (p < 0.05). Hierarchical clustering using gene expression levels (i.e., log2(normalized counts + 1)) of the genes in each co-expression group clustered the 31 samples according to their transfection and/or TNFα exposure status, consistent with phenotypes that they were associated with (Fig. 1B). Group 3 subjects were not perfectly clustered, which may be due to the slight correlation between their eigengenes and donor status. In terms of ontological categories overrepresented by the eigengenes, Group 1 contained genes involved in regulation of actin cytoskeleton; Group 2 contained genes involved in interferon, cytokine-cytokine, and JAK-STAT signaling; and Group 3 contained genes involved in translation, influenza viral RNA transcription and replication, and JAK-STAT signaling (Additional file 1: Table E5).
Fig. 1.
Gene co-expression groups associated with various exposures. A Heatmap of correlations between eigengenes and 13 experimental conditions in three gene co-expression groups. B Heatmaps of gene expression represented by log2(normalized count + 1) for all 31 samples in three gene co-expression groups. Samples in these group can be distinguished based on CEBPD siRNA status, TNFα exposure status and both. BUD budesonide, NT non-targeting
JAK-STAT signaling pathway genes co-expressed in response to both CEBPD knockdown and TNFα exposure
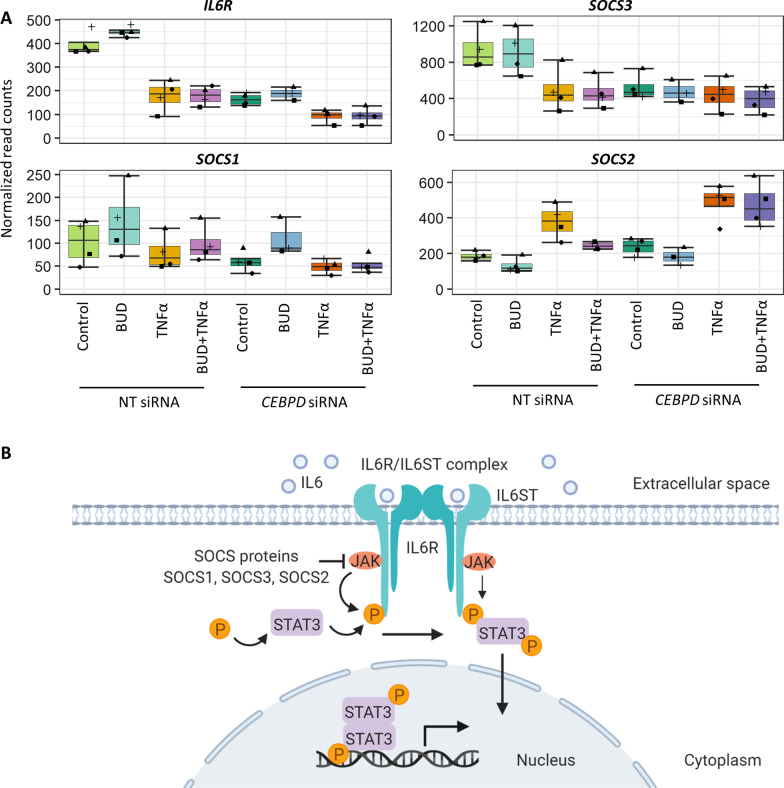
The Group 2 (TNFα exposure-associated) JAK-STAT signaling pathway genes that were overrepresented included IL10RB, IL13RA2, IL15RA, IL7R, LEP, STAT1, STAT4, while the Group 3 (CEBPD knockdown- and TNFα exposure-associated) JAK-STAT signaling pathway genes included CCND3, IL24, IL6R, LIF, PIM1, SOCS1, SOCS2, SOCS3, SPRY4. We focused further on the JAK-STAT signaling pathway genes in Group 3 because its co-expression patterns were associated with a combined phenotype that most relates to the influence of CEBPD on asthma glucocorticoid responses. RNA-Seq results for IL6R, SOCS3, SOCS1 and SOCS2—genes known to participate in IL-6 signaling pathways—across all conditions showed that their expression levels differed with TNFα exposure versus control within the NT siRNA samples differently than within the CEBPD siRNA samples, consistent with the Group 3 phenotype (Fig. 2; Additional file 1: Table E6). Analysis of a ChIP-Seq dataset involving HepG2 and K562 cells found putative CEBPD-binding sites near the transcription start sites (TSS) of each of these four genes, suggesting that CEBPD can directly modulate their transcription (Additional file 1: Fig. E10).
Fig. 2.
CEBPD knockdown influenced ASM expression of genes in the IL-6 receptor signaling pathway. A Expression levels of IL6R, SOCS3, SOCS1, and SOCS2 in response to control, BUD, TNFα, and BUD + TNFα exposures in NT siRNA and CEBPD siRNA transfected cells obtained with RNA-Seq data show that CEBPD knockdown altered their response to BUD, TNFα and/or BUD + TNFα exposure. Boxplots show the median value at the center line, the box spans the inter-quartile range, and the whiskers span the minimum and maximum (without outliers) of normalized read counts (N = 3–4 donors per condition). Individual read count values are displayed as points. B IL-6 receptor signaling pathway diagram indicating known relationships among IL-6R, SOCS and STAT3 proteins. BUD budesonide, NT non-targeting
CEBPD knockdown blunted IL6-induced IL-6R signaling in ASM
Given that IL-6R had the strongest effect among the IL-6 signaling genes with CEBPD knockdown according to RNA-Seq data, we sought to determine the role of CEBPD knockdown on IL-6-induced IL-6R signaling pathways by measuring changes of IL-6R protein levels and downstream phosphorylation of STAT3 (Fig. 2B). The CEBPD siRNA-transfected cells had decreased levels of CEBPD under control exposure relative to NT siRNA samples, a difference that was starker with the BUD exposure induction of CEPBD, suggesting that the knockdown effectively reduced CEBPD protein levels (Additional file 1: Fig. E11). The increase in CEBPD that was elicited with BUD exposure in NT siRNA-transfected cells (p < 0.05) was substantially diminished with CEBPD knockdown (Fig. 3A). In NT siRNA-transfected cells, IL-6R protein levels were significantly increased with BUD versus control exposure (p < 0.001), a change that was abrogated with CEBPD knockdown (Fig. 3B). The expected IL-6R-mediated induction of pSTAT3 by IL-6 was observed in both NT and CEBPD siRNA transfected cells (p-value < 0.005), and while BUD exposure further augmented pSTAT3 levels in NT siRNA transfected cells (p-value < 0.05), this effect was reduced with CEBPD knockdown (Fig. 3C).
Fig. 3.
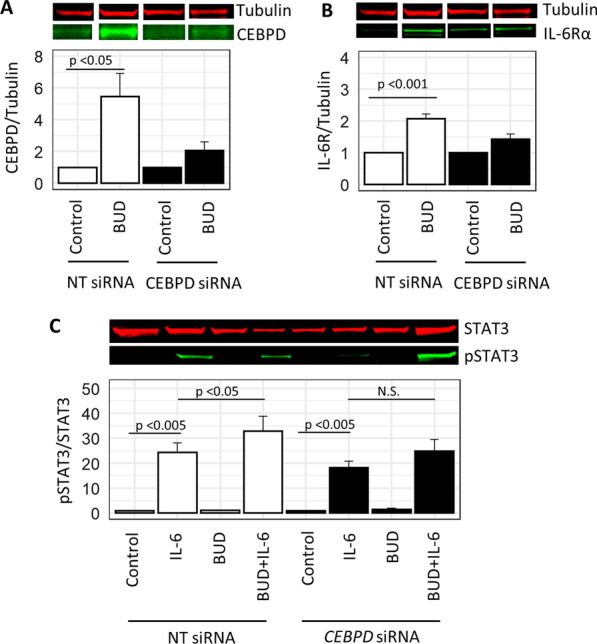
CEBPD knockdown blunted IL-6 receptor protein expression and signaling in ASM. A Representative immunoblot lanes for tubulin and CEBPD expression. Immunoblot band density quantification results for CEBPD (normalized to tubulin under NT siRNA control or CEBPD siRNA control within groups) show that its levels were induced by BUD exposure among NT siRNA-transfected samples, an effect that was substantially reduced with CEBPD siRNA transfection. B Representative immunoblot lanes for tubulin and IL-6R expression. Immunoblot band density quantification results for IL-6R (normalized to tubulin under NT siRNA control or CEBPD siRNA control within groups) were significantly increased with BUD versus control exposure among NT siRNA-transfected cells, an effect that not was significant for BUD versus control exposures with CEBPD knockdown. C Representative immunoblot results examining pSTAT3 normalized to total STAT3 expression under NT siRNA control or CEBPD siRNA control within groups. pSTAT3 was induced with IL-6 exposure and further augmented with addition of BUD exposure in NT siRNA transfected cells. The augmented pSTAT3 induced by BUD + IL-6 versus IL-6 was no longer significant with CEBPD knockdown. Barplots of signal ratios are of height equivalent to the mean across donors, and the error bars represent standard errors (SEs) across replicates with N = 6 donors per condition. Intact immunoblot bands are provided in Additional file 1: Fig. E11. BUD budesonide, NT non-targeting, pSTAT3 phosphorylated STAT3
CEBPD influenced baseline ASM contractility
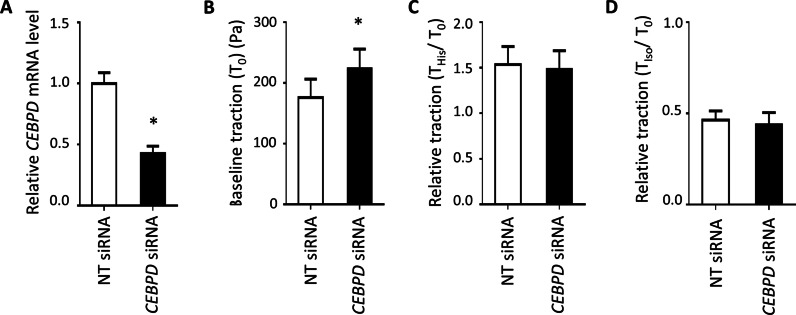
CEBPD siRNA transfection efficiency in ASM cells was confirmed to be 58% for this experiment (Fig. 4A). At baseline, the average cell traction force was significantly higher (p-value < 0.05) in CEBPD knockdown cells (224.4 ± 31.6 Pa, mean ± standard error hereafter) compared to cells transfected with NT siRNA (176.1 ± 30.3 Pa) (Fig. 4B). ASM traction was increased by histamine (contractile agonist) and decreased by isoproterenol (β2 agonist) relative to baseline levels, but these responses did not significantly differ with CEBPD knockdown (Fig. 4C, D).
Fig. 4.
CEBPD influenced baseline ASM contractility. A CEBPD expression reduction in ASM was confirmed using qPCR 48 h after siRNA transfection. B CEBPD knockdown in ASM cells led to a statistically significant higher traction at baseline (T0). CEBPD knockdown in ASM cells did not alter C the contractile response to histamine (His) or D the relaxation response to isoproterenol (Iso) based on the relative traction values. Barplots are of height equivalent to the mean across five donors, and error bars represent standard errors (SEs) across replicates with N = 5 donors per condition. *p-value < 0.05. NT non-targeting
Discussion
We and others have observed a large number of glucocorticoid-responsive genes in ASM cells [20, 21, 36, 37]. Our most recent study found that CEBPD had the largest difference in glucocorticoid-induced expression changes in ASM from non-asthma donors versus fatal asthma donors (log2 fold change of 1.43 versus 0.48 with budesonide exposure) [20], suggesting that differing levels of CEBPD expression may influence glucocorticoid responsiveness in people with asthma. Our present study characterized the ASM transcriptomic responses to glucocorticoid and TNFα exposures in the context of CEBPD knockdown, which involved performing 10 pairwise differential expression comparisons. Due to the large number of differentially expressed genes observed among these many comparisons, we performed a weighted gene co-expression analysis to identify the groups of genes specifically changed in response to CEBPD knockdown in the context of other relevant exposures, thereby facilitating the identification of individual genes and pathways for validation studies of our main trait of interest.
Pairwise differential expression results revealed many changes in ASM with CEBPD knockdown, a large proportion of which were specific to exposure conditions. Our pathway-level results of these exposures recapitulated known pathways, including that TNFα is involved in innate immunity and interferon signaling, and that glucocorticoids alter cytokine-cytokine receptor signaling and smooth muscle contraction. The large number of differentially expressed genes observed in CEBPD siRNA versus NT siRNA transfected samples under glucocorticoid and/or TNFα exposures included expected findings, such as changes in genes related to the ontological categories interferon signaling and downstream signaling events of B cell receptor, as well as novel findings of relevance to asthma, such as the alteration of genes involved in smooth muscle contraction and nitric oxide stimulates guanylate cyclase. Although many genes from among these comparisons are of interest to better understand asthma, we proceeded with WGCNA to focus on groups of genes with similar changes across exposures and transfection status.
WGCNA identifies gene co-expression groups based on their topological similarity across samples, and it is able to identify relationships of these co-expression groups with multiple phenotypes under consideration [28]. We tailored WGCNA to our study goals by (1) including differentially expressed genes from the CEBPD siRNA versus NT siRNA across the four exposure comparisons, and (2) constructing networks that included connections regardless of the direction of expression changed by CEBPD knockdown (i.e., we used an unsigned correlation network). Although use of a selected set of genes biases the identification of gene co-expression groups, in this case, it allowed us to identify three salient gene co-expression groups with expression patterns corresponding to CEBPD knockdown and/or TNFα exposure status. We verified that individual genes within the groups had results consistent with their grouping: CEBPD was among the genes in Group 1 (CEBPD knockdown-associated) and many cytokine-related genes were among the genes in Group 2 (TNFα exposure-associated). Interestingly, TNFα exposure and CEBPD knockdown resulted in greater transcriptomic effects than budesonide: (1) there were substantially more differentially expressed genes identified in the pairwise TNFα versus control or CEBPD siRNA versus NT siRNA, than BUD versus control conditions, and (2) none of the gene co-expression groups were highly correlated with budesonide exposure status. Therefore, Group 3 was deemed most relevant to our question of understanding the impact of CEBPD on asthma-related gene expression changes. The Group 3 (CEBPD knockdown- and TNFα exposure-associated) JAK-STAT pathway genes included some whose expression was decreased with CEBPD knockdown (e.g., IL6R, SOCS3, SOCS1) and some whose expression changed in the opposite direction (e.g., SOCS2), demonstrating that WGCNA was helpful to identify sets of genes that changed under specific conditions, regardless of the direction of this change. Comparison of JAK-STAT pathway genes in Group 3 versus Group 2 was helpful to identify the TNFα-modulated ones that were also changed by CEBPD knockdown, which led us to select the IL-6R pathway for further study.
Consistent with RNA-Seq results showing that IL-6R transcript levels were substantially reduced with CEBPD knockdown in the BUD versus control exposure comparison, immunoblot results showed that CEBPD knockdown resulted in decreased IL-6R protein expression when comparing BUD versus control exposures. Extension of RNA-Seq results to the protein level also revealed that IL-6 receptor signaling vis-à-vis IL-6-induced pSTAT3 expression remained intact, although the fold-change of pSTAT3 induced with BUD + IL-6 versus IL-6 alone was only statistically significantly different among NT siRNA-transfected cells, suggesting an overall reduction of IL-6R signaling with CEBPD knockdown. Future studies are needed to investigate more detailed mechanisms whereby altered CEBPD expression and its posttranslational modifications affect IL-6R signaling in ASM to influence glucocorticoid responses in asthma.
Smooth muscle contraction pathway genes were enriched in (1) genes differentially expressed with CEBPD knockdown under the condition of TNFα exposure and (2) genes differentially expressed with budesonide exposure regardless of CEBPD knockdown status. The traction microscopy results support a potential modest effect of CEBPD knockdown on ASM contractile force at baseline, however, CEBPD had little effect on ASM excitation–contraction coupling. Together, these results suggest that CEBPD alone is not likely to directly regulate ASM contractility in response to glucocorticoid exposure.
Several limitations of our study are worth noting. First, we did not determine whether CEBPD modulated IL6 signaling via membrane-bound IL-6R or trans-signaling of its soluble form. Because prior studies found that membrane-bound IL-6R was not present in ASM, while its soluble form was [38], it is likely that CEBPD influences the IL-6 pathway via trans-signaling. Of note, a specific asthma phenotype has been proposed to correspond to IL-6 trans-signaling, as patients with increased IL-6 trans-signaling had more exacerbations, eosinophilia, and submucosal T cells and macrophages [39], and a coding genetic polymorphism in the IL-6R gene that promotes trans-signaling has been linked to lung function differences in people with severe asthma [40]. Second, additional experiments are necessary to determine whether some of the transcriptomic effects observed may have resulted from direct protein–protein interactions among CEBPD, NF-κB and GR. Third, our statistically significant findings for the effect of CEBPD on IL-6R and pSTAT3 had modest effect sizes, which may be due to relatively long exposure times and resulting compensation by other C/EBP family members. Additional experiments are necessary to determine the time courses of CEBPD effects, as well as the concomitant role of CEBPA, CEBPB, and related proteins on IL-6 signaling.
In summary, we found that CEBPD knockdown resulted in many ASM transcriptomic changes in response to glucocorticoid and TNFα exposures. Among these, CEBPD knockdown influenced expression of several TNFα-induced JAK-STAT pathway genes, including the IL-6 receptor. Further mechanistic insights regarding these CEBPD-mediated ASM transcriptomic changes may lead to an improved understanding of glucocorticoid responses in patients with asthma.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Table E1. RNA-Seq Quality Control Metrics. Table E2. Gene set enrichment analysis results corresponding to the CEBPD siRNA versus NT siRNA comparisons. Table E3. Gene set enrichment analysis results corresponding to the TNFα versus control comparisons. Table E4. Gene set enrichment analysis results corresponding to budesonide exposure. Table E5. Ontological categories enriched within gene co-expression groups. Table E6. RNA-Seq differential expression results for IL6R, SOCS3, SOCS1, and SOCS2 across the 10 comparisons made. Figure E1. Sample quality control prior to RNA-Seq via RT-qPCR of CEBPD and CXCL8. Figure E2. RNA-Seq data quality control. Figure E3. Significant gene set enrichment analysis categories corresponding to the CEBPD siRNA versus NT siRNA comparisons. Figure E4. Overall RNA-Seq results for each exposure were generally consistent with CEBPD knockdown. Figure E5. Significant gene set enrichment analysis categories corresponding to the TNFα versus control comparisons. Figure E6. TNFα-responsive genes whose expression changed with CEBPD knockdown selected from two significantly changed ontological categories. Figure E7. Significant gene set enrichment analysis categories corresponding to budesonide-responsive genes. Figure E8. Selection of soft-thresholding power (β) for weighted gene co-expression network analysis. Figure E9. Correlations between gene co-expression groups and phenotypes. Figure E10. CEBPD-binding sites near select IL-6 signaling pathway genes. Figure E11. Full representative immunoblots and CEBPD/Tubulin expression levels showing adequacy of CEBPD knockdown.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- ASM
Airway smooth muscle
- BUD
Budesonide
- CEBPD
CCAAT/enhancer binding protein D
- ELISA
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- FTTM
Fourier transfer traction microscopy
- GSEA
Gene set enrichment analysis
- GR
Glucocorticoid receptor
- GRE
Glucocorticoid response element
- IHC
Immunohistochemistry
- NF-κB
Nuclear factor κB
- NES
Normalized enrichment score
- NT
Non-targeting
- TSS
Transcription start site
- WGCNA
Weighted gene co-expression network analysis
Author contributions
Designed the study: MK, CK, RAP, QL and BEH. Conducted experiments: MS, XJ, VP, GC, EG, CK, WJ and BL. Analyzed data: MK, ARD, CK and BEH. Wrote the manuscript with input from other co-authors: MK, CK and BEH. Edited and approved the final draft: all authors. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
Funding was provided by National Institutes of Health (NIH) R01 HL133433, R01 HL141992, R01 HL139496, and the Center of Excellence in Environmental Toxicology (P30 ES013508). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Availability of data and materials
RNA-Seq data are available in the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/) under accession GSE146017.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The lung tissue from which airway smooth muscle was derived was provided by the National Disease Research Interchange and the International Institute for the Advancement of Medicine and is obtained commercially from deceased anonymous donors. The University of Pennsylvania Committee on Studies Involving Human Beings, the Rutgers Biomedical and Health Sciences Institutional Review Board, and the Harvard Institutional Review Board have determined that use of these cells does not constitute Human Subjects research since all donor tissue was harvested anonymously and de-identified.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Nurmagambetov T, Kuwahara R, Garbe P. The Economic Burden of Asthma in the United States, 2008–2013. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2018;15:348–356. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201703-259OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chung KF, Wenzel SE, Brozek JL, Bush A, Castro M, Sterk PJ, et al. International ERS/ATS guidelines on definition, evaluation and treatment of severe asthma. Eur Respir J. 2014;43:343–373. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00202013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kan M, Himes BE. Insights into glucocorticoid responses derived from omics studies. Pharmacol Therapeut. 2020;218:107674. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Prakash YS. Airway smooth muscle in airway reactivity and remodeling: what have we learned? Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2013;305:L912–933. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00259.2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Prakash YS, Halayko AJ, Gosens R, Panettieri RA, Camoretti-Mercado B, Penn RB, et al. An Official American Thoracic Society Research Statement: current challenges facing research and therapeutic advances in airway remodeling. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017;195:e4–19. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201611-2248ST. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Slats AM, Sont JK, van Klink RHCJ, Bel EHD, Sterk PJ. Improvement in bronchodilation following deep inspiration after a course of high-dose oral prednisone in asthma. Chest. 2006;130:58–65. doi: 10.1378/chest.130.1.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Trifilieff A, El-Hashim A, Bertrand C. Time course of inflammatory and remodeling events in a murine model of asthma: effect of steroid treatment. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2000;279:L1120–1128. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.2000.279.6.L1120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lakser OJ, Dowell ML, Hoyte FL, Chen B, Lavoie TL, Ferreira C, et al. Steroids augment relengthening of contracted airway smooth muscle: potential additional mechanism of benefit in asthma. Eur Respir J. 2008;32:1224–1230. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00092908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kalliolias GD, Ivashkiv LB. TNF biology, pathogenic mechanisms and emerging therapeutic strategies. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016;12:49–62. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2015.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bradley J. TNF-mediated inflammatory disease. J Pathol. 2008;214:149–160. doi: 10.1002/path.2287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lekstrom-Himes J, Xanthopoulos KG. Biological role of the CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein family of transcription factors. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:28545–28548. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.44.28545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ko C-Y, Chang W-C, Wang J-M. Biological roles of CCAAT/Enhancer-binding protein delta during inflammation. J Biomed Sci. 2015;22:6. doi: 10.1186/s12929-014-0110-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Balamurugan K, Sterneck E. The many faces of C/EBPδ and their relevance for inflammation and cancer. Int J Biol Sci. 2013;9:917–933. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.7224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Yan C, Johnson PF, Tang H, Ye Y, Wu M, Gao H. CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein delta is a critical mediator of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Am J Pathol. 2013;182:420–430. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.10.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Yan C, Ward PA, Wang X, Gao H. Myeloid depletion of SOCS3 enhances LPS-induced acute lung injury through CCAAT/enhancer binding protein delta pathway. FASEB J. 2013;27:2967–2976. doi: 10.1096/fj.12-225797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Do-Umehara HC, Chen C, Urich D, Zhou L, Qiu J, Jang S, et al. Suppression of inflammation and acute lung injury by Miz1 via repression of C/EBP-delta. Nat Immunol. 2013;14:461–469. doi: 10.1038/ni.2566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Liu L, Zhong J, Chen B, Wang W, Xi H, Su X. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP) delta promotes the expression of PTX3 and macrophage phagocytosis during A. fumigatus infection. J Leukoc Biol. 2021;111:1225. doi: 10.1002/JLB.4MA1121-451RR. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lai H-Y, Hsu L-W, Tsai H-H, Lo Y-C, Yang S-H, Liu P-Y, et al. CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein delta promotes intracellular lipid accumulation in M1 macrophages of vascular lesions. Cardiovasc Res. 2017;113:1376–1388. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvx134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ko CY, Chang LH, Lee YC, Sterneck E, Cheng CP, Chen SH, et al. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein delta (CEBPD) elevating PTX3 expression inhibits macrophage-mediated phagocytosis of dying neuron cells. Neurobiol Aging. 2012;33(422):e11–25. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2010.09.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kan M, Koziol-White C, Shumyatcher M, Johnson M, Jester W, Panettieri RA, et al. Airway smooth muscle-specific transcriptomic signatures of glucocorticoid exposure. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2019;61:110–120. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2018-0385OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Himes BE, Jiang X, Wagner P, Hu R, Wang Q, Klanderman B, et al. RNA-Seq transcriptome profiling identifies CRISPLD2 as a glucocorticoid responsive gene that modulates cytokine function in airway smooth muscle cells. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e99625. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0099625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Reddy TE, Pauli F, Sprouse RO, Neff NF, Newberry KM, Garabedian MJ, et al. Genomic determination of the glucocorticoid response reveals unexpected mechanisms of gene regulation. Genome Res. 2009;19:2163–2171. doi: 10.1101/gr.097022.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Poli V. The role of C/EBP isoforms in the control of inflammatory and native immunity functions. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:29279–29282. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.45.29279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Akira S. IL-6-regulated transcription factors. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1997;29:1401–1418. doi: 10.1016/s1357-2725(97)00063-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Nishio Y, Isshiki H, Kishimoto T, Akira S. A nuclear factor for interleukin-6 expression (NF-IL6) and the glucocorticoid receptor synergistically activate transcription of the rat alpha 1-acid glycoprotein gene via direct protein-protein interaction. Mol Cell Biol. 1993;13:1854–1862. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Mitani T, Takaya T, Harada N, Katayama S, Yamaji R, Nakamura S, et al. Theophylline suppresses interleukin-6 expression by inhibiting glucocorticoid receptor signaling in pre-adipocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2018;646:98–106. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2018.04.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kan M, Shumyatcher M, Diwadkar A, Soliman G, Himes BE. Integration of transcriptomic data identifies global and cell-specific asthma-related gene expression signatures. AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2018;2018:1338–1347. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Langfelder P, Zhang B, Horvath S. Defining clusters from a hierarchical cluster tree: the Dynamic Tree Cut package for R. Bioinformatics. 2008;24:719–720. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btm563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sergushichev A. An algorithm for fast preranked gene set enrichment analysis using cumulative statistic calculation. bioRxiv. 2016.
- 30.Hosack DA, Dennis G, Sherman BT, Lane HC, Lempicki RA. Identifying biological themes within lists of genes with EASE. Genome Biol. 2003;4:R70. doi: 10.1186/gb-2003-4-10-r70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Diwadkar AR, Kan M, Himes BE. Facilitating analysis of publicly available ChIP-Seq data for integrative studies. AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2019;2019:371–379. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Gertz J, Savic D, Varley KE, Partridge EC, Safi A, Jain P, et al. Distinct properties of cell-type-specific and shared transcription factor binding sites. Mol Cell. 2013;52:25–36. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.08.037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Butler JP, Tolić-Nørrelykke IM, Fabry B, Fredberg JJ. Traction fields, moments, and strain energy that cells exert on their surroundings. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2002;282:C595–605. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00270.2001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Marsters SA, Sheridan JP, Pitti RM, Huang A, Skubatch M, Baldwin D, et al. A novel receptor for Apo2L/TRAIL contains a truncated death domain. Curr Biol. 1997;7:1003–1006. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(06)00422-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Sherbet GV. Tumour Suppression and Inhibition of Angiogenesis by TXNIP (Thioredoxin Interacting Protein). Molecular Approach to Cancer Management [Internet]. Elsevier; 2017 [cited 2020 May 22]. p. 101–3. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/B9780128128961000106.
- 36.Masuno K, Haldar SM, Jeyaraj D, Mailloux CM, Huang X, Panettieri RA, et al. Expression profiling identifies Klf15 as a glucocorticoid target that regulates airway hyperresponsiveness. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2011;45:642–649. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2010-0369OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Misior AM, Deshpande DA, Loza MJ, Pascual RM, Hipp JD, Penn RB. Glucocorticoid- and protein kinase A-dependent transcriptome regulation in airway smooth muscle. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2009;41:24–39. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2008-0266OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ammit AJ, Moir LM, Oliver BG, Hughes JM, Alkhouri H, Ge Q, et al. Effect of IL-6 trans -signaling on the pro-remodeling phenotype of airway smooth muscle. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2007;292:L199–206. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00230.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Jevnikar Z, Östling J, Ax E, Calvén J, Thörn K, Israelsson E, et al. Epithelial IL-6 trans-signaling defines a new asthma phenotype with increased airway inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019;143:577–590. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2018.05.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Hawkins GA, Robinson MB, Hastie AT, Li X, Li H, Moore WC, et al. The IL6R variation Asp(358)Ala is a potential modifier of lung function in subjects with asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;130:510–515.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.03.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1: Table E1. RNA-Seq Quality Control Metrics. Table E2. Gene set enrichment analysis results corresponding to the CEBPD siRNA versus NT siRNA comparisons. Table E3. Gene set enrichment analysis results corresponding to the TNFα versus control comparisons. Table E4. Gene set enrichment analysis results corresponding to budesonide exposure. Table E5. Ontological categories enriched within gene co-expression groups. Table E6. RNA-Seq differential expression results for IL6R, SOCS3, SOCS1, and SOCS2 across the 10 comparisons made. Figure E1. Sample quality control prior to RNA-Seq via RT-qPCR of CEBPD and CXCL8. Figure E2. RNA-Seq data quality control. Figure E3. Significant gene set enrichment analysis categories corresponding to the CEBPD siRNA versus NT siRNA comparisons. Figure E4. Overall RNA-Seq results for each exposure were generally consistent with CEBPD knockdown. Figure E5. Significant gene set enrichment analysis categories corresponding to the TNFα versus control comparisons. Figure E6. TNFα-responsive genes whose expression changed with CEBPD knockdown selected from two significantly changed ontological categories. Figure E7. Significant gene set enrichment analysis categories corresponding to budesonide-responsive genes. Figure E8. Selection of soft-thresholding power (β) for weighted gene co-expression network analysis. Figure E9. Correlations between gene co-expression groups and phenotypes. Figure E10. CEBPD-binding sites near select IL-6 signaling pathway genes. Figure E11. Full representative immunoblots and CEBPD/Tubulin expression levels showing adequacy of CEBPD knockdown.
Data Availability Statement
RNA-Seq data are available in the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/) under accession GSE146017.