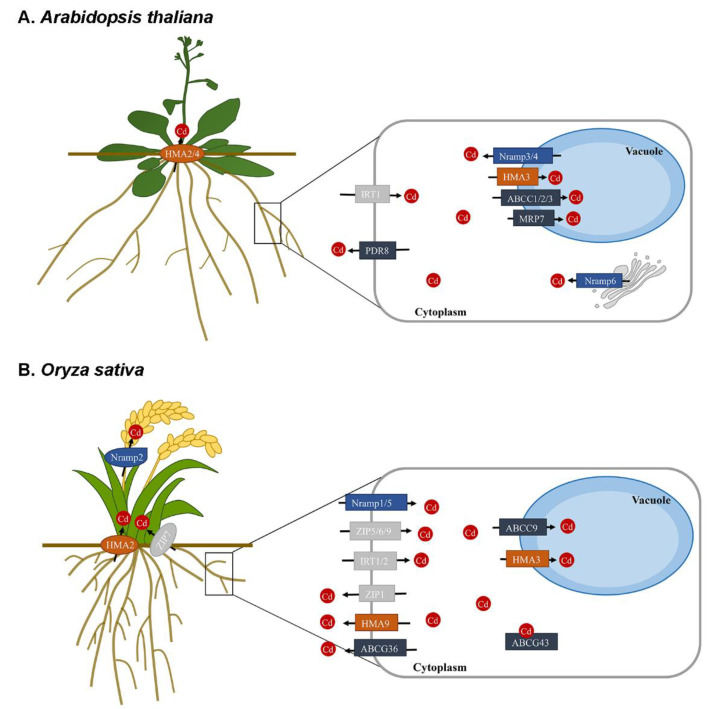
Figure 1.
Uptake and transport of Cd. (A) In Arabidopsis thaliana, AtIRT1 is involved in Cd uptake by the roots. After Cd enters the root cells, it can be sequestered into the vacuole via AtHMA3, AtABCC1, AtABCC2, AtABCC3, and AtMRP7. AtNramp3 and AtNramp4 mediate the transport of Cd from the vacuole into the cytoplasm, while AtNramp6 transport Cd out of its storage compartment. AtHMA2 and AtHMA4 are involved in xylem loading to transport Cd to the shoots. Moreover, AtPDR8 mediates Cd efflux. (B) In O. sativa, OsNramp1, OsNramp5, OsZIP5, OsZIP6, OsZIP9, OsIRT1, and OsIRT2 are involved in Cd uptake by the rice roots. After Cd enters the root cells, it can be transported to the vacuoles, where it is sequestered, by OsHMA3 and OsABCC9. OsABCG43 also aids the sequestration of Cd in the roots. OsHMA2 and OsZIP7 are involved in xylem loading to transport Cd to the shoots. OsNramp2 mediates Cd re-translocation to the grains. Moreover, OsZIP1, OsHMA9, and OsABCG36 mediate Cd efflux in roots.