Abstract
Globally, cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death. Research has focused on the metabolism of carbohydrates, fatty acids, and amino acids to improve the prognosis of cardiovascular diseases. There are three types of branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs; valine, leucine, and isoleucine) required for protein homeostasis, energy balance, and signaling pathways. Increasing evidence has implicated BCAAs in the pathogenesis of multiple cardiovascular diseases. This review summarizes the biological origin, signal transduction pathways and function of BCAAs as well as their significance in cardiovascular diseases, including myocardial hypertrophy, heart failure, coronary artery disease, diabetic cardiomyopathy, dilated cardiomyopathy, arrhythmia and hypertension.
Keywords: branched-chain amino acids, catabolism, cardiovascular diseases, heart failure, coronary artery disease
Introduction
Approximately 17.9 million people die from cardiovascular diseases, representing 32% of global deaths (1). More attention should be given to elucidating the pathogenesis of the disease. As a high energy consuming organ, the heart is more sensitive to nutrient metabolism (2). Therefore, a metabolic defect can have a significant impact on cardiac health and disease development. Traditionally, fatty acids and glucose are the two main metabolic substrates of the heart (3). Recent studies also found that heart failure is associated with ketone body utilization, which functions as a compensatory mechanism in maintaining cardiac energy homeostasis (4, 5). Are there other nutrient ingredients involved in the pathogenesis of heart failure, such as amino acids? Branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) are the most plentiful amino acids in proteins. They belong to the group of essential amino acids, which in animals are only present in small amounts. Aberrant BCAA homeostasis has been observed in a number of disorders, such as type 2 diabetes, liver cirrhosis, renal failure, and cancer (6–9). They present diverse biological functions in the pathogenesis of these diseases. BCAA metabolism has been shown to be effective in preventing or treating hepatic encephalopathy, reducing fatigue during exercise, promoting healing, and stimulating insulin production (10–12). Recently, the development of cardiovascular diseases has also been linked to elevated levels of BCAAs (13–15).
Branched-chain amino acid synthesis, metabolism and catabolites
Although BCAAs are essential amino acids that cannot be synthesized by animals, their synthesis occurs in bacteria, fungi, and plants (16). In these species, BCAAs are derived from the transamino precursor of valine, α-ketoisovaleric acid, which is synthesized by the same enzymes as valine and isoleucine (16). Pyruvate is the source of carbon in valine and leucine, while the carbon in isoleucine is derived from threonine. Unlike most amino acids, the first step of BCAA catabolism does not occur in the liver because branched-chain aminotransferases (BCATs) are the first enzymes in the BCAA catabolic pathway, which have low activity in the liver. In humans, BCAAs are primitively transaminated to form branched-chain α-keto acids (BCKAs) by BCATs (17). There are two genes that encode BCATs: BCAT1 and BCAT2. BCAT1 encodes a cytoplasmic protein and is mainly expressed in the brain, while BCAT2 encodes a mitochondrial protein (18, 19). The second catabolic enzyme of BCAAs, branched-chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase (BCKDH), is a multienzyme complex located on the inner surface of the mitochondrial inner membrane that shares many of the same properties as the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Similar to the PDH complex, BCKDH catalyzes oxidative decarboxylation, releases carbon dioxide (CO2), and adds a coenzyme a (CoA) moiety to the oxidized BCKA product. Branched acyl-CoA ester is generated through irreversible decarboxylation of BCKA. BCKDH is regulated by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. Specific kinase-mediated phosphorylation leads to inactivation, and specific phosphatase-mediated dephosphorylation activates the enzyme (20–22). A mitochondrial-targeted type 2c serine/threonine protein phosphatase, PP2Cm, has been identified as a key phosphatase of BCKDH and plays a critical role in regulating BCAA catabolism and homeostasis. BCKDH kinase is allosterically inhibited by BCKAs, whose maximal affinity is for α-ketoisocaproic acid (α-KIC), allowing the elevation of BCKAs to promote their own oxidation (23). Eventually, the carbons of BCAAs are either lost as carbon dioxide or enter the tricarboxylic acid cycle (Figure 1).
FIGURE 1.
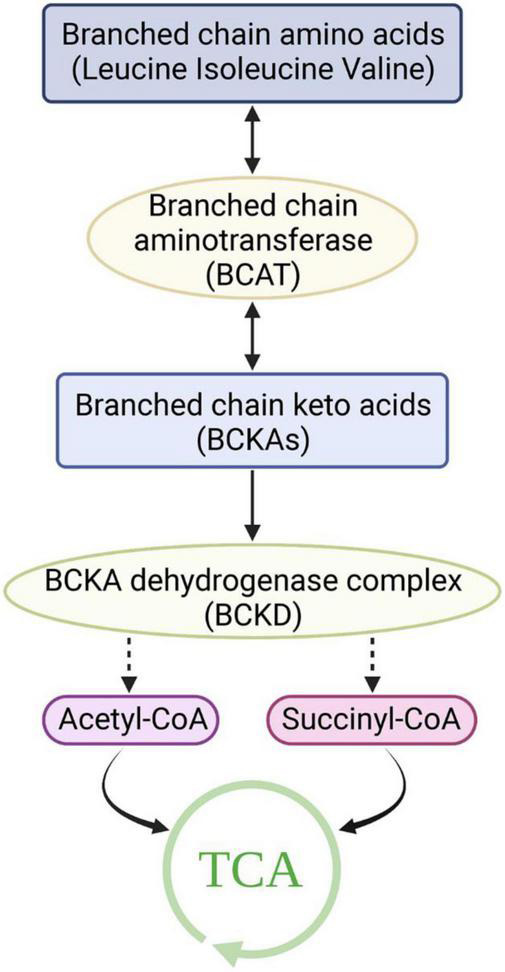
Catabolism of branched-chain amino acids. TCA, Tricarboxylic acid cycle.
Albeit that BCAAs are catabolized in mitochondria, the catabolic intermediates in this process are not trapped in the mitochondrial matrix. For example, 3-hydroxyisobutyric acid (3-HIB), which is part of the valine catabolic pathway, is secreted from muscle cells into plasma, activates endothelial fatty acid transport, stimulates muscle fatty acid uptake in vivo and promotes lipid accumulation in muscle, leading to insulin resistance in mice (24). Meanwhile, one of the leucine oxidation products, acetoacetate, can be detached from the matrix prior to ketone oxidation. Before being oxidized by BCKDH, the α-carbon of α-keto acids can be reduced to generate branched α-hydroxy keto acids, while a small fraction of α-KIC can also be converted to beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate (HMB) by cytoplasmic dioxygenases (25, 26). BCAAs also facilitate the synthesis of several distinctive lipids, ranging from n-acyl amino acids to branched-chain fatty acids and odd-chain fatty acids (27).
Branched-chain amino acid-regulated signaling pathways
mTOR
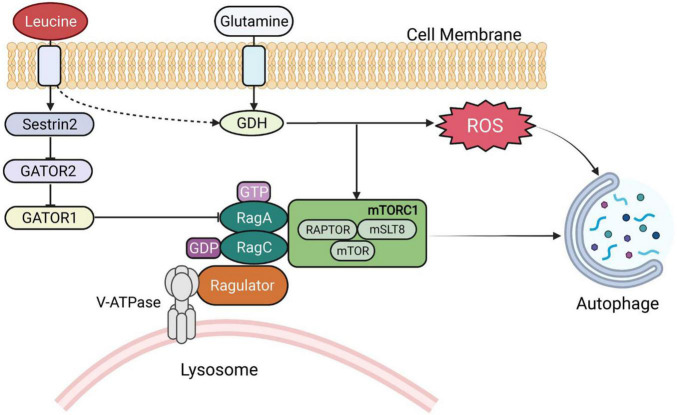
In addition to serving as energy substrates, BCAAs and their metabolites play a critical role in the body in metabolic regulation and signal transduction. The regulation of leucine on the targets of the mTOR pathway is the most intensively studied area (28–30). Leucine activates mTORC1, a key growth regulator, and controls a number of cellular processes, including protein synthesis and cell growth (31–33). mTORC1 is signaled by amino acids through Rag guanosine triphosphatases (GTPases). GATOR1 and GATOR2 regulate Rags, and sestrin2 (a GATOR2-interacting protein) inhibits mTORC1 signaling (33). Therefore, leucine activation of mTORC1 in cells requires Sestrin2, which suggests that Sestrin2 is a leucine sensor of the mTORC1 signaling pathway (33, 34). Notably, a small GTPase called SAR1B was recently found to bind to leucine and activate mTORC1 through conformational changes (35). Meanwhile, both glutamate dehydrogenase and valine metabolites are involved in several signaling pathways (24, 36, 37). BCAAs activate mTOR in various metabolic responses. For example, mTOR activation also triggers metabolic changes in tissues, such as muscle and liver, by altering insulin sensitivity (38–42). BCAAs and BCKAs can also inhibit pyruvate and fatty acids in transport and utilization (39, 43).
Glutamate dehydrogenase
Leucine is a poor substrate for glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) and is a metabolic activator of the enzyme. A dual mechanism for GDH flux regulation of autophagy was identified, both by delivering cellular amino acid availability to MTORC1 and by generating reduced equivalents that interfere with reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation (Figure 2) (44). Meanwhile, in low-glucose states, leucine and α-KIC are strong insulin secretagogues. In contrast, leucine stimulates insulin release by activating glutamate dehydrogenase, and α-KG is formed by the oxidative deamination of glutamate by GDH (45). Protein meal-induced hypoglycemia, hyperinsulinemia and hyperammonia are symptoms caused by GDH mutations resulting in leucine hyperactivation (by reducing GTP inhibition) (46). Additionally, α-KIC functions as a strong insulin secretagogue, in part through its transamination, which generates both leucine to activate GDH and α-KG to enter the TCA cycle (47).
FIGURE 2.
BCAA-regulated signaling pathways. GDH, glutamate dehydrogenase; RAG, RAS-related GTP-binding proteins; ROS, reactive oxygen species.
Branched-chain amino acids in risk factors related to cardiovascular diseases
Inflammation
Chronic inflammation has a pivotal role in cardiovascular diseases, and it is both a marker before the onset of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) and a factor in the death of HFpEF (48, 49). Obesity, also a cardiovascular risk factor, can lead to systemic inflammation in the body and then promote macrophage release of proinflammatory cytokines to infiltrate adipose tissue (50, 51). The role of BCAA catabolism in adipogenesis and resistance to adipocyte inflammation has been elucidated; however, the role of BCAA catabolism in macrophage function is unclear (52, 53). In a recent article, it was mentioned that increased uptake of leucine was found after stimulation of the RAW264.7 mouse macrophage cell line using lipopolysaccharide under normal oxygen supply and hypoxic conditions, suggesting that LPS stimulation of macrophages leads to an increase in BCAAs as alternative carbon sources for glucose and glutamine (54). Another article showed significant anti-inflammatory effects of both acute and chronic BCAA supplementation and highlighted the potential role of isoleucine, one of the BCAAs, in modulating the immune profile of macrophages prior to LPS stimulation (55). Macrophage BCAT1, which interferes with metabolic reprogramming, has also been suggested as an attractive therapeutic target for chronic inflammatory diseases (56). All these results demonstrate that although the exact mechanism is unknown, BCAA metabolites and enzymes in their metabolic pathways may be involved in systemic inflammatory cardiovascular diseases such as HFpEF by causing chronic inflammation in non-cardiac cells such as adipocytes and immune cells.
Aging
The incidence of cardiovascular diseases increases significantly with aging. Downregulation of BCAT1 was found to be a highly significant feature in aged mice (57). A recent clinical trial also suggests that continuous BCAA supplementation may be associated with improved poor nutritional status in elderly patients and that specific BCAA supplementation may also enhance cognitive performance as mitochondrial function improves (58). Meanwhile, several studies have shown that weakness produced by aging is associated with low blood BCAA levels and changes in other amino acids (59, 60). In one study, BCAA consumption was positively correlated with leukocyte telomere length in middle age but negatively correlated with frailty in old age (61). It has been shown that long-term dietary BCAA manipulation impacts lifespan in mice by regulating food intake in a way that involves interactions with other amino acids, such as tryptophan and threonine (30). Although BCAAs have been shown to be associated with aging in many articles and clinical trials, the specific mechanisms involved in aging and the pharmacological targets for exerting interventions are still unclear, and further studies are needed.
Obesity
Obese patients with disorders of glucolipid metabolism have also been found to have atrial and ventricular remodeling (62–64). People with obesity have larger left ventricle dimensions, partly due to both an increased intravascular volume and altered LV filling properties (65). A metabolomic analysis of plasma from obese and lean populations showed abnormal BCAA catabolism and increased plasma BCAA levels in obese people, and this phenomenon is associated with insulin resistance due to obesity (29). Studies have shown that BCAAs are closely associated with abnormalities in glucose and lipid metabolism, but the underlying mechanisms are poorly understood (15, 66, 67). Meanwhile, in brown adipose tissue (BAT), cold stimuli enhance mitochondrial BCAA uptake and oxidation, which leads to enhanced BCAA clearance in the circulation, and in turn, defective BCAA catabolism in BAT results in defective BCAA clearance and thermogenesis, leading to the development of diet-induced obesity and glucose intolerance (68, 69). It was suggested that impaired BAT activity reduced systemic BCAA clearance in the presence of obesity or diabetes, while active BAT served as an important metabolic filter for circulating BCAAs, protecting the body from obesity and insulin resistance (70). However, the specific pathways between abnormal BCAA metabolism and obesity and their possible targets of intervention need further study.
Diabetes mellitus
Diabetes is one of the major risk factors for cardiovascular diseases, and its cause of heart disease is the leading cause of death in diabetic patients. A series of observational studies have shown that elevated levels of circulating BCAAs in vivo are significantly associated with poor metabolism (71–75). It has long been documented that leucine seems to have direct effects on hypothalamic and brainstem processes involved in satiety (76). Several articles have also reported that BCAAs regulate the release of hormones such as leptin, GLP1 and gastrin, which may influence food intake and glucagon levels (77–79). Supplementation of BCAAs to cultured muscle cells resulted in activation of mTOR, impaired insulin-stimulated Akt/protein kinase B phosphorylation and reduced insulin-stimulated glucose uptake (74, 80). In clinical studies, elevated blood levels of BCAAs were positively correlated with insulin resistance and HbA1c levels (81, 82). Several longitudinal studies in different cohorts reported that elevated blood levels of BCAAs predicted future insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) (73, 83). Meanwhile, genetic analysis suggests that elevated plasma levels of BCAAs are associated with an increased risk of developing T2DM (84, 85). This raises another point that elevated BCAAs may be the result of insulin resistance, but it is also possible that elevated BCAAs may in turn cause diabetes through insulin resistance (85). As with diabetes, almost all cardiovascular diseases, such as heart failure and coronary heart diseases, have varying degrees of metabolic disorders, and the role of insulin resistance in cardiovascular diseases has long been reported (86, 87). It is certain that BCAA metabolic abnormalities do exist in obese patients, but whether BCAAs are involved in the altered vascular structure and metabolic disorders present in obese patients needs further elucidation.
Branched-chain amino acids in cardiovascular diseases
Heart failure
As one of the most common cardiovascular diseases, heart failure is a threat to human health. According to the reduction of ejection fraction, heart failure can be divided into heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF). The development of heart failure is associated with major changes in myocardial metabolism. Overexpression of Kruppel-like factor 15 in heart failure inhibits BCAA catabolism and leads to accumulation of BCKAs in the myocardium, which can directly impact mitochondrial function and cellular viability (13). The early stages of heart failure are characterized by compensatory ventricular hypertrophy in response to increased hemodynamic stress, which is also associated with increased circulating BCAAs and BCKAs in humans and animal models (13, 88, 89). Prior diversion of BCKA to the reamination pathway may contribute to the constitutively high rate of protein synthesis, leading to myocardial hypertrophy and poor structural remodeling (21). Investigation of changes in the cardiac phosphorylation proteome after exposure to elevated BCKAs showed that chronic increases in BCKA could lead to the development of pathologic cardiac hypertrophy and impaired cardiac contractility (21). Meanwhile, the gene expression of PP2Cm, a key regulator of BCAA catabolism, is reduced in hypertrophic hearts and further reduced in failing hearts (87). Mouse models carrying the genetically inactivated PP2Cm-encoding gene ppm1k (PP2Cm-KO) show a further decline in cardiac function with increasing age when compared to wild-type mice (90). At the same time, eight weeks after transverse aortic constriction (TAC), PP2CM-KO mice showed a significant reduction in left ventricular ejection fraction, ventricular dilatation, and elevated wet lung weight (90). Abnormal BCAA metabolism can lead to myocardial hypertrophy through insulin resistance, and ventricular remodeling due to myocardial hypertrophy can induce heart failure (91). After upregulation of BCKDH activity with the branched-chain α-keto acid dehydrogenase kinase inhibitor BT2, a reduction in systolic dysfunction and myocardial insulin resistance present in HFrEF was observed along with enhanced BCAA oxidation and reduced accumulation of BCAAs and BCAAs in the heart (13, 92). The role of BCAAs in the pathogenesis of HFpEF, for which no definitive treatment is available, has not been elucidated. However, it is worth noting the metabolism of non-cardiomyocytes, such as macrophages, in recent studies showing that macrophages cause fibrosis and diastolic dysfunction in HFpEF (93–95). Meanwhile, the enzyme BCAT, which initiates BCAA catabolism, regulates macrophage metabolic reprogramming, and the mitochondrial oxidative stress generated by inhibition of BCAA activity may lead to downregulation of metabolites between citrate and succinate in the tricarboxylic acid cycle (56, 96). The role of myocardial and non-myocardial BCAA metabolic pathways in the pathogenesis of heart failure deserves further investigation.
Coronary artery disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is the most common cardiovascular disease (97). Although glucose and fatty acid metabolism have been recognized as core CAD mechanisms (98), scientists have demonstrated an independent relationship between elevated BCAA levels and the risk of CAD, regardless of the nature of the observed mechanism behind the elevated BCAA levels. The association between BCAAs and the risk of coronary heart disease remained significant after adjusting for traditional risk factors for coronary heart disease (99–101). The metabolism of the heart is dominated by fatty acid and glucose metabolism, and the heart consumes much less BCAA than other organs, so it is unlikely that a decrease in cardiac BCAA catabolism alone leads to an increase in plasma BCAAs (102–104). However, inhibition of systemic BCAA catabolism by knocking down the PP2Cm gene leads to elevated circulating and cardiac BCAA levels, which can compete with and inhibit gluconeogenesis in the heart via a non-transcriptional mechanism and exacerbate the cardiac response to ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury (13, 14). A recent discovery showed that BCAA/BCKA enhanced cardiac fatty acid oxidation levels by transcriptionally upregulating PPAR-α expression, thereby exacerbating lipid peroxidation toxicity and cardiac vulnerability to I/R injury (15). In the postinfarct heart, cardiac BCAA catabolism is impaired, resulting in myocardial BCAA accumulation; then, BCAAs activate myocardial mTOR signaling and subsequently contribute to cardiac dysfunction and remodeling following myocardial infarction (MI) (105). The metabolites of valine, one of the BCAAs, α-ketoisovaleric acid and propionyl-CoA show stronger effects on platelet activation than other BCAA metabolites, and propionyl-CoA is a key mediator of the BCAA metabolic pathway that mediates platelet activation. Excessive platelet activation can lead to microthrombosis, which can cause myocardial ischemia and infarction (106, 107). Additionally, dietary BCAA supplementation can not only facilitate platelet activation and increase thrombosis risk but also worsen contractility and increase infarct size following myocardial infarction (105, 106). These results reveal that abnormal branched-chain amino acid catabolism plays a crucial role in CAD (both MI and I/R), and the major signaling pathway mTOR and some of its intermediate metabolites are involved in myocardial metabolic reprogramming, leading to ventricular remodeling.
Diabetic cardiomyopathy
Diabetic cardiomyopathy is a disease of the heart muscle that cannot be explained by hypertension, coronary artery atherosclerotic heart disease, or other heart diseases. A report found decreased BCAA metabolizing enzyme activity in myocardial tissue of mice with diabetic cardiomyopathy, suggesting abnormal BCAA catabolism (108). More importantly, cardiac ischemia–reperfusion injury with enhanced fatty acid oxidation was ameliorated after silencing of the PPARα pathway in mice with impaired BCAA metabolism, suggesting that PPARα may be a downstream pathway of BCAA metabolism leading to diabetic cardiomyopathy (15). A series of studies have suggested significant activation of the leucine-directed mTOR pathway in type 2 diabetic cardiomyopathy, and activation of the pathway also leads to further myocardial injury by inducing cellular autophagy and apoptosis (109, 110). However, autophagy is enhanced in type 1 diabetes but inhibited in type 2 diabetes, implying that the involvement of BCAA catabolism in diabetic cardiomyopathy cannot be simply generalized.
Dilated cardiomyopathy
Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a primary myocardial disease of undetermined cause. It is characterized by left or right ventricular or bilateral ventricular enlargement with reduced ventricular contraction (111). A recent article analyzing specimens from patients with DCM found that inhibition of the lysosomal autophagy pathway was associated with the mTOR pathway, while metabolic analysis revealed a significant increase in valine and leucine in DCM hearts and a significant decrease in the levels of the protein phosphatase PP2Cm (112). An article suggests that embryonic mice lacking the mTOR pathway have significant developmental defects in the myocardium and can rapidly lead to dilated cardiomyopathy (113). However, the specific mechanism of BCAA metabolism involved in DCM is still unclear.
Arrhythmia
A recent article reveals that the mechanisms by which plasma BCAAs content increased in mice contribute to the pro-arrhythmic state are associated not only with genetic BCAT2 deficiency, but also with acquired metabolic disorders such as diabetes, obesity and heart failure in which BCAA metabolism is impaired (114). In addition, when cardiomyocytes derived from human pluripotent stem cells were exposed to a high BCAAs environment, they also developed calcium dysregulation and arrhythmias similar to those in mice (114). A metabolic analysis of plasma samples from patients with cardiovascular disease and a prospective cohort study suggest that a significant correlation between elevated plasma BCAA levels and the occurrence of arrhythmias and strokes (115, 116). However, the specific pathways and genes involved in BCAA metabolic abnormalities leading to arrhythmias have not yet been identified, and more clinical evidence is warranted to validate this BCAA-associated phenotype.
Hypertension
Hypertension is one of the most important risk factors for cardiovascular diseases and a key factor in the damage to blood vessels. Several cohort studies have shown that higher BCAA intake, in particular valine intake, is associated with a higher risk of incident hypertension (117–120). However, due to the diverse pathogenesis of hypertension, the exact mechanism of BCAAs in the development and progression of hypertension has not yet been elucidated, and further investigation is needed to unravel the complexity behind the circulating concentrations of BCAAs.
Conclusion and perspective
Branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) and their metabolites can affect a variety of cellular processes, such as cell growth, protein synthesis, glucose metabolism and lipid metabolism. When BCAA catabolism is impaired, the oxidation of BCAA produces less acetyl coenzyme A and succinyl coenzyme A into the tricarboxylic acid cycle, while the mTOR complex and GDH are continuously activated, which, together with the accumulation of intermediate metabolites BCKAs, can further lead to metabolic reprogramming and reactive oxygen species production, resulting in mitochondrial damage and cellular autophagy. The above processes can not only be directly involved in cardiovascular diseases but also indirectly contribute to cardiovascular diseases by exacerbating systemic chronic inflammation, obesity, aging, diabetes and other cardiovascular disease risk factors (Figure 3). BCAAs have therapeutic potential, yet many controversies remain in the clinical application of BCAAs, and careful studies are needed to elucidate the effectiveness of BCAAs in most indications. Future goals include clarifying the specific mechanisms and therapeutic targets of BCAA involvement in cardiovascular disease and individualizing treatment based on specific patient characteristics.
FIGURE 3.
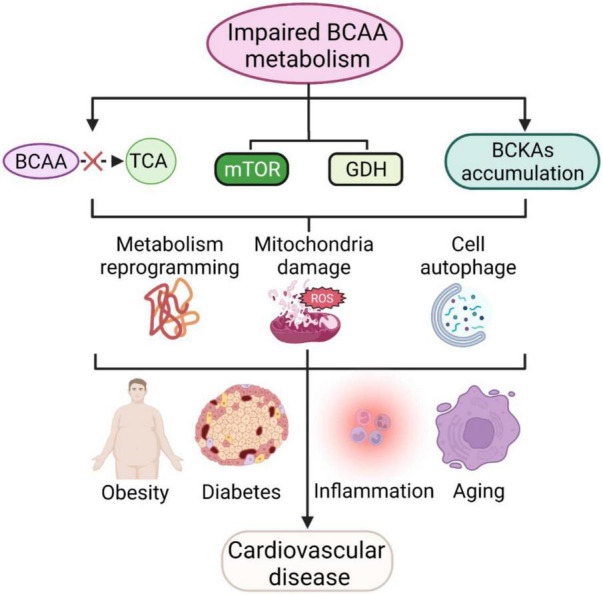
BCAAs and cardiovascular diseases. Impaired BCAA metabolism leads to less BCAA translocation into the TCA, activating mTOR and GDH pathways and accumulating BCKAs and further leads to metabolic reprogramming, mitochondrial damage and cellular autophagy. These processes are also involved in cellular inflammation, aging, obesity and diabetes mellitus, and further contribute to cardiovascular disease.
Author contributions
YX and LJ wrote the manuscript, figure legends, and created the figures. TL revised the manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Funding
This study was supported in part by grants from the Key Research Program of National Clinical Research Center for Geriatrics (Z20191004), the Key Research and Development Program of Sichuan Province (22ZDYF2138), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81970715), and the Innovation Spark Project of Sichuan University (2018SCUH0065).
References
- 1.Ralapanawa U, Sivakanesan R. Epidemiology and the magnitude of coronary artery disease and acute coronary syndrome: a narrative review. J Epidemiol Glob Health. (2021) 11:169–77. 10.2991/jegh.k.201217.001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Cohain AT, Barrington WT, Jordan DM, Beckmann ND, Argmann CA, Houten SM, et al. An integrative multiomic network model links lipid metabolism to glucose regulation in coronary artery disease. Nat Commun. (2021) 12:547. 10.1038/s41467-020-20750-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ormazabal V, Nair S, Elfeky O, Aguayo C, Salomon C, Zuniga FA. Association between insulin resistance and the development of cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2018) 17:122. 10.1186/s12933-018-0762-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Yurista SR, Chong CR, Badimon JJ, Kelly DP, de Boer RA, Westenbrink BD. Therapeutic potential of ketone bodies for patients with cardiovascular disease: JACC state-of-the-art review. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2021) 77:1660–9. 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.12.065 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Deng Y, Xie M, Li Q, Xu X, Ou W, Zhang Y, et al. Targeting mitochondria-inflammation circuit by beta-hydroxybutyrate mitigates HFpEF. Circ Res. (2021) 128:232–45. 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317933 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hattori A, Tsunoda M, Konuma T, Kobayashi M, Nagy T, Glushka J, et al. Cancer progression by reprogrammed BCAA metabolism in myeloid leukaemia. Nature. (2017) 545:500–4. 10.1038/nature22314 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Li JT, Yin M, Wang D, Wang J, Lei MZ, Zhang Y, et al. Bcat2-mediated BCAA catabolism is critical for development of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Nat Cell Biol. (2020) 22:167–74. 10.1038/s41556-019-0455-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Piret SE, Guo Y, Attallah AA, Horne SJ, Zollman A, Owusu D, et al. Kruppel-like factor 6-mediated loss of BCAA catabolism contributes to kidney injury in mice and humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2021) 118:e2024414118. 10.1073/pnas.2024414118 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Tamai Y, Chen Z, Wu Y, Okabe J, Kobayashi Y, Chiba H, et al. Branched-chain amino acids and L-carnitine attenuate lipotoxic hepatocellular damage in rat cirrhotic liver. Biomed Pharmacother. (2021) 135:111181. 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111181 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kachaamy T, Bajaj JS. Diet and cognition in chronic liver disease. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. (2011) 27:174–9. 10.1097/MOG.0b013e3283409c25 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Delany HM, Teh E, Dwarka B, Levenson SM. Infusion of enteral Vs parenteral nutrients using high-concentration branch-chain amino-acids – effect on wound-healing in the postoperative rat. JPEN Parenter Enter. (1991) 15:464–8. 10.1177/0148607191015004464 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Macotela Y, Emanuelli B, Bang AM, Espinoza DO, Boucher J, Beebe K, et al. Dietary leucine – an environmental modifier of insulin resistance acting on multiple levels of metabolism. PLoS One. (2011) 6:e21187. 10.1371/journal.pone.0021187 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Sun H, Olson KC, Gao C, Prosdocimo DA, Zhou M, Wang Z, et al. Catabolic defect of branched-chain amino acids promotes heart failure. Circulation. (2016) 133:2038–49. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.020226 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Li T, Zhang Z, Kolwicz SC, Jr, Abell L, Roe ND, Kim M, et al. Defective branched-chain amino acid catabolism disrupts glucose metabolism and sensitizes the heart to ischemia-reperfusion injury. Cell Metab. (2017) 25:374–85. 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.11.005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Li Y, Xiong Z, Yan W, Gao E, Cheng H, Wu G, et al. Branched chain amino acids exacerbate myocardial ischemia/reperfusion vulnerability via enhancing Gcn2/Atf6/Ppar-alpha pathway-dependent fatty acid oxidation. Theranostics. (2020) 10:5623–40. 10.7150/thno.44836 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.McCourt JA, Duggleby RG. Acetohydroxyacid synthase and its role in the biosynthetic pathway for branched-chain amino acids. Amino Acids. (2006) 31:173–210. 10.1007/s00726-005-0297-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ichihara A, Koyama E. Transaminase of branched chain amino acids. I. Branched chain amino acids-alpha-ketoglutarate transaminase. J Biochem. (1966) 59:160–9. 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128277 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Goto M, Shinno H, Ichihara A. Isozyme patterns of branched-chain amino acid transaminase in human tissues and tumors. Gan. (1977) 68:663–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ichihara A. Isozyme patterns of branched-chain amino acid transaminase during cellular differentiation and carcinogenesis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. (1975) 259:347–54. 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb25431.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Patel MS, Nemeria NS, Furey W, Jordan F. The Pyruvate dehydrogenase complexes: structure-based function and regulation. J Biol Chem. (2014) 289:16615–23. 10.1074/jbc.R114.563148 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Walejko JM, Christopher BA, Crown SB, Zhang GF, Pickar-Oliver A, Yoneshiro T, et al. Branched-chain alpha-ketoacids are preferentially reaminated and activate protein synthesis in the heart. Nat Commun. (2021) 12:1680. 10.1038/s41467-021-21962-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Covian R, Balaban RS. Cardiac Mitochondrial matrix and respiratory complex protein phosphorylation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2012) 303:H940–66. 10.1152/ajpheart.00077.2012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lau KS, Fatania HR, Randle PJ. Regulation of the branched-chain 2-oxoacid dehydrogenase kinase reaction. FEBS Lett. (1982) 144:57–62. 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80568-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Jang C, Oh SF, Wada S, Rowe GC, Liu L, Chan MC, et al. A branched-chain amino acid metabolite drives vascular fatty acid transport and causes insulin resistance. Nat Med. (2016) 22:421–6. 10.1038/nm.4057 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Anderson KA, Huynh FK, Fisher-Wellman K, Stuart JD, Peterson BS, Douros JD, et al. Sirt4 is a lysine deacylase that controls leucine metabolism and insulin secretion. Cell Metab. (2017) 25:838–55.e15. 10.1016/j.cmet.2017.03.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Van Koevering M, Nissen S. Oxidation of leucine and alpha-ketoisocaproate to beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate in vivo. Am J Physiol. (1992) 262(1 Pt 1):E27–31. 10.1152/ajpendo.1992.262.1.E27 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Wallace M, Green CR, Roberts LS, Lee YM, McCarville JL, Sanchez-Gurmaches J, et al. Enzyme promiscuity drives branched-chain fatty acid synthesis in adipose tissues. Nat Chem Biol. (2018) 14:1021–31. 10.1038/s41589-018-0132-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Gu Z, Liu Y, Cai F, Patrick M, Zmajkovic J, Cao H, et al. Loss of Ezh2 reprograms BCAA metabolism to drive leukemic transformation. Cancer Discov. (2019) 9:1228–47. 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-19-0152 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Newgard CB, An J, Bain JR, Muehlbauer MJ, Stevens RD, Lien LF, et al. A branched-chain amino acid-related metabolic signature that differentiates obese and lean humans and contributes to insulin resistance. Cell Metab. (2009) 9:311–26. 10.1016/j.cmet.2009.02.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Solon-Biet SM, Cogger VC, Pulpitel T, Wahl D, Clark X, Bagley E, et al. Branched chain amino acids impact health and lifespan indirectly via amino acid balance and appetite control. Nat Metab. (2019) 1:532–45. 10.1038/s42255-019-0059-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Tomita I, Kume S, Sugahara S, Osawa N, Yamahara K, Yasuda-Yamahara M, et al. Sglt2 inhibition mediates protection from diabetic kidney disease by promoting ketone body-induced mtorc1 inhibition. Cell Metab. (2020) 32:404–19.e6. 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.06.020 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Zhang Y, Swanda RV, Nie L, Liu X, Wang C, Lee H, et al. Mtorc1 couples cyst(e)ine availability with GPX4 protein synthesis and ferroptosis regulation. Nat Commun. (2021) 12:1589. 10.1038/s41467-021-21841-w [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Wolfson RL, Chantranupong L, Saxton RA, Shen K, Scaria SM, Cantor JR, et al. Sestrin2 is a leucine sensor for the mtorc1 pathway. Science. (2016) 351:43–8. 10.1126/science.aab2674 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Saxton RA, Knockenhauer KE, Wolfson RL, Chantranupong L, Pacold ME, Wang T, et al. Structural basis for leucine sensing by the sestrin2-mtorc1 pathway. Science. (2016) 351:53–8. 10.1126/science.aad2087 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Chen J, Ou YH, Luo R, Wang J, Wang D, Guan JL, et al. Sar1b senses leucine levels to regulate mTORC1 signalling. Nature. (2021) 596:281–4. 10.1038/s41586-021-03768-w [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Christensen HN, Hellman B, Lernmark A, Sehlin J, Tager HS, Taljedal IB. In vitro stimulation of insulin release by non-metabolizable, transport-specific amino acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. (1971) 241:341–8. 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90034-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Roberts LD, Bostrom P, O’Sullivan JF, Schinzel RT, Lewis GD, Dejam A, et al. Beta-aminoisobutyric acid induces browning of white fat and hepatic beta-oxidation and is inversely correlated with cardiometabolic risk factors. Cell Metab. (2014) 19:96–108. 10.1016/j.cmet.2013.12.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Chotechuang N, Azzout-Marniche D, Bos C, Chaumontet C, Gausseres N, Steiler T, et al. mTOR, AMPK, and GCN2 coordinate the adaptation of hepatic energy metabolic pathways in response to protein intake in the rat. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. (2009) 297:E1313–23. 10.1152/ajpendo.91000.2008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Saha AK, Xu XJ, Lawson E, Deoliveira R, Brandon AE, Kraegen EW, et al. Downregulation of AMPK accompanies leucine- and glucose-induced increases in protein synthesis and insulin resistance in rat skeletal muscle. Diabetes. (2010) 59:2426–34. 10.2337/db09-1870 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Meijer AJ, Dubbelhuis PF. Amino acid signalling and the integration of metabolism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2004) 313:397–403. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2003.07.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Hinault C, Van Obberghen E, Mothe-Satney I. Role of amino acids in insulin signaling in adipocytes and their potential to decrease insulin resistance of adipose tissue. J Nutr Biochem. (2006) 17:374–8. 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2006.02.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Xiao F, Huang Z, Li H, Yu J, Wang C, Chen S, et al. Leucine deprivation increases hepatic insulin sensitivity via GCN2/mTOR/S6K1 and AMPK pathways. Diabetes. (2011) 60:746–56. 10.2337/db10-1246 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Nishimura J, Masaki T, Arakawa M, Seike M, Yoshimatsu H. Isoleucine prevents the accumulation of tissue triglycerides and upregulates the expression of pparalpha and uncoupling protein in diet-induced obese mice. J Nutr. (2010) 140:496–500. 10.3945/jn.109.108977 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Lorin S, Tol MJ, Bauvy C, Strijland A, Pous C, Verhoeven AJ, et al. Glutamate dehydrogenase contributes to leucine sensing in the regulation of autophagy. Autophagy. (2013) 9:850–60. 10.4161/auto.24083 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Sener A, Malaisse WJL-. Leucine and a nonmetabolized analogue activate pancreatic islet glutamate dehydrogenase. Nature. (1980) 288:187–9. 10.1038/288187a0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Stanley CA, Lieu YK, Hsu BY, Burlina AB, Greenberg CR, Hopwood NJ, et al. Hyperinsulinism and hyperammonemia in infants with regulatory mutations of the glutamate dehydrogenase gene. N Engl J Med. (1998) 338:1352–7. 10.1056/NEJM199805073381904 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Gao Z, Young RA, Li G, Najafi H, Buettger C, Sukumvanich SS, et al. Distinguishing features of leucine and alpha-ketoisocaproate sensing in pancreatic beta-cells. Endocrinology. (2003) 144:1949–57. 10.1210/en.2002-0072 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Ather S, Chan W, Bozkurt B, Aguilar D, Ramasubbu K, Zachariah AA, et al. Impact of noncardiac comorbidities on morbidity and mortality in a predominantly male population with heart failure and preserved versus reduced ejection fraction. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2012) 59:998–1005. 10.1016/j.jacc.2011.11.040 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Lam CS, Lyass A, Kraigher-Krainer E, Massaro JM, Lee DS, Ho JE, et al. Cardiac dysfunction and noncardiac dysfunction as precursors of heart failure with reduced and preserved ejection fraction in the community. Circulation. (2011) 124:24–30. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.979203 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Taube A, Schlich R, Sell H, Eckardt K, Eckel J. Inflammation and metabolic dysfunction: links to cardiovascular diseases. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2012) 302:H2148–65. 10.1152/ajpheart.00907.2011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Jelic S, Lederer DJ, Adams T, Padeletti M, Colombo PC, Factor PH, et al. Vascular inflammation in obesity and sleep Apnea. Circulation. (2010) 121:1014–21. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.900357 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Jung TW, Park HS, Choi GH, Kim D, Lee T. Beta-aminoisobutyric acid attenuates LPS-induced inflammation and insulin resistance in adipocytes through AMPK-mediated pathway. J Biomed Sci. (2018) 25:27. 10.1186/s12929-018-0431-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Zaganjor E, Yoon H, Spinelli JB, Nunn ER, Laurent G, Keskinidis P, et al. Sirt4 is an early regulator of branched-chain amino acid catabolism that promotes adipogenesis. Cell Rep. (2021) 36:109345. 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109345 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Meiser J, Kramer L, Sapcariu SC, Battello N, Ghelfi J, D’Herouel AF, et al. Pro-inflammatory macrophages sustain pyruvate oxidation through pyruvate dehydrogenase for the synthesis of itaconate and to enable cytokine expression. J Biol Chem. (2016) 291:3932–46. 10.1074/jbc.M115.676817 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Bonvini A, Rogero MM, Coqueiro AY, Raizel R, Bella LM, Fock RA, et al. Effects of different branched-chain amino acids supplementation protocols on the inflammatory response of LPS-stimulated raw 264.7 macrophages. Amino Acids. (2021) 53:597–607. 10.1007/s00726-021-02940-w [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Papathanassiu AE, Ko JH, Imprialou M, Bagnati M, Srivastava PK, Vu HA, et al. Bcat1 controls metabolic reprogramming in activated human macrophages and is associated with inflammatory diseases. Nat Commun. (2017) 8:16040. 10.1038/ncomms16040 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Mansfeld J, Urban N, Priebe S, Groth M, Frahm C, Hartmann N, et al. Branched-chain amino acid catabolism is a conserved regulator of physiological ageing. Nat Commun. (2015) 6:10043. 10.1038/ncomms10043 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Buondonno I, Sassi F, Carignano G, Dutto F, Ferreri C, Pili FG, et al. From mitochondria to healthy aging: the role of branched-chain amino acids treatment: mater a randomized study. Clin Nutr. (2020) 39:2080–91. 10.1016/j.clnu.2019.10.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Toyoshima K, Nakamura M, Adachi Y, Imaizumi A, Hakamada T, Abe Y, et al. Increased plasma proline concentrations are associated with sarcopenia in the elderly. PLoS One. (2017) 12:e0185206. 10.1371/journal.pone.0185206 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Le Couteur DG, Ribeiro R, Senior A, Hsu B, Hirani V, Blyth FM, et al. Branched chain amino acids, cardiometabolic risk factors and outcomes in older men: the concord health and ageing in men project. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. (2020) 75:1805–10. 10.1093/gerona/glz192 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Zhang Y, Zhou Q, Yang R, Hu C, Huang Z, Zheng C, et al. Serum branched-chain amino acids are associated with leukocyte telomere length and frailty based on residents from Guangxi longevity county. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:10252. 10.1038/s41598-020-67010-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Gonzalez-Muniesa P, Martinez-Gonzalez MA, Hu FB, Despres JP, Matsuzawa Y, Loos RJF, et al. Obesity. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2017) 3:17034. 10.1038/nrdp.2017.34 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Obokata M, Reddy YNV, Pislaru SV, Melenovsky V, Borlaug BA. Evidence supporting the existence of a distinct obese phenotype of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Circulation. (2017) 136:6–19. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.026807 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Packer M. Epicardial adipose tissue may mediate deleterious effects of obesity and inflammation on the myocardium. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2018) 71:2360–72. 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.03.509 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Vasan RS. Cardiac function and obesity. Heart. (2003) 89:1127–9. 10.1136/heart.89.10.1127 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Green CR, Wallace M, Divakaruni AS, Phillips SA, Murphy AN, Ciaraldi TP, et al. Branched-chain amino acid catabolism fuels adipocyte differentiation and lipogenesis. Nat Chem Biol. (2016) 12:15–21. 10.1038/nchembio.1961 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Zhao H, Zhang F, Sun D, Wang X, Zhang X, Zhang J, et al. Branched-chain amino acids exacerbate obesity-related hepatic glucose and lipid metabolic disorders via attenuating AKT2 signaling. Diabetes. (2020) 69:1164–77. 10.2337/db19-0920 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Newgard CB. Interplay between lipids and branched-chain amino acids in development of insulin resistance. Cell Metab. (2012) 15:606–14. 10.1016/j.cmet.2012.01.024 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Um SH, D’Alessio D, Thomas G. Nutrient overload, insulin resistance, and ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1, S6k1. Cell Metab. (2006) 3:393–402. 10.1016/j.cmet.2006.05.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Yoneshiro T, Wang Q, Tajima K, Matsushita M, Maki H, Igarashi K, et al. Bcaa catabolism in brown fat controls energy homeostasis through Slc25a44. Nature. (2019) 572:614–9. 10.1038/s41586-019-1503-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Wurtz P, Makinen VP, Soininen P, Kangas AJ, Tukiainen T, Kettunen J, et al. Metabolic signatures of insulin resistance in 7,098 young adults. Diabetes. (2012) 61:1372–80. 10.2337/db11-1355 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.O’Connor S, Greffard K, Leclercq M, Julien P, Weisnagel SJ, Gagnon C, et al. Increased dairy product intake alters serum metabolite profiles in subjects at risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Mol Nutr Food Res. (2019) 63:e1900126. 10.1002/mnfr.201900126 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Wang TJ, Larson MG, Vasan RS, Cheng S, Rhee EP, McCabe E, et al. Metabolite profiles and the risk of developing diabetes. Nat Med. (2011) 17:448–53. 10.1038/nm.2307 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Tai ES, Tan MLS, Stevens RD, Low YL, Muehlbauer MJ, Goh DLM, et al. Insulin resistance is associated with a metabolic profile of altered protein metabolism in Chinese and Asian-Indian men. Diabetologia. (2010) 53:757–67. 10.1007/s00125-009-1637-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Newgard CB, An J, Bain JR, Muehlbauer MJ, Stevens RD, Lien LF, et al. A branched-chain amino acid-related metabolic signature that differentiates obese and lean humans and contributes to insulin resistance (Vol 9, Pg 311, 2009). Cell Metab. (2009) 9:565–6. 10.1016/j.cmet.2009.05.001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Cota D, Proulx K, Smith KAB, Kozma SC, Thomas G, Woods SC, et al. Hypothalamic mTOR signaling regulates food intake. Science. (2006) 312:927–30. 10.1126/science.1124147 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Torres-Leal FL, Fonseca-Alaniz MH, Teodoro GFR, de Capitani MD, Vianna D, Pantaleao LC, et al. Leucine supplementation improves adiponectin and total cholesterol concentrations despite the lack of changes in adiposity or glucose homeostasis in rats previously exposed to a high-fat diet. Nutr Metab. (2011) 8:62. 10.1186/1743-7075-8-62 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Chen Q, Reimer RA. Dairy protein and leucine alter GLP-1 release and mRNA of genes involved in intestinal lipid metabolism in vitro. Nutrition. (2009) 25:340–9. 10.1016/j.nut.2008.08.012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Xu GY, Li Y, An WJ, Li SD, Guan YF, Wang NP, et al. Gastric mammalian target of rapamycin signaling regulates ghrelin production and food intake. Endocrinology. (2009) 150:3637–44. 10.1210/en.2009-0372 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Tremblay F, Krebs M, Dombrowski L, Brehm A, Bernroider E, Roth E, et al. Overactivation of S6 kinase 1 as a cause of human insulin resistance during increased amino acid availability. Diabetes. (2005) 54:2674–84. 10.2337/diabetes.54.9.2674 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Lackey DE, Lynch CJ, Olson KC, Mostaedi R, Ali M, Smith WH, et al. Regulation of adipose branched-chain amino acid catabolism enzyme expression and cross-adipose amino acid flux in human obesity. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. (2013) 304:E1175–87. 10.1152/ajpendo.00630.2012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Badoud F, Lam KP, DiBattista A, Perreault M, Zulyniak MA, Cattrysse B, et al. Serum and adipose tissue amino acid homeostasis in the metabolically healthy obese. J Proteome Res. (2014) 13:3455–66. 10.1021/pr500416v [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.McCormack SE, Shaham O, McCarthy MA, Deik AA, Wang TJ, Gerszten RE, et al. Circulating branched-chain amino acid concentrations are associated with obesity and future insulin resistance in children and adolescents. Pediatr Obes. (2013) 8:52–61. 10.1111/j.2047-6310.2012.00087.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Lotta LA, Scott RA, Sharp SJ, Burgess S, Luan JA, Tillin T, et al. Genetic predisposition to an impaired metabolism of the branched-chain amino acids and risk of type 2 diabetes: a Mendelian randomisation analysis. PLoS Med. (2016) 13:e1002179. 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002179 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Wang Q, Holmes MV, Smith GD, Ala-Korpela M. Genetic support for a causal role of insulin resistance on circulating branched-chain amino acids and inflammation. Diabetes Care. (2017) 40:1779–86. 10.2337/dc17-1642 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Azizi PM, Zyla RE, Guan S, Wang C, Liu J, Bolz SS, et al. Clathrin-dependent entry and vesicle-mediated exocytosis define insulin transcytosis across microvascular endothelial cells. Mol Biol Cell. (2015) 26:740–50. 10.1091/mbc.E14-08-1307 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Symons JD, McMillin SL, Riehle C, Tanner J, Palionyte M, Hillas E, et al. Contribution of insulin and AKT1 signaling to endothelial nitric oxide synthase in the regulation of endothelial function and blood pressure. Circ Res. (2009) 104:1085–94. 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.189316 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Ahmad T, Kelly JP, McGarrah RW, Hellkamp AS, Fiuzat M, Testani JM, et al. Prognostic implications of long-chain acylcarnitines in heart failure and reversibility with mechanical circulatory support. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2016) 67:291–9. 10.1016/j.jacc.2015.10.079 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Hunter WG, Kelly JP, McGarrah RW, III, Khouri MG, Craig D, Haynes C, et al. Metabolomic profiling identifies novel circulating biomarkers of mitochondrial dysfunction differentially elevated in heart failure with preserved versus reduced ejection fraction: evidence for shared metabolic impairments in clinical heart failure. J Am Heart Assoc. (2016) 5:e003190. 10.1161/JAHA.115.003190 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Sun H, Lu G, Ren S, Chen J, Wang Y. Catabolism of branched-chain amino acids in heart failure: insights from genetic models. Pediatr Cardiol. (2011) 32:305–10. 10.1007/s00246-010-9856-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Uddin GM, Zhang L, Shah S, Fukushima A, Wagg CS, Gopal K, et al. Impaired branched chain amino acid oxidation contributes to cardiac insulin resistance in heart failure. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2019) 18:86. 10.1186/s12933-019-0892-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Chen M, Gao C, Yu J, Ren S, Wang M, Wynn RM, et al. Therapeutic effect of targeting branched-chain amino acid catabolic flux in pressure-overload induced heart failure. J Am Heart Assoc. (2019) 8:e011625. 10.1161/JAHA.118.011625 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Martini E, Kunderfranco P, Peano C, Carullo P, Cremonesi M, Schorn T, et al. Single-cell sequencing of mouse heart immune infiltrate in pressure overload-driven heart failure reveals extent of immune activation. Circulation. (2019) 140:2089–107. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.041694 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Sager HB, Hulsmans M, Lavine KJ, Moreira MB, Heidt T, Courties G, et al. Proliferation and recruitment contribute to myocardial macrophage expansion in chronic heart failure. Circ Res. (2016) 119:853–64. 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.309001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Liu X, Zhang YB, Deng Y, Yang L, Ou W, Xie MD, et al. Mitochondrial protein hyperacetylation underpins heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in mice. J Mol Cell Cardiol. (2022) 165:76–85. 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2021.12.015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Ko JH, Olona A, Papathanassiu AE, Buang N, Park KS, Costa ASH, et al. Bcat1 affects mitochondrial metabolism independently of leucine transamination in activated human macrophages. J Cell Sci. (2020) 133:jcs247957. 10.1242/jcs.247957 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.GBD 2017 Causes of Death Collaborators. Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2013. Lancet. (2015) 385:117–71. 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61682-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Kolwicz SC, Jr, Purohit S, Tian R. Cardiac metabolism and its interactions with contraction, growth, and survival of cardiomyocytes. Circ Res. (2013) 113:603–16. 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.113.302095 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Young LH, McNulty PH, Morgan C, Deckelbaum LI, Zaret BL, Barrett EJ. Myocardial protein turnover in patients with coronary artery disease. Effect of branched chain amino acid infusion. J Clin Invest. (1991) 87:554–60. 10.1172/JCI115030 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Yang R, Dong J, Zhao H, Li H, Guo H, Wang S, et al. Association of branched-chain amino acids with carotid intima-media thickness and coronary artery disease risk factors. PLoS One. (2014) 9:e99598. 10.1371/journal.pone.0099598 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Yang RY, Wang SM, Sun L, Liu JM, Li HX, Sui XF, et al. Association of branched-chain amino acids with coronary artery disease: a matched-pair case-control study. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. (2015) 25:937–42. 10.1016/j.numecd.2015.06.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.McNulty PH, Jacob R, Deckelbaum LI, Young LH. Effect of hyperinsulinemia on myocardial amino acid uptake in patients with coronary artery disease. Metabolism. (2000) 49:1365–9. 10.1053/meta.2000.9510 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Schwartz RG, Barrett EJ, Francis CK, Jacob R, Zaret BL. Regulation of myocardial amino acid balance in the conscious dog. J Clin Invest. (1985) 75:1204–11. 10.1172/JCI111817 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Turer AT, Stevens RD, Bain JR, Muehlbauer MJ, van der Westhuizen J, Mathew JP, et al. Metabolomic profiling reveals distinct patterns of myocardial substrate use in humans with coronary artery disease or left ventricular dysfunction during surgical ischemia/reperfusion. Circulation. (2009) 119:1736–46. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.816116 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Wang W, Zhang F, Xia Y, Zhao S, Yan W, Wang H, et al. Defective branched chain amino acid catabolism contributes to cardiac dysfunction and remodeling following myocardial infarction. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2016) 311:H1160–9. 10.1152/ajpheart.00114.2016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Xu Y, Jiang H, Li L, Chen F, Liu Y, Zhou M, et al. Branched-chain amino acid catabolism promotes thrombosis risk by enhancing tropomodulin-3 propionylation in platelets. Circulation. (2020) 142:49–64. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.043581 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Ou W, Liang Y, Qing Y, Wu W, Xie MD, Zhang YB, et al. Hypoxic acclimation improves cardiac redox homeostasis and protects heart against ischemia-reperfusion injury through upregulation of O-glcnacylation. Redox Biol. (2021) 43:101994. 10.1016/j.redox.2021.101994 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Yang Y, Zhao M, He X, Wu Q, Li DL, Zang WJ. Pyridostigmine protects against diabetic cardiomyopathy by regulating vagal activity, gut microbiota, and branched-chain amino acid catabolism in diabetic mice. Front Pharmacol. (2021) 12:647481. 10.3389/fphar.2021.647481 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Kanamori H, Takemura G, Goto K, Tsujimoto A, Mikami A, Ogino A, et al. Autophagic adaptations in diabetic cardiomyopathy differ between type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Autophagy. (2015) 11:1146–60. 10.1080/15548627.2015.1051295 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Yu W, Zha W, Ren J. Exendin-4 and liraglutide attenuate glucose toxicity-induced cardiac injury through mTOR/ULK1-dependent autophagy. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2018) 2018:5396806. 10.1155/2018/5396806 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Hershberger RE, Hedges DJ, Morales A. Dilated cardiomyopathy: the complexity of a diverse genetic architecture. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2013) 10:531–47. 10.1038/nrcardio.2013.105 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Caragnano A, Aleksova A, Bulfoni M, Cervellin C, Rolle IG, Veneziano C, et al. Autophagy and inflammasome activation in dilated cardiomyopathy. J Clin Med. (2019) 8:1519. 10.3390/jcm8101519 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Mazelin L, Panthu B, Nicot AS, Belotti E, Tintignac L, Teixeira G, et al. mTOR inactivation in myocardium from infant mice rapidly leads to dilated cardiomyopathy due to translation defects and p53/JNK-mediated apoptosis. J Mol Cell Cardiol. (2016) 97:213–25. 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2016.04.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Portero V, Nicol T, Podliesna S, Marchal GA, Baartscheer A, Casini S, et al. Chronically elevated branched chain amino acid levels are pro-arrhythmic. Cardiovasc Res. (2022) 118:1742–57. 10.1093/cvr/cvab207 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Riedl A, Wawro N, Gieger C, Meisinger C, Peters A, Roden M, et al. Identification of comprehensive metabotypes associated with cardiometabolic diseases in the population-based Kora study. Mol Nutr Food Res. (2018) 62:e1800117. 10.1002/mnfr.201800117 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Tobias DK, Lawler PR, Harada PH, Demler OV, Ridker PM, Manson JE, et al. Circulating branched-chain amino acids and incident cardiovascular disease in a prospective cohort of US women. Circ Genom Precis Med. (2018) 11:e002157. 10.1161/CIRCGEN.118.002157 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Mirmiran P, Teymoori F, Asghari G, Azizi F. Dietary intakes of branched chain amino acids and the incidence of hypertension: a population-based prospective cohort study. Arch Iran Med. (2019) 22:182–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Teymoori F, Asghari G, Mirmiran P, Azizi F. Dietary amino acids and incidence of hypertension: a principle component analysis approach. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:16838. 10.1038/s41598-017-17047-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Flores-Guerrero JL, Connelly MA, Shalaurova I, Garcia E, Bakker SJL, Dullaart RPFA. Metabolomic index based on lipoprotein subfractions and branched chain amino acids is associated with incident hypertension. Eur J Intern Med. (2021) 94:56–63. 10.1016/j.ejim.2021.07.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Flores-Guerrero JL, Groothof D, Connelly MA, Otvos JD, Bakker SJL, Dullaart RPF. Concentration of branched-chain amino acids is a strong risk marker for incident hypertension. Hypertension. (2019) 74:1428–35. 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.119.13735 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]