Abstract
Background and purpose: Central lung tumours can be treated by magnetic resonance (MR)-guided radiotherapy. Complications might be reduced by decreasing the Planning Target Volume (PTV) using mid-position (midP)-based planning instead of Internal Target Volume (ITV)-based planning. In this study, we aimed to verify a method to automatically derive patient-specific PTV margins for midP-based planning, and show dosimetric robustness of midP-based planning for a 1.5T MR-linac.
Materials and methods: Central(n = 12) and peripheral(n = 4) central lung tumour cases who received 8x7.5 Gy were included. A midP-image was reconstructed from ten phases of the 4D-Computed Tomography using deformable image registration. The Gross Tumor Volume (GTV) was delineated on the midP-image and the PTV margin was automatically calculated based on van Herk’s margin recipe, treating the standard deviation of all Deformation Vector Fields, within the GTV, as random error component. Dosimetric robustness of midP-based planning for MR-linac using automatically derived margins was verified by 4D dose-accumulation. MidP-based plans were compared to ITV-based plans. Automatically derived margins were verified with manually derived margins.
Results: The mean D95% target coverage in GTV + 2 mm was 59.9 Gy and 62.0 Gy for midP- and ITV-based central lung plans, respectively. The mean lung dose was significantly lower for midP-based treatment plans (difference:-0.3 Gy; ). Automatically derived margins agreed within one millimeter with manually derived margins.
Conclusions: This retrospective study indicates that mid-position-based treatment plans for central lung Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy yield lower OAR doses compared to ITV-based treatment plans on the MR-linac. Patient-specific GTV-to-PTV margins can be derived automatically and result in clinically acceptable target coverage.
Keywords: MR-Linac, Mid-position planning, Dose accumulation, MRgRT, NSCLC
1. Introduction
Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) is the recommended treatment for inoperable patients with early stage non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). These tumours require a Biologically Effective Dose (BED) of 100 Gy to achieve local control ([1]), but the proximity of central tumours to the mediastinum may prohibit giving such a high dose to the tumour with acceptable risk of toxicity to critical mediastinal structures. Treatment of (ultra)-central lung tumours is therefore controversial as it appears to have a higher rate of complications than treatment of peripheral tumours ([2], [3], [4], [5]).
Thoracic radiotherapy is associated with large and complex geometrical uncertainties, such as anatomical changes over the course of treatment and respiratory motion, which must be incorporated in the treatment plan via margins around the tumour to create the planning target volume (PTV) ([6], [7]). MR-guided radiotherapy enables on-table plan adaptation to the daily anatomy, thereby reducing uncertainties associated with inter-fractional anatomical changes ([8], [9]). Central lung tumours are now routinely treated with MR-guided radiotherapy ([10], [11], [8], [12]).
Respiratory motion is one of the largest sources of geometrical uncertainty for lung radiotherapy. The conventional approach, using an internal target volume (ITV), is highly conservative and leads to unnecessary exposure of healthy tissue. Gating treatment delivery to a particular respiratory phase significantly reduces the uncertainty associated with respiratory motion and thus the irradiated volume ([9]). Clinically, improved dose conformality through gating must be balanced with reductions in duty cycle. Planning on the time-weighted mean position of the tumour, known as the mid-position (midP), also enables a significant reduction of the PTV compared to ITV-based planning whilst maintaining a 100% duty cycle and ensuring dose coverage of the tumour ([13]). The 3D tumour motion can then be regarded as a source of random error when deriving the PTV margin. This 3D motion is generally visually derived from the peak-to-peak (p2p) motion of the tumour along the three Cartesian axes, but can in principle be extracted from the deformation vector fields (DVFs) generated by the deformable image registration (DIR) used to create the mid-position image. Automated derivation of the 3D motion would also be much easier to implement in an online adaptive MR-linac workflow.
In this work, we aimed to verify automatic derivation of margins for central lung tumours and to demonstrate the dosimetric robustness of mid-position based SBRT to respiratory motion on an MR-linac using 4D dose accumulation. Special consideration was given to geometric and dosimetric uncertainties associated with the use of DIR for dose accumulation.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Patient selection and imaging
In this retrospective study, 17 patients (median age: 70, range: 30–86; four female) with NSCLC were included. All patients underwent SBRT on a conventional cone-beam CT-guided linac. Thirteen patients with central lung tumour were selected in chronological order between 12–2017 and 11–2019, of which one patient was excluded due to poor image quality. Another four patients with peripheral lung tumours exhibiting large respiratory motion ( mm) p2p were included to investigate robustness of the derived margins for large tumour movement. Patient data were collected retrospectively under the FAST-ART protocol (IRB reference: 20–519/C). Patients underwent 4D-CT imaging with 10 respiratory phases, from which an averaged 3D-CT image and a midP image ([13], [14]) were reconstructed for ITV-based and midP-based dose planning, respectively (Supp. 6.1).
2.2. Target definition and margin
For each patient, the ITV was delineated on the averaged 3D-CT image taking 4D tumour excursion into account, while the GTV was delineated on the midP-CT image. The ITVs, which were taken from the clinical plans, were delineated by several radiation oncologists (in training) and verified by a second specialized radiation oncologist, whereas the GTVs were delineated by a single radiation oncologist (in training) focused on lung radiotherapy. For the ITV-based treatment plans an isotropic ITV-PTV margin of 3 mm was used following institutional practices. For midP PTV creation, the non-linear van Herk margin recipe was used ([15]),
| (1) |
with the GTV-PTV margin to get target coverage in 90% of the population with the 75% isoline. Furthermore (6.4 mm) is the beam penumbra in lung tissue, the random error component due to breathing, and the residual systematic and random error components, respectively ([16]) (Table S2). Note that the 2 mm delineation uncertainty ([17]) was accounted for a random error () to better reflect the daily target redelineation in MR-linac workflows. A similar delineation uncertainty was assumed for the ITV plans which in clinical practise is re-delineated on the daily motion-averaged MRI ([12]). The other systematic and random interfraction errors taken into account were uncertainty in treatment planning and geometric fidelity of MR-images and intra-fraction drift of the target based on Takao et al. ([18]).
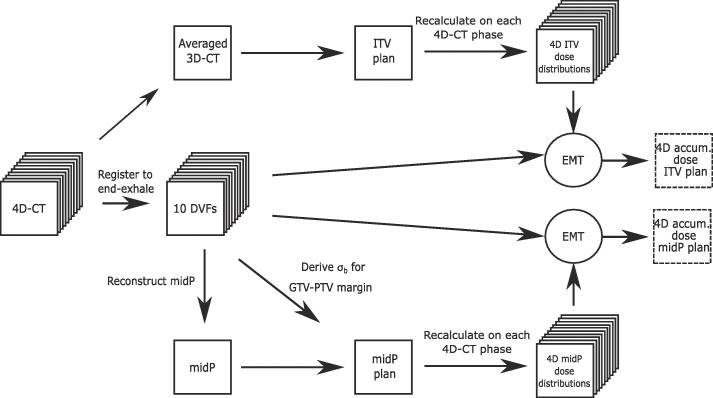
In this study, was directly calculated per voxel from the ten DVFs generated for midP reconstruction (Fig. 1). For each axis, i.e. cranio-caudal (CC), anterior-posterior (AP) and left–right (LR)), the standard deviation (SD) of the ten DVFs was calculated. The automatically-derived median SD of all voxels within the GTV () was used as input for the random error due to tumour motion in the aforementioned margin recipe, which yields automatically-derived anisotropic GTV-PTV margins () specific to each patient.
Fig. 1.
Schematic 4D-dose accumulation workflow including dose warping using energy-mass transfer (EMT) and derivation of the GTV-PTV margin including the standard deviation () of the deformation vector fields (DVFs).
2.3. Treatment planning
Treatment plans were generated in Monaco v5.40.01 for the Unity MR-linac. Two plans were created for each patient: one optimized for the ITV on the averaged 3D-CT, the other plan optimized for the GTV on the midP-CT. Treatment planning was performed using 13–15 intensity-modulated beams, which were angled to avoid entering through uninvolved lung or the patients arms, simulated as positioned along the body ([19]). Further planning details are given in Supp. 6.2.
2.4. Validation of GTV-PTV margins
In order to validate the automatically derived GTV-PTV margins for the midP planning process, the automatically derived was compared to a manually derived . The was derived by manual rigid registration of the tumour region of each 4D-CT phase to the end-exhale phase, resulting in ten displacement vectors. The SD of these displacement vectors is defined as the , and should be approximately the same as the .
In current clinical practice, for midP is typically based on the p2p amplitude of the tumour. The p2p amplitude is manually measured and converted to a random error component by using the rule of thumb that can be approximated as one third of the p2p amplitude ([20], [21]).
All ’s were used as input for the in the van Herk recipe. Bland–Altman analyses ([22]) were performed to compare the margins derived by manual rigid registration (), and the margins determined from the p2p motion (), with the automatically-derived margins () ([22]). The peripheral lung tumour cases were processed in the margin analysis and shown the Bland–Altman plot but were excluded from statistical analysis.
2.5. 4D-dose accumulation
A 4D-dose accumulation was performed to evaluate the dosimetric robustness of each plan under respiratory motion conditions (Fig. 1). For each treatment plan, the dose was recalculated on the ten phases of the 4D-CT using a standalone GPU-Monte-Carlo Dose (GPUMCD) engine ([23]). The dose was then warped and accumulated to the midP-CT using the DVFs generated by the midP reconstruction process. The dose accumulation was regularized to keep energy-mass transfer (EMT) constant ([24]).
2.6. Dosimetric evaluation
Target coverage was evaluated on the GTV expanded with a 2 mm margin (GTV + 2 mm) for both the ITV-based and the midP-based plan. The evaluation margin was used to incorporate one SD of delineation uncertainty ([17]), which is otherwise not accounted for in the 4D-dose accumulation workflow. Lung volume for mean lung dose (MLD) calculation was defined as lung minus GTV. For the central lung tumours, a statistical analysis with a pairwise Wilcoxon-signed rank test was performed to compare the metrics determined from the 4D-accumulated dose. Given the limited number of patients, the statistical analysis of the organ-at-risk (OAR) DVH-parameters was only used for hypothesis generation to provide an overview of the differences between both planning methods.
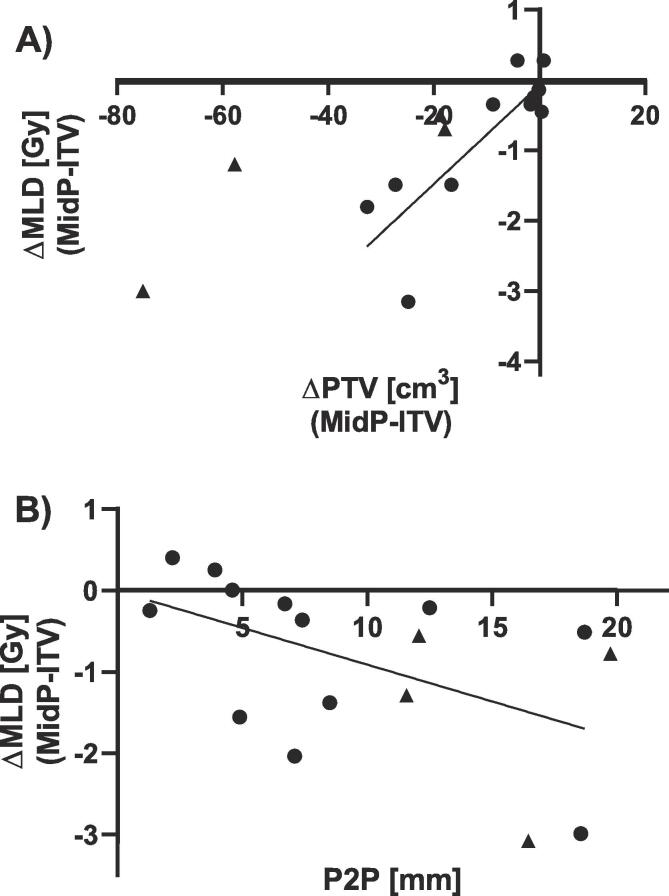
We hypothesized that a larger PTV would correspond to a higher MLD, and that a midP-based treatment would be most beneficial in terms of reduction of MLD for central lung patients with larger p2p tumour motion ([25]). MLD difference between midP- and ITV-based plans was therefore compared with the difference in PTV and p2p-motion. The four peripheral cases were not analyzed statistically, but were included in the figures to show the trend for larger tumour motion.
2.7. DDM and -index
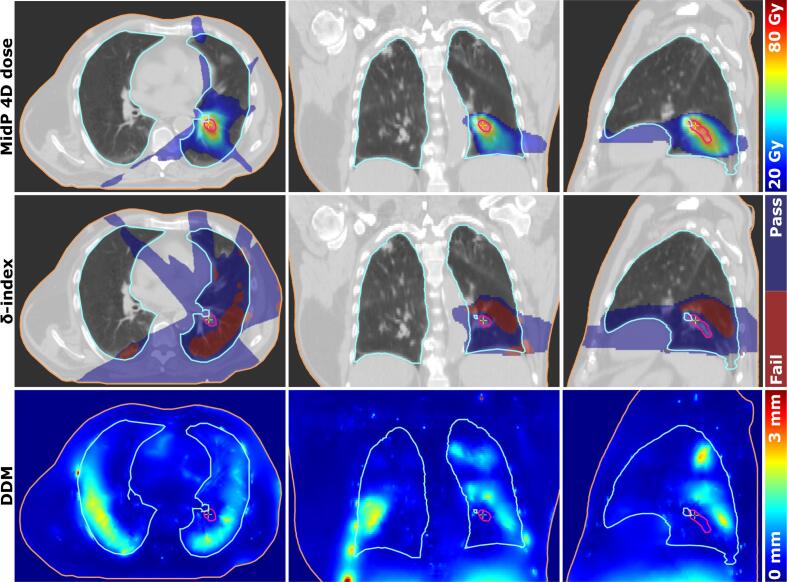
The distance discordance metric (DDM) ([26], [27]) was calculated for each patient to assess the precision of the registration used for midP image reconstruction and dose accumulation. Registration of the end-exhale phase to the end-inhale phase via an intermediate registration to each in-between phase of the 4D-CT results in eight DVFs. The SD of the eight voxel positions in the end-exhale phase gives the DDM value for each voxel, with a lower score indicating higher DIR consistency. The resulting DDM map was then warped to the midP image ([27]).
To determine the uncertainty in the accumulated dose distributions the -index was calculated for all voxels with a dose difference criterion of . The -index is a novel metric to evaluate the uncertainty associated with the dose accumulation process, by incorporating the uncertainty of the registration (i.e, the DDM) and the spatial variation in the 4D-accumulated dose distribution in the neighbourhood of each voxel ([28]). In analogy to the gamma-index, the uncertainty of the 4D-dose accumulation is defined to be acceptable when the -index is 1.
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of margin derivation methods
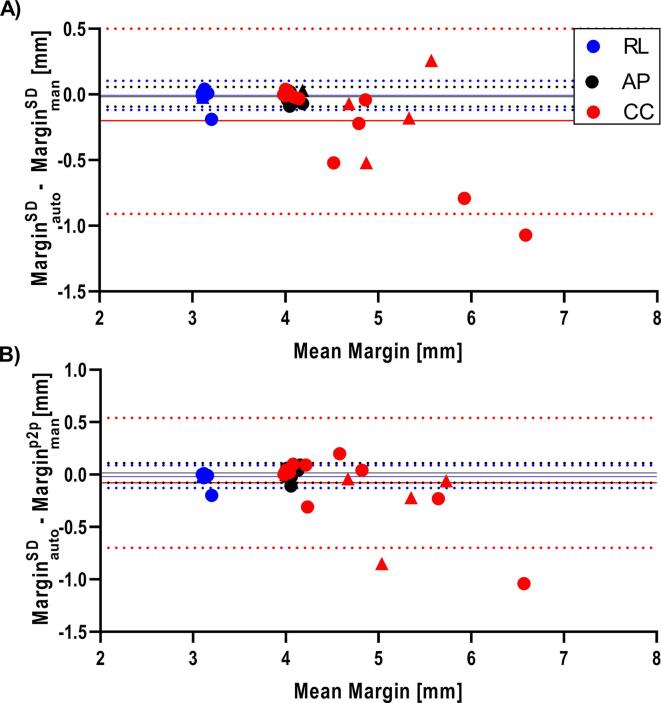
Bland–Altman plots showing the comparisons between automatically-derived margins () with corresponding manually derived margins based on the p2p motion () or the SD () are shown in Fig. 2. For the central lung tumours, the PTV margins in CC direction for and ranged between 4.0–6.1 mm, 4.0–7.1 mm and 4.0–7.1 mm respectively. The margins in AP and RL direction were all four and three millimeter when rounded. The differences between and or were mainly along the CC axis, as expected with the motion predominantly in cranio-caudal direction. Differences between and , and between and , ranged between −1.0 mm to + 0.2 mm and −1.1 mm to + 0.3 mm respectively for the central lung tumour cases, with a trend of larger variation between margin derivation methods for larger target motion. For the peripheral lung tumours with large motion, a similar larger variation was observed between (range margins: 4.7–5.8 mm) and or , with differences from −0.5 to 0.3 mm and −0.9 to −0.04 mm, respectively.
Fig. 2.
(A) Bland–Altman plot of the margin determined from the DVFs ), versus the margin determined based on displacement of the target volume using manual rigid registration (). (B) Bland–Altman plot of the versus the margin based on the manually measured p2p tumour motion (). Central and peripheral tumour cases are represented by a dot and triangle, respectively. Bias (dashed line) and median (solid line) are shown for central lung cases. (AP: anterior-posterior; CC: cranial-caudal; RL: right-left).
After rounding the margins to the nearest millimeter, to mimic the precision of treatment planning systems, the automatically-derived margin was in two instances smaller than the p2p-margin by 1 mm, and in one instance larger by 1 mm. All differences were along the CC axis. No differences were found between margins determined along the AP and RL axes.
3.2. Plan comparison
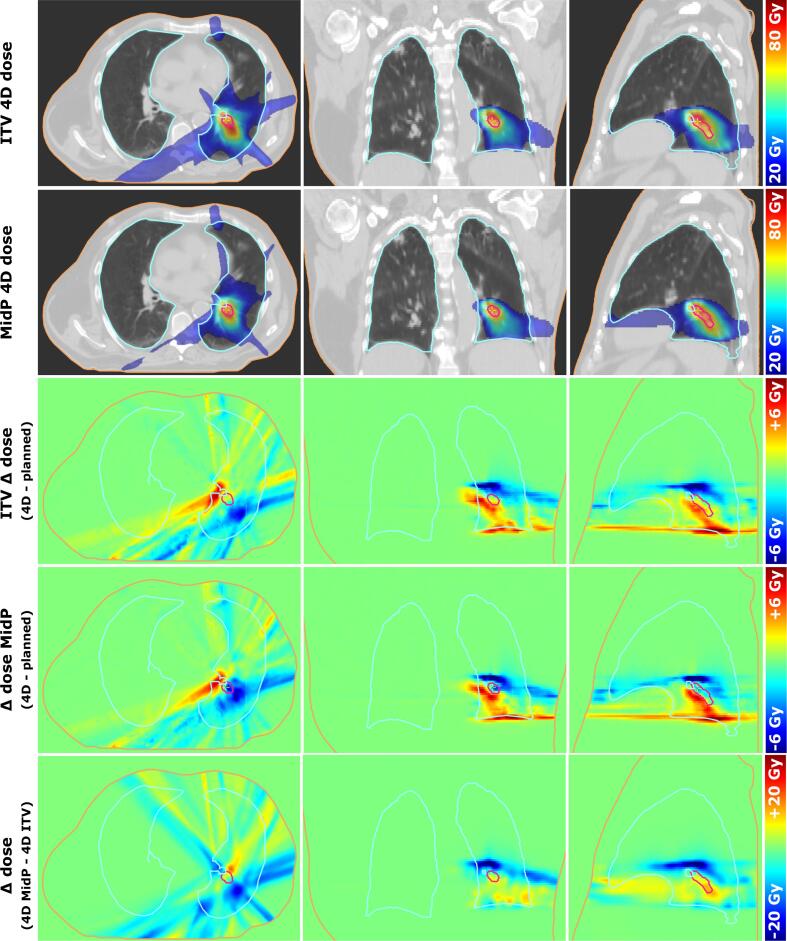
For central lung tumour cases, the mean (SD) PTVs for the ITV-based plans was significantly larger (p = 0.0037) than for the midP-based plans with 40.0 cm3 (41.4 cm3) and 28.9 cm3 (40.7 cm3), respectively (Table S3). The metrics for the target and OAR doses determined for the 4D-dose accumulations for the midP treatment plans were compared to the corresponding 4D-dose accumulations for the ITV-based plans. In the example patient with respiratory motion of 23 mm along the CC-axis, it can be seen that dose was mainly reduced in the CC-direction, by up to 30 Gy, for midP-based plans compared to ITV-based plans (Fig. 3). The mean (SD) D95% coverage of the GTV + 2 mm was 59.9 Gy (4.1 Gy) and 62.0 Gy (4.7 Gy) for the midP and ITV plans for the central lung tumours respectively. The four peripheral lung tumours all got acceptable dose coverage with D95% ranging between 60.1–63.1 Gy and 63.7–68.1 Gy for midP-based and ITV-based dose distributions, respectively.
Fig. 3.
Example patient with 4D-accumulated midP and ITV doses, dose differences to planned dose, and the midP versus ITV dose difference.
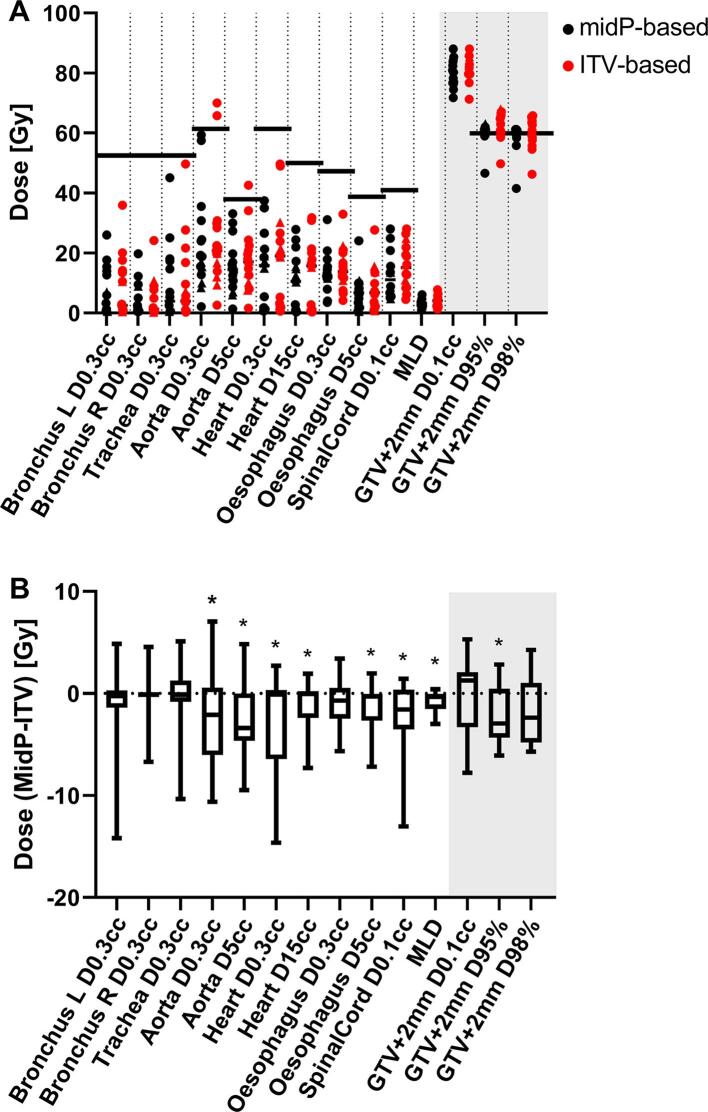
The dose delivered to the target for central lung tumours in midP plans was significantly lower for D95% (-2.9 Gy, p = 0.032) compared to the ITV plan, but not for D98% (-2.3 Gy, p = 0.057) and D0.1 cm3 (+1.3 Gy, p = 0.73) (Fig. 4). The midP-based accumulated doses showed a D95% and D98% closer to the prescribed dose (60 Gy), with the spread (SD) in dose two-third of the ITV-based accumulated plans. Several DVH parameters for OARs were significantly lower, including the MLD, which showed a small yet significant reduction for midP-based versus ITV-based treatment planning of median −0.3 Gy (range:-3.0 Gy + 0.4 Gy; ). The aorta DVH parameters show that in two cases the dose was above the planning constraints for the ITV dose distributions whereas the midP dose distribution was below the planning constraint.
Fig. 4.
(A) DVH metrics for OARs and GTV + 2 mm for midP-based (black) and ITV-based (red) plans. The horizontal lines show the planning constraint for OARs and target prescriptions when applicable. Central cases and peripheral tumour cases are represented by a dot and a triangle, respectively. (B) Difference between planning metrics for OARs and GTV + 2 mm between 4D-accumulated dose distribution of midP-based treatment plan and ITV-based treatment plans only for central lung tumour cases. (*: significant ( = 0.05) with Wilcoxon signed-rank test).
For central and peripheral lung tumour cases, we observed moderate correlations between the difference in MLD and PTV volume (r = 0.84, p = 0.0005) and between the difference in MLD and the p2p-motion of the tumour (r=-0.50, p = 0.093) (Fig. 5).
Fig. 5.
The difference in MLD between the midP-based and ITV-based treatment plans versus A) the difference in PTV volume and B) the amplitude of the p2p motion of the tumour.
3.3. midP-image reconstruction and dose accumulation accuracy
The precision of the registration of the midP image reconstruction and the dose accumulation is shown in Fig. 6, which shows, in this case, high DDM scores corresponding with failing the -index criterion. The mean DDM for all patients was 0.3 mm (range: 0.1–0.9 mm) within the 90% prescribed dose isocontour based on the ITV plan. The -index showed a median pass-rate in the 90% dose region of 99.8% (range: 91.9%-100%) and 100% (range: 92.7% - 100%) for the midP and ITV 4D-dose accumulations of the central lung tumours respectively.
Fig. 6.
Central lung tumour case with 4D-accumulated dose for a midP-based plan, and corresponding -index pass-fail map for the %-prescribed dose region, and the DDM map.
4. Discussion
In this retrospective study, we provided the first successful demonstration of the dosimetric suitability of mid-position-based treatments for central lung SBRT on an MR-linac. Using 4D dose calculation on CT, and EMT mapping, we showed that mid-position-based treatment plans maintain target coverage with slightly reduced dose compared to ITV-based reference plans, while achieving a variable amount of OAR sparing depending mostly on respiratory amplitude and target volume. The four peripheral cases with large tumour motion indicate that with larger motion amplitudes, the target is still covered using midP based treatment planning. Importantly, our dosimetric analysis supported the automatic derivation of patient-specific GTV-to-PTV margins based on the DVFs inherent to the generation of the mid-position CT image. By directly inserting the SD of motion into the margin equation, motion data from multiple deformable registration is evaluated, which increases the robustness against registration outliers. In addition, the simplification that the SD of motion typically corresponds to one-third of the p2p motion is retired. Automating margin calculations in this way speeds up margin creation, and thus opens opportunities for daily margin adaption for MR-linac systems.
It should be noted that clinical experience with stereotactic lung treatments on MR-linac devices is still limited ([9], [29], [11]). Intra-fractional motion management based on MRI guidance holds great promise ([30], [31]) but has not yet achieved its full potential. Currently, ITV-based lung treatments are still the only vendor-supported motion management strategy on the Unity MR-linac. For MRIdian MR-linacs, respiratory gating ensures tight PTV margins to reduce dose to organs-at-risk, with a trade-off on treatment efficiency, which might lead to longer treatment times ([32]). In future, dynamic multi-leaf collimator (MLC) tracking is expected to combine the dosimetric advantages of gating with the 100% duty cycle of ITV/midP deliveries ([33]). In the meantime, this study demonstrates that mid-position-based treatments offer a viable dosimetric improvement over ITV-based deliveries while maintaining a 100% duty cycle. For liver SBRT, it was previously shown that a mid-position-based treatment strategy is feasible on the Unity MR-linac ([34]).
Given the small sample size in this study, the statistical analysis on OAR dose should be considered as exploratory and hypothesis generating. Multiple testing was not performed, given the sample size constraint, and the explorative nature of the study. Validation of these data is needed in a larger cohort. This study is limited to analysing 4D-accumulated dose based on the pre-treatment 4D-CT. ’Snap-shot’ 4D-CTs poorly correlate with motion during treatment ([35], [36], [37]). This limitation can be overcome by creating a mid-position MRI based on 4D-MRI for daily plan adaption ([27]), especially when combined with (automatically) extracted daily GTV-to-PTV margins from the 4D-MRI. MidP MR-image reconstruction was shown to be feasible for daily plan adaptation on an MR-linac ([38]). Underprediction of peak-to-peak target motion during treatment on pre-treatment 4D-CTs is known issue([36], [37]), which will affect the ITV-based more than the midP-based treatment plans as the midP-margin only weakly depends on peak-to-peak motion. 4D-CTs are also prone to image artefacts induced by irregular or slow breathing ([39]). As our mid-position CTs were derived from 4D-CT data, any such artefact could propagate to the mid-position CT, thus causing dose calculation and warping errors. Artefacts outside the beam path were deemed acceptable. In addition, the DDM, a quantitative metric for DIR uncertainty, was calculated. The deformable registration algorithm used in this study does not explicitly account for sliding motion, therefore registration accuracy is limited near those regions. The novel -index generally yielded very high pass rates in the high dose region, indicating a high level of confidence in our 4D-accumulated dose distributions. For one (excluded) patient, the -index showed a very low passing rate, in agreement with the visually assessed low image quality of the underlying 4D-CT. Interestingly, the DDM and -index were able to detect this case with suboptimal midP-image quality, which might in future help to automatilly identify patients that could benefit from a new 4D-CT planning scan. In our margin calculation, delineation uncertainty was assumed to be a random error as the target is re-delineated during each treatment fraction. Further investigation of inter- and intra-observer delineation uncertainty during treatment on an MRI-linac is needed to confirm this assumption. Similar interobserver variation error was assumed for ITV and GTV delineation, as the difference for this error is within one mm between different types of CT reconstructions ([40]). Importantly, adapting plans on daily MRI and accumulating dose across fractions was considered outside the scope of this study. While an in-depth analysis of inter-fractional anatomical changes and plan adaptation is valuable, it is not expected to undermine our findings relating to target coverage under periodic intra-fractional motion conditions. In this study, non-periodic intra-fractional motion, namely baseline drifts or shifts, was accounted for in the margin recipe. In future, baseline motion could be actively mitigated using tumour trailing ([41]), potentially resulting in further margin reductions. In two cases, mid-position based treatment planning resulted in an OAR dose below the dose limit, in contrast to the ITV based treatment plan. Although on average a small dose reduction for the OARs was achieved, for individual patients a large effect on OAR dose can be achieved with mid-position based treatment planning.
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Acknowledgements
Martin F. Fast acknowledge funding by the Dutch Research Council (NWO) through project No. 17515 (BREATHE EASY).
Footnotes
Supplementary data associated with this article can be found, in the online version, athttps://doi.org/10.1016/j.phro.2022.05.002.
Contributor Information
Hans Ligtenberg, Email: H.Ligtenberg-2@umcutrecht.nl.
Martin F. Fast, Email: m.f.fast-2@umcutrecht.nl.
Supplementary data
The following are the Supplementary data to this article:
References
- 1.Onishi H., Araki T., Shirato H., Nagata Y., Hiraoka M., Gomi K., et al. Stereotactic hypofractionated high-dose irradiation for stage I nonsmall cell lung carcinoma: clinical outcomes in 245 subjects in a Japanese multiinstitutional study. Cancer. 2004;101:1623–1631. doi: 10.1002/cncr.20539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Roach M.C., Robinson C.G., Dewees T.A., Ganachaud J., Przybysz D., Drzymala R., et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for central early-stage NSCLC: Results of a prospective phase I/II trial. J Thorac Oncol. 2018;13:1727–1732. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2018.07.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Tekatli H., Haasbeek N., Dahele M., Haan P.D., Verbakel W., Bongers E., et al. Outcomes of hypofractionated high-dose radiotherapy in poor-risk patients with ”ultracentral” non–small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2016;11:1081–1089. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2016.03.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Haseltine J.M., Rimner A., Gelblum D.Y., Modh A., Rosenzweig K.E., Jackson A., et al. Fatal complications after stereotactic body radiation therapy for central lung tumors abutting the proximal bronchial tree. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2016;6:e27–e33. doi: 10.1016/j.prro.2015.09.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Timmerman R., McGarry R., Yiannoutsos C., Papiez L., Tudor K., DeLuca J., et al. Excessive toxicity when treating central tumors in a phase II study of stereotactic body radiation therapy for medically inoperable early-stage lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:4833–4839. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2006.07.5937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Jones, D. ICRU report 50–prescribing, recording and reporting photon beam therapy; 1994. doi:10.1118/1.597396.
- 7.Landberg T., Chavaudra J., Dobbs J., Gerard J.P., Hanks G., Horiot J.C., et al. Report 62. J ICRU. 1999;32. doi: 10.1093/jicru/os32.1.Report62. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Finazzi T., Palacios M.A., Spoelstra F.O., Haasbeek C.J., Bruynzeel A.M., Slotman B.J., et al. Role of on-table plan adaptation in MR-guided ablative radiation therapy for central lung tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2019;104:933–941. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.03.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Finazzi T., Haasbeek C.J., Spoelstra F.O., Palacios M.A., Admiraal M.A., Bruynzeel A.M., et al. Clinical outcomes of stereotactic MR-guided adaptive radiation therapy for high-risk lung tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2020;107:270–278. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2020.02.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Henke L.E., Kashani R., Hilliard J., DeWees T.A., Curcuru A., Przybysz D., et al. In silico trial of MR-guided midtreatment adaptive planning for hypofractionated stereotactic radiation therapy in centrally located thoracic tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2018;102:987–995. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2018.06.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Henke L.E., Olsen J.R., Contreras J.A., Curcuru A., DeWees T.A., Green O.L., et al. Stereotactic MR-guided online adaptive radiation therapy (SMART) for ultracentral thorax malignancies: results of a phase 1 trial. Adv Radiat Oncol. 2019;4:201–209. doi: 10.1016/j.adro.2018.10.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Merckel L., Hackett S., van Lier A., van den Dobbelsteen M., Rasing M., Snoeren L., et al. Po-1161: Feasibility of stereotactic body radiotherapy of (ultra)central lung tumors using an 1.5 T MR-linac. Radiother Oncol. 2021;161:5963–S964. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wolthaus J.W., Sonke J.J., van Herk M., Belderbos J.S., Rossi M.M., Lebesque J.V., et al. Comparison of different strategies to use four-dimensional computed tomography in treatment planning for lung cancer patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;70:1229–1238. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2007.11.042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Zachiu C., Papadakis N., Ries M., Moonen C., de Senneville B.D. An improved optical flow tracking technique for real-time MR-guided beam therapies in moving organs. Phys Med Biol. 2015;60:9003. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/60/23/9003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.van Herk M., Remeijer P., Rasch C., Lebesque J.V. The probability of correct target dosage: dose-population histograms for deriving treatment margins in radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2000;47:1121–1135. doi: 10.1016/S0360-3016(00)00518-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.van Herk M. Errors and margins in radiotherapy. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2004;14:52–64. doi: 10.1053/j.semradonc.2003.10.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Peulen H., Belderbos J., Guckenberger M., Hope A., Grills I., van Herk M., et al. Target delineation variability and corresponding margins of peripheral early stage NSCLC treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol. 2015;114:361–366. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2015.02.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Takao S., Miyamoto N., Matsuura T., Onimaru R., Katoh N., Inoue T., et al. Intrafractional baseline shift or drift of lung tumor motion during gated radiation therapy with a real-time tumor-tracking system. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2016;94:172–180. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2015.09.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.van den Wollenberg W., de Ruiter P., Nowee M.E., Jansen E.P., Sonke J.J., Fast M.F. Investigating the impact of patient arm position in an MR-linac on liver SBRT treatment plans. Med Phys. 2019;46:5144–5151. doi: 10.1002/mp.13826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Sonke J.J., Rossi M., Wolthaus J., van Herk M., Damen E., Belderbos J. Frameless stereotactic body radiotherapy for lung cancer using four-dimensional cone beam CT guidance. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009;74:567–574. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.08.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Bellec J., Arab-Ceschia F., Castelli J., Lafond C., Chajon E. ITV versus mid-ventilation for treatment planning in lung SBRT: a comparison of target coverage and PTV adequacy by using in-treatment 4D cone beam CT. Radiat Oncol. 2020;15:1–10. doi: 10.1186/s13014-020-01496-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Altman D.G., Bland J.M. Measurement in medicine: the analysis of method comparison studies. J R Stat Soc Series D. 1983;32:307–317. doi: 10.2307/2987937. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hissoiny S., Raaijmakers A., Ozell B., Després P., Raaymakers B. Fast dose calculation in magnetic fields with GPUMCD. Phys Med Biol. 2011;56:5119. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/56/16/003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Li H.S., Zhong H., Kim J., Glide-Hurst C., Gulam M., Nurushev T.S., et al. Direct dose mapping versus energy/mass transfer mapping for 4D dose accumulation: fundamental differences and dosimetric consequences. Phys Med Biol. 2013;59:173. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/59/1/173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Menten M.J., Fast M.F., Nill S., Kamerling C.P., McDonald F., Oelfke U. Lung stereotactic body radiotherapy with an MR-linac–quantifying the impact of the magnetic field and real-time tumor tracking. Radiother Oncol. 2016;119:461–466. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2016.04.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Saleh Z.H., Apte A.P., Sharp G.C., Shusharina N.P., Wang Y., Veeraraghavan H., et al. The distance discordance metric–a novel approach to quantifying spatial uncertainties in intra-and inter-patient deformable image registration. Phys Med Biol. 2014;59:733. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/59/3/733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.van de Lindt T.N., Fast M.F., van Kranen S.R., Nowee M.E., Jansen E.P., van der Heide U.A., et al. MRI-guided mid-position liver radiotherapy: validation of image processing and registration steps. Radiother Oncol. 2019;138:132–140. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2019.06.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.van den Dobbelsteen M., Hackett S., Verhoeff J., Merckel L., van Es C., Snoeren L., et al. PD-0865 the delta index: a novel metric to assess dose accumulation uncertainty in MR-guided radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol. 2021;161:S700–S702. doi: 10.1016/S0167-8140(21)07144-9. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Finazzi, T., de Koste, J.R.v.S., Palacios, M.A., Spoelstra, F.O., Slotman, B.J., Haasbeek, C.J., et al. Delivery of magnetic resonance-guided single-fraction stereotactic lung radiotherapy. Phys Imaging Radiat Oncol 2020;14:17–23. doi:10.1016/j.phro.2020.05.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 30.Menten M.J., Wetscherek A., Fast M.F. MRI-guided lung SBRT: Present and future developments. Phys Med. 2017;44:139–149. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmp.2017.02.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Bainbridge H., Salem A., Tijssen R.H.N., Dubec M., Wetscherek A., Es C.V., et al. Magnetic resonance imaging in precision radiation therapy for lung cancer. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2017;6:689. doi: 10.21037/tlcr.2017.09.02. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.de Koste, J.R.v.S., Palacios, M.A., Bruynzeel, A.M., Slotman, B.J., Senan, S., Lagerwaard, F.J.. MR-guided gated stereotactic radiation therapy delivery for lung, adrenal, and pancreatic tumors: a geometric analysis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2018;102:858–866. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2018.05.048. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 33.Uijtewaal P., Borman P.T., Woodhead P.L., Hackett S.L., Raaymakers B.W., Fast M.F. Dosimetric evaluation of MRI-guided multi-leaf collimator tracking and trailing for lung stereotactic body radiation therapy. Med Phys. 2021;48:1520–1532. doi: 10.1002/mp.14772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.van de Lindt T.N., Fast M.F., van den Wollenberg W., Kaas J., Betgen A., Nowee M.E., et al. Validation of a 4D-MRI guided liver stereotactic body radiation therapy strategy for implementation on the MR-linac. Phys Med Biol. 2021;66 doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2019.06.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Dhont J., Vandemeulebroucke J., Burghelea M., Poels K., Depuydt T., Van Den Begin R., et al. The long-and short-term variability of breathing induced tumor motion in lung and liver over the course of a radiotherapy treatment. Radiother Oncol. 2018;126:339–346. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2017.09.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Steiner E., Shieh C.C., Caillet V., Booth J., O’Brien R., Briggs A., et al. Both four-dimensional computed tomography and four-dimensional cone beam computed tomography under-predict lung target motion during radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol. 2019;135:65–73. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2019.02.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Cusumano D., Dhont J., Boldrini L., Chiloiro G., Teodoli S., Massaccesi M., et al. Predicting tumour motion during the whole radiotherapy treatment: a systematic approach for thoracic and abdominal lesions based on real time MR. Radiother Oncol. 2018;129:456–462. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2018.07.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Paulson E.S., Ahunbay E., Chen X., Mickevicius N.J., Chen G.P., Schultz C., et al. 4D-MRI driven MR-guided online adaptive radiotherapy for abdominal stereotactic body radiation therapy on a high field MR-Linac: Implementation and initial clinical experience. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2020;23:72–79. doi: 10.1016/j.ctro.2020.05.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Sentker T., Schmidt V., Ozga A.K., Petersen C., Madesta F., Hofmann C., et al. 4D CT image artifacts affect local control in SBRT of lung and liver metastases. Radiother Oncol. 2020;148:229–234. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2020.04.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Mercieca, S., Belderbos, J.S., De Jaeger, K., Schinagl, D.A., Van Zijp, N.v.d.V., Pomp, J., et al. Interobserver variability in the delineation of the primary lung cancer and lymph nodes on different four-dimensional computed tomography reconstructions. Radiother Oncol 2018;126:325–332. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2017.11.020. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 41.Fast M., van de Schoot A., van de Lindt T., Carbaat C., van der Heide U., Sonke J.J. Tumor trailing for liver SBRT on the MR-Linac. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2019;103:468–478. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2018.09.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.