After a two-year COVID break, the Canadian Urological Association (CUA)-American Urological Association (AUA) Residents and Fellows Program was relaunched this year. The goal of this program is to enhance the clinical and professional development of Canadian urology residents and fellows, with an emphasis in GU oncology, and to improve presentation skills. Selected Canadian residents and fellows attended assigned GU oncology sessions and presented their findings to the CUA Education Advisory Council. Herein is a summary of their findings.
***
Summary 1 – Abstract PD22-04: Immediate radiotherapy vs. observation in patients with node-positive prostate cancer after radical prostatectomy1
Braden Millan
The authors of this trial emulated the design of the RADICALS-RT study to create a hypothetical pragmatic trial of immediate adjuvant radiotherapy (aRT) with androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) vs. observation with salvage radiotherapy (sRT) at relapse in men with pN1 prostate cancer after radical prostatectomy (RP). They included men aged 50–69 years old, pT2-3, Rany, N1, M0, with a pre-treatment prostate-specific antigen (PSA) <50 ng/mL. Those included were treated from 2006–2015 with 60–72 Gy of aRT with or without ADT within 26 weeks of RP. Authors performed a propensity score analysis using stabilized inverse probability treatment re-weighting.
A total of 3510 patients were included in the study, of whom 587 (17%) received aRT (426 or 73% with concurrent ADT). Median followup was 42.3 months, during which time 333 deaths occurred. As outlined in Table 1, baseline characteristics were significantly different in nearly all categories prior to propensity score adjustment.
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics
| Characteristics | Total (%) 3510 (100%) | Observation with sRT 2923 (83%) | aRT 581 (17%) |
p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 62 | 62 | 61 | 0.01 |
| Charlson 0 | 2892 (82) | 2399 (82) | 493 (84) | 0.27 |
| PSA (ng/mL) | 8.5 | 8.5 | 8.4 | 0.62 |
| Gleason score | <0.01 | |||
| 3+3 | 114 (3) | 102 (3) | 12 (2) | |
| 3+4 | 766 (22) | 663 (23) | 103 (18) | |
| 4+3 | 834 (24) | 711 (24) | 123 (21) | |
| 8 | 772 (22) | 634 (22) | 138 (24) | |
| 9–10 | 1024 (29) | 813 (28) | 211 (36) | |
| pT stage | <0.01 | |||
| pT2 | 638 (18) | 584 (20) | 54 (9) | |
| pT3a | 1079 (31) | 918 (31) | 161 (27) | |
| pT3b | 1793 (51) | 1421 (49) | 372 (63) | |
| Positive margins | 1471 (42) | 1100 (38) | 371 (63) | <0.01 |
| LNs removed | 10 (6, 17) | 11 (6, 17) | 9 (5, 15) | <0.01 |
| Concurrent ADT | 426 (73) |
ADT: androgen deprivation therapy; aRT: adjuvant radiotherapy; LN: lymph node; PSA: prostate-specific antigen; sRT: salvage radiotherapy.
Adjusted overall survival (OS) was 94% vs. 89% at five years, and 82% vs. 80% at eight years for aRT with or without ADT vs. observation with sRT (p=0.12) (Figure 1). In analyses examining heterogeneity of treatment effects in subgroups selected a priori, aRT was associated with improved OS for men with Gleason 8–10 disease, two or three positive lymph nodes, or negative surgical margins. Among all other subgroups, aRT and observation with sRT performed equally.
Figure 1.
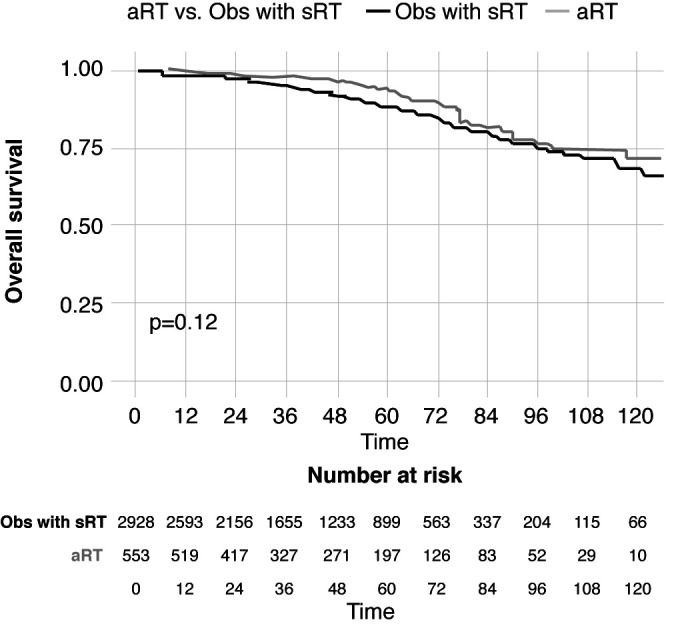
Adjusted overall survival. aRT: adjuvant radiotherapy; Obs: observation; sRT: salvage radiotherapy.
The strengths of this study include a large patient population and the use of advanced statistical analysis with sound methodology. Limitations are that data on the ADT agent and duration, as well as timing of salvage RT in the observation cohort are not captured in the dataset. In summary, for patients with pN1 prostate cancer after RP, the use of aRT with or without ADT or sRT likely needs to be individualized.
Summary 2 – Abstract PLLBA-01: N-803 plus BCG reported to have a clinically significant benefit in BCG-unresponsive bladder cancer2
Ahmad M. AlShammari
The authors of this study revealed that the addition of IL15RaFc super agonist N-803 (Anktiva) to bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) led to unseen-before prolonged complete responses (CR) and disease-free survival (DFS) in patients with BCG-unresponsive non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) with carcinoma in situ (CIS and papillary histology respectively. N-803 is a mutant interleukin-15-based immunostimulatory fusion protein complex that has been shown to promote proliferation and activation of natural killers and CD8+ T cells but not regulatory T cells.
BCG unresponsive NMIBC patients have limited bladdersparing treatment options with poor outcomes. Currently, only two agents have FDA approval, valrubicin and pembrolizumab (Keytruda), with 50% or fewer response rates. Radical cystectomy remains the guideline-recommended standard of care first-line option for this group of patients.
This study enrolled a population of patients with historically confirmed BCG-unresponsive disease with persistent or recurrent CIS, with or without recurrent Ta/T1 disease within 12 months of receiving sufficient BCG. This population was divided into cohorts: those with CIS (n=83) and those with papillary histology (n=77). Patients were given BCG + N-803 induction followed by maintenance courses.
In the CIS cohort, patients had a complete response (CR) of 71% (59/83) and a median duration of CR of 24.1 months. 91% avoided cystectomy, and the 24-month bladder cancerspecific progression-free survival was 96%, defined as progression to MIBC. In the papillary disease group, the authors reported a disease-free survival of 57% at 12 months and 48% at 24months. 95% avoided cystectomy.
Moreover, the medication was reported to be safe with minimal side effects with no systemic levels. In conclusion, these results show a superior efficacy and safety profile of N-803+BCG when compared with other intravesical/systemic options available for BCG unresponsive NMIBC.
Summary 3 – Podium presentation: Results of the intracorporeal robotic vs. open cystectomy (iROC) multicenter, randomized trial
Maylynn Ding
The podium presentation by Dr. Pramit Khetrapal described a trial based on a published protocol and run at nine centers in the U.K. It is the first multicenter, prospective, randomized trial to exclusively study robotic cystectomy with intracorporeal urinary diversion using a primary outcome related to perioperative recovery. A total of 338 patients were recruited from March 2017 to 2020, with 317 ultimately completing cystectomy. Primary outcome was number of days alive and out of hospital within 90 days of surgery. Of the 20 secondary outcomes studied, the presentation highlighted complications within 90 days of surgery, disability based on WHO 2.0 score, quality of life (QoL) based on EQ-5D-5L tool, cancer recurrence, and overall survival (OS).
A robotic approach resulted in 82 days alive and out of hospital within 90 days of surgery vs. 80 days in the open cystectomy group. Overall complication rates were similar, although the robotic cystectomy group was significantly less likely to experience wound-related and thromboembolic complications. Significantly higher QoL in the robotic group was reported at five weeks postoperatively but this difference disappeared by 12 weeks. Similarly, less disability was reported in the robotic group at five and 12 weeks, but this difference disappeared by 26 weeks postoperatively. There was no difference in cancer recurrence or OS.
These findings suggest that much of the benefits of robotic cystectomy occur in the immediate postoperative period. The difference in the primary outcome was statistically significant but small. There was no difference in overall complications or early oncological outcomes. This suggests open cystectomy is acceptable even in this era of robotic surgery.
Limitations include early closure of in-person endpoints assessment due to the pandemic, poor patient adherence to self-reporting measures, and short duration of followup for oncological outcomes.
Summary 4 – Podium presentation: Avoidance of benign renal oncocytoma resection using biopsy CD117 immunostain with radiographic tumor:cortex PEER score: Eight-year experience
Taeweon Lee
In this single-institution experience, authors from Roswell Park Cancer Institute maintained a cohort of patients with radiographic renal mass with CD117 positivity on immunostaining, suspicious for an oncocytic tumor. The current diagnostic dilemma relates to the inability to accurately differentiate benign oncocytic tumors (oncocytoma) from malignant renal cell carcinomas with strong oncocytic features (chromophobe). In this light, the authors applied a novel computed tomography (CT) metric comparing peak enhancement, measured in Hounsfield units, of the suspicious renal lesion and adjacent cortex. The ratio of enhancement above 0.55 (hyperenhancing) was felt to be benign.
Using this metric, the authors reported all 40 patients managed on active surveillance with presumed oncocytoma based on CD117 positivity and peak enhancement ratio >0.55 remained asymptomatic and free of metastasis at median followup of 43 months. The novel diagnostic paradigm consisting of renal mass biopsy, immunostaining, and CT enhancement score thus potentially avoids resection of benign oncocytomas, reducing patient morbidity.
The study was one of many highlights discussed at the AUA annual meeting. It is not hard to imagine that future meetings will similarly offer invaluable advances in technology, knowledge, and at the center of it all, capacity for patient care.
References
- 1.Schaufler C, Kaul S, Fleishman A, et al. Immediate radiotherapy vs. observation in patients with node-positive prostate cancer after radical prostatectomy. AUA Annual Meeting Abstract #PD22-04; May 13–16; New Orleans, LA. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chamie K. IL-15RaFc superagonist N-803 with BCG in BCG-unresponsive non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) CIS and papillary cohorts. AUA Annual Meeting Abstract #PLLBA-01; May 13–16; New Orleans, LA. [Google Scholar]


