Abstract
The protein degradation of alfalfa hay after tannin supplementation was monitored during wethers digestion. Three rumen-cannulated wethers were infused a tannin solution, and water for control, through the cannula. The digestion time-points samples were collected in vivo in the rumen and in vitro in the abomasum, and the small intestine compartments. The digestomic dataset was acquired by identifying and quantifying the peptides resulting from the protein degradation, using high-resolution LC-MS/MS mass spectrometry and label-free quantitation. The digestomic dataset is the compilation of proteomic data acquired in the rumen and peptidomic data acquired in the abomasum and in the small intestine. The proteomic analysis identified 20 Medicago proteins in the rumen fluid, based on 169 peptides of which 140 are unique. The peptidomic analysis identified 28 Medicago proteins in the abomasum, based on 575 peptides of which 363 are unique, and 11 Medicago proteins in the small intestine, based on 94 peptides of which 63 are unique. This digestomic dataset of proteolysis during sheep post rumen digestion after tannin supplementation reveals the protein regions protected by tannin supplementation, and could be reused in studies related to the protein use efficiency by ruminants.
Keywords: Digestomic, Rumen, Proteomic data, Peptidomic data, Dynamic in vitro digestion, Mass spectrometry
Specifications Table
| Subject | Agricultural science |
| Specific subject area | Analysis LC-MS/MS of ruminal digestion products obtained from rumen and a dynamic in vitro digestive system (DIDGI® (abomasum/small intestine)). |
| Type of data | Figure, Tables |
| How the data were acquired | NanoLC-MS/MS (Ultimate 3000 nanoRSLC-QExactive HF-X or LTQ-Orbitrap mass spectrometer (Thermo-Fisher Scientific, Villebon-sur-Yvette, France) |
| Data format | LC-MS/MS Raw data (Thermo-Fisher Scientific, Villebon-sur-Yvette, France) Identification and quantitation data (ProgenesisQI, Nonlinear Dynamics, Waters, Newcastle, UK) |
| Description of data collection | The mass spectrometry data were recorded with Xcalibur, the mass spectrometer control software. These raw data (.raw) were transformed into reprocessed data (.MZNLD) by the ProgenesisQI quantitation software (Nonlinear Dynamics). The quantified peptides and proteins identified by MASCOT (Matrix Science) and/or Peaks (Bioinformatics Solutions Inc) were analyzed by statistical tools integrated in ProgenesisQI, to give information on the hydrolysis of proteins in each studied compartment. Normalization was applied using a scalar factor on each sample to recalibrate them to a reference run. |
| Data source location | • Institution: INRAE • City/Town/Region: Saint-Genès-Champanelle • Country: France |
| Data accessibility | All additional data provided in this article are open access by downloading Excel files:Repository name: Pride project via ProteomeXchange Data identification number: PXD032973, Direct URL to data: https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD032973 |
| Related research article | T. Sayd, C. Chambon, M. Popova, D. P. Morgavi, A. Torrent, S. Blinet, L. Théron, V. Niderkorn. Impact of tannin supplementation on proteolysis during post-ruminal digestion in wethers using a dynamic in vitro system: a plant (Medicago sativa) digestomic approach. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2022, 70, 2221-2230 (https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.1c07378) |
Value of the Data
-
•
The data provide the peptides and proteins identified during sheep digestion in the rumen, and in simulated abomasum and small intestine after tannin supplementation.
-
•
Protein and peptide sequences protected by tannin during sheep digestion are identified and quantified in rumen, abomasum and small intestine.
-
•
This peptidomic and proteomic datasets provide new insights into the animal nutrition and feeding efficiency in ruminants and give new elements to optimise feed supplementation and significantly decrease environmental impact through nitrogen release.
-
•
The digestomic dataset presented can be used to compare with in vivo digestion data to further consider this approach as an alternative to animal experiment according to the ‘R’ principles.
1. Data Description
1.1. Rumen Proteomic
In Rumen, 140 unique peptides were identified from the digestion of 20 medicago proteins with at least two unique peptides (Table 1a and via the PRIDE repository with the dataset identifier PXD032973). The majority of the identified peptides were derived from the 5 most represented medicago sativa proteins. These unique peptides (or peptides without sequence conflicts) for each protein were used for label free quantitation (Table 1b and all the individual raw data acquired during the digestion kinetic in both Control and Tannin groups are available via the PRIDE repository with the dataset identifier PXD032973, https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD032973).
Table 1a.
Proteomic list of proteins identified in the rumen compartment during wether digestion of alfalfa hay supplemented in tannins.
| Protein name | Mass | Accession number | Gene name | Peptide count | Unique peptides | Confidence score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Histone H3.2, partial | 14361.8 | AAB36495 | H3 | 3 | 3 | 79.96 |
| Chlorophyll a/b binding protein | 28312.3 | AAC25775 | CARCAB1 | 7 | 7 | 365.50 |
| Glycolate oxidase, partial | 30550.2 | AAC32392 | GOX | 4 | 4 | 216.68 |
| Rubisco activase, partial | 30018.3 | AAN15946 | Rca | 6 | 6 | 420.07 |
| Heat shock protein 70 | 70996.5 | AAV98051 | HSP70-1 | 10 | 9 | 674.11 |
| Pentameric polyubiquitin, partial | 21187.5 | AAZ32851 | UBQ11 | 4 | 2 | 164.96 |
| Fructose bisphosphate aldolase | 42963.9 | ACP40514 | FBA | 5 | 5 | 303.42 |
| Putative glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | 43000.0 | ACV32597 | GADPH | 13 | 9 | 710.20 |
| ATP1, partial | 37426.0 | ADL63246 | atp1 | 4 | 2 | 157.95 |
| Photosystem I P700 chlorophyll a apoprotein A1 | 83295.9 | AMC31418 | psaA | 2 | 2 | 104.76 |
| Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase | 52626.9 | AMC32005 | rbcL | 50 | 37 | 3952.36 |
| Apocytochrome f | 35948.9 | AWW91860 | petA | 7 | 7 | 370.41 |
| Rab protein | 24012.1 | CAA55865 | Rab | 5 | 5 | 138.28 |
| Ferritin | 28078.8 | CAA65771 | FER | 2 | 2 | 55.43 |
| Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase small chain, chloroplastic | 20251.2 | O65194 | RBCS | 12 | 11 | 900.15 |
| Glutamine synthetase leaf isozyme, chloroplastic | 47115.5 | Q9XQ94 | GS2 | 2 | 2 | 42.93 |
| Actin-7 | 41711.8 | XP_003602545 | actin | 11 | 11 | 839.94 |
| Photosystem I P700 chlorophyll a apoprotein A2 | 82427.3 | YP_001381735 | psaB | 3 | 3 | 120.18 |
| ATP synthase CF1 beta subunit | 52746.5 | YP_009141595 | atpB | 13 | 9 | 747.17 |
| ATP synthase CF1 alpha subunit | 55691.8 | YP_009141617 | atpA | 6 | 4 | 431.89 |
For each identified protein, the protein name, accession number, gene name, and confidence score were given by MASCOT or Peaks search engines. Mass is the protein molecular weight in Da. Peptide count is the number of peptides used for identification. Unique peptides are the number of peptides belonging to only one protein, and used for quantitation.
Table 1b.
Proteomic list of proteins quantified in the rumen compartment during wether digestion of alfalfa hay supplemented in tannins.
| Condition Tannin |
Condition control |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Description | T4 | T5 | T6 | C1 | C2 | C3 | Anova (p) | q Value |
| Histone H3.2, partial | 292999.1 | 213174.7 | 200996.4 | 267962.4 | 2720471.3 | 218560.1 | 0.358 | 0.337 |
| Chlorophyll a/b binding protein | 544875.2 | 258075.3 | 632179.4 | 480376.6 | 1884755.2 | 554884.3 | 0.325 | 0.322 |
| Glycolate oxidase, partial | 314787.0 | 242773.8 | 230646.0 | 28023.1 | 310523.3 | 113454.8 | 0.244 | 0.285 |
| Rubisco activase, partial | 1148583.1 | 626703.3 | 614768.3 | 146612.0 | 569681.5 | 217502.5 | 0.078 | 0.181 |
| Heat shock protein 70 | 635331.7 | 486510.4 | 411899.0 | 1740900.1 | 9479203.8 | 2562796.2 | 0.021 | 0.119 |
| Pentameric polyubiquitin, partial | 1649985.1 | 903976.0 | 974430.7 | 2186301.1 | 10718614.6 | 5000967.9 | 0.042 | 0.132 |
| Fructose bisphosphate aldolase | 666929.8 | 495986.4 | 493078.6 | 328746.5 | 1392891.8 | 1204722.9 | 0.436 | 0.357 |
| Putative glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | 1121232.6 | 502703.1 | 536623.8 | 145669.6 | 2062278.1 | 382199.2 | 0.713 | 0.442 |
| ATP1, partial | 45306.3 | 65751.2 | 30848.5 | 10737.8 | 158880.0 | 127772.6 | 0.763 | 0.458 |
| Photosystem I P700 chlorophyll a apoprotein A1 | 41780.5 | 21835.3 | 66875.6 | 61938.3 | 220868.5 | 135880.4 | 0.082 | 0.181 |
| Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase | 36565782.0 | 14377637.4 | 11799474.5 | 905957.3 | 6623227.4 | 2836924.7 | 0.043 | 0.133 |
| Apocytochrome f | 331301.9 | 230810.8 | 367722.6 | 274847.2 | 2150485.8 | 468034.8 | 0.295 | 0.318 |
| Rab protein | 177677.8 | 106270.1 | 94575.1 | 275243.8 | 1225792.7 | 479982.5 | 0.035 | 0.129 |
| Ferritin | 86707.1 | 65120.6 | 43724.1 | 42948.7 | 299393.6 | 132846.9 | 0.341 | 0.33 |
| Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase small chain, chloroplastic | 18837450.9 | 10471723.5 | 8064851.8 | 996454.8 | 4789446.7 | 2368272.8 | 0.034 | 0.129 |
| Glutamine synthetase leaf isozyme, chloroplastic | 59995.0 | 34972.1 | 30827.6 | 1723.9 | 16568.4 | 8287.3 | 0.056 | 0.147 |
| Actin-7 | 4935346.8 | 4541437.5 | 3165078.9 | 1219273.4 | 12512883.4 | 7159569.7 | 0.85 | 0.475 |
| Photosystem I P700 chlorophyll a apoprotein A2 | 41428.5 | 18559.8 | 53498.3 | 41685.5 | 170371.5 | 30359.5 | 0.422 | 0.355 |
| ATP synthase CF1 beta subunit | 661058.2 | 547722.0 | 414574.4 | 66131.4 | 428958.7 | 755947.1 | 0.435 | 0.357 |
| ATP synthase CF1 alpha subunit | 647667.5 | 426021.6 | 358597.3 | 82394.4 | 695369.1 | 317001.5 | 0.432 | 0.357 |
For each quantified protein, the normalized abundances are given in the three individuals of each comparative group, i.e. ‘Tannin’ (T4, T5, and T6) and ‘Control’ (C1, C2, and C3). The Anova p-value and the power q-value are the results of the quantitative analysis performed using ProgenesisQI software.
1.2. Abomasum Peptidomics
In the abomasum, 363 unique peptides were identified from the digestion of 28 medicago proteins with at least two unique peptides (Table 2a and via the PRIDE repository with the dataset identifier PXD032973). Such as for the rumen proteomic results, the 5 most represented proteins in number of identified peptides account for about 60% of the identified peptides in this digestive compartment. These unique peptides for each protein were used for label-free quantitation (Tables 2b, c and all the individual raw data acquired during the digestion kinetic in both Control and Tannin groups are available via the PRIDE repository with the dataset identifier PXD032973(https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD032973).
Table 2a.
Peptidomic list of proteins identified in the abomasal compartment during wether digestion of alfalfa hay supplemented in tannins.
| Description | Mass | Accession | Gene | Peptide count | Unique peptides | Confidence score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aquaporin-like transmembrane channel protein | 31230.0 | AAB86380 | pAFI 8-1 | 6 | 4 | 340.28 |
| Malate dehydrogenase precursor | 38397.0 | AAB99754 | gmdh | 2 | 2 | 131.57 |
| Chlorophyll a/b binding protein | 28351.0 | AAC25775 | CARCAB1 | 51 | 51 | 3229.86 |
| Glycolate oxidase, partial | 30588.0 | AAC32392 | GOX | 6 | 6 | 367.63 |
| Rubisco activase, partial | 30170.0 | AAN15946 | Rca | 13 | 13 | 691.57 |
| Ferredoxin-dependent glutamate synthase, partial | 26791.5.0 | AAT38954 | gltB_C | 2 | 2 | 89.76 |
| Heat shock protein 70 | 71351.0 | AAV98051 | HSP70-1 | 4 | 2 | 215.29 |
| Pentameric polyubiquitin, partial | 21187.5 | AAZ32851 | UBQ | 4 | 4 | 287.39 |
| Fructose bisphosphate aldolase | 43165.0 | ACP40514 | FBA | 9 | 9 | 455.95 |
| Putative glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | 43258.0 | ACV32597 | GADPH | 16 | 14 | 990.83 |
| Photosystem I P700 chlorophyll a apoprotein A1 | 83471.0 | AMC31418 | psaA | 39 | 38 | 2018.76 |
| Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase | 52993.0 | AMC32005 | rbcL | 205 | 10 | 13889.10 |
| Apocytochrome f | 36040.0 | AWW91860 | petA | 17 | 17 | 1178.71 |
| Photosystem II CP43 chlorophyll apoprotein | 50482.0 | AWW91876 | psbC | 5 | 5 | 240.01 |
| Histone H3, partial | 13915.0 | CAA05554 | H3-1.1 | 6 | 2 | 270.11 |
| Ferritin | 28061.0 | CAA65771 | FER | 2 | 2 | 100.18 |
| Photosystem II protein D2 | 39738.0 | NP_054491 | psbD | 12 | 12 | 666.78 |
| Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase small chain, chloroplastic | 20251.2 | O65194 | RBCS | 33 | 32 | 2142.95 |
| Photosystem II protein D1 | 39111.0 | P04998 | psbA | 15 | 14 | 905.08 |
| Probable aquaporin TIP-type | 25324.4 | P42067 | MCP1 | 5 | 5 | 322.39 |
| Adenosylhomocysteinase | 53744.0 | P50246 | SAHH | 2 | 2 | 69.84 |
| Actin-7 | 41913.0 | XP_003602545 | actin2 | 10 | 9 | 572.66 |
| Photosystem II 47 kDa protein | 56131.0 | YP_001381703 | psbB | 22 | 22 | 1360.88 |
| Photosystem II protein V | 9400.6 | YP_001381711 | psbE | 2 | 2 | 85.46 |
| Photosystem I P700 chlorophyll a apoprotein A2 | 82489.0 | YP_001381735 | psaB | 45 | 45 | 2523.04 |
| Cytochrome b6 | 24112.5 | YP_002149762 | petB | 2 | 2 | 81.96 |
| ATP synthase CF1 beta subunit | 52771.0 | YP_009141595 | atpB | 24 | 21 | 1271.26 |
| ATP synthase CF1 alpha subunit | 55714.0 | YP_009141617 | atpA | 16 | 16 | 982.22 |
For each identified protein, the protein name, accession number, gene name, and confidence score were given by MASCOT or Peaks search engines. Mass is the protein molecular weight in Da. Peptide count is the number of peptides used for identification. Unique peptides are the number of peptides belonging to only one protein, and used for quantitation.
Table 2b.
Peptidomic list of proteins quantified in the abomasal compartment at 15 minutes of wether digestion of alfalfa hay supplemented in tannins.
| Condition Control |
Condition Tannin |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Description | T4 | T5 | T6 | C1 | C2 | C3 | Anova (p value) | q value |
| Aquaporin-like transmembrane channel protein | 1857.3 | 14873.6 | 15050.0 | 73803.0 | 99424.6 | 103865.7 | 0,001 | 0,002 |
| Malate dehydrogenase precursor | 15708.2 | 83843.4 | 36613.2 | 11600.8 | 16443.0 | 10775.8 | 0,001 | 0,002 |
| Chlorophyll a/b binding protein | 5562923.7 | 2930411.5 | 3382917.8 | 5348125.7 | 5878944.7 | 7575674.6 | 0,003 | 0,003 |
| Glycolate oxidase, partial | 442933.8 | 459805.7 | 331436.1 | 90200.2 | 99275.9 | 64640.6 | 0,000 | 0,000 |
| Rubisco activase, partial | 438692.8 | 813921.2 | 392757.9 | 412509.3 | 535492.9 | 354148.6 | 0,101 | 0,045 |
| Ferredoxin-dependent glutamate synthase, partial | 26890.0 | 64330.0 | 8489.0 | 2342.0 | 15645.9 | 5215.6 | 0,003 | 0,002 |
| Heat shock protein 70 | 35482.2 | 36485.2 | 10186.0 | 44275.0 | 38132.3 | 29724.0 | 0,158 | 0,066 |
| Pentameric polyubiquitin, partial | 368210.6 | 590896.4 | 215780.0 | 331694.7 | 269554.2 | 200907.0 | 0,106 | 0,046 |
| Fructose bisphosphate aldolase | 342186.0 | 716798.5 | 201459.4 | 176814.6 | 189979.4 | 150231.5 | 0,015 | 0,010 |
| Putative glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | 461655.7 | 932166.5 | 221701.3 | 414052.7 | 569441.1 | 349280.3 | 0,097 | 0,045 |
| Photosystem I P700 chlorophyll a apoprotein A1 | 571742.2 | 397239.6 | 704973.5 | 855340.1 | 1106649.5 | 1323653.0 | 0,000 | 0,001 |
| Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase | 1722084.7 | 3338112.2 | 3658436.2 | 317144.0 | 301861.9 | 209271.9 | 0,000 | 0,000 |
| Apocytochrome f | 749718.4 | 853491.8 | 1483049.0 | 2039160.4 | 2526285.3 | 2263769.7 | 0,001 | 0,002 |
| Photosystem II CP43 chlorophyll apoprotein | 169847.6 | 47204.8 | 203904.8 | 158969.3 | 230529.1 | 235333.9 | 0,022 | 0,013 |
| Histone H3, partial | 64440.4 | 126107.5 | 41682.6 | 68736.8 | 92847.9 | 46001.0 | 0,453 | 0,148 |
| Ferritin | 107706.4 | 16375.3 | 122897.2 | 25078.1 | 29882.0 | 16768.7 | 0,196 | 0,075 |
| Photosystem II protein D2 | 360817.8 | 419712.0 | 478604.4 | 789312.5 | 948430.9 | 1086873.6 | 0,000 | 0,001 |
| Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase small chain, chloroplastic | 2779311.7 | 4877198.0 | 5256231.9 | 1296395.7 | 1315805.3 | 1001594.3 | 0,000 | 0,000 |
| Photosystem II protein D1 | 322122.5 | 171776.1 | 295420.7 | 343115.8 | 459884.7 | 526318.9 | 0,001 | 0,001 |
| Probable aquaporin TIP-type | 208013.4 | 112229.1 | 100534.1 | 315043.5 | 389293.1 | 297961.0 | 0,002 | 0,002 |
| Adenosylhomocysteinase | 114914.1 | 40278.5 | 29841.7 | 70847.1 | 47868.4 | 96729.5 | 0,582 | 0,173 |
| Actin-7 | 513312.1 | 614990.4 | 272125.6 | 356455.7 | 422855.0 | 436776.3 | 0,583 | 0,173 |
| Photosystem II 47 kDa protein | 1123112.2 | 892606.8 | 1047808.0 | 1151607.5 | 1454630.1 | 1873329.9 | 0,002 | 0,002 |
| Photosystem II protein V | 38829.1 | 46227.1 | 19590.4 | 52927.9 | 55935.3 | 67533.2 | 0,174 | 0,069 |
| Photosystem I P700 chlorophyll a apoprotein A2 | 3493403.0 | 2583678.5 | 3431964.2 | 5972223.7 | 6671674.3 | 7296220.5 | 0,000 | 0,000 |
| Cytochrome b6 | 11001.6 | 3333.6 | 23939.8 | 53939.9 | 36194.8 | 79898.7 | 0,001 | 0,001 |
| ATP synthase CF1 beta subunit | 679841.4 | 1401643.6 | 1103847.6 | 472621.9 | 508287.3 | 375798.9 | 0,000 | 0,000 |
| ATP synthase CF1 alpha subunit | 840661.3 | 1250906.8 | 372485.8 | 394510.4 | 344030.6 | 256158.5 | 0,005 | 0,004 |
For each quantified protein, the normalized abundances are given in the three individuals of each comparative group, i.e. ‘Tannin’ (T4, T5, and T6) and ‘Control’ (C1, C2, and C3). The Anova p-value and the power q-value are the results of the quantitative analysis performed using ProgenesisQI software.
Table 2c.
Peptidomic list of proteins quantified in the abomasal compartment at 60 minutes of wether digestion of alfalfa hay supplemented in tannins.
| Condition Tannin |
Condition Control |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Description | T4 | T5 | T6 | C1 | C2 | C3 | Anova (p) | q value |
| Aquaporin-like transmembrane channel protein | 11126.8 | 22693.2 | 37081.0 | 74011.8 | 90190.1 | 59915.8 | ||
| Malate dehydrogenase precursor | 36884.3 | 73079.4 | 41824.1 | 14081.2 | 12192.5 | 18145.9 | ||
| Chlorophyll a/b binding protein | 3186637.5 | 3556093.4 | 4473847.3 | 7010609.1 | 6083171.1 | 14018136.3 | ||
| Glycolate oxidase, partial | 233396.4 | 450099.4 | 234807.4 | 85122.3 | 153123.6 | 81345.3 | ||
| Rubisco activase, partial | 483170.2 | 937792.7 | 580508.2 | 443229.8 | 422350.3 | 476188.8 | ||
| Ferredoxin-dependent glutamate synthase, partial | 34418.7 | 64292.8 | 38866.7 | 5625.4 | 12864.9 | 4004.9 | ||
| Heat shock protein 70 | 26200.3 | 40583.3 | 26010.2 | 32437.2 | 34562.0 | 49039.4 | ||
| Pentameric polyubiquitin, partial | 267983.8 | 528200.8 | 433079.6 | 322557.6 | 221439.8 | 321410.1 | ||
| Fructose bisphosphate aldolase | 208313.6 | 884946.7 | 296949.2 | 192652.2 | 127326.0 | 201823.1 | ||
| Putative glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | 735020.6 | 1612765.6 | 966962.1 | 409861.4 | 288234.4 | 431239.8 | ||
| Photosystem I P700 chlorophyll a apoprotein A1 | 439332.4 | 539277.7 | 699379.2 | 1000025.0 | 1111527.2 | 1784959.2 | ||
| Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase | 1951203.6 | 2429332.8 | 2413332.0 | 300774.3 | 283832.0 | 194295.1 | ||
| Apocytochrome f | 660016.3 | 977287.3 | 828789.4 | 1694342.9 | 1094491.2 | 2875504.2 | ||
| Photosystem II CP43 chlorophyll apoprotein | 117568.5 | 59045.4 | 124786.3 | 193296.6 | 174766.1 | 341063.8 | ||
| Histone H3, partial | 101891.0 | 123710.4 | 47076.9 | 70381.1 | 81289.0 | 38285.8 | ||
| Ferritin | 22450.4 | 174628.1 | 42922.7 | 57585.6 | 48676.7 | 26881.5 | ||
| Photosystem II protein D2 | 399372.9 | 491889.0 | 538907.3 | 728592.0 | 671841.7 | 1615057.1 | ||
| Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase small chain, chloroplastic | 2930451.6 | 4343816.2 | 3979363.0 | 1095401.7 | 1332840.8 | 1137440.0 | ||
| Photosystem II protein D1 | 195345.6 | 200489.9 | 207922.7 | 331301.5 | 465001.1 | 714769.7 | ||
| Probable aquaporin TIP-type | 178138.0 | 130487.9 | 201598.7 | 340370.4 | 181964.0 | 366407.7 | ||
| Adenosylhomocysteinase | 55913.6 | 115798.9 | 81187.8 | 95923.7 | 42283.9 | 152799.7 | ||
| Actin-7 | 304778.7 | 729244.7 | 451907.0 | 363518.8 | 266950.7 | 678686.1 | ||
| Photosystem II 47 kDa protein | 792014.5 | 888671.8 | 898258.4 | 1279347.8 | 1496798.0 | 2424064.4 | ||
| Photosystem II protein V | 26384.5 | 54253.9 | 38918.1 | 66718.9 | 17525.5 | 108960.3 | ||
| Photosystem I P700 chlorophyll a apoprotein A2 | 2951805.5 | 2550061.7 | 3906789.3 | 5676007.1 | 5584737.3 | 9240266.1 | ||
| Cytochrome b6 | 5720.3 | 8593.6 | 20816.5 | 39401.2 | 69757.3 | 50521.5 | ||
| ATP synthase CF1 beta subunit | 808416.9 | 1256059.1 | 969204.2 | 435569.4 | 608820.1 | 346295.8 | ||
| ATP synthase CF1 alpha subunit | 463554.6 | 1129156.3 | 549360.6 | 324445.3 | 295022.4 | 347029.6 | ||
For each quantified protein, the normalized abundances are given in the three individuals of each comparative group, i.e. ‘Tannin’ (T4, T5, and T6) and ‘Control’ (C1, C2, and C3). The Anova p-value and the power q-value are the results of the quantitative analysis performed using ProgenesisQI software.
1.3. Small Intestine Peptidomics
In the small intestine, 63 peptides were identified from the digestion of 11 medicago proteins with at least two unique peptides (Table 3a and via the PRIDE repository with the dataset identifier PXD032973). In this compartment, unique peptides from the two Ribulose proteins (gene name rbcL and RBCS) represent more than 35% of the identified and quantified peptides (23/63 unique peptides). As for the other two compartments, all identification and quantitation results of those peptides are available in the Tables 3b, c for protein data and all the individual raw data acquired during the digestion kinetic in both Control and Tannin groups are available via the PRIDE repository with the dataset identifier PXD032973 (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD032973).
Table 3a.
Peptidomic list of proteins identified in the small intestine compartment during wether digestion of alfalfa hay supplemented in tannins.
| Description | Mass | Accession name | Gene name | Peptide count | Unique peptides | Confidence score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase large subunit (chloroplast) | 52626.9 | 1043523999 | rbcL | 46 | 19 | 2095.15 |
| Photosystem I P700 apoprotein A2 (chloroplast) | 82427.3 | 1043524008 | psaB | 6 | 3 | 230.12 |
| Photosystem II CP43 chlorophyll apoprotein (chloroplast) | 51907.9 | 1043524011 | psbC | 4 | 4 | 127.68 |
| Photosystem II protein D2 (chloroplast) | 39535.5 | 1043524012 | psbD | 5 | 5 | 200.89 |
| Cytochrome f (chloroplast) | 35300.9 | 1043524028 | petA | 5 | 5 | 200.49 |
| Photosystem II 47 kDa protein (chloroplast) | 55996.1 | 1043524040 | psbB | 5 | 5 | 181.49 |
| 70 kD heatshockprotein, partial | 23312.9 | 1430887 | HSP70 | 2 | 2 | 62.00 |
| Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase small subunit, partial | 11914.6 | 16224234 | RBCS | 4 | 4 | 169.92 |
| Tonoplast intrinsic protein homolog MSMCP1 | 25324.4 | 2443836 | MCP1 | 4 | 4 | 128.37 |
| Chlorophyll a/b binding protein | 28312.3 | 3293555 | CARCAB1 | 9 | 9 | 352.00 |
| ATP synthase CF1 beta subunit | 52516.0 | ANS57890 | atpB | 3 | 3 | 186.3 |
For each identified protein, the protein name, accession number, gene name, and confidence score were given by MASCOT or Peaks search engines. Mass is the protein molecular weight in Da. Peptide count is the number of peptides used for identification. Unique peptides are the number of peptides belonging to only one protein, and used for quantitation.
Table 3b.
Peptidomic list of proteins quantified in the small intestine compartment at 60 minutes of wether digestion of alfalfa hay supplemented in tannins.
| Condition Tannin |
Condition control |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Description | T4 | T5 | T6 | C1 | C2 | C3 | Anova (p) | q value |
| Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase large subunit (chloroplast) | 2687577.2 | 2818529.4 | 1226619.2 | 451227.4 | 596852.1 | 379830.1 | 0,007 | 0,110 |
| Photosystem I P700 apoprotein A2 (chloroplast) | 133604.6 | 68510.9 | 88627.7 | 163463.4 | 215161.5 | 184149.7 | 0,030 | 0,218 |
| Photosystem II CP43 chlorophyll apoprotein (chloroplast) | 2928.9 | 13558.8 | 6172.3 | 3904.2 | 10309.1 | 5845.7 | 0,980 | 0,788 |
| Photosystem II protein D2 (chloroplast) | 33439.6 | 51182.0 | 22199.4 | 38945.7 | 70052.3 | 59448.1 | 0,180 | 0,496 |
| Cytochrome f (chloroplast) | 19619.0 | 8917.2 | 18478.9 | 27646.6 | 62077.3 | 55393.5 | 0,035 | 0,218 |
| Photosystem II 47 kDa protein (chloroplast) | 31756.3 | 45189.4 | 26955.8 | 19559.7 | 40558.7 | 29094.3 | 0,544 | 0,661 |
| 70 kD heatshockprotein, partial | 835293.3 | 1294082.8 | 477954.3 | 901645.6 | 425514.6 | 861686.5 | 0,713 | 0,732 |
| Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase small subunit, partial | 39749.9 | 5976.6 | 13857.0 | 10382.3 | 15178.5 | 4562.0 | 0,481 | 0,661 |
| Tonoplast intrinsic protein homolog MSMCP1 | 28502.2 | 30578.8 | 51972.6 | 71233.2 | 45393.7 | 30251.6 | 0,457 | 0,651 |
| Chlorophyll a/b binding protein | 349628.0 | 213941.8 | 242115.3 | 185068.8 | 420252.7 | 331035.5 | 0,702 | 0,732 |
| ATP synthase CF1 beta subunit | 45849.6 | 48924.2 | 6699.4 | 1721.9 | 1317.4 | 3291.7 | 0,023 | 0,218 |
For each quantified protein, the normalized abundances are given in the three individuals of each comparative group, i.e. ‘Tannin’ (T4, T5, and T6) and ‘Control’ (C1, C2, and C3). The Anova p-value and the power q-value are the results of the quantitative analysis performed using ProgenesisQI software.
Table 3c.
Peptidomic list of proteins quantified in the small intestine compartment at 180 minutes of wether digestion of alfalfa hay supplemented in tannins.
| Condition Tannin |
Condition control |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Description | T4 | T5 | T6 | C1 | C2 | C3 | Anova (p value) | q value |
| Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase large subunit (chloroplast) | 146911.2 | 122501.9 | 193678.7 | 91238.0 | 245590.4 | 72861.7 | 0,161 | 0,729 |
| Photosystem I P700 apoprotein A2 (chloroplast) | 50353.7 | 71072.2 | 57427.4 | 53769.6 | 93352.9 | 51912.2 | 0,731 | 1,000 |
| Photosystem II CP43 chlorophyll apoprotein (chloroplast) | 34860.4 | 16982.5 | 49548.8 | 34934.8 | 4935.1 | 39881.2 | 0,552 | 0,994 |
| Photosystem II protein D2 (chloroplast) | 7084.7 | 17189.1 | 5698.0 | 9867.6 | 38843.0 | 13022.7 | 0,288 | 0,850 |
| Cytochrome f (chloroplast) | 7845.0 | 3759.7 | 5842.5 | 5852.9 | 18523.3 | 5337.0 | 0,424 | 0,983 |
| Photosystem II 47 kDa protein (chloroplast) | 5939.2 | 6256.0 | 4603.9 | 2911.6 | 4532.6 | 2466.4 | 0,054 | 0,729 |
| 70 kD heatshockprotein, partial | 1949391.3 | 2740180.3 | 2339621.9 | 1902679.8 | 1195176.9 | 2751493.7 | 0,426 | 0,983 |
| Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase small subunit, partial | 1306.9 | 2669.6 | 2242.6 | 758.1 | 1721.3 | 1245.2 | 0,178 | 0,729 |
| Tonoplast intrinsic protein homolog MSMCP1 | 8103.3 | 4525.2 | 11330.8 | 10940.8 | 7761.6 | 1849.1 | 0,621 | 0,994 |
| Chlorophyll a/b binding protein | 22083.6 | 30317.9 | 19930.5 | 28820.4 | 144739.9 | 99351.7 | 0,085 | 0,729 |
| ATP synthase CF1 beta subunit | 2423.1 | 3031.7 | 5707.4 | 26.3 | 786.8 | 0.0 | 0,077 | 0,729 |
For each quantified protein, the normalized abundances are given in the three individuals of each comparative group, i.e. ‘Tannin’ (T4, T5, and T6) and ‘Control’ (C1, C2, and C3). The Anova p-value and the power q-value are the results of the quantitative analysis performed using ProgenesisQI software.
2. Experimental Design, Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Designs
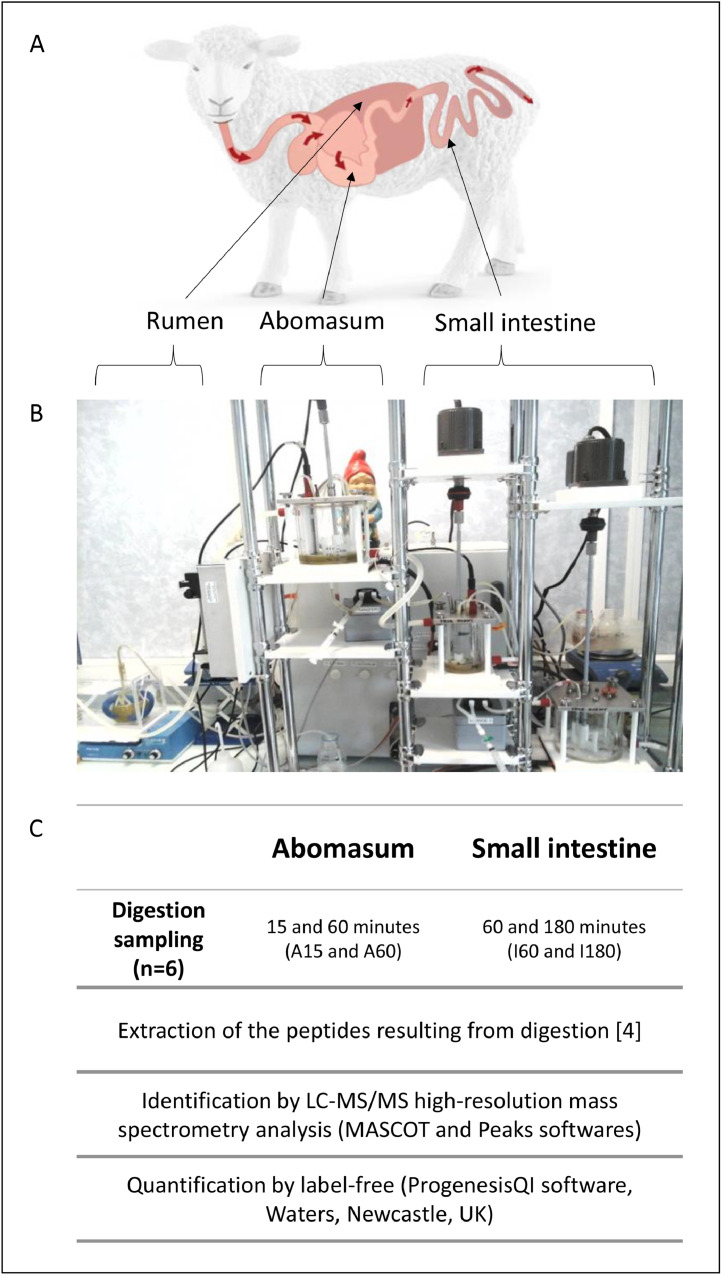
The experiment was conducted at the INRAE Clermont Auvergne Rhône-Alpes center in Theix, France. All animal-related experimental procedures were conducted in accordance with the EU Directive 2010/63/EU, reviewed by the local institutional animal care and use comitee (C2E2A, “Comité d'Ethique pour l'Expérimentation Animale en Auvergne”), and pre-authorized by the French Ministry for Research (approval # 7138-2016092709177605-V5). The protein digestion in the rumen of sheep and in simulated conditions of the abomasum and the small intestine was monitored using a dynamic in vitro digestive system DIDGI® [1] coupled to a digestomic approach (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
Representation of the experimental design, adapted from Sayd et al., 2022. (A) Schematic representation of the ovine digestive tract and (B) the corresponding compartments in the in vitro dynamic digestion system DiDGI®, the abomasum and the small intestine. (C) The sampling and main analysis steps are given for each compartment.
Three rumen-cannulated wethers were fed alfalfa hay and infused daily through the cannula a tannin solution, while three control wethers were infused with water. Standardized ruminal fluid was introduced into a dynamic in vitro digester, which simulated the different digestive compartments in terms of transit rate, pH regulation and digestive enzymes rate [2,3]. Samples were taken along the digestion kinetic and protein degradation in the rumen, the abomasum and the small intestine was determined by the identification and quantitation of peptides after extraction according to Sayd et al. [4].
2.2. LC-MS/MS and Data Analysis
2.2.1. LC-MS/MS Analysis
Peptides (from proteomic (rumen) or digestomic (in vitro digester)) were separated at 400 nl/min (40°C) on a nano HPLC column (Acclaim PepMap RSLC 75um x 25 cm, ThermoScientific) using a gradient of 4-35% acetonitrile (v/v) in 0.1 % (v/v) formic acid within 60 min. The eluted peptides were electrosprayed into nanosources of high resolution mass spectrometers used for this study. Thus, for abomasal and intestinal samples, a LTQ Velos Orbitrap (Thermo scientific) was used and raw data acquired at a resolution of 30000 in full scan (400-2000 m/z). For HCD fragmentation, top 10 method (dynamic exclusion enabled, 60 s) was used and only the most abundant precursors ions in full scan with charge ≥ 2 was activated for fragmentation (collision energy at 37%). For rumen samples, a Q-Exactive HFX was used with 60000 resolution in MS1 (375-1600 m/z) and 15000 in MS/MS (NCE 28) with top 18 method and an exclusion dynamic of 20 s.
2.2.2. Data Analysis
The raw files were processed for quantitation analysis using Progenesis QI software (Nonlinear Dynamics, Waters). For identification, the MS/MS spectra list was exported from the Progenesis QI software as a mascot file (.mgf) to MASCOT (V 2.5) or Peaks (Peaks X+), using the database “Medicago_sativa’’ extracted from NCBI (2020,1099 sequences). The search parameters were set as follow: no enzyme for digestomic analyses and trypsin for proteomic (rumen) analyses, the MS mass tolerance was set at 15 ppm for the peptides and 0.02 Da for the fragments, with a possible mass adduct of methionine oxidation. Peptide identification was validated when ion had a significant Mascot or Peaks score with a false positive rate lower than 0.05. Then, the identification results were re-imported into the Progenesis IQ software for quantitation [5]. Only peptides whose sequence is shared by a single protein were used for the abundance calculation. Quantitative data were normalized based on calculation of scalar factor for each sample which will allow us to recalibrate the sample to a normalization reference run. (normalization method available at: https://www.nonlinear.com/progenesis/qi-for-proteomics/v3.0/faq/how-normalisation-works.aspx. Briefly, this scalar factor, based on all the features intensities required can be represented as αk for each sample: y’i=αkyi, where yi is the measured peptide ion abundance of peptide ion i on sample k, αk is the scalar factor for sample k and y’i is the normalised abundance of peptide ion i on sample k.
Ethics Statements
The experiment was conducted at INRAE Clermont Auvergne Rhône-Alpes centre in France. The experimental procedures on animals were conducted in accordance with the European Union Directive 2010/63/EU, reviewed by the local ethics committee (C2E2A, “Comité d'Ethique pour l'Expérimentation Animale en Auvergne”) and authorised by the French Ministry for Research (no. 7138-2016092709177605-V5).
CRediT Author Statement
Christophe Chambon: Conceptualization, Methodology, Data curation, Writing – original draft preparation, Supervision; Thierry Sayd: Conceptualization, Methodology, Data curation, Writing – original draft preparation; Sylvie Bourillon: Methodology; Laetitia Theron: Methodology, Data curation, Writing – original draft preparation; Vincent Niderkorn: Conceptualization, Methodology, Data curation, Writing – Original draft preparation, Supervision.
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships which have, or could be perceived to have, influenced the work reported in this article.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the H2020 ERA-net project - CORE Organic Cofund - and the cofund from the European Commission, under the project ProYoungStock “Promoting young stock and cow health and welfare by natural feeding systems”. A financial support was also provided by INRAE department ‘Animal physiology and farming’. The authors thank the staff from the Herbipole experimental unit (INRAE Auvergne Rhône-Alpes) for the care of animals.
Data Availability
References
- 1.Ménard O., Cattenoz T., Guillemin H., Souchon I., Deglaire A., Dupont D., Picque D. Validation of a new in vitro dynamic system to simulate infant digestion. Food Chem. 2014;145:1039–1045. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.09.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Minekus M., Alminger M., Alvito P., Balance S., Bohn T., Bourlieu C., Carrière F., Boutrou R., Corredig M., Dupont D., Dufour C., Egger L., Golding M., Karakaya S., Kirkhus B., Le Feunteun S., Lesmes U., Macierzanka A., Mackie A., Marze S., McClements D.J., Ménard O., Recio I., Santos C.N., Singh R.P., Vegarud G.E., Wickham M.S.J., Weitschies W., Brodkorb A. A standardised static in vitro digestion method suitable for food – an international consensus. Food Funct. 2014;5 doi: 10.1039/c3fo60702j. 1113–2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Elashoff J.D., Reedy T.J., Meyer J.H. Analysis of gastric emptying data. Gastroenterology. 1982;83:1306–1312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Sayd T., Chambon C., Santé-Lhoutellier V. Quantification of peptides released during in vitro digestion of cooked meat. Food Chem. 2016;197:1311–1323. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.11.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Theron L., Gueugneau M., Coudy-Gandilhon C., Viala D., Bijlsma A., Butler-Browne G., Maier A., Béchet D., Chambon C. Label-free quantitative protein profiling of vastus lateralis muscle during human aging. Mol. Cell. Proteomics. 2014;13:283–294. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M113.032698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.