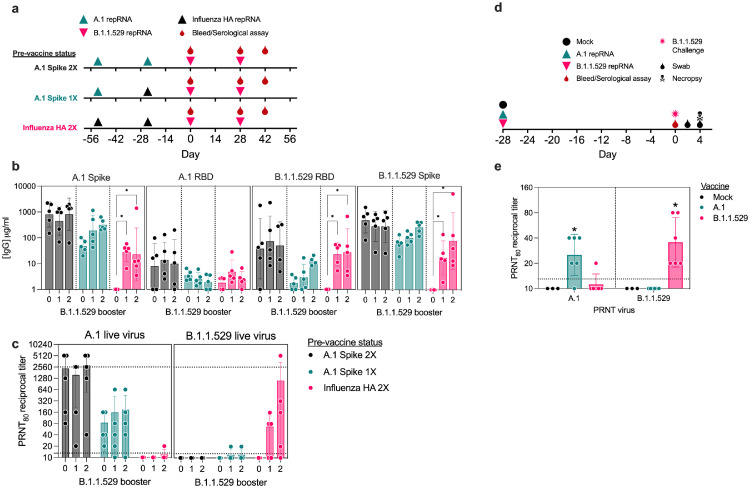
Figure 2.
Antibody responses in pre-immune mice or naïve hamsters. (a) Study design for evaluation of B.1.1.529-repRNA-CoV2S immunogenicity in pre-immune mice. On day -54 and -24 relative C57BL/6 mice (n=5/group) received 1 μg doses in either a prime/boost of A.1-repRNA-CoV2S (A.1 Spike 2X), a prime with A.1-repRNA-CoV2S and boost with influenza HA-repRNA (A.1 Spike 1X), or a prime/boost with influenza HA-repRNA (Influenza HA 2X) prior to all groups receiving a 1 μg boost with B.1.1.529-repRNA-CoV2S on day 0, followed by a bleed and second boost on day 28 with a final bleed on day 42. (b) Sera after 0, 1 or 2 B.1.1.529 boosters were evaluated for binding antibody responses to recombinant A.1 Spike, A.1 receptor binding domain (RBD), or B.1.1.529 RBD by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). (c) Day 28 and 42 sera were evaluated for neutralizing antibody responses against B.1.1.529 virus by 80% plaque reduction neutralization test (PRNT80). Dashed lines indicate limit of detection. (d) Study design for evaluation of comparative immunogenicity and efficacy of a single-dose A.1- or B.1.1.529-repRNA-CoV2S vaccines against B.1.1.529 challenge in Syrian hamsters. Syrian hamsters (n=6/group) were mock vaccinated with saline or with 20 μg of either A.1-repRNA-CoV2S or B.1.1.529-repRNA-CoV2S on day -28. Then on day 0, all animals were bled followed by an intranasal challenge with 1000 tissue culture 50% infectious doses (TCID50) and swabs collected on days 2 and 4 prior to necropsy on day 4 when blood and tissue samples were collected. (E) Day 0 sera was then assayed for A.1 or B.1.1.529-targeted neutralization activity by PRNT80. Dashed lines indicate limit of detection. Indicated statistical comparisons performed using one-way ANOVA of log transformed values with Dunnett's multiple comparison test. *p<0.05. Comparisons without indicated p-values were non-significant (p>0.05).