Abstract
Background
Necrotizing soft tissue infections (NSTI) require immediate radical debridement, broad-spectrum antibiotics and intensive care. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) may be performed adjunctively, but unequivocal evidence for its benefits is still lacking.
Methods
We performed a retrospective single-center study including 192 patients with necrotizing fasciitis or Fournier's gangrene to assess in-hospital mortality and outcome dependent on patient, disease and treatment characteristics with or without HBOT.
Results
The in-hospital mortality rate was 27.6%. Factors associated with increased mortality according to multivariate analysis were higher age, affection of multiple or problem localizations (odds ratio (OR) = 2.88, P = 0.003), ineligibility for HBOT despite clinical indication (OR = 8.59, P = 0.005), pathogens in blood cultures (OR = 3.36, P = 0.002), complications (OR = 10.35, P < 0.001) and sepsis/organ dysfunction (OR = 19.58, P < 0.001). Factors associated with better survival included vacuum-assisted wound closure (OR = 0.17, P < 0.001), larger number of debridements (OR = 0.83, P < 0.001) and defect closure with mesh graft (OR = 0.06, P < 0.001) or flap (OR = 0.09, P = 0.024). When participants were stratified into subgroups without requirement of HBOT (n = 98), treated with HBOT (n = 83) and ineligible for HBOT due to contraindications (n = 11), the first two groups had similar survival rates (75.5% vs. 73.5%) and comparable outcome, although patients with HBOT suffered from more severe NSTI, reflected by more frequent affection of multiple localizations (P < 0.001), sepsis at admission (P < 0.001) and intensive care treatment (P < 0.001), more debridements (P < 0.001) and a larger number of antibiotics (P = 0.001). In the subgroup ineligible for HBOT, survival was significantly worse (36.4%, P = 0.022).
Conclusion
These results point to a benefit from HBOT for treatment of NSTI in critically ill patients.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s13017-022-00448-6.
Keywords: Fournier's gangrene, Debridement, Hyperbaric oxygen therapy, Necrotizing fasciitis, Necrotizing soft tissue infections, Vacuum-assisted wound closure
Background
Necrotizing soft tissue infections (NSTI) are rare, live-threatening diseases associated with a severe systemic inflammatory cascade triggered by bacterial toxins and with a high risk of mortality [1]. Two major types are necrotizing fasciitis (NF) and Fournier’s gangrene (FG), which occur in mono- and polymicrobial variants. Irrespective of the etiology and pathogen spectrum, NSTI require immediate and extensive surgical debridement, broad-spectrum antibiotics and intense supportive care. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) constitutes an adjunct treatment, the beneficial effects of which are attributable to high oxygen gradients in the tissues as a result of breathing 100% oxygen under 1.5–3 times the atmospheric pressure. Hyperoxygenation decelerates the infectious progress by improving the function of neutrophilic granulocytes and reduces tissue oedema [2]. Reactive oxygen species exert bacteriostatic and bactericidal effects on aerobes and anaerobes. Furthermore, high oxygen levels ameliorate tissue regeneration and improve the efficacy of antibiotics, especially in biofilm forming microbes [3]. However, evidence for the benefits of HBOT in terms of survival and clinical outcome of patients with NF and FG is still limited [4, 5].
The aim of our study was to assess in-hospital mortality and outcome of patients with NF and FG treated in our center in the last decade and to analyze the effects of patient, disease and treatment-related factors, particularly HBOT, on these parameters. For the latter, patients were stratified into three groups, one without requirement of HBOT, one treated with HBOT and one ineligible for HBOT despite clinical indication.
Patients and methods
Study cohort
All patients with NF and FG treated in the Department of Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery - Center of Wound Medicine of the Vivantes Klinikum im Friedrichshain in Berlin, Germany between January 01, 2010, and October 01, 2020, were included into the study. Patients were identified by searching the electronic patient administration software (Orbis®, Agfa HealthCare, Bonn, Germany) for the diagnostic codes M72.6 (NF), N49.8 (FG in men) and N76.8 (FG in women) according to the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10). Medical records of all patients were reviewed and checked for fulfillment of study criteria. Inclusion criteria were diagnosis of NF or FG according to clinical, laboratory, intraoperative and histological findings and final diagnosis of NF or FG documented in the records. Exclusion criteria were other NSTI such as gas gangrene, which is already a reimbursed indication for HBOT in Germany, and initially suspected NF or FG which was not confirmed.
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Medicine of Charité University Medicine Berlin (EA2/296/20). It was performed accordant with STROBE guidelines and compliant with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy
The indication and eligibility for HBOT were determined by an interdisciplinary team of plastic surgeons, anesthesiologists and intensive care specialists according to the Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society recommendations [6] and the European consensus conference criteria on hyperbaric medicine [7]. All patients in whom fascial or subfascial tissue destruction was seen intraoperatively and unambiguously vital margins could not be achieved during initial or subsequent debridements or who experienced circulatory deterioration despite radical debridement in the absence of other causes were considered for HBOT. The only absolute contraindication was untreated pneumothorax. Relative contraindications were chemotherapy with bleomycin, cisplatin or doxorubicin, severe hemodynamic instability and until October 2017 morbid obesity.
When deciding for HBOT, intraoperative tympanic paracentesis was carried out. The first HBOT session was administered immediately after debridement under controlled ventilation. Programmed redebridements were scheduled in 24-h intervals until a stabilization of the wound and cessation of tissue necrosis were seen.
Until October 2017, HBOT was performed in a HAUX Starmed 2200/5,5 Multiplace Chamber that was situated in a separate building in a distance of 200 m from the operating room (OR) and the intensive care unit (ICU). Patients had to be transferred on a stretcher in an emergency ambulance. The chamber could not accommodate an entire ICU bed because of a narrow entry door. This implied certain restrictions in patient selection. In particular, morbid obesity and severe hemodynamic instability prevented transport to and accommodation in the chamber in some cases. In October 2017, a new HAUX Starmed Quadro 300–2300/3,3/ICU Multiplace Chamber was put in operation, which is located in-house in 100 m distance from the OR and the ICU and accessible by elevator. Patient transfer into another bed or stretcher is not required any more, as the patients remain in an HBOT-compatible ICU bed. Therefore, morbid obesity ceased to pose a restriction for HBOT. Since the start-up of the new chamber the subgroup of patients ineligible for HBOT is confined to the most critically instable patients, critically ill patients with intention to best supportive care and patients with untreated pneumothorax.
The hyperbaric chambers are affiliated with the Department of Intensive Care Medicine and provide full intensive care equipment. They are staffed with a highly experienced interdisciplinary team around the clock, and patients are monitored by an intensive care specialist throughout the treatment sessions. The standard treatment regimen consists of three dives at a maximum pressure of 300 kPa with a duration of 90 min (TS 300/90) within the first 24 h, followed by a minimum of two further treatments according to TS 240/90 until a stop of disease progression. The treatment algorithm was described in detail by Schmale and colleagues [8].
Data collection
The following patient, disease and treatment characteristics were documented as pseudonymized data: sex, age at admission, transfer from another hospital, diagnosis of NF or FG, disease localization (for categories see Table 1), clinical signs and symptoms at admission, pain (mild/none, intermediate, strong), laboratory parameters at admission (leucocyte count, hemoglobin, C-reactive protein, creatinine, sodium, serum glucose, fibrinogen), pathogen growth in blood cultures collected prior to antibiotic treatment, sepsis according to Sepsis-2 criteria [9] and/or the quick sequential organ failure assessment (qSOFA) score, Laboratory Risk Indicator for NECrotizing fasciitis (LRINEC), modified LRINEC [10], pathogens in wound swabs, tissue samples, urine and stool, histological evidence of fascial involvement, number and kind of comorbidities, number of surgical debridements, time to first debridement (h), vacuum-assisted closure (VAC; yes/no), number of VAC changes, HBOT (no, not indicated vs. yes vs. no, ineligible due to contraindications), number of HBOT cycles, defect coverage, kind and number of antibiotics, antibiotic groups and changes, duration of hospitalization (days (d)), ICU stay (if yes, duration (d)), and complications (for categories, see Tables 2, 4).
Table 1.
Relation of patient and disease characteristics with mortality
| Characteristic | Total, n (%) | Mortality, n (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | Pa | ||
| 192 (100) | 53 (27.6) | 139 (72.4) | ||
| Sex | ||||
| Male | 127 (66.1) | 34 (64.2) | 93 (66.9) | 0.718 |
| Female | 65 (33.9) | 19 (35.8) | 46 (33.1) | |
| Age (years) | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 61.2 (15.1) | 65.7 (14.1) | 59.5 (15.2) | 0.006 |
| < 60 | 87 (45.3) | 15 (28.3) | 72 (51.8) | 0.003 |
| ≥ 60 | 105 (54.7) | 38 (71.7) | 67 (48.2) | |
| Diagnosis | ||||
| Necrotizing fasciitis | 153 (79.7) | 44 (83.0) | 109 (78.4) | 0.479 |
| Fournier's gangrene | 39 (20.3) | 9 (17.0) | 30 (21.6) | |
| Localization | ||||
| Lower extremity | 137 (71.4) | 39 (73.6) | 98 (70.5) | 0.673 |
| Genital/perineal/gluteal | 74 (38.5) | 24 (45.3) | 50 (36.0) | 0.236 |
| Trunk | 40 (20.8) | 14 (26.4) | 26 (18.7) | 0.240 |
| Retroperitonealb | 4 (2.1) | 3 (5.7) | 1 (0.7) | 0.065 |
| Upper extremityb | 10 (5.2) | 3 (5.7) | 7 (5.0) | 1.000 |
| Head/neck | 1 (0.5) | 1 (100.0) | 0 (0.0) | n.d |
| Multiple localizations | 56 (29.2) | 23 (43.4) | 33 (23.7) | 0.007 |
| Initial signs and symptoms | ||||
| Sepsis at admission | 132 (68.8) | 41 (77.4) | 91 (65.5) | 0.112 |
| Positive blood culturec | 69 (44.8) | 30 (65.2) | 39 (36.1) | 0.001 |
| Leucocyte count, mean (SD) | 18.4 (8.3) | 19.3 (9.8) | 18.0 (7.7) | 0.454 |
| CRP, mean (SD) | 259.4 (138.4) | 236.7 (141.0) | 268.3 (136.8) | 0.156 |
| LRINECd, mean (SD) | 7.1 (2.8) | 7.3 (2.9) | 7.1 (2.8) | 0.556 |
| Modified LRINECe, mean (SD) | 10.2 (3.3) | 10.4 (3.4) | 10.2 (3.3) | 0.754 |
| Comorbidities | ||||
| Number, mean (SD) | 2.8 (1.6) | 3.0 (1.5) | 2.7 (1.6) | 0.206 |
| < 3 | 95 (49.5) | 20 (37.7) | 75 (54.0) | 0.044 |
| ≥ 3 | 97 (50.5) | 33 (62.3) | 64 (46.0) | |
| Diabetes mellitus | 93 (48.4) | 27 (50.9) | 66 (47.5) | 0.668 |
| Vascular diseasesf | 58 (30.2) | 16 (30.2) | 42 (30.2) | 0.997 |
| Renal diseases | 52 (27.1) | 16 (30.2) | 36 (25.9) | 0.550 |
| Cardiac diseases | 75 (39.1) | 25 (47.2) | 50 (36.0) | 0.155 |
| Liver diseases | 32 (16.7) | 15 (28.3) | 17 (12.2) | 0.008 |
| Arterial hypertension | 115 (59.9) | 26 (49.1) | 89 (64.0) | 0.058 |
| History of stroke | 15 (7.8) | 5 (9.4) | 10 (7.2) | 0.605 |
| Alcohol abuse | 29 (15.1) | 8 (15.1) | 21 (15.1) | 0.998 |
| Substance abuse (i.v.)b | 10 (5.2) | 5 (9.4) | 5 (3.6) | 0.142 |
| Psychiatric diseasesb | 17 (8.9) | 2 (3.8) | 15 (10.8) | 0.161 |
| Malignant diseases | 29 (15.1) | 12 (22.6) | 17 (12.2) | 0.072 |
| Immunosuppression | 28 (14.6) | 12 (22.6) | 16 (11.5) | 0.051 |
For calculation of percentages, the number of patients in each column (i.e., in the total cohort and in subgroups with and without mortality) was set to 100%
CRP C-reactive protein, i.v. intravenous, n.d. not determined, SD standard deviation
aCharacteristics of subgroups with and without mortality were compared with Chi-squared test for categorical variables, with Mann-Whitney-U test for continuous variables in two categories and with Kruskal-Wallis test for linear variables in three categories. Significant differences are highlighted in bold
bExact Fisher-t-test
cBlood cultures were taken before initiation of antibiotics
dLRINEC: Laboratory Risk Indicator for NECrotizing fasciitis
eThe modified LRINEC could be calculated in 131 participants (n = 61: missing data)
fVascular diseases comprised peripheral arterial occlusive disease, chronic venous insufficiency, deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism
Table 2.
Relation of treatment characteristics with mortality
| Characteristic | Total, n (%) | Mortality, n (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | Pa | ||
| 192 (100) | 53 (27.6) | 139 (72.4) | ||
| Surgical treatment | ||||
| Debridements,b mean (SD) | 7.5 (5.3) | 5.2 (4.2) | 8.3 (5.5) | < 0.001 |
| ≤ 5 | 82 (42.7) | 32 (60.4) | 50 (36.0) | 0.002 |
| > 5 | 110 (57.3) | 21 (39.6) | 89 (64.0) | |
| Time to 1st debrid. ≤ 12 hc | 92 (47.9) | 23 (43.4) | 69 (49.6) | 0.439 |
| Time to 1st debrid. ≤ 24 h | 115 (59.9) | 27 (50.9) | 88 (63.3) | 0.118 |
| VAC therapy | 120 (62.5) | 17 (32.1) | 103 (74.1) | < 0.001 |
| VAC changes, mean (SD) | 5.3 (4.0) | 4.9 (2.6) | 5.4 (4.2) | 0.855 |
| ≤ 5 | 82 (68.3) | 9 (52.9) | 73 (70.9) | 0.141 |
| > 5 | 38 (31.7) | 8 (47.1) | 30 (29.1) | |
| Defect closure | 135 (70.3) | 13 (24.5) | 122 (87.8) | < 0.001 |
| Mesh graft | 109 (56.8) | 8 (15.1) | 101 (72.7) | < 0.001 |
| Flap | 27 (14.1) | 1 (1.9) | 26 (18.7) | 0.003 |
| Amputationd | 46 (24.0) | 17 (32.1) | 29 (20.9) | 0.104 |
| Secondary healing | 37 (19.3) | 6 (11.3) | 31 (22.3) | 0.085 |
| HBOT | ||||
| No, not indicated | 98 (51.1) | 24 (45.3) | 74 (53.2) | 0.022 |
| Yes | 83 (43.2) | 22 (41.5) | 61 (43.9) | |
| No, ineligiblee | 11 (5.7) | 7 (13.2) | 4 (2.9) | |
| Antibiotic therapy | ||||
| Number of AB, mean (SD) | 4.6 (2.2) | 4.3 (2.2) | 4.8 (2.2) | 0.153 |
| ≤ 3 | 67 (34.9) | 24 (45.3) | 43 (30.9) | 0.062 |
| > 3 | 125 (65.1) | 29 (54.7) | 96 (69.1) | |
| AB groups, mean (SD) | 3.3 (1.3) | 3.3 (1.5) | 3.3 (1.3) | 0.885 |
| ≤ 3 | 110 (57.3) | 29 (54.7) | 81 (58.3) | 0.656 |
| > 3 | 82 (42.7) | 24 (45.3) | 58 (41.7) | |
| Changes of AB, mean (SD) | 2.5 (2.1) | 2.0 (2.0) | 2.7 (2.0) | 0.007 |
| ≤ 2 | 115 (59.9) | 37 (69.8) | 78 (56.1) | 0.083 |
| > 2 | 77 (40.1) | 16 (30.2) | 61 (43.9) | |
| Hospital treatment | ||||
| ICU treatment | 172 (89.6) | 52 (98.1) | 120 (86.3) | 0.017 |
| Days in ICU, mean (SD) | 13.3 (16.1) | 13.4 (16.8) | 13.2 (16.0) | 0.815 |
| 0 days | 20 (10.4) | 1 (1.9) | 19 (13.7) | 0.012 |
| 1–7 days | 82 (42.7) | 30 (56.6) | 52 (37.4) | |
| > 7 days | 90 (46.9) | 22 (41.5) | 68 (48.9) | |
| Days in hospital, mean (SD)f | 40.2 (26.3) | 22.8 (25.1) | 46.8 (23.7) | < 0.001 |
| ≤ 40 days | 109 (56.8) | 40 (75.5) | 69 (49.6) | 0.001 |
| > 40 days | 83 (43.2) | 13 (24.5) | 70 (50.4) | |
| Complications | ||||
| Total | 120 (63.5) | 47 (92.2) | 73 (52.9) | < 0.001 |
| Infectionsg | 95 (49.5) | 25 (47.2) | 70 (50.4) | 0.693 |
| Sepsis/organ dysfunctionh | 76 (39.6) | 45 (84.9) | 31 (22.3) | < 0.001 |
| Impaired wound healing | 46 (24.0) | 5 (9.4) | 41 (29.5) | 0.004 |
| Prolonged delirium | 30 (15.6) | 4 (7.5) | 26 (18.7) | 0.057 |
| Stump complications | 14 (7.3) | 2 (3.8) | 12 (8.6) | 0.247 |
| Decubitus | 9 (4.7) | 1 (1.9) | 8 (5.8) | 0.257 |
| Thrombosis | 9 (4.7) | 2 (3.8) | 7(5.0) | 0.711 |
| Anus praeteri, j | 29 (15.1) | 5 (9.4) | 24 (17.3) | 0.259 |
| Ileusi | 4 (2.1) | 2 (3.8) | 2 (1.4) | 0.306 |
| Strokei | 3 (1.6) | 1 (1.9) | 2 (1.4) | 1.000 |
| Cardiac arresti | 3 (1.6) | 2 (3.8) | 1 (0.7) | 0.185 |
| Other complicationsi, k | 11 (5.7) | 5 (9.4) | 6 (4.3) | 0.180 |
For calculation of percentages, the number of patients in each column (i.e., in the total cohort and in subgroups with and without mortality) was set to 100%
AB antibiotics, debrid. Debridement, HBOT hyperbaric oxygen therapy, ICU intensive care unit, SD standard deviation, VAC vacuum-assisted closure
aCharacteristics of subgroups with and without mortality were compared with Chi-squared test for categorical variables and with Mann–Whitney-U test for continuous variables. Significant differences are highlighted in bold
bDebridements included both radical debridements and minor surgical debridements for wound conditioning performed in our hospital and/or in other hospitals or departments prior to admission to our center
cTime to first debridement was calculated from the time of admission to our clinic until debridement
dIn the subgroup with amputation, n = 2 patients (1.0%) obtained a minor amputation, n = 3 (1.6%) a transtibial amputation, n = 3 (1.6%) a knee disarticulation, n = 34 (17.7%) a transfemoral amputation, n = 5 (1.6%) a hip disarticulation and n = 8 (4.2%) an atypical amputation. 18 patients (9.4%) had a reamputation
en = 11 patients were ineligible for HBOT due to factors specified in Additional file 1: Table S1
fDefined as number of days from admission to our or to an external hospital until discharge from our hospital or death
gInfections comprised externally acquired and nosocomial urinary tract infections (n = 63), Clostridium difficile infections (n = 28), pneumonia (n = 9), wound infections (n = 3) and catheter sepsis (n = 23)
hThe category "sepsis/organ dysfunction" contained patients with sepsis and/or subsequent renal failure and/or failure of additional organs
iExact Fisher-t-test
jIn 29 patients (n = 14 with necrotizing fasciitis and n = 15 with Fournier’s gangrene), colostomy was performed prior to admission to our department
kOther complications comprised acute coronary syndrome (n = 1), gastrointestinal bleeding (n = 3), requirement of resuscitation (n = 2), tumor progression (n = 1), hypoxic brain damage (n = 1), hematuria (n = 1), stoma complications (n = 1) and biliary stent occlusion (n = 1)
Table 4.
Treatment characteristics, complications and outcome of patients with and without hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT)
| Characteristic | HBOT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No, not indicated | Yes | No, ineligible | Pa | |
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | ||
| Total (n = 192) | 98 (51.0) | 83 (43.2) | 11 (5.7) | |
| Surgical treatment | ||||
| Debridements,b mean (SD) | 6.0 (4.1) | 9.1 (5.8) | 7.9 (7.3) | < 0.001 |
| Time to 1st debrid. ≤ 12 hc | 33 (33.7) | 51 (61.4) | 8 (72.7) | < 0.001 |
| Time to 1st debrid. ≤ 24 h | 45 (45.9) | 62 (74.7) | 8 (72.7) | < 0.001 |
| VAC therapy | 62 (63.3) | 53 (63.9) | 5 (45.5) | 0.484 |
| VAC changes, mean (SD) | 4.6 (3.0) | 5.9 (4.7) | 8.0 (5.5) | 0.062 |
| Defect coverage | 71 (72.4) | 60 (72.3) | 4 (36.4) | 0.040 |
| Mesh graft | 58 (59.2) | 48 (57.8) | 3 (27.3) | 0.124 |
| Flap | 12 (12.2) | 14 (16.9) | 1 (9.1) | 0.597 |
| Amputation | 21 (21.4) | 20 (24.1) | 5 (45.5) | 0.209 |
| Secondary healing | 14 (14.3) | 20 (24.1) | 3 (27.3) | 0.196 |
| Antibiotic therapy | ||||
| Number of AB, mean (SD) | 4.0 (1.9) | 5.2 (2.2) | 5.6 (2.9) | 0.001 |
| ≤ 3 | 46 (46.9) | 18 (21.7) | 3 (27.3) | 0.002 |
| > 3 | 52 (53.1) | 65 (78.3) | 8 (72.7) | |
| AB groups, mean (SD) | 3.0 (1.3) | 3.6 (1.2) | 3.6 (1.6) | 0.006 |
| ≤ 3 | 67 (68.4) | 39 (47.0) | 4 (36.4) | 0.005 |
| > 3 | 31 (31.6) | 44 (53.0) | 7 (63.6) | |
| Changes of AB, mean (SD) | 2.4 (1.9) | 2.6 (2.0) | 3.2 (3.3) | 0.795 |
| ≤ 2 | 63 (64.3) | 45 (54.2) | 7 (63.6) | 0.374 |
| > 2 | 35 (35.7) | 38 (45.8) | 4 (36.4) | |
| Hospital treatment | ||||
| ICU treatment | 79 (80.6) | 82 (98.8) | 11 (100.0) | < 0.001 |
| Days in ICU, mean (SD) | 8.2 (11.7) | 18.2 (16.8) | 21.4 (28.1) | < 0.001 |
| 0 days | 19 (19.4) | 1 (1.2) | 0 (0.0) | < 0.001 |
| 1–7 days | 52 (53.1) | 24 (28.9) | 6 (54.5) | |
| > 7 days | 27 (27.6) | 58 (69.9) | 5 (45.5) | |
| Days in hospital, mean (SD)d | 39.0 (25.2) | 42.1 (24.7) | 35.6 (44.4) | 0.203 |
| ≤ 40 days | 59 (60.2) | 43 (51.8) | 7 (63.6) | 0.469 |
| > 40 days | 39 (39.8) | 40 (48.2) | 4 (36.4) | |
| Infections | 45 (45.9) | 44 (53.0) | 6 (54.5) | 0.599 |
| Urinary tract infection | 25 (25.5) | 35 (42.2) | 3 (27.3) | 0.054 |
| C. difficile infection | 17 (17.3) | 10 (12.0) | 1 (9.1) | 0.523 |
| Pneumonia | 3 (3.1) | 4 (4.8) | 2 (18.2) | 0.079 |
| Wound infection | 1 (1.0) | 2 (2.4) | 0 (0.0) | 0.688 |
| Catheter sepsis | 7 (7.1) | 13 (15.7) | 3 (27.3) | 0.058 |
| Multiresistent pathogense | 7 (100.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0.031 |
| Complications | ||||
| Total (n = 120) | 54 (56.8) | 57 (68.7) | 9 (81.8) | 0.113 |
| Sepsis/organ dysfunctionf | 32 (32.7) | 35 (42.2) | 9 (81.8) | 0.006 |
| Impaired wound healing | 22 (22.4) | 21 (25.3) | 3 (27.3) | 0.873 |
| Prolonged delirium | 10 (10.2) | 20 (24.1) | 0 (0.0) | 0.013 |
| Stump complications | 5 (5.1) | 7 (8.4) | 2 (18.2) | 0.248 |
| Decubitus | 2 (2.0) | 5 (6.0) | 2 (18.2) | 0.042 |
| Thrombosis/embolism | 4 (4.1) | 3 (3.6) | 2 (18.2) | 0.092 |
| Anus praeter | 6 (6.1) | 20 (24.1) | 3 (27.3) | 0.002 |
| Ileus | 3 (3.1) | 1 (1.2) | 0 (0.0) | 0.604 |
| Stroke | 0 (0.0) | 3 (3.6) | 0.(0.0) | 0.135 |
| Cardiac arrest | 3 (3.1) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0.232 |
| Other complicationsg | 6 (6.1) | 5 (6.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0.701 |
| Outcome | ||||
| Survived | 74 (75.5) | 61 (73.5) | 4 (36.4) | 0.022 |
| No impairment | 16 (21.6) | 8 (13.1) | 1 (25.0) | 0.155 |
| Mild-moderate impairmenth | 38 (51.4) | 31 (50.8) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Severe impairmenti | 20 (27.0) | 22 (36.1) | 3 (75.0) | |
| Return to former homej | 57 (58.2) | 45 (54.2) | 1 (9.1) | 0.008 |
For calculation of percentages, the number of patients in each column (i.e., HBOT no, not indicated, HBOT yes and HBOT no, ineligible) was set to 100%
AB antibiotics, C difficile Clostridium difficile, debrid. Debridement, h hours, ICU intensive care unit, SD standard deviation, VAC vacuum-assisted closure
aCharacteristics of the three subgroups were compared with Chi-squared test for categorical variables and with Kruskal-Wallis test for continuous variables. Significant differences are highlighted in bold
bDebridements included both radical debridements and minor surgical debridements for wound conditioning
cTime to first debridement was calculated from the time of admission to our hospital until debridement
dDefined as number of days from admission to our or to an external hospital until discharge from our hospital or death
eWound infection with multiresistant pathogens
fThe category "sepsis/organ dysfunction" contained patients with sepsis and/or subsequent renal failure and/or failure of additional organs
gOther complications affecting n = 11 patients comprised acute coronary syndrome (n = 1), gastrointestinal bleeding (n = 3), requirement of resuscitation (n = 2), tumor progression (n = 1), hypoxic brain damage (n = 1), hematuria (n = 1), stoma complications (n = 1) and biliary stent occlusion (n = 1)
hMild-moderate impairment included, e.g., remaining wound defects at discharge from hospital and temporary impairment of mobility
iSevere impairment comprised permanent loss of walking ability, permanent confinement to a wheelchair or to bed, incontinence, critical illness neuropathy, or post intensive care syndrome
jReturn to the previous living environment without severe disabling impairment
Co-primary outcome criteria were in-hospital mortality, i.e., mortality in the time between admission to our or another hospital and death or discharge from our hospital, in the total cohort and in HBOT subgroups. Secondary outcome parameters were impairment in survivors (none vs. mild-moderate vs. severe) and return to the previous living environment without severe disabling impairment (yes/no, for definition, see Table 4).
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed with IBM SPSS Statistics 25. For subgroup analyses, patients were stratified according to sex, age, NF or FG, disease localization, number of comorbidities, debridements and VAC changes, HBOT (no, not indicated vs. yes vs. no, ineligible), number of antibiotics, antibiotic groups and changes of antibiotics, duration of ICU treatment and of hospitalization (for categories, see Tables 1–4). Associations between binary and categorical patient, disease and treatment characteristics and mortality were tested for significance with Pearson's Chi-squared test or with Fisher's exact test when the conditions for the Chi-squared test were not fulfilled (expected frequencies < 5). Nonparametric continuous variables were analyzed with Mann-Whitney U test.
To examine associations between patient, disease and treatment characteristics and HBOT, the cohort was subdivided into three groups (HBOT no, not indicated vs. yes vs. no, ineligible, due to factors specified in Additional file 1: Table S1). Chi-squared test and Fisher’s exact test were used for binary and categorical variables and Kruskal-Wallis test for continuous variables.
Cumulative survival of the HBOT subgroups from admission to our or another hospital to death or discharge from our hospital was calculated with the Kaplan–Meier method and graphically displayed by Kaplan–Meier curves. Differences were tested for significance with the log-rank test with two degrees of freedom.
Furthermore, we calculated multivariate logistic regression models with mortality as the dependent variable. The baseline model contained sex, age, problem localization (defined as localization in the retroperitoneal area, head/neck region and/or in multiple localizations; yes/no), number of comorbidities and the LRINEC as independent variables. In models 1–13, one additional parameter at a time was integrated into the baseline model. Results were expressed as odds ratio (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant in all analyses.
Results
Patient and disease characteristics and their impact on mortality
Out of 240 patients with diagnostic codes of NSTI, 192 fulfilled study criteria. All of these were included. Two thirds were male, and the mean age was 61.2 years (Table 1). 78.6% were referred from other departments or hospitals, and 32.3% had received a debridement prior to transfer. Further baseline characteristics are summarized in Table 1.
The overall in-hospital mortality rate was 27.6% without significant differences between patients directly admitted or transferred to our center. Patients who died were significantly older than survivors (P = 0.006). The most common localization was the lower extremity (71.4%), followed by the perianal/genital/gluteal area (38.5%). Affection of multiple localizations was documented in 29.2% and associated with a higher risk of mortality (P = 0.007).
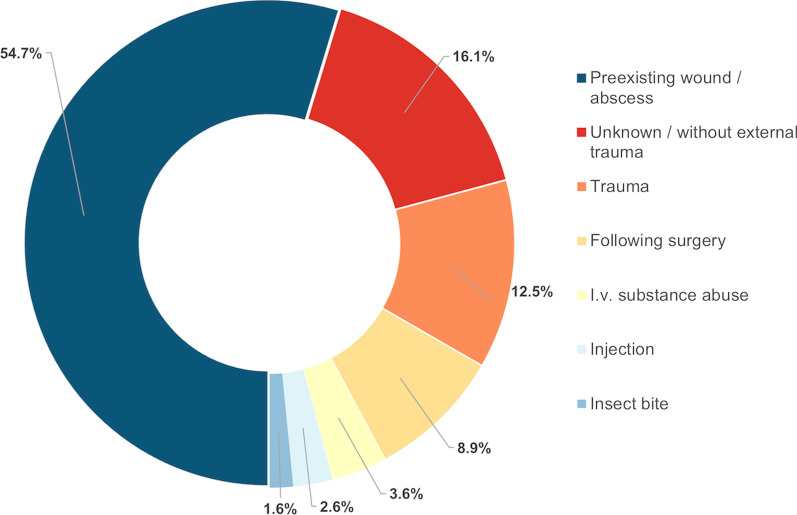
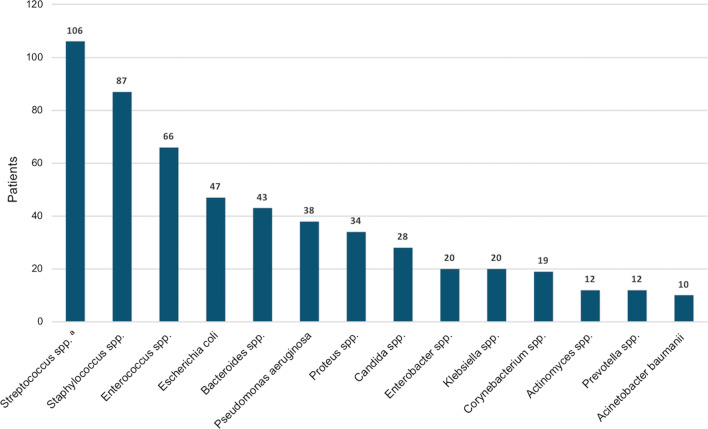
NSTI occurred most frequently on preexisting wounds (54.7%; Fig. 1). The spectrum of pathogens isolated from wound swabs and/or tissue specimens is shown in Fig. 2. Polymicrobial pathogenesis (NSTI type I) was most common (68.8%). Pathogens in blood cultures were detected in 44.8% and associated with higher mortality (P = 0.001; Table 1).
Fig. 1.
Etiology of necrotizing fasciitis and Fournier's gangrene
Fig. 2.
Spectrum of pathogens detected in wound swabs and/or tissue specimens. aStreptococcus spp. comprised most frequently S. pyogenes (n = 29), S. dysgalactiae (n = 18), S. anginosus (n = 12) and S. agalactiae (n = 9). Other pathogens were detected in 81 patients, most frequently Stenotrophomonas maltophilia (n = 7), Serratia spp. (n = 6), Coagulase-negative staphylococci (n = 5), Citrobacter spp. (n = 5) and Fusobacterium spp. (n = 4)
Almost all participants (92.2%) suffered from comorbidities, most frequently from hypertension (59.9%) and diabetes (48.4%, Table 1). Patients with ≥ 3 comorbidities (P = 0.044) or liver disease (P = 0.008) were more likely to have a fatal outcome than others.
Treatments
All patients obtained at least one surgical debridement, 47.9% within 12 h and 59.9% within 24 h after admission (Table 2). Survivors had a larger number of debridements when considering both radical and minor procedures for wound conditioning (P < 0.001). VAC therapy was administered in 62.5% and associated with a higher chance of survival (P < 0.001), similar as defect closure with mesh graft (P < 0.001) or flaps (P = 0.003). Failure to achieve wound closure correlated with a higher risk of mortality (P < 0.001). Amputation was necessary in 24.0%, orchiectomy in 3.6%.
43.2% of the patients underwent HBOT, whereas in 51.1% HBOT was not indicated. Mortality rates were similar in both groups (26.5% vs. 24.5%; Table 4). Eleven patients (5.7%) were ineligible for HBOT due to contraindications specified in Additional file 1: Table S1. These patients were significantly more likely to die than both other groups (mortality rate 63.6%; P = 0.022; Tables 2, 4).
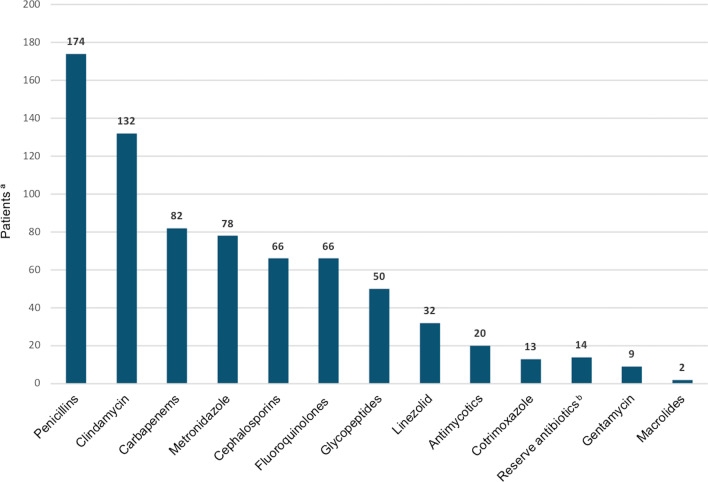
Frequently administered antibiotics are shown in Fig. 3. The mean number of antibiotics applied in each participant was 4.6. Survivors underwent more antibiotic changes than patients who died (P = 0.007; Table 2).
Fig. 3.
Frequently administered antibiotics. aNumber of patients receiving each class of antibiotic. bReserve antibiotics, i.e., antibiotics of last resort used with strict indication, included colistin, daptomycin and tigecycline
The vast majority of patients were treated in the ICU, among them virtually all who died (98.1% vs. 86.3% of the survivors, P = 0.017). The total duration of the hospital stay was significantly longer in survivors (Table 2).
Complications of any kind occurred in 63.5%, more frequently in patients with fatal outcome (P < 0.001; Table 2). In particular, sepsis and organ dysfunction were more common in patients who died (P < 0.001), whereas impaired wound healing occurred more frequently in survivors (P = 0.004).
Subgroup analyses according to HBOT
Patients ineligible for HBOT were younger than both other HBOT subgroups (P = 0.008 in three-group comparison; Table 3). The subgroups treated with HBOT and ineligible for HBOT suffered more frequently from NSTI in the genital/inguinal/perineal area (P = 0.033), on the trunk (P < 0.001) and in multiple localizations (P < 0.001) than patients without indication for HBOT. Furthermore, these two subgroups had significantly higher mean CRP values, leucocyte counts, LRINEC and modified LRINEC scores and rates of sepsis at admission than the subgroup without requirement of HBOT (Table 3).
Table 3.
Patient and disease characteristics of subgroups with and without hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT)
| Characteristic | HBOT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No, not indicated | Yes | No, ineligible | Pa | |
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | ||
| Total (n = 192) | 98 (51.0) | 83 (43.2) | 11 (5.7) | |
| Sex | ||||
| Male | 69 (70.4) | 48 (57.8) | 10 (90.9) | 0.041 |
| Female | 29 (29.6) | 35 (42.2) | 1 (9.1) | |
| Age (years) | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 64.3 (14.1) | 58.8 (15.3) | 52.3 (16.8) | 0.008 |
| < 60 | 35 (35.7) | 44 (53.0) | 8 (72.7) | 0.011 |
| ≥ 60 | 63 (64.3) | 39 (47.0) | 3 (27.3) | |
| Diagnosis | ||||
| Necrotizing fasciitis | 78 (79.6) | 64 (77.1) | 11 (100.0) | 0.207 |
| Fournier's gangrene | 20 (20.4) | 19 (22.9) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Localization | ||||
| Lower extremity | 76 (77.6) | 53 (63.9) | 8 (72.7) | 0.127 |
| Genital/inguinal/perineal | 29 (29.6) | 40 (48.2) | 5 (45.5) | 0.033 |
| Trunk | 9 (9.2) | 26 (31.3) | 5 (45.5) | < 0.001 |
| Retroperitonealb | 1 (1.0) | 3 (3.6) | 0 (0.0) | 0.421 |
| Upper extremityb | 2 (2.0) | 8 (9.6) | 0 (0.0) | 0.052 |
| Head/neck | 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.2) | 0 (0.0) | n.d |
| Multiple localizations | 16 (16.3) | 35 (42.2) | 5 (45.5) | < 0.001 |
| Initial signs and symptoms | ||||
| Sepsis at admission | 49 (50.0) | 74 (89.2) | 9 (81.8) | < 0.001 |
| Positive blood culturec | 32 (46.4) | 30 (40.0) | 7 (70.0) | 0.189 |
| Leucocyte count, mean (SD) | 16.7 (7.7) | 19.8 (8.2) | 21.8 (11.4) | 0.017 |
| CRP, mean (SD) | 235.6 (142.0) | 284.2 (132.0) | 284.5 (126.2) | 0.049 |
| LRINECd, mean (SD) | 6.6 (2.9) | 7.6 (2.5) | 8.3 (2.8) | 0.015 |
| Modified LRINECe, mean (SD) | 9.4 (3.4) | 11.1 (2.8) | 11.0 (4.8) | 0.011 |
| Comorbidities | ||||
| Number, mean (SD) | 3.0 (1.5) | 2.5 (1.7) | 2.6 (1.4) | 0.066 |
| < 3 | 39 (39.8) | 49 (59.0) | 7 (63.6) | 0.022 |
| ≥ 3 | 59 (60.2) | 34 (41.0) | 4 (36.4) | |
| Diabetes mellitus | 51 (52.0) | 35 (42.2) | 7 (63.6) | 0.243 |
| Vascular diseasesf | 36 (36.7) | 19 (22.9) | 3 (27.3) | 0.127 |
| Renal diseases | 28 (28.6) | 20 (24.1) | 4 (36.4) | 0.617 |
| Cardiac diseases | 44 (44.9) | 28 (33.7) | 3 (27.3) | 0.219 |
| Liver diseases | 18 (18.4) | 11 (13.3) | 3 (27.3) | 0.408 |
| Arterial hypertension | 67 (68.4) | 45 (54.2) | 3 (27.3) | 0.012 |
| History of stroke | 7 (7.1) | 8 (9.6) | 0 (0.0) | 0.502 |
| Alcohol abuse | 18 (18.4) | 10 (12.0) | 1 (9.1) | 0.421 |
| Substance abuse (i.v.) | 3 (3.1) | 6 (7.2) | 1 (9.1) | 0.380 |
| Psychiatric diseases | 6 (6.1) | 11 (13.3) | 0 (0.0) | 0.138 |
| Malignant diseases | 16 (16.3) | 10 (12.0) | 3 (27.3) | 0.370 |
| Immunosuppression | 17 (17.3) | 10 (12.0) | 1 (9.1) | 0.523 |
For calculation of percentages, the number of patients in each column (i.e., HBOT no, not indicated, HBOT yes and HBOT no, ineligible) was set to 100%
CRP C-reactive protein, i.v. intravenous, SD standard deviation
aCharacteristics of the three subgroups were compared with Chi-squared test for categorical variables and with Kruskal-Wallis test for continuous variables. Significant differences are highlighted in bold
bExact Fisher-t-test
cBlood cultures were taken before initiation of antibiotics
dLRINEC: Laboratory Risk Indicator for NECrotizing fasciitis
eThe modified LRINEC could be calculated in 131 participants (n = 61: missing data)
fVascular diseases comprised peripheral arterial occlusive disease, chronic venous insufficiency, deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism
HBOT patients received more debridements than both other subgroups (P < 0.001; Table 4). This subgroup and patients ineligible for HBOT were more likely to obtain their first debridement within 12 and 24 h after admission than patients without indication of HBOT (P < 0.001). Defect coverage was attempted less frequently in patients ineligible for HBOT (P = 0.040).
The mean number of antibiotics was highest in the subgroup ineligible for HBOT, followed by the subgroup with HBOT (P = 0.001; Table 4). These two subgroups were also treated in the ICU more frequently (P < 0.001) and for a longer mean duration (P < 0.001) than patients without indication of HBOT. Sepsis and organ dysfunction were documented by far most frequently in patients ineligible for HBOT (81.8%, P = 0.006).
HBOT patients and patients without requirement of HBOT were more likely to survive (P = 0.022) and return to their previous living environment without severe disabling impairment (P = 0.008) than those ineligible for HBOT.
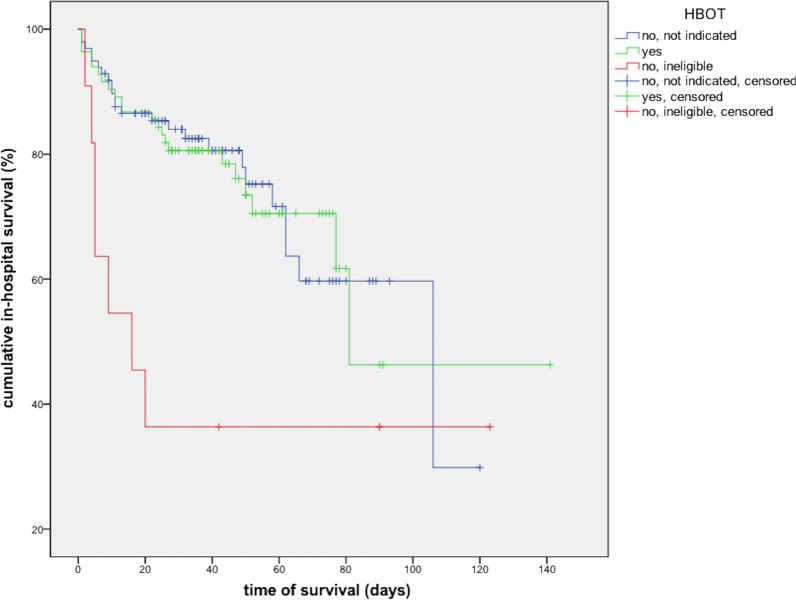
In-hospital survival times were similar in patients without requirement of HBOT compared to HBOT patients, but shorter in the subgroup ineligible for HBOT (mean 82.5 vs. 91.8 vs. 50.3 days, median 106.3 vs. 81.7 vs. 16.5 days; Table 5, Fig. 4, P = 0.045 in log rank test).
Table 5.
In-hospital survival times of patients with and without hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT)
| HBOT | Mean | Median | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| days | SD | 95% CI | Days | SD | 95% CI | |
| Total cohort | 90.5 | 6.6 | 77.5–103.5 | 106.0 | 23.6 | 59.8–152.2 |
| HBOT subgroups | ||||||
| No, not indicated | 82.5 | 6.2 | 70.4–94.6 | 106.0 | 28.8 | 49.5–162.5 |
| Yesa | 91.8 | 10.5 | 71.2–112.4 | 81.0 | n.d | n.d |
| No, ineligible | 50.3 | 16.6 | 17.6–82.9 | 16.0 | 8.3 | 0.0–32.2 |
Mean and median in-hospital survival times were defined as days from admission to our or another hospital until death or discharge from our hospital
CI confidence interval, n.d. not determined, SD standard deviation
aIn the subgroup with HBOT, the SD and 95% CI of the median in-hospital survival time could not be calculated due to lack of variability after the median
Fig. 4.
Kaplan–Meier curve showing cumulative in-hospital survival. Compared to patients without requirement of hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) and patients treated with HBOT, those ineligible for HBOT had significantly lower estimated survival times (P = 0.045 in log rank tests). Discharged patients were censored
Determinants on mortality according to multivariate regression analysis
The baseline multivariate logistic regression model adjusted for sex, age, localization of the NSTI, number of comorbidities and LRINEC showed an increased risk of mortality with rising age (odds ratio (OR) = 1.03, P = 0.017) and infection in a problem localization (OR = 2.88, P = 0.003; Table 6). When additional parameters were included into this model, ineligibility for HBOT (OR = 8.59, P = 0.005), pathogen detection in blood cultures (OR = 3.36, P = 0.002), complications (OR = 10.35, P < 0.001) and sepsis/organ dysfunction (OR = 19.58, P < 0.001) were associated with increased mortality, whereas a larger number of debridements (OR = 0.83, P < 0.001), VAC therapy (OR = 0.17, P < 0.001), defect closure with mesh graft (OR = 0.06, P < 0.001) and with flaps (OR = 0.09, P = 0.024) and a longer duration of the hospital stay (OR = 0.94, P < 0.001) were associated with a lower risk of mortality.
Table 6.
Multivariate logistic regression models including potential determinants associated with mortality
| Characteristic | OR | 95% CI | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline modela | Female | 1.02 | 0.50—2.06 | 0.958 |
| Age, y | 1.03 | 1.01—1.06 | 0.017 | |
| Problem localizationb | 2.88 | 1.44—5.77 | 0.003 | |
| Comorbidities, n | 0.99 | 0.79—1.25 | 0.958 | |
| LRINEC | 1.00 | 0.89—1.13 | 0.992 | |
| Model 1 | Debridements, n | 0.83 | 0.76—0.91 | < 0.001 |
| Model 2 | VAC therapy | 0.17 | 0.08—0.36 | < 0.001 |
| Model 3 | Mesh graft | 0.06 | 0.03—0.16 | < 0.001 |
| Model 4 | Flap | 0.09 | 0.01—0.73 | 0.024 |
| Model 5 | Amputation | 2.09 | 0.98—4.46 | 0.058 |
| Model 6 | HBOT, yes | 1.06 | 0.49—2.30 | 0.884 |
| HBOT no, ineligible | 8.59 | 1.90—38.86 | 0.005 | |
| Model 7 | Positive blood culture | 3.36 | 1.57—7.20 | 0.002 |
| Model 8 | Antibiotic groups, n | 0.97 | 0.74—1.26 | 0.800 |
| Model 9 | ICU treatment | 7.26 | 0.88—59.91 | 0.065 |
| Model 10 | Days in hospital | 0.94 | 0.93—0.96 | < 0.001 |
| Model 11 | Complications | 10.35 | 3.35—32.07 | < 0.001 |
| Model 12 | Infections | 0.72 | 0.36—1.41 | 0.337 |
| Model 13 | Sepsis/organ dysfunction | 19.58 | 8.06—48.20 | < 0.001 |
OR Odds ratio, CI confidence interval, FG Fournier`s gangrene, HBOT hyperbaric oxygen therapy, ICU intensive care unit, LRINEC Laboratory Risk Indicator for NECrotizing fasciitis, n number, NF necrotizing fasciitis, VAC vacuum-assisted closure, y years
aThe baseline model contained mortality as dependent variable and sex, age, problem localization, LRINEC and number of comorbidities as independent variables. In models 1–13, one additional parameter per model was integrated as independent variable. Age, number of comorbidities, number of debridements, number of antibiotic groups and days in hospital were included as continuous variables. The reference group for female was male. The reference category for "HBOT, yes" and "HBOT no, ineligible" contained patients who did not obtain HBOT because it was not indicated. Reference groups for all other parameters consisted of patients without the respective characteristic
bThe category "problem localizations" comprised patients with NF or FG in the retroperitoneal area, head/neck region and/or in multiple localizations. Significant findings are highlighted in bold
Discussion
Mortality rates in NSTI
Our retrospective single-center study includes a relatively large, well-characterized cohort of patients with NF and FG with an in-hospital mortality rate of 27.6%. This rate is rather high compared to the recent literature. The largest systemic review and meta-analysis on adjunctive HBOT in NSTI, which comprised 48,744 patients, showed an in-hospital mortality rate of 9.8% [11]. A recent large prospective, multicenter study reported a 30-day mortality of 19.4% and a septic shock rate of 30% [12]. In our cohort, sepsis at admission was more common (68.8%). Treatment of NSTI in centers with a high annual caseload of these entities generally enhances the chances of favorable outcome, but on the other hand, these centers are prone to receive patients with higher disease severity due to higher expertise and availability of adjunct treatment options [13, 14]. These factors may have contributed to worse outcome in our cohort.
A recent systematic review of 109 studies with 6,051 patients revealed a significant reduction in mortality after the year 2000 [15], while this tendency was not found in subsequent study periods [14]. Improvement in intensive care with decreasing sepsis-related mortality [16] and progress in antibiotic treatment [17] are regarded as main factors contributing to better survival.
Impact of surgical treatment on mortality
Delayed surgery is known to be associated with increased mortality due to NSTI [18], and debridement within 12 h after admission is explicitly recommended [15, 19]. Our HBOT patients and the subgroup ineligible for HBOT had timely debridements significantly more often than the group without need of HBOT. Altogether, only 47.9% of our patients received their first debridement within 12 h after admission to our hospital. However, one third had already obtained a debridement prior to transfer to our center. Outcome of transferred and directly admitted patients was similar, supporting early transport of patients with NSTI to specialized centers as recommended in prior work [13, 20].
VAC therapy and defect reconstruction were associated with a higher chance of survival. These observations should rather be interpreted as correlation than as causality, as defect conditioning and reconstruction require vital wounds and hemodynamic stability. The benefit of defect coverage is nevertheless evident, as it reduces the risk of complications related to large wounds and promotes mobilization, which is essential for convalescence. A larger number of debridements, including minor interventions for wound conditioning, and a longer hospital stay were both significantly associated with survival, which should be interpreted within this line of argumentation.
Impact of HBOT
To our knowledge, this study is the first to stratify patients with NSTI into three groups according to indication and practicability of HBOT. The subgroup treated with HBOT had significantly worse initial conditions and greater disease dissemination and required more arduous treatment compared to patients without indication for HBOT. Nevertheless, rates of survival, defect coverage and hospital discharge without severe disability were similar in both groups, which points to a benefit from HBOT.
Even if HBOT is routinely used for treatment of NSTI in specialized centers worldwide, unequivocal scientific evidence for its benefits has not been provided yet. Many studies investigating its impact on outcome of NSTI demonstrated positive effects [21–29], whereas others did not show significant benefit [30–34]. Past systematic reviews provided only limited evidence on the clinical advantages of HBOT and had difficulties performing reliable meta-analyses due to shortcomings in the design and limited cohort sizes of included studies, high risk of confounding, substantial study heterogeneity and poor concordance of inclusion criteria [4, 5, 35, 36]. According to the latest meta-analysis, HBOT improves the odds for survival of NSTI [11].
In our study, ineligibility for HBOT was associated with increased mortality and significantly worse outcome despite early and frequent surgical debridements, extensive antibiotic therapy and intense supportive care, corresponding to results from a large multicenter database study [31]. The most common reason for withholding HBOT despite available infrastructure and highly experienced staff even after introduction of an in-house hyperbaric chamber was severe hemodynamic instability, e.g., due to septic shock. By contrast morbid obesity prevented HBOT only before the in-house chamber was established. Morbidly obese patients were younger, had less comorbidities and also survived more frequently, albeit commonly with severe physical impairment. As HBOT contributes to better oxygenation of insufficiently perfused fatty tissue, it could be speculated that obese patients benefit particularly from HBOT, although respective clinical evidence is lacking so far.
Diabetes mellitus is known to be one of the main risk factors for NSTI. Concordant with the literature [37, 38], almost half of our participants suffered from this comorbidity. Compared to nondiabetics, patients with diabetes were reported to have a higher risk of a severe disease course [39] and of limp loss due to their NSTI [37, 38]. Therefore, and due to diabetes-associated comorbidities potentiating the risk of adverse outcome, patients with diabetes and NF or FG may be preferentially considered for HBOT. The same applies to immunocompromised patients and patients with concomitant cardiovascular and metabolic diseases that may contribute to particularly severe and complicated disease courses and unfavorable outcome.
HBOT was shown to significantly reduce the risk of amputation in patients with NSTI in earlier studies [11, 24, 40], which encourages its use in patients with limb localization. In our cohort a major amputation of the lower limb was performed in 44 patients. These patients did not differ significantly from others with regard to HBOT, but the percentage of patients with limb loss appeared particularly high in the subgroup ineligible for HBOT.
Another subgroup expected to benefit particularly from HBOT according to the literature are patients with FG. A recent systematic review demonstrated overall mortality rates of 16.6% and 25.9% in patients with FG with and without HBOT [29]. We did no detect accordant differences in our cohort, possibly because of the limited number of patients with FG.
During the whole study period, only one complication possibly related to HBOT was recorded, i.e., a ruptured pulmonal cavern after the first HBOT session. This low rate of complications indicates high safety and good tolerability of HBOT. Therefore, this adjunctive treatment should be offered to patients with severe NF or FG whenever possible, in particular if they suffer from comorbidities which increase the risk of adverse outcome or if they are threatened by limb loss.
Limitations
Due to the single-center design and the limited cohort size, generalizability of our findings may be restricted. However, characteristics of our study population and prognostic factors identified are well compatible with the literature [14, 41]. Although the cohort size is relatively large compared to other single-center studies, the study may be underpowered for assessment of certain impact factors on mortality and outcome. Some subgroups including the one ineligible for HBOT were small. Therefore, relevant risk factors for mortality may have been missed.
Owing to the retrospective study design, some clinical and laboratory parameters were not consistently available and data quality might be inferior to that of prospective studies. Comorbidities were documented in categories without assessing their severity. Use of a classification system for comorbid conditions like the weighted Charlson Comorbidity Index [14, 42] should be considered in future studies. Smoking habits were not consistently documented in the patient records, because many patients were too critically ill to take a detailed smoking history at admission and required long-term ventilation in the further course.
The fact that a large proportion of patients were transferred to our center implicates the possibility of confounding factors originating from transferring hospitals and the risk of selection bias towards patients who were fit enough for transport.
The use of different hyperbaric chambers during the study period could be another source of selection bias. The old HBOT chamber was not suitable for morbidly obese and severely unstable patients. After implementation of the new chamber in October 2017, morbid obesity ceased to pose a restriction and hemodynamically unstable patients could be treated with higher safety. Indeed, the number of patients treated with HBOT increased noticeably after implementation of the new chamber, and the percentage of patients with NF or FG who received HBOT raised from 43% before 2018 to 58% between 2018 and 2020.
Strengths
We present a relatively large retrospective study which provides insight into mortality and outcome of patients with NF and FG treated in a large HBOT center under routine clinical conditions. Our study was performed in a Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery with a certified Center of Wound Medicine and a highly specialized national HBOT center with long-time focus on NSTI and long-standing experience in their treatment. Diagnostic criteria of NF and FG as well as inclusion and exclusion criteria of the study were precisely defined, which is not always the case in retrospective studies on treatment of NSTI. The indication of HBOT was made according to standardized criteria independent of individual preferences of the surgeon or other team members. Clinical and laboratory parameters as well as details on the HBOT sessions, surgical procedures, antibiotic and supportive treatment and complications were documented accurately and comprehensively. Information on defect reconstruction, which is lacking in many other studies, was captured in detail and integrated into the analysis. The impact of various patient-, disease- and treatment-related factors on morbidity and outcome of NF and FG was assessed in multivariate regression models controlling for the key confounding factors.
Patients were stratified according to the indication, but also according to practicability of HBOT, which has not been done in other studies so far but reflects real medical care situations well and allows for a comparison of mortality and outcome close to clinical reality.
Conclusions
We present a relatively large single-center study on mortality and outcome of an accurately characterized cohort of patients with NF and FG treated in a hyperbaric referral center, in which we identified several factors associated with increased mortality: higher age, affection of multiple or problem localizations, ineligibility for HBOT, positive blood cultures, complications and sepsis/organ dysfunction. In patients eligible for HBOT, our data point to a beneficial effect of this procedure. Our study was the first to stratify patients into three groups according to indication and practicability of HBOT, a classification reflecting the clinical situation well. Clearly, further evidence is required to verify our findings as well as the utility of HBOT for NSTI.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1. Supplementary Table S1. Characteristics of patients who were ineligible for hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT).
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr. Daniel Ostapowicz and Katja Knoll, Department of Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery - Center of Wound Medicine, Vivantes Klinikum im Friedrichshain, Berlin for helpful discussion.
Abbreviations
- FG
Fournier’s gangrene
- HBOT
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy
- ICU
Intensive care unit
- LRINEC
Laboratory Risk Indicator for Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infections
- m
Meters
- NF
Necrotizing fasciitis
- NSTI
Necrotizing soft tissue infections
- OR
Operating room
- qSOFA
Quick Sequential Organ Failure Assessment
- VAC
Vacuum-assisted closure
Author contributions
AM, SK and WKP conceived and designed the study. AM, OM, CvH, SK and WKP collected the data. AM and KD performed statistical analysis. AM, CvH, SK and WKP interpreted the data. AM, SK and WKP wrote the manuscript. AM, KD, SK and WKP prepared the figures and tables. KD, OM and CvH critically revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. SK and WKP contributed equally and should be considered as senior authors.
Funding
None.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Medicine of Charité University Medicine Berlin (EA2/296/20).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Susanne Kopp and Wiebke K. Peitsch contributed equally and should be considered as senior authors.
References
- 1.Hysong AA, Posey SL, Blum DM, et al. Necrotizing fasciitis: pillaging the acute phase response. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2020;102(6):526–537. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.19.00591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Memar MY, Yekani M, Alizadeh N, Baghi HB. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy: Antimicrobial mechanisms and clinical application for infections. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;109:440–447. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.10.142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Jensen PØ, Møller SA, Lerche CJ, et al. Improving antibiotic treatment of bacterial biofilm by hyperbaric oxygen therapy: not just hot air. Biofilm. 2019;1:100008. doi: 10.1016/j.bioflm.2019.100008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Faunø Thrane J, Ovesen T. Scarce evidence of efficacy of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in necrotizing soft tissue infection: a systematic review. Infect Dis (Lond) 2019;51(7):485–492. doi: 10.1080/23744235.2019.1597983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cocanour CS, Chang P, Huston JM, et al. Management and novel adjuncts of necrotizing soft tissue infections. Surg Infect (Larchmt) 2017;18(3):250–272. doi: 10.1089/sur.2016.200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Caesar A, Jacoby I. Necrotizing soft tissue infections. In: Moon RE, editor. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy Indications. 14. Florida: Best Publishing Company; 2019. pp. 239–262. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Mathieu D, Marroni A, Kot J. Tenth European Consensus Conference on Hyperbaric Medicine: recommendations for accepted and non-accepted clinical indications and practice of hyperbaric oxygen treatment. Diving Hyperb Med. 2017;47(1):24–32. doi: 10.28920/dhm47.1.24-32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Schmale M, Fichtner A, Pohl C, John E, Bucher M. Hyperbare oxygenation bei nekrotisierenden Weichteilinfektionen: pro [Hyperbaric oxygenation for necrotizing soft tissue infections: pro] Chirurg. 2012;83(11):973–979. doi: 10.1007/s00104-012-2283-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, et al. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3) JAMA. 2016;315(8):801–810. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Borschitz T, Schlicht S, Siegel E, Hanke E, von Stebut E. Improvement of a clinical score for necrotizing fasciitis: “pain out of proportion” and high CRP levels aid the diagnosis. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(7):e0132775. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hedetoft M, Bennett MH, Hyledegaard O. Adjunctive hyperbaric oxygen treatment for necrotising soft-tissue infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diving Hyperb Med. 2021;51(1):34–43. doi: 10.28920/dhm51.1.34-43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Madsen MB, Skrede S, Perner A, et al. Patient’s characteristics and outcomes in necrotising soft-tissue infections: results from a Scandinavian, multicentre, prospective cohort study. Intensive Care Med. 2019;45(9):1241–1251. doi: 10.1007/s00134-019-05730-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Audureau E, Hua C, de Prost N, et al. Mortality of necrotizing fasciitis: relative influence of individual and hospital-level factors, a nationwide multilevel study, France, 2007–12. Br J Dermatol. 2017;177(6):1575–1582. doi: 10.1111/bjd.15615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hedetoft M, Madsen MB, Madsen LB, Hyldegaard O. Incidence, comorbidity and mortality in patients with necrotising soft-tissue infections, 2005–2018: a Danish nationwide register-based cohort study. BMJ Open. 2020;10(10):e041302. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-041302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Nawijn F, Smeeing DPJ, Houwert RM, Leenen LPH, Hietbrink F. Time is of the essence when treating necrotizing soft tissue infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Emerg Surg. 2020;15:4. doi: 10.1186/s13017-019-0286-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Rudd KE, Johnson SC, Agesa KM, et al. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990–2017: analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet. 2020;395(10219):200–211. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32989-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Redman DP, Friedman B, Law E, Still JM. Experience with necrotizing fasciitis at a burn care center. South Med J. 2003;96(9):868–870. doi: 10.1097/00007611-200309000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Boyer A, Vargas F, Coste F, et al. Influence of surgical treatment timing on mortality from necrotizing soft tissue infections requiring intensive care management. Intensive Care Med. 2009;35(5):847–853. doi: 10.1007/s00134-008-1373-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Gelbard RB, Ferrada P, Yeh DD, et al. Optimal timing of initial debridement for necrotizing soft tissue infection: a practice management guideline from the Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2018;85(1):208–214. doi: 10.1097/TA.0000000000001857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Proud D, Bruscino Raiola F, Holden D, Paul E, Capstick R, Khoo A. Are we getting necrotizing soft tissue infections right? A 10-year review. ANZ J Surg. 2014;84(6):468–472. doi: 10.1111/ans.12412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Devaney B, Frawley G, Frawley L, Pilcher DV. Necrotising soft tissue infections: the effect of hyperbaric oxygen on mortality. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2015;43(6):685–692. doi: 10.1177/0310057X1504300604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Soh CR, Pietrobon R, Freiberger JJ, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy in necrotising soft tissue infections: a study of patients in the United States Nationwide Inpatient Sample. Intensive Care Med. 2012;38(7):1143–1151. doi: 10.1007/s00134-012-2558-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Steiner T, Seiffart A, Schumann J, Bucher M. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy in necrotizing soft tissue infections: a retrospective study. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1072:263–267. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-91287-5_42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Wilkinson D, Doolette D. Hyperbaric oxygen treatment and survival from necrotizing soft tissue infection. Arch Surg. 2004;139(12):1339–1345. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.139.12.1339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Creta M, Longo N, Arcaniolo D, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy reduces mortality in patients with Fournier’s Gangrene. Results from a multi-institutional observational study. Minerva Urol Nefrol. 2020;72(2):223–8. doi: 10.23736/S0393-2249.20.03696-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Shaw JJ, Psoinos C, Emhoff TA, Shah SA, Santry HP. Not just full of hot air: hyperbaric oxygen therapy increases survival in cases of necrotizing soft tissue infections. Surg Infect (Larchmt) 2014;15(3):328–335. doi: 10.1089/sur.2012.135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Korhonen K. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy in acute necrotizing infections with a special reference to the effects on tissue gas tensions. Ann Chir Gynaecol Suppl. 2000;89(Suppl 214):7–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Riseman JA, Zamboni WA, Curtis A, Graham DR, Konrad HR, Ross DS. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for necrotizing fasciitis reduces mortality and the need for debridements. Surgery. 1990;108(5):847–850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Schneidewind L, Anheuser P, Schönburg S, Wagenlehner FME, Kranz J. Hyperbaric oxygenation in the treatment of Fournier’s gangrene: a systematic review. Urol Int. 2021;105(3–4):247–256. doi: 10.1159/000511615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Massey PR, Sakran JV, Mills AM, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy in necrotizing soft tissue infections. J Surg Res. 2012;177(1):146–151. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2012.03.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.George ME, Rueth NM, Skarda DE, Chipman JG, Quickel RR, Beilman GJ. Hyperbaric oxygen does not improve outcome in patients with necrotizing soft tissue infection. Surg Infect (Larchmt) 2009;10(1):21–28. doi: 10.1089/sur.2007.085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Shupak A, Shoshani O, Goldenberg I, Barzilai A, Moskuna R, Bursztein S. Necrotizing fasciitis: an indication for hyperbaric oxygenation therapy? Surgery. 1995;118(5):873–878. doi: 10.1016/S0039-6060(05)80278-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Brown DR, Davis NL, Lepawsky M, Cunningham J, Kortbeek J. A multicenter review of the treatment of major truncal necrotizing infections with and without hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Am J Surg. 1994;167(5):485–489. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(94)90240-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Mindrup SR, Kealey GP, Fallon B. Hyperbaric oxygen for the treatment of fournier’s gangrene. J Urol. 2005;173(6):1975–1977. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000158129.56571.05. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Levett D, Bennett MH, Millar I. Adjunctive hyperbaric oxygen for necrotizing fasciitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;1(1):CD007937. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007937.pub2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Jallali N, Withey S, Butler PE. Hyperbaric oxygen as adjuvant therapy in the management of necrotizing fasciitis. Am J Surg. 2005;189(4):462–466. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2005.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Tan JH, Koh BT, Hong CC, et al. A comparison of necrotising fasciitis in diabetics and non-diabetics: a review of 127 patients. Bone Joint J. 2016;98-B(11):1563–8. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.98B11.37526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Cheng NC, Tai HC, Chang SC, Chang CH, Lai HS. Necrotizing fasciitis in patients with diabetes mellitus: clinical characteristics and risk factors for mortality. BMC Infect Dis. 2015;15:417. doi: 10.1186/s12879-015-1144-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Naik D, Jebasingh FK, Thomas N, et al. Necrotizing soft tissue infection of the upper extremities in patients with diabetes mellitus in a tertiary care center-a retrospective study. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2020;14(5):1071–1075. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2020.05.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Escobar SJ, Slade JB, Jr, Hunt TK, Cianci P. Adjuvant hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBO2) for treatment of necrotizing fasciitis reduces mortality and amputation rate. Undersea Hyperb Med. 2005;32(6):437–443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Peetermans M, de Prost N, Eckmann C, Norrby-Teglund A, Skrede S, De Waele JJ. Necrotizing skin and soft-tissue infections in the intensive care unit. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020;26(1):8–17. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2019.06.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Charlson ME, Pompei P, Ales KL, MacKenzie CR. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation. J Chronic Dis. 1987;40(5):373–383. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(87)90171-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1. Supplementary Table S1. Characteristics of patients who were ineligible for hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT).
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.