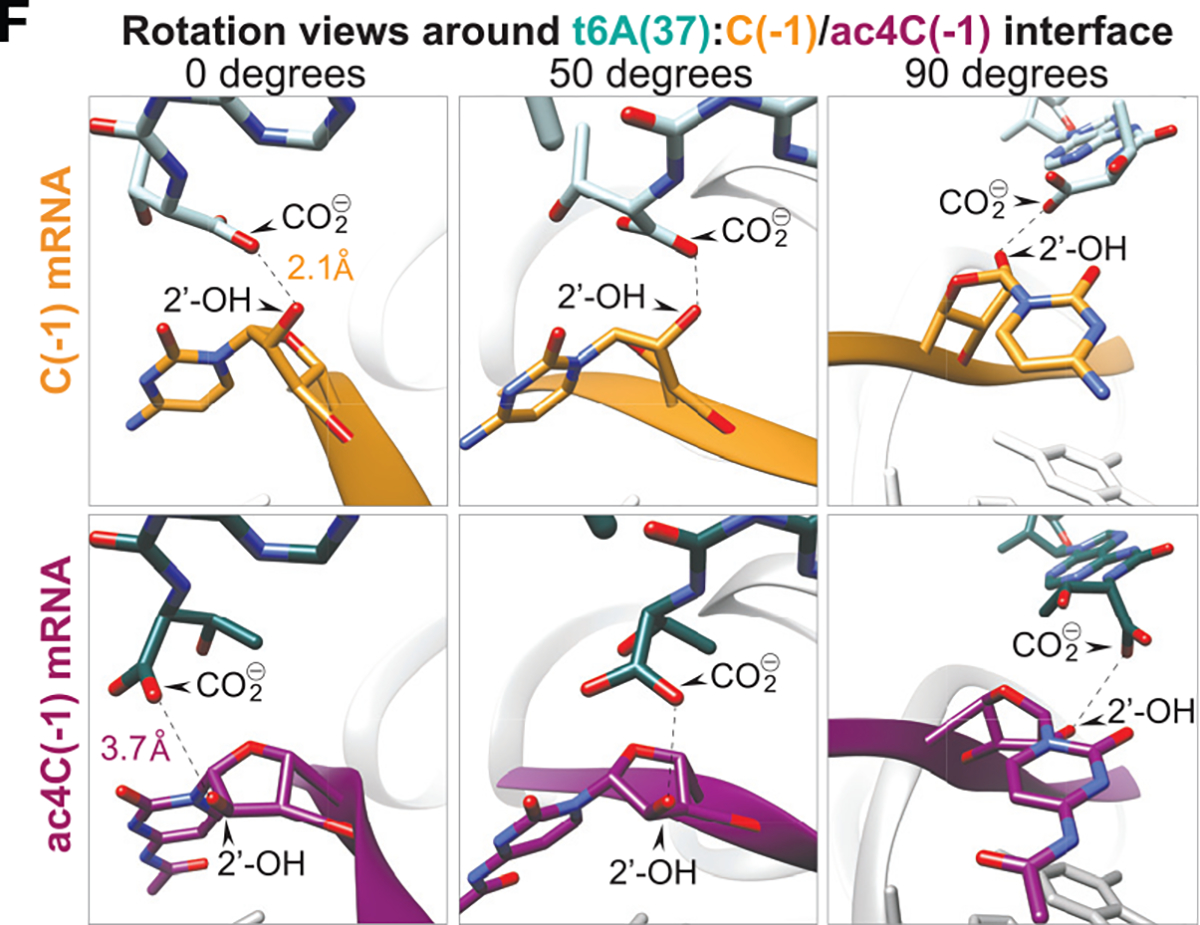
The authors have reported a modeling discrepancy for the cryo-EM complexes shown in Figures 7E and 7F. Automatic real-space refinement during PDB submission identified a range of 2.1–2.7 Å for the intermolecular hydrogen bond detected in the non-acetylated complex. References to the distance between the ribose 2′-OH and t6A carboxyl side chain in 80S initiation complexes formed on non-acetylated mRNA, depicted in Figure 7F, have been modified from “2.1 Å” to “2.1 or 2.7 Å after real-space refinement” to reflect this ambiguity in program-specific parameters. Corresponding labels in the graphical abstract and Figure 7F have also been updated to reflect this new information. The acetylated complex was unaltered and the range does not change the conclusion of the study.
Figure 7F. Acetylation of cytidine at Kozak nucleotide (−1) structurally alters intermolecular interaction with tRNAiMet t6A in 80S initiation complex cryo-EM (corrected).
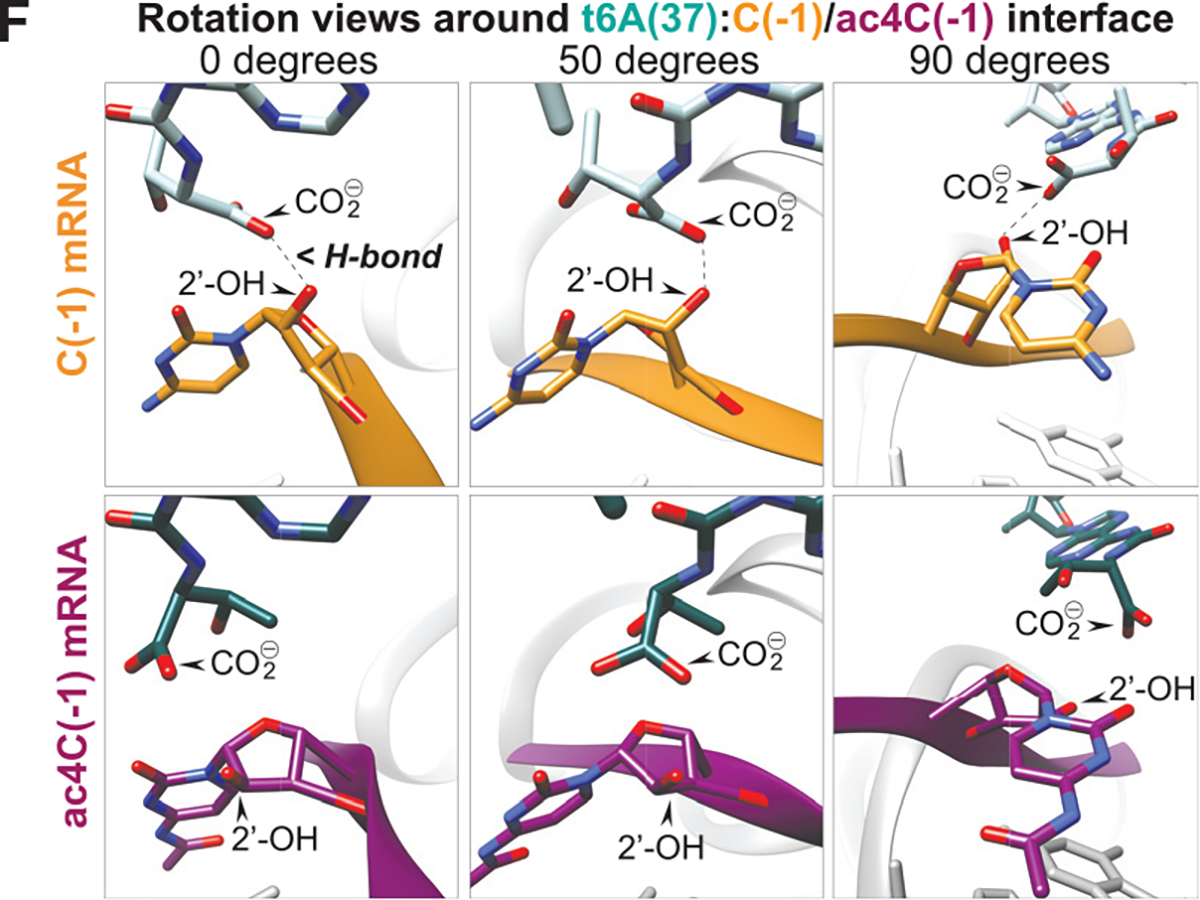
Figure 7F. Acetylation of cytidine at Kozak nucleotide (−1) structurally alters intermolecular interaction with tRNAiMet t6A in 80S initiation complex cryo-EM (original).