Abstract
Cyclic-di-GMP (c-di-GMP) is an essential bacterial second messenger that regulates biofilm formation and pathogenicity. To study the global regulatory effect of individual components of the c-di-GMP metabolic system, we deleted all 12 diguanylate cyclase (dgc) and phosphodiesterase (pde)-encoding genes in E. amylovora Ea1189 (Ea1189Δ12). Ea1189Δ12 was impaired in surface attachment due to a transcriptional dysregulation of the type IV pilus and the flagellar filament. A transcriptomic analysis of surface-exposed WT Ea1189 and Ea1189Δ12 cells indicated that genes involved in metabolism, appendage generation and global transcriptional/post-transcriptional regulation were differentially regulated in Ea1189Δ12. Biofilm formation was regulated by all 5 Dgcs, whereas type III secretion and disease development were differentially regulated by specific Dgcs. A comparative transcriptomic analysis of Ea1189Δ8 (lacks all five enzymatically active dgc and 3 pde genes) against Ea1189Δ8 expressing specific dgcs, revealed the presence of a dual modality of spatial and global regulatory frameworks in the c-di-GMP signaling network.
Author summary
Cyclic-di-GMP dependent regulation, in the context of biofilm formation, has been studied in several bacterial systems. However, there are fewer studies exploring the role of individual genetic components related to cyclic-di-GMP, given the presence of an often large number of diguanylate cyclase and phosphodiesterase enzymes in bacterial systems. To explore the evolutionary dependencies related to cyclic-di-GMP in E. amylovora, we used a collective elimination approach, whereby all of the enzymes involved in cyclic-di-GMP metabolism were eliminated from the system. This approach enabled us to highlight the importance of cyclic-di-GMP in plant xylem colonization due to its effect on surface attachment. Additionally, we highlight the differential regulatory impact of each of the dgc/pde genes on critical virulence factors in E. amylovora with a genetic framework that is not affected by any enzymatic redundancy or antagonism. We further use a transcriptomic approach to reveal evidence of regulatory localization/heterogeneity mediated by each of the dgc genes.
Introduction
The bis (3’,5’)-cyclic diguanosine monophosphate (c-di-GMP) signaling system is a ubiquitous and effective adaptation by which bacteria can gather sensory input from environmental stimuli and correspondingly regulate cellular function to then effectively employ the most appropriate response for survival within a particular environment or for host colonization in a pathogenic context [1,2]. Bacterial c-di-GMP networks consist of diguanylate cyclase (Dgc) enzymes, marked by the presence of a GGDEF motif, that synthesize c-di-GMP from two molecules of guanosine tri-phosphate (GTP) substrate, and phosphodiesterase (Pde) enzymes, containing an EAL and/or HD-GYP domain that c-di-GMP into pGpG (5’-phosphoguanylyl-(3’➔5’)-guanosine). The HD-GYP class of Pdes and oligoribonucleases can directly hydrolyze pGpG into guanosine mono-phosphate (GMP) subunits. In E. amylovora, five active Dgcs (EdcA-E) and three active Pdes (PdeA-C) [EAL domain containing proteins] have been functionally characterized [3,4]. As documented in other bacterial systems including Escherichia coli (29 Dgcs/Pdes), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (38 Dgcs/Pdes), Salmonella enterica [5,6] (20 Dgcs/Pdes), and Vibrio cholerae [7,8] (61 Dgcs/Pdes), the presence of a large number of Dgcs/Pdes and systemic functional redundancy is often observed. The retention of such a high number of Dgcs and Pdes in bacterial pathogen systems raises questions about the evolutionary significance of developing multilayered genetic control strategies.
The primary approach used to study the regulatory effect of individual components of c-di-GMP turnover is by deleting one or more genes in combination and evaluating phenotypic and regulatory changes. In Salmonella, Solano et al. [5] generated a multigene mutant that eliminated 12 dgc genes and Sarenko et al. [9], studied a collective group of single deletion mutants of each of the 29 individual Dgc and Pde encoding genes in Escherichia coli. Both studies indicated that the functional effect of specific Dgcs and Pdes on virulence phenotypes could be either dependent or independent of their metabolic activity towards c-di-GMP. Abel et al. [10] generated a c-di-GMP null strain by deleting the active Dgc and Pde encoding genes in Caulobacter crescentus and demonstrated the impact on growth, motility and surface attachment. While the targeted elimination of one or more genes in the c-di-GMP regulatory system is a straightforward approach that can highlight significant changes in the regulation of critical virulence factors, the presence of multiple other enzymes can, through redundancy or antagonistic enzymatic effect, mask some of the effects occurring due to the loss of one particular gene and thus the resulting downstream regulatory effect. Additionally, the overall regulatory effect of each of these enzyme classes has not been explored in a background that does not include any additional impedance/interaction with any of the other components in the network.
In order to address these concerns and with the overarching aim of exploring the role of the global effect of c-di-GMP on virulence manifestation in the host, we used a c-di-GMP systematic deletion approach in Erwinia amylovora, the causal agent of fire blight disease of rosaceous plants [11]. An evolutionary adaptation that helps E. amylovora systemically colonize the apple host is its ability to attach to the walls of xylem vasculature and form robust biofilms within the xylem channels, thus enabling extensive proliferation of the pathogen during this stage of the disease cycle [12]. Cyclic-di-GMP is one of the critical factors that regulates biofilm formation in E. amylovora [3,4], and elevated intracellular levels of c-di-GMP have been correlated with increased levels of biofilm development in static and flow-based in vitro systems [4,13]. In addition to biofilm formation, c-di-GMP also negatively regulates type III secretion system (T3SS) mediated virulence via the transcriptional downregulation of hrpL (alternate sigma factor required for the transcription of hrp genes) and a reduction in the amount of the T3SS effector DspE (pathogenicity factor) that is transferred into host cells [3,4].
We hypothesized that the retention of multiple Edc and Pde enzymes in this system was due to adaptive functional divergence. To test our hypothesis, we eliminated all 12 genes of the c-di-GMP metabolic network in E. amylovora Ea1189 (Ea1189Δ12), resulting in an E. amylovora strain with no background c-di-GMP formative, degradative, or signaling activity. We then examined the impact of specific Edcs on several virulence factors. A transcriptomic approach was also used to examine the global impact of c-di-GMP during biofilm initiation and to study the regulatory network mediated by specific Edcs.
Results
E. amylovora encodes an array of 12 proteins with GGDEF and/or EAL motifs
The regulatory impact of the edc and pde genes on virulence has been studied separately in E. amylovora through the assessment of phenotypic variation in mutants lacking one or more of these genes [3,4]. In this study, we aimed to decipher the evolutionary role of both the formative and degradative components of the overall c-di-GMP system. In order to do so, we generated a systemic null mutant lacking all 12 genes that encode proteins containing a GGDEF and/or EAL motif (as annotated by Pfam v 33.1) [14]. Proteins containing HD-GYP motifs are absent in E. amylovora [4]. The list of 12 proteins along with their domain architecture is graphically mapped in Fig 1A. EdcA-E have been previously mapped and characterized by Edmunds et al. [3]. The functional traits regulated by PdeA-C have been studied by Kharadi et al. [4]. EAM_3378, EAM_3136 (CsrD) [15], EAM_2449, and EAM_1579 encode proteins with degenerate GGDEF/EAL domains as designated on Pfam [14]. The N-terminal end of all proteins except EdcA, EAM_3378 and EAM_1579 includes a wide array of periplasmic sensory domains and multiple transmembrane helices (as predicted by TMHMM Server v 2.0) [16]. EdcA, PdeC and CsrD contain both GGDEF and EAL domains (Fig 1A).
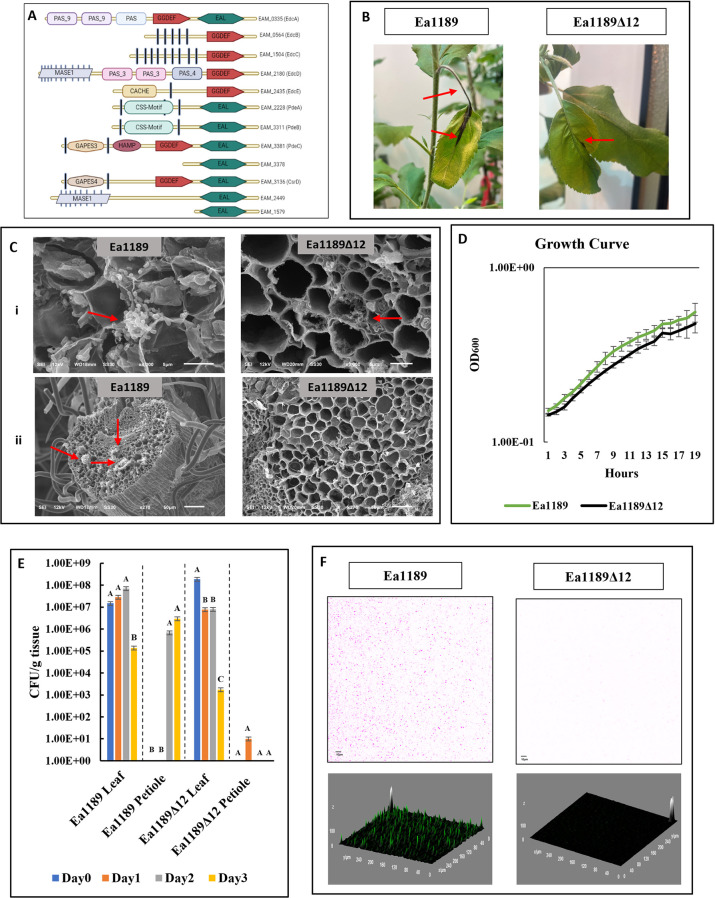
Fig 1. C-di-GMP is essential for host colonization.
A) A representative protein domain architectural overview of all identified proteins in E. amylovora Ea1189 that contain a GGDEF and/or EAL domain. Filled black vertical bars represent transmembrane helices on the N-terminal domain. The image was created using Biorender. B) Images depicting disease progression in apple shoots infected with Ea189 and Ea1189Δ12 at 3dpi. While Ea1189 infected shoots show signs of infection the leaf and the petiole (red arrows), shoots infected with Ea1189Δ12 show minor signs of necrosis limited to the apoplast region in the leaf (red arrow) C) Scanning electron micrographs depicting sectional images of the i) apoplast and ii) xylem tissue of young apple shoot tips 3 dpi with E. amylovora Ea1189 and Ea1189Δ12. Widespread colonization was observed when shoot tips were inoculated with WT Ea1189 in both the apoplast and the xylem. However, shoots inoculated with Ea1189Δ12 showed less severe bacterial colonization in the apoplast and no evidence of any biofilm development within the xylem tissue in the petiole. D) Growth patterns in vitro for Ea1189 and Ea1189Δ12 don’t show any significant difference. E) Bacterial population counts over the course of 3 days post inoculation of young shoot tips with WT Ea1189 and Ea1189Δ12. Leaf and petiole samples were separately examined. Over a time span of 72 hrs, the bacterial population of Ea1189 increases within the petiole and declines within the apoplast, whereas populations of Ea1189Δ12 decline in the leaf tissue and are at undetectable levels in the petiole. Error bars represent standard errors of the means. Tukey’s HSD (honestly significant difference) (P < 0.05) test was used to determine statistical significance over the course of the experiment for each tissue type. F) Z-stacked confocal microscopy images (color inverted) showing the overall attachment occurring within the flow chamber one hour after the introduction of either Ea1189 or Ea1189Δ12 cells into the chamber, followed by the flushing of the chamber with 0.5X PBS. Ea1189 cells displayed widespread even attachment with interspersed patches of elevated fluorescence signal indicating potential multilayered attachment. Ea1189Δ12 cells failed to attach to the chamber surface.
C-di-GMP is essential for systemic host colonization
To determine the impact of a complete c-di-GMP null mutant on virulence in planta, young apple leaves at the tips of branches were inoculated with E. amylovora Ea1189 or Ea1189Δ12 and were tracked for disease progression. Apple branches infected with Ea1189Δ12 showed a significantly-reduced external manifestation of necrotic tissue development, and that such necrosis was limited to apoplastic leaf regions (Fig 1B). Using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), we also checked for any patterns of bacterial proliferation and localization within the apoplast and xylem vessels. E. amylovora Ea1189 cells were detected abundantly in the apoplast 72 hpi (hours post inoculation). In the xylem vessels, Ea1189 cells were able to attach and develop extensive biofilms with an abundance of EPS, thus, functionally impeding the channels (Fig 1C (i and ii)). In contrast, the apoplast region of leaves infected with Ea1189Δ12 showed relatively few pockets of cells with some extracellular material, whereas the xylem vessels showed no microscopic signs of colonization despite the appearance of some minor necrotic lesions on the leaf surface near the site of inoculation and no cellular attachment, exopolysaccharide (EPS) generation, or biofilm formation was detected (Fig 1C (i and ii)). There were no apparent differences in the growth patterns for Ea1189 and Ea1189Δ12 in vitro (Fig 1D). Bacterial population counts taken separately from leaf and petiole tissue of shoots infected with Ea1189 and Ea1189Δ12 indicated that 24 hpi, a majority of the detectable bacterial population was still restricted to the leaf tissue and was detected in shoots infected with both strains at levels similar to ones at the time of inoculation (between 107and 108 CFU/g of tissue) (Fig 1E). At 48 hpi, shoots infected with Ea1189 contained detectable levels of bacterial populations in the petiole at ~106 CFU/g, which then increased slightly at 72 hpi and inversely, the bacterial load decreased in the leaf tissue at 72 hpi (Fig 1E). Within the leaf tissue, Ea1189Δ12 populations followed a similar trend and declined significantly by 72 hpi; however, apart from a minor level of bacteria detected in the apoplast at 24 hpi, there was no detectable bacterial population present in the apoplast during the course of the experiment (Fig 1E).
Surface attachment is a limiting factor for biofilm development and is dependent on c-di-GMP signaling in E. amylovora
Since an initial in vitro assessment indicated a lack of biofilm formation in Ea1189Δ12 compared to WT Ea1189 (further discussed and presented in Fig 2), we analyzed if this was due to an impairment in surface attachment, which could be limiting further biofilm development. We monitored the interaction of GFP labelled cells with the base of the flow chamber upon initial contact using TIRF (total internal reflection fluorescence) microscopy. S1 and S2 Videos present collated images in the form of a time lapse video presenting the dynamics of surface interaction of Ea1189 (S1 Video) and Ea1189Δ12 (S2 Video) cells introduced into the chamber. Ea1189 cells approached the basal portion of the flow cell, and a subset of them would attach in every frame of the video (S1 and S2 Videos). Over time, this led to a saturation of the image frame with GFP signal from attached cells. In contrast, several Ea1189Δ12 cells approached the basal surface but failed to attach irreversibly to the surface. Due to the pace of the video, this occurrence plays out in the form of momentary GFP signal increases and lapses as cells approach and then reproach from the surface (S1 and S2 Videos). An assessment of the flow chamber at the end of this experiment by flushing out the planktonic cells revealed that Ea1189 cells were able to evenly attach to the base of the flow chamber, and Ea1189Δ12 were unable to do so (Fig 1F).
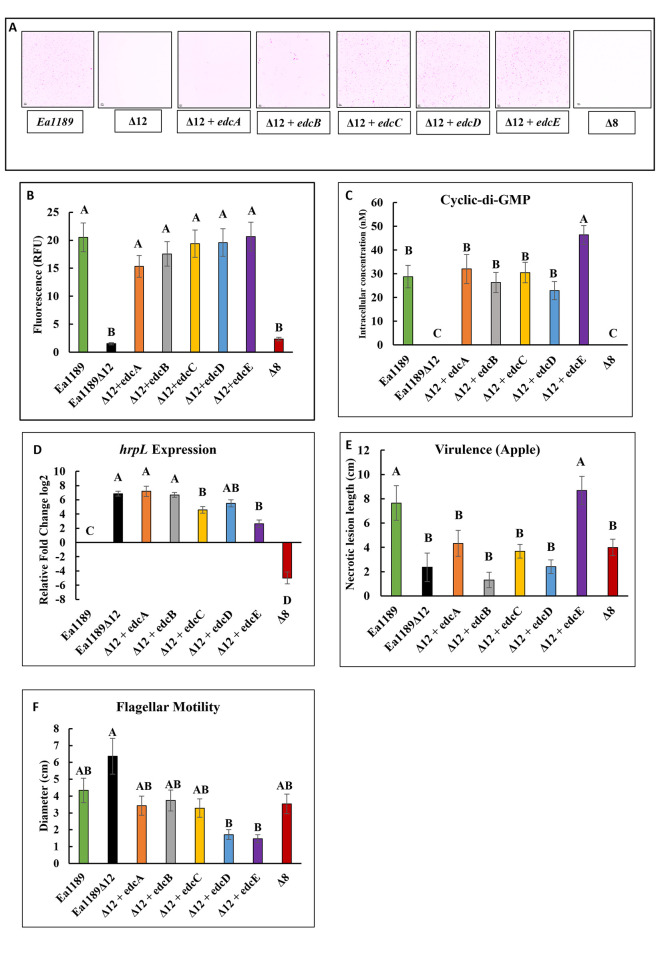
Fig 2. Edcs differentially regulate biofilm formation and virulence.
A) Confocal images (color inverted) and B) relative GFP intensity of flow cells inoculated with GFP labelled WT Ea1189, Ea1189Δ8 Ea1189Δ12 and Ea1189Δ12 complemented with individual edc genes. Bacterial inoculum was introduced into the flow cells and allowed to incubate for 1 h before being flushed out, followed by incubation under flow for 5 h. The flow cells were then imaged along a z-plane to assess the volume of bacterial adhesion to within the chamber. Ea1189Δ12 and Ea1189Δ8 are impaired in biofilm formation relative to Ea1189. Complementation of Ea1189Δ12 with the individual edc genes restores the biofilm formation to levels similar to Ea1189. C) C-di-GMP formation was attenuated in Ea1189Δ8 and Ea1189Δ12, and the complementation of Ea1189Δ12 with edcA-E was able to individually restore c-di-GMP levels to WT Ea1189 levels with the highest increase recorded in Ea1189Δ12/edcE. D) hrpL transcript levels, relative to WT Ea1189 were significantly increased in Ea1189Δ12, and complementation with edcC and edcE was able to significantly reduce the transcript levels as compared to Ea1189Δ12. Ea1189Δ8 had significantly lower hrpL transcript levels compared to Ea1189 and Ea1189Δ12. E) Virulence in apple shoots was significantly reduced in Ea1189Δ8 and Ea1189Δ12 relative to Ea1189. Only complementation with edcE was able to restore WT levels of shoot blight in Ea1189Δ12. F) Flagellar motility was not significantly affected in Ea1189Δ12/ Ea1189Δ8 compared to WT Ea1189. Complementation of Ea1189Δ12 with edcD and edcE was able to significantly reduce motility as compared to Ea1189Δ12. Error bars represent standard errors of the means. Tukey’s HSD (honestly significant difference) (P < 0.05) test was used to determine statistical significance for all experiments.
Diguanylate cyclases differentially contribute to biofilm formation and virulence in E. amylovora
Through the restoration of individual edc genes (edcA-E) in Ea1189Δ12, cells were able to regain the ability to attach to a surface and form biofilms in vitro (Fig 2A). Previous studies, and the c-di-GMP quantitative data from this study, indicated that there were five enzymatically active diguanylate cyclases (EdcA-E) and three phosphodiesterases (PdeA-C) that could quantitatively impact the intracellular levels of c-di-GMP in E. amylovora [3,4]. Further, since proteins with degenerate EAL motifs have been associated with c-di-GMP binding and some downstream regulation, we decided to retain the four other genes in our study (CsrD, EAM_3378, EAM_2449 and EAM_1579) so as to not disrupt any such potential signaling activity [17,18]. Thus, we eliminated the eight genes encoding for these enzymes (edcA-E and pdeA-C), and generated Ea1189Δ8 which was also severely reduced in biofilm formation as quantified within flow cells (Fig 2A and 2B). All five Edcs contributed to attachment, and the restoration of even a single edc gene could restore WT levels of overall biofilm formation in a flow-based system (Fig 2A and 2B). Ea1189Δ12 complemented with edcA-D also generated WT Ea1189 levels of c-di-GMP in vitro, with Ea1189Δ12/edcE generating significantly higher intracellular c-di-GMP levels, relative to Ea1189 (Fig 2C). No c-di-GMP was detected in Ea1189Δ8 (Fig 2C).
hrpL encodes an alternate sigma factor that regulates the transcription of T3SS related genes in E. amylovora [19]. hrpL transcript levels in vitro were significantly elevated in Ea1189Δ12 relative to Ea1189, whereas the transcript levels were significantly reduced in Ea1189Δ8 relative to Ea1189 (Fig 2D). Ea1189Δ12 complemented with edcC or edcE exhibited significantly-reduced hrpL transcript levels relative to the other complemented strains, however all complemented strains exhibited hrpL transcript levels greater that Ea1189 (Fig 2D). Virulence in apple shoots was significantly reduced in Ea1189Δ12 and Ea1189Δ8 relative to Ea1189, and complementation of Ea1189Δ12 with edcE was able to elevate virulence and restore WT levels of shoot blight (Fig 2E). Flagellar motility was not significantly different in both Ea1189Δ12 and Ea1189Δ8 relative to Ea1189 (Fig 2F). The complementation of Ea1189Δ12 with edcD and edcE resulted in significantly reduce levels of motility in the complemented strains as compared to Ea1189Δ12 (Fig 2F).
The type IV pilus in conjunction with the flagellar filament mediates surface attachment in a c-di-GMP dependent manner in E. amylovora
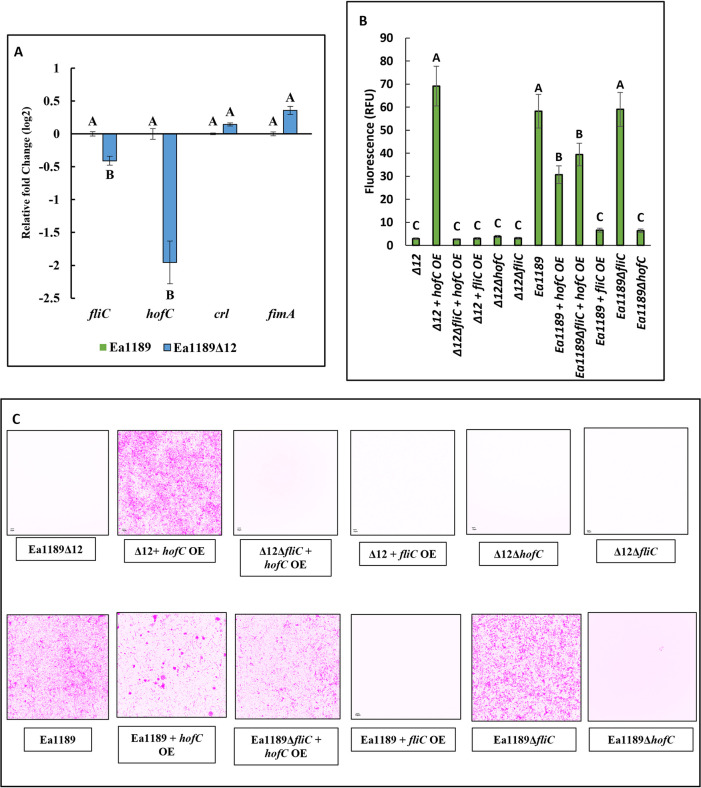
In order to investigate if the systematic deletion of c-di-GMP affected any particular extracellular appendages that could contribute to the lack of surface attachment, we measured the relative transcript abundance of four genes representative of different appendages, including fliC (flagellar filament), hofC (type IV pilus assembly platform protein), crl (curli fimbriae activator) and fimA (fimbrial subunit) [20–24]. Surface-exposed Ea1189Δ12 cells showed a significant decline in the transcript abundance of fliC and hofC, whereas levels of fimA were increased and crl unchanged relative to WT Ea1189 (Fig 3A). Induced overexpression of fliC in Ea1189Δ12 did not result in any visible changes in the level of attachment in flow cells (Fig 3B and 3C). However, the overexpression of hofC significantly elevated attachment in Ea1189Δ12, and restored attachment to the level of the WT Ea1189. Indicative of a co-dependence of the type IV pilus on the flagellum, when hofC was overexpressed in Ea1189Δ12ΔfliC, the level of surface attachment did not increase (Fig 3B and 3C). Ea1189Δ12ΔfliC and Ea1189Δ12ΔhofC also showed no detectable signs of attachment within flow cells (Fig 3B and 3C). In WT Ea1189, relative to Ea1189Δ12, the level of cellular attachment within flow cells was significantly higher. The deletion of fliC in Ea1189, and the overexpression of hofC in both Ea1189 and in Ea1189ΔfliC allowed for the retention of cellular attachment to the flow cell surface, despite a quantitative decline in terms of RFU detection relative to Ea1189 when hofC was overexpressed (Fig 3B and 3C). Attachment to the flow chamber was significantly reduced in Ea1189ΔhofC and when fliC was overexpressed in Ea1189 (Fig 3B and 3C).
Fig 3. Type IV pilus and the flagellum mediate surface attachment.
A) Transcript levels of fliC (flagellar filament) and hofC (type IV pilus assembly platform protein), were significantly reduced in Ea1189Δ12 relative to WT Ea1189. crl (curli fimbriae activator) and fimA (fimbrial subunit) transcript levels were not significantly different among the two strains. B) Relative bacterial adhesion GFP intensity representing the level and C) Confocal z-stacked images (color inverted) of attachment within flow cells 1hr after incubation with Ea1189 and Ea1189Δ12 lacking or overexpressing fliC and/or hofC. The overexpression of hofC could restore attachment in Ea1189Δ12 to WT Ea1189 levels, however, this impact was lost if the overexpression occurred in the absence of fliC. WT Ea1189 showed considerable levels of cellular surface attachment, which diminished upon the overexpression of fliC and the deletion of hofC. The deletion of fliC and/or the overexpression of hofC did alter but did not abolish attachment in Ea1189. Error bars represent standard errors of the means. Tukey’s HSD (honestly significant.
C-di-GMP regulates the transcription of several critical targets during biofilm initiation
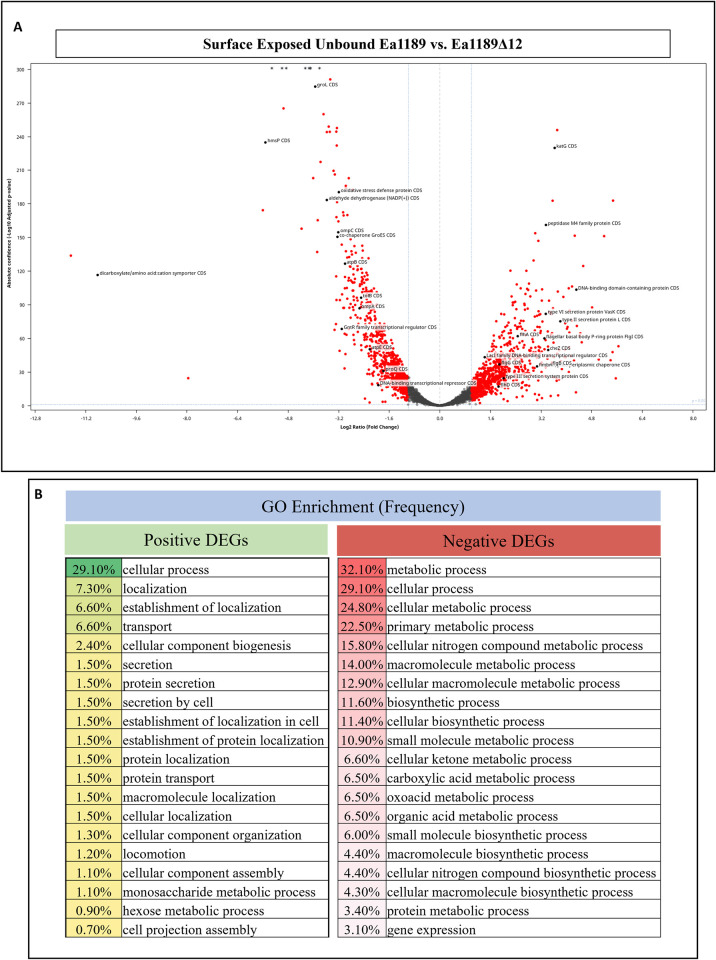
To evaluate the global transcriptional impact of the presence or absence of c-di-GMP during biofilm initiation, we compared the transcriptome of WT Ea1189 and Ea1189Δ12 through an RNAseq assessment of cells harvested from flow chambers after 1 hour of exposure. Overall, we detected a total of 320 positively-affected and 235 negatively-affected differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in Ea1189Δ12 relative to WT Ea1189, based on a DESeq2 FDR cutoff of 0.05 and a fold change of two (log2) (Fig 4A). Gene ontology (GO) enrichment analysis for over-representation in biological function categories indicated that the top 20 categories among the positive DEGs comprised heavily of protein transport, localization and secretion along with cellular movement, whereas the negative DEGs mainly comprised of metabolic and biosynthetic genes (Fig 4B). A complete list of DEGs is provided in supplemental datasheet A. Among the top negatively regulated genes were multiple protease activity related targets including EAM_RS16610 (insulinase encoding gene), htpX, yccA and hslU. Several metabolic genes including rbsD, acs, pckA, gapA, ribB and EAM_RS12095 (NADP encoding gene) were also in the negatively expressed category. The other major categories of negatively expressed genes were those of protein folding/transport and regulatory genes including groL, mglB, pspB, hmsP and EAM_RS05285 (encodes for a leucine-rich repeat domain containing protein). The top 25 negative DEGs and their relevant characteristics including statistical data are listed in Table 1. Among the positively expressed genes were several appendage/transport/secretion system related genes including fimA, sctD, tssJ, sctV, yeeU, tssL and cbtA. Metabolic genes including glgB, glgX, galB, glgC were also among the positive DEGs. The top 25 positive DEGs and their relevant characteristics including statistical data are listed in Table 2. q-RT-PCR was used to validate gene expression data from the RNAseq experiment using a subset of genes (S1A Fig).
Fig 4. Global c-di-GMP dependent regulation during biofilm initiation.
A) A volcano plot highlighting critical differentially expressed genes (DEGs) within surface exposed WT Ea1189 vs. Ea1189Δ12 cells analyzed via RNA-seq analysis. A DESeq2 FDR cutoff p-value of 0.05 was used and all DEGs highlighted in red have a two fold change (log2) in expression. The comparison revealed a total of 320 positively and 235 negatively expressed DEGs with functions including metabolism, extracellular appendage regulation and overall transcriptional/post-transcriptional regulators. B) GO enrichment analysis showing the top 20 overrepresented categories for the positive and negative DEGs, along with the overall frequency of gene/target occurrence within the DEG list.
Table 1. A list of the 25 most negatively regulated genes in Ea1189Δ12 relative to WT Ea1189.
| Locus Tag | Gene ID | Product | Differential Expression Log2 Ratio | Differential Expression p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EAM_RS16610 | insulinase family protein CDS | insulinase family protein | -11.66137022 | 1.9342E-136 |
| EAM_RS16615 | dicarboxylate/amino acid:cation symporter CDS | dicarboxylate/amino acid:cation symporter | -10.81381354 | 5.2721E-119 |
| EAM_RS19445 | hypothetical protein CDS | hypothetical protein | -7.950021219 | 9.05238E-26 |
| EAM_RS11745 | DUF1471 domain-containing protein CDS | DUF1471 domain-containing protein | -5.590416774 | 3.0468E-177 |
| EAM_RS16620 | hmsP CDS | biofilm formation regulator HmsP | -5.50909201 | 4.6447E-238 |
| EAM_RS05505 | amino acid ABC transporter substrate-binding protein CDS | amino acid ABC transporter substrate-binding protein | -5.30482975 | 0 |
| EAM_RS05285 | leucine-rich repeat domain-containing protein CDS | leucine-rich repeat domain-containing protein | -4.983851837 | 0 |
| EAM_RS12130 | APC family permease CDS | APC family permease | -4.936317974 | 1.0207E-268 |
| EAM_RS00070 | rbsD CDS | D-ribose pyranase | -4.850327937 | 0 |
| EAM_RS09500 | htpX CDS | protease HtpX | -4.366262025 | 1.1091E-160 |
| EAM_RS10695 | mglB CDS | galactose/glucose ABC transporter substrate-binding protein MglB | -4.247135295 | 0 |
| EAM_RS09990 | hypothetical protein CDS | hypothetical protein | -4.127207088 | 0 |
| EAM_RS06765 | yccA CDS | FtsH protease modulator YccA | -4.094370008 | 0 |
| EAM_RS02625 | glucitol/sorbitol permease IIC component CDS | glucitol/sorbitol permease IIC component | -4.082619297 | 0 |
| EAM_RS01695 | acs CDS | acetate—CoA ligase | -3.99767443 | 4.442E-206 |
| EAM_RS02150 | groL CDS | chaperonin GroEL | -3.934347101 | 3.1088E-288 |
| EAM_RS12125 | dihydrodipicolinate synthase family protein CDS | dihydrodipicolinate synthase family protein | -3.872046115 | 9.868E-140 |
| EAM_RS07820 | spy CDS | ATP-independent periplasmic protein-refolding chaperone Spy | -3.854421997 | 2.9565E-168 |
| EAM_RS15970 | pckA CDS | phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (ATP) | -3.798261114 | 0 |
| EAM_RS09315 | gapA CDS | glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | -3.766942859 | 1.4129E-220 |
| EAM_RS12115 | 4-hydroxyproline epimerase CDS | 4-hydroxyproline epimerase | -3.671073648 | 1.6735E-263 |
| EAM_RS12095 | aldehyde dehydrogenase (NADP(+)) CDS | aldehyde dehydrogenase (NADP(+)) | -3.568133834 | 2.0155E-186 |
| EAM_RS08865 | pspB CDS | envelope stress response membrane protein PspB | -3.567808565 | 2.2995E-247 |
| EAM_RS14660 | ribB CDS | 3,4-dihydroxy-2-butanone-4-phosphate synthase | -3.507981226 | 2.2124E-252 |
| EAM_RS00630 | hslU CDS | HslU—HslV peptidase ATPase subunit | -3.473822217 | 1.301E-247 |
Table 2. A list of the 25 most positively regulated genes in Ea1189Δ12 relative to WT Ea1189.
| Locus Tag | Gene ID | Product | Differential Expression Log2 Ratio | Differential Expression p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EAM_RS14005 | TIGR03756 family integrating conjugative elementprotein CDS | TIGR03756 family integrating conjugative elementprotein | 5.653778414 | 1.02E-54 |
| EAM_RS14820 | AlpA family phage regulatory protein CDS | AlpA family phage regulatory protein | 5.570644235 | 1.36E-25 |
| EAM_RS16075 | glgB CDS | 1,4-alpha-glucan branching enzyme | 5.483356916 | 7.21E-186 |
| EAM_RS01250 | fimbrial protein A precursor CDS | fimbrial protein A precursor | 5.467190074 | 2.17E-49 |
| EAM_RS16430 | hypothetical protein CDS | hypothetical protein | 5.404620393 | 5.29E-42 |
| EAM_RS19320 | glgX CDS | glycogen debranching protein GlgX | 5.201160707 | 5.60E-154 |
| EAM_RS03470 | hypothetical protein CDS | hypothetical protein | 5.029951978 | 1.09E-42 |
| EAM_RS14000 | integrating conjugative element protein CDS | integrating conjugative element protein | 4.820222392 | 1.09E-89 |
| EAM_RS06020 | YIP1 family protein CDS | YIP1 family protein | 4.539960781 | 4.03E-127 |
| EAM_RS09185 | galB CDS | 4-oxalmesaconate hydratase | 4.49334628 | 2.78E-58 |
| EAM_RS04295 | amino acid ABC transporter permease CDS | amino acid ABC transporter permease | 4.448825708 | 2.15E-66 |
| EAM_RS14195 | sctD CDS | type III secretion system inner membrane ring subunit SctD | 4.42440179 | 4.41E-64 |
| EAM_RS04290 | transporter substrate-binding domain-containing protein CDS | transporter substrate-binding domain-containing protein | 4.339006646 | 5.35E-73 |
| EAM_RS13995 | DNA-binding domain-containing protein CDS | DNA-binding domain-containing protein | 4.322676558 | 9.56E-106 |
| EAM_RS02010 | tssJ CDS | type VI secretion system lipoprotein TssJ | 4.310343973 | 6.61E-13 |
| EAM_RS19315 | glgC CDS | glucose-1-phosphate adenylyltransferase | 4.272326359 | 2.41E-154 |
| EAM_RS03515 | prepilin-type N-terminal cleavage/methylation domain-containing protein CDS | prepilin-type N-terminal cleavage/methylation domain-containing protein | 4.248823084 | 1.03E-41 |
| EAM_RS12610 | chemotaxis response regulator protein-glutamate methylesterase CDS | chemotaxis response regulator protein-glutamate methylesterase | 4.187095164 | 9.64E-78 |
| EAM_RS14190 | sctV CDS | type III secretion system export apparatus subunit SctV | 4.186154654 | 1.22E-108 |
| EAM_RS14010 | TIGR03757 family integrating conjugative elementprotein CDS | TIGR03757 family integrating conjugative elementprotein | 4.13782143 | 7.78E-46 |
| EAM_RS01905 | tssK CDS | type VI secretion system baseplate subunit TssK | 4.109363563 | 6.27E-87 |
| EAM_RS09200 | NAD(P)-dependent oxidoreductase CDS | NAD(P)-dependent oxidoreductase | 4.102789474 | 4.89E-67 |
| EAM_RS14800 | type IV toxin-antitoxin system YeeU family antitoxin CDS | type IV toxin-antitoxin system YeeU family antitoxin | 4.10085975 | 2.44E-37 |
| EAM_RS01910 | type VI secretion system protein TssL, short form CDS | type VI secretion system protein TssL, short form | 4.092459487 | 1.93E-53 |
| EAM_RS14795 | TA system toxin CbtA family protein CDS | TA system toxin CbtA family protein | 4.085573729 | 2.78E-31 |
Regulatory divergence among the diguanylate cyclases of E. amylovora
Some studies have presented evidence of c-di-GMP/ downstream signaling localization in specific regions of the cell during different stages of the cell cycle [25–28]. Thus, we wanted to determine, through a transcriptomic approach, if the overarching pattern of regulatory targets affected by the c-di-GMP generated by each individual Edc enzyme was that of overlap or of divergence. A phylogenetic analysis using a compilation of the top 500 pblast search results (p-value cutoff of 0.05 using a BLOSUM62 matrix with conditional compositional score adjustment) for of all 5 Edcs indicated no evidence of relatively recent acquisition from non-Erwiniaceae species (Sup. datasheet B). This suggested the possibility of functional divergence occurring due to prolonged recurring evolutionary pressure imposed on the genes [29–31].
Initial phenotypic assessments conducted on Ea1189Δ8 indicated that in terms of c-di-GMP production, shoot blight and flagellar motility, Ea1189Δ8 was not significantly different from Ea1189Δ12 (Fig 2A, 2B, 2C, 2E and 2F). However, in terms of hrpL transcription, Ea1189Δ8 showed contrasting trends relative to Ea1189Δ12 with a significant reduction in hrpL transcription relative to WT Ea1189 (Fig 2D). Since any manner of exogenously generated c-di-GMP in Ea1189Δ8 would likely not be hydrolyzed within the cell, we sought to further enrich for this regulatory impact by the induced overexpression of each of the five edc genes in Ea1189Δ8 and then study the DEG patterns through RNAseq.
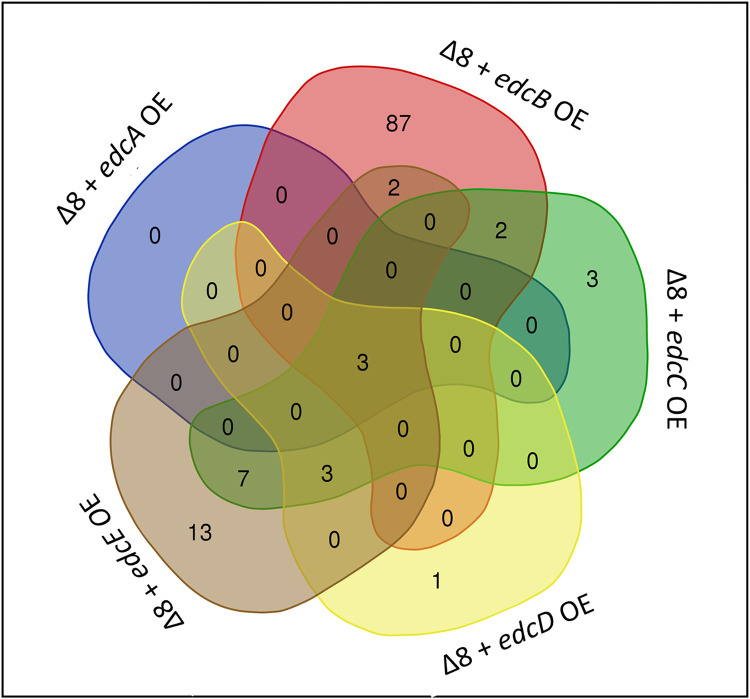
A collective analysis of the transcriptomic patterns for Ea1189Δ8 vs. Ea1189Δ8 overexpressing each of the five edc genes indicated that a total of 121 DEGs (DESeq2 FDR cutoff 0.05 and a fold change of two (log2)) were present collectively among the five datasets (Fig 5A, Sup. Datasheet A). Plotting the data to check for any overlap of genes for the five comparisons showed that a majority of the genes among the overall DEGs were primarily regulated by one of the edc genes. An exception to this was Ea1189Δ8/edcA OE wherein the three (negatively regulated) genes that were filtered through the statistical analysis were the three common DEGs across all five datasets. These genes included EAM_1085 (encodes for a leucine rich repeat domain containing protein), EAM_3468 (encodes for a glycoside hydrolase family protein) and EAM_2517 (unknown product) (Table 3). Relative to Ea1189Δ8, Ea1189Δ8/edcB OE had several metabolic and regulatory genes among the positive and negative DEGs including yqaB, hrpA, hchA, phoH, hutG and rmf (Table 4). Ea1189Δ8/edcB OE had the highest number of DEGs of all included comparisons with the other edcs in this study. Ea1189Δ8/edcC OE uniquely had hslU, hslV and EAM_RS16210 (encodes a zinc/ cadmium/ mercury/ lead-transporting ATPase), three ATPase related genes among the positive DEGs. Also, dnaK, ibpA, casB and cas7e were some regulatory targets related to housekeeping or type I CRISPR system (Table 5). Ea1189Δ8/edcD OE compared to Ea1189Δ8 only had significantly negative DEGs (barring the overexpression of edcD itself) including casB, EAM_RS14585 (encodes a aminotransferase phosphate dependent enzyme) and EAM_RS14565 (encodes a type I polyketide synthase) (Table 6). Ea1189Δ8/edcE OE relative to Ea1189Δ8 in addition to metabolic and regulatory targets had several genes related to the type I CRISPR system among the negative DEGs including casB, cas7e, cas1e, cas5e, cas6e and casA (Table 7). A complete list of all DEGs is provided in supplemental datasheet 1 and heighted DEGs for each individual comparative analysis is provide in Tables 3–7 The RNAseq study was validated through q-RT-PCR for a subset of genes (S1B Fig).
Fig 5. Regulatory divergence among the Edcs.
A) A venn diagram representing the distribution of the DEGs in Ea1189Δ8 strain overexpressing individual edc genes measured via RNAseq. A total of 121 DEGs both positively and negatively affected in expression were found after being filtered through a DESeq2 FDR cutoff of 0.05 with at least a two fold change (log2) individually for each comparative condition of Ea1189Δ8 vs Ea1189Δ8 overexpressing an individual edc gene. Ea1189Δ8 overexpressing edcB had the highest number of uniquely regulated DEGs. There were three DEGs that were downregulated upon the overexpression of every edc gene in Ea1189Δ8. Note that these results also include each of the edc genes themselves in each comparison if filtered through the statistical cutoff requirement. The venn diagram tool software (accessible at bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/Venn/) was used to generate the venn diagram using RNAseq data.
Table 3. A list of the statistically significant differentially regulated genes (Log2 fold change of two) in Ea1189Δ8+edcA OE relative to Ea1189Δ8.
| Locus Tag | Gene ID | Product | Differential Expression Log2 Ratio | Differential Expression p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EAM_RS12275 | hypothetical protein CDS | hypothetical protein | -2.046415814 | 2.69E-08 |
| EAM_RS05285 | leucine-rich repeat domain-containing protein CDS | leucine-rich repeat domain-containing protein | -2.22388315 | 1.14E-05 |
| EAM_RS17045 | glycoside hydrolase family 68 protein CDS | glycoside hydrolase family 68 protein | -2.76359249 | 7.20E-14 |
Table 4. A list of the 15 most positively and negatively regulated genes in Ea1189Δ8+edcB OE relative to Ea1189Δ8.
| Locus Tag | Gene ID | Product | Differential Expression Log2 Ratio | Differential Expression p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EAM_RS02755 | GGDEF domain-containing protein CDS | GGDEF domain-containing protein | 10.52231065 | 6.1851E-189 |
| EAM_RS15020 | DEAD/DEAH family ATP-dependent RNA helicase CDS | DEAD/DEAH family ATP-dependent RNA helicase | 3.837091548 | 1.16277E-13 |
| EAM_RS16040 | glpD CDS | glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | 3.769007801 | 2.3349E-166 |
| EAM_RS19305 | yrbN CDS | protein YrbN | 3.647272094 | 5.19945E-39 |
| EAM_RS12870 | HlyC/CorC family transporter CDS | HlyC/CorC family transporter | 3.200198525 | 5.21317E-57 |
| EAM_RS02090 | pantoate—beta-alanine ligase CDS | pantoate—beta-alanine ligase | 3.161465532 | 2.6906E-14 |
| EAM_RS12890 | yqaB CDS | fructose-1-phosphate/6-phosphogluconate phosphatase | 2.939408173 | 6.28088E-17 |
| EAM_RS19660 | hypothetical protein CDS | hypothetical protein | 2.875871177 | 2.25958E-29 |
| EAM_RS15625 | rplF CDS | 50S ribosomal protein L6 | 2.766997946 | 2.05003E-08 |
| EAM_RS12865 | inner membrane protein YpjD CDS | inner membrane protein YpjD | 2.740181732 | 1.89396E-14 |
| EAM_RS18730 | yidD CDS | membrane protein insertion efficiency factor YidD | 2.706686489 | 2.12804E-30 |
| EAM_RS19655 | hypothetical protein CDS | hypothetical protein | 2.678070834 | 1.05966E-15 |
| EAM_RS15575 | rplQ CDS | 50S ribosomal protein L17 | 2.663892023 | 7.43101E-06 |
| EAM_RS19535 | hypothetical protein CDS | hypothetical protein | 2.648755631 | 9.56953E-08 |
| EAM_RS12880 | glutamate—cysteine ligase CDS | glutamate—cysteine ligase | 2.61623674 | 9.55405E-11 |
| EAM_RS10630 | hypothetical protein CDS | hypothetical protein | -3.779142872 | 8.15852E-22 |
| EAM_RS14150 | Hrp pili protein HrpA CDS | Hrp pili protein HrpA | -3.465753769 | 1.42198E-09 |
| EAM_RS09925 | phoH CDS | phosphate starvation-inducible protein PhoH | -3.304435872 | 3.67098E-10 |
| EAM_RS04570 | hypothetical protein CDS | hypothetical protein | -3.22780552 | 9.51376E-11 |
| EAM_RS01050 | dienelactone hydrolase family protein CDS | dienelactone hydrolase family protein | -3.105210459 | 3.22279E-25 |
| EAM_RS05285 | leucine-rich repeat domain-containing protein CDS | leucine-rich repeat domain-containing protein | -3.014341576 | 2.76182E-19 |
| EAM_RS06155 | hutG CDS | N-formylglutamate deformylase | -3.010799292 | 3.27597E-16 |
| EAM_RS18215 | rmf CDS | ribosome modulation factor | -2.962193193 | 1.30948E-08 |
| EAM_RS18330 | hypothetical protein CDS | hypothetical protein | -2.89078444 | 5.49473E-28 |
| EAM_RS01820 | hchA CDS | protein deglycase HchA | -2.858429374 | 8.44902E-16 |
| EAM_RS02925 | hypothetical protein CDS | hypothetical protein | -2.796397476 | 2.19042E-05 |
| EAM_RS07845 | hypothetical protein CDS | hypothetical protein | -2.788775685 | 2.46288E-13 |
| EAM_RS09335 | yeaG CDS | protein kinase YeaG | -2.784222226 | 6.44011E-12 |
| EAM_RS17045 | glycoside hydrolase family 68 protein CDS | glycoside hydrolase family 68 protein | -2.770732143 | 7.28882E-18 |
| EAM_RS12275 | hypothetical protein CDS | hypothetical protein | -2.729613743 | 1.53082E-27 |
Table 5. A list of the statistically significant differentially regulated genes (Log2 fold change of two) in Ea1189Δ8+edcC OE relative to Ea1189Δ8.
| Locus Tag | Gene ID | Product | Differential Expression Log2 Ratio | Differential Expression p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EAM_RS07310 | sensor domain-containing diguanylate cyclase CDS | sensor domain-containing diguanylate cyclase | 7.11876968 | 1.87E-42 |
| EAM_RS13595 | lysA CDS | diaminopimelate decarboxylase | 3.145640602 | 4.18E-15 |
| EAM_RS16210 | zinc/cadmium/mercury/lead-transporting ATPase CDS | zinc/cadmium/mercury/lead-transporting ATPase | 3.127126824 | 5.96E-31 |
| EAM_RS00635 | hslV CDS | ATP-dependent protease subunit HslV | 2.863823003 | 4.45E-16 |
| EAM_RS03185 | dnaK CDS | molecular chaperone DnaK | 2.461525153 | 8.11E-10 |
| EAM_RS16940 | ibpA CDS | heat shock chaperone IbpA | 2.403589754 | 8.31E-07 |
| EAM_RS02090 | pantoate—beta-alanine ligase CDS | pantoate—beta-alanine ligase | 2.358062352 | 6.00E-09 |
| EAM_RS15020 | DEAD/DEAH family ATP-dependent RNA helicase CDS | DEAD/DEAH family ATP-dependent RNA helicase | 2.3490175 | 6.18E-07 |
| EAM_RS02145 | co-chaperone GroES CDS | co-chaperone GroES | 2.265795717 | 2.62E-09 |
| EAM_RS00630 | hslU CDS | HslU—HslV peptidase ATPase subunit | 2.198704024 | 4.16E-31 |
| EAM_RS15625 | rplF CDS | 50S ribosomal protein L6 | 2.162131775 | 2.28E-06 |
| EAM_RS02100 | cupin domain-containing protein CDS | cupin domain-containing protein | 2.112275705 | 4.16E-16 |
| EAM_RS05285 | leucine-rich repeat domain-containing protein CDS | leucine-rich repeat domain-containing protein | -3.887406921 | 1.50E-37 |
| EAM_RS14565 | type I polyketide synthase CDS | type I polyketide synthase | -2.594131364 | 4.41E-13 |
| EAM_RS17045 | glycoside hydrolase family 68 protein CDS | glycoside hydrolase family 68 protein | -2.5793142 | 1.54E-16 |
| EAM_RS12275 | hypothetical protein CDS | hypothetical protein | -2.400248876 | 2.95E-17 |
| EAM_RS03730 | casB CDS | type I-E CRISPR-associated protein Cse2/CasB | -2.271501335 | 2.32E-29 |
| EAM_RS14585 | aminotransferase class III-fold pyridoxal phosphate-dependent enzyme CDS | aminotransferase class III-fold pyridoxal phosphate-dependent enzyme | -2.200310517 | 4.17E-09 |
| EAM_RS14570 | non-ribosomal peptide synthetase CDS | non-ribosomal peptide synthetase | -2.121916042 | 2.18E-07 |
| EAM_RS18215 | rmf CDS | ribosome modulation factor | -2.054007376 | 2.53E-05 |
| EAM_RS03735 | cas7e CDS | type I-E CRISPR-associated protein Cas7/Cse4/CasC | -2.035412707 | 1.38E-12 |
Table 6. A list of the statistically significant differentially regulated genes (Log2 fold change of two) in Ea1189Δ8+edcD OE relative to Ea1189Δ8.
| Locus Tag | Gene ID | Product | Differential Expression Log2 Ratio | Differential Expression p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EAM_RS10555 | diguanylate cyclase CDS | diguanylate cyclase | 5.778041665 | 2.25E-35 |
| EAM_RS05285 | leucine-rich repeat domain-containing protein CDS | leucine-rich repeat domain-containing protein | -3.266334894 | 4.90259E-27 |
| EAM_RS17045 | glycoside hydrolase family 68 protein CDS | glycoside hydrolase family 68 protein | -2.653853287 | 4.8117E-14 |
| EAM_RS14565 | type I polyketide synthase CDS | type I polyketide synthase | -2.363717088 | 4.30385E-10 |
| EAM_RS03730 | casB CDS | type I-E CRISPR-associated protein Cse2/CasB | -2.222582243 | 3.32759E-14 |
| EAM_RS14585 | aminotransferase class III-fold pyridoxal phosphate-dependent enzyme CDS | aminotransferase class III-fold pyridoxal phosphate-dependent enzyme | -2.146738285 | 1.27856E-09 |
| EAM_RS12275 | hypothetical protein CDS | hypothetical protein | -2.093779402 | 1.12176E-10 |
| EAM_RS14570 | non-ribosomal peptide synthetase CDS | non-ribosomal peptide synthetase | -2.037259516 | 1.01262E-07 |
Table 7. A list of the statistically significant differentially regulated genes (Log2 fold change of two) in Ea1189Δ8+edcE OE relative to Ea1189Δ8.
| Locus Tag | Gene ID | Product | Differential Expression Log2 Ratio | Differential Expression p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EAM_RS11860 | sensor domain-containing diguanylate cyclase CDS | sensor domain-containing diguanylate cyclase | 12.50422101 | 0 |
| EAM_RS00635 | hslV CDS | ATP-dependent protease subunit HslV | 2.83447676 | 4.41E-10 |
| EAM_RS02145 | co-chaperone GroES CDS | co-chaperone GroES | 2.689831641 | 1.23E-11 |
| EAM_RS16940 | ibpA CDS | heat shock chaperone IbpA | 2.640983916 | 3.20E-07 |
| EAM_RS03185 | dnaK CDS | molecular chaperone DnaK | 2.514067921 | 1.52E-09 |
| EAM_RS06745 | hspQ CDS | heat shock protein HspQ | 2.376852632 | 3.70E-07 |
| EAM_RS12775 | clpB CDS | ATP-dependent chaperone ClpB | 2.303745988 | 3.52E-07 |
| EAM_RS14360 | PTS sugar transporter subunit IIB CDS | PTS sugar transporter subunit IIB | 2.254006979 | 5.91E-14 |
| EAM_RS00630 | hslU CDS | HslU—HslV peptidase ATPase subunit | 2.186164935 | 1.37E-27 |
| EAM_RS16210 | zinc/cadmium/mercury/lead-transporting ATPase CDS | zinc/cadmium/mercury/lead-transporting ATPase | 2.142197384 | 6.38E-17 |
| EAM_RS03205 | rpsT CDS | 30S ribosomal protein S20 | 2.067365283 | 6.13E-05 |
| EAM_RS15625 | rplF CDS | 50S ribosomal protein L6 | 2.009381497 | 3.20E-05 |
| EAM_RS05285 | leucine-rich repeat domain-containing protein CDS | leucine-rich repeat domain-containing protein | -4.528529394 | 1.91193E-44 |
| EAM_RS17045 | glycoside hydrolase family 68 protein CDS | glycoside hydrolase family 68 protein | -3.584785314 | 3.81385E-22 |
| EAM_RS14565 | type I polyketide synthase CDS | type I polyketide synthase | -3.20797224 | 8.07891E-25 |
| EAM_RS14570 | non-ribosomal peptide synthetase CDS | non-ribosomal peptide synthetase | -2.836841807 | 4.9235E-17 |
| EAM_RS14585 | aminotransferase class III-fold pyridoxal phosphate-dependent enzyme CDS | aminotransferase class III-fold pyridoxal phosphate-dependent enzyme | -2.62716761 | 6.16167E-19 |
| EAM_RS14575 | KR domain-containing protein CDS | KR domain-containing protein | -2.591188195 | 1.74194E-11 |
| EAM_RS03730 | casB CDS | type I-E CRISPR-associated protein Cse2/CasB | -2.403157946 | 1.80146E-22 |
| EAM_RS12275 | hypothetical protein CDS | hypothetical protein | -2.300109076 | 2.83284E-13 |
| EAM_RS08495 | isocyanide synthase family protein CDS | isocyanide synthase family protein | -2.273812019 | 1.45024E-12 |
| EAM_RS03735 | cas7e CDS | type I-E CRISPR-associated protein Cas7/Cse4/CasC | -2.173201222 | 2.00038E-13 |
| EAM_RS06125 | urocanate hydratase CDS | urocanate hydratase | -2.16671334 | 1.3265E-10 |
| EAM_RS14590 | hypothetical protein CDS | hypothetical protein | -2.155367805 | 8.86444E-05 |
| EAM_RS14580 | polyketide synthase CDS | polyketide synthase | -2.142735466 | 1.48983E-11 |
| EAM_RS03750 | cas1e CDS | type I-E CRISPR-associated endonuclease Cas1e | -2.077795929 | 8.24188E-11 |
| EAM_RS03740 | cas5e CDS | type I-E CRISPR-associated protein Cas5/CasD | -2.058059128 | 2.1109E-11 |
| EAM_RS03745 | cas6e CDS | type I-E CRISPR-associated protein Cas6/Cse3/CasE | -2.054121085 | 5.56701E-13 |
| EAM_RS03725 | casA CDS | type I-E CRISPR-associated protein Cse1/CasA | -2.049727209 | 7.12272E-20 |
| EAM_RS06130 | hutH CDS | histidine ammonia-lyase | -2.035079931 | 6.4966E-08 |
| EAM_RS14560 | type I polyketide synthase CDS | type I polyketide synthase | -2.033125808 | 2.43973E-13 |
Discussion
Cyclic-di-GMP dependent regulation has been studied in many bacterial systems, and the results have highlighted various signaling roles for the second messenger ranging from phase transition to bacteriophage interactions [1,2,26]. A common impediment for studying the systematic impact of the genetic components of c-di-GMP metabolism has been the sheer multiplicity of the included elements [1,32,33]. In this regard, E. amylovora serves as a particularly useful pathogenic model because this organism encodes a fairly condensed set of Dgc and Pde enzymes in its c-di-GMP repertoire, and c-di-GMP regulates all of the most critical virulence factors that facilitate systemic movement through the host and disease progression [3,4].
Attachment and host xylem colonization are entirely dependent on c-di-GMP in E. amylovora. The recovery in surface attachment upon the restoration of any of the edc genes in Ea1189Δ12 signified that the surface interaction was c-di-GMP dependent in a quantitative sense. Further, the type IV pilus was an important determinant of surface attachment and required the flagellar filament as a mediator. Independent of c-di-GMP presence, hofC function was a limiting factor in terms of the ability of cells to attach to surface. However, the dependence on surface sensing through the flagellar filament was more prominent under lower intracellular levels of c-di-GMP. A similar co-dependence on both the flagellum and the pilus for surface attachment has been demonstrated in P. aeruginosa, wherein, upon first surface contact by the flagellar filament, the rotational changes sensed by the motor proteins MotAB result in a rapid increase in c-di-GMP levels which can bind to the effector FimW and regulate type IV pilus-based surface interaction [34]. We highlight that the regulation of attachment can occur through c-di-GMP generated by any of the five Edc sources, making this factor a global target of c-di-GMP generated within E. amylovora cells. Interestingly however, flagellar motility in vitro was not significantly altered in Ea1189Δ12 relative to Ea1189. In similar genetic reductionist studies aimed at understanding the impact of c-di-GMP on multiple phenotypes conducted in Salmonella and Caulobacter crescentus, a c-di-GMP null condition has been associated with altered motility in vitro [5,10]. Since flagellar motility is not a limiting factor in the shoot blight infection model [35], further studies will be necessary to link the impact of c-di-GMP on motility during other stages in the disease cycle.
Contact with a surface during biofilm initiation and the underlying c-di-GMP based regulation had global transcriptomic implications in E. amylovora with over 500 DEGs between surface exposed Ea1189 and Ea1189Δ12. A limitation of this study is the exclusive use of in vitro surface exposure treatments as opposed to studying the interactive dynamics of the pathogen with the host in planta. Transcriptomic studies conducted in P. syringae and Ralstonia solanacearum have revealed the complexity of the host dependent response occurring in bacterial phytopathogens [36,37]. A major physical limitation in our study was the inability of Ea1189Δ12 to colonize the xylem vessels which resulted in us having to rely on in vitro surface exposure using flow cells to be able to collect consistent and high quality RNA samples from our strains, not limited by the abundance of bacterial titer in planta. In this transcriptomic study, genes negatively expressed in Ea1189Δ12 vs. Ea1189 are indicative of targets that are positively regulated by c-di-GMP. Some of the critical regulatory genes in this category were hmsP (biofilm formation regulator) and EAM_RS05285 (leucine rich repeat (LRR) protein encoding gene). HmsP has been reported to be a negative regulator of biofilm formation in Yersinia pestis [38]. While LRR- family proteins are heavily involved in regulating plant bacterial resistance interactions, their link with c-di-GMP has been documented in animal immunogenic interactions involving the STING pathway, specifically by NLRC3 which can get activated by c-di-GMP and feed into the STING trafficking [39,40]. Conversely, genes negatively regulated by c-di-GMP during surface interactions included several type III (T3SS) and type VI secretion system (T6SS) related genes. Our previous work in E. amylovora has indicated that elevated intracellular levels of c-di-GMP can negatively regulate the T3SS transcriptionally [4]. While the impact of the T6SS linked to c-di-GMP has not been explored in E. amylovora, in P. aeruginosa the T6SS protein TfoY can be partially triggered by reduced intracellular levels of c-di-GMP and can lead to altered levels of bacterial killing mediated by the T6SS [41]. Also in P. aeruginosa, the RetS/GacA sensor protein can respond to changing c-di-GMP levels and mediate the switching between the T3SS and T6SS [42]. Overall, these collective targets are indicative of an evolutionary bottleneck making c-di-GMP a limiting factor for host colonization. A similar transcriptomic study in Pseudomonas syringae heterologously overexpressing a Dgc or a Pde revealed that the altered levels of c-di-GMP can impact several genes related to flagellar structure and function, as well as those involved in chemotaxis, metabolism and two component system transduction [43]. The relatively under-researched aspect of our findings is perhaps the multiple positively and negatively regulated metabolic targets dependent on c-di-GMP. Further studies will be required to document the pathway specific impacts of c-di-GMP during biofilm initiation. Our study highlights that surface sensing and biofilm initiation are heavily dependent on c-di-GMP in E. amylovora and require the successful transcriptional regulation of a large network of genes.
In E. amylovora, biofilm formation was a globally impacted by multi-sourced c-di-GMP. In Salmonella, Solano et al. found that four of the twelve Dgcs were involved in cellulose production, and other aspects related to virulence and biofilm formation [5]. The regulatory model under which multiple Dgcs regulate one phenotype is widely present in other pathosystems including Escherichia coli, P. aeruginosa and V. cholerae [7,9,33,44–47]. T3SS expression, quantified via hrpL transcription, was significantly elevated in Ea1189Δ12, which corroborates the existing model of c-di-GMP driven negative regulation of T3SS in E. amylovora [3,4]. Disease progression in apple shoots is dependent on both the T3SS in the apoplast and biofilm formation in the xylem vessels [11,35]. Thus, despite the high levels of hrpL expression in Ea1189Δ12, this strain was unable to colonize the xylem or cause shoot blight. This also holds true for Ea1189Δ12 complemented with individual edc genes wherein higher than WT levels of hrpL expression were recorded in all five strains but this did not result in significant changes in virulence in planta (barring edcE). While our in vitro biofilm assessment indicated that all Edcs could regulate biofilm formation in flow cells, EdcE was the only diguanylate cyclase that enabled Ea1189Δ12 to regain the ability to colonize the xylem as inferred through the progression of shoot blight for these strains. This indicates that phenotypic switching and attachment within the xylem could have evolved to be mainly dependent on EdcE over the other Edcs in E. amylovora. Contrastingly in Ea1189Δ8, it is unclear if the most significant contributor to the observed reduction in virulence is the reduced hrpL expression, the impairment in surface attachment or both. The observation of differential hrpL expression in Ea1189Δ8 compared to Ea1189Δ12 highlights the potential importance of the four degenerate GGDEF/EAL proteins (EAM_3378, CsrD, EAM_2449, EAM_1579) in regulating the T3SS. Evidence suggests that proteins with degenerate GGDEF/EAL domains can serve as c-di-GMP binding receptors and regulate diverse function [48,49]. In E. amylovora, CsrD can regulate amsG transcription by binding to c-di-GMP and modifying the degradation efficacy of RNase E towards the small RNA CsrB [15]. However, the role of these degenerate GGDEF/EAL domain containing proteins is not fully understood in the context of hrpL transcription. Thus, the use of Ea1189Δ8 provided us the ability to study the impact of c-di-GMP metabolism without the interruption of any signaling activity from other potential c-di-GMP effectors.
In addition to the targeted evaluation of the effects of c-di-GMP on virulence factors, we also took an untargeted approach through RNAseq to understand the global transcriptomic map dependent on each of the Edcs. Most of the DEGs affected by each individual Edc were unique and only a small subset were co-regulated by two or more Edcs. A general mix of metabolic, regulatory and structural genes were among the DEGs. The largest number of DEGs were impacted by EdcB, however further investigation is required to implicate this effect on increased c-di-GMP generation or the presence of multiple c-di-GMP targets channeled through this enzyme. The phylogenies of all the Edcs in E. amylovora don’t show signs of very recent acquisition, which could suggest that the spatial effect of each of the Edcs is due to some level of evolution-driven host adaptation [50,51].
Among all the edc overexpression based transcriptomic datasets, a shared factor was the reduced expression of EAM_RS05285 (encodes for a leucine rich repeat domain containing protein) upon the overexpression of each of the edc genes, implying that this gene is negatively regulated by c-di-GMP. However, in the other transcriptomic experiment involving surface exposed Ea1189 and Ea1189Δ12 cells also included in this study, the same gene was found to be positively regulated by c-di-GMP. From this we are able to infer that the regulation of EAM_RS05285 is dependent on the state of the cell and if the cell contacts a surface and on c-di-GMP production within the cell from any edc source.
Apart from edcA, the overexpression of each of the four edc genes (edcB-E) revealed unique regulatory targets. Interestingly the number of differentially regulated genes and the proportion of positively and negatively regulated genes varied in each case as well. For edcB, edcC and edcD this comprised of regulatory and metabolic genes. With the overexpression of edcE in Ea1189Δ8, several genes involved in the type I CRISPR system were negatively regulated. While casB and cas7e were also differentially regulated when edcC and edcD were overexpressed in the same background, the effect became more pronounced with the overexpression of edcE, which had an impact on six CRISPR related genes. CRISPR elements have been used in genotypically categorizing and tracking pathogenic evolution in E. amylovora [52–54]. The type I CRISPR system in E. amylovora was recently reported to be involved in resistance against invasive plasmids and not necessarily against phages [55]. No link has been identified to c-di-GMP regulation in this regard. In terms of regulatory targets, edcB had mostly metabolic targets represented among the top DEGs. hrpA was also downregulated significantly by the overexpression of edcB. While c-di-GMP is known to reduce T3SS expression in E. amylovora from previous studies [3,4], specificities regarding the generative source of the c-di-GMP have not been identified. Further, our phenotypic data measuring virulence and hrpL expression highlights edcC and edcE as being the significant contributors to T3SS when complemented in Ea1189Δ12. While these two sets of experiments differ based on the overexpression or native promoter driven expression of the edc genes, the overall results highlight that T3SS regulation in E. amylovora is dependent on c-di-GMP on a spatiotemporal basis. The overexpression of edcC and edcE resulted in the increased expression of heat shock related proteins including ibpA, dnaK and hspQ. Lon and CsrA have been linked to heat shock response regulation in E. amylovora and the heat shock response of the pathogen is a target for AvrRpt2 mediated resistance to E. amylovora in apple [56–59]. While the link between heat shock response and c-di-GMP has not been studied in E. amylovora, in V. cholerae, Lon was identified as a c-di-GMP receptor that could regulate the stability of TfoY leading to downstream effects on the heat shock response of the pathogen [60]. Thus, our study highlights the complexity of c-di-GMP signaling and the evolutionary importance of utilizing multiple c-di-GMP generative Dgcs in a given pathogenic system. While the distribution of c-di-GMP can be variable depending on the state of the cell and the location within the cell, as previously documented in Caulobacter crescentus [25], further evidence will be needed to document the temporal origin of c-di-GMP from a specific edc/dgc source and its direct impact on specific genetic targets.
In E. amylovora, we hypothesize that the c-di-GMP generated by each of the Edcs can have both localized effects that are unique to each of the Edcs and also that diffused pool/s of c-di-GMP that can be generated through contributions of multiple or all Edcs. A diffused pool of c-di-GMP could be used to regulate some of the shared factors that are impacted by all the Edcs (Fig 6). While our study has focused on c-di-GMP dependent regulation, we are left with some critical unanswered questions about the degradation of c-di-GMP once it has been generated by an Edc enzyme. All three active Pdes in this system are anchored in the cytoplasmic membrane, which could affect their ability to degrade c-di-GMP from varied Edc sources as well as any diffused intracellular pool of c-di-GMP [26]. Further, this raises a consideration that during heterologous expression of a non-native Dgc, an approach which is often used to alter c-di-GMP levels and check the phenotypic impact, the results could be skewed by the presence/absence of localized effects. For such future investigations, we will be able to use Ea1189Δ12 as an ideal background strain to study the localization and generation/hydrolysis dynamics of c-di-GMP within the cell.
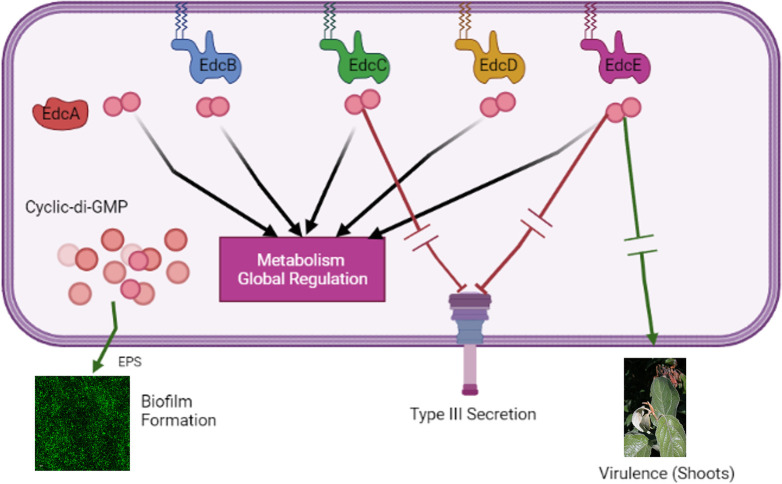
Fig 6. C-di-GMP regulatory model in surface exposed E. amylovora cells.
Our study indicates that there is a dimorphism in the regulatory targets of the c-di-GMP generated by each of the five Edcs. While each Edc uniquely regulates the transcription of several genes, and virulence factors in vitro and in planta, attachment/biofilm formation (dependent on EPS production) is regulated by all the Edcs, thus, leading us to hypothesize about the potential presence of a localized and a diffused pool of c-di-GMP that can achieve these varied regulatory targets. Red inhibitor lines and green arrows indicate negative and positive regulation respectively, with arrow breaks indicating intermediate regulatory steps.
Materials and methods
Bacterial strains, plasmids and growth conditions
All bacterial strains, and plasmids used in this study along with their relevant characteristics are described in Table 8. Unless specified otherwise, E. amylovora strains were grown in Lysogeny broth (LB) amended with one or more of the appropriate antibiotics: ampicillin (Ap; 100 μg/ml), chloramphenicol (Cm; 10 μg/ml), gentamicin (Gm; 10 μg/ml) or kanamycin (Km; 100 μg/ml). Overexpression constructs (hofC OE and fliC OE) were induced using 1 mM isopropyl-b-D-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG).
Table 8. Strains, plasmids and relevant information.
| Strain/Plasmid | Relevant Characteristics | Source |
|---|---|---|
| E. amylovora strains | ||
| Ea1189 | Wild Type | [3] |
| Ea1189Δ8 | Deletion of edcA-E and pdeA-C | This study |
| Ea1189Δ12 | Deletion of edcA-E, pdeA-C, EAM_3378, EAM_3136, EAM_2449 and EAM_1579 | [72] |
| Ea1189Δ12ΔfliC | Deletion of fliC in Ea1189Δ12 | This study |
| Ea1189Δ12ΔhofC | Deletion of hofC in Ea1189Δ12 | This study |
| Ea1189ΔfliC | Deletion of fliC in Ea1189 | This study |
| Ea1189ΔhofC | Deletion of hofC in Ea1189 | This study |
| Ea1189Δ12 + edcA-E | Chromosomal restoration of the indicated gene in Ea1189Δ12 | This study |
| Plasmids | ||
| pKD3 | Cmr cassette flanking FRT* sites; Cmr | [61] |
| pKD4 | Kmr cassette flanking FRT sites; Kmr | [61] |
| pKD46 | L-Arabinose-inducible lambda red recombinase; Apr | [61] |
| pTL18 | IPTG-Inducible FLPase, TetR | [73] |
| pBBR1-MCS5 | Broad-host-range cloning vector**; R6K ori; Gmr | [74] |
| pMP2444 | pBBR1MCS-5 expression gfp under lac promoter, Gmr | [75] |
| pEVS143 | Broad-host-range, IPTG inducible (Ptac) cloning vector; inducible Cmr and GFP Kmr | [76] |
| hofC OE | hofC in pEVS143 | This study |
| fliC OE | fliC in pEVS143 | This study |
| edcA OE | edcA in pEVS143 | [3] |
| edcB OE | edcB in pEVS143 | [3] |
| edcC OE | edcC in pEVS143 | [3] |
| edcD OE | edcD in pEVS143 | [3] |
| edcE OE | edcE in pEVS143 | [3] |
*FRT: Flippase target recognition
**MCS: Multiple cloning site.
Genetic manipulation and bioinformatics
Reference genome sequence for E. amylovora Ea1189 (Accession: FN434113) was obtained from NCBI. Artemis (Java) was used to browse the genome. The standard lambda Red recombinase protocol was used to construct chromosomal deletion mutants [61]. To complement the individual deleted genes, the full-length sequences of the genes were briefly amplified, and the purified gene fragments were transformed into Ea1189Δ12 harboring pKD46 (induced with arabinose) along with a retained CmR/KmR cassettes (originally amplified from pKD3/pKD4 source plasmids) in the target gene being restored. Transformed cells were recovered after an 18 h incubation and were screened for a loss of the resistance cassette, followed by Sanger sequencing to confirm the replacement of the originally deleted gene.
Scanning electron microscopy and bacterial population quantification to monitor xylem colonization in apple shoots
Apple shoots were inoculated as previously described [3]. Strains were grown overnight at 28°C and normalized to an OD600 of 0.2. Scissors dipped in inoculum were used to make an incision between two peripheral veins on young apple leaves (Malus x domestica cv. Gala on M9 rootstock). At 3 dpi, inoculated leaves along with the attached petiole were harvested. Cross sections of the petioles and apoplast tissue were fixed using 2.5% paraformaldehyde-2.5% glutaraldehyde, followed by ethanol dehydration at increasing concentrations as previously described [13]. Samples were imaged using the JEOL 6610LV (Japan Electron Optics Laboratory Ltd., Tokyo, Japan).
In order to quantify the level of bacterial proliferation and movement in apple shoots, the inoculated leaves and petioles were collected from infected shoot tips at 0, 1, 2 and 3 dpi, weighed and crushed in 0.5X phosphate buffered saline (PBS) solution. Serial dilutions were used to determine the population counts for WT Ea1189 and Ea1189Δ12, which were normalized by tissue weight. This study involved three biological replicates. JMP statistical software was used for data analysis.
Growth curve analysis
Strains were grown overnight in LB amended with antibiotics as appropriate. Following this, the strains were sub-cultured in individual wells on a 96 well plate and were adjusted to a starting OD600 of ~0.1 in LB media. This setup was then incubated for 19 hrs in a TECAN Spark spectrophotometer (Tecan, Männedorf, Switzerland) at 28°C, with OD600 measurements taken every hour. This study involved three biological replicates. JMP statistical software was used for data analysis.
Confocal microscopy to monitor attachment and biofilm formation in flow cells
To monitor initial surface interaction and attachment, E. amylovora strains expressing pMP2444::gfp [13] were grown for 18 h at 28°C and normalized to an OD600 of 0.5. A total of 1 ml of inoculum for each strain was introduced into a flow cell chamber in a μ-Slide VI 0.5 glass bottom slide (Ibidi, Martinsried, Germany). Immediately, the base of the flow chamber was repeatedly imaged using a Olympus FlouView 1000 confocal laser scanning microscope (Olympus, MA, USA). Images were acquired for up to 1 h or until the frame was saturated with fluorescent cell signals. Following this, the flow cell chamber was flushed with 5 ml of 0.5X phosphate buffered saline (PBS). To evaluate biofilm formation, following the initial attachment incubation, the flow chamber was subjected to flow (0.5X LB) using a peristaltic pump (Ismatec REGLO Digital 4-CH pump) (Cole-Parmer IL, USA) for 5 h. Fluorescent Z-stacked images were acquired to measure overall attachment and biofilm levels in the flow cell chambers [13]. ImageJ software was used to invert the color on the images, and the RBG plugin was used to process these images and to graph the GFP signal intensity profile for the Z-stacked images [62].
Quantifying intracellular levels of c-di-GMP
Intracellular levels of c-di-GMP were quantified as previously described [3]. Strains were grown in overnight in LB, sub-cultured, collected at mid-log phase and lysed (with 40% acetonitrile and 40% methanol) at -20°C for 1 h. Relative levels of c-di-GMP in the samples was established against a standard curve generated using synthesized c-di-GMP (Axxora Life Sciences Inc., CA, USA) using a Quattro Premier XE instrument (Waters Corp. MA, USA). Three biological replicates were included in the studies. JMP statistical software was used for data analysis.
q-RT-PCR to measure gene expression
To measure hrpL expression, strains were grown overnight in LB at 28°C. Cell cultures were then washed and resuspended in HRP-MM medium and incubated for 6 h [4]. To validate RNA-Seq data, identical sample treatment and collection protocols were used, with the exception of measuring transcript levels only for representative gene targets. RNA extraction and concentration for all samples were conducted using the protocols described for RNA-Seq sample collection. To check the impact of c-di-GMP on attachment appendages gene expression, including fliC, hofC, crl and fimA, WT Ea1189 and Ea1189Δ12 were incubated in a flow cell chamber for 1 h, thus resembling the treatment experienced by the surface treated strains included in the RNAseq experiment. Following surface exposure, the cells were collected from the flow chamber and RNA was extracted using the protocol by Rivas et. al., similar to the protocol for RNAseq sample extraction [63]. cDNA was synthesized using the High Capacity RT kit (Applied Biosystems, CA, USA). SYBR green PCR master mix (Applied Biosystems, CA, USA) was used for quantitative PCR experiments. recA was used as an endogenous control. The delta CT method was used to compare transcriptomic fold changes [64]. Three biological replicates were included in the studies. JMP statistical software was used for data analysis.
Virulence assays
Relative virulence levels of strains were compared using apple shoots as previously described [3]. Apple shoots were inoculated using the same described protocol used to evaluate xylem colonization through SEM. Data was collected in the form of necrotic lesion length along the shoot 8 dpi. JMP statistical software was used for data analysis.
Flagellar motility assay
Relative levels of flagellar motility were quantified in vitro using a previously described protocol [4]. Strains were grown overnight in LB at 28°C. Following this, the OD600 for the cultures was normalized to 0.5. Cultures were stab inoculated onto a motility agar plate and incubated for 48h. Motility was quantified in terms of the diameter of the colony movement using ImageJ software [62]. JMP statistical software was used for data analysis.
RNA-Seq sample acquisition, sequencing, data analysis and overall data integration/modelling
WT E. amylovora Ea1189 and Ea1189Δ12 were grown overnight in LB medium, sub-cultured and harvested at the mid-log phase prior to RNA extraction. To collect cell samples from reflective of the stages of biofilm development, the protocol described in this study to monitor biofilm formation in flow cells remained largely the same (note that the strains were not fluorescently labelled). Inoculum injected into the flow chamber for the strains was collected 1 h after the cells were allowed to interact with the surfaces in the flow chamber before being collected for RNA extraction. For the other comparative RNAseq study presented in the study, Ea1189Δ8 and Ea1189Δ8 complemented with overexpression vectors for edcA-E individually were all grown overnight in LB medium, followed by a sub-culturing, IPTG (1mM) induction as appropriate and sample collection at mid-log phase at which stage they were processed for RNA extraction. Three biological replicates were included in the study.
For RNA extraction, as per a previously described protocol [63], cells were washed with 0.1% N-lauryl sarcosine sodium salt, followed by treatment with the lysis buffer (1% SDS in 10 mM EDTA and 50 mM sodium acetate, pH 5.1) and a 5 min incubation in boiling water. The extracted RNA was treated for residual DNA contamination using the TURBO DNA-free kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, MA, USA), and concentrated using the RNA Clean and Concentrator-25 kit (Zymo Research, CA, USA). The ‘Unbound’ samples were treated after their collection from the flow chamber, for the other two sample types, the initial lysis and wash steps were conducted by injecting the buffers directly into the flow chamber and suctioning the fluid out.
RNA samples were analyzed for quality control on the Agilent 4200 TapeStation (Agilent Technologies, CA, USA). The QIAseq FastSelect 5S/16S/23S rRNA removal kit was used to treat samples prior to library prep with the TruSeq Stranded Total RNA Library Prep Kit (Illumina, CA, USA). Sequencing was conducted on the Illumina HiSeq 4000 at 50 bp single-end reads.
For data analysis, adaptor barcodes were filtered using Trimmomatic v 0.36 (single end criteria: ILLUMINACLIP:TruSeq3-SE:2:30:10 LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:15) [65]. Trimmed sequences were mapped to the E. amylovora ATCC-49946 genome using Bowtie v 2.4.1. HTSeq v 0.11.2 [66,67]. Differential expression analysis was conducted using DESeq2 v 3.12 with an FDR cutoff of 0.05 and a minimum accepted fold change of 2 (log2) [68]. Geneious software was used for volcano plot generation. Gene ontology enrichment analysis was conducted using BiNGO on the Cytoscape platform [69,70]. Biological GO enrichment was assessed with an FDR cutoff of 0.01.
For phylogenetic analysis of each of each of the Edcs, BLASTp program from NCBI was used with the parameters set to searching within the entire non-redundant protein database, with a cutoff threshold of 1e-05 using the BLOSUM62 matrix with conditional compositional score matrix adjustment (Existence 11 Extension 1). We then acquired the fast minimum evolution phylogenetic tree generated for the top 250 matches and compiled them for all the twelve genes in our study for collective analysis [71].
Supporting information
(XLSX)
(XLSX)
(PDF)
Graph summarizing the RNAseq and q-RT-PCR based examination of fold changes in the expression of representative genes (from both RNAseq studies) A) atpG and fliG in Ea1189Δ12 relative to WT Ea1189 and B) EAM_2517 and EAM_1085 in Ea1189Δ8 over expressing edcA-E individually relative to Ea1189Δ8. Error bars represent standard error of the means.
(TIF)
(MP4)
(MP4)
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the assistance provided by the MSU RTSF core in RNA-Seq sample prep, along with Carol Flegler and Melinda Frame at the MSU Center for Advanced Microscopy for their assistance with SEM and CLSM.
Data Availability
The datasets generated and analyzed in this study are available in the National Center for Biotechnology Information Sequence Read Archive repository (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra) with the following Bioproject accession number: PRJNA808311.
Funding Statement
This project was supported by funds from the Agriculture and Food Research Initiative Competitive Grants Program Grants no. 2015-67013-23068 (GWS) and 2020-51181-32158 (GWS) from the USDA National Institute of Food and Agriculture, and by Michigan State University AgBioResearch (GWS). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Hengge R. Principles of c-di-GMP signalling in bacteria. Nature Reviews Microbiology. 2009;7(4):263–73. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2109 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Jenal U, Reinders A, Lori C. Cyclic di-GMP: second messenger extraordinaire. Nature Reviews Microbiology. 2017;15(5):271–84. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2016.190 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Edmunds AC, Castiblanco LF, Sundin GW, Waters CM. Cyclic di-GMP modulates the disease progression of Erwinia amylovora. Journal of bacteriology. 2013;195(10):2155–65. doi: 10.1128/JB.02068-12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kharadi RR, Castiblanco LF, Waters CM, Sundin GW. Phosphodiesterase genes regulate amylovoran production, biofilm formation, and virulence in Erwinia amylovora. Applied and environmental microbiology. 2019;85(1):e02233–18. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02233-18 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Solano C, Garcia B, Latasa C, Toledo-Arana A, Zorraquino V, Valle J, et al. Genetic reductionist approach for dissecting individual roles of GGDEF proteins within the c-di-GMP signaling network in Salmonella. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(19):7997–8002. Epub 2009/05/07. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0812573106 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2683120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cowles KN, Willis DK, Engel TN, Jones JB, Barak JD. Diguanylate cyclases AdrA and STM1987 regulate Salmonella enterica exopolysaccharide production during plant colonization in an environment-dependent manner. Applied and environmental microbiology. 2016;82(4):1237–48. doi: 10.1128/AEM.03475-15 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Conner JG, Zamorano-Sanchez D, Park JH, Sondermann H, Yildiz FH. The ins and outs of cyclic di-GMP signaling in Vibrio cholerae. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2017;36:20–9. Epub 2017/02/09. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2017.01.002 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC5534393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Galperin MY, Nikolskaya AN, Koonin EV. Novel domains of the prokaryotic two-component signal transduction systems. FEMS microbiology letters. 2001;203(1):11–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2001.tb10814.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sarenko O, Klauck G, Wilke FM, Pfiffer V, Richter AM, Herbst S, et al. More than Enzymes That Make or Break Cyclic Di-GMP-Local Signaling in the Interactome of GGDEF/EAL Domain Proteins of Escherichia coli. mBio. 2017;8(5). Epub 2017/10/12. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01639-17 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC5635695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Abel S, Bucher T, Nicollier M, Hug I, Kaever V, Abel zur Wiesch P, et al. Bi-modal distribution of the second messenger c-di-GMP controls cell fate and asymmetry during the Caulobacter cell cycle. PLoS genetics. 2013;9(9):e1003744. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003744 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Smits T, Duffy B, Sundin G, Zhao Y, Rezzonico F. Erwinia amylovora in the genomics era: from genomes to pathogen virulence, regulation, and disease control strategies. Journal of Plant Pathology. 2017;99(Special issue):7–23. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Koczan JM, McGrath MJ, Zhao Y, Sundin GW. Contribution of Erwinia amylovora exopolysaccharides amylovoran and levan to biofilm formation: implications in pathogenicity. Phytopathology. 2009;99(11):1237–44. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-99-11-1237 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kharadi RR, Sundin GW. Physiological and microscopic characterization of cyclic-di-GMP-mediated autoaggregation in Erwinia amylovora. Frontiers in Microbiology. 2019;10:468. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00468 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Finn RD, Bateman A, Clements J, Coggill P, Eberhardt RY, Eddy SR, et al. Pfam: the protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42(Database issue):D222–30. Epub 2013/11/30. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1223 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3965110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kharadi RR, Sundin GW. CsrD regulates amylovoran biosynthesis and virulence in Erwinia amylovora in a novel cyclic-di-GMP dependent manner. Molecular Plant Pathology. 2022; 23:1154–1169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Krogh A, Larsson B, von Heijne G, Sonnhammer EL. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: application to complete genomes. J Mol Biol. 2001;305(3):567–80. Epub 2001/01/12. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.4315 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Yang F, Tian F, Li X, Fan S, Chen H, Wu M, et al. The degenerate EAL-GGDEF domain protein Filp functions as a cyclic di-GMP receptor and specifically interacts with the PilZ-domain protein PXO_02715 to regulate virulence in Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions. 2014;27(6):578–89. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-12-13-0371-R [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Chin KH, Kuo WT, Yu YJ, Liao YT, Yang MT, Chou SH. Structural polymorphism of c-di-GMP bound to an EAL domain and in complex with a type II PilZ-domain protein. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2012;68(Pt 10):1380–92. Epub 2012/09/21. doi: 10.1107/S0907444912030594 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wei ZM, Beer SV. hrpL activates Erwinia amylovora hrp gene transcription and is a member of the ECF subfamily of sigma factors. J Bacteriol. 1995;177(21):6201–10. Epub 1995/11/01. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.21.6201-6210.1995 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC177461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Koczan JM, Lenneman BR, McGrath MJ, Sundin GW. Cell surface attachment structures contribute to biofilm formation and xylem colonization by Erwinia amylovora. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011;77(19):7031–9. Epub 2011/08/09. doi: 10.1128/AEM.05138-11 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3187075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Song WS, Yoon S-i. Crystal structure of FliC flagellin from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its implication in TLR5 binding and formation of the flagellar filament. Biochemical and biophysical research communications. 2014;444(2):109–15. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.01.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ueki T, Walker DJ, Woodard TL, Nevin KP, Nonnenmann SS, Lovley DR. An Escherichia coli chassis for production of electrically conductive protein nanowires. ACS synthetic biology. 2020;9(3):647–54. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.9b00506 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Arnqvist A, Olsén A, Pfeifer J, Russell DG, Normark S. The Crl protein activates cryptic genes for curli formation and fibronectin binding in Escherichia coli HB101. Molecular microbiology. 1992;6(17):2443–52. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01420.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Nagano K, Hasegawa Y, Abiko Y, Yoshida Y, Murakami Y, Yoshimura F. Porphyromonas gingivalis FimA fimbriae: fimbrial assembly by fimA alone in the fim gene cluster and differential antigenicity among fimA genotypes. 2012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Christen M, Kulasekara HD, Christen B, Kulasekara BR, Hoffman LR, Miller SI. Asymmetrical distribution of the second messenger c-di-GMP upon bacterial cell division. Science. 2010;328(5983):1295–7. doi: 10.1126/science.1188658 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hengge R. High-Specificity Local and Global c-di-GMP Signaling. Trends in Microbiology. 2021. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2021.02.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Shikuma NJ, Fong JC, Yildiz FH. Cellular levels and binding of c-di-GMP control subcellular localization and activity of the Vibrio cholerae transcriptional regulator VpsT. PLoS pathogens. 2012;8(5):e1002719. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002719 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.O’Connor JR, Kuwada NJ, Huangyutitham V, Wiggins PA, Harwood CS. Surface sensing and lateral subcellular localization of WspA, the receptor in a chemosensory-like system leading to c-di-GMP production. Molecular microbiology. 2012;86(3):720–9. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Wolf YI, Rogozin IB, Kondrashov AS, Koonin EV. Genome alignment, evolution of prokaryotic genome organization, and prediction of gene function using genomic context. Genome research. 2001;11(3):356–72. doi: 10.1101/gr.gr-1619r [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Mira A, Ochman H, Moran NA. Deletional bias and the evolution of bacterial genomes. Trends in Genetics. 2001;17(10):589–96. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9525(01)02447-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ochman H, Moran NA. Genes lost and genes found: evolution of bacterial pathogenesis and symbiosis. Science. 2001;292(5519):1096–9. doi: 10.1126/science.1058543 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Sellner B, Prakapaitė R, van Berkum M, Heinemann M, Harms A, Jenal U. A new sugar for an old phage: a c-di-GMP-dependent polysaccharide pathway sensitizes Escherichia coli for bacteriophage infection. Mbio. 2021;12(6):e03246–21. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03246-21 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Valentini M, Filloux A. Biofilms and cyclic di-GMP (c-di-GMP) signaling: lessons from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other bacteria. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2016;291(24):12547–55. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R115.711507 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Laventie B-J, Sangermani M, Estermann F, Manfredi P, Planes R, Hug I, et al. A surface-induced asymmetric program promotes tissue colonization by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Cell host & microbe. 2019;25(1):140–52. e6. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2018.11.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kharadi RR, Schachterle JK, Yuan X, Castiblanco LF, Peng J, Slack SM, et al. Genetic dissection of the Erwinia amylovora disease cycle. Annual review of phytopathology. 2021;59:191–212. doi: 10.1146/annurev-phyto-020620-095540 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Nobori T, Velásquez AC, Wu J, Kvitko BH, Kremer JM, Wang Y, et al. Transcriptome landscape of a bacterial pathogen under plant immunity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2018;115(13):E3055–E64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Jacobs JM, Babujee L, Meng F, Milling A, Allen C. The in planta transcriptome of Ralstonia solanacearum: conserved physiological and virulence strategies during bacterial wilt of tomato. MBio. 2012;3(4):e00114–12. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00114-12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Bobrov AG, Kirillina O, Perry RD. The phosphodiesterase activity of the HmsP EAL domain is required for negative regulation of biofilm formation in Yersinia pestis. FEMS Microbiology Letters. 2005;247(2):123–30. doi: 10.1016/j.femsle.2005.04.036 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Gassmann W, Hinsch ME, Staskawicz BJ. The Arabidopsis RPS4 bacterial-resistance gene is a member of the TIR-NBS-LRR family of disease-resistance genes. The Plant Journal. 1999;20(3):265–77. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1999.t01-1-00600.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Zhang L, Mo J, Swanson KV, Wen H, Petrucelli A, Gregory SM, et al. NLRC3, a member of the NLR family of proteins, is a negative regulator of innate immune signaling induced by the DNA sensor STING. Immunity. 2014;40(3):329–41. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.01.010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Metzger LC, Stutzmann S, Scrignari T, Van der Henst C, Matthey N, Blokesch M. Independent regulation of type VI secretion in Vibrio cholerae by TfoX and TfoY. Cell reports. 2016;15(5):951–8. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.03.092 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Moscoso JA, Mikkelsen H, Heeb S, Williams P, Filloux A. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa sensor RetS switches type III and type VI secretion via c-di-GMP signalling. Environmental microbiology. 2011;13(12):3128–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2011.02595.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Wang T, Cai Z, Shao X, Zhang W, Xie Y, Zhang Y, et al. Pleiotropic effects of c-di-GMP content in Pseudomonas syringae. Applied and environmental microbiology. 2019;85(10):e00152–19. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00152-19 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Zhu B, Liu C, Liu S, Cong H, Chen Y, Gu L, et al. Membrane association of SadC enhances its diguanylate cyclase activity to control exopolysaccharides synthesis and biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Environmental microbiology. 2016;18(10):3440–52. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.13263 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Jain R, Behrens AJ, Kaever V, Kazmierczak BI. Type IV pilus assembly in Pseudomonas aeruginosa over a broad range of cyclic di-GMP concentrations. J Bacteriol. 2012;194(16):4285–94. Epub 2012/06/12. doi: 10.1128/JB.00803-12 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3416225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Hengge R, Galperin MY, Ghigo JM, Gomelsky M, Green J, Hughes KT, et al. Systematic Nomenclature for GGDEF and EAL Domain-Containing Cyclic Di-GMP Turnover Proteins of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 2016;198(1):7–11. Epub 2015/07/08. doi: 10.1128/JB.00424-15 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4686207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Simm R, Morr M, Kader A, Nimtz M, Römling U. GGDEF and EAL domains inversely regulate cyclic di-GMP levels and transition from sessility to motility. Molecular microbiology. 2004;53(4):1123–34. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04206.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Yang F, Tian F, Li X, Fan S, Chen H, Wu M, et al. The degenerate EAL-GGDEF domain protein Filp functions as a cyclic di-GMP receptor and specifically interacts with the PilZ-domain protein PXO_02715 to regulate virulence in Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2014;27(6):578–89. Epub 2014/02/20. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-12-13-0371-R . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Chou SH, Galperin MY. Diversity of Cyclic Di-GMP-Binding Proteins and Mechanisms. J Bacteriol. 2016;198(1):32–46. Epub 2015/06/10. doi: 10.1128/JB.00333-15 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4686193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Toft C, Andersson SG. Evolutionary microbial genomics: insights into bacterial host adaptation. Nature Reviews Genetics. 2010;11(7):465–75. doi: 10.1038/nrg2798 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Didelot X, Walker AS, Peto TE, Crook DW, Wilson DJ. Within-host evolution of bacterial pathogens. Nature Reviews Microbiology. 2016;14(3):150–62. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2015.13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.McGhee GC, Sundin GW. Erwinia amylovora CRISPR elements provide new tools for evaluating strain diversity and for microbial source tracking. PLoS ONE. 2012; 7:e41706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Rezzonico F, Smits TH, Duffy B. Diversity, evolution, and functionality of clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat (CRISPR) regions in the fire blight pathogen Erwinia amylovora. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 2011;77(11):3819–29. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00177-11 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Mendes RJ, Luz JP, Santos C, Tavares F. CRISPR genotyping as complementary tool for epidemiological surveillance of Erwinia amylovora outbreaks. PLoS One. 2021;16(4):e0250280. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0250280 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Parcey M, Gayder S, Castle AJ, Svircev AM. Function and application of the CRISPR-Cas system in the plant pathogen Erwinia amylovora. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 2022;88(7):e02513–21. doi: 10.1128/aem.02513-21 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Eastgate J, Taylor N, Coleman M, Healy B, Thompson L, Roberts I. Cloning, expression, and characterization of the lon gene of Erwinia amylovora: evidence for a heat shock response. Journal of bacteriology. 1995;177(4):932–7. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.4.932-937.1995 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Lee JH, Ancona V, Chatnaparat T, Yang H-w, Zhao Y. The RNA-binding protein CsrA controls virulence in Erwinia amylovora by regulating RelA, RcsB, and FlhD at the posttranscriptional level. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions. 2019;32(10):1448–59. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-03-19-0077-R [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Lee JH, Ancona V, Zhao Y. Lon protease modulates virulence traits in Erwinia amylovora by direct monitoring of major regulators and indirectly through the Rcs and Gac-Csr regulatory systems. Molecular plant pathology. 2018;19(4):827–40. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12566 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Schröpfer S, Vogt I, Broggini GAL, Dahl A, Richter K, Hanke M-V, et al. Transcriptional profile of AvrRpt2EA-mediated resistance and susceptibility response to Erwinia amylovora in apple. Scientific reports. 2021;11(1):1–14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Joshi A, Mahmoud SA, Kim S-K, Ogdahl JL, Lee VT, Chien P, et al. c-di-GMP inhibits LonA-dependent proteolysis of TfoY in Vibrio cholerae. PLoS genetics. 2020;16(6):e1008897. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008897 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Datsenko KA, Wanner BL. One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(12):6640–5. Epub 2000/06/01. doi: 10.1073/pnas.120163297 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC18686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Schneider CA, Rasband WS, Eliceiri KW. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods. 2012;9(7):671–5. Epub 2012/08/30. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2089 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC5554542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Rivas R, Vizcaino N, Buey RM, Mateos PF, Martinez-Molina E, Velazquez E. An effective, rapid and simple method for total RNA extraction from bacteria and yeast. J Microbiol Methods. 2001;47(1):59–63. Epub 2001/09/22. doi: 10.1016/s0167-7012(01)00292-5 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Rao X, Huang X, Zhou Z, Lin X. An improvement of the 2^(-delta delta CT) method for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction data analysis. Biostat Bioinforma Biomath. 2013;3(3):71–85. Epub 2013/08/01. ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4280562. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B. Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics. 2014;30(15):2114–20. Epub 2014/04/04. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4103590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Langmead B, Salzberg SL. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat Methods. 2012;9(4):357–9. Epub 2012/03/06. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1923 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3322381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Anders S, Pyl PT, Huber W. HTSeq—a Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics. 2015;31(2):166–9. Epub 2014/09/28. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu638 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4287950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Love MI, Huber W, Anders S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014;15(12):550. Epub 2014/12/18. doi: 10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4302049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS, Wang JT, Ramage D, et al. Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome research. 2003;13(11):2498–504. doi: 10.1101/gr.1239303 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Maere S, Heymans K, Kuiper M. BiNGO: a Cytoscape plugin to assess overrepresentation of gene ontology categories in biological networks. Bioinformatics. 2005;21(16):3448–9. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti551 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Johnson M, Zaretskaya I, Raytselis Y, Merezhuk Y, McGinnis S, Madden TL. NCBI BLAST: a better web interface. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36(Web Server issue):W5–9. Epub 2008/04/29. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn201 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2447716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Kharadi RR, Selbmann K, Sundin GW. The cyclic di-GMP network is a global regulator of phase-transition and attachment-dependent host colonization in Erwinia amylovora. bioRxiv. 2021:2021.02.01.429191. doi: 10.1101/2021.02.01.429191 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Long T, Tu KC, Wang Y, Mehta P, Ong NP, Bassler BL, et al. Quantifying the integration of quorum-sensing signals with single-cell resolution. PLoS Biol. 2009;7(3):e68. Epub 2009/03/27. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000068 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2661960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Kovach ME, Elzer PH, Hill DS, Robertson GT, Farris MA, Roop RM 2nd, et al. Four new derivatives of the broad-host-range cloning vector pBBR1MCS, carrying different antibiotic-resistance cassettes. Gene. 1995;166(1):175–6. Epub 1995/12/01. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(95)00584-1 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Stuurman N, Pacios Bras C, Schlaman HR, Wijfjes AH, Bloemberg G, Spaink HP. Use of green fluorescent protein color variants expressed on stable broad-host-range vectors to visualize rhizobia interacting with plants. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2000;13(11):1163–9. Epub 2000/11/04. doi: 10.1094/MPMI.2000.13.11.1163 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Dunn AK, Millikan DS, Adin DM, Bose JL, Stabb EV. New rfp- and pES213-derived tools for analyzing symbiotic Vibrio fischeri reveal patterns of infection and lux expression in situ. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006;72(1):802–10. Epub 2006/01/05. doi: 10.1128/AEM.72.1.802-810.2006 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC1352280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
(XLSX)
(XLSX)
(PDF)
Graph summarizing the RNAseq and q-RT-PCR based examination of fold changes in the expression of representative genes (from both RNAseq studies) A) atpG and fliG in Ea1189Δ12 relative to WT Ea1189 and B) EAM_2517 and EAM_1085 in Ea1189Δ8 over expressing edcA-E individually relative to Ea1189Δ8. Error bars represent standard error of the means.
(TIF)
(MP4)
(MP4)
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated and analyzed in this study are available in the National Center for Biotechnology Information Sequence Read Archive repository (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra) with the following Bioproject accession number: PRJNA808311.