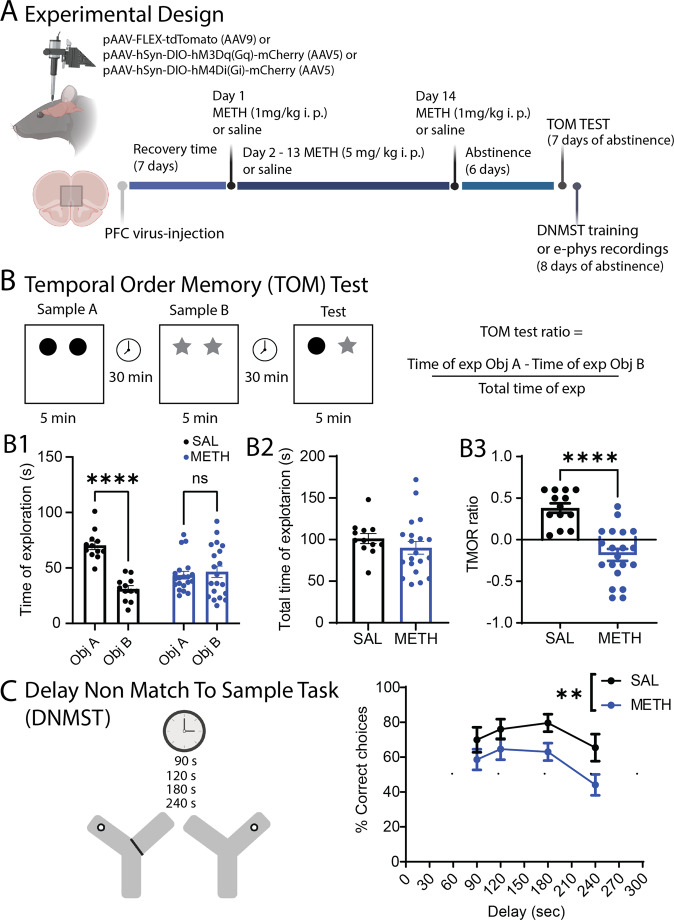
Fig. 1. Experimental design and behavioral assessments.
A Schematic illustration of the experimental design. We infuse either pAAV- FLEX-tdTomato, pAAV-hsyn-DIO-hM3Dq (Gq) or pAAV-hsyn-DIO-hM4Di (Gi) DREADDS in the PFC of PV-Cre rats followed by repeated METH or SAL in home cage treatment. Cognitive tests and electrophysiological assessments are performed after 7–10 days of abstinence. B Schematic representation of the Temporal Order Memory (TOM) test. B1 Total time of exploration for each object. Saline animals spend more time with the old object [Main effect of object: SAL Object A. 70.33 ± 3.8 vs SAL Object B. 31.00 ± 3.0; Mixed effect analysis ANOVA, F(1,30) = 35.32, ****p < 0.0001., Holm–Sidak post-hoc test]. On the other hand, METH animals do not show preference for any particular object [METH Object A. 43.5 ± 3.4 vs METH Object B. 46.5 ± 5.1; Mixed effect analysis ANOVA, F(1,30) = 1.053, ns p = 0.66, Holm–Sidak post-hoc test]. B2 There was no difference in the total time of exploration between groups [SAL total time 101.3 ± 6.0; METH total time 90.5 ± 7.6; t(31) = 0.3172, ns, SAL n = 13, METH n = 20]. B3 METH induces a significant decrease in the TOM test ratio [t(31) = 5.657, ****p < 0.0001, SAL n = 13, METH n = 20]. C Schematic representation of the Delay No Match to Sample Test. The graph shows METH-induced impairment in working memory [Main effect by drug: Two-way ANOVA, F(1,115) = 11.3 **p = 0.001, SAL n = 12; METH n = 20]. The schematic illustration was created using BioRender.com.