Abstract
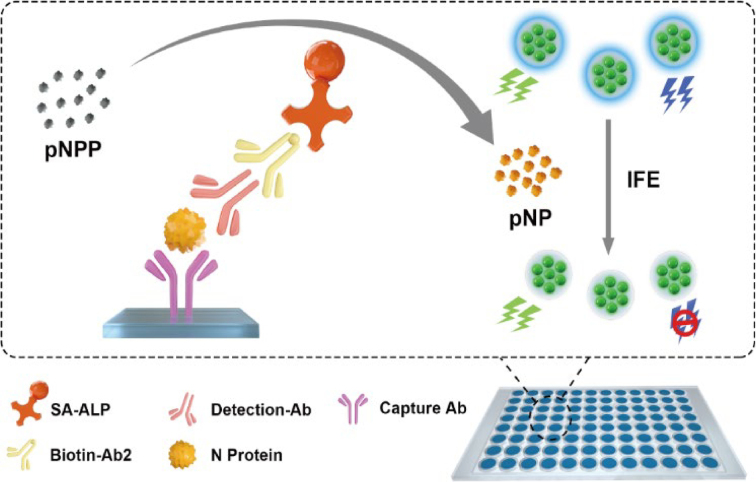
The global pandemic caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) virus has necessitated rapid, easy-to-use, and accurate diagnostic methods to monitor the virus infection. Herein, a ratiometric fluorescence enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was developed using Si-fluorescein isothiocyanate nanoparticles (FITC NPs) for detecting SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid (N) protein. Si-FITC NPs were prepared by a one-pot hydrothermal method using 3-aminopropyl triethoxysilane (APTES)-FITC as the Si source. This method did not need post-modification and avoided the reduction in quantum yield and stability. The p-nitrophenyl (pNP) produced by the alkaline phosphatase (ALP)-mediated hydrolysis of p-nitrophenyl phosphate (pNPP) could quench Si fluorescence in Si-FITC NPs via the inner filter effect. In ELISA, an immunocomplex was formed by the recognition of capture antibody/N protein/reporter antibody. ALP-linked secondary antibody bound to the reporter antibody and induced pNPP hydrolysis to specifically quench Si fluorescence in Si-FITC NPs. The change in fluorescence intensity ratio could be used for detecting N protein, with a wide linearity range (0.01–10.0 and 50–300 ng/mL) and low detection limit (0.002 ng/mL). The concentration of spiked SARS-CoV-2 N protein could be determined accurately in human serum. Moreover, this proposed method can accurately distinguish coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and non-COVID-19 patient samples. Therefore, this simple, sensitive, and accurate method can be applied for the early diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 virus infection.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Supplementary material (characterization of Si-FITC NPs (FTIR spectrum, XRD spectra, and synchronous fluorescence spectra); condition optimization of ALP response (fluorescence intensity ratio change); mechanism investigation of ALP response (fluorescence lifetime decay curves and UV—vis absorption spectra); detection of N protein using commercial ELISA Kit; analytical performance of assays for ALP detection or SARS-CoV-2 N protein detection; and determination results of SARS-CoV-2 N protein in human serum) is available in the online version of this article at 10.1007/s12274-022-4740-5.
Keywords: Si-fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) nanoparticles, ratiometric fluorescent probe, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), inner filter effect, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
Electronic Supplementary Material
Ratiometric fluorescence immunoassay of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein via Si-FITC nanoprobe-based inner filter effect
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2021YFA0910900), the National Natural Science Foundation (No. 22104147), Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS (No. 2021359), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong (Nos. 2018B030306046 and 2020A1515111130), Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Synthetic Genomics (No. 2019B030301006), Shenzhen Science and Technology Program (No. KQTD20180413181837372), and Shenzhen Outstanding Talents Training Fund.
Footnotes
Guobin Mao, Yang Yang, and Shijie Cao contributed equally to this work.
Contributor Information
Yingxia Liu, Email: yingxialiu@hotmail.com.
Yingxin Ma, Email: yx.ma1@siat.ac.cn.
References
- [1].Ma Y X, Mao G B, Huang W R, Wu G Q, Yin W, Ji X H, Deng Z S, Cai Z M, Zhang X E, He Z K, et al. Quantum dot nanobeacons for single RNA labeling and imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019;141:13454–13458. doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b04659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [2].Devi P, Saini S, Kim K H. The advanced role of carbon quantum dots in nanomedical applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019;141:111158. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2019.02.059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [3].Zhong Y L, Peng F, Bao F, Wang S Y, Ji X Y, Yang L, Su Y Y, Lee S T, He Y. Large-scale aqueous synthesis of fluorescent and biocompatible silicon nanoparticles and their use as highly photostable biological probes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013;135:8350–8356. doi: 10.1021/ja4026227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [4].So W Y, Li Q, Legaspi C M, Redler B, Koe K M, Jin R C, Peteanu L A. Mechanism of ligand-controlled emission in silicon nanoparticles. ACS Nano. 2018;12:7232–7238. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.8b03273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [5].Han Y X, Chen Y L, Liu J J, Niu X Y, Ma Y X, Ma S D, Chen X G. Room-temperature synthesis of yellow-emitting fluorescent silicon nanoparticles for sensitive and selective determination of crystal violet in fish tissues. Sens. Actuators B:Chem. 2018;263:508–516. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2018.02.163. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [6].Zhou Y F, Zhang Y, Zhong Y L, Fu R, Wu S C, Wang Q, Wang H Y, Su Y Y, Zhang H M, He Y. The in vivo targeted molecular imaging of fluorescent silicon nanoparticles in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nano Res. 2018;11:2336–2346. doi: 10.1007/s12274-017-1677-1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [7].Han J F, Zhang L, Cui M Y, Su Y Y, He Y. Rapid and accurate detection of lymph node metastases enabled through fluorescent silicon nanoparticles-based exosome probes. Anal. Chem. 2021;93:10122–10131. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.1c01010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [8].Jiao Y, Gao Y F, Meng Y T, Lu W J, Liu Y, Han H, Shuang S M, Li L, Dong C. One-step synthesis of label-free ratiometric fluorescence carbon dots for the detection of silver ions and glutathione and cellular imaging applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2019;11:16822–16829. doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b01319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [9].Park S H, Kwon N, Lee J H, Yoon J, Shin I. Synthetic ratiometric fluorescent probes for detection of ions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020;49:143–179. doi: 10.1039/C9CS00243J. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [10].Yue Y K, Huo F J, Ning P, Zhang Y B, Chao J B, Meng X M, Yin C X. Dual-site fluorescent probe for visualizing the metabolism of Cys in living cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017;139:3181–3185. doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b12845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [11].Lan M H, Zhang J F, Chui Y S, Wang P F, Chen X F, Lee C S, Kwong H L, Zhang W J. Carbon nanoparticle-based ratiometric fluorescent sensor for detecting mercury ions in aqueous media and living cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2014;6:21270–21278. doi: 10.1021/am5062568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [12].Zou C C, Foda M F, Tan X C, Shao K, Wu L, Lu Z C, Bahlol H S, Han H Y. Carbon-dot and quantum-dot-coated dual-emission core_satellite silica nanoparticles for ratiometric intracellular Cu2+ imaging. Anal. Chem. 2016;88:7395–7403. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.6b01941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [13].Mao G B, Cai Q, Wang F B, Luo C L, Ji X H, He Z K. One-step synthesis of Rox-DNA functionalized CdZnTeS quantum dots for the visual detection of hydrogen peroxide and blood glucose. Anal. Chem. 2017;89:11628–11635. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.7b03053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [14].Ma J W, Chen Y G, Chen L, Wang L Y. Ternary Pd-Ni-P nanoparticle-based nonenzymatic glucose sensor with greatly enhanced sensitivity achieved through active-site engineering. Nano Res. 2017;10:2712–2720. doi: 10.1007/s12274-017-1474-x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [15].Chu B B, Wang H Y, Song B, Peng F, Su Y Y, He Y. Fluorescent and photostable silicon nanoparticles sensors for realtime and long-term intracellular pH measurement in live cells. Anal. Chem. 2016;88:9235–9242. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.6b02488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [16].Yan X, Li H X, Han X S, Su X G. A ratiometric fluorescent quantum dots based biosensor for organophosphorus pesticides detection by inner-filter effect. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015;74:277–283. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2015.06.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [17].Li H Y, Lin H Y, Lv W X, Gai P P, Li F. Equipment-free and visual detection of multiple biomarkers via an aggregation induced emission luminogen-based paper biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020;165:112336. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2020.112336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [18].Zhang J Y, Zhou R H, Tang D D, Hou X D, Wu P. Optically-active nanocrystals for inner filter effect-based fluorescence sensing: Achieving better spectral overlap. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019;110:183–190. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2018.11.002. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [19].Zhai W Y, Wang C X, Yu P, Wang Y X, Mao L Q. Single-layer MnO2 nanosheets suppressed fluorescence of 7-hydroxycoumarin: Mechanistic study and application for sensitive sensing of ascorbic acid in vivo. Anal. Chem. 2014;86:12206–12213. doi: 10.1021/ac503215z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [20].Li X, Liu P, Niu X H, Ye K, Ni L, Du D, Pan J M, Lin Y H. Tri-functional Fe-Zr bi-metal-organic frameworks enable high-performance phosphate ion ratiometric fluorescent detection. Nanoscale. 2020;12:19383–19389. doi: 10.1039/D0NR04531D. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [21].Zhu N, Zhang D Y, Wang W L, Li X W, Yang B, Song J D, Zhao X, Huang B Y, Shi W F, Lu R J, et al. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020;382:727–733. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [22].Ravi N, Cortade D L, Ng E, Wang S X. Diagnostics for SARS-CoV-2 detection: A comprehensive review of the FDA-EUA COVID-19 testing landscape. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020;165:112454. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2020.112454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [23].Wang, Y.; Yan, T. H.; Mei, K. N.; Rao, D. P.; Wu, W. J.; Chen, Y.; Peng, Y. P.; Wang, J. Y.; Wu, S. Q.; Zhang, Q. C. Nanomechanical assay for ultrasensitive and rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 based on peptide nucleic acid. Nano Res., in press, 10.1007/s12274-022-4333-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- [24].Jang A S, Kumar P P P, Lim D K. Attomolar sensitive magnetic microparticles and a surface-enhanced Raman scattering-based assay for detecting SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid targets. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2022;14:138–149. doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c17028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [25].Chen M R, Cui D Z, Zhao Z Y, Kang D, Li Z, Albawardi S, Alsageer S, Alamri F, Alhazmi A, Amer M R, et al. Highly sensitive, scalable, and rapid SARS-CoV-2 biosensor based on In2O3 nanoribbon transistors and phosphatase. Nano Res. 2022;15:5510–5516. doi: 10.1007/s12274-022-4190-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [26].Mao G B, Zhang Q, Yang Y L, Ji X H, He Z K. Facile synthesis of stable CdTe/CdS QDs using dithiol as surface ligand for alkaline phosphatase detection based on inner filter effect. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2019;1047:208–213. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2018.10.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [27].Chen W, Habibul N, Liu X Y, Sheng G P, Yu H Q. FTIR and synchronous fluorescence heterospectral two-dimensional correlation analyses on the binding characteristics of copper onto dissolved organic matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015;49:2052–2058. doi: 10.1021/es5049495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [28].Zhao D, Li J, Peng C Y, Zhu S Y, Sun J, Yang X R. Fluorescence immunoassay based on the alkaline phosphatase triggered in situ fluorogenic reaction of o-phenylenediamine and ascorbic acid. Anal. Chem. 2019;91:2978–2984. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.8b05203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [29].Wei Q S, Zhou D X, Li X Q, Chen Y W, Bian H T. Structural dynamics of dimethyl sulfoxide aqueous solutions investigated by ultrafast infrared spectroscopy: Using thiocyanate anion as a local vibrational probe. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2018;122:12131–12138. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.8b10058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [30].Vu H P, Moreau J W. Thiocyanate adsorption on ferrihydrite and its fate during ferrihydrite transformation to hematite and goethite. Chemosphere. 2011;119:987–993. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.09.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [31].Castro M C, Gurzenda S, Turra C M, Kim S, Andrasfay T, Goldman N. Reduction in life expectancy in Brazil after COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2021;27:1629–1635. doi: 10.1038/s41591-021-01437-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [32].Yang Y, Yang M H, Yuan J, Wang F X, Wang Z Q, Li J X, Zhang M X, Xing L, Wei J L, Peng L, et al. Laboratory diagnosis and monitoring the viral shedding of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Innovation. 2020;1:100061. doi: 10.1016/j.xinn.2020.100061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [33].Dinnes J, Deeks J J, Berhane S, Taylor M, Adriano A, Davenport C, Dittrich S, Emperador D, Takwoingi Y, Cunningham J, et al. Rapid, point-of-care antigen and molecular-based tests for diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021;2021:CD013705. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013705.pub2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [34].Kang S S, Yang M, Hong Z S, Zhang L P, Huang Z X, Chen X X, He S H, Zhou Z L, Zhou Z C, Chen Q Y, et al. Crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein RNA binding domain reveals potential unique drug targeting sites. Acta Pharm. Sin. B. 2020;10:1228–1238. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.04.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Ratiometric fluorescence immunoassay of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein via Si-FITC nanoprobe-based inner filter effect