Abstract
Background
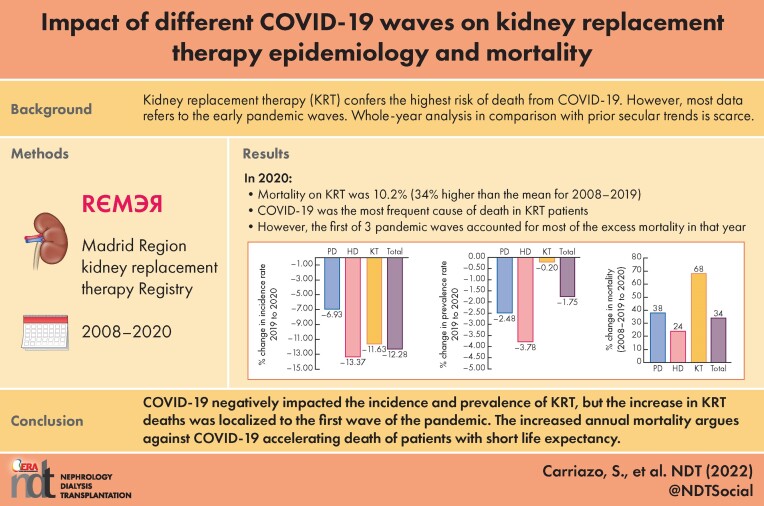
Kidney replacement therapy (KRT) confers the highest risk of death from COVID-19. However, most data refer to the early pandemic waves. Whole year analysis in comparison with prior secular trends are scarce.
Methods
We present the 2020 REMER Madrid KRT registry, corresponding to the Spanish Region hardest hit by COVID-19.
Results
In 2020, KRT incidence decreased 12% versus 2019 while KRT prevalence decreased (−1.75%) for the first time since records began and the number of kidney transplants (KT) decreased by 16%. Mortality on KRT was 10.2% (34% higher than the mean for 2008–2019). The 2019 to 2020 increase in mortality was larger for KT (+68%) than for HD (+24%) or PD (+38%). The most common cause of death was infection (n = 419, 48% of deaths), followed by cardiovascular (200, 23%). Deaths from infection increased by 167% year over year and accounted for 95% of excess deaths in 2020 over 2019. COVID-19 was the most common cause of death (68% of infection deaths, 33% of total deaths). The bulk of COVID-19 deaths (209/285, 73%) occurred during the first COVID-19 wave, which roughly accounted for the increased mortality in 2020. Being a KT recipient was an independent risk factor for COVID-19 death.
Conclusions
COVID-19 negatively impacted the incidence and prevalence of KRT, but the increase in KRT deaths was localized to the first wave of the pandemic. The increased annual mortality argues against COVID-19 accelerating death of patients with short life expectancy and the temporal pattern of COVID-19 mortality suggests that appropriate healthcare may improve outcomes.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease, COVID-19, hemodialysis, kidney replacement therapy, kidney transplantation, mortality, peritoneal dialysis
Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract.
Contributor Information
Sol Carriazo, Department of Nephrology and Hypertension, IIS-Fundacion Jimenez Diaz UAM, Madrid, Spain; RICORS2040; Madrid, Spain.
Manuel I Aparicio-Madre, RЄMЭЯ. Oficina Regional de Coordinación de Trasplantes de la Comunidad de Madrid, Madrid, Spain.
Fernando Tornero-Molina, Hospital del Sureste; Madrid, Spain.
Milagros Fernández-Lucas, Hospital Universitario Ramón y Cajal. Universidad de Alcalá, IRYCIS. Madrid, Spain.
Vicente Paraiso-Cuevas, Hospital del Henares, Madrid, Spain.
Emilio González-Parra, Department of Nephrology and Hypertension, IIS-Fundacion Jimenez Diaz UAM, Madrid, Spain; RICORS2040; Madrid, Spain; Departamento de Medicina, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, 28049 Madrid, Spain.
Francisco del Río-Gallegos, RЄMЭЯ. Oficina Regional de Coordinación de Trasplantes de la Comunidad de Madrid, Madrid, Spain.
María Marques-Vidas, Departamento de Medicina, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, 28049 Madrid, Spain; Hospital Puerta de Hierro; Madrid, Spain.
Roberto Alcázar-Arroyo, Hospital Infanta Leonor; Madrid, Spain.
Judith Martins-Muñoz, Hospital de Getafe; Madrid, Spain.
Rafael Sánchez-Villanueva, Hospital La Paz, Madrid, Spain.
Beatriz Gil-Casares, Hospital del Sureste; Madrid, Spain.
Eduardo Gutiérrez-Martínez, Hospital 12 de Octubre; Madrid, Spain.
María Pilar Martínez-Rubio, Centro de Diálisis El Pilar; Madrid, Spain.
Alberto Ortiz, Department of Nephrology and Hypertension, IIS-Fundacion Jimenez Diaz UAM, Madrid, Spain; RICORS2040; Madrid, Spain; Departamento de Medicina, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, 28049 Madrid, Spain.
REMER:
Maria Ángeles Goicoechea Diezhandino, María Luisa Rodriguez Ferrero, Soraya Abad Estébanez, Milagros Fernández Lucas, Nuria Rodríguez Mendiola, Martha Díaz Domínguez, Sandra Elias Triviño, Victor Burguera Vion, Carlos Jiménez Martín, Auxiliadora Bajo Rubio, Rafael Selgas Gutiérrez, Ángel Alonso Melgar, Laura Espinosa Román, José María Portolés Pérez, Beatriz Sánchez Sobrino, Rosario Llópez Carratalá, José Antonio Herrero Calvo, Isabel Pérez Flores, Ana Isabel Sánchez Fructuoso, Paula Jara Caro-Espada, Da Elena Gutiérrez Solís, Catalina Martín-Cleary, Ana Ramos Verde, Jesús Hernández Pérez, Guillermina Barril Cuadrado, Martín Giorgi González, Antonio Fernández Perpén, Cristina Bernis Carro, Patricia Martínez Miguel, María Fuensanta Moreno Barrio, Hanane Bouarich, María Pérez Fernández, Enrique Gruss Vergara, Gema María Fernández Juárez, Eduardo Gallego Valcarce, Ana Tato Ribera, Juan Carlos Herrero Berrón, María Teresa Naya Nieto, Alfonso Cubas Alcaraz, Fernando Tornero Molina, Beatriz Gil-Casares Casanova, Elda Besada Estévez, Vicente Paraíso Cuevas, Jesús Benito García, Alicia García Pérez, Valeria Sáiz Prestel, Patricia de Sequera Ortiz, Rocío Echarri Carrillo, M Covadonga Hevia Ojanguren, Ma del Carmen Jiménez Herrero, Simona Alexandru, Saúl Enrique Pampa Saico, Rosa Sánchez Hernández, Rocío Zamora González-Mariño, Laura Rodríguez-Osorio Jiménez, Beatriz Durá Gurpide, Elisa Ruiz Cicero, Cristina Albarracín Sierra, Ramón Delgado Lillo, María Delgado Yagüe, D Jorge Valencia Alonso, Raquel Gota Ángel, Aurelio Sanz Guajardo, Carlos Jiménez Martín, Jesús Hernández Pérez, Karina Ruth Furaz Czerpak, Ángel Agustín Méndez Abreu, Ana Botella Lorenzo, Javier Naranjo Sanz, María Teresa Villaverde Ares, Sandra Castellano Gasch, María del Pilar Martínez Rubio, Patricia Nora Estrada Villanueva, José Ramón Berlanga Alvarado, Ana María Blanco Santos, Carmen Gámez Matías, Pablo Mateos Hernández, and Marta Sanz Sainz
Supplementary Material
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.