Abstract
Introduction:
The role of parenchyma-sparing resections (PSR) and lymph node dissection in small (<3cm) non-functional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PNET) is unlikely to be studied in a prospective randomized clinical trial. By combining data from 4 high volume pancreatic centers we compared postoperative and long-term outcomes of patients who underwent PSR with patients who underwent oncologic resections.
Patients and Methods:
Retrospective review of prospectively collected clinicopathologic data of patients who underwent pancreatectomy between 2000 and 2021 was collected from four high volume institutions. Parenchyma- and lymph node-sparing resections (enucleation and central pancreatectomy) were compared to those who underwent oncologic resections with lymphadenectomy (pancreaticoduodenectomy, distal pancreatectomy). Statistical testing was performed using Chi- squared test and t test, survival estimates with Kaplan Meier method and multivariate analysis using Cox proportional hazard model.
Results:
Of 810 patients with small sporadic non-functional PNETs, 121 (14.9%) had enucleations, 100 (12.3%) had central pancreatectomies and 589 (72.7%) patients underwent oncologic resections. The median age was 59 years and 48.2% were female with a median tumor size of 2.5 cm. After case- control matching for tumor size, 221 patients were selected in each group. Patients with PSR were more likely to undergo minimally invasive operations (32.6% vs. 13.6%, p<0.001), had less intraoperative blood loss (358 ml vs. 511 ml, p<0.001) and had shorter operative times (180 min vs. 330 min, p<0.001) than patients undergoing oncologic resections. While the mean number of lymph nodes harvested was lower for PSR (n=1.4 vs. n=9.9, p<0.001), the mean number of positive lymph nodes was equivalent to oncologic resections (n=1.1 vs. n=0.9, p=0.808). Although the rate of all postoperative complications was similar for PSR and oncologic resections (38.5% vs. 48.2%, p=0.090), it was higher for central pancreatectomies (38.5% vs. 56.6%, p=0.003). Long-term median disease-free survival (DFS) (190.5 m vs. 195.2 m, p=0.506) and overall survival (OS) (197.9 m vs. 192.6 m, p=0.372) were comparable.
Of the 810 patients 136 (16.7%) had no lymph nodes resected. These patients experienced less blood loss, shorter operations (p<0.001), and lower postoperative complication rates as compared to patients who had lymphadenectomies (39.7% vs. 56.9%, p=0.008). Median DFS (197.1m vs. 191.9m, p=0.837) and OS (200m vs. 195.1m, p=0.827) were similar for patients with no lymph nodes resected and patients with negative lymph nodes (N0) after lymphadenectomy.
Conclusion:
In small <3cm non-functional PNETs, parenchyma- and lymph node-sparing resections are associated with lower blood loss, shorter operative times, and lower complication rates when compared to oncologic resections, and have similar long-term oncologic outcomes.
Mini-Abstract
The aim of the study is to compare postoperative and long-term outcomes of patients who underwent parenchyma-sparing resections with patients who underwent oncologic resections for pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. In small non-functional PNETs, parenchyma-sparing resections are associated with lower blood loss, shorter operative times, and lower complication rates when compared to oncologic resections, and have similar long-term oncologic outcomes.
Introduction
Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PNET) are a rare entity and represent only 1–2% of all pancreatic neoplasms1,2. The majority of PNETs are non-functional and identified incidentally3. A small percentage are functional or symptomatic and require surgical resection4. However, the management of small sporadic non-functional PNETs continues to be controversial. Small retrospective studies with limited follow-up suggest that observation is equivalent to resection in small PNETs <2cm5–7. The European Neuroendocrine Tumor Society (ENETS) Guidelines and the North American Neuroendocrine Tumor Society Consensus Guidelines, however, propose parenchyma-sparing resections (PSR) like enucleation or central pancreatectomy for sporadic non-functional PNETs smaller than 2cm8,9. Yet, the long-term outcomes of PSR and oncologic resections have never been studied in a clinical trial.
The advantage of PSR includes preservation of endocrine and exocrine pancreatic function10. However, these procedures bear a higher risk of positive resection margins and do not include oncologic lymph node dissections11. Currently, insufficient data exist in the literature to determine whether parenchyma-sparing resections or oncologic resections portend an improved disease-free and overall survival.
The role of PSR and lymph node dissection in small (<3cm) non-functional PNETs is unlikely to be studied in a prospective randomized clinical trial. By combining data from 4 high volume centers we aimed to determine the long-term oncologic outcomes of patients who underwent PSR to patients who underwent oncologic resections for PNETs <3cm.
Methods
Patients and study parameters
Approval for the study was obtained from the IRB of all participating institutions. Patients who underwent PSR (enucleation, central pancreatectomy) or oncologic resections (pancreatoduodenectomy (PD), distal pancreatectomy, or total pancreatectomy) for PNETs were identified from prospectively maintained databases of the participating centers. Patients with functional tumors, hereditary syndromes, multifocal disease, distant metastases, and tumors larger than 3cm were excluded from the study. The study period spanned from 2000 to 2021. The following patient baseline parameters were obtained: age, gender, ASA score, body mass index (BMI). ASA score was dichotomized as I-II and III-IV. Operative procedures were PSR such as enucleation and central pancreatectomy as well as oncologic resections including pancreatoduodenectomy, distal and total pancreatectomy. At all centers, patients were considered for a PSR when it appeared technically feasible and there was no evidence of potential lymph node metastasis. Operative parameters analyzed in the study were minimal-invasive procedures, intraoperative blood loss in ml and operation time in min. Lymph node resection was classified as lymph node-sparing resection, lymph node resection with negative lymph nodes and lymph node resection with positive lymph nodes. Lymph node-sparing resections were performed if the multidisciplinary team determined lymph node involvement as unlikely and decided to perform neither standard lymphadenectomy nor lymph node sampling.
Histopathological parameters evaluated in the analysis were tumor size, T stage, N stage, Ki-67 index, grading according to the 2010 WHO classification12, R status, number of lymph nodes harvested, number of positive lymph nodes, lymphovascular invasion and perineural invasion (PNI). T stage was dichotomized as T1–2 versus T3–4 and grading was dichotomized as G1 versus G2–3. Ki-67 index was dichotomized to Ki-67 index <3 and >3. R status was according to UICC/AJCC criteria as R0 if no tumor cells were detected at the resection margin versus R1 if tumor cells were present less than 1mm from the resection margin13. TNM staging was performed according to the 8th edition of the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC)14. Postoperative parameters were postoperative complications, postoperative morbidity according to the Clavien-Dindo Classification, clinically relevant postoperative pancreatic fistula (POPF)15, postoperative pancreatic hemorrhage (PPH)16, delayed gastric emptying (DGE)17, reoperation postoperative mortality within 30 days. Overall survival time was defined from surgery until death of any cause, and disease-free survival was from surgery until recurrence.
Statistics
Descriptive missing data analysis with percentage missing data per variable and per case as well as missing data patterns was performed. Assuming missing as random process, multiple imputations for missing data using the chained equations method was implemented with the R package mice for data imputation18 in case of less than 10% missing data per variable and per case18. Continuous and categorical variables were expressed as mean/standard error and absolute/relative frequencies. A 1:1 propensity score-based matching was performed for baseline parameters of patients with PSR and oncological resection (variables: age, gender, ASA score, BMI). A1:1 matching of both groups for tumor size was based on the ‘nearest-neighbor method’. Statistical testing was performed by Chi- squared test for categorial variables, and Student t test for continuous variables. Median overall and recurrence-free survival estimates were determined with Kaplan Meier method, and log-rank-test and survival analyses were performed with Cox proportional hazard model. The significance level was set to p < 0.05 (two-sided). All confidence intervals (CI) reported were 95% confidence intervals. For statistical analysis, IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, version 25, was used.
Results
Patient baseline parameters
A total of 1742 patients underwent pancreatic resections for PNETs from 2000 to 2021 and were identified from prospectively maintained databases at the four participating centers. After excluding patients with distant metastasis, multifocal PNETs, hereditary syndromes, functional tumors and a tumor size of more than 3 cm, 810 patients remained and were included in the study. PSR were performed in 221 (27.3%) patients, while 589 (72.7%) underwent oncologic resections. Median age was 59 years and 392 (48.4%) patients were female. Baseline characteristics and histopathological parameters of these patients are displayed in table 1.
Table 1.
Baseline, operative and histopathological parameters of patients who underwent parenchyma- sparing resections versus oncologic resections
| Baseline and Operative Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total cohort | PSR | Oncologic resection | ||
| Total n | 810 (100.0) | 221 (27.3) | 589 (72.7) | |
| Parameter | n(%)/mean (SE) | n(%)/mean (SE) | n(%)/mean (SE) | p-value |
| Age in years | 59 (0.90) | 55 (0.95) | 53 (0.91) | 0.731 |
| Gender | ||||
| Female | 392 (48.4) | 110 (49.8) | 282 (47.9) | 0.618 |
| ASA score | ||||
| III-IV | 352 (43.4) | 93 (43.9) | 259 (44.0) | 0.999 |
| BMI in kg/m2 | 30.4 (1.13) | 30.3 (0.7) | 30.5 (1.22) | 0.208 |
| Minimal invasive procedures | 296 (36.5) | 72 (32.6) | 224 (38.0) | 0.29 |
| Blood loss (ml) | 374.3 (29.3) | 209.1 (24.8) | 411.2 (30.3) | <0.001 |
| Operative time(min) | 259.0 (7.2) | 180 (8.3) | 272.6 (6.3) | <0.001 |
| Histopathological parameters | ||||
| WHO Grading | ||||
| G1 | 626 (77.3) | 192 (86.8) | 434 (73.7) | |
| G2 | 168 (20.8) | 28 (12.7) | 140 (23.8) | |
| G3 | 16 (1.9) | 1 (0.4) | 15 (2.5) | <0.001 |
| Ki-67 Index | ||||
| >3 | 195 (24.1) | 29 (13.1) | 166 (28.5) | 0.002 |
| Vascular invasion | 155 (19.3) | 28 (13.9) | 127 (21.6) | 0.011 |
| Perineural invasion | 168 (20.7) | 18 (8.9) | 150 (25.5) | <0.001 |
| Lymph nodes harvested | ||||
| Yes | 674 (83.3) | 111 (40.2) | 550 (93.4) | <0.001 |
| Number of lymph nodes harvested | 11.9 (0.3) | 1.4 (0.2) | 14.0 (0.4) | <0.001 |
| Lymph nodes positive | 0.9 (0.07) | 0.9 (0.09) | 1.59 (0.07) | 0.127 |
| Positive nodal status | 128 (15.8) | 15 (18.5) | 113 (19.2) | 0.988 |
| T stage (AJCC 8th ed.) | ||||
| T3–4 | 126 (15.4) | 19 (8.6) | 107 (18.1) | 0.049 |
| R status | ||||
| R+ | 95 (11.7) | 58 (26.2) | 37 (6.3) | <0.001 |
PSR: Parenchyma-sparing resection; ASA: American Society of Anesthesiologists; BMI: Body mass index
For these 810 patients the median follow-up time was 208 months, disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS) were 180 months and 195 months (Fig. 1). On multivariate analysis Ki67 index (HR 6.482, 95%CI 1.947–8.978, p=0.002) and vascular invasion (HR 2.875, 95%CI 1.191–6.943, p=0.019) are prognostic for DFS, while ASA score (HR 4.045, 95%CI 1.753–9.332, p=0.001) is prognostic for OS. A total of 128 patients (15.8%) had positive lymph nodes (N+). As compared to patients with N0 (n=546), N+ patients experienced a shorter DFS (117.1 m vs. 191.9 m, p<0.001) and OS (169.1 m vs. 195.1 m, p<0.001).
Figure 1.
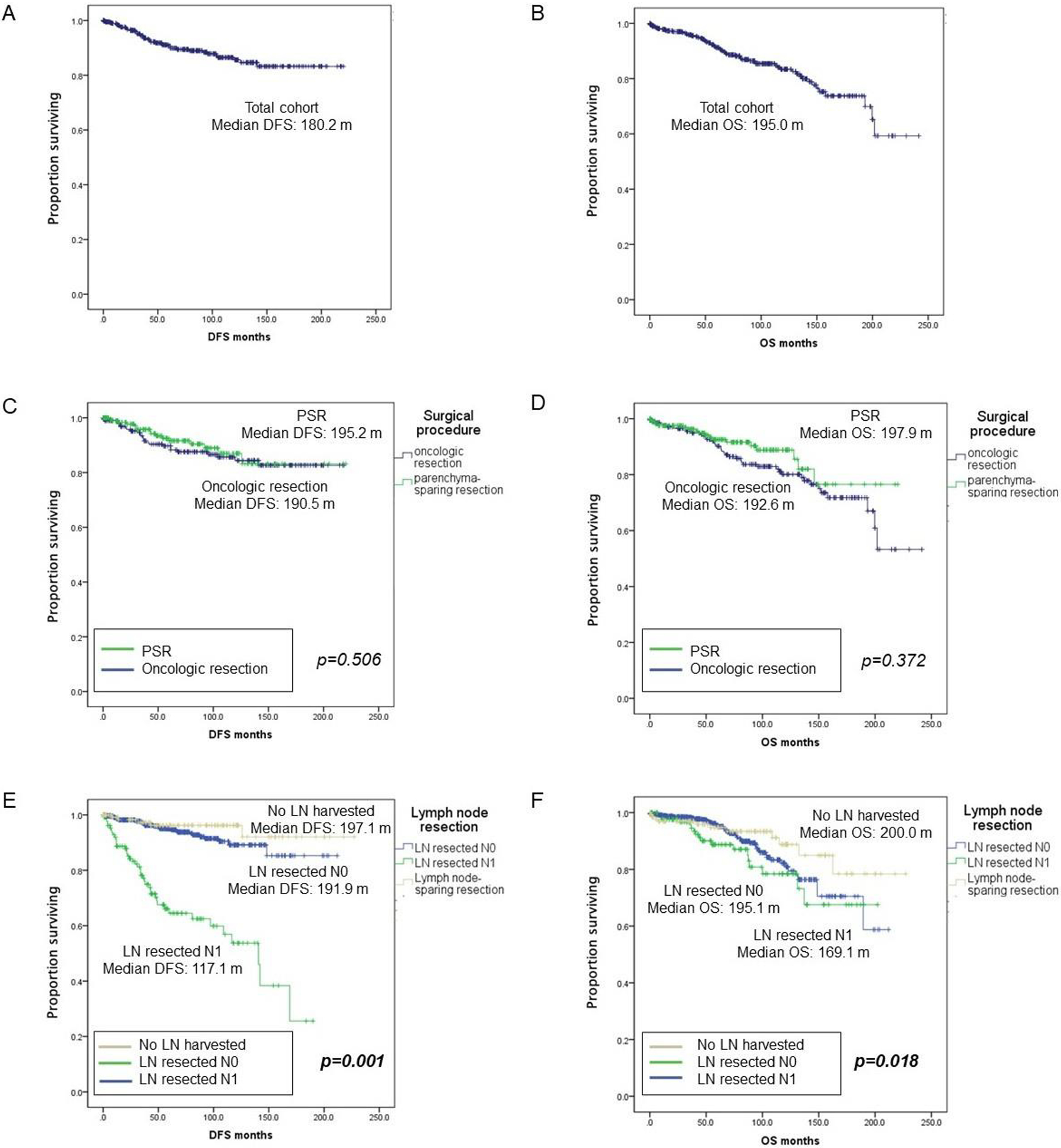
Disease-free-survival in patients undergoing oncologic resections versus parenchyma- sparing resections and no lymph node resection versus lymph node resections
PSR: Parenchyma-sparing resection, LN: lymph node; DFS: Disease-free survival; OS: Overall survival
Propensity score-based matching
For propensity score matching 221 patients with PSR were compared to 221 patients undergoing oncologic resections. Baseline parameters including age, gender, ASA score, and BMI were well- balanced in the two groups (Table 2). For patients undergoing PSR 121 patients (14.9%) had an enucleation and 100 patients (12.3%) had a central pancreatectomy, while for those undergoing oncologic resections 75 had a pancreatoduodenectomy (33.9%), 144 a distal pancreatectomy (65.1%) and 2 a total pancreatectomy (1.0%). PSR were more frequently performed minimally-invasively than oncologic resections (32.6% vs. 13.6%, p<0.001). Patients undergoing PSR experienced reduced blood loss (mean 209.1 ml vs. 511.2 ml, p<0.001) and shorter operative times (mean 180 min vs. 330 min, p<0.001) than patients undergoing oncologic resections.
Table 2.
Baseline and operative parameters of matched patients who underwent parenchyma-sparing resections versus oncologic resections
| Baseline and Operative Parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| PSR | Oncologic resection | ||
| Total n | 221 (50.0) | 221 (50.0) | |
| Parameter | n(%)/mean (SE) | n(%)/mean (SE) | p-value |
| Age in years | 55 (0.95) | 55 (0.99) | 0.842 |
| Gender | |||
| Female | 110 (49.8) | 106 (48.0) | 0.775 |
| ASA score | |||
| III-IV | 93 (43.9) | 101 (45.7) | 0.419 |
| BMI in kg/m2 | 30.3 (0.7) | 29.2 (1.65) | 0.555 |
| Minimal invasive procedures | 72 (32.6) | 30 (13.6) | <0.001 |
| Blood loss in ml | 209.1 (24.8) | 511.2 (37.4) | <0.001 |
| Operative time in min | 180.0 (8.3) | 330.0 (23.2) | <0.001 |
| Tumor size in cm | 2.1 (0.10) | 2.1 (0.11) | 0.999 |
| Histopathological parameters | |||
| WHO Grading | |||
| G1 | 192 (86.8) | 169 (76.4) | |
| G2 | 28 (12.7) | 48 (21.7) | |
| G3 | 1 (0.4) | 4 (1.9) | <0.001 |
| Ki-67 Index | |||
| >3 | 29 (13.1) | 41 (18.6)) | <0.001 |
| Vascular invasion | 28 (13.9) | 41 (20.9) | 0.065 |
| Perineural invasion | 18 (8.9) | 42 (21.8) | <0.001 |
| Lymph nodes harvested | |||
| Yes | 111 (40.2) | 195 (88.2) | <0.001 |
| Number of lymph nodes harvested | 1.4 (0.2) | 9.9 (0.6) | <0.001 |
| Lymph nodes positive | 0.9 (0.09) | 1.1 (0.08) | 0.808 |
| Positive nodal status | 15 (6.7) | 17 (7.7) | 0.999 |
| T stage (AJCC 8th ed.) | |||
| T3–4 | 19 (8.6) | 44 (20.4) | <0.001 |
| R status | |||
| R+ | 58 (26.2) | 18 (8.1) | <0.001 |
PSR: Parenchyma-sparing resection; ASA: American Society of Anesthesiologists; BMI: Body mass index
Histopathology
Despite propensity score matching, patients undergoing PSR had a lower rate of T3–4 tumors (8.6% vs. 20.4%, p<0.001) and had a higher R+ resection rate (26.2% vs. 8.1%, p<0.001) than patients who had oncologic resections (Table 2). PSR resulted in a lower number of lymph nodes harvested (median 0 vs. 9, p<0.001), however, the median number of positive lymph nodes (0 vs. 0, p=0.808) and the rate of N1 disease (6.7% vs. 7.7%, p=0.999) did not differ between patients undergoing PSR or oncologic resections. High risk features such as perineural invasion (8.9% vs. 21.8%, p<0.001), WHO grade 2–3 tumors (13.1% vs. 23.6%, p<0.001) and Ki-67 >3 (13.1% vs. 18.6%, p<0.001) were also less commonly identified in PNETs undergoing PSR as compared to oncologic resections in the matched cohorts.
Long-term Outcomes
OS and DFS did not differ between patients undergoing a PSR or an oncologic resection in the matched cohorts (Fig. 1). Interestingly when examining the whole cohort of 810 patients, as well as the two subgroups, DFS did not differ between patients with negative and those with microscopically positive resection margins (R0 193 m vs. R1 152 m, p=0.90). A total of 95 (11.7%) patients had positive resection margins, of which 58 patients had PSR. Unlike DFS, OS for the total cohort of patients was decreased in patients with positive margins as compared to those with negative resection margins (204 m vs. 144 m, p<0.001). Importantly, margin status did not affect OS in patients with negative lymph nodes (n=410, R0 208.6 m vs. R1 201.8 m, p=0.65), but did for patients with positive resection margins (n= 32, R0 172.8 m vs. R1 110.2 m, p=0.05) (Table 3).
Table 3.
R status, lymph node status and overall survival
| Univariate analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median OS | HR | 95%Cl (lower, upper) | p-value | |
| Total cohort, N0 (n=410) | ||||
| R Status | ||||
| R0 | 208.6 | |||
| R+ | 201.8 | 1.654 | 0.191, 4.321 | 0.648 |
| Parenchyma-sparing resections, N0 (n=66) | ||||
| R Status | ||||
| R0 | 141.2 | |||
| R+ | 120.5 | 2.464 | 0.223, 7.121 | 0.462 |
OS: Overall survival; HR: Hazard ratio; CI: Confidence interval
In the matched cohort, 152 (34.4%) patients had a tumor size of less than 2 cm and 290 (65.6%) patients had tumors larger than 2 cm. DFS for PSR and oncologic resections were equivalent in patients with PNETs < 2cm (PSR 200.4 m vs. oncologic resection 200.6 m, p=0.73) and those > 2cm (PSR 174.6 m vs. oncologic resection 176.3 m, p=0.95). There was also no difference in OS for either procedure in patients with PNETs smaller than 2cm (PSR 210.7 m vs. oncologic resection 215.4 m, p=0.430) or larger than 2cm (PSR 187.2 m vs. oncologic resection 175.1 m, p=0.73).
Postoperative morbidity
Postoperative complication rates for enucleations (n=121) and central pancreatectomies (n=100) were compared to oncologic resections (Table 4). Enucleations demonstrated a trend for higher postoperative complication rates (48.4% vs. 38.5%, p=0.09) and higher rates of severe postoperative complications >IIIA according to the Clavien-Dindo Classification (19.0% vs. 11.8%, p=0.08), but not an increase in 30 day post operative mortality. The most common severe complications were POPF grade B-C in 21.3% of patients with enucleations. There was a trend for higher POPF grade B-C rates in patients with enucleations as compared to oncologic resections (21.3% vs. 8.1%, p=0.09). There was no difference for DGE or PPH.
Table 4.
Postoperative morbidity in enucleations vs. oncologic resections and central pancreatectomies vs. oncologic resections
| Postoperative complications | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Oncologic resections | Enucleations | ||
| Total n | 221 | 121 | |
| Parameter | n(%)/mean (SE) | n(%)/mean (SE) | p-value |
| Postoperative complications | |||
| No | 136 (61.5) | 62 (51.6) | |
| Yes | 85 (38.5) | 59 (48.4) | 0.087 |
| Clavien Dindo Classification | |||
| 0-IIB | 195 (88.2) | 97 (81.0) | |
| IIIA-IVB | 26 (11.8) | 23 (19.0) | 0.077 |
| POPF grade B/C | 18 (8.1) | 26 (21.3) | 0.098 |
| DGE | 6 (2.7) | 5 (4.1) | 0.313 |
| PPH | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.8) | 0.876 |
| Reoperation | 1 (0.5) | 0 (0.0) | 0.999 |
| Postoperative | |||
| 30 day mortality | 1 (0.5) | 0 (0.0) | 0.999 |
| Length of stay (days) | 7.3 (5.7) | 7.5 (8.1) | 0.832 |
| Readmission within 30 days | 46 (20.1) | 24 (19.8) | 0.134 |
| Oncologic resections | Central pancreatectomies | ||
| Total n | 221 | 100 | |
| Parameter | n(%)/mean (SE) | n(%)/mean (SE) | p-value |
| Postoperative complications | |||
| No | 136 (61.5) | 43 (43.4) | |
| Yes | 85 (38.5) | 56 (56.6) | 0.003 |
| Clavien Dindo Classification | |||
| 0-IIB | 195 (88.2) | 80 (80.8) | |
| IIIA-IVB | 26 (11.8) | 19 (19.2) | 0.044 |
| POPF grade B/C | 18 (8.1) | 20 (20.2) | 0.032 |
| DGE | 6 (2.7) | 4 (4.0) | 0.244 |
| PPH | 0 (0.0) | 5 (5.1) | 0.021 |
| Reoperation | 1 (0.5) | 4 (4.0) | 0.033 |
| Postoperative | |||
| 30 day mortality | 1 (0.5) | 1 (1.1) | 0.524 |
| Length of stay (days) | 7.3 (5.7) | 7.9 (4.8) | 0.252 |
| Readmission within 30 days | 46 (20.1) | 23 (23.0) | 0.305 |
POPF: Postoperative pancreatic fistula; DGE: Delayed gastric emptying; PPH: Postoperative pancreatic hemorrhage
Central pancreatectomies were associated with a higher rate of postoperative morbidity (56.6% vs. 38.5%, p=0.003) and a higher rate of severe postoperative complications >IIIA according to the Clavien Dindo Classification (19.2% vs. 11.8%, p=0.04) as compared to oncologic resections. Central pancreatectomy patients experienced higher rates of POPF grade B/C (20.2% vs. 8.1%, p=0.03) and post-pancreatectomy hemorrhage (5.1% vs. 0.0%, p=0.02) as well as higher reoperation rates (4.0% vs. 0.5%, p=0.03) but no higher 30 day post operative mortality than patients undergoing oncologic resections.
Lymph-node-sparing procedures versus lymph node dissection
In the total cohort of 810 patients, 136 (16.8%) patients had no lymph nodes harvested and 674 patients had at least one lymph node removed. Positive lymph nodes were identified in 128 (15.8%) patients. There were no statistically significant differences in age, gender, BMI and ASA score between patients who had no lymph nodes harvested and those patients undergoing lymph node dissection with negative lymph nodes (LND-N0) and patients undergoing lymph node dissection with positive lymph nodes (LND-N+). Tumors in the group with no LNs harvested and LND-N0 were more often located in the body and tail of the pancreas (83.8% and 64.8%), while the majority of patients in the LND-N+ group had pancreatic head tumors (67.2%, p<0.001). Patients who had no LNs harvested were more likely to undergo PSR as compared to LND-N0 and LND-N+ patients (66.2% vs. 7.3% vs. 4.7%, p<0.001) and more commonly underwent minimally invasive procedures (38.5%). When no LNs were harvested it was associated with reduced blood loss (mean 225.1 ml vs. 378.9 ml vs. 471.4 ml, p<0.001), shorter operative times (mean 177.7 min vs. 262.3 min vs. 297.5 min, p<0.001), and lower rates of postoperative morbidity (39.7% vs. 53.1% vs. 47.0%, p=0.008) as compared to LND- N0 and LND-N+ patients. Patients who had no LNs resected experienced lower rates of DGE (2.4% vs. 12.9% vs. 14.4%, p=0.02), but there was no difference in POPF grade B/C, reoperation rates, or postoperative morbidity when compared to patients undergoing lymph node dissections (Table 5).
Table 5.
Lymph-node-sparing resections versus lymph node dissection: Baseline and operative parameters and morbidity
| No Lymph Nodes resected | Lymph node dissection, N0 | Lymph node dissection, N+ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total n | 136 (16.8) | 546 (67.4) | 128 (15.8) | |
| Parameter | n(%)/mean (SE) | n(%)/mean (SE) | n(%)/mean (SE) | p-value |
| Age in years | 56.2 (1.1) | 58.8 (0.5) | 59.1 (1.1) | 0.065 |
| Sex | ||||
| Female | 66 (48.5) | 72 (56.3) | 250 (45.8) | |
| Male | 70 (51.5) | 56 (43.7) | 296 (54.2) | 0.102 |
| BMI in kg/m2 | 30.8 (0.6) | 29.5 (0.9) | 29.0 (0.9) | 0.311 |
| Tumor Site | ||||
| Head | 17 (12.5) | 185 (33.9) | 86 (67.2) | <0.001 |
| Tail/body | 114 (83.8) | 354 (64.8) | 42 (32.8) | |
| Complete pancreas | 5 (3.7) | 7 (1.3) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Operative parameters | ||||
| Parameter | n(%)/mean (SE) | n(%)/mean (SE) | n(%)/mean (SE) | p-value |
| Minimal invasive | 210 (38.5) | 32 (25.0) | 59 (43.4) | 0.005 |
| procedures Blood loss (ml) | 225.1 (1.2) | 378.9 (2.2) | 471.4 (1.5) | <0.001 |
| Operative time (min) | 177.7 (1.7) | 262.3 (1.4) | 297.5 (1.3) | <0.001 |
| Postoperative complications | ||||
| Postoperative complications | ||||
| No | 82 (60.3) | 256 (56.9) | 55 (43.0) | |
| Yes | 54 (39.7) | 290 (53.1) | 73 (47.0) | 0.008 |
| POPF grade B/C | 20 (14.7) | 100 (18.3) | 18 (14.0) | 0.183 |
| DGE | 2 (2.4) | 50 (12.9) | 13 (14.4) | 0.018 |
| PPH | 2 (4.0) | 4 (2.9) | 3 (8.6) | 0.304 |
| Reoperation | 1 (0.7) | 10 (1.8) | 4 (3.1) | 0.354 |
| 30 day mortality | 1 (0.7) | 2 (0.4) | 0 (0.0) | 0.999 |
| Length of stay (days) | 7.8 (7.5) | 7.3 (4.1) | 6.7 (2.7) | 0.362 |
| 30 day morbidity | 10 (7.3) | 33 (6.0) | 6 (4.6) | 0.446 |
BMI: Body mass index; POPF: Postoperative pancreatic fistula; DGE: Delayed gastric emptying; PPH: Postoperative pancreatic hemorrhage
Patients who had no LNs harvested (n= 136) experienced DFS and OS rates equivalent to N0 patients (n= 546) (197.1 m vs. N0 191.9 m, p=0.74 and 200.0 m vs. N0 195.1 m, p=0.87).
Discussion
The surgical approach to small (<3cm) non-functional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PNET) is unlikely to be studied with a prospective randomized clinical trial. By assembling a large cohort of patients from four high-volume centers we aimed to provide guidance on the oncologic safety and clinical decision making for these patients. We demonstrated that parenchyma-sparing resections (PSR) and lymph node-sparing procedures are oncologically safe for both PNETs < 2cm and those 2–3cm. Despite higher margin positive resection rates in PSR, long-term oncologic outcomes of PSR and oncologic resection were equivalent. In this cohort of 810 patients, oncologic operations such as pancreaticoduodenectomy and distal pancreatectomy increased postoperative morbidity and did not improve patient prognosis.
Improved imaging modalities have led to an increased rate of incidentally discovered small sporadic non-functional PNETs19. While the NANET and ENET guidelines, based on retrospective studies, recommend observation for small non-functioning PNETs <2cm with no evidence of invasion, the surgical management of PNETs <3cm remains controversial20. For lesions <2cm, the ongoing prospective observational trial evaluating oncologic safety of observation in PNETs < 2cm will allow for improved evidence based guidance (ASPEN, NCT03084770)21.
For those patients who are considered for surgical removal of their PNETs PSR compared to oncologic resections have been actively debated. Large cohort studies and meta-analyses have shown that PSR helps to preserve endocrine and exocrine pancreatic function19,22,23. Ideal candidates for PSR are PNETs with low-risk histologic and anatomical features. However, these criteria are not met in all cases, and a negative resection margin cannot always be obtained24. Additionally, a complete oncologic lymph node dissection is difficult to perform when sparing pancreatic parenchyma11. For small sporadic PNETs large cohort studies evaluating the effect of a PSR compared to an oncologic operation on long-term outcomes have not been performed. The role of lymph node dissection has also not been extensively evaluated. Due to these many unanswered questions, the rate of PSR remains low (12–17.7%)25.
To understand if an oncologic operation is required to optimize long-term outcomes for patients with PNETS <3cm we compared patients who underwent PSR such as enucleation or central pancreatectomy to those who had an oncologic resection, such as a Whipple or distal pancreatectomy and splenectomy. Enucleations were associated with the highest rate of positive resection margins, similar to other studies documenting an R1 resection in 16–32%19,25–27. Despite a higher rate of microscopically positive margins (26% vs 8%) and a lower number of lymph nodes harvested with PSR, DFS (190m vs. 195 m) and OS (197 m vs. 192m) were equivalent between the two cohorts.
Interestingly, R status was a determinant of OS but not DFS in the entire cohort of 810 patients (204 m vs. 144 m). Looking at subgroups of N0 and N1 patients, R status remained a prognostic factor for OS only in N1 patients (R0 172.8 m vs. R1 110.2 m). In summary, R status appears not to impact long- term outcomes in patients undergoing PSR or oncologic resections if lymph nodes are not involved, as opposed to patients who have nodal involvement.
Our results compare to smaller cohort studies investigating long-term outcomes and the oncologic safety of PSR. Cherif et al. compared 67 patients with enucleations and central pancreatectomies to 66 patients with standard oncologic resections28. Patients included in this study had a median tumor size of 15 mm (range 3–40mm). The overall and recurrence-free 5-year survival after PSR for non- functional tumors was as high as 96 and 98%. Uccelli et al. evaluated enucleations and central pancreatectomies in 22 patients and did not detect recurrence or death over a short-term follow-up period24. Median tumor size in this cohort was 13mm for enucleations and 30mm for central pancreatectomies. Liu et al. found equivalent long-term outcomes for PSR and oncologic resections in PNETs <2cm29. A wide range of tumor size cut-offs have been proposed in previous studies8,29,30. In this large patient cohort there was no difference in long-term outcomes for PSR or oncologic resections for patients with PNETs < 2cm, as well as those 2–3cm. Our data supports PSR in patients with non-functioning sporadic PNETs smaller than 3cm.
The likelihood of lymph node metastasis in PNETs increases with size. A recent study reported on 210 sporadic PNETs <2cm31. Median tumor size in this study was 15mm and parenchyma-sparing procedures were performed in 42% of the patients. Lymph nodes were harvested in 136 of 210 patients and only 10.6% of patients with harvested lymph nodes had lymph node metastasis.
Recurrence rates are high in lymph node positive patients but remain low in node negative patients with small tumors32. In our study, lymph nodes were harvested in 88.2% of patients undergoing oncologic resections, but in only 40.2% of PSR patients. However, the rate of patients with positive lymph nodes was equivalent in both groups (PSR 6.7% vs. oncologic resection 7.7%) and DFS and OS were similar for both resection types. Irrespective of resection type, patients with positive lymph nodes experienced reduced DFS and OS. Only patients with positive lymph nodes experienced reduced DFS and OS, while those with negative lymph nodes and no lymph nodes resected had equivalent long- term outcomes. Standard lymphadenectomy in all patients with non-functional PNETs smaller than 3cm does not appear to improve long-term outcomes. Instead, careful patient selection for lymph node-sparing resections can help reduce short and long term postoperative morbidity without impairing long-term outcomes in selected patients. Reviewing preoperative imaging for suspicious lymph nodes and performing endoscopic ultrasound guided FNA can help to determine nodal status prior to an operation in patients with small PNETs33. Lymph node-sparing procedures should be considered in patients without suspicious lymph nodes on imaging or high-risk features on endoscopic ultrasound guided FNA.
We demonstrated equivalent disease-free and overall survival for patients undergoing PSR and oncologic resections. Patients who had oncologic resections had higher rates of grade 2–3 tumors, stage T3–4, perineural and lymphovascular invasion. Detailed data on preoperative factors for treatment decision making was unfortunately not available from the registry database. An important requirement for PSR at all centers was the absence of suspicious lymph nodes on pre operative imaging and intra operative evaluation. Despite a higher proportion of high risk pathologic features in patients who had oncologic resections, long-term outcomes did not differ for parenchyma-sparing procedures as compared to oncologic resections.
Our study demonstrated favorable results for PSR in terms of intraoperative blood loss and operative times, however, central pancreatectomies were associated with increased postoperative morbidity, mainly pancreatic fistulas as compared to oncologic resections. Previous studies have shown conflicting results of PSR-related morbidity ranging from high pancreas-specific complications to low overall morbidity10,25,28,29,34. Hüttner et al. performed a meta-analysis of 22 observational studies reporting on oncologic resections and PSR in PNET35. The authors found less blood loss, shorter operative times, and shorter hospital stay in PSR patients and similar rates of postoperative morbidity and mortality for both groups. Heterogeneous results of previous studies may be explained by the different morbidity profiles and varying proportions of enucleations and central pancreatectomies. Our study demonstrated higher postoperative complications rates as well as higher POPF and PPH rates, especially for central pancreatectomies as it involves two pancreatic transection planes in a soft pancreas. Other studies confirmed postoperative morbidity of 54–62% and POPF rates of more than 25% in central pancreatectomies36–39. We therefore recommend carefully weighing postoperative morbidity rates against pancreatic gland preservation when considering patients for central pancreatectomies.
A limitation of this study is its retrospective nature potentially introducing selection and information bias. However, all data in this study was collected in a prospectively maintained database at four high volume centers with extensive experience in the treatment of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. A further limitation of this study is that data on endocrine and exocrine insufficiency after PSR or oncologic resection was not available from the database. Another limitation is the lack of data regarding decision making on parenchyma- and lymph node sparing resection. Preoperative imaging to determine suspicious lymph nodes or local tumor infiltration was unfortunately not available for this study. As a prospective randomized trial is unlikely in this rare tumor entity for PSR, we believe, however, that the current analysis provides meaningful insights and treatment guidance for sporadic PNETs <3cm.
In conclusion, parenchyma-sparing and lymph node-sparing resections are safe in patients with non- functional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors <3cm. Oncologic resections are associated with higher blood loss, longer operative times, and higher complication rates for similar long-term oncologic outcomes. Parenchyma- and lymph node-sparing resections should be considered for patients with non-functional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors <3cm amenable to localized resection and no evidence of lymph node involvement or high-risk features.
Acknowledgement
Loeffler Family Foundation funding of PANDA
Footnotes
Conflicts of Interest and Source of Funding:
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- 1.Halfdanarson TR, Rabe KG, Rubin J, et al. Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PNETs): incidence, prognosis and recent trend toward improved survival. Ann Oncol Off J Eur Soc Med Oncol. 2008;19:1727–1733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Cai L, Michelakos T, Deshpande V, et al. Role of Tumor-Associated Macrophages in the Clinical Course of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors (PanNETs). Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2019;25:2644–2655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Metz DC, Jensen RT. Gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumors: pancreatic endocrine tumors. Gastroenterology. 2008;135:1469–1492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Haynes AB, Deshpande V, Ingkakul T, et al. Implications of incidentally discovered, nonfunctioning pancreatic endocrine tumors: short-term and long-term patient outcomes. Arch Surg Chic Ill 1960. 2011;146:534–538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Zandee WT, de Herder WW. The Evolution of Neuroendocrine Tumor Treatment Reflected by ENETS Guidelines. Neuroendocrinology. 2018;106:357–365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sadot E, Reidy-Lagunes DL, Tang LH, et al. Observation versus Resection for Small Asymptomatic Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors: A Matched Case-Control Study. Ann Surg Oncol. 2016;23:1361–1370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gaujoux S, Partelli S, Maire F, et al. Observational study of natural history of small sporadic nonfunctioning pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98:4784–4789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Falconi M, Eriksson B, Kaltsas G, et al. ENETS Consensus Guidelines Update for the Management of Patients with Functional Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors and Non- Functional Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors. Neuroendocrinology. 2016;103:153–171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Halfdanarson TR, Strosberg JR, Tang L, et al. The North American Neuroendocrine Tumor Society Consensus Guidelines for Surveillance and Medical Management of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors. Pancreas. 2020;49:863–881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Beger HG. Benign Tumors of the Pancreas-Radical Surgery Versus Parenchyma-Sparing Local Resection-the Challenge Facing Surgeons. J Gastrointest Surg Off J Soc Surg Aliment Tract. 2018;22:562–566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Pea A, Tanno L, Nykänen T, et al. Comparison of Oncological and Surgical Outcomes Between Formal Pancreatic Resections and Parenchyma-Sparing Resections for Small PanNETs (<2 cm): Pancreas2000 Research and Educational Program (Course 9) Study Protocol. Front Med. 2020;7:559–559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Rindi G Nomenclature and classification of neuroendocrine neoplasms of the digestive system. WHO Classif Tumours Dig Syst. 2010;13–14. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Raut CP, Tseng JF, Sun CC, et al. Impact of resection status on pattern of failure and survival after pancreaticoduodenectomy for pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg. 2007;246:52–60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Amin MB, Greene FL, Edge SB, et al. The Eighth Edition AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: Continuing to build a bridge from a population-based to a more “personalized” approach to cancer staging. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67:93–99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bassi C, Marchegiani G, Dervenis C, et al. The 2016 update of the International Study Group (ISGPS) definition and grading of postoperative pancreatic fistula: 11 Years After. Surgery. 2017;161:584–591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Wente MN, Veit JA, Bassi C, et al. Postpancreatectomy hemorrhage (PPH)–an international study group of pancreatic surgery (ISGPS) definition. Surgery. 2007;142:20–25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Wente MN, Bassi C, Dervenis C, et al. Delayed gastric emptying (DGE) after pancreatic surgery: a suggested definition by the International Study Group of Pancreatic Surgery (ISGPS). Surgery. 2007;142:761–768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Van Buuren S, Groothuis-Oudshoorn K. mice: Multivariate imputation by chained equations in R. J Stat Softw. 2011;45:1–67. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Landoni L, Marchegiani G, Pollini T, et al. The Evolution of Surgical Strategies for Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors (Pan-NENs): Time-trend and Outcome Analysis From 587 Consecutive Resections at a High-volume Institution. Ann Surg. 2019;269:725–732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Zhang R-C, Ma J, Mou Y-P, et al. Short- and Long-Term Outcomes of Laparoscopic Organ- Sparing Resection for Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms. World J Surg. 2020;44:3795–3800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Partelli S, Ramage JK, Massironi S, et al. Management of Asymptomatic Sporadic Nonfunctioning Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms (ASPEN) ≤2 cm: Study Protocol for a Prospective Observational Study. Front Med. 2020;7:1009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Cherif R, Gaujoux S, Couvelard A, et al. Parenchyma-sparing resections for pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. J Gastrointest Surg Off J Soc Surg Aliment Tract. 2012;16:2045–2055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Mauriello C, Napolitano S, Gambardella C, et al. Conservative management and parenchyma- sparing resections of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: Literature review. Int J Surg Lond Engl. 2015;21 Suppl 1:S10–14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Uccelli F, Gavazzi F, Capretti G, et al. Parenchyma-sparing surgery for pancreatic endocrine tumors. Updat Surg. 2016;68:313–319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Mintziras I, Keck T, Werner J, et al. Indications for resection and perioperative outcomes of surgery for pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms in Germany: an analysis of the prospective DGAV StuDoQ|Pancreas registry. Surg Today. 2019;49:1013–1021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Cienfuegos JA, Rotellar F, Salguero J, et al. A single institution’s 21-year experience with surgically resected pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: an analysis of survival and prognostic factors. Rev Espanola Enfermedades Dig Organo Of Soc Espanola Patol Dig. 2016;108:689–696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Fischer L, Bergmann F, Schimmack S, et al. Outcome of surgery for pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms. Br J Surg. 2014;101:1405–1412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Cherif R, Gaujoux S, Couvelard A, et al. Parenchyma-sparing resections for pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. J Gastrointest Surg Off J Soc Surg Aliment Tract. 2012;16:2045–2055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Liu X, Chin W, Pan C, et al. Risk of malignancy and prognosis of sporadic resected small (≤2 cm) nonfunctional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Gland Surg. 2021;10:219–232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Lindner K, Binte D, Hoeppner J, et al. Resection of Non-Functional Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms-A Single-Center Retrospective Outcome Analysis. Curr Oncol Tor Ont. 2021;28:3071–3080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Sallinen VJ, Le Large TYS, Tieftrunk E, et al. Prognosis of sporadic resected small (≤2 cm) nonfunctional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors - a multi-institutional study. HPB. 2018;20:251–259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Pulvirenti A, Javed AA, Landoni L, et al. Multi-institutional Development and External Validation of a Nomogram to Predict Recurrence After Curative Resection of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors. Ann Surg. 2021;274:1051–1057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Javed AA, Pulvirenti A, Razi S, et al. Grading Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors via Endoscopic Ultrasound-guided Fine Needle Aspiration: A Multi-Institutional Study. Ann Surg. Epub ahead of print January 25, 2022. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000005390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Wolk S, Distler M, Kersting S, et al. Evaluation of central pancreatectomy and pancreatic enucleation as pancreatic resections--A comparison. Int J Surg Lond Engl. 2015;22:118–124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hüttner FJ, Koessler-Ebs J, Hackert T, et al. Meta-analysis of surgical outcome after enucleation versus standard resection for pancreatic neoplasms. Br J Surg. 2015;102:1026–1036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Paiella S, De Pastena M, Faustini F, et al. Central pancreatectomy for benign or low-grade malignant pancreatic lesions - A single-center retrospective analysis of 116 cases. Eur J Surg Oncol J Eur Soc Surg Oncol Br Assoc Surg Oncol. 2019;45:788–792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Dumitrascu T, Barbu ST, Purnichescu-Purtan R, et al. Risk factors for surgical complications after central pancreatectomy. Hepatogastroenterology. 2012;59:592–598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Crippa S, Bassi C, Warshaw AL, et al. Middle pancreatectomy: indications, short- and long-term operative outcomes. Ann Surg. 2007;246:69–76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Hank T, Sandini M, Ferrone CR, et al. Association Between Pancreatic Fistula and Long-term Survival in the Era of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. JAMA Surg. 2019;154:943–951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


