Abstract
Background
Urinary retention remains a frequent postoperative complication, associated with patient discomfort and delayed discharge following general thoracic surgery (GTS). We aimed to develop and prospectively validate a predictive model of postoperative urinary retention (POUR) among GTS patients.
Methods
We retrospectively developed a predictive model using data from the Society of Thoracic Surgeons GTS Database at our institution. The patient study cohort included adults undergoing elective in-patient surgical procedures without a history of renal failure or Foley catheter on entry to the recovery suite (August 2013 to March 2017). Multivariable logistic regression models identified factors associated with urinary retention, and a nomogram to aid medical decision making was developed. The predictive model was validated in a cohort of GTS patients between April 2017 and November 2018 using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis.
Results
The predictive model was developed from 1484 GTS patients, 284 of whom (19%) experienced postoperative urinary retention within 24 hours of the operation. Risk factors for POUR included older age, male sex, higher preoperative creatinine, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, primary diagnosis, primary procedure, and use of postoperative patient-controlled analgesia. A logistic nomogram for estimating the risk of POUR was created and validated in 646 patients, 65 of whom (10%) had urinary retention. The ROC curves of development and validation models had similar favorable c-statistics (0.77 vs 0.72; P > .05).
Conclusions
Postoperative urinary retention occurs in nearly 20% of patients undergoing major GTS. Using a validated predictive model may help by targeting certain patients with prophylactic measures to prevent this complication.
Key Words: urinary retention, postoperative, thoracic surgery
Abbreviations and Acronyms: GTS, general thoracic surgery; POUR, postoperative urinary retention; ROC, receiver operating characteristic; STS, Society of Thoracic Surgeons
Graphical abstract
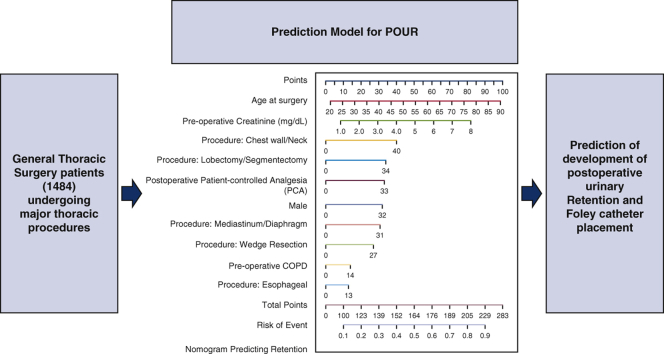
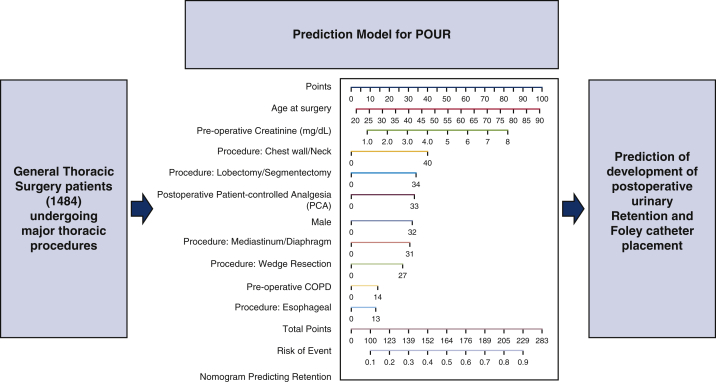
The number of general thoracic surgery patients included to evaluate risk factors for postoperative urinary retention (POUR) using a nomogram to predict patients at risk of POUR.
Nomogram to predict postoperative urinary retention after general thoracic surgery.
Central Message.
Risk factors for postoperative urinary retention following general thoracic surgery procedures were used to develop a nomogram.
Perspective.
In this study, up to one-fifth of patients undergoing general thoracic surgery procedures experienced postoperative urinary retention (POUR). We identified risk factors associated with POUR and developed a nomogram that was then validated. This nomogram can help identify patients at risk of POUR and guide perioperative management.
Postoperative urinary retention (POUR) can result in increased patient morbidity and delayed hospital discharge. Prior studies of POUR have shown an incidence rate of 5% to 70%, and risk factors for POUR have been identified for multiple surgical subspecialties, including general thoracic surgery (GTS).1, 2, 3, 4, 5 Prophylactic pharmacologic and intraoperative practices can be implemented in effort to prevent POUR.6 However, such measures should be reserved for patients at significant risk of POUR to optimize cost and efficiency and prevent patient exposure to the risk of additional side effects, such as urinary tract trauma and infection.7 Quantifying the risk for POUR and developing a predictive model would be a useful aid to the physician's medical decision making process.
In developing a treatment plan, the ideal scenario would improve patient outcomes, minimize risk, and improve efficiency. Although a generalized protocol that serves this purpose in every patient would be ideal, this is not feasible. To most effectively meet these goals, the specific risks for each individual patient must be considered. A commonly used method of quantifying risks for a proposed outcome has been the nomogram.8, 9, 10, 11, 12 Prognostic nomograms assign a score that appropriately allocates the weighted risk of each variable. Kim and colleagues3 previously analyzed potential risk factors for POUR in what they termed “minor thoracic surgery” (only 2 lobectomies were included in the study) and aimed to develop a predictive model for these procedures. Their model included age >40 years, male sex, diabetes mellitus, and lung resection as risk factors for POUR. No such nomogram had been developed to predict POUR following major GTS procedures, however.
We hypothesized that risk factors of POUR can be identified using multivariable risk factor analysis, and that a nomogram could be constructed to help stratify the risk for POUR. We then validated the nomogram to test the predictive ability of our model.
Methods
We used the Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) GTS database to identify patients who underwent GTS procedures between August 1, 2013, and March 31, 2017, at a tertiary medical center.13 Inclusion criteria included age >18 years with at least 1 STS major GTS procedure. Exclusion criteria were age <18 years, same-day discharge, outpatient procedure, intensive care unit admission, preoperative or intraoperative urinary catheter use, preoperative chronic renal dysfunction, and preoperative use of dialysis. The included cases were retrospectively reviewed for POUR, which we defined as the placement of a urinary catheter within 24 hours after surgery. Those who had a urinary catheter placed at >24 hours after surgery were not considered to have POUR. Our protocol was to have a Foley catheter placed in patients who were unable to urinate within 6 hours after arrival to the surgical floor. In-and-out catheterizations were not performed during the study period.
The cohort was then examined for preoperative demographics, comorbidities, diagnoses, operation types, urinary tract factors (ie, history of benign prostatic hyperplasia, history of other urinary tract pathology, and preoperative use of such medications as tamsulosin), preoperative epidural catheter placement, preoperative paravertebral block, postoperative use of patient-controlled analgesia (PCA), laboratory values, clinical characteristics including severity of illness as indicated by Zubrod score (1-5), and intraoperative variables, including duration of operative procedure and volume of intraoperative intravenous fluid administration. Initially, a univariate analysis was conducted for all variables chosen in our study. This analysis was followed by stepwise model selection to create a multivariable logistic regression model that was used to identify key risk factors associated with postoperative urinary retention. The analysis was performed using standard statistical software (SAS version 9.3; SAS Institute, Cary, NC).
Significant risk factors were then used to create a nomogram with assigned scores according to their projected impact on POUR. This was done by subjecting these risk factors to stepwise model selection for further analysis, which allowed us to quantify the degree of risk per variable on a numeric scale. The multivariable logistic regression model values can be used to make sense of the nomogram design. The factors containing the highest odds ratios were assigned the highest score, with the remainder of the variables following suit in a descending fashion. By doing so, each risk is assigned an appropriate score according to its projected impact. Although most of the risk factors are categorical and also binary, age at surgery and preoperative creatinine levels are continuous variables. Therefore, age was set on a scale of 10-year increments by which each 10-year increase in age elicits a higher score on the scale. Similarly, creatinine levels were set to a scale with 1.0 mg/dL increments. The assignment of specific scores per risk factor are designed to allocate the appropriate weight per risk factor, which begins to develop a profile for certain patients that pose increased risk. By gathering the information specified on this tool, physicians can develop an overall predicted risk for POUR. An example of how to use this nomogram is provided in Figure 1, along with the tool.
Figure 1.
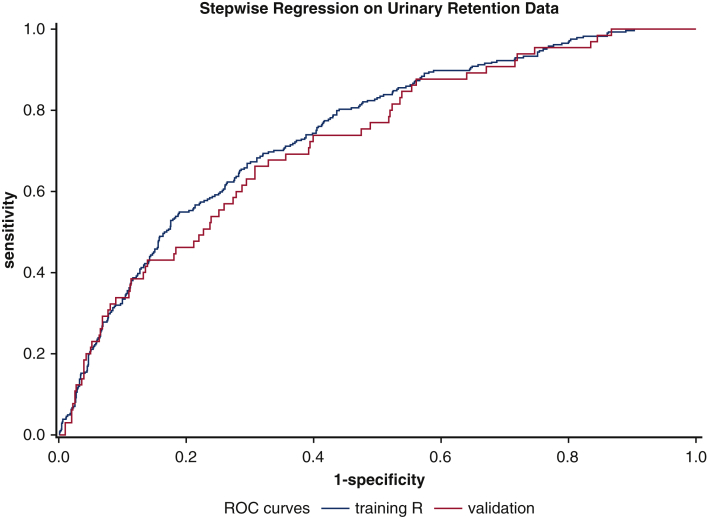
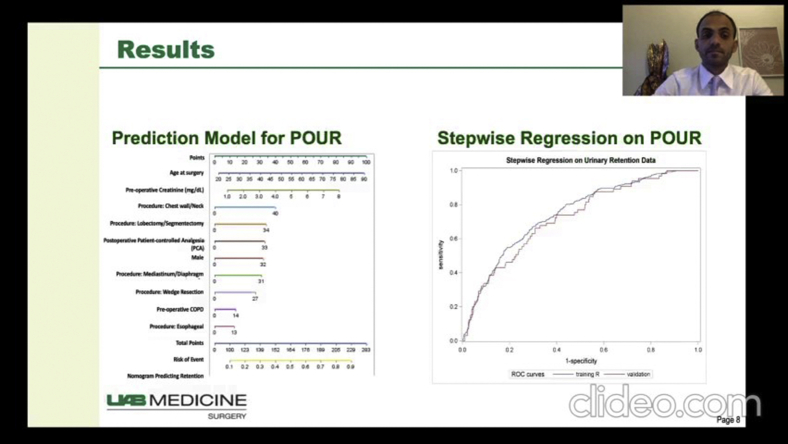
Comparison of ROC curves of training data versus validation data. Training model C-statistic, 0.77 (95% CI, 0.71-0.82); validation model C-statistic, 0.72 (P > .05). ROC, Receiver operating characteristic.
The developed nomogram was then validated using a second cohort from the STS GTSD at the same tertiary medical center with a study period from April 1, 2017, through November 30, 2018. A total of 1452 consecutive GTS procedures were identified and screened using the same process as for the original cohort. The eligible validation cohort went through a simulation process using the developed nomogram to predict the incidence of POUR. Results from the validation cohort were tested by comparing the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) values of study data versus validation data. This project was approved by the University of Alabama at Birmingham's Institutional Review Board (170417003; April 25, 2017).
Patient consent for inclusion in this study and consent to use their information for this research report were included in the general preoperative consent and were not required for Institutional Review Board approval.
Results
The original 5348 identified cases were narrowed down to an eligible study cohort of 1484 cases after the screening process. These procedures included lobectomy/segmentectomy (32%), wedge resection (28%), decortication (12%), and others (28%). The mean patient age was 59 years (range, 18-91 years), 51% were male, and 17% were black. Common comorbidities were hypertension (56%), prior cardiothoracic surgery (37%), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) (25%), and coronary artery disease (17%). The majority of the patients had a Zubrod score of 1 (55%), followed by Zubrod scores of 2 (21%), 0 (17%), 3 (6%), and 4 (1%). The mean (SD) preoperative creatinine concentration was 0.96 (0.45) mg/dL. Nineteen percent of the patients had 24-hour POUR. Table 1 presents the patients' demographic and clinical characteristics. Univariate analysis of STS thoracic procedure type as a risk factor for POUR is shown in Table 2.
Table 1.
Basic cohort demographic and clinical characteristics
| Characteristic | Overall (N = 1484) | Urinary retention (N = 284) | No urinary retention (N = 1200) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographics | ||||
| Age at surgery, y, mean (SD) | 59.1 (15.1) | 65.7 (12.0) | 57.5 (15.3) | <.001 |
| Male sex, n (%) | 51 | 197 (69.4) | 560 (46.7) | <.001 |
| White race, n (%) | 251 (88.4) | 966 (80.5) | .002 | |
| Comorbidities, n (%) | ||||
| Body mass index | 27.9 (6.6) | 27.4 (5.7) | 28.1 (6.8) | .086 |
| Current smoker | 296 (20.0) | 54 (19.0) | 242 (20.3) | .640 |
| Past smoker | 632 (42.7) | 156 (54.9) | 476 (39.8) | <.001 |
| Never smoked | 551 (37.3) | 74 (26.1) | 477 (39.9) | <.001 |
| Diabetes | 284 (19.2) | 61 (21.5) | 223 (18.7) | .279 |
| Hypertension | 828 (56.0) | 188 (66.2) | 640 (53.6) | <.001 |
| Pulmonary hypertension | 24 (1.6) | 4 (1.4) | 20 (1.7) | 1.000 |
| Congestive heart failure | 76 (5.1) | 17 (6.0) | 59 (4.9) | .472 |
| Coronary artery disease | 247 (16.7) | 73 (25.7) | 174 (14.6) | <.001 |
| Peripheral vascular disease | 76 (5.1) | 22 (7.7) | 54 (4.5) | .027 |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | 373 (25.2) | 104 (36.6) | 269 (22.5) | <.001 |
| Transient ischemic attack | 34 (2.3) | 7 (2.5) | 27 (2.3) | .836 |
| Cerebrovascular accident | 44 (3.0) | 10 (3.5) | 34 (2.8) | .547 |
| Prior cardiothoracic surgery | 551 (37.3) | 128 (45.1) | 423 (35.4) | .002 |
| Preoperative chemotherapy, current malignancy | 162 (11.0) | 34 (12.0) | 128 (10.7) | .541 |
| Preoperative thoracic radiation therapy | 147 (9.9) | 32 (11.3) | 115 (9.6) | .405 |
| Interstitial fibrosis | 59 (4.0) | 15 (5.3) | 44 (3.7) | .216 |
| Steroids | 150 (10.1) | 26 (9.2) | 124 (10.4) | .540 |
| Preoperative creatinine level | 1.0 (0.5) | 1.1 (0.6) | 0.9 (0.4) | <.001 |
| Preoperative hemoglobin level | 12.8 (2.1) | 13.2 (2.0) | 12.7 (2.2) | .001 |
| Normal activity, no symptoms | 248 (16.8) | 38 (13.4) | 210 (17.6) | .089 |
| Symptoms, fully ambulatory | 813 (55.0) | 176 (62.0) | 637 (53.3) | .008 |
| Symptoms, in bed ≤50% of the time | 313 (21.2) | 60 (21.1) | 253 (21.2) | .987 |
| Symptoms, in bed >50% but <100% of the time | 94 (6.4) | 9 (3.2) | 85 (7.1) | .014 |
| Bedridden | 11 (0.7) | 1 (0.4) | 10 (0.8) | .701 |
| Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) | 83 (5.6) | 33 (11.7) | 50 (4.2) | <.0001 |
| Any other urinary tract pathology | 109 (7.4) | 24 (8.5) | 85 (7.1) | .417 |
| Preoperative tamsulosin use | 89 (6.0) | 39 (13.8) | 50 (4.2) | <.0001 |
| Other BPH medication use | 17 (1.1) | 6 (2.1) | 11 (0.9) | .088 |
| Intraoperative/postoperative factors | ||||
| Emergent, n (%) | 2 (0.1) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (0.2) | 1.000 |
| Urgent, n (%) | 35 (2.4) | 0 (0.0) | 35 (2.9) | .001 |
| Elective, n (%) | 1444 (97.3) | 284 (100) | 1160 (96.7) | <.001 |
| Palliative, n (%) | 3 (0.2) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (0.3) | 1.000 |
| Duration of procedure, min, mean (SD) | 110.3 (134.2) | 117.7 (107.3) | 108.5 (139.9) | .223 |
| Postoperative patient-controlled analgesia, n (%) | 255 (17.3) | 69 (24.6) | 186 (15.6) | <.001 |
| Preoperative epidural catheter, n (%) | 43 (2.9) | 5 (1.8) | 38 (3.2) | .199 |
| Preoperative paravertebral catheter, n (%) | 106 (7.2) | 23 (8.2) | 83 (7.0) | .490 |
SD, Standard deviation.
Table 2.
Univariate analysis of Society of Thoracic Surgeons thoracic procedure types by 24-hour urinary retention
| Thoracic procedure | Overall (N = 1484), n (%) | Urinary retention (N = 284), n (%) | No urinary retention (N = 1200), n (%) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lobectomy/segmentectomy | 476 (32.1) | 122 (25.6%) | 354 (74.4%) | <.0001 |
| Wedge resection | 401 (27.0) | 76 (19.0) | 325 (81.0) | .9123 |
| Mediastinum/diaphragm | 187 (12.6) | 31 (16.6) | 156 (83.4) | .3412 |
| Decortication | 156 (10.5) | 13 (8.3) | 143 (91.7) | .0003 |
| Esophageal | 76 (5.1) | 15 (19.7) | 61 (80.3) | .8915 |
| Chest wall/neck | 50 (3.4) | 13 (26) | 37 (74) | .2095 |
| Pleura | 44 (3.0) | 6 (13.6) | 38 (86.4) | .3464 |
| Other | 94 (6.3) | 8 (8.5) | 86 (91.5) | .0068 |
| Open procedure | 214 (14.5) | 51 (23.8) | 163 (76.1) | .0582 |
| MIS procedure | 1262 (85.3) | 230 (18.2) | 1032 (81.8) | .0348 |
MIS, Minimally invasive surgical.
On analysis, demographic variables that displayed significantly increased risk when analyzed individually were male sex (P < .001), white race (P = .002), and age (P < .001), with the mean age 8.2 years older in the patients with urinary retention compared with those without urinary retention. Comorbidities with increased risk were past smoker status (P < .001), hypertension (P < .001), coronary artery disease (P < .001), COPD (P < .001), prior cardiac surgery (P = .002), elevated creatinine level (P < .001), Zubrod1 (P = .008), and Zubrod3 (P = .014). History of benign prostatic hyperplasia, preoperative use of tamsulosin, and postoperative use of PCA were also found to be statistically significant risk factors for POUR in univariate analysis. When evaluating specific diagnoses and procedures, the STS procedure groups chest wall, lobectomy/segmentectomy, esophageal surgery, mediastinum/diaphragm, and wedge resection were significant risk factors for POUR. In addition, the majority of patients underwent minimally invasive procedures (significant in decreasing POUR in VATS or robotic; 85.3%), and this variable was found to be statistically in univariate analysis (P = .0348) (Table 2). Variables displaying significantly decreased risk of POUR included having never smoked (P < .001) and elevated hemoglobin level (P = .001).
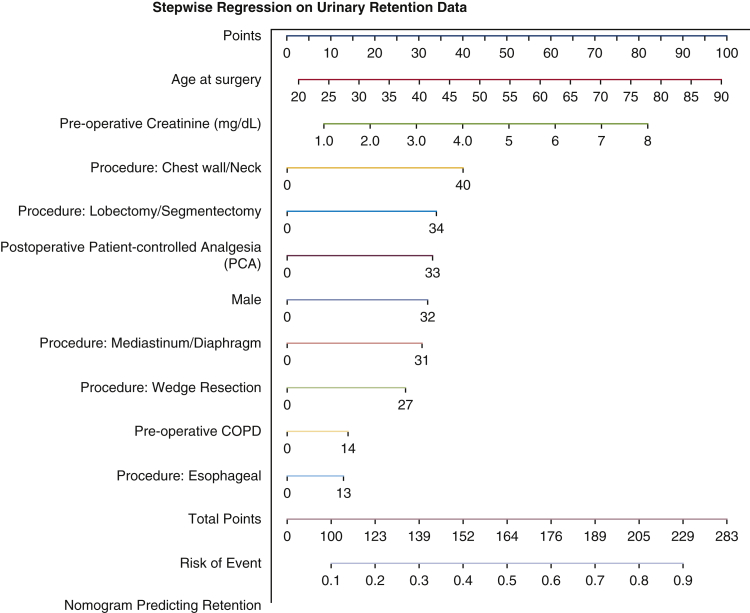
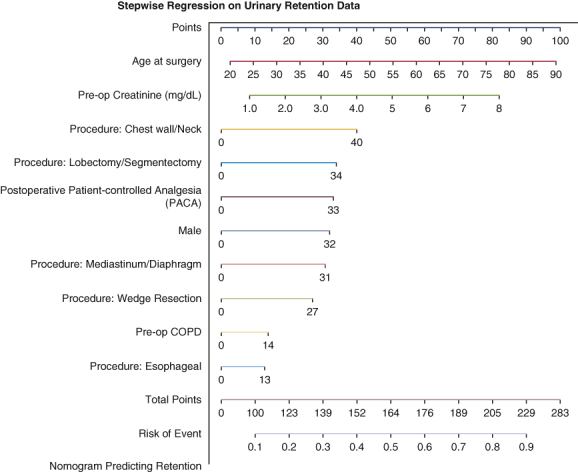
After the initial analysis, a stepwise model selection identified variables for entry into a multivariable logistic regression model (Table 3), which produced an analysis of proposed variables with a significant risk for POUR. The analysis revealed an increased risk of POUR for incremental 10-year increase in age (P < .0001), male sex (P < .001), incremental 1.0 mg/dL increase in creatinine (P = .05), preoperative COPD (P < .01), STS procedure group including chest wall versus other procedures (P < .01), lobectomy/segmentectomy versus other procedures (P < .01), mediastinum/diaphragm versus other procedures (P < .01), wedge resection versus other procedures (P < .01), and postoperative use of PCA (P < .0001) (Table 3). Esophageal versus other procedures and a minimally invasive approach were not found to be significant in the multivariate analysis (Table 3). A prognostic nomogram was constructed using these variables placed on a scale and assigned scores based on the projected risk impact (Figure 2). The patients' POUR predictive factors and outcomes are shown in Figure 3.
Table 3.
Multivariable logistic regression model predicting postoperative 24-hour urinary retention in patients who underwent general thoracic procedures (N = 1480), 2013-2018
| Parameter | Odds ratio (95% confidence interval) | P value |
|---|---|---|
| Age at surgery (10-y increase) | 1.60 (1.41-1.81) | <.0001 |
| Male sex | 2.96 (2.19-3.99) | <.0001 |
| Postoperative patient-controlled analgesia | 3.07 (2.06-4.60) | <.0001 |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | 1.64 (1.20-2.22) | <.01 |
| Last preoperative creatinine (1.0 mg/dL increase) | 1.32 (1.00-1.75) | .05 |
| Procedure group | ||
| Chest wall vs other procedures∗ | 3.90 (1.65-9.18) | <.01 |
| Lobectomy/segmentectomy vs other procedures | 3.20 (1.98-5.18) | <.0001 |
| Mediastinum/diaphragm vs other procedures | 2.84 (1.58-5.11) | <.01 |
| Wedge resection vs other procedures | 2.47 (1.51-4.05) | <.01 |
| Esophageal vs other procedures | 1.54 (0.73-3.29) | .26 |
Other procedures include decortication, pleura, or others not indicated in the procedure groups listed above.
Figure 2.
Nomogram predicting postoperative urinary retention (POUR) in general thoracic surgery patients. The total points for a 65-year-old male patient who had a preoperative creatinine level of 3.0 mg/dL, history of preoperative chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), underwent lobectomy, and had postoperative patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) use, can be calculated as 65 (age) + 32 (male) + 30 (creatinine × 10) + 14 (preoperative COPD) + 34 (lobectomy) + 33 (postoperative PCA) = 208 approximately, with a predicted probability of POUR (indicated by the line of risk of event) around 0.8.
Figure 3.
The number of general thoracic surgery patients included to evaluate risk factors for postoperative urinary retention (POUR) using the nomogram to predict patients at risk of POUR. COPD, Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
A model was created to compare the study cohort with the validation cohort (Table 4), which consisted of 646 consecutive major GTS procedures performed between April 1, 2017, and November 30, 2018. Variables that displayed significant between-group differences were STS esophageal procedure group (P < .0001) and postoperative use of PCA (P < .005). When comparing the ROC curves of the study cohort and the validation cohort (Figure 1), the predictive validation model's C-statistic (0.72) lay within the confidence interval range of the predictive of the study cohort's C-statistic of 0.77 (0.71-0.78).
Table 4.
Characteristics of the training and validation datasets
| Parameter | Training (N = 1484) | Validation (N = 628) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age at surgery, y, mean (SD) | 59.1 (15.1) | 59.0 (15.9) | .9682 |
| Male sex, n (%) | 757 (51.0) | 312 (49.7) | .5765 |
| Postoperative patient-controlled analgesia, n (%) | 255 (17.3) | 78 (12.4) | .0054 |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, n (%) | 373 (25.2) | 112 (21.4) | .0809 |
| Last preoperative creatinine, mg/dL, mean (SD) | 1.0 (0.5) | 1.0 (0.9) | .5056 |
| Procedure group, n (%) | |||
| Chest wall/neck | 50 (3.4) | 24 (3.8) | .6053 |
| Lobectomy/segmentectomy | 476 (32.1) | 192 (30.6) | .4974 |
| Mediastinum/diaphragm | 187 (12.6) | 68 (10.8) | .2530 |
| Wedge resection | 401 (27.0) | 163 (26.0) | .6127 |
| Esophageal | 76 (5.1) | 81 (12.9) | <.0001 |
| Other procedures∗ | 94 (6.3) | 29 (4.6) | .1237 |
SD, Standard deviation.
Other procedures include decortication, pleura, or others not indicated in the procedure groups listed above.
Discussion
In this study, we developed and validated a nomogram that predicts postoperative urinary retention among patients undergoing general thoracic procedures. Our findings show that older age, male sex, postoperative PCA use, higher preoperative creatinine level, COPD, and primary procedure pose significant risks for POUR. The validation process for our study involved identification of a second cohort that would go through the same screening process as our first cohort. When comparing the identified significant risk factors from the study cohort, the 2 cohorts were largely similar; exceptions were a lower percentage of white patients, a higher number of esophageal procedures, and a longer average procedure time (23 minutes longer) in the validation cohort. As shown by the ROC curve comparison, the results from the validation set confirm the findings of our study set within an acceptable range. Both the study set value of 0.77 and the validation set value of 0.72 confirm good models.
POUR is a common adverse outcome following surgery across many different subspecialties, with a reported incidence as high as 70%.2,3 Our definition of POUR (inability to void postoperatively that necessitated required Foley catheter placement within 24 hours after surgery) is more consistent with that of Mason and colleagues1 in their systematic review and meta-analysis (postoperative patient catheterization for difficulty in voiding in the early postoperative period, typically <24 hours). However, this is different from the study by Keita and colleagues,14 where bladder volume >600 mL on ultrasound was an important part of their definition of POUR. On the other hand, Patel and colleagues15 defined POUR as the inability to void spontaneously, necessitating in-and-out straight urethral catheterization or Foley catheter placement. This differed from our study, in which POUR was defined as requiring Foley catheter placement. The rate of POUR in our study was 19%. A previous study of “minor” thoracic surgeries described a risk of 11.6% in their cohort.3 With POUR comes a number of cascading complications, such as urinary tract infection, increased length of stay, and the associated risks of urinary catheter placement.16, 17, 18 These complications pose additional threats to patient morbidity and have a negative impact on healthcare economics by increasing the cost of treatment.
Data are limited on specific risks that predict POUR in patients following major GTS procedures as defined by the STS. In 2015, Kim and colleagues3 established a predictive model for POUR following minor GTS procedures. Their team identified specific increased risks in patients age >40 years, male sex, diabetes mellitus, and candidates for lung resection.3 When expanding research beyond the scope of thoracic surgery alone, risks for POUR across multiple surgical subspecialties are male sex, increased age, and use of epidural.1,19,20 Although our study did not find any significance risks with diabetes, it did find an increased risk of POUR with increased age, male sex, history of COPD, higher preoperative creatinine level, lung resection, and postoperative PCA use. The report from the STS and the European Society of Thoracic Surgeons and the recommendations of the Enhanced Recovery After Surgery Society consider it reasonable to place a transurethral catheter in patients with thoracic epidural anesthesia without any further elaboration as to who should get a Foley catheter postoperatively and what the stepwise approach for POUR should be. This is due mainly to the lack of consensus of the definition of POUR across studies and the heterogeneity of the cohort.21
Much previous effort has been directed at developing and validating nomogram for use in both clinical and surgical management.8, 9, 10, 11, 12,22 A nomogram is a proven approach to providing cheap, efficient, and effective aid to medical decision making. For the specific purposes of the present study, the nomogram that we developed is an important contribution to the protocol of developing a treatment plan for major GTS cases. The likelihood of developing POUR is an important consideration in patient management decision when considering the detrimental effects that can occur, including bladder distention, risk of infection, and increased cost and length of stay.16, 17, 18 This tool will allow surgeons to anticipate downstream complications and make decisions to prophylactically intervene, leading to increased precision of care.
The study's retrospective design and single-institution dataset are important limitations. It is important to note that we excluded patients with a Foley catheter placed intraoperatively or preoperatively, a group that does not adhere to a specific or strict criterion and is likely to be variable between institutions and even surgeons within a single institution. By excluding these patients, which presumably represent some of the patients at highest risk for POUR, the study may have had a selection bias; our study cohort may be dissimilar to populations in hospitals in which routine intraoperative use of Foley catheters is more common. The nomogram developed in this study ideally will benefit from further validation in a prospective model with increased numbers in a real-time fashion. Furthermore, we believe that the use of this nomogram could facilitate prospective trials evaluating prophylactic intervention (eg, administration of tamsulosin preoperatively) in patients at high risk for POUR.
In conclusion, we successfully identified significant risk factors associated with POUR following major GTS procedures, and developed a nomogram prototype to predict the overall risk of POUR and validated it with acceptable C-statistics values. This nomogram can be introduced into clinical practice for validation sometime in the near future (Video 1).
Video 1.
The relevant findings of this study, highlighting the importance of applying the prediction model for postoperative urinary retention in general thoracic surgery patients. Video available at: https://www.jtcvs.org/article/S2666-2736(21)00112-1/fulltext.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
The Journal policy requires editors and reviewers to disclose conflicts of interest and to decline handling or reviewing manuscripts for which they may have a conflict of interest. The editors and reviewers of this article have no conflicts of interest.
Supplementary Data
The relevant findings of this study, highlighting the importance of applying the prediction model for postoperative urinary retention in general thoracic surgery patients. Video available at: https://www.jtcvs.org/article/S2666-2736(21)00112-1/fulltext.
References
- 1.Mason S.E., Scott A.J., Mayer E., Purkayastha S. Patient-related risk factors for urinary retention following ambulatory general surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Surg. 2016;211:1126–1134. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2015.04.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Golubovsky J.L., Ilyas H., Chen J., Tanenbaum J.E., Mroz T.E., Steinmetz M.P. Risk factors and associated complications for postoperative urinary retention after lumbar surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine J. 2018;18:1533–1539. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2018.01.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kim K.W., Lee J.I., Kim J.S., Lee Y.J., Choi W.J., Jung H., et al. Risk factors for urinary retention following minor thoracic surgery. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2015;20:486–492. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivu445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kritika Agrawal K., Majhi S., Garg R. Post-operative urinary retention: review of literature. World J Anesthesiol. 2019;8:1–12. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Young J., Geraci T., Milman S., Maslow A., Jones R.N., Ng T. Risk factors for reinsertion of urinary catheter after early removal in thoracic surgical patients. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2018;156:430–435. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2018.02.076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Toyonaga T., Matsushima M., Sogawa N., Jiang S.F., Matsumura N., Shimojima Y., et al. Postoperative urinary retention after surgery for benign anorectal disease: potential risk factors and strategy for prevention. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2006;21:676–682. doi: 10.1007/s00384-005-0077-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Baldini G., Bagry H., Aprikian A., Carli F. Postoperative urinary retention: anesthetic and perioperative considerations. Anesthesiology. 2009;110:1139–1157. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e31819f7aea. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tevis S.E., Weber S.M., Kent K.C., Kennedy G.D. Nomogram to predict postoperative readmission in patients who undergo general surgery. JAMA Surg. 2015;150:505–510. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2014.4043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Guo L.W., Jiang L.M., Gong Y., Zhang H.H., Li X.G., He M., et al. Development and validation of nomograms for predicting overall and breast cancer-specific survival among patients with triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Manag Res. 2018;10:5881–5894. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S178859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Xiao Z., Yan Y., Zhou Q., Liu H., Huang P., Zhou Q., et al. Development and external validation of prognostic nomograms in hepatocellular carcinoma patients: a population based study. Cancer Manag Res. 2019;11:2691–2708. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S191287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Wang X., Mao M., Xu G., Lin F., Sun P., Baklaushev V.P., et al. The incidence, associated factors, and predictive nomogram for early death in stage IV colorectal cancer. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2019;34:1189–1201. doi: 10.1007/s00384-019-03306-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Attiyeh M.A., Fernández-Del Castillo C., Al Efishat M., Eaton A.A., Gönen M., Batts R., et al. Development and validation of a multi-institutional preoperative nomogram for predicting grade of dysplasia in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs) of the pancreas: a report from the Pancreatic Surgery Consortium. Ann Surg. 2018;267:157–163. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000002015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) STS general thoracic surgery database data specifications. https://www.sts.org/sites/default/files/documents/STSThoracicDataSpecsV2_41.pdf Available at:
- 14.Keita H., Diouf E., Tubach F., Brouwer T., Dahmani S., Mantz J., et al. Predictive factors of early postoperative urinary retention in the postanesthesia care unit. Anesth Analg. 2005;101:592–596. doi: 10.1213/01.ANE.0000159165.90094.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Patel J.A., Kaufman A.S., Howard R.S., Rodriguez C.J., Jessie E.M. Risk factors for urinary retention after laparoscopic inguinal hernia repairs. Surg Endosc. 2015;29:3140–3145. doi: 10.1007/s00464-014-4039-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Gandhi S.D., Patel S.A., Maltenfort M., Anderson D.G., Vaccaro A.R., Albert T.J., et al. Patient and surgical factors associated with postoperative urinary retention after lumbar spine surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2014;39:1905–1909. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000000572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lamonerie L., Marret E., Deleuze A., Lembert N., Dupont M., Bonnet F. Prevalence of postoperative bladder distension and urinary retention detected by ultrasound measurement. Br J Anaesth. 2004;92:544–546. doi: 10.1093/bja/aeh099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Saint S. Clinical and economic consequences of nosocomial catheter-related bacteriuria. Am J Infect Control. 2000;28:68–75. doi: 10.1016/s0196-6553(00)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sung K.H., Lee K.M., Chung C.Y., Kwon S.S., Lee S.Y., Ban Y.S., et al. What are the risk factors associated with urinary retention after orthopaedic surgery? Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:613216. doi: 10.1155/2015/613216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Darrah D.M., Griebling T.L., Silverstein J.H. Postoperative urinary retention. Anesthesiol Clin. 2009;27:465–484. doi: 10.1016/j.anclin.2009.07.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Batchelor T.J.P., Rasburn N.J., Abdelnour-Berchtold E., Brunelli A., Cerfolio R.J., Gonzalez M., et al. Guidelines for enhanced recovery after lung surgery: recommendations of the Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS®) Society and the European Society of Thoracic Surgeons (ESTS) Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2019;55:91–115. doi: 10.1093/ejcts/ezy301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.He C., Zhong L., Zhang Y., Cai Z., Lin X. Development and validation of a nomogram to predict liver metastasis in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: a large cohort study. Cancer Manag Res. 2019;11:3981–3991. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S200684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
The relevant findings of this study, highlighting the importance of applying the prediction model for postoperative urinary retention in general thoracic surgery patients. Video available at: https://www.jtcvs.org/article/S2666-2736(21)00112-1/fulltext.