Abstract
Background
Acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) elicits a robust cardiomyocyte death and inflammatory responses despite timely revascularization.
Objectives
This phase 1, open-label, single-arm, first-in-human study aimed to assess the safety and efficacy of combined intracoronary (IC) and intravenous (IV) transplantation of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells (UMSC01) for heart repair in STEMI patients with impaired left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF 30-49%) following successful reperfusion by percutaneous coronary intervention.
Methods
Consenting patients received the first dose of UMSC01 through IC injection 4-5 days after STEMI followed by the second dose of UMSC01 via IV infusion 2 days later. The primary endpoint was occurrence of any treatment-related adverse events and the secondary endpoint was changes of serum biomarkers and heart function by cardiac magnetic resonance imaging during a 12-month follow-up period.
Results
Eight patients gave informed consents, of whom six completed the study. None of the subjects experienced treatment-related serious adverse events or major adverse cardiovascular events during IC or IV infusion of UMSC01 and during the follow-up period. The NT-proBNP level decreased (1362 ± 1801 vs. 109 ± 115 pg/mL, p = 0.0313), the LVEF increased (52.67 ± 12.75% vs. 62.47 ± 17.35%, p = 0.0246), and the wall motion score decreased (26.33 ± 5.57 vs. 22.33 ± 5.85, p = 0.0180) at the 12-month follow-up compared to the baseline values. The serial changes of LVEF were 0.67 ± 3.98, 8.09 ± 6.18, 9.04 ± 10.91, and 9.80 ± 7.56 at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months, respectively as compared to the baseline.
Conclusion
This pilot study shows that combined IC and IV transplantation of UMSC01 in STEMI patients with impaired LVEF appears to be safe, feasible, and potentially beneficial in improving heart function. Further phase 2 studies are required to explore the effectiveness of dual-route transplantation of UMSC01 in STEMI patients.
Keywords: intracoronary, intravenous, umbilical mesenchymal stem cell, acute myocardial infarction, human pilot trial
Graphical Abstract
Eligible STEMI patients with a LVEF of 30-49% received the first dose of UMSC01 through IC injection 4-5 days after STEMI and the second dose of UMSC01 via IV infusion 2 days after IC. The culprit arteries were patent with comparable FEV1% and decreases in cardiac enzymes after IC + IV infusion. The LVEF increased at 12-month follow-up by cardiac MRI. 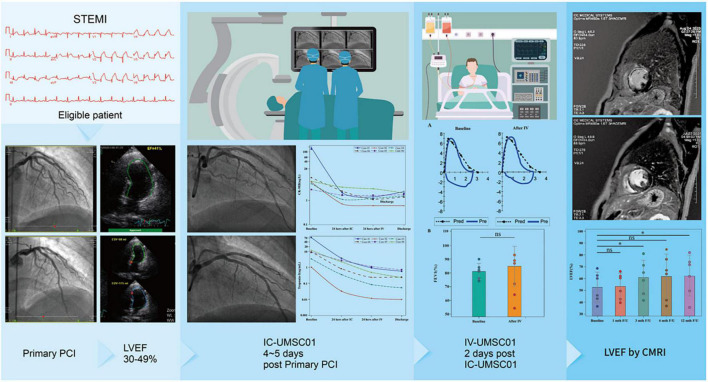
Introduction
Acute myocardial infarction (AMI) elicits a robust cardiomyocyte death despite timely revascularization and optimal treatment (1). Acute injury initiates substantial inflammatory response, which causes cardiomyocyte damage and triggers cardiac fibrosis (2). Limitation of the initial injury and appropriate regulation of the immune response are essential to improve healing and reduce unfavorable left ventricular remodeling (3, 4). Stem cell-based therapies have been proposed as a promising strategy to reduce cardiomyocyte death and modulate immune reactions, leading to reduced myocardial scarring and improved cardiac function regardless of ischemic or non-ischemic cardiomyopathy (5–8).
Bone marrow mononuclear cells (BMNCs) and circulating progenitor/stem cells delivered via the intracoronary (IC) or intravenous (IV) route constitute the most commonly used cell types, with doses ranging between 106 and 109 in published clinical studies (9–12). Recently, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have drawn much attention because of their anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects (13–16), and their effectiveness has been documented in many clinical trials (17, 18).
Previous studies in animals and humans have suggested that the dose of transplanted cells plays an important role in determining eventual myocardial function indices (19). Delivering sufficient cells by repeated transplantation might be necessary to overcome low retention and survival rates in the infarcted myocardium (7, 19). It has also been shown that three repeated doses of cells are superior to one dose of equivalent number of cells in relation to LVEF improvement, possibly due to greater antifibrotic and anti-inflammatory actions (20). There are various strategies regarding repeated transplantation, which involves the different combinations including deliver method, time interval and cell dose. Yao et al. demonstrated that repeated IC infusion of BMNCs 3 months after the first transfer is feasible and beneficial in patients with a large AMI (19). However, there has been no study in evaluating the feasibility and safety by combing IC and IV administration to achieve a sufficiently higher dose of umbilical cord-derived MSCs in patients with AMI.
To enhance the effect of cell-based therapy in post-AMI cardiac repair, we investigated umbilical-MSCs as a therapeutic candidate. Although neither IC nor IV transplantation are ideal, they can complement each other (21). We hypothesized that a combined IC and subsequent IV umbilical-MSCs transplantation enables a synergistic anti-inflammatory and direct cell repair effect, which is beneficial in patients with AMI. Here, we first assessed the safety and explored the preliminary efficacy of umbilical cord-derived MSCs (UMSC01) by combining IC and IV stem cell administration.
Materials and methods
Study design and patients
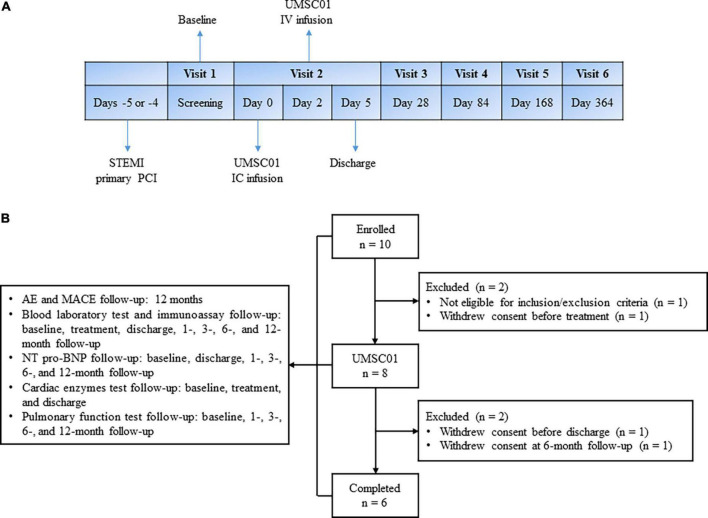
This was a phase one, open-label, single-arm, single- center study in patients with acute ST-elevation MI (STEMI). Eligible patients who presented with first-ever STEMI were consecutively recruited. All of the subjects were hospitalized from the day of primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PPCI), until the third day after IV infusion of UMSC01. IC infusion of UMSC01 was performed 4–5 days via the index culprit artery after successful revascularization. The day of IC infusion of UMSC01 was designed as Day 0 and IV infusion of UMSC01 was carried out on Day 2. After discharge, all subjects were followed up at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months for endpoint evaluation, as shown in Figure 1A.
FIGURE 1.
Study design and subject disposition. (A) Eligible patients who presented with first-ever ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) were consecutively recruited. All of the subjects were hospitalized from the day of primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), until the third day after IV infusion of UMSC01. IC infusion of UMSC01 was performed 4–5 days via the index culprit artery after successful revascularization. The day of IC infusion of UMSC01 was designed as Day 0 and IV infusion of UMSC01 was carried out on Day 2. After discharge, all subjects were followed up at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months for endpoint evaluation. (B) Between August 20, 2019, and August 2, 2020, we screened 10 patients with STEMI, of whom eight eligible patients provided written informed consent to participate in the clinical trial (NCT04056819). Two subjects withdrew consent during the follow-up period. Six subjects were followed up for the primary and secondary endpoints at 12 months. AE, adverse event; MACE, major adverse cardiovascular events; NT-pro-BNP, amino-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide.
Male or female, aged between 20 and 76 years who presented with typical ischemic chest pain within 12 h of symptom onset and were diagnosed with first-time acute STEMI were considered eligible for the study. The infarct-related artery should be successfully revascularized by PPCI with a thrombolysis in myocardial infarction (TIMI) flow ≥ 2 suitable for cell infusion. After revascularization, STEMI patients should fulfill an echocardiography-determined left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of ≥30% and <50% for enrollment. Patients with profound cardiogenic shock requiring mechanical support or those who had previous or incident significant valvular heart diseases were excluded. The full list of the inclusion and exclusion criteria can be found in online Supplementary material.
This study complied with the ethical principles of Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of China Medical University Hospital (CMUH107-REC1-088). The trial was monitored by an independent data and safety monitoring board who met as planned to assess adverse events.
Preparation of UMSC01
On the day before administration, the cryopreserved UMSC01 cells were thawed in a 37°C water bath. The cell suspension was washed three times to minimize residual reagents during the manufacturing process. The cell pellet was then resuspended in normal saline at a final cell density of ∼1 × 107 cells/mL for administration. The cell identity test showed that ≥95% of cells expressed CD73, CD90, and CD105, while the expression level of CD11b, CD19, CD45, CD34, and human leukocyte antigen-DR isotype (HLA-DR) was ≤2%. The final volume of UMSC01 for infusion (drug product) was resuspended in 0.9% saline containing a cell dose of either 1 × 107 for IC or 9 × 107 for IV infusion in AT-Closed Vial (Aseptic Technology, Gembloux, Belgium), while fulfilling the following product release criteria: cell viability by trypan blue (>70%), purity test by endotoxin examination (<0.25 EU/mL), and sterility test by gram staining and direct inoculation. The stepwise preparation of UMSC01 cells was described in the Supplementary Methods.
Intracoronary administration of UMSC01
We used the stop-flow technique for IC injection of UMSC01 with positioning of an over-the-wire balloon catheter within the segment of the previously deployed stent in the infarct-related artery (22). Briefly, 1 × 107 of UMSC01 in packed AT-Closed Vial® was mixed in 14 mL normal saline with 10,000 U/L heparin and directly injected using the over-the-wire balloon catheter in three treatment cycles. Each treatment cycle included 1.5 min of balloon inflation for cell injection, followed by 1.5 min balloon deflation for coronary reperfusion. Three cycles of cell injection were completed within 15 min. After completion of cell infusion, coronary angiography was repeated to confirm the patency of coronary artery flow. Then, patients were transferred to the intensive care unit for overnight observation. Blood pressures, heart rate, oxygenation, and ECGs were continuously monitored throughout the procedure.
Intravenous administration of UMSC01
For IV infusion of UMSC01, 9 × 107 of UMSC01 mixed in 141 mL normal saline with 10,000 U/L heparin was administered via an antecubital vein at a flow rate of 2.5 mL/minute within 60 min. Blood pressures, heart rate, oxygenation, and ECGs were closely monitored throughout the procedure. Pulmonary function test with a ratio of the first second of forced expiration to the forced vital capacity (FEV1%) was measured before and 24 h after IV infusion. After completing the IV infusion of UMSC01, patients were transferred to the intensive care unit for overnight observation.
Study endpoints
The primary endpoints for the study were emergence of any suspected or unexpected serious adverse reaction and occurrence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) including death, recurrent AMI, stroke, and target-vessel revascularization. The secondary endpoints were changes of the serum level of amino-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) from baseline to discharge and at 1-, 3-, 6-, and 12-month follow-up and left ventricular function evaluated by cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (CMRI) from baseline to 1-, 3-, 6-, and 12-month follow-up.
Statistical analyses
All analyses were performed on patients who completed the entire study from the time of screening to the 12-month follow-up. Continuous variables are presented as mean and standard deviation, and categorical variables are presented as frequency and percentage. To compare the differences between baseline and follow-ups, paired t-tests were performed for efficacy endpoints to have more statistical power when the normality assumptions were not violated. Wilcoxon signed-rank tests were used for safety endpoints or non-normally distributed data. The Shapiro–Wilk method was adopted for normality tests because of small sample sizes. A two-sided p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. All statistical analyses were performed using SAS software, version 9.4 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, United States).
Results
Subject disposition
Between August 20, 2019, and August 2, 2020, we screened 10 patients with ST-elevation AMI, of whom eight eligible patients provided written informed consent to participate in the clinical trial (NCT04056819). Two subjects withdrew consent during the follow-up period. Six subjects were followed up for the primary and secondary endpoints at 12 months. The subject disposition is shown in Figure 1B.
Patient characteristics
Baseline characteristics of the study subjects are shown in Table 1. All the enrolled subjects were males with a mean age of 61 ± 10 years. All the infarct-related arteries (left anterior descending artery in four patients and right coronary artery in two patients) underwent successful revascularization with TIMI 3 flow. The mean LVEF by echocardiography after PPCI was 43.0 ± 2.7 (range, 39.9-46.3%), which was associated with a baseline New York Heart Association functional class of II in all study subjects. None of the subjects had significant valvular heart disease, new-onset atrial fibrillation, or mechanical ventilation support. Following successful PPCI revascularization, all patients received guideline-directed medical treatment including dual-antiplatelet, β-blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors/angiotensin II receptor blockers, and statins.
TABLE 1.
Baseline characteristics of the study subjects.
| . | Patient 1 | Patient 2 | Patient 3 | Patient 4 | Patient 5 | Patient 6 | Mean ± SD/n (%) |
| Age (year) | 53 | 48 | 70 | 71 | 56 | 70 | 61 ± 10 |
| Gender | |||||||
| Male | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 6 (100.00) |
| Height (cm) | 166 | 180 | 164 | 165 | 178 | 165 | 170 ± 7 |
| Weight (kg) | 83 | 78 | 58 | 61 | 96 | 62 | 73 ± 15 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 30.1 | 24.1 | 21.6 | 22.4 | 30.3 | 22.8 | 25.2 ± 3.9 |
| Smoking | Y | Y | EXa | Y | Y | Y | 5 (83.33) |
| Vital signs | |||||||
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 141 | 130 | 132 | 127 | 115 | 90 | 123 ± 18 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 89 | 75 | 77 | 74 | 79 | 61 | 76 ± 9 |
| Heart rate (bpm) | 91 | 75 | 58 | 49 | 81 | 99 | 76 ± 19 |
| Oximetry (%) | – | 95 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 99 ± 2 |
| Medical history | |||||||
| Type 2 diabetes mellitus | N | N | N | N | Y | N | 1 (16.67) |
| Hypertension | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | 4 (66.67) |
| Dyslipidemia | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | N | 4 (66.67) |
| Old myocardial infarction | N | N | N | N | N | N | 0 (0.00) |
| Prior heart failure | N | N | N | N | N | N | 0 (0.00) |
| Coronary artery disease | N | N | Y | N | N | N | 1 (16.67) |
| ESRD | N | N | N | N | N | N | 0 (0.00) |
| Stroke | N | N | N | N | N | N | 0 (0.00) |
| COPD | N | N | Y | N | N | N | 1 (16.67) |
| Liver cirrhosis | N | N | N | N | N | N | 0 (0.00) |
| Cancer | N | N | N | N | N | N | 0 (0.00) |
| Infarct-related artery | |||||||
| LM | N | N | N | N | N | N | 0 (0.00) |
| LAD | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | 4 (66.67) |
| LCX | N | N | N | N | N | N | 0 (0.00) |
| RCA | N | N | Y | Y | N | N | 2 (33.33) |
| Culprit vessel TIMI flow after PCI | |||||||
| 0 | N | N | N | N | N | N | 0 (0.00) |
| 1 | N | N | N | N | N | N | 0 (0.00) |
| 2 | N | N | N | N | N | N | 0 (0.00) |
| 3 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 6 (100.00) |
| Killip classification | |||||||
| I | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | 5 (83.33) |
| II | N | N | N | N | N | N | 0 (0.00) |
| III | N | N | N | N | N | N | 0 (0.00) |
| IV | N | Y | N | N | N | N | 1 (16.67) |
| NYHA functional classification | |||||||
| I | N | N | N | N | N | N | 0 (0.00) |
| II | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 6 (100.00) |
| III | N | N | N | N | N | N | 0 (0.00) |
| IV | N | N | N | N | N | N | 0 (0.00) |
| LVEF (%) by echocardiography after PCI | 40.7 | 42.5 | 46.0 | 46.3 | 39.9 | 42.6 | 43.0 ± 2.7 |
| Significant valvular heart disease | N | N | N | N | N | N | 0 (0.00) |
| New onset atrial fibrillation | N | N | N | N | N | N | 0 (0.00) |
| Laboratory test at emergency room | |||||||
| AST (IU/L) | 116 | 13 | 16 | 13 | 52 | 15 | 38 ± 41 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.95 | 1.59 | 1.05 | 1.14 | 0.91 | 1.19 | 1.14 ± 0.25 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 83 | 47 | 70 | 63 | 86 | 60 | 68 ± 15 |
| Sodium (mmol/L) | 138 | 140 | 139 | 141 | 140 | 143 | 140 ± 2 |
| Potassium (mmol/L) | 3.3 | 3.9 | 3.8 | 4.1 | 4.0 | 4.2 | 3.9 ± 0.3 |
| RBC (106/μL) | 6.04 | – | – | 5.38 | 5.58 | 4.88 | 5.47 ± 0.48 |
| WBC (103/μL) | 13.7 | 18.2 | 8.2 | 15.0 | 10.5 | 5.3 | 11.8 ± 4.7 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 17.6 | 16.2 | 14.5 | 15.4 | 16.6 | 16.4 | 16.1 ± 1.1 |
| Platelet count (103/μL) | 219 | 288 | 213 | 233 | 249 | 251 | 242 ± 27 |
| Troponin-I (ng/mL) | 0.3769 | 0.2800 | <0.0100 | 0.0371 | <0.0100 | 0.2808 | 0.2437 ± 0.1451 |
| Medications | |||||||
| Aspirin | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 6 (100.00) |
| Clopidogrel | N | Y | N | N | N | N | 1 (16.67) |
| Ticagrelor | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | 5 (83.33) |
| Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitors | N | N | N | Y | Y | N | 2 (33.33) |
| Heparin | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 6 (100.00) |
| Beta blockers | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 6 (100.00) |
| ACEI/ARB | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 6 (100.00) |
| MRA | N | N | N | N | N | N | 0 (0.00) |
| Statins | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 6 (100.00) |
| Vasopressor | N | N | N | N | N | N | 0 (0.00) |
| Mechanical ventilation | N | N | N | N | N | N | 0 (0.00) |
| IABP | N | Y | N | N | N | N | 1 (16.67) |
aEx-smoker.
ACEI, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB, angiotensin ii receptor blocker; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; BMI, body mass index; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; ESRD, end-stage renal disease; IABP, intra-aortic balloon pump; LAD, left anterior descending artery; LCX, left circumflex artery; LM, left main; LVEF, left ventricular ejection fraction; MRA, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist; NYHA, New York heart association; PCI, percutaneous coronary intervention; RBC, red blood cell; RCA, right coronary artery; SD, standard deviation; TIMI, thrombolysis in myocardial infarction; WBC, white blood cell.
Characterization of UMSC01
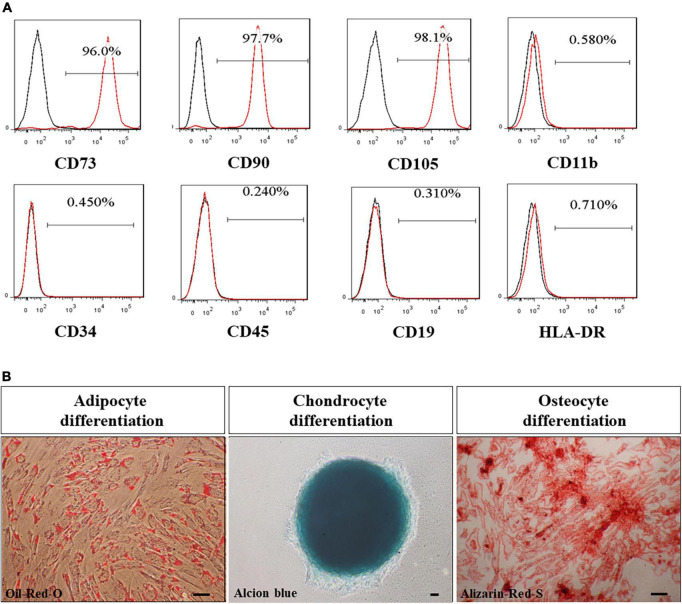
The clinical grade of UMSC01 was certified and identified by surface markers, which showed uniformly high expression (≥95%) of CD73, CD90, and CD105 but low expression (≤2%) of CD11b, CD34, CD45, CD19, and HLA-DR (Figure 2A). The capacity of the potency assay for in vitro differentiation into mesodermal lineages of adipocytes, chondrocytes, and osteocytes was confirmed by Oil-Red-O, Alcian-Blue and Alizarin-Red staining, respectively (Figure 2B). The final drug substance and drug product of UMSC01 were released after passing all the criteria including cell viability, microbiological tests, endotoxin level, and Gram staining.
FIGURE 2.
Characterization of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells (UMSC01). (A) The clinical grade of UMSC01 was certified and identified by surface markers, which showed uniformly high expression (≥95%) of CD73, CD90, and CD105 but low expression (≤2%) of CD11b, CD34, CD45, CD19, and HLA-DR. (B) The potency assay for the capacity of in vitro differentiation into mesodermal lineages of adipocytes, chondrocytes, and osteocytes was confirmed by Oil-Red-O, Alcian-Blue and Alizarin-Red staining, respectively. Bar = 50 μm. CD, cluster of differentiation; HLA, human leukocyte antigen.
Primary endpoints for safety
There were no significant changes in the blood pressures, heart rates, or oxygenation status before and after IC injection or IV infusion of UMSC01 (Supplementary Figure S1). The culprit arteries remained patent at the end of IC infusion in all subjects, and a steady decrease was seen in troponin-I (18.05 ± 27.46 vs. 1.66 ± 1.49 ng/L, p = 0.0313) and creatine kinase-MB (CK-MB; 30.7 ± 61.3 vs. 1.9 ± 1.0 ng/L, p = 0.0313) levels at 24 h compared to the baseline values (graphical abstract). The FEV1% was comparable (81.17 ± 5.74 vs. 84.83 ± 14.52%, p = 0.6875) at the end of IV infusion of UMSC01 (Graphical Abstract). There were significant differences in the levels of blood urea nitrogen (14 ± 3 vs. 19 ± 2 mg/dL, p = 0.0313), serum potassium (3.6 ± 0.2 vs. 4.2 ± 0.2 meq/L, p = 0.0313), white blood cell count (9.9 ± 2.9 vs. 6.5 ± 2.1 103/μL, p = 0.0313), platelet count (204 ± 32 vs. 227 ± 38 103/μL, p = 0.0313), and the plasma IgG (1050 ± 292 vs. 1225 ± 342 mg/dL, p = 0.0313) between baseline and 12-month follow-up, however these values were within normal ranges and were not associated with any clinically relevant events (Table 2). The carcinoembryonic antigen level (4.27 ± 4.19 vs. 2.71 ± 1.22 ng/mL, p = 0.2188) and immunology parameters including CD3 (55.3 ± 12.3 vs. 58.9 ± 6.1%, p = 0.4375), CD4/CD8 (2.8 ± 1.2 vs. 2.1 ± 0.8, p = 0.0938), anti-HLA antibodies (0.6 ± 0.4 vs. 0.6 ± 0.7%, p = 0.7500), and panel reactive antibody assay (0.4 ± 0.4 vs. 0.4 ± 0.5%, p = 0.6250) were not significantly different between baseline and at the 12-month follow-up. During the study period, none of the subjects experienced serious adverse events or major adverse cardiovascular events (Table 3). One patient had a unilateral inguinal hernia at 5-month of follow-up and was subsequently hospitalized for operation, which was adjudicated as a non-treatment related serious adverse event. There were three non-treatment related adverse events consisting of a non-ischemic chest pain, a mild superficial skin rash, and a localized eczema, respectively in three subjects.
TABLE 2.
Serial laboratory tests during the study period.
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 | Case 5 | Case 6 | Mean ± SD | P-valuea | |
| AST (IU/L) | ||||||||
| Baseline | 109 | 26 | 36 | 67 | 41 | 53 | 55 ± 30 | – |
| After IC injection | 58 | 16 | 20 | 18 | 24 | 20 | 26 ± 16 | 0.0313 |
| After IV infusion | 56 | 17 | 26 | 19 | 13 | 17 | 25 ± 16 | 0.0313 |
| 1-Month follow-up | 52 | 19 | 23 | 18 | 19 | 21 | 25 ± 13 | 0.0313 |
| 3-Month follow-up | 66 | 16 | 27 | 20 | 17 | 19 | 28 ± 19 | 0.0313 |
| 6-Month follow-up | 30 | 23 | 21 | 28 | 15 | 29 | 24 ± 6 | 0.0313 |
| 12-Month follow-up | 39 | 32 | 25 | 17 | 16 | 15 | 24 ± 10 | 0.0625 |
| ALT (IU/L) | ||||||||
| Baseline | 122 | 14 | 15 | 29 | 54 | 25 | 43 ± 41 | – |
| After IC injection | 91 | 20 | 17 | 25 | 48 | 24 | 38 ± 28 | 0.4688 |
| After IV infusion | 95 | 20 | 23 | 23 | 31 | 22 | 36 ± 29 | 0.4688 |
| 1-Month follow-up | 82 | 14 | 25 | 16 | 41 | 27 | 34 ± 25 | 0.2500 |
| 3-Month follow-up | 81 | 14 | 33 | 18 | 26 | 25 | 33 ± 25 | 0.3750 |
| 6-Month follow-up | 40 | 33 | 19 | 35 | 19 | 36 | 30 ± 9 | 1.0000 |
| 12-Month follow-up | 55 | 27 | 18 | 12 | 14 | 16 | 24 ± 16 | 0.2188 |
| BUN (mg/dL) | ||||||||
| Baseline | 14 | 10 | 12 | 13 | 19 | 14 | 14 ± 3 | − |
| After IC injection | 12 | 11 | 12 | 16 | 16 | 10 | 13 ± 3 | 0.5000 |
| After IV infusion | – | 11 | 13 | 17 | 11 | 10 | 12 ± 3 | 0.9375 |
| 1-Month follow-up | 26 | 10 | 13 | 13 | 16 | 19 | 16 ± 6 | 0.3750 |
| 3-Month follow-up | 16 | 15 | 14 | 19 | 22 | 16 | 17 ± 3 | 0.0313 |
| 6-Month follow-up | 18 | 12 | 12 | 20 | 22 | 16 | 17 ± 4 | 0.0625 |
| 12-Month follow-up | 20 | 19 | 16 | 21 | 20 | 18 | 19 ± 2 | 0.0313 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | ||||||||
| Baseline | 0.77 | 0.79 | 0.77 | 1.08 | 0.85 | 1.06 | 0.89 ± 0.15 | − |
| After IC injection | 0.72 | 0.93 | 0.82 | 0.98 | 0.83 | 1.09 | 0.90 ± 0.13 | 0.9063 |
| After IV infusion | 0.81 | 0.98 | 0.85 | 0.89 | 0.87 | 1.19 | 0.93 ± 0.14 | 0.3438 |
| 1-Month follow-up | 1.01 | 1.09 | 1.04 | 1.25 | 0.95 | 1.25 | 1.10 ± 0.13 | 0.0313 |
| 3-Month follow-up | 0.89 | 1.06 | 1.05 | 1.49 | 0.86 | 1.02 | 1.06 ± 0.23 | 0.0938 |
| 6-Month follow-up | 0.89 | 0.93 | 0.95 | 1.31 | 0.84 | 0.97 | 0.98 ± 0.17 | 0.1563 |
| 12-Month follow-up | 0.82 | 1.13 | 0.86 | 1.36 | 0.77 | 1.05 | 1.00 ± 0.23 | 0.2188 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | ||||||||
| Baseline | 106 | 105 | 100 | 67 | 93 | 69 | 90 ± 18 | − |
| After IC injection | 114 | 87 | 93 | 75 | 96 | 67 | 89 ± 17 | 0.9375 |
| After IV infusion | 100 | 82 | 89 | 84 | 91 | 60 | 84 ± 13 | 0.3125 |
| 1-Month follow-up | 77 | 72 | 71 | 57 | 82 | 57 | 69 ± 10 | 0.0313 |
| 3-Month follow-up | 89 | 75 | 70 | 46 | 92 | 72 | 74 ± 16 | 0.0938 |
| 6-Month follow-up | 89 | 87 | 78 | 54 | 95 | 77 | 80 ± 14 | 0.1563 |
| 12-Month follow-up | 98 | 69 | 88 | 52 | 105 | 70 | 80 ± 20 | 0.2500 |
| Sodium (mmol/L) | ||||||||
| Baseline | 138 | 141 | 139 | 141 | 141 | 136 | 139 ± 2 | – |
| After IC injection | 137 | 139 | 139 | 141 | 139 | 139 | 139 ± 1 | 0.8750 |
| After IV infusion | 135 | 140 | 139 | 140 | 141 | 139 | 139 ± 2 | 0.7500 |
| 1-Month follow-up | 139 | 143 | 140 | 142 | 142 | 139 | 141 ± 2 | 0.0313 |
| 3-Month follow-up | 138 | 141 | 141 | 144 | 142 | 139 | 141 ± 2 | 0.1250 |
| 6-Month follow-up | 139 | 141 | 142 | 141 | 142 | 140 | 141 ± 1 | 0.1250 |
| 12-Month follow-up | 141 | 142 | 139 | 143 | 139 | 140 | 141 ± 2 | 0.2500 |
| Potassium (mmol/L) | ||||||||
| Baseline | 3.3 | 3.9 | 3.7 | 3.7 | 3.3 | 3.7 | 3.6 ± 0.2 | – |
| After IC injection | 3.5 | 3.8 | 3.8 | 3.4 | 3.5 | 4 | 3.7 ± 0.2 | 0.5938 |
| After IV infusion | 3.8 | 3.8 | 3.9 | 3.4 | 3.5 | 4.2 | 3.8 ± 0.3 | 0.2813 |
| 1-Month follow-up | 3.6 | 4.4 | 3.5 | 3.7 | 3.8 | 3.9 | 3.8 ± 0.3 | 0.1875 |
| 3-Month follow-up | 4.1 | 4.1 | 4.2 | 4 | 4.5 | 4.2 | 4.2 ± 0.2 | 0.0313 |
| 6-Month follow-up | 3.6 | 4.1 | 3.9 | 3.8 | 3.9 | 4 | 3.9 ± 0.2 | 0.0313 |
| 12-Month follow-up | 4.2 | 4.4 | 4.1 | 4.1 | 4.2 | 3.9 | 4.2 ± 0.2 | 0.0313 |
| RBC (10 6 /uL) | ||||||||
| Baseline | 5.14 | 4.67 | 6.87 | 4.79 | 4.89 | 4.57 | 5.16 ± 0.86 | – |
| After IC injection | 5.17 | 4.53 | 6.24 | 4.23 | 4.59 | 4.08 | 4.81 ± 0.80 | 0.0625 |
| After IV infusion | 5.48 | 4.57 | 6.10 | 4.37 | 4.47 | 4.14 | 4.86 ± 0.76 | 0.0938 |
| 1-Month follow-up | 5.16 | 4.77 | 6.55 | 5.20 | 4.64 | 4.21 | 5.09 ± 0.80 | 0.8438 |
| 3-Month follow-up | 5.04 | 4.57 | 6.44 | 4.88 | 4.87 | 3.84 | 4.94 ± 0.85 | 0.0938 |
| 6-Month follow-up | 5.21 | 5.04 | 6.61 | 4.70 | 4.92 | 3.88 | 5.06 ± 0.89 | 0.6875 |
| 12-Month follow-up | 5.07 | 4.79 | 6.58 | 4.40 | 4.79 | 4.07 | 4.95 ± 0.87 | 0.1563 |
| WBC (10 3 /μL) | ||||||||
| Baseline | 11.0 | 15.2 | 8.1 | 8.1 | 9.4 | 7.7 | 9.9 ± 2.9 | – |
| After IC injection | 7.2 | 11.1 | 6.4 | 6.8 | 9.9 | 6.8 | 8.0 ± 2.0 | 0.0625 |
| After IV infusion | 8.1 | 11.4 | 5.8 | 6.9 | 11.0 | 8.1 | 8.6 ± 2.2 | 0.2188 |
| 1-Month follow-up | 7.4 | 7.2 | 5.1 | 5.9 | 7.8 | 5.1 | 6.4 ± 1.2 | 0.0313 |
| 3-Month follow-up | 6.7 | 9.1 | 5.9 | 7.2 | 8.3 | 4.8 | 7.0 ± 1.6 | 0.0313 |
| 6-Month follow-up | 6.7 | 8.0 | 5.5 | 5.8 | 6.7 | 6.9 | 6.6 ± 0.9 | 0.0313 |
| 12-Month follow-up | 6.0 | 10.7 | 6.0 | 5.2 | 6.0 | 4.9 | 6.5 ± 2.1 | 0.0313 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | ||||||||
| Baseline | 15.6 | 13.8 | 15.1 | 14.1 | 15.3 | 15.4 | 14.9 ± 0.7 | − |
| After IC injection | 15.9 | 13.7 | 14.2 | 12.9 | 14.3 | 13.5 | 14.1 ± 1.0 | 0.0938 |
| After IV infusion | 16.7 | 13.4 | 13.9 | 13.4 | 14.0 | 13.8 | 14.2 ± 1.3 | 0.1563 |
| 1-Month follow-up | 15.7 | 14.9 | 15.2 | 15.2 | 14.3 | 13.8 | 14.9 ± 0.7 | 0.8750 |
| 3-Month follow-up | 15.3 | 13.7 | 14.6 | 13.7 | 14.9 | 12.5 | 14.1 ± 1.0 | 0.0313 |
| 6-Month follow-up | 16.0 | 14.6 | 15.2 | 13.7 | 14.7 | 12.7 | 14.5 ± 1.2 | 0.7500 |
| 12-Month follow-up | 15.7 | 15.0 | 15.3 | 13.1 | 14.8 | 13.0 | 14.5 ± 1.2 | 0.6875 |
| Platelet count (10 3 /μL) | ||||||||
| Baseline | 173 | 262 | 192 | 180 | 209 | 205 | 204 ± 32 | – |
| After IC injection | 204 | 467 | 211 | 161 | 214 | 203 | 243 ± 111 | 0.2500 |
| After IV infusion | 232 | 517 | 231 | 174 | 233 | 229 | 269 ± 123 | 0.0625 |
| 1-Month follow-up | 172 | 293 | 193 | 189 | 224 | 247 | 220 ± 45 | 0.0938 |
| 3-Month follow-up | 175 | 313 | 204 | 324 | 251 | 253 | 253 ± 59 | 0.0313 |
| 6-Month follow-up | 182 | 352 | 238 | 230 | 216 | 263 | 247 ± 58 | 0.0313 |
| 12-Month follow-up | 195 | 301 | 224 | 202 | 212 | 227 | 227 ± 38 | 0.0313 |
| Carcinoembryonic antigen (ng/mL) | ||||||||
| Baseline | 3.16 | 3.69 | 1.84 | 3.37 | 1.00 | 12.57 | 4.27 ± 4.19 | – |
| After IC injection | 2.86 | 2.63 | 2.15 | 2.46 | 0.98 | 10.71 | 3.63 ± 3.53 | 0.1563 |
| After IV infusion | 3.67 | 2.64 | 1.84 | 3.28 | 0.99 | 9.84 | 3.71 ± 3.16 | 0.3125 |
| 1-Month follow-up | 2.26 | 3.22 | 1.80 | 2.32 | 0.82 | 7.18 | 2.93 ± 2.22 | 0.0313 |
| 3-Month follow-up | 2.44 | 3.18 | 1.85 | 4.02 | 1.34 | 5.44 | 3.05 ± 1.51 | 0.5625 |
| 6-Month follow-up | 2.77 | 2.69 | 2.41 | 2.45 | 0.79 | 4.17 | 2.55 ± 1.08 | 0.1563 |
| 12-Month follow-up | 3.20 | 3.31 | 2.10 | 2.23 | 0.95 | 4.48 | 2.71 ± 1.22 | 0.2188 |
| CK (IU/L) | ||||||||
| Baseline | 2163 | 289 | 331 | 610 | 186 | 335 | 652 ± 753 | − |
| 24 h after IC injection | 231 | 47 | 80 | 129 | 123 | 118 | 121 ± 62 | 0.0313 |
| 24 h after IV infusion | 128 | 42 | 94 | 70 | 83 | 96 | 86 ± 29 | 0.0313 |
| Discharge | 150 | 38 | 107 | 79 | 62 | 69 | 84 ± 39 | 0.0313 |
| CD3 (%) | ||||||||
| Baseline | 52.6 | 76.8 | 49.8 | 41.1 | 50.6 | 60.6 | 55.3 ± 12.3 | − |
| After IC injection | 60.5 | 59.7 | − | 42.3 | − | 43.7 | 51.6 ± 9.9 | 0.6250 |
| After IV infusion | 58.9 | − | 39.5 | 36.8 | 64.7 | 68.1 | 53.6 ± 14.5 | 0.6250 |
| 1-Month follow-up | 58.6 | 55.7 | 60.7 | 41.0 | 60.3 | 74.1 | 58.4 ± 10.6 | 0.5625 |
| 3-Month follow-up | 60.8 | 67.1 | 48.6 | 34.8 | 54.8 | 63.1 | 54.9 ± 11.8 | 1.0000 |
| 6-Month follow-up | 69.3 | 63.7 | 54.4 | 52.1 | 54.6 | 64.0 | 59.7 ± 6.9 | 0.3125 |
| 12-Month follow-up | 57.5 | 64.8 | 56.5 | 48.9 | 60.6 | 65.3 | 58.9 ± 6.1 | 0.4375 |
| CD4/CD8 | ||||||||
| Baseline | 2.1 | 1.8 | 4.0 | 3.4 | 4.1 | 1.2 | 2.8 ± 1.2 | – |
| After IC injection | 1.8 | 2.0 | − | 3.4 | − | 1.9 | 2.3 ± 0.8 | 0.6250 |
| After IV infusion | 1.6 | − | 5.1 | 2.5 | 3.7 | 1.7 | 2.9 ± 1.5 | 1.0000 |
| 1-Month follow-up | 1.6 | 1.3 | 4.4 | 2.3 | 4.4 | 1.1 | 2.5 ± 1.5 | 0.3125 |
| 3-Month follow-up | 1.5 | 1.6 | 4.1 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 0.8 | 2.3 ± 1.4 | 0.0625 |
| 6-Month follow-up | 1.7 | 1.5 | 3.0 | 2.6 | 2.6 | 0.6 | 2.0 ± 0.9 | 0.0313 |
| 12-Month follow-up | 2.0 | 1.4 | 3.4 | 2.4 | 2.0 | 1.2 | 2.1 ± 0.8 | 0.0938 |
| IgG (mg/dL) | ||||||||
| Baseline | 759 | 1100 | 1430 | 1020 | 689 | 1300 | 1050 ± 292 | – |
| After IC injection | 931 | 1050 | 1490 | 806 | 677 | 922 | 979 ± 280 | 0.5625 |
| After IV infusion | 967 | 1210 | 1440 | 930 | 649 | 1380 | 1096 ± 302 | 0.4375 |
| 1-Month follow-up | 970 | 1120 | 1530 | 1180 | 932 | 1760 | 1249 ± 329 | 0.0313 |
| 3-Month follow-up | 892 | 1250 | 1650 | 1270 | 943 | 1570 | 1263 ± 311 | 0.0313 |
| 6-Month follow-up | 917 | 1210 | 1790 | 1060 | 914 | 1510 | 1234 ± 352 | 0.0313 |
| 12-Month follow-up | 823 | 1180 | 1740 | 1160 | 947 | 1500 | 1225 ± 342 | 0.0313 |
| IgM (mg/dL) | ||||||||
| Baseline | 208.0 | 140.0 | 72.5 | 97.4 | 30.1 | 44.9 | 98.8 ± 66.2 | – |
| After IC injection | 226.0 | 169.0 | 71.0 | 94.1 | 19.1 | 25.2 | 100.7 ± 82.0 | 1.0000 |
| After IV infusion | 272.0 | 174.0 | 70.3 | 105.0 | 20.6 | 36.2 | 113.0 ± 95.2 | 0.6875 |
| 1-Month follow-up | 235.0 | 160.0 | 74.2 | 129.0 | 24.6 | 47.0 | 111.6 ± 78.8 | 0.1563 |
| 3-Month follow-up | 220.0 | 146.0 | 75.4 | 161.0 | 28.9 | 41.8 | 112.2 ± 75.4 | 0.2188 |
| 6-Month follow-up | 208.0 | 133.0 | 82.2 | 110.0 | 18.9 | 37.8 | 98.3 ± 68.7 | 1.0000 |
| 12-Month follow-up | 181.0 | 116.0 | 80.5 | 119.0 | 21.7 | 37.9 | 92.7 ± 58.7 | 0.4375 |
| Anti-HLA antibodies (%) | ||||||||
| Baseline | 0.7 | 0.2 | 1.0 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 1.1 | 0.6 ± 0.4 | – |
| After IC injection | 1.9 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 ± 0.6 | 0.9063 |
| After IV infusion | 1.7 | 0.4 | 0.7 | 0.3 | 3.9 | 0.4 | 1.2 ± 1.4 | 0.6875 |
| 1-Month follow-up | 2.4 | 0.9 | 2.4 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 0.1 | 1.5 ± 0.9 | 0.0938 |
| 3-Month follow-up | 0.7 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.1 | 0.6 | 0.5 ± 0.3 | 0.3750 |
| 6-Month follow-up | 0.8 | 1.9 | 0.7 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 0.9 | 1.0 ± 0.5 | 0.5625 |
| 12-Month follow-up | 0.3 | 0.2 | 1.9 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 0.6 ± 0.7 | 0.7500 |
| Panel reactive antibody assay (%) | ||||||||
| Baseline | 0.40 | 0.20 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 0.30 | 1.20 | 0.4 ± 0.4 | – |
| After IC injection | 1.20 | 0.10 | 0.40 | 0.20 | 0.40 | 0.70 | 0.5 ± 0.4 | 0.8125 |
| After IV infusion | 1.00 | 0.10 | 0.40 | 0.10 | 0.50 | 0.10 | 0.4 ± 0.4 | 1.0000 |
| 1-Month follow-up | 0.60 | 0.30 | 1.50 | 0.90 | 0.50 | 0.10 | 0.7 ± 0.5 | 0.3125 |
| 3-Month follow-up | 0.20 | 0.10 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 0.50 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.0625 |
| 6-Month follow-up | 0.30 | 0.70 | 0.50 | 1.20 | 0.40 | 0.80 | 0.7 ± 0.3 | 0.3438 |
| 12-Month follow-up | 0.10 | 0.10 | 1.30 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 0.30 | 0.4 ± 0.5 | 0.6250 |
aWilcoxon signed-rank test.
ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; BUN, blood urea nitrogen; CD, cluster of differentiation; CK, creatine kinase; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; HLA, human leukocyte antigen; Ig, immunoglobulin; IC, intracoronary; IV, intravenous; RBC, red blood cell; WBC, white blood cell; SD, standard deviation.
TABLE 3.
Adjudication of treatment related adverse events among study subjects.
| Case 01 | Case 02 | Case 03 | Case 04 | Case 05 | Case 06 | n (%) | |
| SUSAR a | N | N | N | N | N | N | 0 (0.00) |
| SAE | |||||||
| Death | N | N | N | N | N | N | 0 (0.00) |
| Life-threateningb | N | N | N | N | N | N | 0 (0.00) |
| Hospitalizationc | N | N | N | N | N | Y | 1 (16.67) |
| Disability/Incapacity | N | N | N | N | N | N | 0 (0.00) |
| Congenital anomaly/Birth defect | N | N | N | N | N | N | 0 (0.00) |
| AE d | |||||||
| Chest pain | N | N | N | N | N | Y | 1 (16.67) |
| Severity | – | – | – | – | – | Mild | |
| Relationship with study IP | – | – | – | – | – | Unrelated | |
| Eczema | N | Y | N | N | N | N | 1 (16.67) |
| Severity | – | Mild | – | – | – | – | |
| Relationship with study IP | – | Unrelated | – | – | – | – | |
| Inguinal hernia | N | N | N | N | N | Y | 1 (16.67) |
| Severity | – | – | – | – | Moderate | ||
| Relationship with study IP | – | – | – | – | Unrelated | ||
| Rash | N | N | N | N | Y | N | 1 (16.67) |
| Severity | – | – | – | – | Mild | – | |
| Relationship with study IP | – | – | – | – | Unrelated | – | |
| MACE | N | N | N | N | N | N | 0 (0.00) |
aThe nature and severity of which is not consistent with the applicable drug information.
bThe subject was at risk of death at the time of event.
cThe subject required hospitalization or prolonged existing hospitalization.
dAny untoward medical occurrence in a patient or clinical investigation subject administered a harmaceutical drug and which did not necessarily have to have a causal relationship with this treatment.
AE, adverse event; MACE, major adverse cardiovascular events; IP, investigational product; SAE, serious adverse event; SUSAR, suspected and unexpected serious adverse reaction; TEAE, treatment emergent adverse event.
Secondary endpoints for efficacy
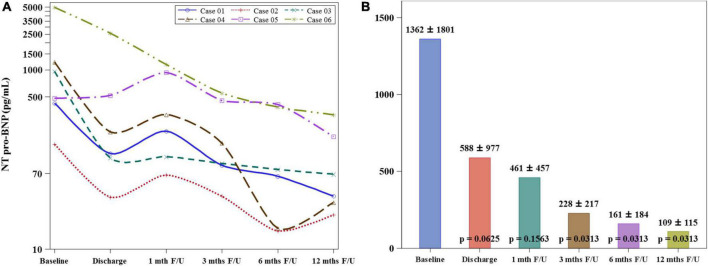
The mean serum level of NT-proBNP decreased significantly at 12-month follow-up when compared to the value at baseline (1362 ± 1801 vs. 109 ± 115 pg/mL, p = 0.0313) (Figure 3). The stroke volume increased from 64.34 ± 11.44 ml/per beat to 84.11 ± 5.26 ml/per beat (p = 0.0033) and LVEF from 52.67 ± 12.75% to 62.47 ± 17.35% (p = 0.0246), while the wall motion score decreased from 26.33 ± 5.57 to 22.33 ± 5.85 (p = 0.0180) at the 12-month follow-up compared to the baseline levels by CMRI (Graphical Abstract and Figure 4). The New York Heart Association functional classification improved from class II at baseline to class I at 12-month follow-up in all study subjects.
FIGURE 3.
Comparison of NT pro-BNP levels between baseline and 12-month follow-up. (A) The serum level of NT pro-BNP of individual study patients shows a consistent declination pattern from baseline to 12-month follow-up. (B) The mean serum level of NT-proBNP decreased significantly at 12-month follow-up when compared to the value at baseline.
FIGURE 4.
Regional left ventricular wall motion score (RLVWMS) and stroke volume evaluated by cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (CMRI). (A) The representative CMRIs of individual study patient at baseline and 12-month follow-up. The RLVWMS decreased (B) and the stroke volume increased (C) at 12-month follow-up compared to the baseline levels.
Discussion
We report a phase I clinical trial of combined IC and IV delivery of UMSC01 that reached the specified endpoints: STEMI patients safely received cell transplantation in this dual-route administration until the 12-month follow-up. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first-in-human study to demonstrate the safety and feasibility of a combined delivery method in AMI patients with STEMI and heart failure. Under the current study design, we observed an improvement in LVEF and functional status, which encourages a randomized double-blind phase II study.
Strengths of UMSC01
To explore the appropriate human MSCs for clinical applications, pluripotent-like markers for culturing MSCs that retain potent survival and self-renewal abilities should be thoroughly investigated. In our previous preclinical report (23), an insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R) expressing sub-population in human MSCs, including umbilical cord-MSCs, were cultured in platelet-derived growth factor-BB (PDGF-BB)-containing human umbilical cord serum (hUCS) and displayed longer survival and stronger proliferation potential. Through intercellular receptor transactivation between CXCR4 and IGF1R signaling pathways, implantation of IGF1R+ MSCs showed significant improvement in neurological function in a stroke model. In this clinical study, we translated the experimental setting by replacing the hUCS with commercially available platelet rich plasma containing high levels of PDGF-BB for culturing UMSC01 to treat the STEMI patients. The preliminary result found that UMSC01 administration might provide not only a safe but also a functional improvement strategy for STEMI patients in this pilot study. A larger-scale placebo-controlled trial is mandatory for demonstrating the definite clinical efficacy in the future.
In patients with AMI, a recent meta-analysis study demonstrated that transplantation of MSCs significantly improves left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) (24). Although Both BMNCs and MSCs contribute to an improvement of cardiac function in the clinical setting of AMI, it is important to know which type of stem cell could outperform the other (25). So far, there is no clinical trial with head-to-head comparison in evaluating the clinical efficacy between BMNCs and MSCs in patients with AMI. Interestingly, Hosseinpour et al. 25 reported that transplantation of MSCs might result in better LVEF improvement than BMNCs in a meta-analysis study. Among the different types of MSCs, umbilical cord-derived MSCs can be easily obtained and cultured (26, 27). Umbilical cord-derived MSCs have shown immunomodulatory and tissue-repair effects with low immunogenicity, which makes them ideal candidates for allogeneic adoptive transfer therapy (28, 29).
Mode of delivery
Stem cell-based cardiac therapy involves the transplantation of cells via various delivery methods. Currently, there are three main routes of cell implantation—intramyocardial (transepicardial or transendocardial), IC, and IV (7). Each delivery technique aims to transfer an adequate number of cells to the infarct site of the heart and to maximize the retention rate of cells, thus improving engraftment and facilitating robust therapeutic outcomes (30). Nevertheless, irrespective of the route of cell delivery, low retention remains a major hurdle limiting the beneficial effects of cell transplantation (31). To date, the vast majority of animal and clinical studies on stem cell therapy in cardiovascular disease have chosen a single delivery method. It is possible that combined IC and IV stem cell transplantation provides more benefits than IC or IV delivery alone (21). The combination of IC and IV for cell delivery, like IC alone, increases the number of cells homing to the injured area of the myocardium, while subsequent IV stem cell treatment allows for a higher cell dose and also exerts systemic anti-inflammatory effects to achieve better therapeutic outcome. Importantly, a study conducted by Liu et al. used a combined approach of cell delivery (IC injection with IV infusion) in a porcine model of chronic myocardial ischemia (32). Their results showed that umbilical cord-MSCs improved the left ventricular function, perfusion, and remodeling. In addition, there was a significant reduction in fibrosis and apoptosis (32). In our study design, we were able to deliver a total of 108 UMSC01 uneventfully. There was no any treatment-related adverse events, including coronary occlusion, immune reaction, or tumor formation. As a pilot phase one study, it is not possible to draw a solid conclusion regarding the efficacy of UMSC01 transplantation. Nevertheless, another randomized clinical trial is ongoing, which compares single with double IC infusion of umbilical cord-derived Wharton’s jelly MSCs in patients with AMI (33). The result may provide better understanding of the effect of repeated transplantation of this cell type on myocardial function (LVEF).
Timing of delivery
Following STEMI, the key events include an acute inflammatory phase in the first 4 days, resolution and repair phase within 2 weeks, and a remodeling phase after 2 weeks (34, 35). Blunting the infarct-triggered inflammation and promotion of late healing are important for the reduction of abnormal cardiac remodeling (36–38). It has been extensively studied in previous studies regarding time of delivery in stem cell therapy after AMI (39–43). For BMNCs, it was suggested to deliver stem cells 3–7 days after AMI for improvement of myocardial function (24). Consistently, a meta-analysis also shows a higher efficacy if MSCs transplantation was performed within the first week following AMI (24). In our study, IC treatment on the 4–5th day post-MI ensured a stable post-AMI condition and was able to modulate the acute immune response and shape acute inflammation. The IV cell administration on the 6–7th day post-MI improved the myocardial repair process and modified scar replacement. A longer stem cell treatment period that covered the golden first 2 weeks after AMI potentially augmented the regeneration effect.
Cell therapy for acute myocardial infarction in post-BAMI era
In most stem cell-treated AMI trials, transplanted cells were BMNCs and the benefits in cardiac regeneration were mixed and uncertain (10). To date, the autologous bone marrow cell therapy in AMI trial (BAMI) is the largest study of stem-based cell therapy for AMI in the world. Initially, BAMI was designed to establish whether BMNCs reduced mortality in patients with STEMI by IC infusion. Unfortunately, the low number of cases was unable to show a significant difference in improving survival between patients and the case–control group. In contrast to BMNCs, MSCs show consistent findings of improvement in cardiac function. MSCs, especially UMSC01, have multiple differentiation capabilities, immune exemption, easy access, large-scale expansion, and ethical advantages. The work by Gao et al. (29) demonstrated that IC delivery of UMSC01 could significantly improve myocardial viability and cardiac function in patients with STEMI. Furthermore, in our study, we showed that UMSC01 delivery using this novel administration method is safe and feasible in human beings. Although we did not include a control group in this trial, the enrolled patients showed an improvement in cardiac function, regional wall motion, heart failure symptoms, and biomarkers, indicating that UMSC01 transplantation might be beneficial in post-AMI cardiac repair.
Over the last two decades, almost 100 blinded and unblinded AMI clinical trials worldwide have shown an excellent safety profile of cell-based therapy but have reported mixed and uncertain results on its potential benefits (9, 10, 21, 44). Of note, the number of enrolled patients in many of the clinical trials were not sufficient to test the benefits of stem cell transplantation when combined with the current guideline-directed AMI therapy (44, 45). The BAMI trial failed to demonstrate that BMNC therapy improves survival in patients with AMI due to low enrollment and low mortality rates. However, the BAMI researchers observed the clinical benefit of reduced heart failure associated hospitalization in patients receiving BMNC therapy (45). In a recent meta-analysis study, Attar et al. further confirmed that BMNC therapy improved clinical outcomes in terms of reinfarction and hospitalization for heart failure (46). Thus, it is crucial to identify a better cell type, optimal dose, and route of transplantation to strengthen the therapeutic effect and achieve a statistical significance in the post-BAMI era (10).
Study limitations
This study had some limitations. First, although this pilot trial was designed to determine whether the novel approach of combined IC and IV delivery of UMSC01 in STEMI patients is safe, the sample size of six analyzable subjects was relatively small. Second, placebo-treated patients were not included in this phase I study. The efficacy of UMSC01 transplantation remains unclear. However, stem cell-treated patients exhibited improvement in heart function after a 12-month follow-up period. Third, this study focused mainly on the safety and feasibility of the combined IC and IV methods and thus did not provide comprehensive multimodality imaging in the assessment of efficacy. Lastly, in this pilot study, although we observed no significant changes of several immunology parameters including CD3, CD4/CD8, anti-HLA antibodies, and panel reactive antibody assay between baseline and at the 12-month follow-up, it is indeed necessary to measure more immunology/inflammatory markers such as IL-6 and IL-10 in the future phase II study.
Conclusion
In this pilot study, our approach of IC injection combined with IV infusion of UMSC01 in STEMI patients with impaired LVEF appears to be safe, feasible, and potentially beneficial in improving cardiac systolic function and heart failure symptoms up to 12 months after treatment. As this is the first trial of dual-route transplantation of stem cells in humans, larger randomized and placebo-controlled phase II studies are required to demonstrate the efficacy of this novel approach.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by the Research Ethics Committee of China Medical University Hospital (CMUH107-REC1-088). The trial was monitored by an independent data and safety monitoring board who met as planned to assess adverse events. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
L-CH, Y-NL, and W-CS: conception and design, provision of study material or patients, data analysis and interpretation, manuscript writing, and final approval of manuscript. MH, C-RL, S-SC, Y-CW, J-YC, S-YL, K-YL, and Y-KL: provision of study material or patients, collection of data, data analysis and interpretation, and final approval of manuscript. M-YW, W-YT, M-YS, C-TH, C-KT, L-TC, C-LC, C-LL, and K-CH: data analysis and interpretation, final approval of manuscript. D-YC and C-HT: financial support and administrative support. K-CC and L-BJ: financial support, conception and design, provision of study material or patients, data analysis and interpretation, manuscript writing, and final approval of manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Abbreviations
- ACC
American College of Cardiology
- AE
adverse event
- AHA
American Heart Association
- AMI
acute myocardial infarction
- BMNC
bone marrow mononuclear cell
- CD
cluster of differentiation
- CEA
carcinoembryonic antigen
- CK-MB
creatine kinase-myocardial band
- CMRI
cardiac magnetic resonance imaging
- CXCR4
C-X -C Motif Chemokine Receptor 4
- ECG
electrocardiography
- FEV1
forced expiratory volume in 1 s
- HLA
human leukocyte antigen
- hUCS
human umbilical cord serum
- IABP
intra-aortic balloon pump
- IC
intracoronary
- ICU
intensive care unit
- Ig
immunoglobulin
- IGF1R
insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor
- IV
intravenous
- LVEF
left ventricular ejection fraction
- MACE
major adverse cardiovascular events
- MOLLI
modified look-locker inversion recovery
- MSC
mesenchymal stem cell
- NT pro-BNP
amino-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide
- PCI
percutaneous coronary intervention
- PDGF-BB
platelet-derived growth factor-BB
- RLVWMS
regional left ventricular wall motion score
- SAE
serious adverse event
- STEMI
ST-elevation myocardial infarction
- SUSAR
suspected and unexpected serious adverse reaction
- TIMI
thrombolysis in myocardial infarction
- UC-MSC
umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell.
Funding
This study was supported by Ever Supreme Bio Technology Co., Ltd. and Ministry of Economic Affairs ROC A + program. This study was supported in part by Taiwan Ministry of Health and Welfare Clinical Trial Center (MOHW110-TDU-B-212-124004) and China Medical University Hospital (DMR-111-105). The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
C-HT was the founder of Ever Supreme Bio Technology. W-CS, D-YC, K-CC, and L-BJ were stockholders of the Ever Supreme Bio Technology. W-CS was employed by Ever Supreme Bio Technology and China Medical University Hospital. C-TH, C-KT, L-TC, and C-LC were employed by Ever Supreme Bio Technology. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcvm.2022.961920/full#supplementary-material
References
- 1.Yeh RW, Sidney S, Chandra M, Sorel M, Selby JV, Go AS. Population trends in the incidence and outcomes of acute myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. (2010) 362:2155–65. 10.1056/NEJMoa0908610 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Frangogiannis NG. The inflammatory response in myocardial injury, repair, and remodelling. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2014) 11:255–65. 10.1038/nrcardio.2014.28 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Panahi M, Papanikolaou A, Torabi A, Zhang JG, Khan H, Vazir A, et al. Immunomodulatory interventions in myocardial infarction and heart failure: A systematic review of clinical trials and meta-analysis of IL-1 inhibition. Cardiovasc Res. (2018) 114:1445–61. 10.1093/cvr/cvy145 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Huang S, Frangogiannis NG. Anti-inflammatory therapies in myocardial infarction: Failures, hopes and challenges. Br J Pharmacol. (2018) 175:1377–400. 10.1111/bph.14155 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Makkar RR, Smith RR, Cheng K, Malliaras K, Thomson LE, Berman D, et al. Intracoronary cardiosphere-derived cells for heart regeneration after myocardial infarction (caduceus): A prospective, randomised phase 1 trial. Lancet. (2012) 379:895–904. 10.1016/s0140-6736(12)60195-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Wagner MJ, Khan M, Mohsin S. Healing the broken heart; the immunomodulatory effects of stem cell therapy. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:639. 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00639 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hsiao LC, Carr C, Chang KC, Lin SZ, Clarke K. Stem cell-based therapy for ischemic heart disease. Cell Transplant. (2013) 22:663–75. 10.3727/096368912X655109 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hsiao LC, Perbellini F, Gomes RS, Tan JJ, Vieira S, Faggian G, et al. Murine cardiosphere-derived cells are impaired by age but not by cardiac dystrophic dysfunction. Stem Cells Dev. (2014) 23:1027–36. 10.1089/scd.2013.0388 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Banerjee MN, Bolli R, Hare JM. Clinical studies of cell therapy in cardiovascular medicine: Recent developments and future directions. Circ Res. (2018) 123:266–87. 10.1161/circresaha.118.311217 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Carbone RG, Monselise A, Bottino G, Negrini S, Puppo F. Stem cells therapy in acute myocardial infarction: A new era?. Clin Exp Med. (2021) 21:231–7. 10.1007/s10238-021-00682-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Mathiasen AB, Qayyum AA, Jørgensen E, Helqvist S, Kofoed KF, Haack-Sørensen M, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cell treatment in patients with ischaemic heart failure: Final 4-year follow-up of the MSC-HF trial. Eur J Heart Fail. (2020) 22:884–92. 10.1002/ejhf.1700 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bolli R, Kahlon A. Time to end the war on cell therapy. Eur J Heart Fail. (2020) 22:893–7. 10.1002/ejhf.1767 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Jiang W, Xu J. Immune modulation by mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Prolif. (2020) 53:e12712. 10.1111/cpr.12712 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Saldaña L, Bensiamar F, Vallés G, Mancebo FJ, García-Rey E, Vilaboa N. Immunoregulatory potential of mesenchymal stem cells following activation by macrophage-derived soluble factors. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2019) 10:58. 10.1186/s13287-019-1156-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gao F, Chiu SM, Motan DA, Zhang Z, Chen L, Ji HL, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells and immunomodulation: Current status and future prospects. Cell Death Dis. (2016) 7:e2062. 10.1038/cddis.2015.327 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lin YN, Ibrahim A, Marbán E, Cingolani E. Pathogenesis of arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy: Role of inflammation. Basic Res Cardiol. (2021) 116:39. 10.1007/s00395-021-00877-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Galipeau J, Sensébé L. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: Clinical Challenges and Therapeutic Opportunities. Cell Stem Cell. (2018) 22:824–33. 10.1016/j.stem.2018.05.004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hashmi S, Ahmed M, Murad MH, Litzow MR, Adams RH, Ball LM, et al. Survival after mesenchymal stromal cell therapy in steroid-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Haematol. (2016) 3:e45–52. 10.1016/s2352-3026(15)00224-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Yao K, Huang R, Sun A, Qian J, Liu X, Ge L, et al. Repeated autologous bone marrow mononuclear cell therapy in patients with large myocardial infarction. Eur J Heart Fail. (2009) 11:691–8. 10.1093/eurjhf/hfp062 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Tang XL, Nakamura S, Li Q, Wysoczynski M, Gumpert AM, Wu WJ, et al. Repeated administrations of cardiac progenitor cells are superior to a single administration of an equivalent cumulative dose. J Am Heart Assoc. (2018) 7:e007400. 10.1161/JAHA.117.007400 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Liu C, Han D, Liang P, Li Y, Cao F. The current dilemma and breakthrough of stem cell therapy in ischemic heart disease. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2021) 9:636136. 10.3389/fcell.2021.636136 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zhang R, Yu J, Zhang N, Li W, Wang J, Cai G, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells transfer in patients with st-segment elevation myocardial infarction: single-blind, multicenter, randomized controlled trial. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2021) 12:33. 10.1186/s13287-020-02096-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lee HT, Chang HT, Lee S, Lin CH, Fan JR, Lin SZ, et al. Role of IGF1R(+) MSCs in modulating neuroplasticity via CXCR4 cross-interaction. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:32595. 10.1038/srep32595 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Attar A, Bahmanzadegan Jahromi F, Kavousi S, Monabati A, Kazemi A. Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation after acute myocardial infarction: A meta-analysis of clinical trials. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2021) 12:600. 10.1186/s13287-021-02667-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Hosseinpour A, Kheshti F, Kazemi A, Attar A. Comparing the effect of bone marrow mono-nuclear cells with mesenchymal stem cells after acute myocardial infarction on improvement of left ventricular function: A meta-analysis of clinical trials. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2022) 13:203. 10.1186/s13287-022-02883-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Fong CY, Chak LL, Biswas A, Tan JH, Gauthaman K, Chan WK, et al. Human Wharton’s jelly stem cells have unique transcriptome profiles compared to human embryonic stem cells and other mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Rev Rep. (2011) 7:1–16. 10.1007/s12015-010-9166-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Singh A, Singh A, Sen D. Mesenchymal stem cells in cardiac regeneration: A detailed progress report of the last 6 years (2010-2015). Stem Cell Res Ther. (2016) 7:82. 10.1186/s13287-016-0341-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Bartolucci J, Verdugo FJ, González PL, Larrea RE, Abarzua E, Goset C, et al. Safety and efficacy of the intravenous infusion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in patients with heart failure: A phase 1/2 randomized controlled trial (Rimecard trial [randomized clinical trial of intravenous infusion umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on cardiopathy]). Circ Res. (2017) 121:1192–204. 10.1161/circresaha.117.310712 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Gao LR, Chen Y, Zhang NK, Yang XL, Liu HL, Wang ZG, et al. Intracoronary infusion of wharton’s jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells in acute myocardial infarction: Double-blind, randomized controlled trial. BMC Med. (2015) 13:162. 10.1186/s12916-015-0399-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wollert KC, Drexler H. Clinical applications of stem cells for the heart. Circ Res. (2005) 96:151–63. 10.1161/01.Res.0000155333.69009.63 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Terrovitis J, Lautamäki R, Bonios M, Fox J, Engles JM, Yu J, et al. Noninvasive quantification and optimization of acute cell retention by in vivo positron emission tomography after intramyocardial cardiac-derived stem cell delivery. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2009) 54:1619–26. 10.1016/j.jacc.2009.04.097 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Liu CB, Huang H, Sun P, Ma SZ, Liu AH, Xue J, et al. Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stromal cells improve left ventricular function, perfusion, and remodeling in a porcine model of chronic myocardial ischemia. Stem Cells Transl Med. (2016) 5:1004–13. 10.5966/sctm.2015-0298 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Attar A, Nouri F, Yazdanshenas A, Hessami K, Vosough M, Abdi-Ardekani A, et al. Single Vs. double intracoronary injection of mesenchymal stromal cell after acute myocardial infarction: The study protocol from a randomized clinical trial: Booster-taha7 trial. Trials. (2022) 23:293. 10.1186/s13063-022-06276-y [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Prabhu SD. Healing and repair after myocardial infarction: The forgotten but resurgent basophil. J Clin Invest. (2021) 131:e150555. 10.1172/jci150555 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Prabhu SD, Frangogiannis NG. The biological basis for cardiac repair after myocardial infarction: from inflammation to fibrosis. Circ Res. (2016) 119:91–112. 10.1161/circresaha.116.303577 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Zhang J, Bolli R, Garry DJ, Marbán E, Menasché P, Zimmermann WH, et al. Basic and translational research in cardiac repair and regeneration: JACC state-of-the-art review. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2021) 78:2092–105. 10.1016/j.jacc.2021.09.019 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.de Couto G, Liu W, Tseliou E, Sun B, Makkar N, Kanazawa H, et al. Macrophages mediate cardioprotective cellular postconditioning in acute myocardial infarction. J Clin Invest. (2015) 125:3147–62. 10.1172/jci81321 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Cheng B, Chen HC, Chou IW, Tang TW, Hsieh PC. Harnessing the early post-injury inflammatory responses for cardiac regeneration. J Biomed Sci. (2017) 24:7. 10.1186/s12929-017-0315-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Choudry F, Hamshere S, Saunders N, Veerapen J, Bavnbek K, Knight C, et al. A randomized double-blind control study of early intra-coronary autologous bone marrow cell infusion in acute myocardial infarction: The regenerate-ami clinical trialdagger. Eur Heart J. (2016) 37:256–63. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv493 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Traverse JH, Henry TD, Pepine CJ, Willerson JT, Zhao DX, Ellis SG, et al. Effect of the use and timing of bone marrow mononuclear cell delivery on left ventricular function after acute myocardial infarction: The time randomized trial. JAMA. (2012) 308:2380–9. 10.1001/jama.2012.28726 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Traverse JH, Henry TD, Ellis SG, Pepine CJ, Willerson JT, Zhao DX, et al. Effect of intracoronary delivery of autologous bone marrow mononuclear cells 2 to 3 weeks following acute myocardial infarction on left ventricular function: The latetime randomized trial. JAMA. (2011) 306:2110–9. 10.1001/jama.2011.1670 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Zhang S, Sun A, Xu D, Yao K, Huang Z, Jin H, et al. Impact of timing on efficacy and safetyof intracoronary autologous bone marrow stem cells transplantation in acute myocardial infarction: A pooled subgroup analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin Cardiol. (2009) 32:458–66. 10.1002/clc.20575 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Delewi R, Hirsch A, Tijssen JG, Schachinger V, Wojakowski W, Roncalli J, et al. Impact of intracoronary bone marrow cell therapy on left ventricular function in the setting of st-segment elevation myocardial infarction: A collaborative meta-analysis. Eur Heart J. (2014) 35:989–98. 10.1093/eurheartj/eht372 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Bolli R. Cell therapy for acute myocardial infarction: Requiescat in pace. Eur Heart J. (2020) 41:3711–4. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa802 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Mathur A, Fernandez-Aviles F, Bartunek J, Belmans A, Crea F, Dowlut S, et al. The effect of intracoronary infusion of bone marrow-derived mononuclear cells on all-cause mortality in acute myocardial infarction: The bami trial. Eur Heart J. (2020) 41:3702–10. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa651 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Attar A, Hosseinpour A, Hosseinpour H, Kazemi A. Major cardiovascular events after bone marrow mononuclear cell transplantation following acute myocardial infarction: An updated post-bami meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. (2022) 22:259. 10.1186/s12872-022-02701-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.