Abstract
Recent studies have revealed important functions of several microRNAs (miRNAs) in the pathogenesis of human diseases. miR-324 is an example of miRNAs with crucial impacts on the pathogenesis of a wide range of disorders. Gene ontology studies have indicated possible role of miR-324 in responses of cells to the leukemia inhibitory factor, long-term synaptic potentiation, positive regulation of cytokines production and sensory perception of sound. In human, miR-324 is encoded by MIR324 gene which resides on chromosome 17p13.1. In the current manuscript, we provide a concise review of the role of miR-324 in the pathogenesis of cancers as well as non-cancerous conditions such as aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage, diabetic nephropathy, epilepsy, pulmonary/renal fibrosis, ischemic stroke and ischemia reperfusion injuries. Moreover, we summarize the role of this miRNA as a prognostic marker for malignant disorders.
Keywords: miR-324, cancer, biomarker, expreesion, prognostic
Introduction
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small regulatory molecules that have principal roles in several cellular processes. They DNA sequences coding these transcripts are mainly transcribed into primary miRNAs. Primary miRNAs are then processed into the precursor and mature miRNAs through a multistep process. miRNAs principally affect genes expression through binding with the 3′ UTR of the target mRNAs. This interaction induces degradation of mRNAs or repression of their translation. In some cases, miRNAs can interact with 5′ UTR or even coding or promoter regions (O'Brien et al., 2018). Notably, the interplay between miRNAs and their targets is dynamic. It depends on subcellular localization of miRNAs, quantities of both miRNAs and target transcripts, and the affinity of miRNA-target interaction which is mainly determined by the mode of base pairing (O'Brien et al., 2018).
miR-324 is an example of miRNAs with crucial impacts on the pathogenesis of human disorders. This miRNA participates in gene silencing. Gene ontology studies have indicated possible role of miR-324 in diverse processes, namely responses of cells to the leukemia inhibitory factor, long-term synaptic potentiation, positive regulation of cytokines production and sensory perception of sound (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/442898). In human, miR-324 is encoded by MIR324 gene which is located on chromosome 17p13.1.
Through interaction with a variety of RNA molecules, miR-324 participates in the etiopathology of several cancers as well as non-cancerous disorders such as aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage, anorectal malformation, cardiac diseases, diabetic nephropathy, epilepsy, HIV lipodystrophy, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, ischemic stroke, myocardial ischemia reperfusion (I/R) injuries, nerve injury, osteoarthritis, Parkinson’s disease, polycystic ovarian syndrome, renal fibrosis and thermal injury.
In the current manuscript, we provide a concise review of the role of miR-324 in the pathogenesis of mentioned disorders. Moreover, we summarize the role of this miRNA as a prognostic marker for malignant disorders.
Role of miR-324 in cancers
Cervical cancer
Cervical cancer is an example of cancers in which miR-324 is dysregulated. However, different studies in this type of cancer have reported inconsistent results regarding the pattern of expression and exact role of miR-324 in cervical cancer. This inconsistency might be explained by different roles of miR-324-5p and miR-324-3p. Zhang et al. (2020) have shown that upregulation of the cytoplasmic long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) LINC00511 leads to downregulation of miR-324 in cervical cancer cell lines. DRAM1 has been identified as a target of miR-324 in these cells. Both miR-324-5p mimics and LINC00511 targeting siRNAs reverse the oncogenic effects of DRAM1 on cervical cancer cells. Cumulatively, LINC00511 has been found to act as a competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA). This lncRNA regulates activity of miR-324-5p/DRAM1 axis and promotes progression of cervical cancer irrespective of the presence of HPV (Zhang et al., 2020). Similarly, through gain- and loss- experiments, Jiang et al. have shown that miR-324-5p inhibits colony construction, proliferative ability, migration, invasive properties and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in cervical cancer. The sponging effect of TPT1-AS1 on miR-324-5p leads to enhancement of cell growth and metastases in this type of cancer (Jiang et al., 2018).
Conversely, Shi et al. (2020) have reported upregulation of miR-324 in cervical cancer cells and clinical samples. They have also shown that the tumor suppressor lncRNA H1FX-AS1 acts as a ceRNA for miR-324-3p to surge expression of DACT1 (Shi et al., 2020). Figure 1 shows the impact of miR-324 in cervical carcinogenesis.
FIGURE 1.
Role of miR-324 in progression of cervical cancer.
Colorectal cancer
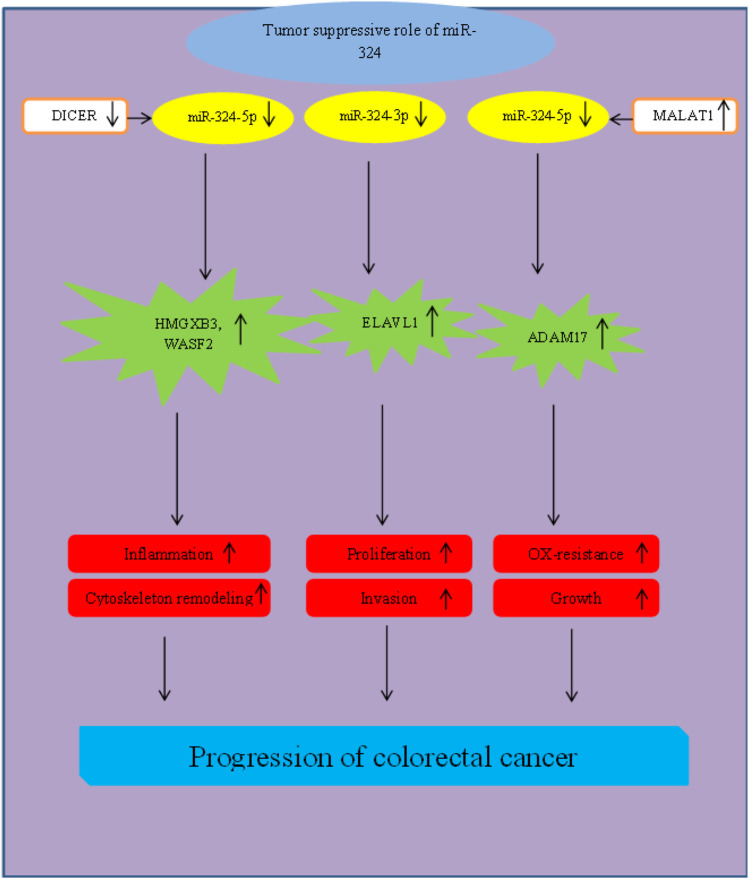
In colorectal cancer, both miR-324-5p (Huang et al., 2022) and miR-324-3p (Xiao et al., 2019) have been found to be downregulated. An in vitro study in colorectal cancer cells has shown the sponging effects of VPS9D1-AS1 on miR-324-5p and demonstrated this mechanism as the underlying cause of downregulation of miR-324-5p in these cells. In line with the observed targeting of ITGA2 3′ UTR by miR-324-5p targets, miR-324-5p knock-down or forced over-expression of ITGA2 has reduced the impact of VPS9D1-AS1 silencing in colorectal cancer cells. Taken together, VPS9D1-AS1/miR-324-5p/ITGA2 axis has been reported to affect pathogenesis of colorectal cancer (Huang et al., 2022). Another study has confirmed the role of Dicer in the regulation of expression of miR-324. Assessment of expression profile of colorectal cancer cell lines as well as intestinal epithelial cells of mice has shown significant reduction of miR-324-5p expression after deletion of Dicer. miR-324-5p has been shown to bind to the 3′ UTRs of HMGXB3 and WASF-2, two important molecules with essential roles in cell motility and cytoskeleton remodeling. Intraperitoneal administration of a miR-324-5p agonist has reduced chronic inflammatory responses and cytoskeleton remodeling of colorectal epithelial cells and reestablished intestinal barrier integrity in Dicer-deleted cells of mice. Cumulatively, DICER/miR-324-5p/HMGXB3/WASF-2 axis has been found to affect colorectal tumorigenesis through modulation of cytoskeleton remodeling and intestinal barrier function (Sun et al., 2017). MALAT1/miR-324-3p/ADAM17 (Fan et al., 2020) and miR-324-3p/ELAVL1 (Xiao et al., 2019) axes are two other molecular axes participating in the pathogenesis of colorectal cancer (Figure 2).
FIGURE 2.
Role of miR-324 in progression of colorectal cancer.
Gastric cancer
In gastric cancer, two different studies have reported upregulation of miR-324-5p (Tang et al., 2021a; Zheng et al., 2021), while another study has reported downregulation of this miRNA (Xie et al., 2021). miR-324-3p has also been reported to be upregulated in gastric cancer tissues (Sun et al., 2018). Circ0049447/miR-324-5p (Tang et al., 2021a) and Circ0091994/miR-324-5p/HMGA1 (Xie et al., 2021) axes have been shown to affect gastric tumorigenesis (Figure 3).
FIGURE 3.
Role of miR-324 in progression of gastric cancer.
Brain tumors
Different experiments in brain tumors have confirmed tumor suppressor role of miR-324. For instance, SERPINE2 has been found to induce proliferation of glioblastoma cells and inhibit their apoptosis via influencing activity of miR-324-5p/BCL2 axis (Li et al., 2021). Moreover, the oncogenic lncRNA NEAT1 promotes progression of glioma through sponging miR-324-5p and inducing expression of KCTD20 (Zhang et al., 2021). Finally, miR-324-5p could hamper cell proliferation and Temozolomide (TMZ) resistance via targeting EZH2 (Zhi et al., 2017) (Figure 4).
FIGURE 4.
Role of miR-324 in progression of brain tumors.
Hepatocellular carcinoma
In hepatocellular carcinoma, miR-324-5p has been shown to be downregulated (Huang et al., 2020a), while miR-324-3p has been upregulated (Tuo et al., 2017). Comprehensive assessment of expression profile of plasma exosomes in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma has led to identification of a novel differentially expressed lncRNA, namely RP11-85G21.1 (lnc85) which has been shown to promote proliferation and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through binding with miR-324-5p (Huang et al., 2020a). CircZNF83/miR-324-5p/CDK16 (Zhao et al., 2021a), LINC00491/miR-324-5p/ROCK1 (Wan g et al., 2021) and YY1/linc01134/miR-324-5p/IGF2BP1 (Rong et al., 2020) are other molecular axes that influence pathogenesis of this type of cancer (Figure 5).
FIGURE 5.
Role of miR-324 in progression of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Other types of cancer
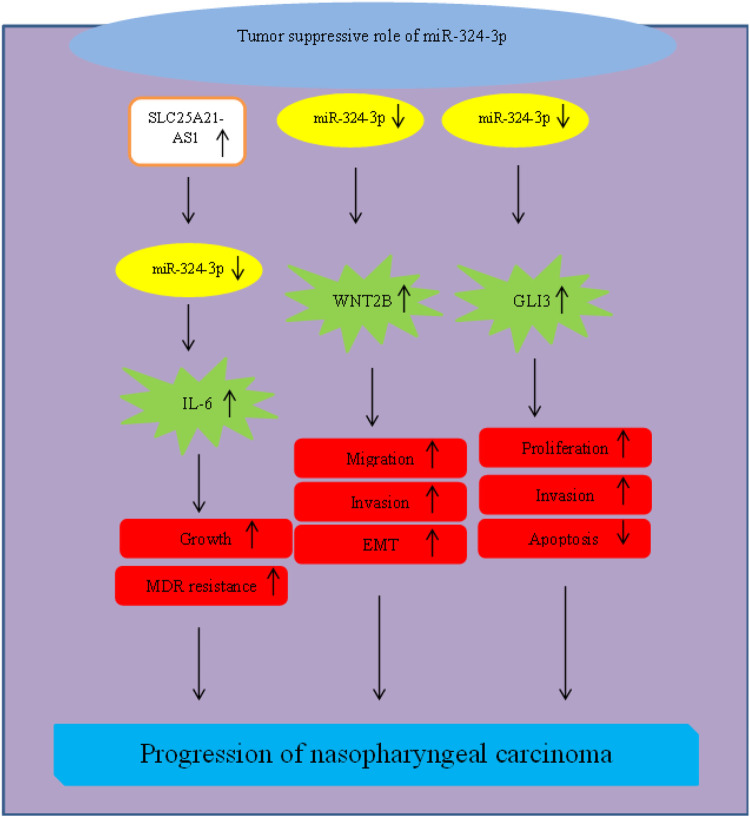
In nasopharyngeal carcinoma, miR-324-3p has been shown to exert a tumor suppressor role. This miRNA could exert this effect through targeting GLI3 (Zhang et al., 2017), WNT2B (Liu et al., 2017) and SMAD7 (Xu et al., 2015). Moreover, the oncogenic role of SLC25A21-AS1 in this type of cancer has been found to be exerted through sponging miR-324-3p and increasing expression of IL-6 (Wang et al., 2020a) (Figure 6).
FIGURE 6.
Role of miR-324 in progression of nasopharyngeal cancer.
Studies in other types of cancers have also indicated importance of miR-324 in the evolution and progression of cancer (Table 1).
TABLE 1.
miR-324 in cancers (ANCS, adjacent non-cancerous sample; OX, oxaliplatin; TMZ, temozolomide; MDR, multidrug resistance; FNA, fine needle aspiration; LNM, lymph node metastasis).
| Tumor type | Expression | Samples | Downstream targets | Upstream molecules | Description | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bladder cancer (BC) | miR-324 (3p, 5p) upregulated in TCGA database, miR-324-5p upregulated in 22 BC tissues versus 13 ANCSs | TCGA database, 22 BC tissues and 13 ANCSs | PTPRD, RCAN1, AMHR2, EYA4, UNC5C, SETBP1,CDC42BPA, APOLD1 and GPX3 | — | miR-324 (3p, 5p) upregulation could promote proliferation, colony formation ability, and invasiveness. | Tsai et al. (2020) |
| Breast cancer | miR-324-3p (down) | 45 pairs of cancer tissues and ANCSs/mice | ACK1 | LINC00963 | LINC00963 via miR-324-3p/ACK1 axis could promote malignancy features and radioresistance. | Zhang et al. (2019a) |
| Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) | miR-324-3p (down) | 70 pairs of TNBC tissues and ANCSs/mice | SUDS3, caspase3 | SNHG22 | SNHG22 via miR-324-3p/SUDS3 can promote tumorigenesis. | Fang et al. (2020) |
| Cervical cancer (CC) | miR-324-5p (down) | GEPIA database, 19 pairs of CC tissues and ANCSs | DRAM1 | LINC00511 | LINC00511 via miR-324-5p/DRAM1 axis could provoke tumorigenesis. | Zhang et al. (2020) |
| miR-324-3p (up) | 50 pairs of CC tissues and ANCSs/mice | DACT1, cleaved Caspase 3, and Bcl-2 | H1FX-AS1 | H1FX-AS1 through miR-324-3p/DACT1 axis could block cell proliferation. | Shi et al. (2020) | |
| miR-324-5p (down) | 40 pairs of CC tissues and ANCSs/mice | SP1, E-cadherin, vimentin | TPT1-AS1 | TPT1-AS1via miR-324-5p/SP1 could promote tumorigenesis. | Jiang et al. (2018) | |
| Colorectal cancer (CRC) | miR-324-5p (down) | TCGA database, 23 pairs of cancer tissues and ANCSs/mice | ITGA2 | VPS9D1-AS1 | VPS9D1-AS1 via miR-324-5p/ITGA2 could increase tumorigenesis. | Huang et al. (2022) |
| miR-324-5p (down) | Mice | HMGXB3 and WASF-2 | DICER | DICER/miR-324-5p via HMGXB3/WASF-2 targeting could impede CRC tumorigenesis. | Sun et al. (2017) | |
| miR-324-3p (down) in Ox-resistant tissues and cells | 40 Ox-resistant and 40 Ox-sensitive CRC tissues/mice | ADAM17, Bcl-2, Cleaved caspase-3, E-cadherin and Vimentin | MALAT1 | MALAT1 via miR-324-3p/ADAM17 axis regulation could enhance tumorigenesis, and Ox-resistance. | Fan et al. (2020) | |
| miR-324-3p (down) | — | ELAVL1, MMP-9, uPA, and uPAR | — | miR-324-3p via ELAVL1 suppression could prevent cell proliferation. | Xiao et al. (2019) | |
| Endometrial carcinoma | miR-324-5p (down) | 10 endometrial cancer and 10 normal endometrial specimens/mice | HMGA1 | Circ0067835 | Circ0067835 via miR-324-5p/HMGA1 axis could enhance cell proliferation. | Li u et al. (2020) |
| Gastric cancer (GC) | miR-324-5p (up) | 30 pairs of GC tissues and ANCSs/mice | PTPRD | Circ0049447 | Circ0049447 via miR-324-5p targeting could prevent tumorigenesis. | Tang et al. (2021a) |
| miR-324-5p (down) | 5 pairs of GC tissues and ANCSs/mice | HMGA1 | Circ0091994 | Circ0091994 through miR-324-5p/HMGA1 targeting could provoke tumorigenesis. | Xie et al. (2021) | |
| miR-324-3p (up) | 68 pairs of GC tissues and ANCSs/mice | Smad4, β-catenin, cyclin D1, CD44, c-jun, c-Met, and TCF-1 | — | miR-324-3p via Smad4/Wnt signaling pathway regulation could promote cell growth and migration, and repress apoptosis. | Sun et al. (2018) | |
| miR-324-5p (up) | 122 pairs of GC tissues and ANCSs | PTEN | — | miR-324-5p via PTEN regulation could impede cell proliferation and provoke cell apoptosis. | Zheng et al. (2021) | |
| Glioblastoma | miR-324-5p (down) | 46 pairs of glioblastoma samples and normal brain specimens/mice | BCL2, PCNA, Ki67, cyclinD1, Bax, cleaved caspase3 | SERPINE2 | SERPINE2 via miR-324-5p/BCL2 regulation could promote cell proliferation. | Li et al. (2021) |
| Glioma | miR-324-5p (down) | TCGA and CGGA database, 43 pairs of glioma tissues and ANCSs/mice | KCTD20, CDK4, cyclin D1, Bcl2, Bax | NEAT1 | NEAT1 through miR-324-5p/KCTD20 regulation could promote tumorigenesis. | Zhang et al. (2021) |
| miR-324-5p (down) | CGGA database, 8 normal brain samples, 8 grade II and 8 grade IV glioma samples/mice | EZH2, DKK1 and p21 | — | miR-324-5p via EZH2 targeting could hamper cell proliferation and TMZ resistance. | Zhi et al. (2017) | |
| Hemangioma | miR-324-3p (down) | 16 tissues from proliferative hemangiomas and 14 from involuting hemangiomas | PDRG1 | FOXD2-AS1 | FOXD2-AS1 via miR-324-3p/PDRG1 regulation could increase cell proliferation. | Zhao et al. (2020) |
| Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) | miR-324-5p (down) | Blood samples of 116 HCC patients, 43 liver cirrhosis patients, and 52 healthy controls | MMP2, MMP9, Bcl-2, cyclin D1, cyclin B1, c-myc | Lnc85 | Lnc85 by miR-324-5p regulation could promote proliferation and migration. | Huang et al. (2020a) |
| miR-324-5p (down) | 46 pairs of HCC and normal tissues/mice | IGF2BP1 | YY1, linc01134 | YY1/linc01134/miR-324-5p/IGF2BP1 could participate in the HCC malignancy. | Rong et al. (2020) | |
| miR-324-5p (down) | 11 pairs of HCC tumor and ANCSs | ETS1, SP1, MMP2, MMP9 | — | miR-324-5p via ETS1 and SP1 targeting suppresses cell migration and invasion. | Cao et al. (2015) | |
| miR-324-3p (up in HBV-associated HCC) | Blood samples from 96 HBV-associated HCC cases, 52 HBV-unrelated HCC cases, 72 chronic hepatitis B patients, and 76 normal subjects | — | — | miR-324-3p participates in the progression of HBV-associated hepatitis to HCC. | Zhao et al. (2021b) | |
| miR-324-3p (up) | 73 pairs of HCC tissues and ANCSs/mice | DACT1, β-catenin, c-Myc and cyclin D1 | — | miR-324-3p via DACT1 targeting could promote cell viability. | Tuo et al. (2017) | |
| miR-324-5p (down) | 42 airs of HCC tissues and ANCSs/mice | CDK16, JAK2/STAT3, Bax, Bcl-2, cleaved caspase3 | GL63, CircZNF83 | GL63 through regulation of and circZNF83/miR-324-5p/CDK16 axis and suppression of JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway could prevent tumorigenesis. | Zhao et al. (2021a) | |
| miR-324-5p (down) | 60 pairs of HCC and ANCSs/mice | ROCK1 | LINC00491 | LINC00491 via miR-324-5p/ROCK1 could induce proliferation, and inhibit apoptosis. | Wan g et al. (2021) | |
| Lung cancer | miR-324-5p (up) | TCGA and GTEx project/100 pairs of lung cancer tissues and ANCSs | FBXO11 | GATA6-AS1 | GATA6-AS1 through regulation of miR-324-5p/FBXO11 and SNAIL could inhibit cell proliferation. | Wang et al. (2020b) |
| miR-324-5p (-) | — | RAP1A, Bcl-2, cleaved caspase-3 and cleaved PARP | PCAT-1 | PCAT-1 via miR-324-5p/RAP1A increases proliferation and inhibits apoptosis. | Huang et al. (2020b) | |
| miR-324 (up) | TCGA database | GPX3, RCAN1 and MGAT3 | — | miR-324-5p promotes cell proliferation and invasion, while miR-324-3p only increases cell proliferation. | Lin et al. (2018) | |
| Lung squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC) | miR-324-3p (up) | Plasma from 395 patients with different tumors and 195 healthy controls | 331 genes | — | miR-324-3p level could act as an early detection and prognostic marker. | Gao et al. (2016) |
| miR-324-3p (up) | TCGA/36 lung tissues | FAM46C | — | miR-296-5p, miR-324-3p, and miR-3928-3p could suppress FAM46C to induce MYC expression and cell proliferation. | Xia et al. (2018) | |
| Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) | miR-324-3p (down) | 40 pairs of lung adenocarcinoma specimens | Cyclin D1, ki-67 | LOXL1-AS1 | LOXL1-AS1 via downregulation of miR-324-3p enhances cell proliferation. | Xie et al. (2019) |
| Melanoma | miR-324-5p (down) | 50 melanoma tissues and 50 normal skin tissues | CDK16 | HCG18 | HCG18 via miR-324-5p/CDK16 regulation could promote cell proliferation. | Zhang et al. (2022) |
| Multiple myeloma (MM) | miR-324-3p (-) | — | Wnt, β-Catenin, RUNX2 and ALP | LINC00461 | LINC00461 reduces Wnt/β-catenin activity to inhibit the osteoblast differentiation through miR-324-3p targeting. | Wu et al. (2022) |
| miR-324-5p (down) | Primary plasma cells of 26 MM patients and 2 healthy controls | BTRC, MTSS1, MMP2, MMP9, DZIP3, HECW2, UBR2, VHL, CBL | — | miR-324-5p could inhibit proliferative and migratory capacities of cells through suppression of ubiquitination pathway. | Zhang et al. (2018) | |
| Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) | miR-324-3p (down) | 54 NPC tissues and 34 normal and chronic inflammatory nasopharyngeal mucosal tissues | GLI3, E-cadherin, vimentin | — | miR-324-3p via GLI3 targeting could suppress cell proliferation. | Zhang et al. (2017) |
| miR-324-3p (down) | 39 Primary NPC and 21 normal nasopharyngeal epithelium (NPE) tissues | WNT2B, E-cadherin and Vimentin | — | miR-324-3p via WNT2B targeting could suppress migration and invasion of cells. | Liu et al. (2017) | |
| miR-324-3p (down) | GEO dataset, 76 pairs of NPC samples and ANCSs/mice | IL-6 | SLC25A21-AS1 | SLC25A21-AS1 via miR-324-3p/IL-6 axis could increase cell growth and MDR. | Wang et al. (2020a) | |
| miR-324-3p (-) | 80 primary NPC tissues | SMAD7 | — | miR-324-3p via SMAD7 targeting could reduce cell growth rate and promote apoptosis. | Xu et al. (2015) | |
| Ovarian cancer | miR-324-5p (up) | — | GLI1 | — | miR-324-5p downregulation could be considered as a modality for treatment of ovarian cancer | Suardi et al. (2020) |
| miR-324-3p (down) | TCGA database/mice | LY6K, E-cadherin, N-cadherin and vimentin | ZNF252P-AS1 | ZNF252P-AS1 via miR-324-3p/LY6K targeting could promote cell proliferation, invasion, migration, and EMT, but prevent apoptosis. | Geng et al. (2022) | |
| Pancreatic cancer (PC) | miR-324-3p (down) | GEO database/40 pairs of PC tissues and ANCSs | Bcl-2, Bax and Cleaved caspase-3 | LINC01320 | LINC01320 via miR-324-3p targeting could inhibit growth, migration and invasion. | Meng et al. (2021) |
| miR-324-5p (up) | 18 pairs of PC tissues and ANCSs/mice | KLF3, PCNA, BAX | — | miR-324-5p via KLF3 silencing could promote tumorigenesis. | Wan et al. (2020) | |
| Papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) | miR-324-5p (up in LNM+) | 41 PTC tissues (LNM+, −) and 143 FNA samples (LNM+, −) | — | — | miR-324-5p increases proliferation, migration and invasion of cells but inhibits apoptosis. | Yang et al. (2017) |
| miR-324-3p (down) | GEO and TCGA database/40 pairs of PTC tissues and ANCSs | LASP1 | MIAT | MIAT by miR-324-3p/LASP1 targeting could provoke PTC proliferation and invasion. | Liu et al. (2019a) | |
| miR-324-5p (up) | — | PTPRD | — | miR-324-5p via PTPRD/CEBPD axis could participate in the progression of cancer via VEGF. | Yang et al. (2020) | |
| Prostate cancer (PCa) | miR-324-5p (down) | TCGA database/57 PCa tissues/mice | TGFBR1 | PCAT7 | PCAT7 via regulation of miR-324-5p/TGFBR1 axis and activation of TGF-b/SMAD signaling could increase cell migration, invasion, and EMT and bone metastases. | Lang et al. (2020) |
The impact of miR-324 on therapeutic response
In addition, miR-324 participates in the response of cancer cells to therapeutic agents. For instance, according to Wu et al. study on HEK-293, PC9, HCC827 cell lines and mice model of lung cancer, lncRNA APCDD1L-AS1 via regulation of miR-1322/miR-1972/miR-324-3p/SIRT5 axis could cause upregulation of EGFR and induce resistance to icotinib (Wu et al., 2021).
The prognostic role of miR-324 in cancers
The impact of dysregulation of miR-324 in tumor tissues on patients' survival has been assessed through Kaplan-Meier analysis. Moreover, multivariate Cox analysis has shown association between expression levels of miR-324 and clinical data (Table 2). For instance, miR-324 has been among miRNA whose expression levels in breast cancer tissues have been associated with tumor size or lymph node involvement depending on the status and expression levels of hormone receptors, HER2, and Ki-67 (Kalinina et al., 2021). In bladder cancer, over-expression of miR-324-5p has been associated with clinical stage. Besides, significant associations have been observed between high miR-324-3p and miR-324-5p expression levels and poor overall survival (Tsai et al., 2020). On the other hand, in glioma samples, lower level of miR-324-5p has been associated with high grade (grade III and grade IV) (Zhi et al., 2017).
TABLE 2.
Prognostic role of miR-324 in cancers (OS, overall survival; DFS, disease free survival).
| Samples | Kaplan meier | Multivariate Cox analysis | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 414 bladder cancer tissues | High miR-324-5p and 5p expression levels were correlated with OS. | Over-expression of miR-324-5p was associated with clinical stage. A significant association was detected between miR-324-3p and 5p expressions and poor OS. | Tsai et al. (2020) |
| 45 breast cancer tissues | — | Expression of miR-324-3p was associated with tumor size and TNM stage. | Zhang et al. (2019a) |
| 156 breast cancer tissues | — | miR-324 expression was associated with tumor size in luminal B HER2-negative tumors. Upregulation of miR-324 was associated with age <50 and HER2 + status in ER+ and/or PR+ tumors with low Ki-67. | Kalinina et al. (2021) |
| TCGA database for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, and esophageal adenocarcinoma | High expression of miR-324-5p was related to poor prognosis and OS. | — | Chen et al. (2021a) |
| 68 gastric cancer tissues | — | Expression level of miR-324-3p was associated with tumor size. | Sun et al. (2018) |
| 122 gastric cancer tissues | Overexpression of miR-324-5p was associated with poor OS. | Over-expression of miR-324-5p was associated with lymph node metastases and advanced TNM stage. | Zheng et al. (2021) |
| CGGA database, 8 grade II and 8 grade IV glioma tissues | Low level of miR-324-5p was associated with poor survival | Lower level of miR-324-5p was associated with high grade. | Zhi et al. (2017) |
| Blood samples from 96 HBV-related HCC patients | High serum level of miR-324-2p in HBV-related HCC patients was associated with poor OS. | Serum levels of miR-324-2p in HBV-related HCC patients were associated with cirrhosis, tumor size, and clinical stage. | Zhao et al. (2021b) |
| 73 HCC tissues | Upregulation of miR-324-3p was associated with shorter OS and DFS. | Upregulation of miR-324-3p was associated with larger tumor size, multiple tumoral nodules and higher TNM stage. | Tuo et al. (2017) |
| Primary plasma cells of 26 MM patients | — | Expression of miR-324-5p was negatively associated with stage. | Xia et al. (2018) |
| 54 Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) tissues | Higher level of miR-324-3p was associated with longer survival time. | Expression level of miR-324-3p was associated with level of differentiation, TNM stage, and lymph node metastases. | Zhang et al. (2018) |
| 39 NPC tissues | — | Lower level of miR-324-3p was associated with tumor T classification, clinical stage and lymph node metastases. | Zhang et al. (2017) |
| 80 NPC tissues | Low expression of miR-324-3p was associated with poor OS and recurrence-free survival | Low expression of miR-324-3p was associated with EBV infection, advanced clinical stage, and high rates of radioresistance. | Liu et al. (2017) |
| OV TCGA database | Over-expression of miR-324-3p was related with higher survival rate. | — | Xu et al. (2015) |
| TCGA database for LSCC | Over-expression of miR-324-3p was related to with worse prognosis. | — | Geng et al. (2022) |
Role of miR-324 in non-malignant disorders
miR-324 has been among dysregulated miRNAs in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) patients. Notably, miR-324-3p has been shown to be upregulated in SAH patients with delayed cerebral infarction (DCI) as well as non-DCI group. Yet, no significant difference has been detected in expression levels between patients with and without DCI (Su et al., 2015). Another investigation has revealed importance of miR-324-3p in the pathogenesis of anorectal malformations and demonstrated that Rno_circ_0005139 can increase cell proliferation and apoptosis via influencing activity of miR-324-3p/Wnt5a axis (Liu et al., 2020a). In the context of cardiac disorders, NFAT4 has been shown to regulate miR-324-5p/Mtfr1 axis to enhance mitochondrial fission and cardiomyocyte apoptosis and aggravate pathogenic events in the myocardial infarction (Wang et al., 2015). Table 3 summarizes the impact of miR-324 in the pathogenesis of non-neoplastic conditions.
TABLE 3.
miR-324 in non-malignant diseases (DCI, Delayed cerebral infarction; IEC, intestinal epithelial cells; MCD, minimal change disease; HG, high glucose; Ucn, Urocortin; OGD/R, oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation; NOF, neck of the femur; EX, aerobic exercise; SED, sedentary).
| Disease | Expression | Samples | Downstream targets | Other related molecules | Description | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) | miR-324-3p (up) | Blood samples from 20 SAH with DCI, 20 without DCI, and 20 controls | — | miR-324 could be considered as a potential biomarker of SAH. | Su et al. (2015) | |
| Anorectal malformation | miR-324-3p (up) | Rat | Wnt5a | Rno-circ_0005139 | Rno_circ_0005139 via miR-324-3p/Wnt5a targeting could increase cell proliferation. | Liu et al. (2020a) |
| Cardiac disease | miR-324-5p (down) | Mice | Mtfr1, caspase-3 | NFAT4 | NFAT4 through miR-324-5p/Mtfr1 axis could increase mitochondrial fission, cardiomyocyte apoptosis and myocardial infarction. | Wang et al. (2015) |
| Diabetic nephropathy (DN) | miR-324-3p (down in DN) | Renal tissues from 10 MCD patients and 9 DN/rat | DUSP1, collagen I, collagen IV, fibronectin | NR-038323 | NR-038323 induced by HG via miR-324-3p/DUSP1/p38MAPK and ERK1, 2 regulations could mitigate renal fibrosis. | Ge et al. (2019) |
| Epilepsy | miR-324-5p (-) | Mice | Kv4.2 | — | miR-324-5p via Kv4.2 targeting could decrease A-type potassium currents and increase the frequency of seizures. | Tiwari et al. (2019) |
| Epilepsy | miR-324 (-) | Mice | Suox and Cd300lf | — | miR-324 via Suox and Cd300lf targeting could play role in neurological disease | Hayman et al. (2021) |
| HIV lipodystrophy | miR-324-5p (down in HIV lipodystrophic cases) | subcutaneous abdominal fat from 11 persons with HIV, 9 with and 9 without lipodystrophy, and 9 uninfected individuals/mice | Ltbp2, Wisp2, and Nebl | — | miR-324-5p absence and Ltbp2 suppression could cause dysregulation in different adipose differentiation and inflammation markers which led to HIV lipodystrophy. | Srinivasa et al. (2021) |
| Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) | miR-324-5p | Blood samples from 10 IPF patients and 10 healthy controls | 13 different genes | Circ100906 | Circ100906 via miR-324-5p targeting could participate in IPF pathogenesis. | Li et al. (2018) |
| Influenza A | miR-324-5p (down) | GEO database/nasopharyngeal swabs from 4 healthy individuals and 9 patients with swine influenza (H1N1) | PB1, CUEDC2, type I interferon, type III interferon, and ISGs | — | miR-324-5p could suppress H5N1 replication by targeting of PB1and cellular CUEDC2 gene. | Kumar et al. (2018) |
| Ischemic stroke (IS) | miR-324-5p (down) | GEO database, Blood samples from 80 cases of acute ischemic stroke patients and 80 cases of healthy controls/rat | RAN, caspase-3 | — | In ischemic stroke, miR-324-5p downregulation and subsequently RAN upregulation could prevent neuronal cell proliferation and glucose uptake and promote apoptosis. | Gu et al. (2020) |
| IS | miR-324-3p (down) | Rat | VEGFA | SNHG11 | Dexmedetomidine via regulation of SNHG11/miR-324-3p/VEGFA pathway and oxidative stress markers could improve neurological trauma after OGD/R. | Chen et al. (2021b) |
| Tuberculosis (TB) | miR-324-5p (down) | 50 pulmonary TB patients and 50 healthy cases | CTLA4 | Circ0003528 | Circ0003528 through miR-324-5p/CTLA4 axis could cause tuberculosis related macrophage polarization. | Huang et al. (2020c) |
| Myocardial ischemia reperfusion (I/R) injuries | miR-324-3p (down) | Rat | BRCA1, BIM, STAT2, PDE4a, CASQ1, NFAT5, XBP1, MAP3K12, CPT2, FoxO1, MTRF1, TAZ | — | Ucn-1, 2 prescriptions via miR-324-3p upregulation and downregulation of various genes associated with apoptosis could exert protective effects on heart. | Díaz et al. (2017) |
| Neurological damages | miR-324-5p (down) | Mice | CCL5,p-CREB, p-ERK1/2 | — | miR-324-5p downregulation or CCL5 upregulation associated with dicer deficiency via MAPK/CREB signaling pathway suppression could exacerbate neurodegeneration. | Sun et al. (2019) |
| Nerve injury | miR-324-3p (-) | Rat | VEGFB | CircAnks1a | CircAnks1a via miR-324-3p/VEGFB axis could augment hypersensitivity to pain. | Zhang et al. (2019b) |
| Osteoarthritis (OA) | miR-324-5p (up) | OA cartilage from patients with joint replacement, healthy cartilage from patients with fracture of the NOF/mice | GLI1, SMO in human, Gpc1in mice | — | The regulatory function of miR-324-5p on hedgehog pathway is species- dependent. | Woods et al. (2019) |
| Parkinson disease (PD) | miR-324 (down in EX-PD group) | Rat | Vdac1 | — | In EX-PD group, downregulation of miR-324 via CaMK/mTOR signaling pathway regulation could influence UCH-L1 level and repress progression of PD. | Liu et al. (2019b) |
| Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) | miR-324 (down) | 15 PCOS and 15 normal ovarian tissues | WNT2B, Bax, caspase-3, and Bcl-2 | — | miR-324 over-expression via WNT2B targeting could promote cell apoptosis. | Yuanyuan et al. (2019) |
| Myocardial infarction (MI) | miR-324-5p (-) | Rat | TOLLIP | — | Upregulated miR-324-5p via TOLLIP targeting could increase proliferation, migration and post-MI myocardial repair. | Ji et al. (2021) |
| Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) | miR-324-5p (down) | Blood samples from 14 healthy volunteers and 12 IPAH patients/lung tissue from 6 PAH patients and control tissues from 6 patients with bronchial carcinoma/mice | Notch4, ETS-1, caspase3/7 | — | KLF2-induced miR-324-5p reduces proliferative and angiogenic responses and disease progression. | Sindi et al. (2020) |
| Pulmonary inflammatory disease | miR-324-3p (up) | — | IKβ-α, IKKβ, IL-6, IL-8, TNF-α, p-P65, ICAM-1, and VCAM-1. | H19 | Dexamethasone via H19/miR-324-3p axis could decrease pulmonary inflammation. | Chen et al. (2021c) |
| Renal fibrosis | miR-324-3p (up) | Rat | Prep | ACE | ACE inhibition via miR-324-3p/Prep/Ac-SDKP axis could alleviate fibrosis. | Macconi et al. (2012) |
| Renal fibrosis | miR-324-3p (up) | 6 normal, 11 mild fibrosis, and 13 moderate fibrosis tissues/mice | NRG1, ATG5, ATG7, LC3II, and LC3I, P62, Collagen I, Fibronectin, and a-SMA | LncRNA 74.1 | LncRNA 74.1 via regulation of miR-324-3p/NRG1/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway could promote autophagy and mitigate fibrosis. | Tang et al. (2021b) |
| Seizure | miR-324-5p (up) | Mice | Kv4.2 | — | miR-324-5p downregulation and Kv4.2 enhancement could diminish seizures. | Gross et al. (2016) |
| Thermal injury and burns | miR-324-5p (up) | — | CDK16 | TPT1-AS1 | TPT1-AS1 through miR-324-5p/CDK16 axis could increase cell viability and ECM production while hamper apoptosis. | Luo et al. (2021) |
Liu et al. (2021) have examined miR-324-3p expression levels in primary Granulosa cells (GCs) retrieved from the follicles of ovarian tissue in the follicular phase from high- and low-yielding goats and found that upregulation of chi-miR-324-3p can inhibit GCs proliferation via targeting DENND1A gene and consequently downregulating expression of GCs proliferation markers such as LHR, cyclin D2, and CDK4 (Liu et al., 2021).
The importance of miR-324 in skeletal muscle differentiation has been investigated in different studies. According to Liu et al. (2020b) study in mice models, mouse C2C12 myoblasts and human HEK293T cell line, miR-324-5p has been over-expressed in skeletal muscle. Through targeting lncDum and Pm20d1, this miRNA could inhibit myoblasts differentiation and lipid aggregation (Liu et al., 2020b).
In the bone remodeling process in the body, small extracellular vesicles (sEVs) secreted by mature osteoclasts play an important role. One of the upregulated miRNAs in sEVs is miR-324. This miRNA that could cause differentiation and mineralization of bone progenitor cells by through silencing of ARHGAP1 and subsequent stimulation of RhoA/ROCK pathway (Liang et al., 2021).
According to miRNome analysis in muscle specimens of spinal muscular atrophy patients and controls and in vitro and in vivo experiments, miR-324-5p has been identified as a differentially expressed miRNA. So, in addition to the assessment of SMN2 copy number, measurement of this miRNA in SMA patients can be helpful in prognosis anticipation (Abiusi et al., 2021).
Discussion
Dysregulation of miR-324 has been described in a variety of tumor types and cancer cell lines. Most of studies have stated downregulation of miR-324 in these samples. However, some inconsistencies exist in certain types of cancers. For instance, both miR-324-3p and miR-324-5p have been reported to be upregulated in bladder cancer. In liver and cervical cancers, miR-324-5p is downregulated, while miR-324-3p is upregulated. In contrast, in ovarian, thyroid and pancreatic cancers, miR-324-5p has been found to be upregulated, while miR-324-3p has been down-regulated. Finally, in gastric and lung cancer, no consistent pattern has been reported. Thus, although the observed inconsistencies in expression pattern and function of miR-324 might be explained by different functions of miR-324-5p and miR-324-3p, tissue-dependent factors are also involved.
Several lncRNAs and circular RNAs such as LINC00963, LINC01320, LINC00461, LINC00491, LINC01134, LINC00511, SNHG22, H1FX-AS1, TPT1-AS1, VPS9D1-AS1, MALAT1, NEAT1, FOXD2-AS1, Lnc85, GATA6-AS1, PCAT-1, LOXL1-AS1, SLC25A21-AS1, ZNF252P-AS1, MIAT, PCAT7, Circ0067835, Circ0049447, Circ0091994 and CircZNF83 have been shown to act as a sponge for miR-324 and decrease its bioavailability. Cumulatively, changes in the expression of these molecules are the most appreciated route of regulation of expression of miR-324. Future studies are needed to find other mechanisms of dysregulation of miR-324 in different tissues.
Additionally, miR-324 has important functions in the pathogenesis of a number of non-malignant conditions such as pulmonary and renal fibrosis as well as I/R injuries. Based on the high burden of ischemic stroke and myocardial infarction on the public health, further assessment of the role of miR-324 in these conditions can facilitate design of appropriate preventive or curative strategies. In SAH, significant upregulation of miR-324 has indicated that this miRNA can be a potential biomarker. Most notably, this miRNA has high accuracy for differentiation of SAH patients from healthy controls (AUC values of 0.97 and 0.96 for DCI, non-DCI groups, respectively) (Su et al., 2015). Moreover, miR-324 has been found to be up-regulated in osteoarthritis cartilage and regulate Hh signaling. Since, miR-324-5p has been shown to regulate osteogenesis in human mesenchymal stem cells (Woods et al., 2019), it can be regarded as a possible target for therapeutic modalities for osteoarthritis. Additionally, miR-324-5p expression has been shown to be altered in the brain samples of suicide victims with depression (Smalheiser et al., 2012) and in the amygdala in posttraumatic stress disorder (Balakathiresan et al., 2014), indicating the importance of this miRNA in the pathogenesis of neuropsychiatric conditions and its possible role as a biomarkers for this kind of disorders.
Cumulatively, miR-324 is a candidate for design of novel therapeutic strategies for neoplastic and non-neoplastic conditions, since it has been found to be dysregulated in a variety of disorder. Moreover, in vitro and in vivo studies have shown that amelioration of miR-324 levels can reverse pathologic events occurred in these disorders. However, tissue-specific expression and function of this miRNA should be considered before introduction of any treatment modality in clinical settings.
Author contributions
SG-F wrote the draft and revised it. SK and BH collected the data and designed the tables and figures. All the authors read and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
- Abiusi E., Infante P., Cagnoli C., Lospinoso Severini L., Pane M., Coratti G., et al. (2021). SMA-miRs (miR-181a-5p, -324-5p, and -451a) are overexpressed in spinal muscular atrophy skeletal muscle and serum samples. eLife 1, e68054. 10.7554/eLife.68054 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balakathiresan N. S., Chandran R., Bhomia M., Jia M., Li H., Maheshwari R. K., et al. (2014). Serum and amygdala microRNA signatures of posttraumatic stress: Fear correlation and biomarker potential. J. Psychiatr. Res. 57, 65–73. 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2014.05.020 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao L., Xie B., Yang X., Liang H., Jiang X., Zhang D., et al. (2015). MiR-324-5p suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma cell invasion by counteracting ECM degradation through post-transcriptionally downregulating ETS1 and SP1. PloS one 10 (7), e0133074. 10.1371/journal.pone.0133074 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen N., Wang Z., Yang X., Geng D., Fu J., Zhang Y., et al. (2021). Integrated analysis of competing endogenous RNA in esophageal carcinoma. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 12 (1), 11–27. 10.21037/jgo-20-615 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y., Fan Z., Wu Q. (2021). Dexmedetomidine improves oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation (OGD/R) -induced neurological injury through regulating SNHG11/miR-324-3p/VEGFA axis. Bioengineered 12 (1), 4794–4804. 10.1080/21655979.2021.1957071 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y., Zhang C., Xiao C. X., Li X. D., Hu Z. L., He S. D., et al. (2021). Dexamethasone can attenuate the pulmonary inflammatory response via regulation of the lncH19/miR-324-3p cascade. J. Inflamm. 18 (1), 1. 10.1186/s12950-020-00266-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Díaz I., Calderón-Sánchez E., Toro R. D., Ávila-Médina J., de Rojas-de Pedro E. S., Domínguez-Rodríguez A., et al. (2017). miR-125a, miR-139 and miR-324 contribute to Urocortin protection against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Sci. Rep. 7 (1), 8898. 10.1038/s41598-017-09198-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan C., Yuan Q., Liu G., Zhang Y., Yan M., Sun Q., et al. (2020). Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 regulates oxaliplatin-resistance via miR-324-3p/ADAM17 axis in colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Cell Int. 20, 473. 10.1186/s12935-020-01549-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang X., Zhang J., Li C., Liu J., Shi Z., Zhou P., et al. (2020). Long non-coding RNA SNHG22 facilitates the malignant phenotypes in triple-negative breast cancer via sponging miR-324-3p and upregulating SUDS3. Cancer Cell Int. 20 (1), 252. 10.1186/s12935-020-01321-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao X., Wang Y., Zhao H., Wei F., Zhang X., Su Y., et al. (2016). Plasma miR-324-3p and miR-1285 as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for early stage lung squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 7 (37), 59664–59675. 10.18632/oncotarget.11198 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ge Y., Wang J., Wu D., Zhou Y., Qiu S., Chen J., et al. (2019). lncRNA NR_038323 suppresses renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy by targeting the miR-324-3p/DUSP1 Axis. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 17, 741–753. 10.1016/j.omtn.2019.07.007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geng L., Wang Z., Tian Y. (2022). Down-regulation of ZNF252P-AS1 alleviates ovarian cancer progression by binding miR-324-3p to downregulate LY6K. J. Ovarian Res. 15 (1), 1. 10.1186/s13048-021-00933-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross C., Yao X., Engel T., Tiwari D., Xing L., Rowley S., et al. (2016). MicroRNA-Mediated downregulation of the potassium channel Kv4.2 contributes to seizure onset. Cell Rep. 17 (1), 37–45. 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.08.074 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu J., Gui S., Hu L., Kong L., Di M., Wang Y., et al. (2020). Downregulated miRNA-324-5p aggravates neuronal injury induced by oxygen-glucose deprivation via modulating RAN. Exp. Ther. Med. 19 (1), 658–664. 10.3892/etm.2019.8249 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayman D. J., Modebadze T., Charlton S., Cheung K., Soul J., Lin H., et al. (2021). Increased hippocampal excitability in miR-324-null mice. Sci. Rep. 11 (1), 10452. 10.1038/s41598-021-89874-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang G., Yang Y., Lv M., Huang T., Zhan X., Kang W., et al. (2022). VPS9D1-AS1, a novel long-non-coding RNA, acts as a tumor promoter by regulating the miR-324-5p/ITGA2 axis in colon adenocarcinoma. Am. J. Transl. Res. 14 (2), 955–966. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang N., Dai W., Li Y., Sun J., Ma C., Li W., et al. (2020). LncRNA PCAT-1 upregulates RAP1A through modulating miR-324-5p and promotes survival in lung cancer. Arch. Med. Sci. 16 (5), 1196–1206. 10.5114/aoms.2019.84235 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang X., Sun L., Wen S., Deng D., Wan F., He X., et al. (2020). RNA sequencing of plasma exosomes revealed novel functional long noncoding RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 111 (9), 3338–3349. 10.1111/cas.14516 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Z., Yao F., Liu J., Xu J., Guo Y., Su R., et al. (2020). Up-regulation of circRNA-0003528 promotes mycobacterium tuberculosis associated macrophage polarization via down-regulating miR-224-5p, miR-324-5p and miR-488-5p and up-regulating CTLA4. Aging 12 (24), 25658–25672. 10.18632/aging.104175 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ji Z., Wang C., Tong Q. (2021). Role of miRNA-324-5p-modified adipose-derived stem cells in post-myocardial infarction repair. Int. J. Stem Cells 14 (3), 298–309. 10.15283/ijsc21025 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang H., Huang G., Zhao N., Zhang T., Jiang M., He Y., et al. (2018). Long non-coding RNA TPT1-AS1 promotes cell growth and metastasis in cervical cancer via acting AS a sponge for miR-324-5p. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 37 (1), 169. 10.1186/s13046-018-0846-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Kalinina T., Kononchuk V., Alekseenok E., Abdullin G., Sidorov S., Ovchinnikov V., et al. (2021). Associations between the levels of estradiol-progesterone-and testosterone-sensitive MiRNAs and main clinicopathologic features of breast cancer. J. Pers. Med. 12 (1), 4. 10.3390/jpm12010004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar A., Kumar A., Ingle H., Kumar S., Mishra R., Verma M. K., et al. (2018). MicroRNA hsa-miR-324-5p suppresses H5N1 virus replication by targeting the viral PB1 and host CUEDC2. J. Virol. 92 (19), e01057–18. 10.1128/JVI.01057-18 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang C., Dai Y., Wu Z., Yang Q., He S., Zhang X., et al. (2020). SMAD3/SP1 complex-mediated constitutive active loop between lncRNA PCAT7 and TGF-β signaling promotes prostate cancer bone metastasis. Mol. Oncol. 14 (4), 808–828. 10.1002/1878-0261.12634 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li D., Li L., Chen X., Yang W., Cao Y. (2021). Circular RNA SERPINE2 promotes development of glioblastoma by regulating the miR-361-3p/miR-324-5p/BCL2 signaling pathway. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 22, 483–494. 10.1016/j.omto.2021.07.010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li R., Wang Y., Song X., Sun W., Zhang J., Liu Y., et al. (2018). Potential regulatory role of circular RNA in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Med. 42 (6), 3256–3268. 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3892 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y., Chang Y., Cai Y. (2020). Circ_0067835 sponges miR-324-5p to induce HMGA1 expression in endometrial carcinoma cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 24 (23), 13927–13937. 10.1111/jcmm.15996 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang M., Yin X., Zhang S., Ai H., Luo F., Xu J., et al. (2021). Osteoclast-derived small extracellular vesicles induce osteogenic differentiation via inhibiting ARHGAP1. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 23, 1191–1203. 10.1016/j.omtn.2021.01.031 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin M. H., Chen Y. Z., Lee M. Y., Weng K. P., Chang H. T., Yu S. Y., et al. (2018). Comprehensive identification of microRNA arm selection preference in lung cancer: miR-324-5p and -3p serve oncogenic functions in lung cancer. Oncol. Lett. 15 (6), 9818–9826. 10.3892/ol.2018.8557 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C., Li G., Yang N., Su Z., Zhang S., Deng T., et al. (2017). miR-324-3p suppresses migration and invasion by targeting WNT2B in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 17, 2. 10.1186/s12935-016-0372-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu D., Qu Y., Cao Z. N., Jia H. M. (2020). Rno_circ_0005139 regulates apoptosis by targeting Wnt5a in rat anorectal malformations. World J. Gastroenterol. 26 (29), 4272–4287. 10.3748/wjg.v26.i29.4272 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu W., Li L., Liu S., Wang Z., Kuang H., Xia Y., et al. (2019). MicroRNA expression profiling screen miR-3557/324-targeted CaMK/mTOR in the rat striatum of Parkinson's disease in regular aerobic exercise. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 7654798. 10.1155/2019/7654798 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu W., Wang Z., Wang C., Ai Z. (2019). Long non-coding RNA MIAT promotes papillary thyroid cancer progression through upregulating LASP1. Cancer Cell Int. 19, 194. 10.1186/s12935-019-0913-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y., Chen Y., Zhou Z., He X., Tao L., Jiang Y., et al. (2021). chi-miR-324-3p regulates goat Granulosa cell proliferation by targeting DENND1A. Front. Vet. Sci. 8, 732440. 10.3389/fvets.2021.732440 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y., Wang J., Zhou X., Cao H., Zhang X., Huang K., et al. (2020). miR-324-5p inhibits C2C12 cell differentiation and promotes intramuscular lipid deposition through lncDUM and PM20D1. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 22, 722–732. 10.1016/j.omtn.2020.09.037 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo J., You H., Zhan J., Guo G., Cheng X., Zheng G., et al. (2021). Long non-coding RNA TPT1-AS1 alleviates cell injury and promotes the production of extracellular matrix by targeting the microRNA-324-5p/CDK16 axis in human dermal fibroblasts after thermal injury. Exp. Ther. Med. 22 (2), 843. 10.3892/etm.2021.10275 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macconi D., Tomasoni S., Romagnani P., Trionfini P., Sangalli F., Mazzinghi B., et al. (2012). MicroRNA-324-3p promotes renal fibrosis and is a target of ACE inhibition. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 23 (9), 1496–1505. 10.1681/ASN.2011121144 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meng H., Guo K., Zhang Y. (2021). Effects of lncRNA LINC01320 on proliferation and migration of pancreatic cancer cells through targeted regulation of miR-324-3p. J. Healthc. Eng. 2021, 4125432. 10.1155/2021/4125432 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien J., Hayder H., Zayed Y., Peng C. (2018). Overview of microRNA biogenesis, mechanisms of actions, and circulation. Front. Endocrinol. 9, 402. 10.3389/fendo.2018.00402 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rong Z., Wang Z., Wang X., Qin C., Geng W. (2020). Molecular interplay between linc01134 and YY1 dictates hepatocellular carcinoma progression. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 39 (1), 61. 10.1186/s13046-020-01551-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi X., Huo J., Gao X., Cai H., Zhu W. (2020). A newly identified lncRNA H1FX-AS1 targets DACT1 to inhibit cervical cancer via sponging miR-324-3p. Cancer Cell Int. 20, 358. 10.1186/s12935-020-01385-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sindi H. A., Russomanno G., Satta S., Abdul-Salam V. B., Jo K. B., Qazi-Chaudhry B., et al. (2020). Therapeutic potential of KLF2-induced exosomal microRNAs in pulmonary hypertension. Nat. Commun. 11 (1), 1185. 10.1038/s41467-020-14966-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smalheiser N. R., Lugli G., Rizavi H. S., Torvik V. I., Turecki G., Dwivedi Y., et al. (2012). MicroRNA expression is down-regulated and reorganized in prefrontal cortex of depressed suicide subjects. PLoS One 7 (3), e33201. 10.1371/journal.pone.0033201 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasa S., Garcia-Martin R., Torriani M., Fitch K. V., Carlson A. R., Kahn C. R., et al. (2021). Altered pattern of circulating miRNAs in HIV lipodystrophy perturbs key adipose differentiation and inflammation pathways. JCI insight 6 (18), e150399. 10.1172/jci.insight.150399 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su X. W., Chan A. H., Lu G., Lin M., Sze J., Zhou J. Y., et al. (2015). Circulating microRNA 132-3p and 324-3p profiles in patients after acute aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. PloS one 10 (12), e0144724. 10.1371/journal.pone.0144724 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suardi R. B., Ysrafil Y., Sesotyosari S. L., Martien R., Wardana T., Astuti I., et al. (2020). The effects of combination of mimic miR-155-5p and antagonist miR-324-5p encapsulated chitosan in ovarian cancer SKOV3. Asian pac. J. Cancer Prev. 21 (9), 2603–2608. 10.31557/APJCP.2020.21.9.2603 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun C., Zhu L., Ma R., Ren J., Wang J., Gao S., et al. (2019). Astrocytic miR-324-5p is essential for synaptic formation by suppressing the secretion of CCL5 from astrocytes. Cell Death Dis. 10 (2), 141. 10.1038/s41419-019-1329-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun G. L., Li Z., Wang W. Z., Chen Z., Zhang L., Li Q., et al. (2018). miR-324-3p promotes gastric cancer development by activating Smad4-mediated Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. J. Gastroenterol. 53 (6), 725–739. 10.1007/s00535-017-1408-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun L. N., Xing C., Zhi Z., Liu Y., Chen L. Y., Shen T., et al. (2017). Dicer suppresses cytoskeleton remodeling and tumorigenesis of colorectal epithelium by miR-324-5p mediated suppression of HMGXB3 and WASF-2. Oncotarget 8 (34), 55776–55789. 10.18632/oncotarget.18218 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang K. W., Guo Z. X., Wu Z. H., Zhou C., Sun J., Wang X., et al. (2021). Circ_0049447 acts as a tumor suppressor in gastric cancer through reducing proliferation, migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Chin. Med. J. 134 (11), 1345–1355. 10.1097/CM9.0000000000001494 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang S., Xiao G., Yuan Q., Lin W., Yuan X., Fang X., et al. (2021). Long non-coding RNA ENST00000453774.1 confers an inhibitory effect on renal fibrosis by inhibiting miR-324-3p to promote NRG1 expression. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 9, 580754. 10.3389/fcell.2021.580754 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari D., Brager D. H., Rymer J. K., Bunk A. T., White A. R., Elsayed N. A., et al. (2019). MicroRNA inhibition upregulates hippocampal A-type potassium current and reduces seizure frequency in a mouse model of epilepsy. Neurobiol. Dis. 130, 104508. 10.1016/j.nbd.2019.104508 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai K. W., Kuo W. T., Jeng S. Y. (2020). microRNA-324 plays an oncogenic role in bladder cancer cell growth and motility. Transl. Cancer Res. 9 (2), 707–716. 10.21037/tcr.2019.12.01 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuo H., Wang Y., Wang L., Yao B., Li Q., Wang C., et al. (2017). MiR-324-3p promotes tumor growth through targeting DACT1 and activation of Wnt/β-catenin pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 8 (39), 65687–65698. 10.18632/oncotarget.20058 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W., Yang T., Li D., Huang Y., Bai G., Li Q., et al. (2021). LINC00491 promotes cell growth and metastasis through miR-324-5p/ROCK1 in liver cancer. J. Transl. Med. 19 (1), 504. 10.1186/s12967-021-03139-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wan Y., Luo H., Yang M., Tian X., Peng B., Zhan T., et al. (2020). miR-324-5p contributes to cell proliferation and apoptosis in pancreatic cancer by targeting KLF3. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2518, 432–442. 10.1016/j.omto.2020.07.011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang K., Zhang D. L., Long B., An T., Zhang J., Zhou L. Y., et al. (2015). NFAT4-dependent miR-324-5p regulates mitochondrial morphology and cardiomyocyte cell death by targeting Mtfr1. Cell Death Dis. 6 (12), e2007. 10.1038/cddis.2015.348 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X., Wang C., Xu H., Xie H. (2020). Long non-coding RNA slc25a21-AS1 promotes multidrug resistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by regulating miR-324-3p/IL-6 Axis. Cancer Manag. Res. 12, 3949–3957. 10.2147/CMAR.S251820 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z., Pan L., Yang L., Lv P., Mai S., Wang Y., et al. (2020). Long non-coding RNA GATA6-AS1 sponges miR-324-5p to inhibit lung cancer cell proliferation and invasion. Onco. Targets. Ther. 13, 9741–9751. 10.2147/OTT.S256336 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods S., Barter M. J., Elliott H. R., McGillivray C. M., Birch M. A., Clark I. M., et al. (2019). miR-324-5p is up regulated in end-stage osteoarthritis and regulates Indian Hedgehog signalling by differing mechanisms in human and mouse. Matrix Biol. 77, 87–100. 10.1016/j.matbio.2018.08.009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J., Zheng C., Wang Y., Yang Z., Li C., Fang W., et al. (2021). Correction to: LncRNA apcdd1l-AS1 induces icotinib resistance by inhibition of EGFR autophagic degradation via the miR-1322/miR-1972/miR-324-3p-SIRT5 axis in lung adenocarcinoma. Biomark. Res. 9 (1), 25. 10.1186/s40364-021-00279-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Y., Zhang Z., Wu J., Hou J., Ding G. (2022). The exosomes containing LINC00461 originated from multiple myeloma inhibit the osteoblast differentiation of bone mesenchymal stem cells via sponging miR-324-3p. J. Healthc. Eng. 2022, 3282860. 10.1155/2022/3282860 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Xia E., Kanematsu S., Suenaga Y., Elzawahry A., Kondo H., Otsuka N., et al. (2018). MicroRNA induction by copy number gain is associated with poor outcome in squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. Sci. Rep. 8 (1), 15363. 10.1038/s41598-018-33696-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao X., Gu Y., Wang G., Chen S. (2019). c-Myc, RMRP, and miR-34a-5p form a positive-feedback loop to regulate cell proliferation and apoptosis in multiple myeloma. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 122, 526–537. 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.10.207 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie N., Fei X., Liu S., Liao J., Li Y. (2019). LncRNA LOXL1-AS1 promotes invasion and proliferation of non-small-cell lung cancer through targeting miR-324-3p. Am. J. Transl. Res. 11 (10), 6403–6412. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie Y., Liu Z., Zhu H. (2021). Knockdown of hsa_circ_0091994 constrains gastric cancer progression by suppressing the miR-324-5p/HMGA1 axis. Aging 13 (16), 20598–20608. 10.18632/aging.203450 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu J., Ai Q., Cao H., Liu Q. (2015). MiR-185-3p and miR-324-3p predict radiosensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma and modulate cancer cell growth and apoptosis by targeting SMAD7. Med. Sci. Monit. 21, 2828–2836. 10.12659/MSM.895660 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y., Xia S., Ni X., Ni Z., Zhang L., Wang W., et al. (2017). MiR-324-5p assists ultrasonography in predicting lymph node metastasis of unifocal papillary thyroid microcarcinoma without extracapsular spread. Oncotarget 8 (48), 83802–83816. 10.18632/oncotarget.19717 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y., Xia S., Zhang L., Wang W., Chen L., Zhan W., et al. (2020). MiR-324-5p/PTPRD/CEBPD axis promotes papillary thyroid carcinoma progression via microenvironment alteration. Cancer Biol. Ther. 21 (6), 522–532. 10.1080/15384047.2020.1736465 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuanyuan Z., Zeqin W., Xiaojie S., Liping L., Yun X., Jieqiong Z., et al. (2019). Proliferation of ovarian Granulosa cells in polycystic ovarian syndrome is regulated by MicroRNA-24 by targeting wingless-type family member 2B (WNT2B). Med. Sci. Monit. 25, 4553–4559. 10.12659/MSM.915320 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang C., Lv H., Zhang F., Ji A. (2022). LncRNA HCG18 facilitates melanoma progression by modulating miR-324-5p/CDK16 axis. Am. J. Transl. Res. 14 (2), 1246–1257. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang H. Q., Sun Y., Li J. Q., Huang L. M., Tan S. S., Yang F. Y., et al. (2017). The expression of microRNA-324-3p as a tumor suppressor in nasopharyngeal carcinoma and its clinical significance. Onco. Targets. Ther. 10, 4935–4943. 10.2147/OTT.S144223 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., Li Y., Liu Y., Xu G., Hei Y., Lu X., et al. (2021). Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 regulates glioma cell proliferation and apoptosis by competitively binding to microRNA-324-5p and upregulating KCTD20 expression. Oncol. Rep. 46 (1), 125. 10.3892/or.2021.8076 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang L., Liu D., Tang B., Xu A., Huang H., Su Y., et al. (2018). MicroRNA-324-5p suppresses the migration and invasion of MM cells by inhibiting the SCF(β-TrCP) E3 ligase. Oncol. Lett. 16 (4), 5331–5338. 10.3892/ol.2018.9245 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang N., Zeng X., Sun C., Guo H., Wang T., Wei L., et al. (2019). LncRNA LINC00963 promotes tumorigenesis and radioresistance in breast cancer by sponging miR-324-3p and inducing ACK1 expression. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 18, 871–881. 10.1016/j.omtn.2019.09.033 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Zhang S. B., Lin S. Y., Liu M., Liu C. C., Ding H. H., Sun Y., et al. (2019). CircAnks1a in the spinal cord regulates hypersensitivity in a rodent model of neuropathic pain. Nat. Commun. 10 (1), 4119. 10.1038/s41467-019-12049-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X., Wang Y., Zhao A., Kong F., Jiang L., Wang J., et al. (2020). Long non-coding RNA LINC00511 accelerates proliferation and invasion in cervical cancer through targeting miR-324-5p/DRAM1 Axis. Onco. Targets. Ther. 13, 10245–10256. 10.2147/OTT.S255067 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao J. A., Nie W., Dong L., Liu W., Wei W. (2021). A curcumin analog GL63 inhibits the malignant behaviors of hepatocellular carcinoma by inactivating the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway via the circular RNA zinc finger protein 83/microRNA-324-5p/cyclin-dependent kinase 16 axis. J. gastroenterology hepatology 36 (10), 2967–2977. 10.1111/jgh.15545 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao L., Yang Q., Liu J. (2021). Clinical value evaluation of microRNA-324-3p and other available biomarkers in patients with HBV infection-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 8 (6), ofab108. 10.1093/ofid/ofab108 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao T., Zhang J., Ye C., Tian L., Li Y. (2020). lncRNA FOXD2-AS1 promotes hemangioma progression through the miR-324-3p/PDRG1 pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 20, 189. 10.1186/s12935-020-01277-w [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng Z., Li J., An J., Feng Y., Wang L. (2021). High miR-324-5p expression predicts unfavorable prognosis of gastric cancer and facilitates tumor progression in tumor cells. Diagn. Pathol. 16 (1), 5. 10.1186/s13000-020-01063-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhi T., Yu T., Pan M., Nie E., Wu W., Wang X., et al. (2017). EZH2 alteration driven by microRNA-524-5p and microRNA-324-5p promotes cell proliferation and temozolomide resistance in glioma. Oncotarget 8 (56), 96239–96248. 10.18632/oncotarget.21996 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]