Abstract
Background: Due to resistance to conventional therapy, a blood–brain barrier that results in poor drug delivery, and a high potential for metastasis, glioblastoma (GBM) presents a great medical challenge. Since the repertoire of the possible therapies is very limited, novel therapeutic strategies require new drugs as well as new approaches. The multiple roles played by L-tryptophan (Trp) in tumorigenesis of GBM and the previously found antiproliferative properties of Trp-bearing dendrimers against this malignancy prompted us to design novel polyfunctional peptide-based dendrimers covalently attached to N1-alkyl tryptophan (Trp) residues. Their antiproliferative properties against GBM and normal human astrocytes (NHA) and their antioxidant potential were tested. Methods: Two groups of amphiphilic peptide dendrimers terminated with N1-butyl and N1-aminopentane tryptophan were designed. The influence of dendrimers on viability of NHA and human GBM cell lines, displaying different genetic backgrounds and tumorigenic potentials, was determined by the MTT test. The influence of compounds on the clonogenic potential of GBM cells was assessed by colony-formation assay. Dendrimers were tested for radical scavenging potency as well as redox capability (DPPH, ABTS, and FRAP models). Results: Several peptide dendrimers functionalized with N1-alkyl-tryptophan at 5 µM concentration exhibited high selectivity towards GBM cells retaining 85–95% viable NHA cells while killing cancer cells. In both the MTT and colony-formation assays, compounds 21 (functionalized with N1-butyl-Trp and (+)8 charged) and 25 (functionalized with N1-aminopentane-Trp and (+)12 charged) showed the most promise for their development into anticancer drugs. According to ABTS, DPPH, and FRAP antioxidant tests, dendrimers functionalized with N1-alkylated Trp expressed higher ROS-scavenging capacity (ABTS and DPPH) than those with unsubstituted Trp. Conclusions: Peptide dendrimers functionalized with N1-alkyl-tryptophan showed varying toxicity to NHA, while all were toxic to GBM cells. Based on their activity towards inhibition of GBM viability and relatively mild effect on NHA cells the most advantageous were derivatives 21 and 25 with the respective di-dodecyl and dodecyl residue located at the C-terminus. As expected, peptide dendrimers functionalized with N1-alkyl-tryptophan expressed higher scavenging potency against ROS than dendrimers with unsubstituted tryptophan.
Keywords: dendrimers, glioblastoma, viability, colony-formation assay, reactive oxygen species
1. Introduction
Among various types of cancer experienced by humans, glioblastoma (GBM) is one of the most aggressive and most common malignancies of the central nervous system (CNS) [1,2]. Despite significant progress that has been made recently in the development of therapeutic strategies in cancer therapy, GBM demonstrates particular treatment challenges involving resistance to conventional therapy, localization in the brain that results in suppression of drug delivery by blood–brain barrier, high potential for metastasis, intratumoral heterogeneity at the molecular and cellular level, etc. [3,4,5]. In view of the significant tumor heterogeneity and diverse resistance mechanisms, not only novel therapeutic approaches but also an enhanced knowledge of molecular mechanisms related to disease genesis, progression, and growth is necessary [6,7,8,9].
Among many compounds that have emerged as promising novel chemotherapeutics are dendrimers [10] and branched, polyfunctional nanosized molecules [11,12,13]. Due to their particular structure they are proposed as vehicles in drug delivery as various nanocarriers [14,15,16] or as more complex structures combining therapeutic and diagnostic capability (theranostics) [17,18,19,20]. Recently, design of dendrimeric nanomolecules either with intrinsic anticancer activity alone or associated with the presence of chelated metal cations have emerged [21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28].
We have previously demonstrated that the second generation poly-lysine dendrimers terminated with 2-chlorobenzyloxycarbonyl (2-Cl-Z) residue inhibit the proliferation of GBM cell lines without expressing significant toxicity against non-tumoral CNS cells (neurons and glia) [29]. Cytotoxic effect was enhanced when dendrimers contained indole residue (side chain of tryptophan) at the C-terminal position. On the other hand, peptide dendrimers functionalized with p-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) expressed activity against the human melanoma cell line, also playing a protective role in neurons [30]. Moreover, dendrimers rich in L-tryptophan (Trp) on one side and containing PABA residues on the other side of the so-called non-symmetric bola structure effectively reduced cell proliferation and long-term colony formation propensity in GBM and neuroblastoma cell lines [31].
Trp is an aromatic amino acid that is often found in hydrophobic tails of peptides or membrane proteins spanning lipid bilayers [32]. Due to its hydrophobic character and ability to be involved in hydrogen bonding, pi–cation, and other non-covalent interactions it is often located at water/lipid bilayer interface, where it plays a role of an anchor and protein structure stabilizer [33,34].
Another recently discovered aspect of Trp biochemistry is the involvement of tryptophan catabolic products in the silencing response of the immune system. In particular, the oxidative enzyme indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) is capable of depleting tryptophan in tumor cells and the local microenvironment in favor of kynurenine. Trp disappearance and kynurenine accumulation cooperate to mediate immunosuppression in tumors and tumor-draining lymph nodes [35,36]. Thus, search for the selective IDO inhibitors became a new target in basic research and clinical GBM immunotherapy [37]. Among low-molecular-weight inhibitors of IDO, 1-methyl-L-tryptophan (1MT) was found to selectively restore T-cell proliferation, overcoming cells resistance to therapy [38,39]. Furthermore, Sun et al., reported significant cytotoxic properties for simple N1-alkyl-modified Trp derivatives [40]. We have shown previously, that accumulation of Trp residues in peptide dendrimers of so-called bola structure resulted in significant antioxidant and radical scavenging properties along with variable anticancer activity [31].
Therefore, we hypothesized that further chemical modification of Trp-rich dendrimers towards more hydrophobic structures may improve intracellular penetration along with anticancer activity. Since biological activity of dendrimers depends both on structure of the branched part and also on the number and spatial distribution of the active groups [10], fragments from the peptide dendrimers previously successfully exploited as anti-GBM agents (left side of the bola structure), have been used as scaffolds [31]. This new modification involved introduction at the N1-position of Trp, of either alkyl or alkyl-amino residue. While an alkyl chain increases molecular hydrophobicity, addition of alkyl-amino groups enhances their cationic character.
The two new series of dendrimers were evaluated for in vitro cell toxicity against primary human astrocytes and three GBM cell lines varying with respect to tumorigenic potential and molecular alterations (LN229, T98G, and U87MG) [41]. Studies were extended to testing dendrimers for their ability to influence colony formation process. These compounds were also tested for molecular antioxidant capacity by applying ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP), and radical-scavenging ability in 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) and 2,2′-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulphonic acid) diammonium salt (ABTS) laboratory tests.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Procedures
All solvents and reagents were of analytical grade and were used without further purification. All solvents were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (Steinheim, Germany). Mass spectra were recorded with a Mariner ESI time-of-flight mass spectrometer (PerSeptive Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) for the samples prepared in MeOH. The 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR spectra were recorded using a Bruker Advance spectrometer (Karlsruhe, Germany) at 500/125 or 400/100 MHz, respectively, using deuterated solvents and TMS as an internal standard. Chemical shifts are reported as δ values in parts per million, and coupling constants are given in hertz. The optical rotations ([α]D25) were measured with JASCO J-1020 digital polarimeter (Ishikawa-machi, Hachioji, Tokyo, Japan). Melting points were recorded on a Köfler hot-stage apparatus (Wagner & Munz, München, Germany) and are uncorrected. Thin-layer chromatography (TLC) was performed on aluminum sheets with silica gel 60 F254 from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany). Column chromatography (CC) was carried out using silica gel (230–400 mesh) from Merck or Sephadex LH20 (Biosciences, Upsala, Sweden). The TLC spots were visualized by treatment with 1% alcoholic solution of ninhydrin and heating.
2.2. Synthesis of N1-Susbstituted Tryptophanes
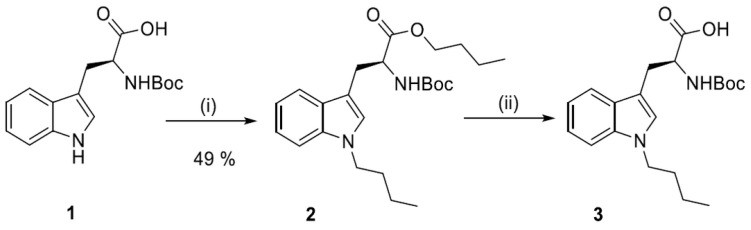
The basic substrate i.e., N1-Boc-1-butylotryptophan (3), was obtained initially by the two-step procedure reported by Sun et al. [40]—i.e., one pot esterification and N1-alkylation of Boc-Trp-OH (1) with 3 equivalents of n-butyl bromide in the presence of NaOH (2 equation) in DMSO, followed by basic hydrolysis of the ester 2 (Scheme 1).
Scheme 1.
Synthesis of N1-Boc-1-butylotryptophan (3). (i) n-BuBr, NaOH, DMSO, 60 °C, 6 h; (ii) 1M NaOH, DMSO, r.t., 30 min.
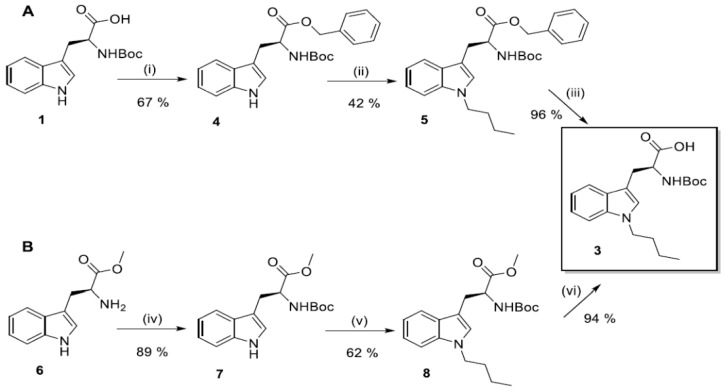
Since the first reaction step was inefficient, (ester 2 was obtained in only 16% yield), product 3 was obtained according to a common procedure of indole N1-alkylation, either starting from substrate 1 or 6 (Scheme 2A or Scheme 2B).
Scheme 2.
Synthesis of N1-Boc-1-butylotryptophan (3). (A)—(i) BnBr, Cs2CO3, DMF, rt., 6 h.; (ii) n-BuBr, NaH, DMF, 0 °C, 1.5 h.; (iii) H2/10% Pd-C, MeOH, 3.5 h.; (B)—(iv) (Boc)2O, NaOH, H2O/dioksan, r.t., 24 h; (v) n-BuBr, NaH, DMF, 0 °C, 2.5 h; (vi) (1) 1M NaOH, MeOH, 50 °C, 1.5 h; (2) 1M HCl.
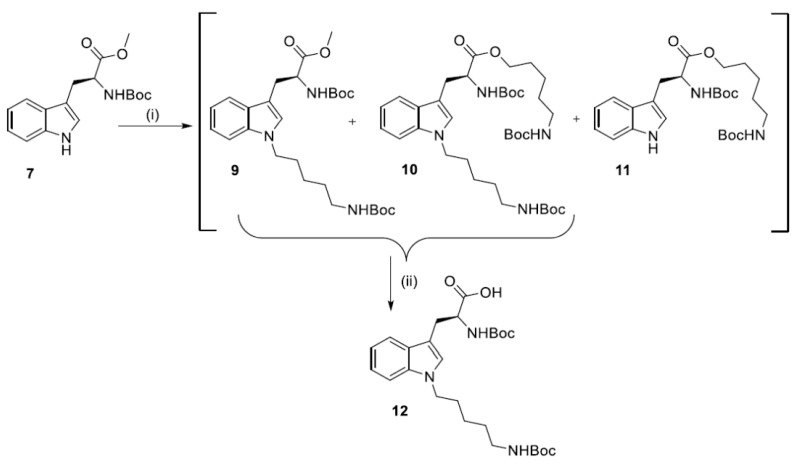
Introduction of alkyl chain in N1-position of Trp increases the lipophilic character of the resulting dendrimers. An increase of a number of positive charges was another modification that was also considered. Therefore, the N1-position of Trp was substituted with 5-(Boc-amino)pentyl residue (Scheme 3).
Scheme 3.
Synthesis of N1-Boc-1-[5-(Boc-amino)pentyl]tryptophan (12). (i) MeSO2O(CH2)5NHBoc, NaH, DMF, r.t., 24 h; (ii) (1) 1M NaOH, MeOH, 50 °C, 2 h; (2) 1M HCl.
Synthesis of N1-Boc-1-[5-(Boc-amino)pentyl]tryptophan (12) was performed via N1-alkylation of Boc-Trp-OMe (7) with 5-(Boc-amino)pentyl mesylate and NaH at room temperature for 24 h (Scheme 3). The crude product obtained by extraction was immediately hydrolyzed in basic conditions. The pure product N1-Boc-1-[5-(Boc-amino)pentylo]tryptophan (12) was obtained in 35.8% yield by silica column chromatography. It was a highly hygroscopic white powder with 105.9–108.4 °C melting point.
2.3. Synthesis of Dendrimers Functionalized with N1-Alkyl Tryptophanes
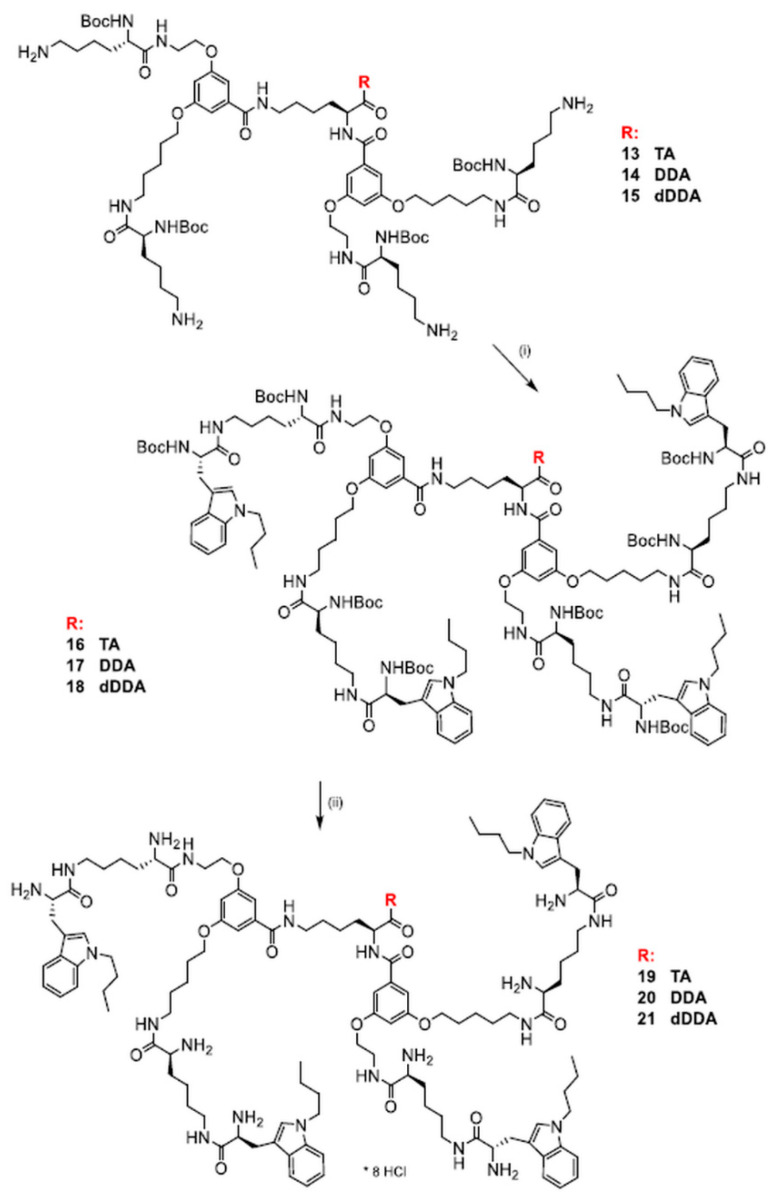
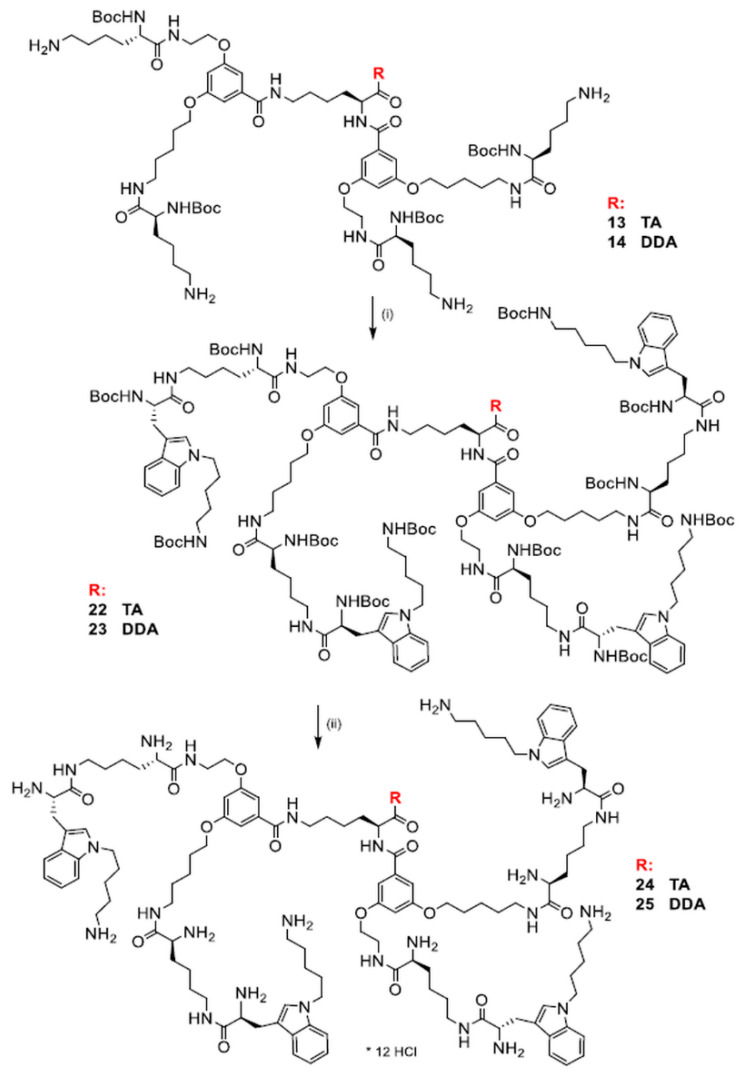
Synthesis of the final dendrimers functionalized with N1-butyltryptophan was performed by coupling the previously described [42], intermediate dendrimers 13, 14, and 15 with N1-Boc-1-butylotryptophan (3) using EDC/HOBt in DMF with an additional amount of Et3N (3.6 equation) (Scheme 4). Size-exclusion chromatography with Sephadex LH-20 column and MeOH as eluent, followed by silica-gel chromatography using CHCl3/MeOH (100:1→15:1 gradient) provided dendrimers 16–18 with yields in the range 35.8–71.4% (Table 1). N1-Boc-deprotection was accomplished by dissolution of the dendrimer in the minimal amount of MeOH and treatment with saturated solution of HCl in EtOAc until disappearance of the substrate (Scheme 4). Solvents were evaporated and the remaining solid was treated several times with MeOH and evaporated to remove an excess of HCl. Finally, size-exclusion chromatography was applied with a Sephadex LH-20 filled column and MeOH as eluent. Dendrimers were kept in desiccator over P2O5. Deprotected dendrimers 19–21 are hygroscopic octa-hydrochlorides obtained in 89.8–97.6% yield range (Table 1).
Scheme 4.
Synthesis of dendrimers with terminal N1-butyltryptophan residue (16–18 and 19–21), where TA, DDA, and dDDA denote tryptamine, dodecylamine, and di-dodecylamine, respectively; (i) 3, EDC/HOBt, Et3N, DMF, 48–96 h; (ii) sat. HCl/EtOAc.
Table 1.
Physicochemical data for dendrimers 16–25.
| N1-Protected Dendrimers | Final Dendrimers | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yield (%) | m.p. (°C) | (α)_D25 (c 1, MeOH) | Rf (CHCl3/MeOH 8:1) | No | Yield. (%) | m.p. (°C) | (α)D25 (c 1, MeOH) |
| 16 | 56.6 | 120–122 | −6.5 | 0.46 | 19 | 97.6 | 182–184.5 | +18.0 |
| 17 | 35.8 | 102–104.5 | −5.4 | 0.55 | 20 | 89.8 | 174–177 | +12.3 |
| 18 | 71.4 | 94–97 | −7.1 | 0.60 | 21 | 95.8 | 175–178 | +8.9 |
| 22 | 78.9 | 117–119.5 | −6.5 | 0.44 | 24 | 97.8 | 189–192 | +6.3 |
| 23 | 68.1 | 99–102 | −5.7 | 0.52 | 25 | 89.5 | 184–187 | +6.6 |
Analytical data, i.e., ESI MS spectra with mass assignments, 1H and 13C NMR spectra along with chemical shifts assignment, molar ellipticity, and melting points for the final dendrimers are available in Supplementary Materials.
Synthesis of dendrimers terminated with (5-aminopentyl)tryptophan residues was performed in the same conditions yielding the respective dendrimers 24 and 25 in total yields not exceeding 22% (Scheme 5).
Scheme 5.
Synthesis of dendrimers terminated with 1-(5-aminopentyl)tryptophan (22, 23, and 24, 25, where TA, and DDA denote tryptamine and dodecylamine, respectively; (i) 12, EDC/HOBt, Et3N, DMF, 96 h; (ii) sat. HCl/EtOAc.
Boc-protected dendrimers were initially purified by size-exclusion chromatography on Sephadex LH-20 filled column using MeOH as eluent. Finally, silica-gel chromatography using CHCl3/MeOH with (100:1→15:1 gradient) was applied providing Boc-protected dendrimers 22–23 with the respective yields 68.1 and 78.9% (Table 1). N1-Boc- deprotection was performed by dissolution of the dendrimer in the minimal amount of MeOH and treatment with saturated solution of HCl in EtOAc, followed by the same purification route as in the case of dendrimers 19–21, i.e., multiple evaporation of MeOH to remove HCl, followed by size-exclusion chromatography and drying over P2O5 (Scheme 5). Deprotected dendrimers 24–25 are hygroscopic dodeca-hydrochlorides obtained in the respective 89.5 and 97.8% yields (Table 1). The final dendrimers were characterized by electrospray mass spectrometry (ESIMS) and 1H and 13C NMR spectrometry. 1H and 13C NMR spectra showed no extra peaks suggesting at least 95% purity of the final dendrimers.
2.4. Human GBM Cell Lines and Human Astrocytes Culture
T98G human GBM cell line purchased from ATCC (American Type Culture Collection, Manassas, VA, USA) was maintained in Minimum Essential Medium Eagle (MEM) (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Gibco, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Grand Island, NY, USA), 50 U/mL penicillin (Gibco), 50 μg/mL streptomycin (Gibco), and 1% non-essential amino acids (Gibco). U87MG cell line purchased from Sigma-Aldrich was maintained in Eagle’s Minimum Essential Medium (EMEM) (ATCC) supplemented with 50 U/mL penicillin, 50 μg/mL streptomycin, and 15% FBS (Gibco). LN229 cell line (kindly provided by Rafał Krętowski, PhD, Department of Pharmaceutical Biochemistry, Medical University of Białystok, Poland) was maintained in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) (Gibco) and supplemented with glucose (final concentration 4.5 g/L), 10% FBS, 50 U/mL penicillin, and 50 μg/mL streptomycin (Gibco). The cells were routinely tested for mycoplasma contamination using Mycoplasma Detection Kit-Quick Test (Biotool, Stratech Scientific Limited, Cambridge, UK). The used passage numbers were below 25. Normal human astrocytes (NHA) were purchased from ScienCell Research Laboratories (Carlsbad, CA, USA) and cultured in the astrocyte medium according to the manufacturer’s instruction. The cells were incubated at 37 °C, 5% CO2, and 95% humidity.
2.5. Cell Survival
Cell survival was determined by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide (MTT) conversion into formazan. Briefly, the cells were seeded into 24-well plates at a density of 4 × 104 cells/well and incubated overnight at 37 °C. After this time, the cells were treated with increasing concentrations (1, 5, 20 µM) of dendrimers (19, 20, 21, 24, and 25) or dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (Sigma-Aldrich) (the final concentration of DMSO did not exceed 0.1% v/v). After a 1 h incubation at 37 °C, the dendrimer-containing medium was replaced with the fresh one and the cells were cultured for the next 48 h. Subsequently, the cells were washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) (Sigma-Aldrich) and incubated in the culture medium with MTT (Sigma-Aldrich) solution at the final concentration of 0.5 mg/mL for 2 h at 37 °C. Then, the medium was replaced with 100% DMSO and absorbance was read at 570 nm using Elisa Bio-Rad Microplate Reader (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). Each compound in each concentration was tested in triplicate in a single experiment and five independent experiments were performed.
2.6. Colony-Forming Assay
LN229, U87MG, or T98G cells were seeded in six-well plates (100 cells/well) and allow to attach for 24 h. Next, cells were treated with increasing concentrations (1, 5, 20 µM) of dendrimers (19, 20, 21, 24, or 25) or DMSO (Sigma-Aldrich) for 1 h. Subsequently, the medium was replaced with a fresh one and cells were cultured for 14 days. Next, cell culture plates containing colonies were gently washed with PBS (Sigma-Aldrich) and fixed with 4% formaldehyde for 10 min. Colonies were stained with 0.5% crystal violet solution in 25% methanol for 10 min and the grossly visible colonies were counted. Three independent experiments were performed.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Results are reported as means and standard deviations. The statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism 7 (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA, USA). The statistical significance was determined by one-way analysis of variance (one-way ANOVA). * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.005 was considered as statistically significant.
2.8. Antioxidant Assays
2.8.1. Chemicals
2,4,6-tris(2-pyridyl)-s-triazine (TPTZ), iron(III) chloride hexahydrate, acetic acid (≥99.0%), sodium acetate, 6-hydroxy-2,5,7,8-tetramethylchromane-2-carboxylic acid (Trolox®), HCl, 2,2′-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulphonic acid) diammonium salt (ABTS), potassium persulfate, and 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl radical (DPPH), were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Steinheim, Germany). All solvents (methanol and water) and reagents that are used in this study were HPLC or of analytical grade.
2.8.2. Ferric Reducing Antioxidant Power (FRAP)
The FRAP assay was performed according to previously described method [43] with some modifications [44]. Fresh FRAP solution was prepared each time. The stock solution included 2.40 mL of acetate buffer (300 mM, pH 3.6), 0.24 mL 10 mM TPTZ solution in 40 mM HCl, and 0.24 mL of 20 mM FeCl3 × 6H2O in water. The mixture was protected from light and kept at 37 °C before using a 240 μL sample. Trolox or solvent (blank sample) standard solution was added to FRAP stock solution. The absorbance was measured at 593 nm after 15 min. Final concentration of methanolic solutions of the studied dendrimers were in the range 0–24 μM and Trolox® solutions from 0 to 50 μM. All determinations were carried out in triplicate and the data are presented as Trolox-equivalent activity (TEAC).
2.8.3. ABTS Assay
ABTS assay was based on a previously published method [45] with some modifications [46], using Trolox®, a water-soluble analogue of vitamin E, as a standard. ABTS•+ radical cation was produced by dissolution 10 mg solid ABTS in a mixture of water and 2.4 mM potassium persulfate aqueous solution (final concentration of ABTS 2 mM). The stock solution was kept in the dark at room temperature for 12–16 h. The ABTS•+ solution was then diluted with distilled water to obtain an absorbance of 1.05 ± 0.05 at 734 nm. To the 240 μL sample, solvent or Trolox standard solution, 2.88 mL of ABTS•+ solution was added, and absorbance was measured after 10 min. Results of the ability of dendrimers to scavenge cation radical ABTS are presented as Trolox-equivalent antioxidant capacity (TEAC) and as IC50 parameter. All analyses were performed in triplicate and the results were expressed as the mean value ± standard deviation.
2.8.4. DPPH Assay
Experiments were performed according to [47], with small modifications [46]. Primarily, 2 × 10−3 mol/L of DPPH radical reagent was prepared in methanol. This solution was kept in the dark at room temperature for 2 h. The DPPH• solution was then diluted with methanol to obtain an absorbance of 0.95 ± 0.05 at 517 nm. 240 μL of the solvent, sample or Trolox standard solutions were mixed with 2.88 mL of DPPH radical solution and after 15 min, the absorbance were measured. Results were expressed as Trolox-equivalent antioxidant capacity (TEAC) values (μM). In the concentration range investigated, 50% of radical scavenge (IC50) was not achieved. All experiments were repeated in triplicate and the results were shown as the mean value ± standard deviation.
3. Results
3.1. Molecular Design
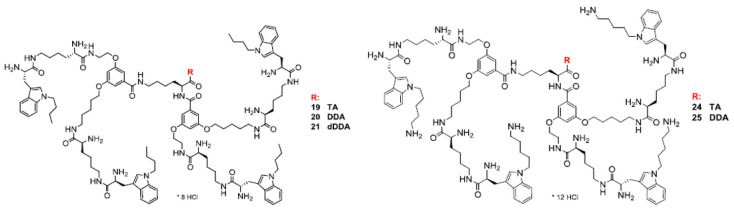
Previously, we have studied several groups of dendrimers bearing 1 to 5 indole residues that, depending on the dendrimer geometry, expressed antimicrobial [42] or anticancer properties [31]. For some of them significant antioxidant capacity was detected along with ability to protect glutamate stressed primary rat cerebellar neurons [30]. We anticipated that dendrimeric structure will potentiate effect of a single residue, making observation of biological effect more visible. The present design involved synthesis of two groups of dendrimers with hydrophobic interior and indole N1-atom substituted with N1-alkyl (19–21) or N1-alkyl-amino residue (24–25) (Figure 1). The C-terminal position was substituted by different hydrophobic residues, including an aromatic indole ring from tryptamine or lipophilic dodecylamine (DDA) or di-dodecylamine (DDDA). Since compounds were prepared as poly-hydrochlorides, various protonation levels were achieved: (+)8 charged compounds 19–21 and (+)12 charged compounds 24–25. The final dendrimers were characterized by electrospray mass spectrometry (ESIMS) and 1H and 13C NMR spectrometry. 1H and 13C NMR spectra showed no extra peaks suggesting at least 95% purity of the final dendrimers (Supplementary Materials). It was of interest to see if such molecular architecture could modulate selectivity of dendrimers towards GBM versus the non-tumorigenic cells or their molecular antioxidant activity.
Figure 1.
Chemical structure of the designed dendrimers.
3.2. Susceptibility of Human GBM Cells and Primary Human Astrocytes to Treatment with Dendrimers
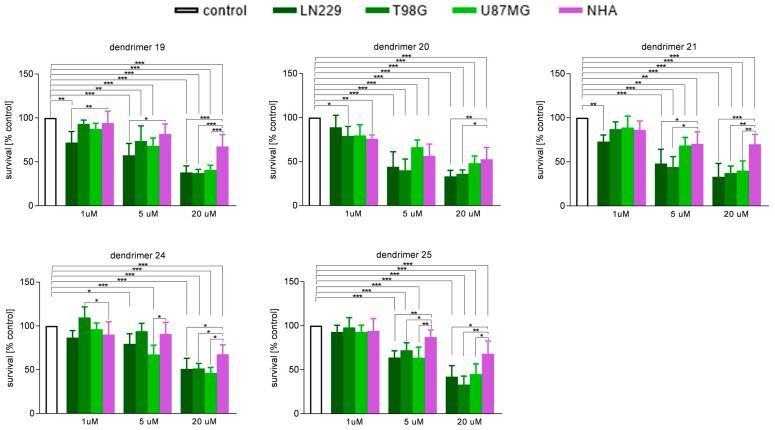
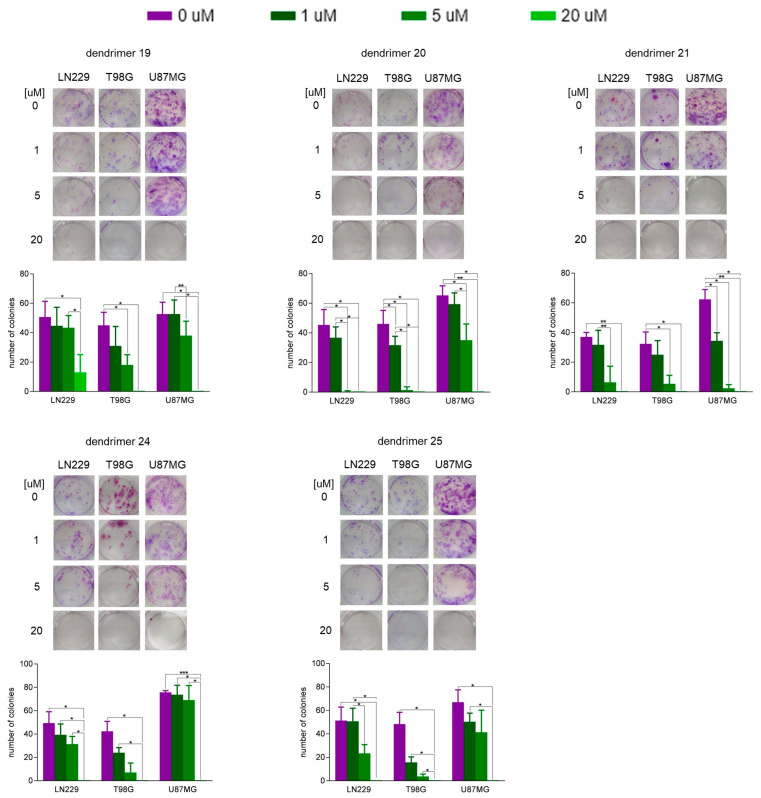
To assess the optimal dendrimer concentration providing anticipated cytotoxic activity in the malignant cells with minimal negative impact on the normal nervous system cells, viability of human normal astrocytes (NHA) and GBM cells was tested in vitro. Cells were cultured for 1 h in the presence of dendrimers belonging to two structural groups (19–21) and (24 and 25) in various concentrations. As shown in Figure 2, there was no dependence of protonation of dendrimers on viability of NHA assessed 48 h after the challenge. There was even an inverse relationship: (+)12 charged are less damaging to NHA than (+)8 if we compare compounds in 5 µM concentration. On the other hand, all molecules tested similarly reduced viability of GBM cells (Figure 2). In the colony-forming test (14 days after 1 h exposure to dendrimers), the most efficient in inhibition of cell proliferation were compounds 20, 21, 24 and 25, as shown on Figure 3. While only dendrimers 21 and 25 were simultaneously safe for NHA (Figure 2) and harmful for GBM cells (Figure 3), it can be assumed that this behavior was, rather, related to the hydrophobicity of the compounds. The tested compounds were versatile in their ability to inhibit the division of three different types of GBM.
Figure 2.
Influence of dendrimers on viability of human glioblastoma LN229, T98G, and U87MG cells and primary astrocytes. Cells were treated with increasing concentrations (1, 5, and 20 µM) of dendrimer 19, 20, 21, 24, and 25 for 1 h. Subsequently, the dendrimer-containing medium was replaced with the fresh medium. After the next 48 h, cells survival was assessed by MTT assay. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 5) expressed as percentage of control (DMSO-treated cells). * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.005 (one-way ANOVA).
Figure 3.
Influence of dendrimers on clonogenic potential of human glioblastoma LN229, T98G, and U87MG cells. Cells were treated with increasing concentrations (1, 5, and 20 µM) of dendrimer 19, 20, 21, 24, and 25 for 1 h. Subsequently, the dendrimer-containing medium was replaced with the fresh medium. After the next 14 days, colonies were stained and counted. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.005 (one-way ANOVA).
3.3. Antioxidant Properties: Radical Scavenging Potency (DPPH and ABTS) and Redox Potential (FRAP) of Dendrimers
Redox potential and radical scavenging potency of the new groups of peptide dendrimers functionalized with N1-substituted Trps were evaluated. Generally, two types of tests can be used to study antioxidant capacity of any individual compound or natural isolates. The first, and also the most common is the ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) test that is based on the electron transfer (ET) mechanism and reflects the compound’s ability to reduce Fe(III) cation to the lower oxidation state Fe(II). The second group of assays involves interactions of compounds with free radicals: neutral radical scavenging assay shows capability of a compound to interact with stable neutral radicals prepared from 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), whereas the second test shows scavenging power against cationic radicals prepared from 2,2′-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulphonic acid) (ABTS). Tests of the latter group use different models of antioxidative mechanism. While DPPH assay shows the capacity of antioxidant to transfer electron, ABTS assay determines cationic free radical scavenging activity involving both electron and hydrogen transfer mechanisms. In all tests, the reference compound is Trolox, a known radical scavenger.
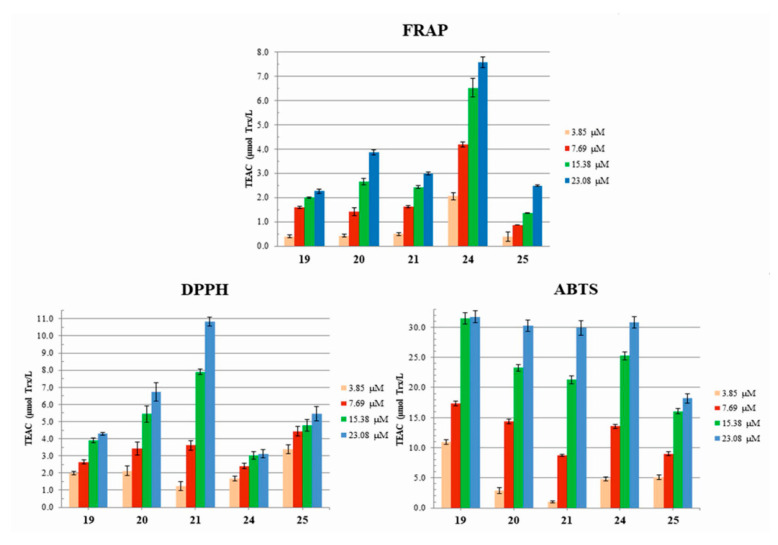
The antioxidant potential in terms of FRAP model for the studied compounds: +(8) charged 19–21 (N1-butyl-Trp terminated arms and tryptamine (TA), dodecylamine (DDA) or di-dodecylamine (DDDA) residue located at C-terminus)) and +(12) charged 24 and 25 (four N1-aminopentyl-Trp terminated arms and TA or DDA residue located at C-terminus) is shown in Figure 4. From the collection of dendrimers only compound 24 expressed a significantly higher TEAC value than the other compounds.
Figure 4.
Antioxidant potential expressed as Trolox-equivalent activity (TEAC) of the selected 19–21 and 24, 25 dendrimers at four concentrations (3.85, 7.69, 15.38, and 23.08 µM) measured as ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP), neutral radicals scavenging ability (DPPH), or cationic radicals scavenging ability (ABTS) in relation to the known concentrations of Trolox.
The results of DPPH and ABTS tests for the studied group of dendrimers at four concentrations (3.78, 7.69, 15.38, and 23.08 µM) are shown in Figure 4. Considering absolute TEAC values, individual dendrimers showed different level of scavenging capacity in both tests, being generally better scavengers of radical cations than single-electron-bearing neutral radicals. In the ABTS model a two-fold increase in dedrimer concentration yielded, as expected, ca. double TEAC values, except for 19 and 25, where, for the highest concentration (23.08 µM), increase was marginal, suggesting that compounds approached Trolox activity.
4. Discussion
The amino-acid-containing dendrimers presented here are branched version of amphiphilic, natural peptides (AMP) known for several decades as primary defense molecules of the innate immune system. In addition to their numerous functions (antimicrobial, antifungal, antiprotozoal, immunomodulatory, etc.), anticancer properties of AMPs are of great importance [48,49,50,51,52].
Design of the present Trp-rich peptide dendrimers with N1-atom substituted with N1-alkyl (19–21) or N1-alkylamino residue (24–25) (Figure 2) was prompted by multiple functions played by Trp, e.g., structural stabilization of the spanning membrane peptides and proteins [32,33,34], antioxidant properties [53,54], and involvement of its catabolic products in development of immunosuppression in cancer disease [35,36,37]. According to the current knowledge, natural peptides express variability of anticancer mechanisms, including membrane disintegration and induction of apoptosis by reactive-oxygen-species accumulation. Our own studies on Trp-rich amphiphilic dendrimeric peptides of the bola structure revealed moderate activity against GBM cells [31].
The goal of this study was to evaluate the influence of five newly designed peptide dendrimers on human GBM cells. Bearing in mind a significant heterogeneity of GBM, we used three cell lines varying with respect to molecular background and tumorigenic potential [41]. All tested dendrimers reduced viability and clonogenic potential of GBM cells to different extents. The differences in sensitivity to each of the compounds observed between particular cell lines most likely result from the aforementioned biodiversity of cell lines used in this study. Indeed, several groups have documented a differential response of those three cell lines to various therapeutic approaches [55,56,57,58]. Here, compared to T98G and LN229 cells, U87MG cells turned out to be less susceptible to dendrimer-mediated toxicity, which was particularly pronounced in colony-forming assay. In comparison to U87MG, T98G cells display high expression of multidrug resistance protein 1 (MRP1), which is one of the representative members of the ATP-binding cassette superfamily of transporters that is involved in resistance to chemotherapeutic agents in cancer patients [59]. However, as showed by Kang et al., 2005 alpha-tocopheryl succinate (TOS), a vitamin E analogue, decreased intracellular GSH concentration and blocked MRP1 function in T98G, so, co-treatment of TOS and anticancer drug etoposide sensitized T98G cells to the drug more efficiently then U87MG cells [59]. In our analysis, T98G and LN229 cells were sensitive to the tested dendrimers, so we may assume that their action may be related to GSH and inhibition of MRP1. Basically, variation in cell responses to the tested compounds may result from different genetic modifications of the cells. As shown in 34 randomly chosen human glioma cell lines, the status of TP53, p16, p14ARF, and PTEN tumor-suppressor genes could participate in biological pathways that are functioning separately/independently in glioma cells and did not correlate with tumorigenicity or any clinical parameters [41]. Clearly, further studies are required to elucidate the reasons of this varied sensitivity of different GBM cells to the dendrimers as well as their mechanisms of action. The problem of delivering drugs to the brain is important because the blood–brain barrier is impermeable to most compounds. However, nanoparticles (<1000 nm), including dendrimers, may pass through or bypass the BBB depending on how the compound is administered, as detailed in the Hersh et al., 2022 review [60].
It is worth emphasizing, that a potential anti-glioma drug should display cytotoxic activity in tumor cells without affecting normal cells. In this study, dendrimers 21 and 25 turned out to simultaneously be safe for NHA and harmful for GBM cells. Moreover, as compound 24 was the most toxic to all cells in the MTT and colony formation tests, and at the same time displayed the greatest iron reduction ability in the FRAP test, we can speculate that the selective toxicity of 21 and 25 dendrimers to GBM is probably not due to this property.
Another important issue which has to be taken into consideration is the time of treatment with potential drugs and mode of action. The effect of 1 h treatment of cells with new dendrimers on their viability, as assessed 48 h later, or on clonogenicity observed after 14 days was shown by us. In the paper by Khoei et al., 2016, U87MG cells cultured in spheroids were treated with the well-known antioxidant resveratrol (20 µM) alone or in combination with iododeoxyuridine (IUdR 1 µM) for 67 h without any effect on cell viability or clonogenicity observed 10 day later. However, combined treatment of resveratrol and IUdR sensitized cells to subsequent irradiation with 60Co (2 Gy) [61]. Resveratrol (trans-3,4,5′-trihydroxystilbene) inhibits HIF1-a protein expression in the hypoxia condition in cancer cells [62]. It can therefore be assumed that the new dendrimers exerted toxic effects on GBM during short-term treatment in a different mechanism than that of resveratrol during the long-term and poorly effective treatment of U87MG cells.
Metabolically controlled accumulation of ROS, typical for cancer cells, induces oxidative stress and may lead to such pro-tumorigenic processes as phospholipid oxidation, DNA instability, and production of disadvantageous metal cations at a higher oxidation state. Furthermore, recent evidence has accumulated that ROS also have a role as signaling molecules in regulation cancer-cell proliferation, metastasis, angiogenesis, etc., [63,64] or inducing cancer-cell apoptosis [3,4,5,53,54,65]. It can be speculated that introduction of exogenous chemotherapeutics with antioxidant activity would affect GBM cells in a positive or negative way. Since the unsubstituted indole ring present in Trp and indolamine has antioxidant properties [66,67] an important issue is contribution of N1-alkyl residues to stabilization of the generated Trp cation radicals, (presumably by (1-n) hydrogen atom transfer mechanism (1-n HAT)) [68], in terms of magnitude and biological response of GBM cells. Dendrimers were tested for antioxidant capacity focusing on three models—ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP), interactions with free radicals: neutral radical scavenging assay (DPPH), and scavenging power against cationic radicals (ABTS).
Interestingly, in the DPPH model, TEAC values increased with an increase of basicity of the C-terminal nitrogen atom in the dDDA > DDA > TA fashion, whereas in ABTS model this trend was reversed (Figure 4). Taking into account structural differences between these two groups of dendrimers, the possible primary mechanism in the DPPH conditions involves hydrogen and electron transfer from the above electron-rich center and to less extent from numerous indole rings. For the same reasons, the highest reductive capabilities (FRAP) were expressed by compound 24. All compounds were very effective in scavenging the ABTS cation radical. The magnitude of the dendrimer’s redox potential was visible by comparison with the known data for clinically used alpha-tocopherol and resveratrol. As shown by Gülçin at al., 2010, radical scavenging potency of alpha-tocopherol at ca 4.4 µM concentration (relevant to our 3.85 µM), is slightly lower and ca 5.5 higher than potency of Trolox in the respective DPPH and ABTS models [69]. Resveratrol was much more potent than Trolox in both tests. Since none of our compounds expressed that level of activity one might assume that their involvement in enhancing ROS production was mild. Instead, they might slightly reduce the amount of ROS generated by GBM cells. Previously, an important role of ROS generation in TOS-induced, caspase-independent apoptosis of cancer cells was shown [70]. However, human lung cancer A549 and H460 cells were much more sensitive to TOS-induced apoptosis than the T98G and U87MG cells indicating that ROS generation is not the primary destruction mechanism for GBM. Moreover, exploratory metabolomics study detected elevated serum levels of a panel of molecules with antioxidant properties as well as oxidative-stress-generated compounds [71]. This study points out a latent biomarker for future glioblastoma consisting of γ-tocopherol, α-tocopherol, erythritol, erythronic acid, myo-inositol, cystine, 2-keto-L-gluconic acid, hypoxanthine, and xanthine, all involved in antioxidant metabolism. Unfortunately, the mechanisms of association between the serum metabolite pattern and future GBM development are not known.
As found by Su et al., 2020, the number and distribution of cationic centers is another important aspect during development of an active secondary structure of a linear anticancer peptides [52]. In the present case, enhanced cationicity of compounds 24 and 25 did not correlate with an increased activity. This might originate from the effect of back-folding, well known in dendrimer chemistry, i.e., H-bonding interactions of the N1-aminopentyl residue with hydrogen-bond acceptors located inside of the dendrimer molecule that might change molecular availability for interactions with cell membranes [72].
As shown in Table 1 (Materials and Methods), hydrophobicity of dendrimers is mostly defined by lipophilicity of the substituent located at C-terminal position. For the N1-Boc protected dendrimers, the retention factor (Rf) visualized on the TLC plate with the use of (CHCl3/MeOH (8:1)) solvent system increased in the order: tryptamine < dodecylamine < di-dodecylamine, i.e., 0.46, 0.55, and 0.60, for the respective compounds 19, 20, and 21. Substitution of tryptophan N1-atom by 5-aminopentane residue resulted in small decrease of Rf, as shown in the first group, i.e., 0.44 vs. 0.46 (compound 10 vs. 24) and 0.55 vs. 0.52 (compound 20 vs. 24).
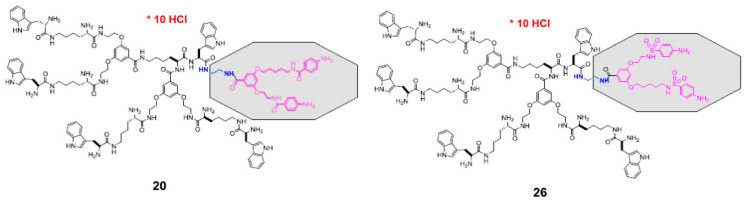
In the present group of compounds, the radical-stabilization effect gained due to (1-n HAT) mechanism should increase TEAC values in both DPPH and ABTS models, when compared to the two previously studied compounds with similar structures shown in Figure 5 [31]. Indeed, at 15.38 µM dendrimer concentration, averaged TEAC values reached ca. 7.9 in DPPH model and ca. 30 µM Trolox/L in ABTS model, in comparison with TEAC’s for the bola dendrimers that reached values 5.5 and 25 µM Trolox/L, for the DPPH and ABTS models, respectively. This factor might be important if electrons annihilating radicals produced by GBM are transferred from tryptophanes.
Figure 5.
Structures of the selected compounds from [31]: originally compounds 20 and 26, showing left side of the bola structure that represents Trp-unsubstituted version of the present compounds 19—21 and 24, 25. Right side is functionalized with two p-aminobenzoic acid (PABA, 20) or p-aminobenzenosulfonic acid (PAS, 26) residues.
Summing up, the results of three tests indicated that functionalization of dendrimer scaffolds with either N1-butyl-Trp or N1-aminopentyl-Trp increases their antioxidant potential, when compared to dendrimers with unsubstituted Trp [31]. Moreover, compounds described here are versatile in their ability to inhibit the division of three different types of GBM and have a mild influence on normal astrocytes. It is worth mentioning that these compounds display higher anti-GBM activity compared to aforementioned dendrimers with unsubstituted Trp, which were tested in our previous study [31].
It should be noted that the MTT and colony-forming assays differ from each other not only in terms of duration, but they also examine different phenomena. While the MTT test evaluates cell metabolism, the colony-forming assay examines cell clonogenicity. Since compounds 21 and 25 turned out to be toxic towards GBM cells in both assays, and relatively not harmful to NHA, it is tempting to speculate that they are the most promising anti-GBM derivatives. However, the dendrimer’s toxicity is not correlated with their antioxidant potential. Therefore, the next step is to investigate whether these compounds enter the cells or interact with the cell membranes as can be suggested by the high lipophilicity and positive charge of the molecules tested. Both factors contribute to the mechanism of anticancer activity expressed by some natural antimicrobial peptides [49].
5. Conclusions
We tested the potential of a rationally designed novel series of dendrimeric peptides to reduce survival and hold back the clonogenic potential of three GBM cell lines. The results showed that exposure of GBM cells to dendrimers for one hour has a short and long-term effect—significantly high cytotoxicity when measured after 48 h and arrest of colony formation detected after 14 days.
These study highlighted the major aspects of molecular design. Dendrimers with hydrophobic interior and lipophilic substituents: DDA and DDDA located at C-terminus exhibit moderate toxicity in GBM cells compared to NHA. Although N1-alkylation of Trp yielded derivatives with enhanced radical scavenging activity, their antioxidant potency was lower than that of the clinically used α-tocopherol and resveratrol.
Abbreviations
| CNS | central nervous system |
| GBM | glioblastoma |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| NHA | normal human astrocytes |
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/biom12081116/s1, S1: Synthesis and analytical data.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.U.-L., B.Z. and M.S. (Monika Szeliga); methodology, M.S. (Marta Sowińska), M.M. and M.S. (Monika Szeliga); investigation, M.S. (Marta Sowińska), M.M. and M.S. (Monika Szeliga); writing—original draft preparation, B.Z., M.S. (Monika Szeliga) and Z.U.-L.; writing—review and editing, M.S. (Monika Szeliga), B.Z. and Z.U.-L.; visualization, M.S. (Marta Sowińska), M.M. and M.S. (Monika Szeliga); funding acquisition, Z.U.-L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Funding Statement
This research was funded by NATIONAL SCIENCE CENTRE of Poland, grant number UMO-2015/19/ST5/03547.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Tewarie I.A., Senders J.T., Kremer S., Devi S., Gormley W.B., Arnaout O., Smith T.R., Broekman M.L.D. Survival prediction of glioblastoma patients—Are we there yet? A systematic review of prognostic modeling for glioblastoma and its clinical potential. Neurosurg. Rev. 2020;44:2047–2057. doi: 10.1007/s10143-020-01430-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ostrom Q.T., Cioffi G., Gittleman H., Patil N., Waite K., Kruchko C., Barnholtz-Sloan J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2012–2016. Neuro Oncol. 2019;21((Suppl. S5)):v1–v100. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noz150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Dymova M., Kuligina E., Richter V. Molecular Mechanisms of Drug Resistance in Glioblastoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021;22:6385. doi: 10.3390/ijms22126385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Stavrovskaya A.A., Shushanov S.S., Rybalkina E.Y. Problems of glioblastoma multiforme drug resistance. Biochemistry. 2016;81:91–100. doi: 10.1134/S0006297916020036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Rajaratnam V., Islam M., Yang M., Slaby R., Ramirez H., Mirza S. Glioblastoma: Pathogenesis and Current Status of Chemotherapy and Other Novel Treatments. Cancers. 2020;12:937. doi: 10.3390/cancers12040937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Burster T., Traut R., Yermekkyzy Z., Mayer K., Westhoff M.A., Bischof J., Knippschild U. Critical View of Novel Treatment Strategies for Glioblastoma: Failure and Success of Resistance Mechanisms by Glioblastoma Cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021;9:695325. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.695325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Medikonda R., Dunn G., Rahman M., Fecci P., Lim M. A review of glioblastoma immunotherapy. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2020;151:41–53. doi: 10.1007/s11060-020-03448-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Guan Q., Zhou L.-L., Li Y.-A., Li W.-Y., Wang S., Song C., Dong Y.-B. Nanoscale Covalent Organic Framework for Combinatorial Antitumor Photodynamic and Photothermal Therapy. ACS Nano. 2019;13:13304–13316. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.9b06467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Menjoge A.R., Kannan R.M., Tomalia D.A. Dendrimer-based drug and imaging conjugates: Design considerations for nanomedical applications. Drug Discov. Today. 2010;15:171–185. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2010.01.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Tomalia D.A., Nixon L.S., Hedstrand D.M. The Role of Branch Cell Symmetry and Other Critical Nanoscale Design Parameters in the Determination of Dendrimer Encapsulation Properties. Biomolecules. 2020;10:642. doi: 10.3390/biom10040642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kannan R.M., Nance E., Kannan S., Tomalia D.A. Emerging concepts in dendrimer-based nanomedicine: From design principles to clinical applications. J. Intern. Med. 2014;276:579–617. doi: 10.1111/joim.12280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Tomalia D., Reyna L., Svenson S. Dendrimers as multi-purpose nanodevices for oncology drug delivery and diagnostic imaging. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2007;35:61–67. doi: 10.1042/BST0350061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wicki A., Witzigmann D., Balasubramanian V., Huwyler J. Nanomedicine in cancer therapy: Challenges, opportunities, and clinical applications. J. Control Release. 2015;200:138–157. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.12.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hossen S., Hossain M.K., Basher M.K., Mia M.N.H., Rahman M.T., Uddin M.J. Smart nanocarrier-based drug delivery systems for cancer therapy and toxicity studies: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2019;15:1–18. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2018.06.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Sapra R., Verma R.P., Maurya G.P., Dhawan S., Babu J., Haridas V. Designer Peptide and Protein Dendrimers: A Cross-Sectional Analysis. Chem. Rev. 2019;119:11391–11441. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Caminade A.-M. Phosphorus Dendrimers as Nanotools against Cancers. Molecules. 2020;25:3333. doi: 10.3390/molecules25153333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Wróbel K., Wołowiec S., Markowicz J., Wałajtys-Rode E., Uram Ł. Synthesis of Biotinylated PAMAM G3 Dendrimers Substituted with R-Glycidol and Celecoxib/Simvastatin as Repurposed Drugs and Evaluation of Their Increased Additive Cytotoxicity for Cancer Cell Lines. Cancers. 2022;14:714. doi: 10.3390/cancers14030714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Patil C. Micro and Nanotechnologies, Nanocarriers for Cancer Diagnosis and Targeted Cancer Therapy. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2019. pp. 107–128. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Thakkar S., Sharma D., Kalia K., Tekade R.K. Tumor microenvironment targeted nanotherapeutics for cancer therapy and diagnosis: A review. Acta Biomater. 2019;101:43–68. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.09.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Majoros I.J., Myc A., Thomas T., Mehta C.B., Baker J.R. PAMAM Dendrimer-Based Multifunctional Conjugate for Cancer Therapy: Synthesis, Characterization, and Functionality. Biomacromolecules. 2006;7:572–579. doi: 10.1021/bm0506142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Del Olmo N.S., Maroto-Díaz M., Gómez R., Ortega P., Cangiotti M., Ottaviani M.F., de la Mata F.J. Carbosilane metallodendrimers based on copper (II) complexes: Synthesis, EPR characterization and anticancer activity. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2017;177:211–218. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2017.09.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Del Olmo N.S., Bajo A.M., Ionov M., Garcia-Gallego S., Bryszewska M., Gomez R., de la Mata F.J. Cyclopentadienyl ruthenium(II) carbosilane metallodendrimers as a promising treatment against advanced prostate cancer. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020;199:112414. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Michlewska S., Ionov M., Shcharbin D., Maroto-Díaz M., Ramirez R.G., de la Mata F.J., Bryszewska M. Ruthenium metallodendrimers with anticancer potential in an acute promyelocytic leukemia cell line (HL60) Eur. Polym. J. 2017;87:39–47. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2016.12.011. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Dufès C., Keith W.N., Bilsland A., Proutski I., Uchegbu I.F., Schätzlein A.G. Synthetic Anticancer Gene Medicine Exploits Intrinsic Antitumor Activity of Cationic Vector to Cure Established Tumors. Cancer Res. 2005;65:8079–8084. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-4402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Janaszewska A., Lazniewska J., Trzepiński P., Marcinkowska M., Klajnert-Maculewicz B. Cytotoxicity of Dendrimers. Biomolecules. 2019;9:330. doi: 10.3390/biom9080330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Janiszewska J., Swieton J., Lipkowski A.W., Urbanczyk-Lipkowska Z. Low molecular mass peptide dendrimers that express antimicrobial properties. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2003;13:3711–3713. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2003.08.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Touaibia M., Roy R. Glycodendrimers as anti-adhesion drugs against type 1 fimbriated E-coli uropathogenic infections. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2007;7:1270–1283. doi: 10.2174/138955707782795610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.McCarthy T.D., Karellas P., Henderson S.A., Giannis M., O’Keefe D.F., Heery G., Paull J.R.A., Matthews B.R., Holan G. Dendrimers as Drugs: Discovery and Preclinical and Clinical Development of Dendrimer-Based Microbicides for HIV and STI Prevention. Mol. Pharm. 2005;2:312–318. doi: 10.1021/mp050023q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Janiszewska J., Posadas I., Játiva P., Bugaj-Zarebska M., Urbanczyk-Lipkowska Z., Ceña V. Second Generation Amphiphilic Poly-Lysine Dendrons Inhibit Glioblastoma Cell Proliferation without Toxicity for Neurons or Astrocytes. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0165704. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0165704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Sowinska M., Morawiak M., Bochyńska-Czyż M., Lipkowski A.W., Ziemińska E., Zabłocka B., Urbanczyk-Lipkowska Z. Molecular Antioxidant Properties and In Vitro Cell Toxicity of the p-Aminobenzoic Acid (PABA) Functionalized Peptide Dendrimers. Biomolecules. 2019;9:89. doi: 10.3390/biom9030089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Sowińska M., Szeliga M., Morawiak M., Ziemińska E., Zabłocka B., Urbańczyk-Lipkowska Z. Peptide Dendrimers with Non-Symmetric Bola Structure Exert Long Term Effect on Glioblastoma and Neuroblastoma Cell Lines. Biomolecules. 2021;11:435. doi: 10.3390/biom11030435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Pal S., Koeppe R.E., Chattopadhyay A. Membrane electrostatics sensed by tryptophan anchors in hydrophobic model peptides depends on non-aromatic interfacial amino acids: Implications in hydrophobic mismatch. Faraday Discuss. 2020;232:330–346. doi: 10.1039/D0FD00065E. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Khemaissa S., Sagan S., Walrant A. Tryptophan, an Amino-Acid Endowed with Unique Properties and Its Many Roles in Membrane Proteins. Crystals. 2021;11:1032. doi: 10.3390/cryst11091032. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Holt A., Killian J.A. Orientation and dynamics of transmembrane peptides: The power of simple models. Eur. Biophys. J. 2009;39:609–621. doi: 10.1007/s00249-009-0567-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Zamanakou M., Germenis A.E., Karanikas V. Tumor immune escape mediated by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. Immunol. Lett. 2007;111:69–75. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2007.06.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Wainwright D.A., Balyasnikova I.V., Chang A.L., Ahmed A.U., Moon K.S., Auffinger B., Lesniak M.S. IDO expression in brain tumors increases the recruitment of regulatory T cells and negatively impacts survival. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012;18:6110–6121. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-2130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Le Naour J., Galluzzi L., Zitvogel L., Kroemer G., Vacchelli E. Trial watch: IDO inhibitors in cancer therapy. OncoImmunology. 2020;9:1777625. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2020.1777625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Qian F., Villella J., Wallace P.K., Mhawech-Fauceglia P., Tario J.D., Andrews C., Matsuzaki J., Valmori D., Ayyoub M., Frederick P.J., et al. Efficacy of Levo-1-Methyl Tryptophan and Dextro-1-Methyl Tryptophan in Reversing Indoleamine-2,3-Dioxygenase–Mediated Arrest of T-Cell Proliferation in Human Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Cancer Res. 2009;69:5498–5504. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Lewis H.C., Chinnadurai R., Bosinger S.E., Galipeau J. The IDO inhibitor 1-methyl tryptophan activates the aryl hydrocarbon receptor response in mesenchymal stromal cells. Oncotarget. 2017;8:91914–91927. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Sun T., Li Z.-L., Tian H., Wang S.-C., Cai J. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel 1-Alkyltryptophan Analogs as Potential Antitumor Agents. Molecules. 2009;14:5339–5348. doi: 10.3390/molecules14125339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Ishii N., Maier D., Merlo A., Tada M., Sawamura Y., Diserens A.C., Van Meir E.G. Frequent co-alterations of TP53, p16/CDKN2A, p14ARF, PTEN tumor suppressor genes in human glioma cell lines. Brain Pathol. 1999;9:469–479. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.1999.tb00536.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Sowińska M., Laskowska A., Guśpiel A., Solecka J., Bochynska-Czyż M., Lipkowski A.W., Trzeciak K., Urbanczyk-Lipkowska Z. Bioinspired Amphiphilic Peptide Dendrimers as Specific and Effective Compounds against Drug Resistant Clinical Isolates of E. coli. Bioconjugate Chem. 2018;29:3571–3585. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.8b00544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Benzie I.F.F., Strain J.J. The ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of “antioxidant power”: The FRAP assay. Anal. Biochem. 1996;239:70–76. doi: 10.1006/abio.1996.0292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Katalinić V., Milos M., Modun D., Musić I., Boban M. Antioxidant effectiveness of selected wines in comparison with (+)-catechin. Food Chem. 2004;86:593–600. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2003.10.007. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Re R., Pellegrini N., Proteggente A., Pannala A., Yang M., Rice-Evans C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999;26:1231–1237. doi: 10.1016/S0891-5849(98)00315-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Biskup I., Golonka I., Gamian A., Sroka Z. Antioxidant activity of selected phenols estimated by ABTS and FRAP methods. Adv. Hyg. Exp. Med. 2013;67:958–963. doi: 10.5604/17322693.1066062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Brand-Williams W., Cuvelier M.E., Berset C. Use of a free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 1995;28:25–30. doi: 10.1016/S0023-6438(95)80008-5. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 48.da Silva AM B., Silva-Gonçalves L.C., Oliveira F.A., Arcisio-Miranda M. Pro-necrotic Activity of Cationic Mastoparan Peptides in Human Glioblastoma Multiforme Cells Via Membranolytic Action. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018;55:5490–5504. doi: 10.1007/s12035-017-0782-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Tornesello A.L., Borrelli A., Buonaguro L., Buonaguro F.M., Tornesello M.L. Antimicrobial Peptides as Anticancer Agents: Functional Properties and Biological Activities. Molecules. 2020;25:2850. doi: 10.3390/molecules25122850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Dennison S.R., Whittaker M., Harris F., Phoenix D.A. Anticancer α-Helical Peptides and Structure/Function Relationships Underpinning Their Interactions with Tumour Cell Membranes. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2006;7:487–499. doi: 10.2174/138920306779025611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Riedl S., Zweytick D., Lohner K. Membrane-active host defense peptides—Challenges and perspectives for the development of novel anticancer drugs. Chem. Phys. Lipids. 2011;164:766–781. doi: 10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2011.09.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Su B.C., Wu T.H., Hsu C.H., Chen J.Y. Distribution of positively charged amino acid residues in antimicrobial peptide epinecidin-1 is crucial for in vitro glioblastoma cytotoxicity and its underlying mechanisms. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2020;315:108904. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2019.108904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Nogueira V., Park Y., Chen C.-C., Xu P.-Z., Chen M.-L., Tonic I., Unterman T., Hay N. Akt Determines Replicative Senescence and Oxidative or Oncogenic Premature Senescence and Sensitizes Cells to Oxidative Apoptosis. Cancer Cell. 2008;14:458–470. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2008.11.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Trachootham D., Zhou Y., Zhang H., Demizu Y., Chen Z., Pelicano H., Huang P. Selective killing of oncogenically transformed cells through a ROS-mediated mechanism by beta-phenylethyl isothiocyanate. Cancer Cell. 2006;10:241–252. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2006.08.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Van Loenhout J., Freire Boullosa L., Quatannens D., De Waele J., Merlin C., Lambrechts H., Deben C. Auranofin and Cold Atmospheric Plasma Synergize to Trigger Distinct Cell Death Mechanisms and Immunogenic Responses in Glioblastoma. Cells. 2021;10:2936. doi: 10.3390/cells10112936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Shaw P., Kumar N., Privat-Maldonado A., Smits E., Bogaerts A. Cold Atmospheric Plasma Increases Temozolomide Sensitivity of Three-Dimensional Glioblastoma Spheroids via Oxidative Stress-Mediated DNA Damage. Cancers. 2021;13:1780. doi: 10.3390/cancers13081780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Dave N., Chow L.M., Gudelsky G.A., LaSance K., Qi X., Desai P.B. Preclinical Pharmacological Evaluation of Letrozole as a Novel Treatment for Gliomas. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015;14:857–864. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-14-0743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Velazquez F.N., Miretti M., Baumgartner M.T., Caputto B.L., Tempesti T.C., Prucca C.G. Effectiveness of ZnPc and of an amine derivative to inactivate Glioblastoma cells by Photodynamic Therapy: An in vitro comparative study. Sci. Rep. 2019;9:3010. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-39390-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Kang Y.-H., Lee E., Youk H.-J., Kim S.H., Lee H.J., Park Y.-G., Lim S.-J. Potentiation by alpha-tocopheryl succinate of the etoposide response in multidrug resistance protein 1-expressing glioblastoma cells. Cancer Lett. 2005;217:181–190. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2004.07.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Hersh A.M., Alomari S., Tyler B.M. Crossing the Blood-Brain Barrier: Advances in Nanoparticle Technology for Drug Delivery in Neuro-Oncology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022;23:4153. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Khoei S., Shoja M., Mostaar A., Faeghi F. Effects of resveratrol and methoxyamine on the radiosensitivity of iododeoxyuridine in U87MG glioblastoma cell line. Exp. Biol. Med. 2016;241:1229–1236. doi: 10.1177/1535370215622583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Zhang Q., Tang X., Lu Q.Y., Zhang Z.F., Brown J., Le A.D. Resveratrol inhibits hypoxia-induced accumulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and VEGF expression in human tongue squamous cell carcinoma and hepatoma cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2005;4:1465–1474. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-05-0198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Reczek C.R., Chandel N.S. The Two Faces of Reactive Oxygen Species in Cancer. Annu. Rev. Cancer Biol. 2017;1:79–98. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cancerbio-041916-065808. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Zhang V.X., Sze KM F., Chan L.K., Ho DW H., Tsui Y.M., Chiu Y.T., Ng IO L. Antioxidant supplements promote tumor formation and growth and confer drug resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma by reducing intracellular ROS and induction of TMBIM1. Cell Biosci. 2021;11:217. doi: 10.1186/s13578-021-00731-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Trachootham D., Alexandre J., Huang P. Targeting cancer cells by ROS-mediated mechanisms: A radical therapeutic approach? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009;8:579–591. doi: 10.1038/nrd2803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Mor M., Spadoni G., Diamantini G., Bedini A., Tarzia G., Silva C., Vacondio F., Rivara M., Plazzi P.V., Franceschinit D., et al. Antioxidant and cytoprotective activity of indole derivatives related to melatonin. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2003;527:567–575. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-0135-0_65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Suzen S., Cihaner S.S., Coban T. Synthesis and Comparison of Antioxidant Properties of Indole-Based Melatonin Analogue Indole Amino Acid Derivatives. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2011;79:76–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1747-0285.2011.01216.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Nechab M., Mondal S., Bertrand M.P. 1,n-Hydrogen-atom transfer (HAT) reactions in which n’5: An updated inventory. Chemistry. 2014;20:16034–16059. doi: 10.1002/chem.201403951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Gülçin I. Antioxidant properties of resveratrol: A structure–activity insight. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2010;11:210–218. doi: 10.1016/j.ifset.2009.07.002. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Kang Y.-H., Lee E., Choi M.-K., Ku J.-L., Kim S.H., Park Y.-G., Lim S.-J. Role of reactive oxygen species in the induction of apoptosis by α-tocopheryl succinate. Int. J. Cancer. 2004;112:385–392. doi: 10.1002/ijc.20424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Björkblom B., Wibom C., Jonsson P., Mörén L., Andersson U., Johannesen T.B., Langseth H., Antti H., Melin B. Metabolomic screening of pre-diagnostic serum samples identifies association between α- and γ-tocopherols and glioblastoma risk. Oncotarget. 2016;7:37043–37053. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Svenson S., Tomalia D.A. Dendrimers in biomedical applications—reflections on the field. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012;64:102–115. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2012.09.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.