Abstract
We investigated the genetic interactions between mutations affecting chromosome structure and partitioning in Bacillus subtilis. Loss-of-function mutations in spoIIIE (encoding a putative DNA translocase) and smc (involved in chromosome structure and partitioning) caused a synthetic lethal phenotype. We constructed a conditional mutation in smc and found that many of the spoIIIE smc double-mutant cells had a chromosome bisected by a division septum. The growth defect of the double mutant was exacerbated by a null mutation in the chromosome partitioning gene spo0J. These results suggest that mutants defective in nucleoid structure are unable to move chromosomes out of the way of the invaginating septum and that SpoIIIE is involved in repositioning these bisected chromosomes during vegetative growth.
Chromosome partitioning is an accurate and efficient process in bacteria. Several genes that play roles in chromosome partitioning in Bacillus subtilis have been characterized, including smc, spo0J, and spoIIIE (1, 4, 9, 20, 28). SMC proteins are found in prokaryotes, eukaryotes, and archaea and are involved in a wide range of processes that affect chromosomes, including partitioning, sister chromatid cohesion, dosage compensation, condensation, supercoiling, and recombination (1, 3, 5, 8, 11, 12, 14, 19, 20, 27) (for reviews, see references 7, 10, and 26). SMC proteins have an N-terminal nucleoside triphosphate-binding domain, two long coiled-coil regions separated by a hinge, and a C-terminal signature DA-box motif (13). SMC proteins were first identified in eukaryotes but have now been found to be encoded by most prokaryotic genomes sequenced to date (1, 18).
The B. subtilis SMC protein is involved in chromosome structure and partitioning (1, 20), and its function may be analogous to that of MukB in Escherichia coli (21). smc null mutants are temperature sensitive for growth in rich medium. Under permissive conditions, smc null mutants have abnormal nucleoids and approximately 10% of the cells are anucleate (1, 20). A recent biochemical characterization indicates that B. subtilis SMC is an antiparallel homodimer (18) that has the ability to aggregate and/or renature single-stranded DNA in ATP-dependent reactions in vitro (6). The mode of involvement of these SMC activities in chromosome partitioning and nucleoid structure is unknown.
spo0J of B. subtilis is required for faithful chromosome partitioning (and sporulation). Spo0J is a member of the ParB family of partition proteins (22), and spo0J null mutant cells are ∼1 to 2% anucleate, a frequency ∼100-fold higher than that of the wild type (9). Spo0J binds to multiple sites in the origin region of the chromosome (15) and forms a large nucleoprotein complex that is visible by the use of immunofluorescence microscopy or a Spo0J-green fluorescent protein fusion (4, 16). This complex may play a role in pairing newly replicated sister origin regions or in the structural organization of the origin region (1, 15). Consistent with the notion that both SMC and Spo0J are involved in chromosome organization and structure, an smc spo0J double mutant has a synthetic lethal phenotype in rich medium (1).
SpoIIIE is involved in postseptational chromosome segregation during sporulation (28, 30). spoIIIE mutants are unable to sporulate, and development is arrested with the forespore chromosome bisected by the asymmetric division septum. SpoIIIE localizes to the sporulation septum (29), has similarity to DNA translocases, and has been proposed to pump the chromosome destined for the forespore across the polar septum. SpoIIIE is also required for efficient segregation during vegetative growth when normal cell division or chromosome partitioning has been perturbed (25). Thus, during vegetative growth, SpoIIIE may be a backup mechanism for chromosome partitioning when normal partitioning is defective.
smc spoIIIE double mutants appear to have a synthetic lethal phenotype.
We attempted to construct an smc spoIIIE double mutant by combining an smc null mutation (Δsmc::kan) with one of two different spoIIIE mutations, spoIIIE36 (29) and spoIIIE null (23). spoIIIE36 contains three missense mutations clustered near a region of SpoIIIE that shows similarity to Tra proteins (30). The spoIIIE null mutation is a deletion-insertion, with a deletion of codons 86 to 667 (of 787) and an insertion of a spectinomycin resistance cassette (23). Interestingly, the two spoIIIE mutations cause different phenotypes with respect to cell-type-specific gene expression (28).
Competent cells of the spoIIIE36 (PL656) and ΔspoIIIE (PL422) mutants were transformed with chromosomal DNA from a Δsmc::kan strain (RB35) and plated at 24°C on a glucose-supplemented defined minimal medium (S750) and on Luria-Bertani (LB) medium. We were unable to isolate stable spoIIIE36 Δsmc transformants on either type of medium, suggesting that combining Δsmc and spoIIIE36 caused a synthetic lethal phenotype. We were able to isolate a transformant containing both smc and spoIIIE null mutations on minimal medium at 24°C, but this strain was stable only in the presence of spectinomycin (used to select for ΔspoIIIE::spc). The Δsmc ΔspoIIIE double mutant was extremely sick; colonies did not become visible until after 4 days at 24°C and were very small. Culturing of the strain without spectinomycin or at higher temperatures resulted in poorer growth and the accumulation of suppressors.
A conditional allele of smc.
To test smc spoIIIE double mutants, we constructed a conditional allele of smc. smc was placed under the control of the LacI-repressible, isopropyl-β-d-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG)-inducible promoter Pspac. The Pspac-smc spoIIIE+ strain (RB68) was grown in LB liquid medium at 37°C in both the presence (induced) and the absence (repressed) of IPTG (Fig. 1 legend). The phenotype in the absence of IPTG was similar to though less severe than that of an smc null mutant: the nucleoid structure was abnormal, and anucleate cells accumulated (Fig. 2B). However, in contrast to the Δsmc::kan mutant, the Pspac-smc mutant (in the absence of IPTG) was able to form colonies at 37°C on LB medium. Thus, there appears to be low-level expression of smc in the Pspac-smc mutant in the absence of IPTG.
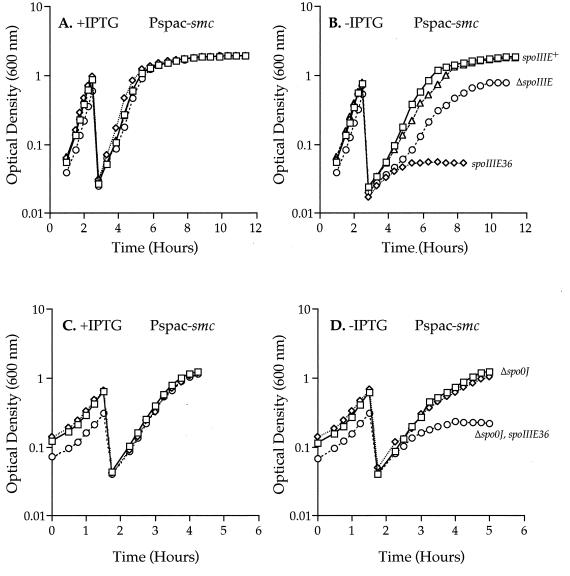
FIG. 1.
Growth of Pspac-smc strains. Cells were grown overnight on solid LB medium with 1 mM IPTG and then inoculated into prewarmed (37°C) LB medium containing 5 μg of chloramphenicol/ml with (+) (A and C) or without (−) (B and D) 1 mM IPTG. Cultures were diluted once during the experiments (note the drops in optical density at around 2 h) to keep the cells in the exponential phase of growth. It takes several generations of growth in the absence of IPTG to express the Smc mutant phenotype. (A and B) Effects of depleting SMC from spoIIIE mutant cells. Symbols: Pspac-smc spoIIIE+ (RB68), squares; Pspac-srb ΔspoIIIE (RB91), triangles; Pspac-smc spoIIIE36 (RB69), diamonds; Pspac-smc ΔspoIIIE (RB82), circles. (C and D) Effect of Δspo0J on the Pspac-smc spoIIIE mutants. Symbols: Pspac-smc spoIIIE+ (RB68), squares; Pspac-smc Δspo0J (RB74), diamonds; Pspac-smc Δspo0J spoIIIE36 (RB75), circles. Note that the scales on the x axes in the top and bottom panels are different. To place the smc gene under the control of the Pspac promoter, a PCR fragment including the ribosome binding site and the 5′ end of smc was generated and directionally cloned into the HindIII and SphI sites of pAG58 (primer sequences are available on request). The resulting plasmid, pRB21, was integrated into the chromosome by a single crossover. pRB21 (Pspac-smc) was transformed into AG174 (wild type) to generate strain RB68 (Pspac-smc), into PL656 (spoIIIE36) to generate RB69 (Pspac-smc spoIIIE36), and into strain PL422 (ΔspoIIIE) to generate strain RB82 (Pspac-smc ΔspoIIIE). RB74 (Pspac-smc Δspo0J) was constructed by integrating pRB21 by a single crossover into strain AG1468 (Δspo0J). RB75 (Pspac-smc Δspo0J spoIIIE36) was constructed by integrating pRB21 by a single crossover into strain RB1 (Δspo0J spoIIIE36). The srb gene was placed under the control of the Pspac promoter by PCR amplifying the ribosome binding site and 5′ end of srb and cloning the fragment into pAG58. This plasmid was integrated into the chromosome by a single crossover into strain PL422 to generate RB91 (Pspac-srb ΔspoIIIE).
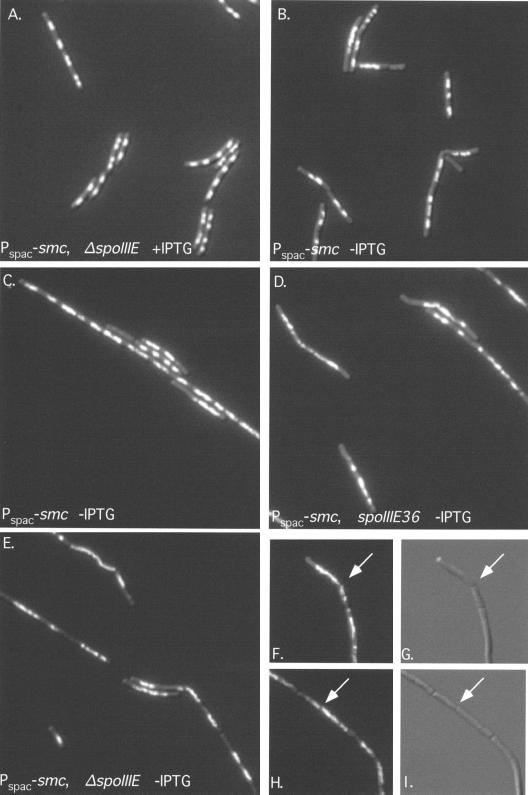
FIG. 2.
Chromosome partitioning phenotypes of Pspac-smc strains. Cells were grown as described in the legend to Fig. 1 and in the text. Cells were fixed with methanol and visualized by a combination of fluorescence and Nomarski microscopy as described elsewhere (1). The DNA was stained with the DNA-specific dye 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). (A) RB82 (Pspac-smc ΔspoIIIE) grown in the presence of IPTG; (B) Pspac-smc spoIIIE+ (RB68) grown without IPTG for six generations; (C) Pspac-smc spoIIIE+ (RB68) grown without IPTG for nine generations; (D) Pspac-smc spoIIIE36 (RB69) grown without IPTG (cells taken approximately one generation before the cessation of growth); (E) Pspac-smc ΔspoIIIE (RB82) grown without IPTG (cells taken approximately one generation before the cessation of growth); (F to I) Examples of the CUT phenotype: combination Nomarski and fluorescence microscopy of smc spoIIIE double-mutant cells (F and H), and Nomarski images only of the same cells (G and I). Arrows indicate examples of a nucleoid bisected by a septum.
Because smc is the second gene of a three-gene operon, we also depleted Srb, which is encoded by the gene immediately downstream of smc, and found that Srb depletion was not involved in the phenotypes associated with smc depletion (data not shown). A previous study investigating the effects of depleting SMC and Srb obtained similar results (20).
Depletion of SMC from cells containing spoIIIE mutations.
We constructed Pspac-smc spoIIIE double mutants and characterized the phenotypes caused by depletion of SMC following removal of IPTG. When strains harboring Pspac-smc and either spoIIIE36 (RB69) or the spoIIIE null mutation (RB82) were depleted of SMC (following removal of IPTG), growth slowed and eventually ceased (Fig. 1B). When depleted of SMC, the two spoIIIE mutants behaved somewhat differently; the spoIIIE36 mutant had a more severe phenotype than the spoIIIE null mutant. For approximately four generations after removal of IPTG, the Pspac-smc spoIIIE36 strain (RB69) grew similarly to the Pspac-smc spoIIIE+ strain (RB68). After this time, growth of the double mutant slowed and then ceased after approximately six or seven generations (Fig. 1B). The Pspac-smc ΔspoIIIE strain (RB82) had a longer period of slow growth before all growth ceased at approximately 9 to 11 generations after removal of the IPTG. A similar stoppage of growth was not observed when SMC was depleted from spo0J mutant cells (see below) or when Srb was depleted in either of the spoIIIE mutant backgrounds (Fig. 1B and data not shown). Also, no difference in growth was observed when these strains were grown in the presence of IPTG (smc+) (Fig. 1A), indicating that neither spoIIIE mutation significantly affects growth. These results demonstrate that spoIIIE is required for growth of smc mutant cells.
We measured the viability (plating efficiency) of the Pspac-smc spoIIIE mutant cells after growth in the absence of IPTG. Cells were grown in LB medium, and samples were taken at the time growth ceased (approximately six and nine generations after removal of IPTG for Pspac-smc spoIIIE36 and Pspac-smc ΔspoIIIE, respectively). Samples were plated under permissive conditions (LB medium in the presence of 1 mM IPTG). Depleting SMC in an otherwise wild-type background (RB68) resulted in ∼50% of the cells still being viable compared to strains grown in the presence of IPTG. Pspac-smc spoIIIE36 (RB69) and Pspac-smc ΔspoIIIE (RB82) exhibited ∼97 and ∼85% loss of viability, respectively. Neither spoIIIE mutation alone had any detectable effect on cell viability. The difference in the viabilities of Pspac-smc spoIIIE36 (RB69) and Pspac-smc ΔspoIIIE (RB82) correlates with the growth phenotypes (Fig. 1B).
smc spoIIIE double mutants have a CUT phenotype.
We analyzed the Pspac-smc spoIIIE double mutants for chromosome partitioning defects. Samples were taken for analysis approximately one generation before cessation of growth (approximately five and eight generations without IPTG for Pspac-smc spoIIIE36 [RB69] and Pspac-smc ΔspoIIIE [RB82], respectively). Pspac-smc spoIIIE+ (RB68) was grown for six and nine generations without IPTG for comparison. In all three cases, cells displayed a typical smc phenotype (Fig. 2). Nucleoids had a decondensed appearance, and anucleate cells were present in all strains. The frequency of anucleate cells did not differ significantly between the three strains and was ∼10%.
In addition to anucleate cells, the Pspac-smc spoIIIE mutants had many cells with a chromosome bisected by a division septum (Fig. 2F to I). This phenotype is similar to that of the CUT mutants of Schizosaccharomyces pombe (interestingly, two of these S. pombe CUT mutants turned out to have mutations affecting smc genes) (24).
Examples of CUT chromosomes are shown in Fig. 2F to I. In the Pspac-smc single mutant, ∼10% of septa were observed to bisect a chromosome (Table 1). In contrast, in the Pspac-smc spoIIIE36 double mutant, ∼38% of septa bisected a chromosome after five generations in the absence of IPTG (Table 1). Similarly, after eight generations without smc expression, the Pspac-smc ΔspoIIIE double mutant (RB82) had an increase in CUT chromosomes over the number exhibited by the Pspac-smc spoIIIE+ single mutant (RB68) (∼30% versus ∼20%), but the overall difference was less pronounced. These results are consistent with the spoIIIE36 mutation causing a more severe phenotype than the ΔspoIIIE mutation in combination with Pspac-smc.
TABLE 1.
Effect of SMC depletion on CUT chromosomes
| Straina | Relevant genotype | % CUTb |
|---|---|---|
| RB68 (6) | Pspac-smc spoIIIE+ | 10.6 (34/320) |
| RB69 | Pspac-smc spoIIIE36 | 38.0 (274/721) |
| RB68 (9) | Pspac-smc spoIIIE+ | 19.6 (115/588) |
| RB82 | Pspac-smc ΔspoIIIE | 29.9 (191/638) |
Strains were grown in LB medium at 37°C in the presence or absence of IPTG. For strain RB68, the number of generations in the absence of IPTG is indicated in parentheses.
The percentage of septa that bisect a chromosome. RB69 and RB82 were grown in the absence of IPTG for approximately five and eight generations, respectively. Data are cumulative from several experiments. The pair of numbers in parentheses includes the number of septa bisecting a chromosome and the total number of septa. When grown in the presence of IPTG, no CUT chromosomes (<1 in 603) were observed in these strains.
We suspect that the CUT phenotype might be contributing to the loss of viability of the Pspac-smc spoIIIE double mutants. Presumably, in the spoIIIE+ cells, some of these CUT chromosomes are resolved by the action of SpoIIIE pumping the chromosome through the septum, whereas in the spoIIIE mutants a CUT chromosome is likely to be a terminal event. We have not detected induction of the SOS response, as measured by induction of a dinC-lacZ fusion (2), in the Pspac-smc spoIIIE double mutants (data not shown). The SOS response has been detected in ftsK mutants of E. coli (17); the C-terminal domain of FtsK is similar to that of SpoIIIE.
Why does spoIIIE36 cause a more severe defect? The major distinction between the two mutations is that spoIIIE36 encodes a protein that correctly localizes to the septum (29) whereas the null mutation likely results in a complete lack of protein (23). One possibility is that when a chromosome is bisected by a septum, the chromosome is then grabbed by SpoIIIE and pumped through the septum. We suspect that the defective spoIIIE36 gene product still makes contact with the chromosome but cannot complete translocation, in effect holding the chromosome in place. Any chromosome caught in the way of the septum in spoIIIE36 cells would be trapped, and a full complement of the genome would not be received by the daughter cells. In a spoIIIE null mutant, the chromosome would not be held in place and might be able to move out of the way of the invaginating septum, causing an increase in the number of viable cells compared to spoIIIE36 mutants. However, the outcome is eventually the same: in the absence of SMC, the ΔspoIIIE mutant cells do not survive. The loss of viability is likely due to a combination of the CUT phenotype and other, uncharacterized effects on the chromosome.
Exacerbation of the smc spoIIIE mutant phenotype by a spo0J null mutation.
A Δspo0J Δsmc double mutation gives rise to more anucleate cells and causes a greater disruption of nucleoid structure than the single Δsmc mutation (1). In addition, the double mutation results in synthetic lethality on LB medium. We hypothesized that the more severe the segregation defect, the more important the backup partitioning function of SpoIIIE becomes. Therefore, we depleted SMC from a Δspo0J spoIIIE36 mutant.
Depleting SMC from cells harboring both Δspo0J and spoIIIE36 mutations resulted in cessation of growth earlier than for cells with spoIIIE36 alone. Strains containing Pspac-smc spo0J+ spoIIIE+ (RB68), Pspac-smc Δspo0J spoIIIE+ (RB74), or Pspac-smc Δspo0J spoIIIE36 (RB75) were grown in LB medium at 37°C with (Fig. 1C) or without (Fig. 1D) IPTG. Although the Δsmc Δspo0J double mutant is not viable on LB medium, depletion of SMC from spo0J cells (RB74) did not result in cessation of growth, even after 10 generations (∼20% of the cells were anucleate, versus ∼10% for RB68, consistent with previous results [1]). In contrast, the triple-mutant (Pspac-smc Δspo0J spoIIIE36) strain ceased growth approximately four or five generations after removal of IPTG, a full two generations before the Pspac-smc spoIIIE36 (RB69) mutant. The Δspo0J spoIIIE36 double mutant had no growth defect.
Summary.
We have demonstrated that SpoIIIE, a putative DNA translocase capable of pumping DNA through a septum, is required for the viability of smc mutant cells. Our results suggest that in smc mutants the bulk of the chromosome is not being properly partitioned out of the way of the invaginating septum and that the SpoIIIE protein provides a critical backup partitioning mechanism to pump DNA through the septum when normal partitioning is disrupted. These results support and extend earlier work demonstrating a postseptational partitioning role for SpoIIIE during vegetative growth (25). Our results suggest that nucleoid structure is extremely important, if not essential, for proper nucleoid partitioning and that the postseptational partitioning provided by SpoIIIE helps to resolve defects. Clearly, spoIIIE does not substitute completely for the lack of smc function, but it can help the cell overcome the partitioning defect in enough cases to yield viable cells.
Mutations in B. subtilis smc and E. coli mukB cause strikingly similar phenotypes (1, 20, 21). Interestingly, it was recently reported that an E. coli mukB and ftsK double mutant, which has a postseptational partitioning function, could not be isolated (31). This further suggests that SMC and MukB play similar roles in nucleoid structure and chromosome partitioning. We suspect that the disruption in nucleoid structure causes the partitioning defect, although a more direct role for SMC in chromosome partitioning is possible.
Acknowledgments
We thank members of our lab for useful discussions and Katherine Lemon and Petra Levin for comments on the manuscript.
R.A.B. was supported, in part, by postdoctoral fellowship GM19302 from NIH. This work was also supported in part by Public Health Service grant GM41934 from NIH to A.D.G.
REFERENCES
- 1.Britton R A, Lin D C, Grossman A D. Characterization of a prokaryotic SMC protein involved in chromosome partitioning. Genes Dev. 1998;12:1254–1259. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.9.1254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Cheo D L, Bayles K W, Yasbin R E. Cloning and characterization of DNA damage-inducible promoter regions from Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1991;173:1696–1703. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.5.1696-1703.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Chuang P T, Albertson D G, Meyer B J. DPY-27: a chromosome condensation protein homolog that regulates C. elegans dosage compensation through association with the X chromosome. Cell. 1994;79:459–474. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90255-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Glaser P, Sharpe M E, Raether B, Perego M, Ohlsen K, Errington J. Dynamic, mitotic-like behavior of a bacterial protein required for accurate chromosome partitioning. Genes Dev. 1997;11:1160–1168. doi: 10.1101/gad.11.9.1160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Guacci V, Koshland D, Strunnikov A. A direct link between sister chromatid cohesion and chromosome condensation revealed through the analysis of MCD1 in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1997;91:47–57. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)80008-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hirano M, Hirano T. ATP-dependent aggregation of single-stranded DNA by a bacterial SMC homodimer. EMBO J. 1998;17:7139–7148. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.23.7139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hirano T. SMC-mediated chromosome mechanics: a conserved scheme from bacteria to vertebrates? Genes Dev. 1999;13:11–19. doi: 10.1101/gad.13.1.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hirano T, Mitchison T J. A heterodimeric coiled-coil protein required for mitotic chromosome condensation in vitro. Cell. 1994;79:449–458. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90254-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ireton K, Gunther IV N W, Grossman A D. spo0J is required for normal chromosome segregation as well as the initiation of sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1994;176:5320–5329. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.17.5320-5329.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Jessberger R, Frei C, Gasser S M. Chromosome dynamics: the SMC protein family. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1998;8:254–259. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(98)80149-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Jessberger R, Riwar B, Baechtold H, Akhmedov A T. SMC proteins constitute two subunits of the mammalian recombination complex RC-1. EMBO J. 1996;15:4061–4068. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kimura K, Hirano T. ATP-dependent positive supercoiling of DNA by 13S condensin: a biochemical implication for chromosome condensation. Cell. 1997;90:625–634. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80524-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Koshland D, Strunnikov A. Mitotic chromosome condensation. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1996;12:305–333. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.12.1.305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lieb J D, Albrecht M R, Chuang P T, Meyer B J. MIX-1: an essential component of the C. elegans mitotic machinery executes X chromosome dosage compensation. Cell. 1998;92:265–277. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80920-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lin D C, Grossman A D. Identification and characterization of a bacterial chromosome partitioning site. Cell. 1998;92:675–685. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81135-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lin D C H, Levin P A, Grossman A D. Bipolar localization of a chromosome partition protein in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:4721–4726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.9.4721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Liu G, Draper G C, Donachie W D. FtsK is a bifunctional protein involved in cell division and chromosome localization in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1998;29:893–903. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1998.00986.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Melby T E, Ciampaglio C N, Briscoe G, Erickson H P. The symmetrical structure of structural maintenance of chromosomes (SMC) and MukB proteins: long, antiparallel coiled coils, folded at a flexible hinge. J Cell Biol. 1998;142:1595–1604. doi: 10.1083/jcb.142.6.1595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Michaelis C, Ciosk R, Nasmyth K. Cohesins: chromosomal proteins that prevent premature separation of sister chromatids. Cell. 1997;91:35–45. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Moriya S, Tsujikawa E, Hassan A K, Asai K, Kodama T, Ogasawara N. A Bacillus subtilis gene-encoding protein homologous to eukaryotic SMC motor protein is necessary for chromosome partition. Mol Microbiol. 1998;29:179–187. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1998.00919.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Niki H, Jaffe A, Imamura R, Ogura T, Hiraga S. The new gene mukB codes for a 177 kd protein with coiled-coil domains involved in chromosome partitioning of E. coli. EMBO J. 1991;10:183–193. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07935.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ogasawara N, Yoshikawa H. Genes and their organization in the replication origin region of the bacterial chromosome. Mol Microbiol. 1992;6:629–634. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01510.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Pogliano K, Hofmeister A E M, Losick R. Disappearance of the ςE transcription factor from the forespore and the SpoIIE phosphatase from the mother cell contributes to establishment of cell-specific gene expression during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1997;179:3331–3341. doi: 10.1128/jb.179.10.3331-3341.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Saka Y, Sutani T, Yamashita Y, Saitoh S, Takeuchi M, Nakaseko Y, Yanagida M. Fission yeast cut3 and cut14, members of a ubiquitous protein family, are required for chromosome condensation and segregation in mitosis. EMBO J. 1994;13:4938–4952. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06821.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Sharpe M E, Errington J. Postseptational chromosome partitioning in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995;92:8630–8634. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.19.8630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Strunnikov A V. SMC proteins and chromosome structure. Trends Cell Biol. 1998;8:454–459. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(98)01370-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Strunnikov A V, Hogan E, Koshland D. SMC2, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene essential for chromosome segregation and condensation, defines a subgroup within the SMC family. Genes Dev. 1995;9:587–599. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.5.587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wu L J, Errington J. Bacillus subtilis SpoIIIE protein required for DNA segregation during asymmetric cell division. Science. 1994;264:572–575. doi: 10.1126/science.8160014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Wu L J, Errington J. Septal localization of the SpoIIIE chromosome partitioning protein in Bacillus subtilis. EMBO J. 1997;16:2161–2169. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.8.2161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wu L J, Lewis P J, Allmansberger R, Hauser P M, Errington J. A conjugation-like mechanism for prespore chromosome partitioning during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Genes Dev. 1995;9:1316–1326. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.11.1316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Yu X-C, Weihe E K, Margolin W. Role of the C terminus of FtsK in Escherichia coli chromosome segregation. J Bacteriol. 1998;180:6424–6428. doi: 10.1128/jb.180.23.6424-6428.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]