Summary
Propylene glycol is a ubiquitous sustainable chemical that have several industrial applications. It can be used as a non-toxic antifreeze, moisturizers, and in cosmetics products. Commercial production of propylene glycol uses petroleum-based propylene oxide. Therefore, there is a need to develop alternative and renewable propylene glycol production routes. Renewable propylene glycol can be produced from catalytic hydrogenolysis of glycerol. This study reviews different catalyst for glycerol hydrogenolysis, the reaction mechanism, and process challenges. Additionally, previous studies related to the economic and environmental assessment of propylene glycol production are presented in detail. The technology readiness level of different production pathways were outlined as well as the challenges and future direction of propylene glycol production from glycerol and other renewable feedstocks. Catalytic transfer hydrogenolysis, a process that uses renewable H-donors in liquid medium for hydrogenolysis reaction is also discussed and compared with conventional hydrogenolysis.
Subject areas: Industrial chemistry, Catalysis, Organic chemistry
Graphical abstract
Industrial chemistry; Catalysis; Organic chemistry
Introduction
Glycerol is one of the major products obtained during biodiesel processing through the transesterification reaction. The reaction converts animal fats or vegetable oils and alcohols into biodiesel in the presence of a catalyst (Badday et al., 2012). However, transesterification reaction produces significant quantities of crude glycerol that makes it unattractive from environmental and economic viewpoint. It should be noted that crude glycerol production has increased in recent years due to the elevated demand and supply of biodiesel. Crude glycerol comprises of about 10 wt.% of the final products obtained during the transesterification reaction (Leal et al., 2016). Crude glycerol has low commercial value due to its heterogeneous composition. It contains about 80% glycerol and 20% impurities including water, soap, methanol, fatty acid methyl esters (FAMEs), and inorganic elements (Leal et al., 2016). Therefore, it is imperative to develop alternative methods for the conversion of crude glycerol into value-added chemicals.
Recently, there has been significant interest in the conversion of glycerol to value-added chemicals in order to reduce the overall cost of biodiesel production. Tan et al., (2013) reviewed different methods that uses glycerol as feedstocks for the production of green chemicals. The authors also outlined various value-added products and biofuels that could be obtained from glycerol. The advances in the conversion of glycerol to chemicals such as acrolein, glycerol carbonate, propylene glycol (1,2-propanediol), ethanol, and lactic acid were discussed (Tan et al., 2013). Monteiro et al., (2018) identified propylene glycol, 1,3-propanediol, and hydrogen as the main glycerol-derived products that have attracted research interest recently.
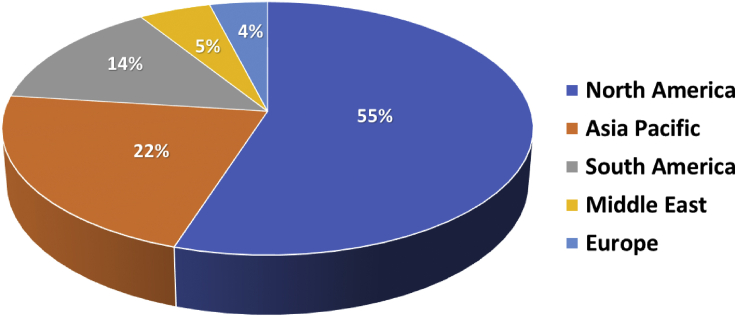
Propylene glycol is a promising chemical with numerous applications including as an antifreeze, cosmetics agent, moisturizer, solvent, surfactant, and a preservative (Jiménez et al., 2020). Commercially it can be produced from the hydrolysis of propylene oxide (Mitta et al., 2018). However, propylene oxide is obtained from petrochemical feedstocks. Factors such as environmental pollution, climate change, and declining petroleum reserves are major concerns that have promoted interest in alternative production routes (Okolie et al., 2021). The Chemical market reporter noted that the overall production of propylene glycol in the United States is about 1400 million pounds per year (Sara et al., 2016). Moreover, the domestic consumption of the chemical is predicted to increase by 4% each year (Sara et al., 2016). The global scenario for propylene glycol production is presented in Figure 1 with the North America accounting for over 55% of the global production. Other regions such as Asia and South America also produce about 22% and 14% of propylene glycol, respectively. The main manufacturers are the Dow Chemical Company (United States), BASF (Germany), and LyondellBasell Industries N.V. (The Netherlands) (Sara et al., 2016).
Figure 1.
Global distribution of propylene glycol production in 2021
Data obtained from MMR, (2021).
It should be emphasized that the propylene glycol market is also experiencing severe challenges due to the fluctuating fossil fuel prices. Therefore, new processes that can meet the increasing global demand of propylene glycol are required. Propylene glycol could also be produced from a more environmentally friendly routes by using renewable feedstocks such as glycerol. The conversion of glycerol to propylene glycol could help mitigate the challenges of glycerol production while producing enough propylene glycol to meet the elevating demand. Glycerol can be converted to propylene glycol via the selective hydrogenolysis reaction in the presence of a metallic catalyst and hydrogen in a batch or continuous reactor (Nanda et al., 2016). The source of hydrogen for the process is also a major concern. The produced propylene glycol is known as renewable propylene glycol (RPG) if the hydrogen is from renewable sources such as biomass gasification or electrolysis or when the process is performed with hydrogen generated in situ via an external hydrogen transfer.
Several studies have been reported on the catalytic conversion of glycerol to propylene glycol (Freitas et al., 2018; Seretis and Tsiakaras, 2016). Some authors have also studied the selective hydrogenolysis process using hydrogen generated in situ (Freitas et al., 2018). Several reviews have also been documented on the selective hydrogenolysis of glycerol to propylene glycol using a metallic catalyst. Bozga et al., (2011) outlined the influence of metallic catalyst such as Cu, Ni, Co, and noble metal-based catalysts on the conversion of glycerol to propylene glycol. Vasiliadou and Lemonidou, (2015) reviewed the reaction mechanism of glycerol to propylene glycol. The authors also outlined the effect of reaction parameters (temperature, catalyst loading, hydrogen pressure, and glycerol concentration) and reaction medium (acidic/alkaline) on propylene glycol yield. Nanda et al., (2016) discussed the advances in catalyst preparation and activation method. However, most of the available studies are scattered in literature. Table 1 compares the present study with reviews related to propylene glycol production. Based on the information in Table 1, studies on the advances in RPG production methods and industrial application have been scantly reported. Therefore, the current review presents the advances and progress in RPG production from glycerol. In addition, the industrial applications of RPG are outlined. The present review would not only complement the previous studies but also provide information that could be useful in the optimization and scale-up the glycerol to RPG conversion processes.
Table 1.
Comparisons between the present study and previous review articles related to propylene glycol production from glycerol
| Review title | Main focus | References |
|---|---|---|
| Conversion of glycerol to propanediol and acrolein by heterogeneous catalysis |
|
Bozga et al.,(2011) |
| Recent advancements in catalytic conversion of glycerol into propylene glycol: |
|
Nanda et al., (2016) |
| Glycerol transformation to value-added C3 diols: Reaction mechanism, kinetic, and engineering aspects. |
|
Vasiliadou and Lemonidou, (2015) |
| Catalytic transfer hydrogenolysis as an efficient route in cleavage of lignin and model compounds |
|
Zhang, (2018) |
| Insights on production mechanism and industrial applications of renewable propylene glycol |
|
This study |
Propylene glycol production routes
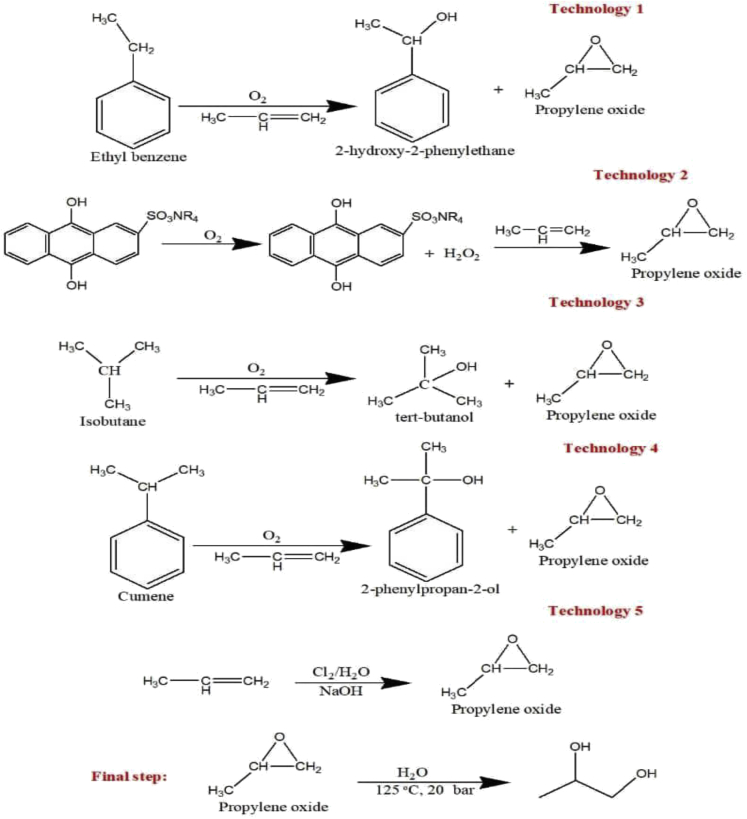
Propylene glycol is often produced from several pathways by using different feedstocks. It can be synthesized commercially from the hydration of propylene oxide (Nanda et al., 2016). At present, there are five different technologies used for the industrial production of propylene glycol as shown in Figure 2. They include the (1) styrene monomer process employed by LyondellBasel and Shell, (2) the anthraquinone process used by Dow Chemical and BASF, (3) the tert-butyl alcohol process used by LyondellBasel and Huntsman Corp, (4) the cumene hydroperoxide process used by Sumitomo Chemicals, and (5) the chlorohydrine process by Dow Chemical (Martin and Murphy, 2000). Other processes such as the catalytic hydrogenation of lactic acid or the fermentation of glycerol in the presence of microorganisms could also produce propylene glycol (Nanda et al., 2016; Seretis and Tsiakaras, 2016). Thermochemical processes occurring in the presence of heat and thermal energy could also convert carbohydrates such as xylitol and sorbitol into propylene glycol in the presence of a reducing agent (Sun and Liu, 2011). The hydrogenolysis of carbohydrates to propylene glycol involves two main steps. The first step occurs in the presence of metal catalyst and involves the dehydrogenation of polyols to carbonyl intermediates. Following the first step, the cleavage of specific C–C and C–O bonds occurs in a basic medium through the retroaldol condensation (Nanda et al., 2016; Sun and Liu, 2011).
Figure 2.
Different technologies for the commercial production of propylene glycol
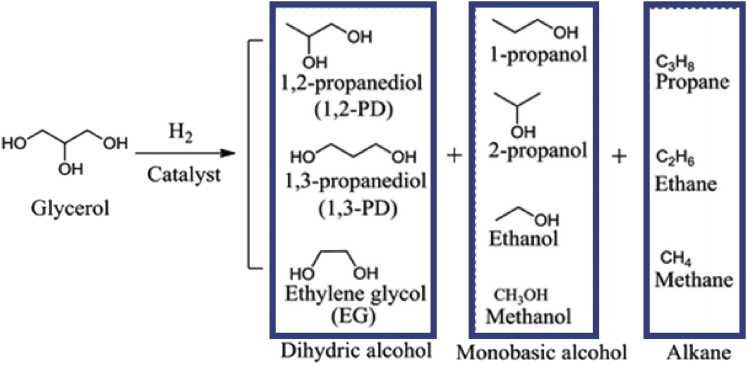
The production of RPG from glycerol occurs through a reaction known as selective hydrogenolysis. The process involves the breaking of C–O bonds, removal of hydroxyl groups, followed by the simultaneous addition of hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst as shown in Figure 3 (Sharma et al., 2014). It should be emphasized that when one side hydroxyl group is removed from glycerol RPG is produced. Moreover, the dissociation of the hydroxyl groups present in the middle generates 1,3-propanediol. Many side products such as ethylene glycols, methanol propanol, and methane can also be produced from the reaction (Wang et al., 2015).
Figure 3.
Products obtained from the catalytic hydrogenolysis of glycerol
Hydrogenolysis of glycerol to RPG is an environmentally benign and cost-effective route compared to the conventional methods described in Figure 2. In addition, the conventional methods use petrochemical feedstocks and significant amount of water, thus producing byproducts such as di-and tri-propylene glycol (Nanda et al., 2016). The separation of the byproducts also increases the overall process economics.
Hydrogenolysis reaction mechanisms
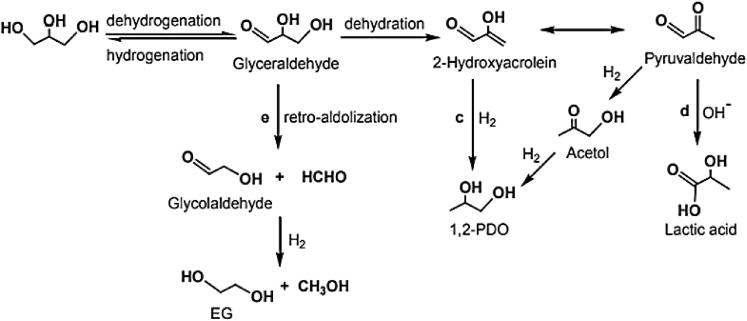
As stated in the previous section, the hydrogenolysis of glycerol occurs via series of parallel and consecutive reaction pathways. These reactions often lead to the formation of products such as RPG, 1,3-propanediol, lactic acid, alcohols, and sometimes gases (Feng and Xu, 2014). It should be noted that a clear understanding of RPG reaction mechanism is important for the effective design of improved catalysts and process optimization. Previous studies (Feng and Xu, 2014; Martin et al., 2013; Rajkhowa et al., 2017) proposed two main reaction mechanisms for the conversion of glycerol to propanediols: dehydration–hydrogenation mechanism and dehydrogenation–dehydration–hydrogenation mechanism. Other mechanisms such as direct hydrolysis mechanism (Amada et al., 2011), chelation–hydrogenolysis mechanism (Feng and Xu, 2014), and etherification–hydrogenation mechanism (Feng and Xu, 2014) have also been suggested in previous years.
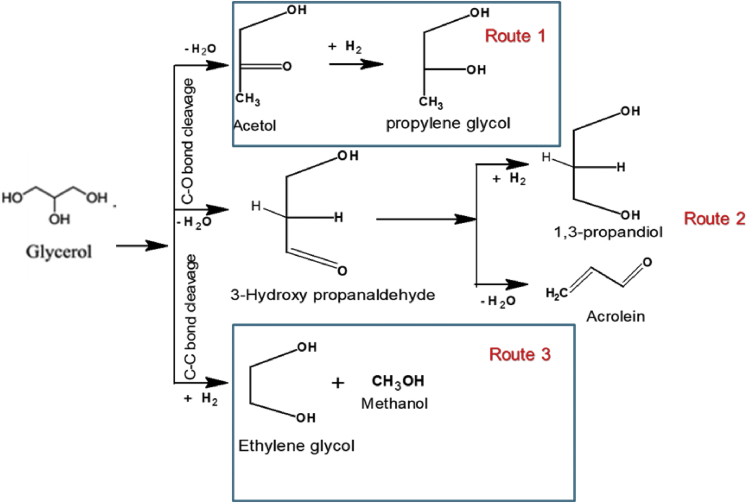
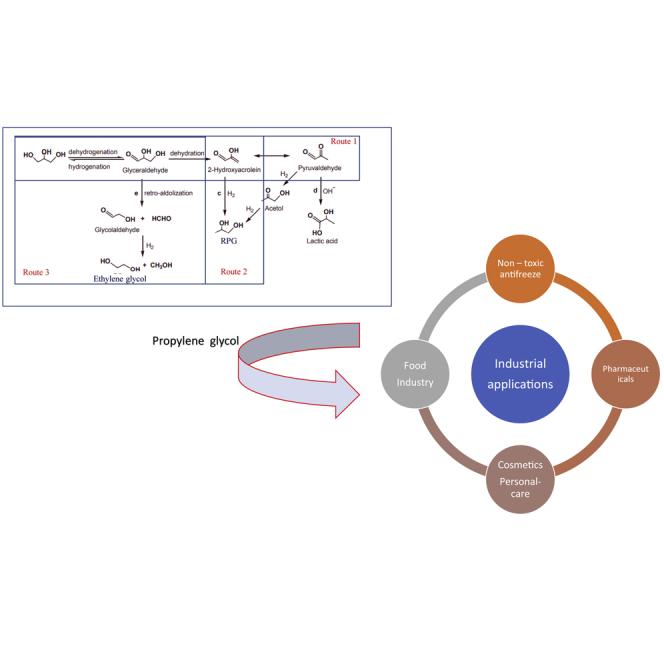
The dehydration–hydrogenation mechanism involves glycerol conversion to RPG via a reactive intermediate (acetol and its enol tautomer). The intermediate is subsequently hydrogenated to RPG (route 1 in Figure 4). Similarly, 1,3-propanediol can also be synthesized from the same route through the dehydration of glycerol to 3-hydroxypropanal and subsequent hydrogenation (route 2 in Figure 4) (Feng and Xu, 2014). It should be emphasized that direct hydrogenation of glycerol through the C–C bond cleavage leads to the formation of ethylene glycol and methanol (route 3).
Figure 4.
An overview of the reaction mechanism for the dehydration–hydrogenation mechanism of glycerol to RPG
The dehydration–hydrogenation mechanism is promoted under acidic conditions in the presence of acidic sites while the hydrogenation step is promoted by a metal (Feng and Xu, 2014; Martin et al., 2013). Thus, hydrogenolysis catalysts are designed to have an acidic site and also contain a metal promoter.
The dehydrogenation–dehydration–hydrogenation mechanism is prevalent when the reaction is performed in the presence of a basic medium (Feng et al., 2016). The mechanism proceeds through the reversible dehydrogenation of glycerol to glyceraldehyde over the metal sites. Subsequently, the produced glyceraldehyde is dehydrated by losing water molecules to produce to 2-hydroxyacrolein, which is finally hydrogenated to RPG (route 2 in Figure 5). It should be mentioned that there is a possibility of a side reaction in this route that involves the conversion of 2-hydroxyacrolein to pyruvaldehyde by keto-enol tautomerism (route 1 in Figure 5). Moreover, the pyruvaldehyde can also undergo hydrogenation to form acetol which is subsequently hydrogenated to RPG. Pyruvaldehyde could also undergo oxidation under basic conditions to form lactic acid.
Figure 5.
An overview of the dehydrogenation–dehydration–hydrogenation mechanism for the hydrogenolysis of glycerol to RPG and other side reactions
An overview of the reaction mechanism for the dehydration–hydrogenation.
Moreover, another important side reaction in this pathway is the formation of ethylene glycol (route 3 in Figure 5) via glyceraldehyde to glycolaldehyde and subsequent hydrogenation. It is important to ensure that the forward reaction (dehydrogenation) proceeds faster leading to the formation of glyceraldehyde. Previous studies have demonstrated that the addition of a specific base such as LiOH or NaOH could promote dehydration reaction (Feng et al., 2014; Feng and Xu, 2014).
Catalysts for hydrogenolysis of glycerol to propylene glycol
Hydrogenolysis reactions can be performed in the presence of homogeneous or heterogeneous catalyst. Homogeneous catalysts such as tungstic acid, sulfuric acid, and rhodium complex have been tested for the conversion of glycerol to RPG by several researchers (Che, 1987; Wang et al., 2015). Che, (1987) patented a one-step conversion process that uses syngas at 200°C and 32 MPa pressure in the presence of rhodium complex and tungstic acid homogeneous catalyst. The reaction produced RPG and 1,3-propanediol yields of 23% and 20%, respectively. In year 2000, Shell Oil Company patented a process that uses homogeneous palladium complex mixed water and sulfolane for the production of propylene glycol (Chaminand et al., 2004). The mixture also contains methane sulfonic acid as catalyst. It should be mentioned that products such as RPG, 1-propanol, and 1,3-propanediol were obtained from the process in the ratio of 22:47:31, respectively. Although promising, the use of homogeneous catalysts for RPG production has several limitations including separation and recovery of products, corrosion issues, use of expensive and toxic solvent as well as economic and environmental concerns (Nanda et al., 2016). Therefore, research focus was directed toward the development of heterogeneous catalysts to address these issues.
Heterogeneous catalyst used for glycerol to RPG can group based on the type of metals as transition (e.g. Co, Cu, and Ni) or noble metals (e.g. Pt, Rh, Ru, Pd, Ir, and Re). The noble metals are preferred because of their high selectivity toward RPG as well as high glycerol conversion (Freitas et al., 2018). Noble metal catalysts could also be used with various supports such as ZrO2, Al2O3, SiO2, TiO2, Fe2O3, and CaO (Sara et al., 2016). Catalysts supports help to provide stability, promote metal dispersion, and ensure that there is contact between the metal and the reactants.
Several studies have reported the use of supported noble metal catalysts for the conversion of glycerol to RPG. Roy et al., (2010) used a mixture of 5 wt.% Ru and Pt on Al2O3 support with in situ hydrogen for the conversion of glycerol to RPG. The reaction was performed in a multiple slurry reactor at 493 K for 6 h. The authors reported an optimal glycerol conversion of 50% and 47.2 % RPG selectivity (Roy et al., 2010). Miyazawa et al., (2007) used Ru supported on carbon materials combined with Amberlyst ion-exchange resins. They reported a maximum glycerol conversion and RPG selectivity of 48.8% and 70.2%, respectively. The reaction was performed at 8.0 MPa initial hydrogen pressure, 10 h reaction time, 15 mg Ru/C, and 453 K (Miyazawa et al., 2007). A lower glycerol conversion (19.8%) and RPG selectivity (31.9%) was reported with Pt metal supported on amorphous silica-alumina (Gandarias et al., 2010). Although noble metal-based catalysts are active, they are expensive and have the tendency to promote the cleavage of C–C bonds, leading to lower selectivity of RPG (Sara et al., 2016). In contrast, transition metals are inexpensive alternative sources for RPG production.
Cu-based transition metal catalyst has shown promising glycerol conversion and RPG selectivity during hydrogenolysis reaction for 400 h duration, 220°C, and 20 bar pressure. Cu has the ability to selectively cleave C–O bonds without affecting the C–C bond (Mane and Rode, 2012). This is a major requirement for increasing the selectivity of RPG. It should be mentioned that detailed catalysts characterization including the XRD, XPS, HR-TEM, and TPR results indicated that the catalysts exist in different forms including CuO and CuAl2O4, along with Cu0 and Cu1+ species. Moreover, the activity of Cu can be improved by dispersion on acidic supports including Al2O3, SiO2, functionalized carbon nanotubes (CNT), and ZrO2 (Gandarias et al., 2010; Mane and Rode, 2012) or by combination with other metals. Wu et al., (2011) studied glyceol hydrogenolysis over Cu–Ru catalyst supported on CNT at 4 MPa of H2 and 200°C for 6 h. The catalysts led to 99.8% glycerol conversion and 86.5 % RPG yield which is relatively higher compared to the use of pure metal catalyst on CNT support ( 31.3% conversion and 91.1% RPG selectivity) (Wu et al., 2011). The increased conversion and RPG selectivity was attributed to the synergistic effect between Cu and Ru.
Cu-based catalysts are often in their oxide form and require in situ reduction with enormous hydrogen pressure to produce Cu metal. However, few researchers have studied the addition of another metal to help eliminate the pre-reduction step. Zhou et al., (2010) used Cu and Ag metals supported on γ-Al2O3 at 200°C, 1.5 MPa initial H2 pressure for 10 h. The catalysts showed up to 100% RPG selectivity and 27% glycerol conversion without the pre-reduction step (Zhou et al., 2010). The authors noted that the addition of Ag also helped in the elimination of the pre-reduction step. Sharma et al., (2014) patented a catalyst comprising of Cu:Zn:Cr:Zr in the ratio of 3:2:1:3. The catalysts produced 100% conversion of glycerol and 97% RPG selectivity at 250°C, 4.0 MPa of H2 for 10 h. Moreover, the catalyst was reused 4 times with a slight decline in the conversion observed. Therefore, the authors concluded that the introduction of Zn and Zr into the Cu:Cr catalysts matrix helped improve the glycerol conversion and RPG selectivity (Sharma et al., 2014).
Ni is another promising and cost-effective transition metal used for the hydrogenolysis of glycerol to RPG. Ni is an hydrogenation catalyst and has been studied for selective hydrogenolysis reaction without using external hydrogen (Mane and Rode, 2012). Yin et al., (2009) showed that Raney Ni is a versatile catalyst for RPG production without the addition of external hydrogen. Jiménez-Morales et al., (2012) reported about 50% RPG selectivity and 30% glycerol conversion at 473 K and 2.4 MPa of H2 pressure with Ni supported on SBA-15 silica and promoted with Ce. Yu et al.,(2010) developed a novel procedure for synthesizing Ni/AC. The procedure involves metal impregnation, carbothermal reduction, and KBH4 treatment to enhance the acidity of the catalyst. The synthesized catalysts produced 43.3% glycerol conversion and 76.1% selectivity at 200°C, 5 MPa H2 for 6 h (Yu et al., 2010). Table 2 summarizes previous studies on the use of metal-based catalyst for hydrogenolysis of glycerol to propylene glycol.
Table 2.
Studies on the conventional catalytic hydrogenolysis of glycerol to renewable propylene glycol
| Catalyst and reaction conditions | Glycerol conversion/RPG selectivity | References |
|---|---|---|
| Catalyst: Cu–Cr. Pressure= 4.15 MP, temp=210°C, time =10 h, catalyst=5% w/w of glycerol |
Conversion= 52%, Selectivity= 88% |
Ma et al., (2010) |
| Catalyst: 5 wt.% Ru/Al2O3 and 5 wt.% Pt/Al2O3 mixtures. No external hydrogen, time: 6 h, temp= 220°C. |
Conversion= 50.1%, Selectivity= 47.2% |
Roy et al., (2010) |
| Catalyst: 5 % Ni/gamma-Al2O3. 5 mass% aqueous solution, 20 mL; initial H2 pressure, 8.0 MPa; reaction temperature, 453 K |
Conversion= 12%, Selectivity= 74% |
Ueda et al., (2010) |
| Catalyst: Cu/Al 20 wt% glycerol aqueous solution (100 mL), 7 MPa H2 pressure, 0.8 g catalyst, 493 K, 5 h. |
Conversion= 38%, Selectivity= 91% |
Mane et al., (2010) |
| Catalyst: CuO/ZnO. 15 g glycerol, 65 mL H2O, 180°C, 80 bar H2, 0.08 mol Cu (50%), 5 mmol H2WO4. |
Conversion= 21 %, Selectivity= 17 % |
Chaminand et al., (2004) |
| Catalyst = Ru/C 20 mass%; glycerol aqueous solution 20 ml; 8.0 MPa initial H2 pressure; 10 h reaction time; 15 mg Ru/C; 140 mmol H+ in the resins; temp= 453 K. |
Conversion= 48.8 %, Selectivity= 70.2 % |
Miyazawa et al., (2007) |
| Catalyst= 1% Pt/Amorphous silica–alumina Catalyst samples used under 493 K reaction temperature, 45 bar pressure, 41mL |
Conversion= 19.8 %, Selectivity= 31.9 % |
Gandarias et al., (2010) |
| Cu–Ni catalysts with ZSM-5 and Al2O3 catalyst pressure= 4 MPa, temp=250°C, time =6 h, catalyst=10% w/w of glycerol | Conversion= 87%, Selectivity= 27% |
Freitas et al., (2018) |
| Catalyst: Bimetallic Cu-Ni catalysts supported on mesoporous alumina. Atmospheric pressure, temp=220°C, time =10 h, catalyst=33% w/w of glycerol |
Conversion= 60%, selectivity= 20% | Yun et al., (2014) |
| Catalyst: Cu/Al2O3 pressure= 8 MPa, temp=230°C, time =6 h, catalyst=10% w/w of glycerol | Conversion= 94.7%, Selectivity= 90% |
Rajkhowa et al., (2017) |
| SiO2–Al2O3 supported 65% Ni catalyst pressure= 8 MPa, temp=240°C, time = 240 min, catalyst=10% w/w of glycerol. Gas to liquid phase volume ratio of 1.4 | Conversion= 73.6%, Selectivity= 59% |
Seretis and Tsiakaras., (2016) |
| Catalyst: Cu-Al pressure= 2 MPa, temp=220°C, time = 50 h, catalyst=10% w/w of glycerol. | Conversion= 91 %, Selectivity= 75 % |
Mane and Rode., (2012) |
Catalytic transfer hydrogenolysis
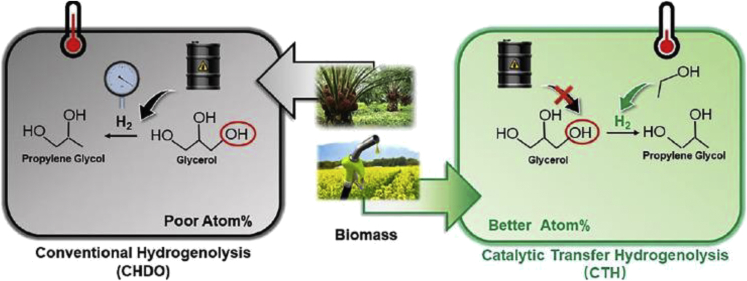
Catalytic transfer hydrogenolysis (CTH) is perceived as one of environmentally friendly alternative to conventional hydrogenolysis that occurs without the addition of external hydrogen. CTH requires much milder reaction temperature and lower operating pressure (Sun et al., 2022). The process occurs in the presence of a catalyst that facilitates the production of renewable hydrogen donors in the liquid medium. Additionally, CTH is more energy efficient and economically viable due to the absence of external hydrogen. However, the success of CTH is based on the development of an effective bifunctional catalyst that can simultaneously enhance in situ hydrogen production and hydrogenolysis reaction. Figure 6 outlines the difference between conventional hydrogenolysis and CTH. Several researchers have assessed the development of different bifunctional catalysts to facilitate CTH reaction. Moreover, a wide range of transition metals including Cu, Ni, Ru, Pt, Pd, and Ru have the ability to catalyze CTH reaction and have been extensively studied. Feng et al., (2015) studied the performance of a series of bifunctional catalyst comprising of PdCu-KF/γ-Al2O3 during CTH reaction. Specifically, a catalyst with composition of Pd:Cu:KF = 0.05:1:0.5 produced almost 100 percent glycerol conversion and RPG selectivity of 98.3%. Pd catalysts are often preferred due to their promising hydrothermal stability and high selectivity for the cleavage of C–O bonds over C–C bonds.
Figure 6.
Comparison between conventional hydrogenolysis and catalytic transfer hydrogenolysis (CTH)
Reproduced from Sun et al.,(2022).
In another study, iron-oxide support was screened with different metals including Pt, Pd, and Ni. The bifunctional catalysts were tested for the CTH of glycerol (Von Held Soares et al., 2017). The activity of the selected metals for CTH was in the order of Pt > Pd > Ni. Furthermore, 1 wt.% Pt on iron-oxide support (1.0Pt/Fe3O4) showed the best performance among the catalysts with 81% glycerol conversion and 79% RPG selectivity (Von Held Soares et al., 2017).
Kant et al., (2017) performed a comprehensive screening of different bimetallic catalyst comprising of Ni, Cu, Zn, and Zr supported on H-beta catalysts. It should be noted that the Ni and Cu transition metals were selected due to their low cost and ability to promote hydrogen formation. Ni-Zr catalyst was the most promising catalyst with 73% glycerol conversion. In addition, it was reported that the H-beta support contains increased Brønsted acidity.
Zn has the ability to promote the conversion of glycerol to RPG when deposited on a Pd surface (Sun et al., 2017). Therefore, a monoclinic zirconia-supported PdZn (PdZn/m-ZrO2) was synthesized and tested for the CTH reaction. Although promising conversion and selectivity were attained with the catalyst, the leaching of Zn from the PdZn alloy phases led to catalysts deactivation. To prevent the deactivation, physical mixtures of Pd/m-ZrO2 and ZnO were directly used for the CTH reaction. Thus, producing layers of PdZn alloy on Pd surfaces that prevented the Zn leaching (Sun et al., 2017).
Industrial applications of propylene glycol
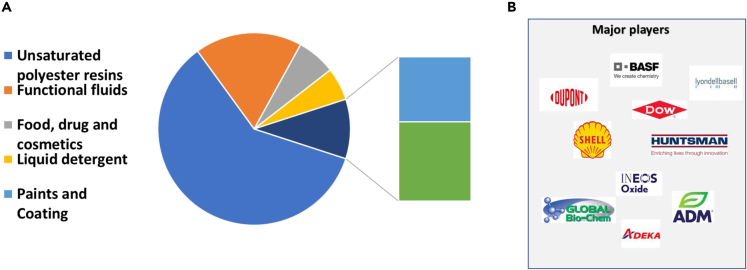
Propylene glycol is an extremely hygroscopic and non-toxic compound. In addition, it is miscible with water and most solvent. The physical properties of propylene glycol are summarized in Table 3. The boiling point of propylene glycol (187.3°C) is relatively higher than that of pure water therefore it can be separated from water through simple distillation. Also, it has a lower freezing point of –60°C and viscosity of 60.5 cPps. The miscibility of propylene glycol with water and other solvents as well as its unique physical properties makes it suitable for different industrial applications as an antifreeze, pharmaceutical, cosmetics, and food industry solvents. Propylene glycol could also be used as coatings, paints, adhesives, lubricants and greases, polishes, and waxes. Figure 7 shows the worldwide market of propylene glycol in 2017 as well as its industrial applications. The next section outlines different areas where propylene glycol could be applied industrially.
Table 3.
Overview of propylene glycol physical properties
| Physical properties | Value |
|---|---|
| Color and form | Colorless, viscous and stable hygroscopic liquid |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Freezing point (oC) | -60 |
| Boiling point (oC) | 187.3 |
| Flash point (oC) | 107 |
| Specific heat at room temperature (cal/g) | 0.59 |
| Surface tension at room temperature (dynes/cm) | 0.37 |
| Solubility | Miscible with water, acetone, and chloroform; soluble in ether; miscible with water, alcohol, and many organic solvents |
| Viscosity at 20oC (Cps) | 60.5 |
| Vapor pressure at 20oC (mmHg) | 0.05 |
Adapted from Sara et al., (2016).
Figure 7.
Propylene glycol market share and key players in the propylene glycol production
(A) Propylene glycol market share.
(B) Key players in the propylene glycol production.
Data obtained from PGM, (2022).
Non-toxic antifreeze (including automotive industry and buildings)
An antifreeze is used to attain freezing-point latency during cold climates. Compared to ethylene glycol, propylene glycol is preferable as a non-toxic antifreeze. It can reduce the freezing point of water by disrupting ice crystals formation. Ethylene glycol is an extremely toxic chemical that is often transformed into calcium oxalate crystals when ingested (Lucy Bell, 2020). The produced calcium oxalate crystals often build up in the heart, lungs, and kidney, thus resulting in irrecoverable health issues. In addition, ethylene glycol is characterized by a sweet taste and smell that could be accidentally ingested by pets or children.
Propylene glycol can also be used to maintain the integrity of DNA. Most times environmental samples that uses DNA for research are often stored in absolute ethanol. However, ethanol is expensive, and limited due to transportation restrictions especially in remote locations, and it is often classified as an hazardous chemicals (Sales et al., 2019). In addition, a long ethanol evaporation period is needed to prevent polymerase chain reaction inhibition. Recent experimental studies show that propylene glycol-based antifreeze is a suitable alternative to ethanol for preserving macroinvertebrate DNA from bulk-benthos DNA samples (Robinson et al., 2021). In another study, RPG has been evaluated as potential antifreeze for water-based fracturing fluid and liquid additives in newly developed oil fields (Wu et al., 2021). Study by Perez et al., (2019) shows that propylene glycol is a cryoprotective agent that could be used as a promising ingredient for treating cellular tissues and organs to prevent ice crystal’s formation at low temperatures (Perez et al., 2019).
Recently, Abu-Hamdeh et al., (2022) developed a novel antifreeze nanofluid comprising of carbon nanotubes and ethylene glycol/propylene glycol. The nanofluid was used for the cooling of batteries. The authors stated that the developed nanofluid could also be used for other similar electrical systems such as a radiator. The developed antifreeze showed promising performance for battery cooling systems. Another study demonstrates the application of propylene glycol as an antifreeze agent in geothermal heat exchangers (Bartolini et al., 2020). The authors assessed the economic and environmental analysis of using four different fluids including propylene glycol (25wt.% and 33 wt.%), calcium chloride, and pure water as antifreeze agents in geothermal heat exchangers. Their results show that propylene glycol and calcium chloride are promising antifreeze from economic and environmental perspectives (Bartolini et al., 2020). Propylene glycol is also used as an antifreeze for aircraft and automotives (Bokov et al., 2022). In Canada, propylene glycol is commonly used to protect the heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems from freezing due to extreme weathers.
Food and beverage industry
Propylene glycol also finds applications in the food industry as a preservative, solvent, and moisture removal agent (Lucy Bell, 2020). Propylene glycol is used as an additive in several food products because it is not self-reactive and hygroscopic. Food additives refer to substances that are not consumed as food but added intentionally to food for one or more technological benefits. Food additives can be antioxidants, emulsifiers, preservatives, or stabilizers. Propylene glycol is a promising food additive because of its ability to attract water molecules thus improving the texture, taste, appearance, and shelf life of food. In addition, it is a very good food preservative and an excellent humectant. It can be used as an antioxidant, dough strengthener, emulsifier, stabilizer, thickener, and texturizer in foods (Blekas, 2016; CFR, 2022). Propylene glycol is also used as a dough strengthener because of its ability to modify the starch and gluten in dough thereby improving the stability (Blekas, 2016).
Propylene glycol is recognized by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as a relatively safe substance for use as a food additive. It is found in so many foods including packaged foods, drink mixes, desserts, and premarinated ham and turkey (Jacob et al., 2018). Propylene glycol is also present in many condiments, frozen vegetables, dairy products, and bread as preservatives. Recent studies by Bokov et al., (2022) confirm that propylene glycol is not harmful or poisonous to the body when ingested. Although, few incidents of intoxication have been reported due to the consumption of extremely high doses. Shayanmehr et al., (2021) showed that propylene glycol is an effective co-solvent when mixed with sunflower oil for the production of linoleic acid used for milk enrichment.
Pharmaceuticals
Propylene glycol is a beneficial chemical found in a variety of pharmaceutical and health-care products. Often used to retain moisture and prevent the dryness of skin in alcohol-based hand sanitizers (Bokov et al., 2022). It is a promising solvent in several oral and injectable drugs (Bokov et al., 2022). Drugs have to penetrate into the deeper skin layers or permeate the skin for effective action. Moreover, the human skin represents an effective, selective barrier to chemical permeation. It should be mentioned that very few selective drugs possess the physicochemical properties required for this route of delivery (Duracher et al., 2009). Moreover, most of the drugs do not have the capacity to penetrate the skin in doses needed for efficiency systematic therapy. Therefore, propylene glycol is often used to improve drug permeation through the skin (Carrer et al., 2020). Moreover, the enhanced miscibility of propylene glycol with water enables it to be used as a solvent for pharmaceutical formulations that are insoluble including diazepam and benzodiazepine (Lucy Bell, 2020).
Propylene glycol is added to drug formulation to enhance the solubility of hydrophobic compounds (Co and Gunnerson, 2019). Ceftriaxone is a promising third generation cephalosporin antibiotic approved by the FDA for the treatment of infections such as gonorrhea (Raja et al., 2020), pneumonia (Flanders et al., 2006), and bacterial meningitis (Molyneux et al., 2011). Propylene glycol polymer has been reported as an efficient stabilization agent for metal nanoparticles used in colorimetric assay for ceftriaxone (Raja et al., 2020). Compared to the conventional analytical methods such as liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) and fluorimetry, the propylene glycol polymer-enhanced stabilization agent is more effective.
Acetaminophen (ACP, N-acetyl-p-aminophenol) is an analgesic drug that is widely use independently or combined with other drugs to manage pain or even as an antipyretic agent. It is extensively used because of its low allergy risk (Amann and Peskar, 2002). Moreover, the drug is administered to patients who are biased to salicylate (Amann and Peskar, 2002). It should be emphasized that acetaminophen is classified by the biopharmaceutics classification system as a class III drug exhibiting reduced water solubility (14.3 mg ml−1 at 25°C ) and low permeability (Barzegar-Jalali et al., 2022). These properties adversely influence its dissolution kinetics thereby limiting the design of its liquid formulations. Propylene glycol can be used as a solvent to study and optimize the solubility behavior of important drugs such as acetaminophen (Romdhani et al., 2020) and sulfacetamide (Osorio et al., 2020).
Other applications including cosmetics and personal care products
Cosmetic and personal care products are also major areas where propylene glycol is often used. Propylene glycol can be used for diverse purposes ranging from skin conditioning agent to viscosity decreasing agent, as a cosmetic solvent, or ingredients for fragrance (Fiume et al., 2012). The hygroscopic nature of propylene glycol enhances its application in moisturizers and hair care products. Moreover, the polymer also minimizes bacterial growth and promotes the shelf life of cosmetics and personal care products (Lucy Bell, 2020).
Electronic cigarette (e-cigarette) is used as a safe substitute to tobacco smoking, or as a smoking interruption device. Propylene glycol has been used as a promising liquid for e-cigarettes when mixed with glycerin (Lucy Bell, 2020). The liquid mixtures act as a carrier for nicotine and flavorings and enhance vapor generation. It should be mentioned that e-cigarette formulation contains between 89%–90% of propylene glycol (Cotta et al., 2017). Previous studies show that the use of propylene glycol in e-cigarettes do not pose a significant health issue through the inhalation route (Cotta et al., 2017).
Economic and environmental assessment of hydrogenolysis process
The economic and environmental impact of different RPG production routes should be assessed and compared with the commercial production pathways. That way critical decisions related to the commercial implementation of the technologies would be presented. Additionally, techno-economic analysis (TEA) is a very important tool used to determine the profitability of a new technology as well as its market competitiveness (Okolie et al., 2022). Also, the life cycle assessment (LCA) is a popular method employed in assessing the environmental aspects associated with a product over its life cycle including the production and consumptions stages. TEA is often integrated with LCA for effective decision making whether to move a project or a proposal forward.
Few studies have assessed the TEA of RPG production from glycerol via several routes (Table 4). Earlier studies by Gonzalez-Garay et al., (2017) compared the economic and environmental impacts of the commercial propylene glycol production process from propylene oxide with three hydrogenolysis routes (Table 4). Among the selected route, non-isothermal hydrogenolysis at ambient pressure and external hydrogen is the most promising from economic and environmental considerations. Another study by Nachtergaele et al., (2019) applied the LCA approach to evaluate the environmental impact of RPG production from three different routes. Hydrogenolysis reaction led to a decline in GHG emissions by 60%. Furthermore, the emitted CO2 eq. declined by 36%–38% when a combined heat and power system on-site is adopted (Nachtergaele et al., 2019).
Table 4.
Studies associated with the techno-economic and life cycle assessment of hydrogenolysis of glycerol to propylene glycol
| Technology | Study objectives | Key findings | References |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Route 1: Isothermal hydrogenolysis at high pressure and external hydrogen Route 2: Non-isothermal hydrogenolysis at ambient pressure and external hydrogen. Route 3: Isothermal hydrogenolysis at high pressure and in situ generated hydrogen |
Petroleum-derived propylene oxide production method was compared with three different hydrogenolysis routes. |
|
Gonzalez-Garay et al., (2017) |
|
Route 1: Propylene glycol production from petroleum-derived feedstocks Route 2: Hydrogenolysis with glycerol from fatty acid production. Route 3:Hydrogenolysis with glycerol from biodiesel production. |
Environmental effect of implementing different feedstock for renewable propylene glycol production. | A transition from petroleum-based economy to renewables-based results in a decrease in the environmental impact between 40% and 60% kg CO2 eq. | Nachtergaele et al., (2019) |
|
Route 1: Hydrogenolysis with hydrogen from an external source. Route 2: Hydrogenolysis with hydrogen produced locally from glycerol steam reforming. |
Assess the technical and economic impacts of two renewable propylene glycol production routes based on the source of hydrogen. |
|
Jiménez et al., (2020) |
| Hydrogenolysis of crude glycerol with external hydrogen | Evaluate the economic viability combined acrolein and propylene glycol production from crude glycerol | Net present value of USD 376,600,000 was obtained from the production process. | Supramono and Ashshiddiq, (2021) |
|
Route 1: Catalytic hydrogenolysis with external hydrogen Route 2: Catalytic transfer hydrogenolysis |
Assess the energy economic and environmental impacts of the two propylene glycol production pathways. |
|
Sun et al., (2022) |
Jiménez et al., (2020) designed two alternative routes for RPG production based on the sources of hydrogen. Route 1 includes the hydrogenolysis of glycerol with hydrogen from an external source. In contrast, hydrogen was produced from glycerol steam reforming in route 2. Economic analysis of the two routes shows that the use of glycerol steam reforming as hydrogen source led to an increase in the cost of RPG production from 1.36 US$/kg to 9.01 US$/kg. Moreover, the annual net profit from the RPG production process also decreased by 70%.
Supramono and Ashshiddiq, (2021) proposed and assessed the economic viability of a process for the conversion of crude glycerol to RPG and acrolein. A net present value, payback period, and internal rate of return of USD 376 million, 1.26 years, and 149.9%, respectively, was obtained from the process. However, the authors did not perform a detailed cash flow analysis for the proposed design. Also, the methodology employed in the study was not clear. Additionally, the minimum selling price of RPG and acrolein was not presented.
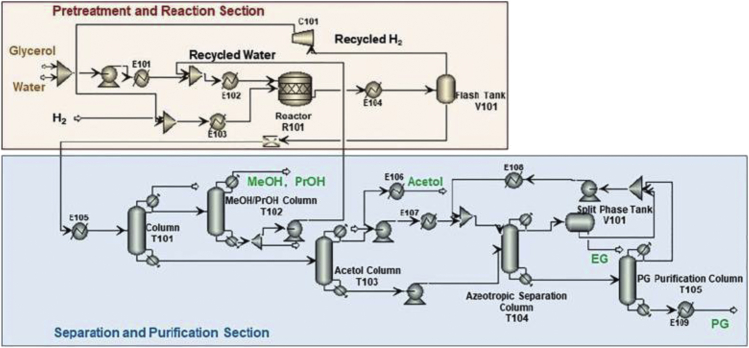
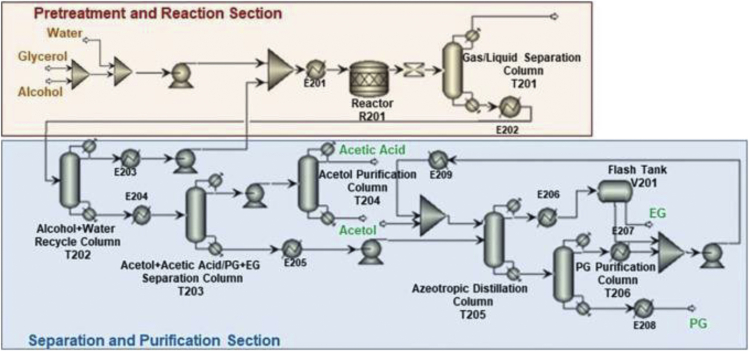
Recently, Sun et al., (2022) performed a detailed energy, economic, and environmental assessment of two RPG production routes. Route 1 is based on catalytic hydrogenolysis with external hydrogen (Figure 8). On the contrary, route 2 is based on catalytic transfer hydrogenolysis (CTH) whereby the hydrogen is supplied by renewable H-donors in liquid medium as shown in Figure 9. The CTH process in route 2 requires less energy compared to route 1. Furthermore, there is about 64% decline in CO2 emissions in route 2 compared to route 1. This is attributed to the elimination of external hydrogen source provided from natural gas. CTH process also led to a decline in the total investment cost by 7%.
Figure 8.
Schematic representation of the catalytic hydrogenolysis of glycerol to RPG
Adapted from Sun et al., (2022).
Figure 9.
Schematic representation of the catalytic transfer hydrogenolysis
Adapted from Sun et al.,(2022).
Technology readiness level of hydrogenolysis of glycerol to RPG
The maturity level of different RPG production routes can be assessed using the technology readiness level (TRL) metrics. Through the TRL methodology, the maturity level of a new technology can be evaluated and compared against alternatives using factors such as economic viability, environmental impacts, and process performance (Dovichi Filho et al., 2021). Moreover, TRL can be used as a tool for screening and identification of risks inherent in new projects (Beims et al., 2019).
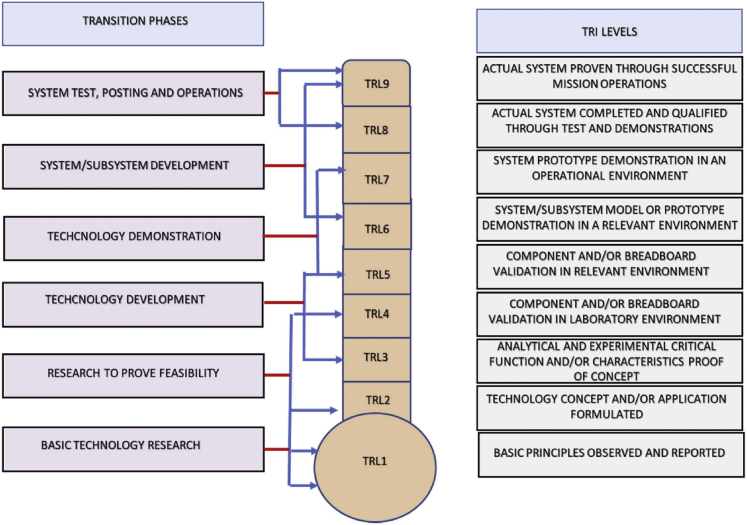
TRL of a technology can be divided into different levels which are in accordance with the U.S. Department of Defense (Figure 10). It should be noted the level ranges from level 1 (related to the conceptual stage) to level 9 (commercialization stage). Regarding the TRL of RPG, it should be noted that although most of the proposed technology are relatively new, several researchers have embraced them (Marchesan et al., 2019). Table 5 outlines the maturity level of different RPG production pathways. There are several lab scale plants for RPG production using feedstock such as glycerol cellulose, lactic acid, and glucose. Moreover, Dow Company successfully designed a pilot plant facility at the Halterman Custom Processing Facility in Houston (Chatterjee et al., 2011).
Figure 10.
Different levels and definitions of TRL
Adapted from Okolie et al., (2022).
Table 5.
Maturity level of renewable propylene glycol production
| Level of maturity | Renewable propylene glycol production process | References |
|---|---|---|
| Lab scale |
|
Clomburg and Gonzalez, (2011) Marchesan et al., (2019) Veeravalli and Mathews, (2018) Xi et al., (2011) Xiao et al., (2013) |
| Pilot scale |
|
Rosales-Calderon and Arantes, (2019) |
| Demonstration scale | NA | |
| Commercial scale |
|
Marchesan et al., (2019) |
NA, Not available.
In 2011, Archer Daniels Midlands (ADM) was able to build a large-scale industrial RPG production facility at its Decatur, Illinois facility using a rhenium-promoted catalyst (EESI, 2018). The next year, BASF partnered with Oleon to build and open another RPG production plant in Belgium (EESI, 2018). Today, ADM uses plant-based glycerol, a co-product in the production of biodiesel for RPG production. The ADM RPG production facility has 100,000 million metric tons of RPG (ADM, 2022). ADM had stated that the use of soybean-derived and canola-derived glycerol in the RPG production facility led to a 61% decline in greenhouse gas emissions compared to the petroleum-based feedstocks. In China, about 5.2 kilo tons per year of RPG is produced with sorbitol as feedstock (Rosales-Calderon and Arantes, 2019).Since the catalytic conversion of glycerol to RPG has been adopted commercially by few companies, a TRL level of at least 8 would be suitable to describe the technology. However, the conversion of bio-based feedstocks such as cellulose, glucose, and lactic acid to RPG is still at its infancy stage and could be assigned TRL levels between 2 and 4.
Challenges and future prospects
Although the sustainable production of propylene glycol from several feedstocks has attracted attention from academic and industrial aspects, there are several challenges that need to be addressed. Hydrogenolysis of biodiesel-derived glycerol to RPG is the most common route and has been commercialized industrially; however, the source of hydrogen is still a major concern. Most studies have recommended that hydrogen can be supplied externally without accounting for the source. If hydrogen comes from natural gas or petroleum resources, then the produced propylene glycol should not be called renewable.
A feasible alternative would be to directly integrate hydrogen production processes with the hydrogenolysis reaction to promote circular economy. However, this would require detailed process design, energy, and exergy analysis as well as energy optimization. Such studies have not been reported. More important, the economic and environmental assessment of the integrated processes is scarcely reported.
Glycerol is an abundant biodiesel production by-product; therefore, the conversion of crude glycerol to green chemicals and polymers has been a source of academic and industrial research (Shenbagaraj et al., 2021). Green chemical such as lactic acid, ethylene glycol, and acetol can also be converted to propylene glycol through catalytic hydrogenolysis. However, more research is required to develop an efficiency catalyst that can be recycled easily and also produce a maximum propylene glycol selectivity.
Industrial production of RPG from hydrogenolysis of glycerol uses copper-chromite catalysis and a two-step synthesis including the novel reactive-distillation and acetol hydrogenation. Moreover, the selected route for the production of acetol and propylene glycol from glycerol includes a vapor-phase reaction over the copper-chromite catalyst in a packed bed reactor. In the presence of hydrogen, the vapor-phase reaction facilitates the conversion of glycerol to propylene glycol in a single reactor. Although this approach has been demonstrated in a continuous process, challenges of scalability and catalyst recycling still remain.
Earlier studies have demonstrated that RPG could be produced without an external hydrogen source through the CTH process (Sun et al., 2022). However, further research in terms of catalysts development and process scale-up is still needed.
Conclusions
Propylene glycol is a ubiquitous green chemical that has several industrial uses including as an antifreeze, cosmetics, agent, moisturizer, solvent, surfactant, and a preservative. However, majority of the worldwide consumption of propylene glycol is from petroleum-based propylene oxide, a process that is characterized by greenhouse gas emission release. Hydrogenolysis of glycerol is an alternative route for the production of propylene glycol. Catalytic hydrogenolysis can occur in the presence of external hydrogen or through the use of renewable H-donors in liquid medium. If the external source of hydrogen is supplied from renewable sources, the produced propylene glycol is called renewable propylene glycol (RPG).
The present review outlines different RPG production routes, hydrogenolysis mechanisms, and potential industrial applications of propylene glycol. Presently, there are five different technologies used for the industrial production of propylene glycol They include the (1) styrene monomer process employed by LyondellBasel and Shell, (2) the anthraquinone process used by Dow Chemical and BASF, (3) the tert-butyl alcohol process used by LyondellBasel and Huntsman Corp, (4) the cumene hydroperoxide process used by Sumitomo Chemicals, and (5) the chlorohydrine process by Dow Chemical. These technologies were comprehensively discussed in this paper. Additionally, previous studies related to the economic and environmental assessment of RPG production are presented in detail. TRL of different production pathways was presented as well as the challenges and future direction of RPG production. Additionally, industrial applications of propylene glycol as a non-toxic antifreeze, moisturizers, and in cosmetics products are discussed.
Acknowledgments
The author would like to thank Kingsley O. Iwuozor from the University of Lagos, Nigeria and Fredrick Omoarukhe from the University of Ilorin, Nigeria for preparing the organic diagrams.
References
- Abu-Hamdeh N.H., Karimipour A., Hatamleh R.I., Sajadi S.M. Improve the rheological and thermal performances of the antifreeze liquids for cooling the batteries and radiators in automobiles via provide a new hybrid material composed from carbon nanotubes in ethylene glycol/propylene glycol. J. Energy Storage. 2022;52:104982. doi: 10.1016/J.EST.2022.104982. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- ADM . 2022. Propylene Glycol | ADM.https://www.adm.com/en-us/products-services/industrial-biosolutions/products/propylene-glycol/ [Google Scholar]
- Amada Y., Shinmi Y., Koso S., Kubota T., Nakagawa Y., Tomishige K. Reaction mechanism of the glycerol hydrogenolysis to 1, 3-propanediol over Ir-ReOx/SiO2 catalyst. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2011;105:117–127. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2011.04.001. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Amann R., Peskar B.A. Anti-inflammatory effects of aspirin and sodium salicylate. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2002;447:1–9. doi: 10.1016/S0014-2999(02)01828-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badday A.S., Abdullah A.Z., Lee K.T., Khayoon M.S. Intensification of biodiesel production via ultrasonic-assisted process: a critical review on fundamentals and recent development. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012;16:4574–4587. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2012.04.057. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Bartolini N., Casasso A., Bianco C., Sethi R. Environmental and economic impact of the antifreeze agents in geothermal heat exchangers. Energies. 2020;13:5653. doi: 10.3390/en13215653. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Barzegar-Jalali M., Jafari P., Jouyban A. Acetaminophen solubility in aqueous solutions of betaine-propylene glycol natural deep eutectic solvent at different temperatures. J. Mol. Liq. 2022;349:118199. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2021.118199. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Beims R.F., Simonato C.L., Wiggers V.R. Technology readiness level assessment of pyrolysis of trygliceride biomass to fuels and chemicals. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019;112:521–529. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2019.06.017. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Blekas G.A. Food additives: classification, uses and regulation. Encycl. Food Heal. 2016:731–736. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-384947-2.00304-4. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Bokov D., Al-Ethafa L.F.M., Abilmazhinov Y., Thangavelu L., Surendar A., Pokrovskii M., Abdelbasset W.K. Study on the preservative properties of glycol on food. Food Sci. Technol. 2022;42 doi: 10.1590/fst.39021. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Bozga E.R., Plesu V., Bozga G., Bildea C.S., Zaharia E. Conversion of glycerol to propanediol and acrolein by heterogeneous catalysis. Rev. Chim. 2011;62:646–654. [Google Scholar]
- Carrer V., Alonso C., Pont M., Zanuy M., Córdoba M., Espinosa S., Barba C., Oliver M.A., Martí M., Coderch L. Effect of propylene glycol on the skin penetration of drugs. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2020;312:337–352. doi: 10.1007/s00403-019-02017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CFR CFR - Code of federal regulations title 21. 2022. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfcfr/CFRSearch.cfm?fr=50.25
- Chaminand J., Djakovitch L., Gallezot P., Marion P., Pinel C., Rosier C. Glycerol hydrogenolysis on heterogeneous catalysts. Green Chem. 2004;6:359–361. doi: 10.1039/b407378a. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Che T.M. 1987. Production of propanediols. [Google Scholar]
- Clomburg J.M., Gonzalez R. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for the production of 1, 2-propanediol from glycerol. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2011;108:867–879. doi: 10.1002/bit.22993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Co I.N., Gunnerson K.J. Iatrogenic and poison-derived acid base disorders. Crit. Care Nephrol. 2019:417–423.e2. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-323-44942-7.00071-6. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Cotta K.I., Stephen C.D., Mohammad N.U. A Review on the Safety of Inhalation of Propylene Glycol in E-cigarettes. Glob. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2017;2 doi: 10.19080/gjpps.2017.02.555584. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Dovichi Filho F.B., Castillo Santiago Y., Silva Lora E.E., Escobar Palacio J.C., Almazan del Olmo O.A. Evaluation of the maturity level of biomass electricity generation technologies using the technology readiness level criteria. J. Clean. Prod. 2021;295:126426. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126426. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Duracher L., Blasco L., Hubaud J.C., Vian L., Marti-Mestres G. The influence of alcohol, propylene glycol and 1, 2-pentanediol on the permeability of hydrophilic model drug through excised pig skin. Int. J. Pharm. 2009;374:39–45. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2009.02.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EESI . 2018. Biobased Buzz: Renewable Propylene Glycol – Early Success in Renewable Chemical Market | Article | EESI.http://www.eesi.org/articles/view/biobased-buzz-renewable-propylene-glycol-early-success-in-renewable-chemica [Google Scholar]
- Feng J., Xu B. Reaction mechanisms for the heterogeneous hydrogenolysis of biomass-derived glycerol to propanediols. Prog. React. Kinet. Mech. 2014;39:1–15. doi: 10.3184/97809059274714X13874723178485. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Feng J., Xiong W., Xu B., Jiang W., Wang J., Chen H. Basic oxide-supported Ru catalysts for liquid phase glycerol hydrogenolysis in an additive-free system. Catal. Commun. 2014;46:98–102. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2013.11.031. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Feng Y.S., Liu C., Kang Y.M., Zhou X.M., Liu L.L., Deng J., Xu H.J., Fu Y. Selective hydrogenolysis of glycerol to 1, 2-propanediol catalyzed by supported bimetallic PdCu-KF/γ-Al2O3. Chem. Eng. J. 2015;281:96–101. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.06.087. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Feng J., Zhang Y., Xiong W., Ding H., He B. Hydrogenolysis of glycerol to 1, 2-propanediol and ethylene glycol over ru-co/zro2 catalysts. Catalysts. 2016;6:51. doi: 10.3390/catal6040051. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Fiume M.M., Bergfeld W.F., Belsito D.V., Hill R.A., Klaassen C.D., Liebler D., Marks J.G., Shank R.C., Slaga T.J., Snyder P.W., Andersen F.A. Safety Assessment of Propylene Glycol, Tripropylene Glycol, and PPGs as Used in Cosmetics. Int. J. Toxicol. 2012;31:245S–260S. doi: 10.1177/1091581812461381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanders S.A., Dudas V., Kerr K., McCulloch C.E., Gonzales R. Effectiveness of ceftriaxone plus doxycycline in the treatment of patients hospitalized with community-acquired pneumonia. J. Hosp. Med. 2006;1:7–12. doi: 10.1002/jhm.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freitas I.C., Manfro R.L., Souza M.M. Hydrogenolysis of glycerol to propylene glycol in continuous system without hydrogen addition over Cu-Ni catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018;220:31–41. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.08.030. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Gandarias I., Arias P.L., Requies J., Güemez M., Fierro J.L.G. Hydrogenolysis of glycerol to propanediols over a Pt/ASA catalyst: the role of acid and metal sites on product selectivity and the reaction mechanism. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2010;97:248–256. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2010.04.008. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Garay A., Gonzalez-Miquel M., Guillen-Gosalbez G. High-value propylene glycol from low-value biodiesel glycerol: a techno-economic and environmental assessment under uncertainty. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017;5:5723–5732. doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b00286. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob S.E., Scheman A., McGowan M.A. Propylene Glycol. Dermatitis. 2018;29:3–5. doi: 10.1097/DER.0000000000000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez R.X., Young A.F., Fernandes H.L. Propylene glycol from glycerol: Process evaluation and break-even price determination. Renew. Energy. 2020;158:181–191. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2020.05.126. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez-Morales I., Vila F., Mariscal R., Jiménez-López A. Hydrogenolysis of glycerol to obtain 1, 2-propanediol on Ce-promoted Ni/SBA-15 catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012;117–118:253–259. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.01.027. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Kant A., He Y., Jawad A., Li X., Rezaei F., Smith J.D., Rownaghi A.A. Hydrogenolysis of glycerol over Ni, Cu, Zn, and Zr supported on H-beta. Chem. Eng. J. 2017;317:1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.02.064. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Leal A.L., Soria M.A., Madeira L.M. Autothermal reforming of impure glycerol for H2 production: Thermodynamic study including in situ CO2 and/or H2 separation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 2016;41:2607–2620. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2015.11.132. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Lucy Bell Y. 5 Uses of Propylene Glycol. Reag. Chem. 2020 https://www.chemicals.co.uk/blog/5-uses-of-propylene-glycol [Google Scholar]
- Ma Z., Xiao Z., Van Bokhoven J.A., Liang C. A non-alkoxide sol-gel route to highly active and selective Cu-Cr catalysts for glycerol conversion. J. Mater. Chem. 2010;20:755–760. doi: 10.1039/b917546f. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Mane R.B., Rode C.V. Simultaneous glycerol dehydration and in situ hydrogenolysis over Cu-Al oxide under an inert atmosphere. Green Chem. 2012;14:2780–2789. doi: 10.1039/c2gc35661a. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Mane R.B., Hengne A.M., Ghalwadkar A.A., Vijayanand S., Mohite P.H., Potdar H.S., Rode C.V. Cu:Al nano catalyst for selective hydrogenolysis of glycerol to 1, 2-propanediol. Catal. Letters. 2010;135:141–147. doi: 10.1007/s10562-010-0276-5. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Marchesan A.N., Oncken M.P., Maciel Filho R., Wolf Maciel M.R. A roadmap for renewable C2-C3 glycols production: a process engineering approach. Green Chem. 2019;21:5168–5194. doi: 10.1039/c9gc02949d. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Martin A.E., Murphy F.H. Glycols, propylene glycols. Kirk-Othmer Encycl. Chem. Technol. 2000 doi: 10.1002/0471238961.1618151613011820.a01. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Martin A., Armbruster U., Gandarias I., Arias P.L. Glycerol hydrogenolysis into propanediols using in situ generated hydrogen - A critical review. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2013;115:9–27. doi: 10.1002/ejlt.201200207. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Mitta H., Seelam P.K., Ojala S., Keiski R.L., Balla P. Tuning Y-zeolite based catalyst with copper for enhanced activity and selectivity in vapor phase hydrogenolysis of glycerol to 1, 2-propanediol. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2018;550:308–319. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2017.10.019. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazawa T., Koso S., Kunimori K., Tomishige K. Glycerol hydrogenolysis to 1, 2-propanediol catalyzed by a heat-resistant ion-exchange resin combined with Ru/C. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2007;329:30–35. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2007.06.019. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- MMR . 2021. Global Bio-Based Propylene Glycol Market Forecast and Analysis -2027.https://www.maximizemarketresearch.com/market-report/global-bio-based-propylene-glycol-market/71603/ [Google Scholar]
- Molyneux E., Nizami S.Q., Saha S., Huu K.T., Azam M., Bhutta Z.A., Zaki R., Weber M.W., Qazi S.A., CSF 5 Study Group 5 versus 10 days of treatment with ceftriaxone for bacterial meningitis in children: A double-blind randomised equivalence study. Lancet. 2011;377:1837–1845. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60580-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monteiro M.R., Kugelmeier C.L., Pinheiro R.S., Batalha M.O., da Silva César A. Glycerol from biodiesel production: Technological paths for sustainability. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018;88:109–122. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2018.02.019. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Nachtergaele P., De Meester S., Dewulf J. Environmental sustainability assessment of renewables-based propylene glycol at full industrial scale production. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2019;94:1808–1815. doi: 10.1002/jctb.5951. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Nanda M.R., Yuan Z., Qin W., Xu C.C., Charles) Recent advancements in catalytic conversion of glycerol into propylene glycol: a review. Catal. Rev. 2016;58:309–336. doi: 10.1080/01614940.2016.1166005. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Okolie J.A., Tabat M.E., Gunes B., Epelle E.I., Mukherjee A., Nanda S., Dalai A.K. A techno-economic assessment of biomethane and bioethanol production from crude glycerol through integrated hydrothermal gasification, syngas fermentation and biomethanation. Energy Convers. Manag. X. 2021;12:100131. doi: 10.1016/j.ecmx.2021.100131. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Okolie J.A., Epelle E.I., Tabat M.E., Orivri U., Amenaghawon A.N., Okoye P.U., Gunes B. Waste biomass valorization for the production of biofuels and value-added products: a comprehensive review of thermochemical, biological and integrated processes. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022;159:323–344. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2021.12.049. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Osorio I.P., Martínez F., Delgado D.R., Jouyban A., Acree W.E. Solubility of sulfacetamide in aqueous propylene glycol mixtures: measurement, correlation, dissolution thermodynamics, preferential solvation and solute volumetric contribution at saturation. J. Mol. Liq. 2020;297:111889. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2019.111889. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Perez A.F., Taing K.R., Quon J.C., Flores A., Ba Y. Effect of type i antifreeze proteins on the freezing and melting processes of cryoprotective solutions studied by site-directed spin labeling technique. Crystals. 2019;9:352. doi: 10.3390/cryst9070352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PGM . 2022. Propylene Glycol Market Size, Share, Trends, Analysis, Forecast 2022-2027.https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/reports/propylene-glycol-market [Google Scholar]
- Raja D.A., Musharraf S.G., Shah M.R., Jabbar A., Bhanger M.I., Malik M.I. Poly(propylene glycol) stabilized gold nanoparticles: An efficient colorimetric assay for ceftriaxone. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020;87:180–186. doi: 10.1016/J.JIEC.2020.03.041. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Rajkhowa T., Marin G.B., Thybaut J.W. A comprehensive kinetic model for Cu catalyzed liquid phase glycerol hydrogenolysis. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017;205:469–480. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.12.042. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson C.V., Porter T.M., Wright M.T.G., Hajibabaei M. Propylene glycol-based antifreeze is an effective preservative for dna metabarcoding of benthic arthropods. Freshw. Sci. 2021;40:77–87. doi: 10.1086/712232. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Romdhani A., Martínez F., Almanza O.A., Jouyban A., Acree W.E. Solubility of acetaminophen in (ethanol + propylene glycol + water) mixtures: Measurement, correlation, thermodynamics, and volumetric contribution at saturation. J. Mol. Liq. 2020;318:114065. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2020.114065. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Rosales-Calderon O., Arantes V. A review on commercial-scale high-value products that can be produced alongside cellulosic ethanol. Biotechnol. Biofuels. 2019;12:1–58. doi: 10.1186/s13068-019-1529-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy D., Subramaniam B., Chaudhari R.V. Aqueous phase hydrogenolysis of glycerol to 1,2-propanediol without external hydrogen addition. Catal. Today. 2010 doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2010.01.007. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Sales N.G., Wangensteen O.S., Carvalho D.C., Mariani S. Influence of preservation methods, sample medium and sampling time on eDNA recovery in a neotropical river. Environ. DNA. 2019;1:119–130. doi: 10.1002/edn3.14. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Sara M., Rouissi T., Brar S., Biorefinery J.B.-P.C. Elsevier; 2016. Propylene Glycol: An Industrially Important C3 Platform Chemical. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Seretis A., Tsiakaras P. Hydrogenolysis of glycerol to propylene glycol by in situ produced hydrogen from aqueous phase reforming of glycerol over SiO2-Al2O3 supported nickel catalyst. Fuel Process. Technol. 2016;142:135–146. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2015.10.013. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma R.V., Kumar P., Dalai A.K. Selective hydrogenolysis of glycerol to propylene glycol by using Cu:Zn:Cr:Zr mixed metal oxides catalyst. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2014;477:147–156. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2014.03.007. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Shayanmehr M.R., Elhamirad A.H., Armin M. Optimization of conjugated linoleic acid (Cla) synthesis conditions applying it in milk enrichment. J. Res. Innov. Food Sci. Technol. 2021;9:375–388. doi: 10.22101/jrifst.2020.216650.1145. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Shenbagaraj S., Sharma P.K., Sharma A.K., Raghav G., Kota K.B., Ashokkumar V. Gasification of food waste in supercritical water: An innovative synthesis gas composition prediction model based on Artificial Neural Networks. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 2021;46:12739–12757. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2021.01.122. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Sun J., Liu H. Selective hydrogenolysis of biomass-derived xylitol to ethylene glycol and propylene glycol on supported Ru catalysts. Green Chem. 2011;13:135–142. doi: 10.1039/c0gc00571a. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Sun Q., Wang S., Liu H. Selective hydrogenolysis of glycerol to propylene glycol on supported Pd catalysts: promoting effects of ZnO and mechanistic assessment of active PdZn alloy surfaces. ACS Catal. 2017;7:4265–4275. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.7b00995. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Sun P., Zhang W., Yu X., Zhang J., Xu N., Zhang Z., Liu M., Zhang D., Zhang G., Liu Z., Yang C., Yan W., Jin X. Hydrogenolysis of glycerol to propylene glycol: energy, tech-economic, and environmental studies. Front. Chem. 2022;9:778579. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2021.778579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Supramono D., Ashshiddiq J.A. Economic potential of the manufacture of acrolein and propylene glycol from glycerol. AIP Conf. Proc. 2021;2376:020003. doi: 10.1063/5.0064725. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Tan H.W., Abdul Aziz A.R., Aroua M.K. Glycerol production and its applications as a raw material: a review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013;27:118–127. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2013.06.035. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda N., Nakagawa Y., Tomishige K. Conversion of glycerol to ethylene glycol over Pt-modified Ni catalyst. Chem. Lett. 2010;39:506–507. doi: 10.1246/cl.2010.506. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Vasiliadou E.S., Lemonidou A.A. Glycerol transformation to value added C3 diols: reaction mechanism, kinetic, and engineering aspects. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Energy Environ. 2015;4:486–520. doi: 10.1002/wene.159. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Veeravalli S.S., Mathews A.P. Exploitation of acid-tolerant microbial species for the utilization of low-cost whey in the production of acetic acid and propylene glycol. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018;102:8023–8033. doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-9174-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Held Soares A., Atia H., Armbruster U., Passos F.B., Martin A. Platinum, palladium and nickel supported on Fe3O4 as catalysts for glycerol aqueous-phase hydrogenolysis and reforming. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2017;548:179–190. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2017.07.023. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Zhou J., Guo X. Catalytic hydrogenolysis of glycerol to propanediols: a review. RSC Adv. 2015;5:74611–74628. doi: 10.1039/c5ra11957j. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Z., Mao Y., Wang X., Zhang M. Preparation of a Cu–Ru/carbon nanotube catalyst for hydrogenolysis of glycerol to 1, 2-propanediol via hydrogen spillover. Green Chem. 2011;13:1311–1316. doi: 10.1039/c0gc00809e. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Wu G., Chen S., Meng X., Wang L., Sun X., Wang M., Sun H., Zhang H., Qin J., Zhu D. Development of Antifreeze Fracturing Fluid Systems for Tight Petroleum Reservoir Stimulations. Energy Fuels. 2021;35:12119–12131. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.1c01819. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Xi Y., Jackson J.E., Miller D.J. Characterizing lactic acid hydrogenolysis rates in laboratory trickle bed reactors. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011;50:5440–5447. doi: 10.1021/ie1023194. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao Z., Jin S., Pang M., Liang C. Conversion of highly concentrated cellulose to 1, 2-propanediol and ethylene glycol over highly efficient CuCr catalysts. Green Chem. 2013;15:891–895. doi: 10.1039/c3gc40134k. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Yin A.Y., Guo X.Y., Dai W.L., Fan K.N. The synthesis of propylene glycol and ethylene glycol from glycerol using Raney Ni as a versatile catalyst. Green Chem. 2009;11:1514–1516. doi: 10.1039/b913395j. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Yu W., Xu J., Ma H., Chen C., Zhao J., Miao H., Song Q. A remarkable enhancement of catalytic activity for KBH4 treating the carbothermal reduced Ni/AC catalyst in glycerol hydrogenolysis. Catal. Commun. 2010;11:493–497. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2009.12.009. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Yun Y.S., Park D.S., Yi J. Effect of nickel on catalytic behaviour of bimetallic Cu-Ni catalyst supported on mesoporous alumina for the hydrogenolysis of glycerol to 1, 2-propanediol. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2014;4:3191–3202. doi: 10.1039/c4cy00320a. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J. Catalytic transfer hydrogenolysis as an efficient route in cleavage of lignin and model compounds. Green Energy Environ. 2018;3:328–334. doi: 10.1016/j.gee.2018.08.001. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou J., Guo L., Guo X., Mao J., Zhang S. Selective hydrogenolysis of glycerol to propanediols on supported Cu-containing bimetallic catalysts. Green Chem. 2010;12:1835–1843. doi: 10.1039/c0gc00058b. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, K., Hall, K., Tell, S. (2011). Glycerol to Propylene Glycol. upenn.edu PhD Thesis.